An Efficient Clinical Decision Support Framework Using IoMT Based on Explainable and Trustworthy Artificial Intelligence with Transformer Model and Blockchain-Integrated Chunking
Abstract
1. Introduction
- This research enables secure, reliable, and efficient transmission of health data by integrating content-defined chunking and blockchain technologies together for the first time in an edge–cloud AI architecture.
- The fragmentation approach, combined with blockchain integrity verification, prevents the acceptance of faulty or incomplete data blocks, thereby reducing the retry rate and associated transmission costs.
- While in the literature chunking is only used for deduplication purposes, in this study the chunking approach is implemented as a transmission module that optimises the reliable transmission of IoMT stress data. Combined with blockchain logging, both verifiable reliability and traceable integrity are ensured.
- This paper aims to achieve higher accuracy and training efficiency compared to classical machine learning and deep learning approaches by using a Transformer-based model for multivariate time series stress detection within the proposed architecture.
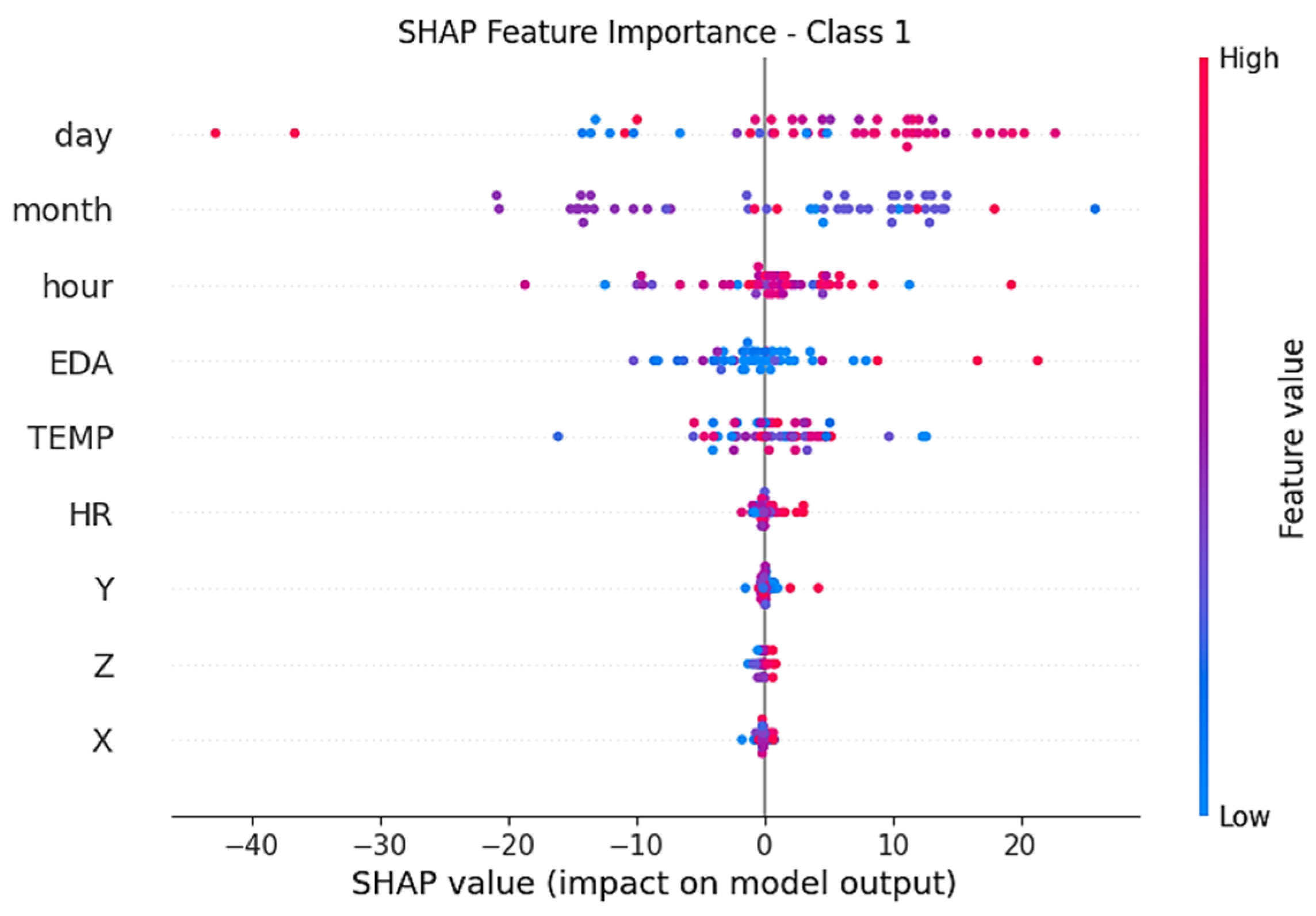
- SHAP-based explainability methods have increased the confidence of health providers by making clinical estimates transparent and understandable.
- The proposed architecture offers significant contributions in real-time stress detection and clinical decision support, which are critical for scalable, secure, and interpretable IoMT-based decision support systems.
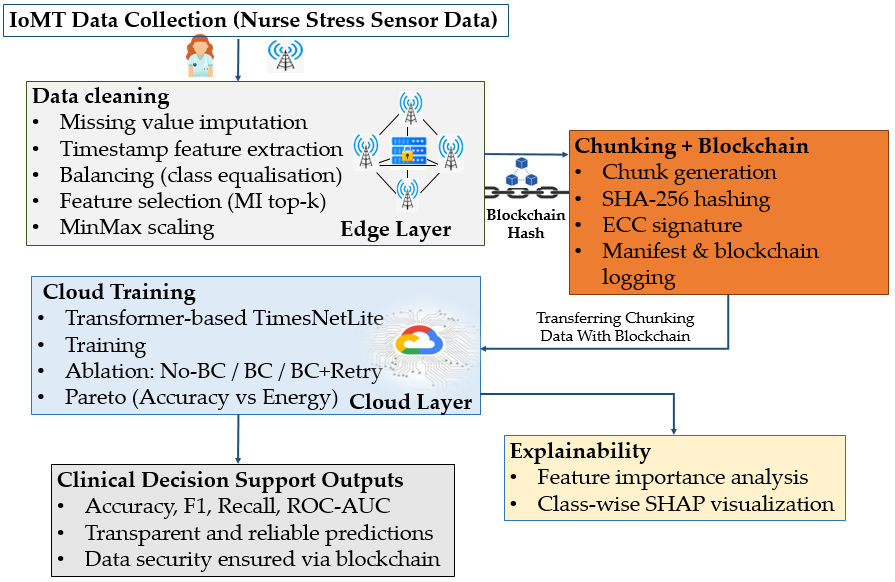
2. Proposed Method
- Data acquisition from IoT devices: The Nurse Stress dataset was used to simulate the IoMT ecosystem in healthcare [21]. This dataset contains multivariate sensor data reflecting stress levels. The data was first imported into the edge device.
- Pre-processing and feature selection on the edge device: The data were processed on the edge device, unnecessary columns were removed, and dimensionality reduction (PCA) and data balancing (SMOTE) methods were applied. Thus, the communication load was reduced and data imbalances that reduce the model performance were eliminated.
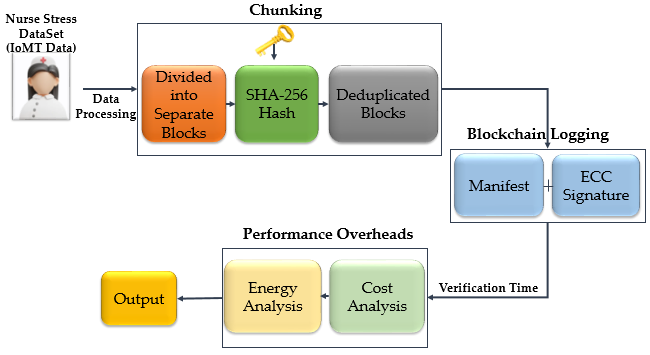
- Blockchain and chunking integration: The data was divided into small pieces by the content-defined chunking method. The hash value of each chunk was generated and stored on the blockchain, thus preventing data duplication and ensuring data integrity, immutability, and traceability. Chunk sizes and hash calculations were recorded experimentally, and these parameters were then used to calculate the communication and storage overhead.
- Secure transfer to the cloud: The data processed on the edge device and validated with the blockchain was securely transferred to the cloud environment. The integrity of the transmitted data is guaranteed by checking the compatibility of the hash values.
- Transformer-based model training: Transformer-based deep learning models with high capacity to analyse multivariate time series were trained in the cloud environment.
- Integration of XAI: SHAP was integrated to ensure transparency of the model outputs. Thus, clinicians and end-users can interpret the features on which the model’s decisions are based.
- Cost- and energy-efficiency calculations: To evaluate the practical applicability of the system, measurements such as upload time, verification time, communication volume, chunk sizes, blockchain verification times, and energy consumption (Joule) were performed.
2.1. Dataset and IoMT Context
2.2. Cloud–Edge and Blockchain-Chunking Framework for Stress Data
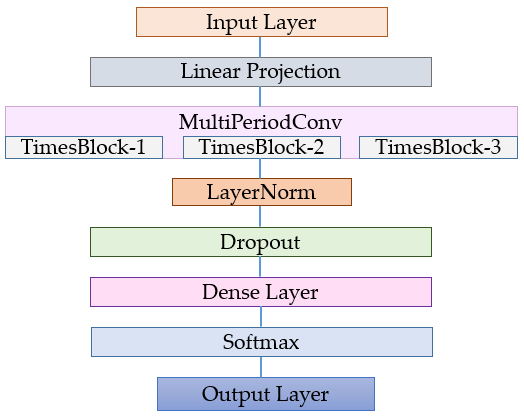
2.3. Transformer Model for Sensor Data
3. Experimental Results
3.1. Model Comparison and Selection
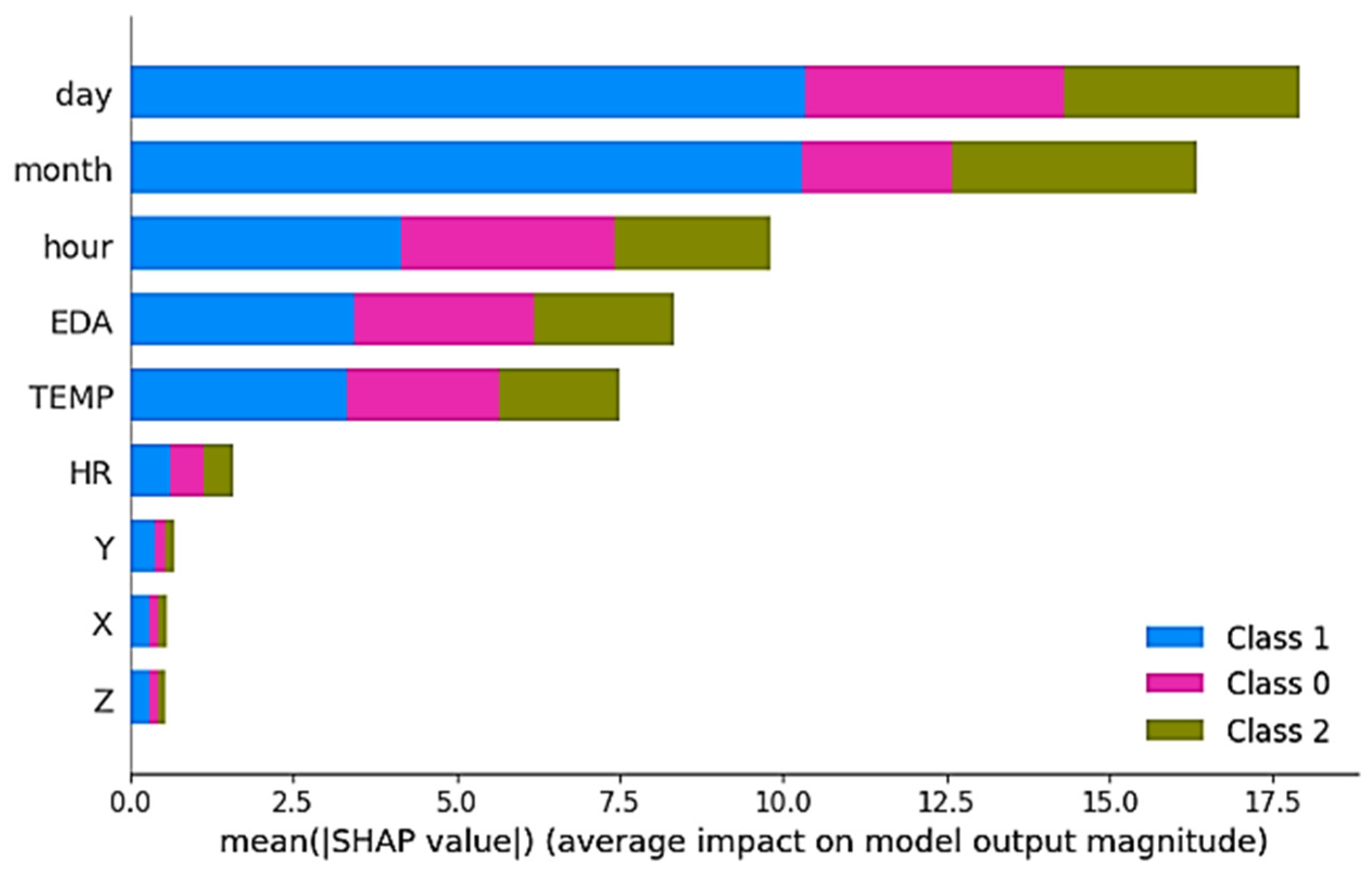
3.2. Explainability Analysis
3.3. Blockchain + Chunking + Energy/Cost Analyses
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, T.; Lu, Y.; Wang, J.; Dai, H.N.; Zheng, X.; Jia, W. EIHDP: Edge-Intelligent Hierarchical Dynamic Pricing Based on Cloud-Edge-Client Collaboration for IoT Systems. IEEE Trans. Comput. 2021, 70, 1285–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaioannou, M.; Karageorgou, M.; Mantas, G.; Sucasas, V.; Essop, I.; Rodriguez, J.; Lymberopoulos, D. A Survey on Security Threats and Countermeasures in Internet of Medical Things (IoMT). Trans. Emerg. Telecommun. Technol. 2022, 33, e4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghubaish, A.; Salman, T.; Zolanvari, M.; Unal, D.; Al-Ali, A.; Jain, R. Recent Advances in the Internet-of-Medical-Things (IoMT) Systems Security. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 8707–8718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manickam, P.; Mariappan, S.A.; Murugesan, S.M.; Hansda, S.; Kaushik, A.; Shinde, R.; Thipperudraswamy, S.P. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) Assisted Biomedical Systems for Intelligent Healthcare. Biosensors 2022, 12, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hederman, L.; Berry, D.; Ormazabal, A. Clinician’s Perspective on Trusting Patient Generated Health Data for Use in Clinical Decision-Making: A Qualitative Interview Study. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems, L’Aquila, Italy, 22–24 June 2023; pp. 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Sun, L.; Jiang, X.; Ren, H.; Guo, Y. Edge-Cloud Computing and Artificial Intelligence in Internet of Medical Things: Architecture, Technology and Application. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 101079–101092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishor, A.; Chakraborty, C. Artificial Intelligence and Internet of Things Based Healthcare 4.0 Monitoring System. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2022, 127, 1615–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baygin, M.; Yaman, O.; Baygin, N.; Karakose, M. A Blockchain-Based Approach to Smart Cargo Transportation Using UHF RFID. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 188, 116030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakhan, A.; Mohammed, M.A.; Kozlov, S.; Rodrigues, J.J.P.C. Mobile-Fog-Cloud Assisted Deep Reinforcement Learning and Blockchain-Enabled IoMT System for Healthcare Workflows. Trans. Emerg. Telecommun. Technol. 2024, 35, e4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kai, C.; Zhou, H.; Yi, Y.; Huang, W. Collaborative Cloud-Edge-End Task Offloading in Mobile-Edge Computing Networks with Limited Communication Capability. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 2021, 7, 624–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, J.; Puthal, D.; Yeun, C.Y. Next Generation Healthcare with Explainable AI: IoMT-Edge-Cloud Based Advanced eHealth. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 4–8 December 2023; pp. 7327–7332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieber, J.; Kirrane, S. Why Model Why? Assessing the Strengths and Limitations of LIME. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2012.00093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marvin, G.; Alam, M.G.R. Explainable Feature Learning for Predicting Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU) Admissions. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Biomedical Engineering, Computer and Information Technology for Health (BECITHCON), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 4–5 December 2021; pp. 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslanoğlu, K.; Karaköse, M. Examining Patients’ Length of Stay Estimation with Explainable Artificial Intelligence Methods. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Emerging Trends in Mathematical Sciences & Computing (IEMSC-24), Kolkata, India, 2–4 February 2024; pp. 296–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forti, S.; Ferrari, G.L.; Brogi, A. Secure Cloud-Edge Deployments, with Trust. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2020, 102, 775–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ometov, A.; Molua, O.L.; Komarov, M.; Nurmi, J. A Survey of Security in Cloud, Edge, and Fog Computing. Sensors 2022, 22, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y. Cloud-Edge Orchestration for the Internet of Things: Architecture and AI-Powered Data Processing. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 12792–12805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, L.T.; Xie, X.; Jin, J.; Jamal Deen, M. A Cloud-Edge Computing Framework for Cyber-Physical-Social Services. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2017, 55, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, B.; Yahya, W.; Lin, Y.D.; Ali, A. Offloading Using Traditional Optimization and Machine Learning in Federated Cloud-Edge-Fog Systems: A Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2023, 25, 1199–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, K.T.; Arrayyan, A.Z.; Hayati, N.; Firdaus; Damarjati, C.; Bakar, A.; Chen, H.C. A Review on the Application of Internet of Medical Things in Wearable Personal Health Monitoring: A Cloud-Edge Artificial Intelligence Approach. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 21437–21452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raval , P. Nurse Stress Prediction Wearable Sensors [Data Set]. Kaggle, 2023. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/priyankraval/nurse-stress-prediction-wearable-sensors (accessed on 27 October 2025).
- Dwivedi, R.; Mehrotra, D.; Chandra, S. Potential of Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) Applications in Building a Smart Healthcare System: A Systematic Review. J. Oral Biol. Craniofacial Res. 2022, 12, 302–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Gupta, G.P.; Tripathi, R. An Ensemble Learning and Fog-Cloud Architecture-Driven Cyber-Attack Detection Framework for IoMT Networks. Comput. Commun. 2021, 166, 110–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Nehra, M.; Kumar, R.; Dilbaghi, N.; Hu, T.Y.; Kumar, S.; Kaushik, A.; Li, C.Z. Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)-Integrated Biosensors for Point-of-Care Testing of Infectious Diseases. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 179, 113074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razdan, S.; Sharma, S. Internet of Medical Things (IoMT): Overview, Emerging Technologies, and Case Studies. IETE Tech. Rev. 2022, 39, 775–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhao, F.; Shankar, A.; Maple, C.; Peter, J.D.; Kim, B.G.; Slowik, A.; Parameshachari, B.D.; Lv, J. Explainable AI for Medical Image Analysis in Medical Cyber-Physical Systems: Enhancing Transparency and Trustworthiness of IoMT. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2025, 29, 2365–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, S.; Kataria, A.; Kumar, S.; Tiwari, P. Federated Learning for Secure IoMT-Applications in Smart Healthcare Systems: A Comprehensive Review. Knowl-Based Syst. 2023, 274, 110658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ausín, J.L.; Ramos, J.; Lorido, A.; Molina, P.; Duque-Carrillo, J.F. Wearable and Noninvasive Device for Integral Congestive Heart Failure Management in the IoMT Paradigm. Sensors 2023, 23, 7055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Zhou, A.; Liu, Y.; Chang, R.N.; Hsu, C.H.; Wang, S. A Cloud-Edge Collaboration Framework for Cognitive Service. IEEE Trans. Cloud Comput. 2022, 10, 1489–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, J. FedHome: Cloud-Edge Based Personalized Federated Learning for In-Home Health Monitoring. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2020, 21, 2818–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Dong, S.; Sun, S.; Wang, X.; Yang, G.; Wu, W.; Li, S.; De Albuquerque, V.H.C. Salient Object Detection in the Distributed Cloud-Edge Intelligent Network. IEEE Netw. 2020, 34, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Samah, A.; Ghaffa, D.; Abdullah, N.F.; Kamal, N.; Nordin, R.; Dela Cruz, J.C.; Magwili, G.V.; Mercado, R.J. Deployment of TinyML-Based Stress Classification Using Computational Constrained Health Wearable. Electronics 2025, 14, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, R.; Singh, D. Predictive Analytics for Stress Management in Nursing: A Machine Learning Approach Using Wearable IoT Devices. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2025, 15557, 60–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Xue, W.; Hou, D. Federated Learning for Nurse Stress Prediction Using Wearable Sensors: Integrating Biomechanical Data. Mol. Cell. Biomech. 2025, 22, 1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D. Chunking Algorithms. In Data Deduplication in High Performance Storage Systems; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 25–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruba, S.; Kalpana, A.M. Advanced Chunk-Based Data Deduplication Framework for Secure Data Storage in Cloud Using Hybrid Heuristic Assisted Optimal Key-Based Encryption. Wirel. Netw. 2025, 31, 3467–3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, R.; Vetrithangam, D. SmartChunk: A Hybrid Content-Based Chunking Algorithm with Hash De-Duplication for Effective Data Deduplication in Cloud Storage System. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Innovative Communication and Electrical and Computer Engineering (ICICEC), Davangere, India, 24–25 October 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onmalwar, V.M.; Vinoth Kumar, C.N.S. Cloud-Based Encryption and Chunking for Data Management. Lect. Notes Netw. Syst. 2025, 1234, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tmeizeh, M.; Rodríguez-Domínguez, C.; Hurtado-Torres, M.V. File Chunking Towards On-Chain Storage: A Blockchain-Based Data Preservation Framework. Clust. Comput. 2024, 27, 13531–13546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, S.B.; Jothi, K. A Robust Model for a Healthcare System with Chunk-Based RAID Encryption in a Multitenant Blockchain Network. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2024, 15, 1238–1249. [Google Scholar]
- Tmeizeh, M.; Rodríguez-Domínguez, C.; Hurtado-Torres, M.V. Optimizing Blockchain File Storage: Enhancing Performance and Reducing Ledger Size with Adaptive Compression and Advanced Data Structures. Clust. Comput. 2025, 28, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusztai, T.; Nastic, S. ChunkFunc: Dynamic SLO-Aware Configuration of Serverless Functions. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2025, 36, 1237–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, T.; Dong, N.; Li, W.; Cao, J. Edge Computing with Artificial Intelligence: A Machine Learning Perspective. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 55, 3555802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, G.; Guo, P. Federated Learning in Cloud-Edge Collaborative Architecture: Key Technologies, Applications and Challenges. J. Cloud Comput. 2022, 11, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, C.; Nguyen, D.T.; Njah, Y.; Tran, N.H.; Nguyen, K.K.; Cheriet, M. Share-to-Run IoT Services in Edge Cloud Computing. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Ma, A. IoT Application Modules Placement and Dynamic Task Processing in Edge-Cloud Computing. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 12771–12781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Li, L.; Guan, Q. Energy-Efficient and Delay-Guaranteed Workload Allocation in IoT-Edge-Cloud Computing Systems. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 78685–78697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haji, L.; Ahmed, O.; Dino, H.; Haji, L.M.; Ahmad, O.M.; Zeebaree, S.R.M.; Dino, H.I.; Zebari, R.R.; Shukur, H.M. Impact of Cloud Computing and Internet of Things on the Future Internet. Technol. Rep. Kansai Univ. 2020, 62, 2179–2190. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, L.M.; Piran, M.J.; Han, D.; Min, K.; Moon, H. A Survey on Internet of Things and Cloud Computing for Healthcare. Electronics 2019, 8, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anikwe, C.V.; Nweke, H.F.; Ikegwu, A.C.; Egwuonwu, C.A.; Onu, F.U.; Alo, U.R.; Teh, Y.W. Mobile and Wearable Sensors for Data-Driven Health Monitoring System: State-of-the-Art and Future Prospect. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 202, 117362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angel, N.A.; Ravindran, D.; Vincent, P.M.D.R.; Srinivasan, K.; Hu, Y.C. Recent Advances in Evolving Computing Paradigms: Cloud, Edge, and Fog Technologies. Sensors 2022, 22, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacanin, N.; Zivkovic, M.; Bezdan, T.; Venkatachalam, K.; Abouhawwash, M. Modified Firefly Algorithm for Workflow Scheduling in Cloud-Edge Environment. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 9043–9068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Lin, B.; Chen, Z.; Wolter, K.; Min, G. Energy-Efficient Offloading for DNN-Based Smart IoT Systems in Cloud-Edge Environments. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2022, 33, 683–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Cheng, S.; Lu, G.; Zhou, H.; Jia, B.; You, Y. AutoChunk: Automated Activation Chunk for Memory-Efficient Long Sequence Inference. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), Vienna, Austria, 7–11 May 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Le, K.; Ho, T.V.; Tran, D.; Chau, D.T. ChunkFormer: Masked Chunking Conformer for Long-Form Speech Transcription. In Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Hyderabad, India, 6–11 April 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourtzis, D.; Angelopoulos, J.; Panopoulos, N. Blockchain Integration in the Era of Industrial Metaverse. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.M.; Saraniemi, S. Trust in Blockchain-Enabled Exchanges: Future Directions in Blockchain Marketing. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2023, 51, 914–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Shiwakoti, R.K.; Jarvis, R.; Mordi, C.; Botchie, D. Accounting and Auditing with Blockchain Technology and Artificial Intelligence: A Literature Review. Int. J. Account. Inf. Syst. 2023, 48, 100598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gousia, H.; Sparsh, S.; Sara, I.; Imtiaz, A.; Shaima, Q.; Malik, I. Blockchain Technology: Benefits, Challenges, Applications, and Integration of Blockchain Technology with Cloud Computing. Future Internet 2022, 14, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh-The, T.; Gadekallu, T.R.; Wang, W.; Yenduri, G.; Ranaweera, P.; Pham, Q.-V.; da Costa, D.B.; Liyanage, M. Blockchain for the Metaverse: A Review. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2023, 143, 401–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Yu, X. A Survey on Blockchain Technology and Its Security. Blockchain Res. Appl. 2022, 3, 100067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seok, B.; Park, J.; Park, J.H. A Lightweight Hash-Based Blockchain Architecture for Industrial IoT. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devika, K.N.; Bhakthavatchalu, R. Parameterizable FPGA Implementation of SHA-256 Using Blockchain Concept. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Communication and Signal Processing (ICCSP), Melmaruvathur, India, 4–6 April 2019; pp. 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Wan, H.; Li, B.; Yan, X. Chaotic Parallel Hash Engine with Dynamic Stochastic Diffusion for Blockchain and Cloud Security. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 37945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Pang, X.; Qian, H. PartitionChain: A Scalable and Reliable Data Storage Strategy for Permissioned Blockchain. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2021, 35, 4124–4136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, S.; Dey, T.; Mukherjee, A.; Bhattacharya, P.; De, D. FedChain: Decentralized Federated Learning and Blockchain-Assisted System for Sustainable Irrigation. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2025, 71, 2243–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Brain, G.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention Is All You Need. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30 (NIPS 2017), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Available online: https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2017/hash/3f5ee243547dee91fbd053c1c4a845aa-Abstract.html (accessed on 6 October 2025).
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, S.; Peng, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Xiong, H.; Zhang, W. Informer: Beyond Efficient Transformer for Long Sequence Time-Series Forecasting. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence 2021, Virtually, 2–9 February 2021; Available online: https://ojs.aaai.org/index.php/AAAI/article/view/17325 (accessed on 6 October 2025).
- Akuthota, U.C.; Bhargava, L. Transformer-Based Intrusion Detection for IoT Networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2025, 12, 6062–6067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Hu, T.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Wang, J. TimesNet: Temporal 2D-Variation Modeling for General Time Series Analysis. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2210.02186. [Google Scholar]
- ElkanaEbinazer, S. Hybrid Encryption with Greylag Goose Optimizer-Based Swin Transformer for Secured Data Deduplication and Anomaly Detection for Cloud-Based IoMT Applications. SSRN 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakarthik, R.; Suneel, S.; Thatipudi, J.G.; Jaganraja, V.; Vohra, M.; Gopinath, D. FogMedX-Transform: A Transformer-Based Task Interoperability Framework for Energy-Efficient Fog-Enabled IoMT. In Proceedings of the 8th Innovative Computing Technologies (ICICT), Hyderabad, India, 12–13 December 2025; pp. 1771–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalakoti, R.; Nomm, S.; Bahsi, H. Explainable Transformer-Based Intrusion Detection in Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) Networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA), Miami, FL, USA, 18–20 December 2024; pp. 1164–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Ref. | Method | Computing Paradigm | Data Processing and Train–Test Split | Model | Performance Evaluation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [32] | TinyML-based with NearMiss-1 balancing and Min-Max normalisation | Edge (Raspberry Pi RP2040) | NearMiss undersampling, random state: 42, MinMaxScaler, train/val/test: 60/20/20 | KNN | Val_Accuracy: 98% Val_Precision: 98% Val_Recall: 98% Val_F1: 98% Test_Accuracy: 98% Test_Precision: 98% Test_Recall: 98% Test_F1: 98% |
| [33] | Feature ranking and ROC validation | Centralised | 1% subsampling for pretests, Random_state: 42, MinMaxScaler, Z-score normalisation, missing value handling, train/test: 80/20 | KNN | Val_Accuracy: 90% Val_Precision: 91% Val_Recall: 90% Val_F1: 91% Test_Accuracy: 90% Test_Precision: 91% Test_Recall: 90% Test_F1: 91% |
| [34] | Federated learning | Cloud–edge + federated learning | Duplicate removal, Pearson correlation, timestamp, Z-score normalisation, client split: 80/20, global val/test: 50/50 | Neural network | Global accuracy: 90% Precision: 85% Recall: 85% F1: 85% CL accuracy: 97% FL accuracy: 93% |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Embedding dimension | 128 |
| Layers | 3 |
| Periods | (3, 5, 7, 9, 11) (only TimesNet) |
| Dropout | 0.1 |
| Batch size | 32 |
| Learning rate (LR) | 0.001 |
| Optimizer | Adam |
| Epochs | 20 |
| Cross-validation | 5 × 5 repeated stratified k-fold (25-fold) |
| Split | 70% train, 20% validation, 10% test |
| Feature Selection | 9 |
| Model | Accuracy (%) (Mean ± STD) | Precision (%) (Mean ± STD) | Recall (%) (Mean ± STD) | F1-Score (%) (Mean ± STD) | ROC-AUC (%) (Mean ± STD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TimesNet | 99.6 ± 0.08 | 99.6 ± 0.08 | 99.6 ± 0.08 | 99.6 ± 0.08 | 99.8 ± 0.13 |
| PatchTST | 99.5 ± 0.06 | 99.5 ± 0.06 | 99.5 ± 0.06 | 99.5 ± 0.06 | 99.8 ± 0.04 |
| TransformerEncoder | 99.5 ± 0.04 | 99.5 ± 0.04 | 99.5 ± 0.04 | 99.5 ± 0.04 | 99.8 ± 0.01 |
| Autoformer | 99.3 ± 0.08 | 99.3 ± 0.08 | 99.3 ± 0.08 | 99.3 ± 0.08 | 99.7 ± 0.06 |
| NST | 99.1 ± 0.07 | 99.1 ± 0.07 | 99.1 ± 0.07 | 99.1 ± 0.07 | 99.7 ± 0.03 |
| Model | Accuracy (%) (Val/Test) | Precision (%) (Val/Test) | Recall (%) (Val/Test) | F1-Score (%) (Val/Test) | ROC-AUC (%) (Val/Test) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TimesNet | 99.6/99.6 | 99.6/99.6 | 99.6/99.6 | 99.6/99.6 | 99.9/99.9 |
| PatchTST | 99.6/99.6 | 99.6/99.6 | 99.6/99.6 | 99.6/99.6 | 99.9/99.9 |
| TransformerEncoder | 99.6/99.6 | 99.6/99.6 | 99.6/99.6 | 99.6/99.6 | 99.9/99.9 |
| Autoformer | 99.4/99.4 | 99.4/99.4 | 99.4/99.4 | 99.4/99.4 | 99.8/99.8 |
| NST | 99.2/99.2 | 99.2/99.2 | 99.2/99.2 | 99.2/99.2 | 99.7/99.7 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| manifest_hash | 0824bab5176126c7e3fe9be96eb20163d7018a751610c70a30d6c7b102bfeelf |
| ecc_signature | 42248d1fd75bc733d152bb28087fbb56ea374829945ea7c05ce4e1b378cb6be |
| timestamp | 1,759,346,521.7381518 |
| Chunk Size | Number of Chunks | Retries | Retry Ratio | Verification Time (s) | Upload Cost (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 64 | 26,374 | 1318 | 0.049973 | 0.024687 | 0.002984 |
| 128 | 13,187 | 659 | 0.049973 | 0.013822 | 0.002984 |
| 256 | 6593 | 329 | 0.049971 | 0.006675 | 0.002984 |
| 512 | 3296 | 164 | 0.049757 | 0.003138 | 0.002984 |
| 1024 | 1648 | 82 | 0.049757 | 0.001657 | 0.002984 |
| Scenario | Accuracy (%) | Train Time (s) | Avg. Power (W) | GPU Energy (J) | Verification Time (s) | Retry Ratio | Upload Cost (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TimesNet | 99.5 | 4804.817 | 30.178 | 141,831.937 | 0 | 0 | 0.0029 |
| TimesNet + BC | 99.3 | 4822.324 | 30.131 | 142,009.955 | 0.016 | 0 | 0.0029 |
| TimesNet + BC + Retry | 99.3 | 4852.261 | 30.062 | 142,642.564 | 0.017 | 0.049 | 0.0029 |
| Ref. | Dataset | Method | Security/Data Integrity | Model | XAI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proposed work (Ours) | Nurse Stress (IoMT Sensor) | Chunk–SHA256–ECC, Blockchain Logging, TimesNet | Chunk-Level Integrity, ECC Signature, Blockchain Manifest | Transformer (TimesNet) | SHAP |
| [37] | Linux/TREC | Hybrid CDC + hash deduplication | No data integrity, compression orientated | – | – |
| [39] | On-chain dataset | Chunk hashing + manifest combination | SHA-256 hash + manifest validation | – | – |
| [40] | Health (EHR) | Chunk–RAID + AES encryption + blockchain | AES-256 + RAID integrity | Basic ML | – |
| [41] | Cloud storage | Adaptive compression + advanced chunking | SHA-256 + ECC validation | – | – |
| [60] | IoT sensor data | Blockchain + federated learning | FL parameters registered on the blockchain | Transformer-based FL | XAI |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Arslanoğlu, K.; Karaköse, M. An Efficient Clinical Decision Support Framework Using IoMT Based on Explainable and Trustworthy Artificial Intelligence with Transformer Model and Blockchain-Integrated Chunking. Diagnostics 2026, 16, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics16010007
Arslanoğlu K, Karaköse M. An Efficient Clinical Decision Support Framework Using IoMT Based on Explainable and Trustworthy Artificial Intelligence with Transformer Model and Blockchain-Integrated Chunking. Diagnostics. 2026; 16(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics16010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleArslanoğlu, Kübra, and Mehmet Karaköse. 2026. "An Efficient Clinical Decision Support Framework Using IoMT Based on Explainable and Trustworthy Artificial Intelligence with Transformer Model and Blockchain-Integrated Chunking" Diagnostics 16, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics16010007
APA StyleArslanoğlu, K., & Karaköse, M. (2026). An Efficient Clinical Decision Support Framework Using IoMT Based on Explainable and Trustworthy Artificial Intelligence with Transformer Model and Blockchain-Integrated Chunking. Diagnostics, 16(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics16010007






