EM-DeepSD: A Deep Neural Network Model Based on Cell-Free DNA End-Motif Signal Decomposition for Cancer Diagnosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. An Overview of EM-DeepSD
2.2. Data Collection and Preprocessing
2.3. Extract EM Profiles
2.4. The Architecture of End-Motif Signal Decomposition Deep Learning Framework (EM-DeepSD)
2.5. Motif Diversity Score (MDS)
2.6. “Founder” End-Motif Profiles (F-Profiles)
2.7. Develop Optimized Motif Diversity Score (MDS-SDs) Based on Signal Decomposition
2.8. Performance Evaluation Metrics
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
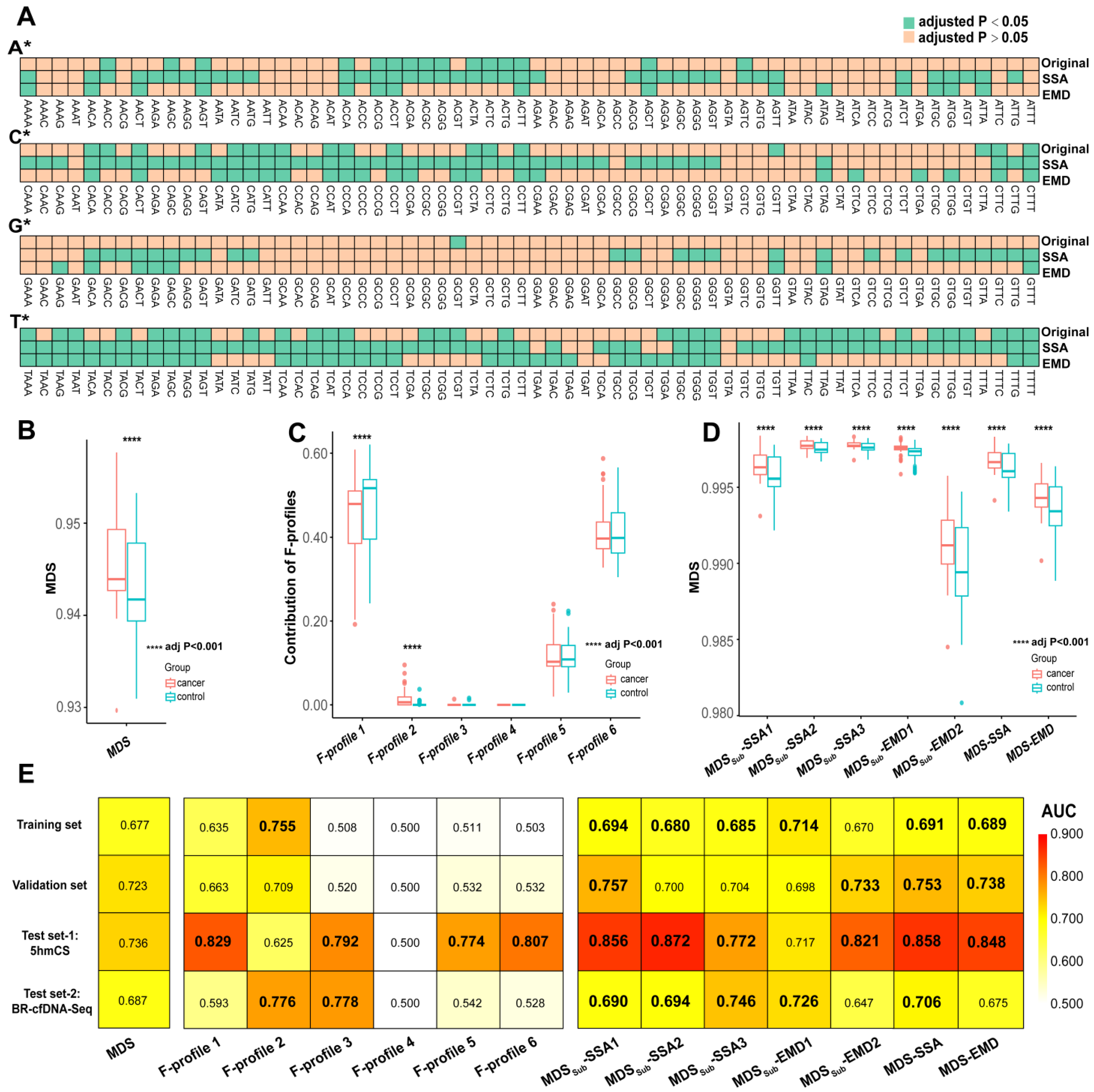
3.1. EM Profiles of cfDNA Differences Between Cancer and Control Groups
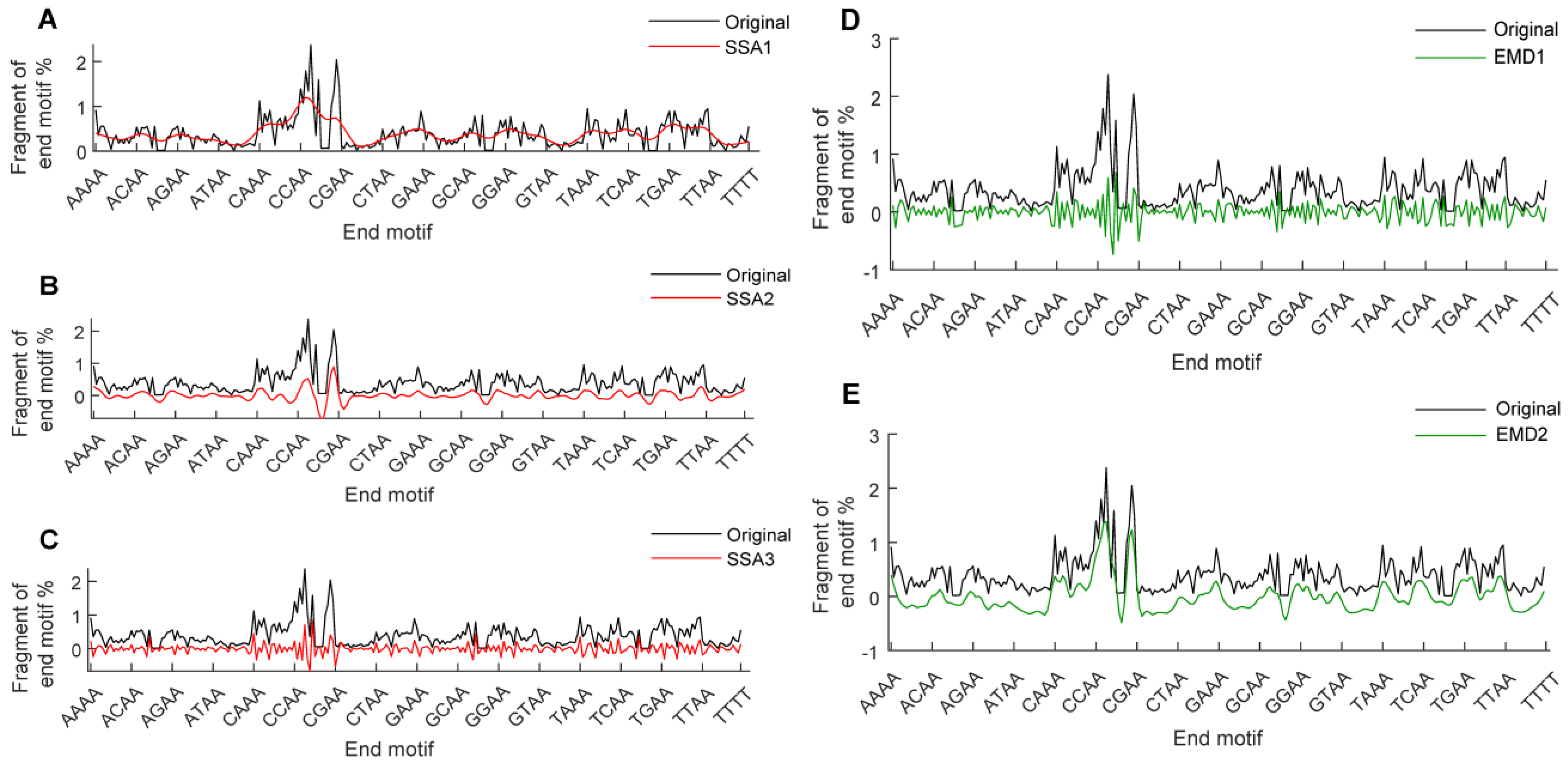
3.2. Signal Decomposition of EM Profiles and the Construction of MDS-SDs
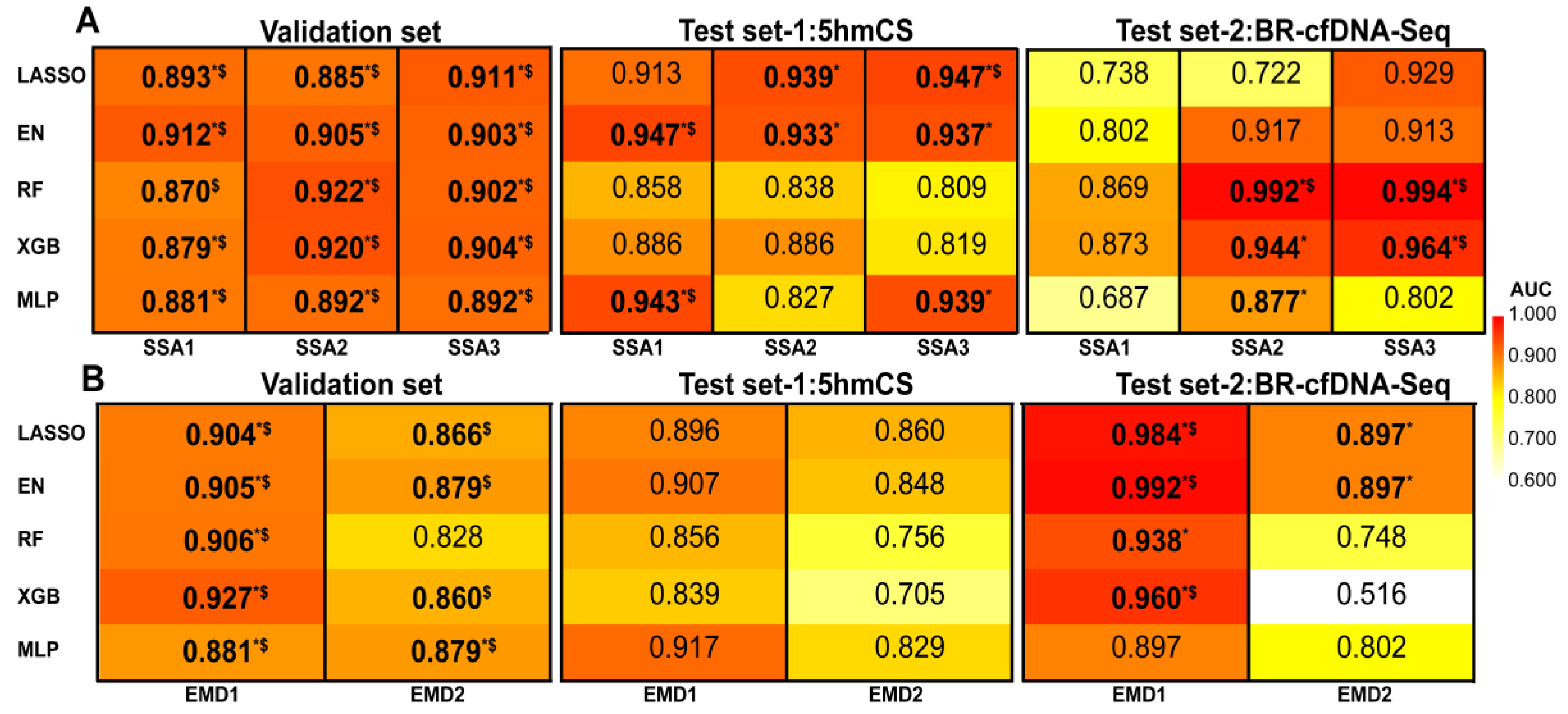
3.3. Machine Learning Based on Signal Decomposition Further Enhances Cancer Diagnosis Accuracy
3.4. Development and Validation of EM-DeepSD Framework
3.5. Ablation Testing of EM-DeepSSA Model and the Impact of SSA Window Length on Cancer Assessment
3.6. Influence of Clinical Features on Model Prediction
4. Discussion
4.1. Challenges in Cancer Diagnosis Using the EM Profiles of cfDNA
4.2. EM-DeepSD Is Capable of Enhancing the Accuracy of Cancer Diagnosis
4.3. Advantages, Limitations and Future Directions
4.4. Implications for Clinical Practice
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 4-mer EMs profile | the first 4 bases at cfDNA’s 5′ end |
| 5hmCS | 5-hydroxymethylcytosine sequencing |
| 95% CI | 95% confident interval |
| ACC | accuracy |
| AUC | Area Under Curve |
| BC | breast cancer |
| BH | Benjamini-Hochberg |
| BR-cfDNA-Seq | Broad-range cell-free DNA sequencing |
| cfDNA | cell-free DNA |
| CRC | colorectal cancer |
| EMD | Empirical Mode Decomposition |
| EM-DeepSD | end-motif signal decomposition deep learning framework |
| EN | Elastic Net Regression |
| F1 | F1-score |
| GBM | glioblastoma |
| GC | Gastric cancer |
| HCC | hepatocellular carcinoma |
| HNSCC | head and neck squamous cell carcinoma |
| LASSO | Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator |
| LC | lung cancer |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| MDS | Motif Diversity Score |
| ML | machine learning |
| MLP | Multilayer Perceptron |
| NPC | nasopharyngeal carcinoma |
| PC | pancreatic cancer |
| PE | Permutation Entropy |
| RF | Random Forest |
| SEN | sensitivity |
| SPE | specificity |
| SSA | Singular Value Decomposition |
| WGBS | Whole Genome Bisulfite Sequencing |
| WGS | Whole Genome Sequencing |
| XGBoost | eXtreme Gradient Boosting |
References
- Serpas, L.; Chan, R.W.Y.; Jiang, P.; Ni, M.; Sun, K.; Rashidfarrokhi, A.; Soni, C.; Sisirak, V.; Lee, W.S.; Cheng, S.H.; et al. Dnase1l3 deletion causes aberrations in length and end-motif frequencies in plasma DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Sun, K.; Peng, W.; Cheng, S.H.; Ni, M.; Yeung, P.C.; Heung, M.M.S.; Xie, T.; Shang, H.; Zhou, Z.; et al. Plasma DNA End-Motif Profiling as a Fragmentomic Marker in Cancer, Pregnancy, and Transplantation. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 664–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Kang, G.; Jiang, P.; Qiao, R.; Lam, W.K.J.; Yu, S.C.Y.; Ma, M.L.; Ji, L.; Cheng, S.H.; Gai, W.; et al. Epigenetic analysis of cell-free DNA by fragmentomic profiling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2209852119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Swarup, N.; Li, F.; Kordi, M.; Lin, C.C.; Yang, S.C.; Huang, W.L.; Aziz, M.; Kim, Y.; Chia, D.; et al. Distinct Features of Plasma Ultrashort Single-Stranded Cell-Free DNA as Biomarkers for Lung Cancer Detection. Clin. Chem. 2023, 69, 1270–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.T.C.; Nguyen, T.H.; Doan, N.N.T.; Pham, T.M.Q.; Nguyen, G.T.H.; Nguyen, T.D.; Tran, T.T.T.; Vo, D.L.; Phan, T.H.; Jasmine, T.X.; et al. Multimodal analysis of methylomics and fragmentomics in plasma cell-free DNA for multi-cancer early detection and localization. Elife 2023, 12, RP89083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Chan, R.W.Y.; Cheung, P.P.H.; Ni, M.; Wong, D.K.L.; Zhou, Z.; Ma, M.L.; Huang, L.; Xu, X.; Lee, W.S.; et al. Fragmentomics of urinary cell-free DNA in nuclease knockout mouse models. PLoS Genet. 2022, 18, e1010262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, T.; Pan, M.; Shi, H.; Wang, L.; Bai, Y.; Ge, Q. Cell-Free DNA Fragmentomics: The Novel Promising Biomarker. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fan, X.; Bao, H.; Xia, F.; Wan, J.; Shen, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wei, Y.; Wu, X.; et al. Utility of Circulating Free DNA Fragmentomics in the Prediction of Pathological Response after Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy in Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer. Clin. Chem. 2023, 69, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, N.; Wu, X.; Tang, W.; Bao, H.; Si, C.; Shao, P.; Li, D.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, D.; et al. Multi-Dimensional Fragmentomics Enables Early and Accurate Detection of Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Res. 2024, 84, 3286–3295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Meng, X.Y.; Zhou, X. Systematically Evaluating Cell-Free DNA Fragmentation Patterns for Cancer Diagnosis and Enhanced Cancer Detection via Integrating Multiple Fragmentation Patterns. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, e2308243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Xuan, Y.; Shi, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, A.; Li, N.; Yang, S.; He, X.; Zhao, G.; et al. Leveraging cfDNA fragmentomic features in a stacked ensemble model for early detection of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Rep. Med. 2024, 5, 101664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Ma, M.L.; Chan, R.W.Y.; Lam, W.K.J.; Peng, W.; Gai, W.; Hu, X.; Ding, S.C.; Ji, L.; Zhou, Q.; et al. Fragmentation landscape of cell-free DNA revealed by deconvolutional analysis of end motifs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2220982120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Liu, J.; Chen, K.; Li, X. Language model enables end-to-end accurate detection of cancer from cell-free DNA. Brief. Bioinform. 2024, 25, bbae053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibon, M.; Evgeniou, T. To combine or not to combine: Selecting among forecasts and their combinations. Int. J. Forecast. 2005, 21, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundby, R.T.; Szymanski, J.J.; Pan, A.; Jones, P.A.; Mahmood, S.Z.; Reid, O.H.; Srihari, D.; Armstrong, A.E.; Chamberlain, S.; Burgic, S.; et al. Early detection of malignant and pre-malignant peripheral nerve tumors using cell-free DNA fragmentomics. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 30, 4363–4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.E.; Shen, Z.; Long, S.R.; Wu, M.C.; Shih, H.H.; Zheng, Q.; Yen, N.-C.; Tung, C.C.; Liu, H.H. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1998, 454, 903–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghofrani Jahromi, M.; Parsaei, H.; Zamani, A.; Dehbozorgi, M. Comparative Analysis of Wavelet-based Feature Extraction for Intramuscular EMG Signal Decomposition. J. Biomed. Phys. Eng. 2017, 7, 365–378. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Sun, J.; Yang, H.; Guo, T.; Pan, J.; Wang, W. The heart sound classification of congenital heart disease by using median EEMD-Hurst and threshold denoising method. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2025, 63, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhongade, D.; Captain, K.; Dahiya, S. EEG-based schizophrenia detection: Integrating discrete wavelet transform and deep learning. Cogn. Neurodyn. 2025, 19, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, W.; Yang, C.; Kou, M.; Zhang, K.; Liu, X. Prediction of Patient Visits for Skin Diseases through Enhanced Evolutionary Computation and Ensemble Learning. J. Med. Syst. 2025, 49, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsaei, H.; Stashuk, D.W.; Rasheed, S.; Farkas, C.; Hamilton-Wright, A. Intramuscular EMG signal decomposition. Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 38, 435–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Zhu, X.; Huang, C.; Yang, X.; Wen, F.; Zhong, M. A New Approach for Stock Price Analysis and Prediction Based on SSA and SVM. Int. J. Inf. Technol. Decis. Mak. 2019, 18, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantari, M. Forecasting COVID-19 pandemic using optimal singular spectrum analysis. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2021, 142, 110547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Tomar, H.; Mehla, V.K.; Komaragiri, R.; Kumar, M. Stationary wavelet transform based ECG signal denoising method. ISA Trans. 2021, 114, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, A.J.; Lopes-Dos-Santos, V.; Dupret, D.; Nobre, A.C.; Woolrich, M.W. EMD: Empirical Mode Decomposition and Hilbert-Huang Spectral Analyses in Python. J. Open Source Softw. 2021, 6, 2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Tong, S.; Tong, Z.; Cong, F. Signal Identification of Gear Vibration in Engine-Gearbox Systems Based on Auto-Regression and Optimized Resonance-Based Signal Sparse Decomposition. Sensors 2021, 21, 1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cura, O.K.; Akan, A.; Yilmaz, G.C.; Ture, H.S. Detection of Alzheimer’s Dementia by Using Signal Decomposition and Machine Learning Methods. Int. J. Neural Syst. 2022, 32, 2250042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munguía-Siu, A.; Vergara, I.; Espinoza-Rodríguez, J.H. The Use of Hybrid CNN-RNN Deep Learning Models to Discriminate Tumor Tissue in Dynamic Breast Thermography. J. Imaging 2024, 10, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Yang, M.; Liu, J.; Chen, K.; Li, X. Development of a deep learning model for cancer diagnosis by inspecting cell-free DNA end-motifs. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2024, 8, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiecinski, J.; Grodecki, K.; Pieszko, K.; Dabrowski, M.; Chmielak, Z.; Wojakowski, W.; Niemierko, J.; Fijalkowska, J.; Jagielak, D.; Ruile, P.; et al. Preprocedural CT angiography and machine learning for mortality prediction after transcatheter aortic valve replacement. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2025. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.W.; Peng, Y.H.; Liu, C.T.; Chen, H.; Chu, L.Y.; Chen, H.L.; Wu, Z.Y.; Wei, W.Q.; Xu, L.Y.; Wu, F.C.; et al. Machine learning technique-based four-autoantibody test for early detection of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: A multicenter, retrospective study with a nested case-control study. BMC Med. 2025, 23, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Guo, H.; Li, Q.; Chen, K.; Xu, J.; Ma, Y.; Lin, Z.; Zhou, X.; Chen, B. Machine Learning-Enhanced Cerebrospinal Fluid N-Glycome for the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma. J. Proteome Res. 2025. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feher, B.; de Souza Oliveira, E.H.; Mendes Duarte, P.; Werdich, A.A.; Giannobile, W.V.; Feres, M. Machine learning-assisted prediction of clinical responses to periodontal treatment. J. Periodontol. 2025. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stackpole, M.L.; Zeng, W.; Li, S.; Liu, C.C.; Zhou, Y.; He, S.; Yeh, A.; Wang, Z.; Sun, F.; Li, Q.; et al. Cost-effective methylome sequencing of cell-free DNA for accurately detecting and locating cancer. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristiano, S.; Leal, A.; Phallen, J.; Fiksel, J.; Adleff, V.; Bruhm, D.C.; Jensen, S.; Medina, J.E.; Hruban, C.; White, J.R.; et al. Genome-wide cell-free DNA fragmentation in patients with cancer. Nature 2019, 570, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Xie, Y.; Feng, X.; Li, Y.; Shen, L.; Chen, Y. Artificial intelligence in gastrointestinal cancer research: Image learning advances and applications. Cancer Lett. 2025, 614, 217555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shen, H.; Chen, K.; Li, X. Large language model produces high accurate diagnosis of cancer from end-motif profiles of cell-free DNA. Brief. Bioinform. 2024, 25, bbae430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Shi, Y.; Cheng, S.H.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Shi, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Ma, M.L.; Ding, S.C.; et al. Transformer-based deep learning for accurate detection of multiple base modifications using single molecule real-time sequencing. Commun. Biol. 2025, 8, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.R.; Ahn, J.M.; Lee, J.; Kim, D.; Park, J.; Jeong, B.H.; Oh, D.; Kim, S.M.; Jung, G.C.; Choi, B.H.; et al. Integrating Plasma Cell-Free DNA Fragment End Motif and Size with Genomic Features Enables Lung Cancer Detection. Cancer Res. 2025. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Rahman, C.R.; Getty, V.; Odinokov, D.; Baruah, P.; Carrié, H.; Lim, A.J.; Guo, Y.A.; Poh, Z.W.; Sim, N.L.; et al. A deep-learning model for quantifying circulating tumour DNA from the density distribution of DNA-fragment lengths. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2025, 9, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, M.; Heidary, M.; Mechri, A.; Da Silva, K.; Gorse, M.; Dixon, V.; von Grafenstein, K.; Bianchi, C.; Hego, C.; Rampanou, A.; et al. Noninvasive Multicancer Detection Using DNA Hypomethylation of LINE-1 Retrotransposons. Clin. Cancer Res. 2025, 31, 1275–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehmood, F.; Arshad, S.; Shoaib, M. ADH-Enhancer: An attention-based deep hybrid framework for enhancer identification and strength prediction. Brief. Bioinform. 2024, 25, bbae030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Dong, P.; Guo, S.; Tao, C.; Chen, W.; Zhao, W.; Wang, J.; Cheung, R.; Villanueva, A.; Fan, J.; et al. Hypomethylation in HBV integration regions aids non-invasive surveillance to hepatocellular carcinoma by low-pass genome-wide bisulfite sequencing. BMC Med. 2020, 18, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.X.; Yin, S.; Ma, L.; Wheeler, A.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, B.; Xiong, J.; Zhang, W.; Hu, J.; et al. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine signatures in cell-free DNA provide information about tumor types and stages. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 1231–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, F.; Andrews, S.R. Bismark: A flexible aligner and methylation caller for Bisulfite-Seq applications. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1571–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.C.; Jiang, P.; Chan, C.W.; Sun, K.; Wong, J.; Hui, E.P.; Chan, S.L.; Chan, W.C.; Hui, D.S.; Ng, S.S.; et al. Noninvasive detection of cancer-associated genome-wide hypomethylation and copy number aberrations by plasma DNA bisulfite sequencing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 18761–18768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.K.; Krishnan, S. A singular spectrum analysis-based model-free electrocardiogram denoising technique. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020, 188, 105304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Choi, Y.J.; Kim, I.K.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, H.; Baik, S.H.; Kim, N.K.; Lee, K.Y. LASSO-Based Machine Learning Algorithm for Prediction of Lymph Node Metastasis in T1 Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 53, 773–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitheiser, M.; Capper, D.; Seegerer, P.; Lehmann, A.; Schüller, U.; Müller, K.R.; Klauschen, F.; Jurmeister, P.; Bockmayr, M. Machine learning models predict the primary sites of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma metastases based on DNA methylation. J. Pathol. 2022, 256, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Li, Y.; Huang, T. Using Machine Learning Methods to Study Colorectal Cancer Tumor Micro-Environment and Its Biomarkers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devi, S.; Gaikwad, S.R.; Harikrishnan, R. Prediction and Detection of Cervical Malignancy Using Machine Learning Models. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2023, 24, 1419–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long Short-Term Memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Guo, S.; Duan, Q.; Zhang, W.; Gao, S.; Jing, W.; Jiang, G.; Kong, X.; Li, P.; Li, Y.; et al. Detection and characterization of pancreatic and biliary tract cancers using cell-free DNA fragmentomics. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 43, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


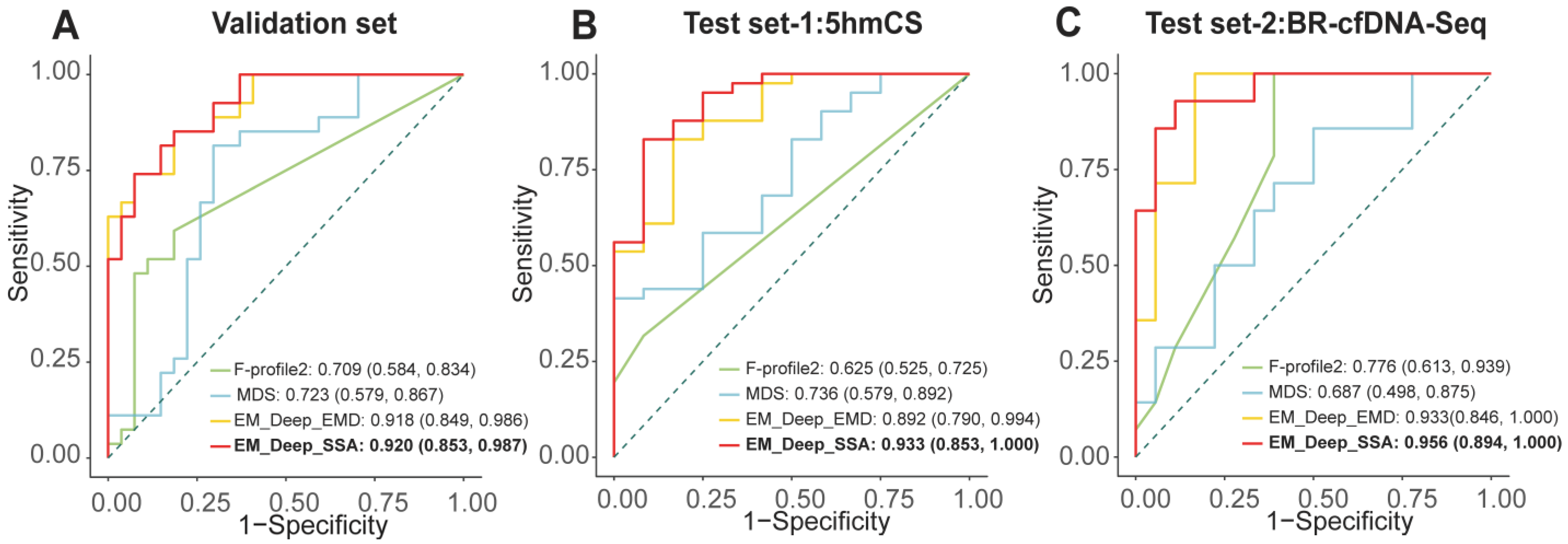
| Data Set | Method | Sensitivity | Specificity | Accuracy | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Validation set | |||||
| MDS | 0.741 (0.537, 0.889) | 0.704 (0.498, 0.862) | 0.722 (0.581, 0.831) | 0.727 | |
| F-profile 2 | 0.593 (0.388, 0.776) | 0.815 (0.619, 0.937) | 0.704 (0.562, 0.816) | 0.667 | |
| EM_Deep_EMD | 0.852 (0.662, 0.958) | 0.815 (0.619, 0.937) | 0.833 (0.702, 0.916) | 0.836 | |
| EM_Deep_SSA | 0.852 (0.663, 0.958) | 0.815 (0.619, 0.937) | 0.833 (0.702, 0.916) | 0.836 | |
| Test set-1 | |||||
| MDS | 0.976 (0.871, 0.999) | 0.250 (0.054, 0.572) | 0.811 (0.676, 0.901) | 0.889 | |
| F-profile 2 | 0.317 (0.181, 0.481) | 0.917 (0.615, 0.998) | 0.453 (0.318, 0.595) | 0.473 | |
| EM_Deep_EMD | 0.805 (0.651, 0.912) | 0.833 (0.516, 0.979) | 0.811 (0.676, 0.901) | 0.868 | |
| EM_Deep_SSA | 0.829 (0.679, 0.928) | 0.917 (0.615, 0.998) | 0.849 (0.719, 0.928) | 0.895 | |
| Test set-2 | |||||
| MDS | 1.000 (0.768, 1.000) | 0.000 (0.000, 0.185) | 0.438 (0.268, 0.621) | 0.609 | |
| F-profile 2 | 1.000 (0.768, 1.000) | 0.500 (0.260, 0.740) | 0.719 (0.530, 0.856) | 0.757 | |
| EM_Deep_EMD | 1.000 (0.768, 1.000) | 0.556 (0.308, 0.785) | 0.750 (0.562, 0.879) | 0.778 | |
| EM_Deep_SSA | 1.000 (0.768, 1.000) | 0.667 (0.410, 0.867) | 0.813 (0.630, 0.921) | 0.813 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Z.-Y.; Huang, C.-L.; Wang, T.-M.; Zhou, S.-H.; Pei, L.; Jia, W.-H.; Jia, W.-H. EM-DeepSD: A Deep Neural Network Model Based on Cell-Free DNA End-Motif Signal Decomposition for Cancer Diagnosis. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1156. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091156
Zhao Z-Y, Huang C-L, Wang T-M, Zhou S-H, Pei L, Jia W-H, Jia W-H. EM-DeepSD: A Deep Neural Network Model Based on Cell-Free DNA End-Motif Signal Decomposition for Cancer Diagnosis. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(9):1156. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091156
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Zhi-Yang, Chang-Ling Huang, Tong-Min Wang, Shi-Hao Zhou, Lu Pei, Wen-Hui Jia, and Wei-Hua Jia. 2025. "EM-DeepSD: A Deep Neural Network Model Based on Cell-Free DNA End-Motif Signal Decomposition for Cancer Diagnosis" Diagnostics 15, no. 9: 1156. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091156
APA StyleZhao, Z.-Y., Huang, C.-L., Wang, T.-M., Zhou, S.-H., Pei, L., Jia, W.-H., & Jia, W.-H. (2025). EM-DeepSD: A Deep Neural Network Model Based on Cell-Free DNA End-Motif Signal Decomposition for Cancer Diagnosis. Diagnostics, 15(9), 1156. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091156





