Machine Learning in Microwave Medical Imaging and Lesion Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Lesion Classification
2.1. Brain
2.2. Breast
2.3. Others
3. Estimation and Monitoring
4. Image Reconstruction
4.1. Brain Imaging
4.2. MW Breast Imaging
4.3. Neck Tumor Imaging
4.4. Thermoacoustic Imaging
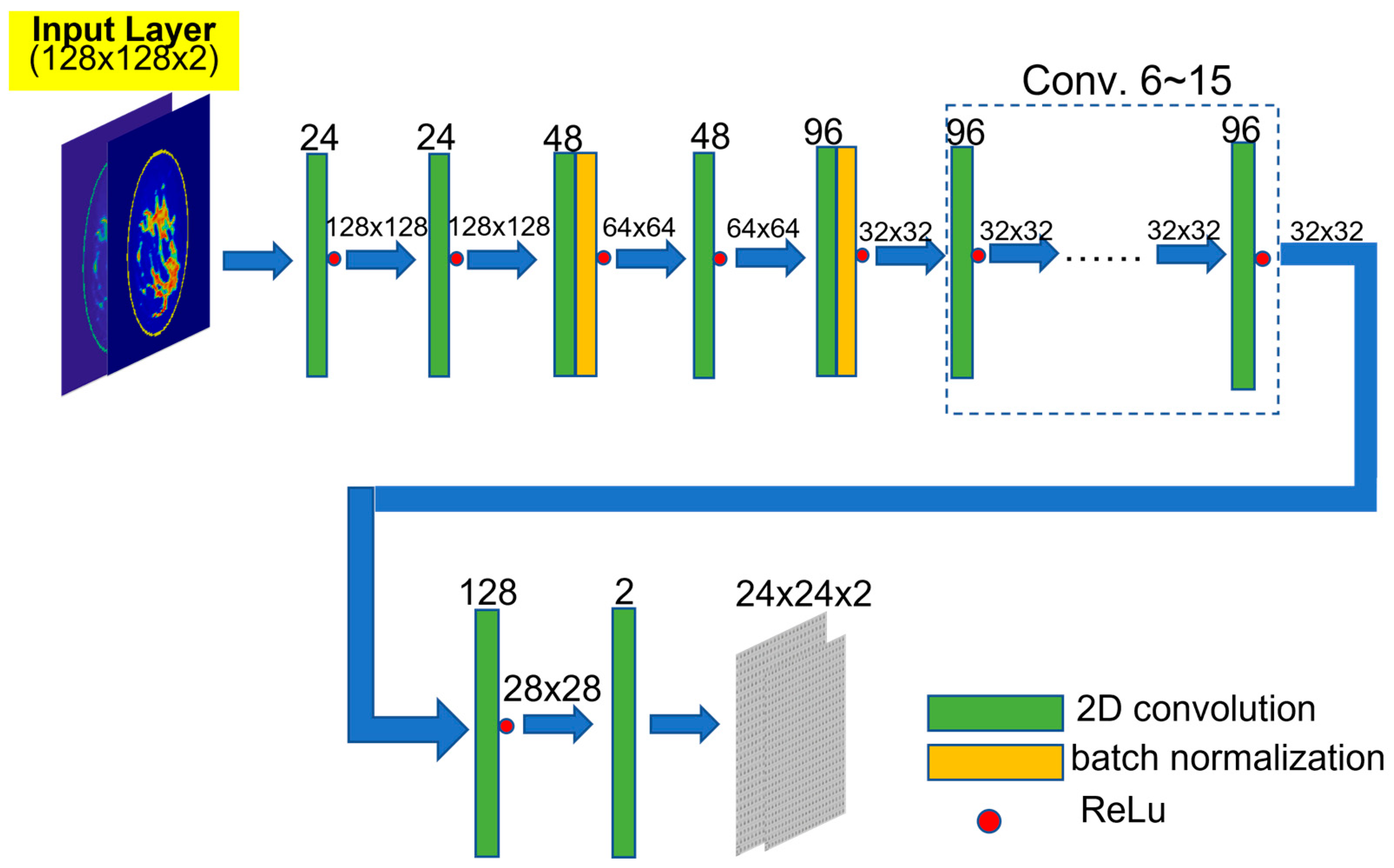
5. Microwave Image Postprocessing
6. Phantom Generation and Forward Computation
7. Conclusions and Outlook
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nikolova, N.K. Microwave imaging for breast cancer. IEEE Microw. Mag. 2011, 12, 78–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Zhou, B.; Wang, G. UWB microwave imaging for early detection breast cancer. J. Microw. 2005, 21, 66–70. [Google Scholar]
- Tournier, P.; Bonazzoli, M.; Dolean, V.; Rapetti, F.; Hecht, F.; Nataf, F.; Aliferis, I.; El Kanfoud, I.; Migliaccio, C.; de Buhan, M.; et al. Numerical modeling and high-speed parallel computing: New perspectives on tomographic microwave imaging for brain stroke detection and monitoring. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2017, 59, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, B.J.; Abbosh, A.M.; Mustafa, S.; Ireland, D. Microwave system for head imaging. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2014, 63, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, S.M.; Fear, E.C.; Okoniewski, M.; Matyas, J.R. Exploring joint tissues with microwave imaging. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2010, 58, 2307–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCollough, W.J.; McCollough, T.R.; Shao, W.; Edalati, A.; Leslie, J.R. Microwave Imaging Device. U.S. Patent 9,869,641, 16 January 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yilmaz, T.; Foster, R.; Hao, Y. Radio-frequency and microwave techniques for non-invasive measurement of blood glucose levels. Diagnostics 2019, 9, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; McCollough, W. Multiple-GPU-based frequency-dependent finite-difference time domain formulation using MATLAB parallel computing toolbox. Prog. Electromagn. Res. M 2017, 60, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicer, M.B. Diagnostic of patients with COVID-19 pneumonia using passive medical microwave radiometry (MWR). Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, X.; Chen, X.; Xu, X.; Xie, L.; Chen, X.; Hong, Z.; Bai, H.; Liu, X.; Chen, Q.; Li, L.; et al. Recent Development in X-Ray Imaging Technology: Future and Challenges. Research 2021, 26, 9892152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alruily, M.; Said, W.; Mostafa, A.M.; Ezz, M.; Elmezain, M. Breast Ultrasound Images Augmentation and Segmentation Using GAN with Identity Block and Modified U-Net 3+. Sensors 2023, 23, 8599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feinberg, D.A.; Beckett, A.J.S.; Vu, A.T.; Stockmann, J.; Huber, L.; Ma, S.; Ahn, S.; Setsompop, K.; Cao, X.; Park, S.; et al. Next-generation MRI scanner designed for ultra-high-resolution human brain imaging at 7 Tesla. Nat. Methods 2023, 20, 2048–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Shao, W.; Wang, G. On the resolution of UWB microwave imaging of tumors in random breast tissue. In Proceedings of the IEEE Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium, Washington, DC, USA, 3–8 July 2005; Volume 3, pp. 831–834. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, W.; McCollough, T.R.; McCollough, W.J. A phase shift and sum method for UWB radar imaging in dispersive media. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2019, 67, 2018–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Adams, R.S. Multi-polarized microwave power imaging algorithm for early breast cancer detection. Prog. Electromagn. Res. M 2012, 23, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Yu, S.; Dong, H.; Slabaugh, G.; Dragotti, P.L.; Ye, X.; Liu, F.; Arridge, S.; Keegan, J.; Guo, Y.; et al. DAGAN: Deep de-aliasing generative adversarial networks for fast compressed sensing MRI reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 37, 1310–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Du, Y. SPECT image reconstruction by deep learning using a two-step training method. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, sp1, 1353. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Liang, X.; Dong, X.; Xie, Y.; Cao, G. A sparse-view CT reconstruction method based on combination of denseNet and deconvolution. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 37, 1407–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Wu, D.; Gong, K.; Dutta, J.; Kim, J.H.; Son, Y.D.; Kim, H.K.; El Fakhri, G.; Li, Q. Penalized PET reconstruction using deep learning prior and local linear fitting. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 37, 1478–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdum, A.; Erramshetty, M. Distorted born iterative method with back-propagation improves permittivity reconstruction. Int. J. Microw. Wirel. Technol. 2022, 15, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Adams, R.S. UWB microwave imaging for early breast cancer detection: A novel confocal imaging algorithm. In Proceedings of the IEEE Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium, Spokane, WA, USA, 3–8 July 2011; pp. 707–709. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, W.; Adams, R.S. UWB imaging with multi-polarized signals for early breast cancer detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium, Toronto, ON, Canada, 11–17 July 2010; pp. 1397–1400. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, A.; Islam, M.T.; Rahim, S.K.A.; Rahman, A.; Rahman, T.; Arshad, H.; Khandakar, A.; Ayari, M.A.; Chowdhury, M.E.H. A lightweight deep learning based microwave brain image network model for brain tumor classification using reconstructed microwave brain (RMB) images. Biosensors 2023, 13, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, A.; Islam, M.T.; Rahman, T.; Chowdhury, M.E.H.; Tahir, A.; Kiranyaz, S.; Mat, K.; Beng, G.K.; Soliman, M.S. Brain Tumor Segmentation and Classification from Sensor-Based Portable Microwave Brain Imaging System Using Lightweight Deep Learning Models. Biosensors 2023, 13, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, A.; Islam, R.; Islam, M.T.; Kirawanich, P.; Soliman, M.S. FT-FEDTL: A fine-tuned feature-extracted deep transfer learning model for multi-class microwave-based brain tumor classification. Comput. Biol. Med. 2024, 183, 109316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Z.; Ding, Y.; Chen, Y.; Cree, M.J. Wearable microwave medical sensing for stroke classification and localization: A space-division-based decision-tree learning method. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2023, 71, 6906–6917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Mandal, B.; Biswas, B.; Chatterjee, S.; Banerjee, S.; Mitra, D.; Augustine, R. Microwave antenna-assisted machine learning: A paradigm shift in noninvasive brain hemorrhage detection. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 37179–37191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, F.; Chen, X.; Zeng, D.; Ullah, R.; Nawaz, R.; Xu, J.; Arslan, T. A deep learning approach for non-invasive Alzheimer’s monitoring using microwave radar data. Neural Netw. 2025, 181, 106778. [Google Scholar]
- Woten, D.A.; Lusth, J.; EI-Shenawee, M. Interpreting artificial neural networks for microwave detection of breast cancer. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2007, 17, 825–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschini, S.; Autorino, M.M.; Ambrosanio, M.; Pascazio, V.; Baselice, F. A deep learning approach for diagnosis support in breast cancer microwave tomography. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimer, T.; Pistorius, S. The diagnostic performance of machine learning in breast microwave sensing on an experimental dataset. IEEE J. Electromagn. RF Microw. Med. Biol. 2022, 6, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- University of Manitoba Breast Microwave Imaging Dataset (UM-BMID). Available online: https://github.com/UManitoba-BMS/UM-BMID (accessed on 1 October 2007).
- Oliveira, B.L.; Godinho, D.; O’Halloran, M.; Glavin, M.; Jones, E.; Conceição, R.C. Diagnosing breast cancer with microwave technology: Remaining challenges and potential solutions with machine learning. Diagnostics 2018, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zastrow, E.; Davis, S.K.; Lazebnik, M.; Kelcz, F.; Van Veen, B.D.; Hagness, S.C. Development of Anatomically Realistic Numerical Breast Phantoms with Accurate Dielectric Properties for Modeling Microwave Interactions with the Human Breast. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2008, 55, 2792–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojabi, P.; Khoshdel, V.; Lovetri, J. Tissue-type classification with uncertainty quantification of microwave and ultrasound breast imaging: A deep learning approach. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 182092–182104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L. Holographic microwave image classification using a convolutional neural network. Micromachines 2022, 13, 2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sani, L.; Vispa, A.; Loretoni, R.; Duranti, M.; Ghavami, N.; Sánchez-Bayuela, D.A.; Caschera, S.; Paoli, M.; Bigotti, A.; Badia, M.; et al. Breast lesion detection through MammoWave device: Empirical detection capability assessment of microwave images’ parameters. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, B.; Khalesi, B.; Ghavami, N.; Sani, L.; Vispa, A.; Badia, M.; Dudley, S.; Ghavami, M.; Tiberi, G. 3D Huygens principle based microwave imaging through MammoWave device: Validation through phantoms. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 106770–106780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Bayuela, D.A.; Ghavami, N.; Tiberi, G.; Sani, L.; Vispa, A.; Bigotti, A.; Raspa, G.; Badia, M.; Papini, L.; Ghavami, M.; et al. A multicentric, single arm, prospective, stratified clinical investigation to confirm MammoWave’s ability in breast lesions detection. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MammoWave. Available online: https://www.ubt-tech.com/ (accessed on 12 June 2023).
- Rana, S.P.; Dey, M.; Loretoni, R.; Duranti, M.; Ghavami, M.; Dudley, S.; Tiberi, G. Radiation-free microwave technology for breast lesion detection using supervised machine learning model. Tomography 2023, 9, 105–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Galazis, C.; Popov, L.; Ovchinnikov, L.; Kharybina, T.; Vesnin, S.; Losev, A.; Goryanin, I. Dynamic weight agnostic neural networks and medical microwave radiometry (MWR) for breast cancer diagnostics. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozsobaci, N.P.; Onemli, E.; Aydinalp, C.; Yilmaz, T. Measurement and analysis of in vivo microwave dielectric properties collected from normal, benign, and malignant rat breast tissues: Classification using supervised machine learning algorithms. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 4006911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, D.; Yang, D.; Cai, M.; Hao, W. Evaluation of acute tonic cold pain from microwave transcranial transmission signals using multi-entropy machine learning approach. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 2780–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, A.Y.; Cavagnaro, M.; Crocco, L. Hyperthermia treatment monitoring via deep learning enhanced microwave imaging: A numerical assessment. Cancers 2023, 15, 1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataldo, A.; Cino, L.; Distante, C.; Maietta, G.; Masciullo, A.; Mazzeo, P.L.; Schiavoni, R. Integrating microwave reflectometry and deep learning imaging for in-vivo skin cancer diagnostics. Measurement 2024, 235, 114911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.; Guo, L.; Bialkowski, K.; Bialkowski, A. An explainable deep learning method for microwave head stroke localization. IEEE J. Electromagn. RF Microw. Med. Biol. 2023, 7, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariano, V.; Vasquez, J.A.T.; Casu, M.R.; Vipiana, F. Brain stroke classification via machine learning algorithms trained with a linearized scattering operator. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.; Song, H.; Xiao, X.; Liu, G.; Lu, M.; Liu, Y. A fused learning and enhancing method for accurate and noninvasive hydration status monitoring with UWB microwave based on phantom. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2023, 71, 4027–4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Yu, Q.; Li, Q.; Song, H.; Kikkawa, T. Precise noninvasive estimation of glucose using UWB microwave with improved neural networks and hybrid optimization. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 2500410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xiao, X.; Yang, C.; Kikkawa, T. Combined approach to estimate blood glucose level in noninvasive monitoring: Ultra-wide band microwave and cascaded general regression neural network. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 5105–5114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, N.; Abdolrazzaghi, M.; Light, P.E.; Musilek, P. In-human testing of a non-invasive continuous low-energy microwave glucose sensor with advanced machine learning capabilities. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 241, 115668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Hong, R.; Zhao, L.; Hu, H.; Liu, Q. A hybrid neural network electromagnetic inversion scheme (HNNEMIS) for super-resolution 3-D microwave human brain imaging. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2022, 70, 6277–6286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Xiao, L.; Cheng, Y.; Hong, R.; Liu, Q. Machine-learning-based inversion scheme for super-resolution three-dimensional microwave human brain imaging. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2022, 21, 2437–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Xiao, L.; Zhao, L.; Honh, R.; Liu, Q. A 3-D full convolution electromagnetic reconstruction neural network (3-D FCERNN) for fast super-resolution electromagnetic inversion of human brain. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, F.; Guo, L.; Bialkowski, A.; Abbosh, A. Transfer deep learning for dielectric profile reconstruction in microwave medical imaging. IEEE J. Electromagn. RF Microw. Med. Biol. 2024, 8, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, S.; Zamani, A.; Brankovic, A.; Bialkowski, K.S.; Abbosh, A. Stroke classification with microwave signals using explainable wavelet convolutional neural network. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Informat. 2024, 28, 5667–5675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, W.; Guo, L.; Bialkowski, K.; Abbosh, A.; Bialkowski, A. Clutter removal for microwave head imaging via self-supervised deep learning techniques. IEEE J. Electromagn. RF Microw. Med. Biol. 2024, 8, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, F.; Guo, L.; Bialkowski, A.; Abbosh, A. Integrated boundary-overlap-size metric for local assessment of deep learning methods in medical microwave imaging. IEEE J. Electromagn. RF Microw. Med. Biol. 2024; early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AI-Saffar, A.; Guo, L.; Abbosh, A. Graph attention network in microwave imaging for anomaly localization. IEEE J. Electromagn. RF Microw. Med. Biol. 2022, 6, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, S.; Brankovic, A.; Awal, M.A.; Rezaeieh, S.A.; Keating, S.E.; Abbosh, A.; Zamani, A. HepNet: Deep neural network for classification of early-stage hepatic steatosis using microwave signals. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Informat. 2024, 29, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Du, Y. Microwave imaging by deep learning network: Feasibility and training method. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2020, 68, 5626–5635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, U.; Zhu, P.; Kidera, S. Deep learning enhanced contrast source inversion for microwave breast cancer imaging modality. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Informat. 2022, 6, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Kidera, S. Complex permittivity reconstruction using skin surface reflection and neural network for microwave breast imaging. Biomed. Health Informat. 2023, 7, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noritake, K.; Kidera, S. Surface clutter suppression with FDTD recovery signal for microwave UWB mammography. IEICE Trans. Electron. 2020, E103-C, 9586–9598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosanio, M.; Franceschini, S.; Pascazio, V.; Baselice, F. An end-to-end deep learning approach for quantitative microwave breast imaging in real-time applications. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazebnik, M.; Popovic, D.; McCartney, L.; Watkins, C.B.; Lindstrom, M.J.; Harter, J.; Sewall, S.; Ogilvie, T.; Magliocco, A.; Breslin, T.M.; et al. A large-scale study of the ultrawideband microwave dielectric properties of normal, benign and malignant breast tissues obtained from cancer surgeries. Phys. Med. Biol. 2007, 52, 6093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richmond, J. Scattering by a dielectric cylinder of arbitrary cross section shape. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1965, 13, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghouts, M.; Ambrosanio, M.; Franceschini, S.; Autorino, M.M.; Pascazio, V.; Baselice, F. Microwave breast sensing via deep learning for tumor spatial localization by probability maps. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bicer, M.B. Radar-based microwave breast imaging using neurocomputational modals. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dachena, C.; Fedeli, A.; Fanti, A.; Lodi, M.B.; Fumera, G.; Randazzo, A. Microwave imaging of the neck by means of artificial neural networks for tumor detection. IEEE Open J. Antennas Propag. 2021, 2, 1044–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, S.; Shang, S.; Qin, X.; Jia, X.; Li, D.; Cui, Z.; Xu, T.; Niu, G.; Bouakaz, A.; et al. Detection and monitoring of thermal lesions induced by microwave ablation using ultrasound imaging and convolutional neural networks. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Informat. 2020, 24, 965–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, C.; Jiang, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X. Deep-learning-enabled microwave-induced thermoacoustic tomography based on sparse data for breast cancer detection. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2022, 70, 6336–6348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Li, C.; Liu, D.; Wang, B.; Zhang, L.; Ma, Y.; Xu, K.; Wang, X. Quantitative reconstruction of dielectric properties based on deep-learning-enabled microwave-induced thermoacoustic tomography. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2023, 71, 2652–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xi, Z.; Jin, G.; Jiang, W.; Wang, B.; Cai, X.; Wang, X. Deep-learning-enabled microwave-induced thermoacoustic tomography based on ResAttU-net for transcranial brain hemorrhage detection. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 70, 2350–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, S.; Liu, D.; Li, C.; Wang, B.; Wang, X. Deep-learning-based microwave-induced thermoacoustic tomography applying realistic properties of ultrasound transducer. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2024, 72, 5983–5993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshdel, V.; Ashraf, A.; LoVetri, J. Enhancement of multimodal microwave-ultrasound breast imaging using a deep-learning technique. Sensors 2019, 19, 4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoshdel, V.; Asefi, M.; Ashraf, A.; LoVetri, J. Full 3D microwave breast imaging using a deep-learning technique. J. Imaging 2020, 6, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurrant, D.; Omer, M.; Abdollahi, N.; Mojabi, P.; Fear, E.; LoVetri, J. Evaluating performance of microwave image reconstruction algorithms: Extracting tissue types with segmentation using machine learning. J. Imaging 2021, 7, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Ran, P.; Rodet, T.; Lesselier, D. Breast imaging by convolutional neural networks from joint microwave and ultrasonic data. IEEE Trans. Antenna Propag. 2022, 70, 6265–6276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanzo, S.; Flores, A.; Buonanno, G. Fast and accurate CNN-based machine learning approach for microwave medical imaging in cancer detection. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 66063–66075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Zhou, B. Dielectric breast phantoms by generative adversarial network. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2022, 70, 6256–6264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Zhou, B. Near-field microwave scattering formulation by a deep learning method. IEEE Trans Microw. Theory Tech. 2022, 70, 5077–5084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Shao, W.; Wang, G. UWB microwave imaging for early breast cancer detection: Effect of the coupling medium on resolution. In Proceedings of the 2004 Asia-Pacific Radio Science Conference, Qingdao, China, 24–27 August 2004; pp. 431–434. [Google Scholar]
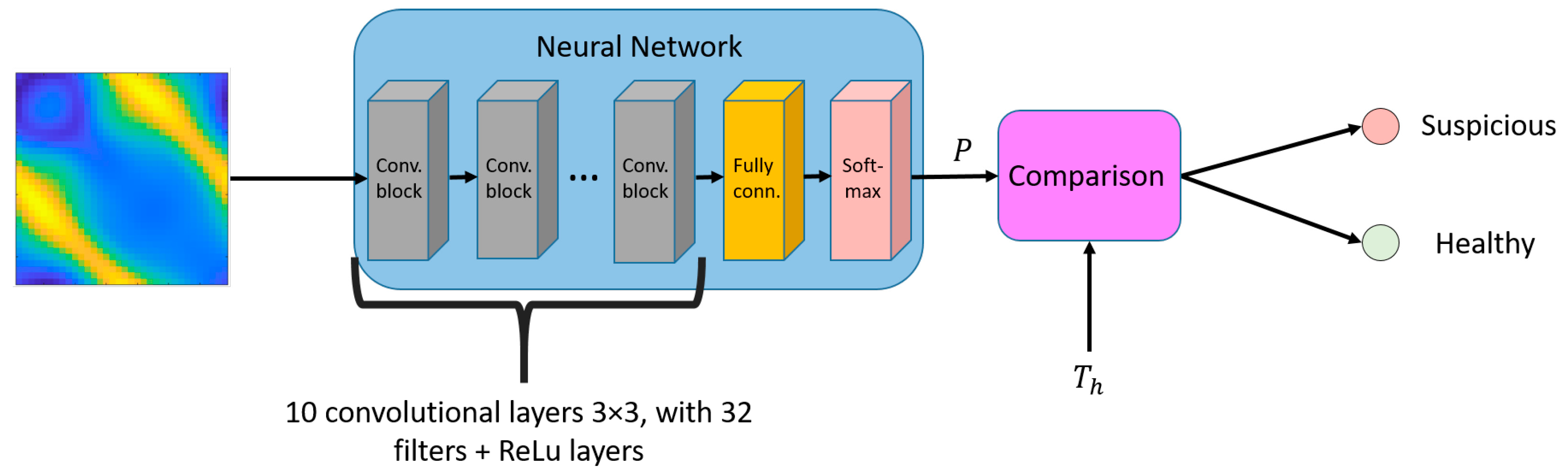

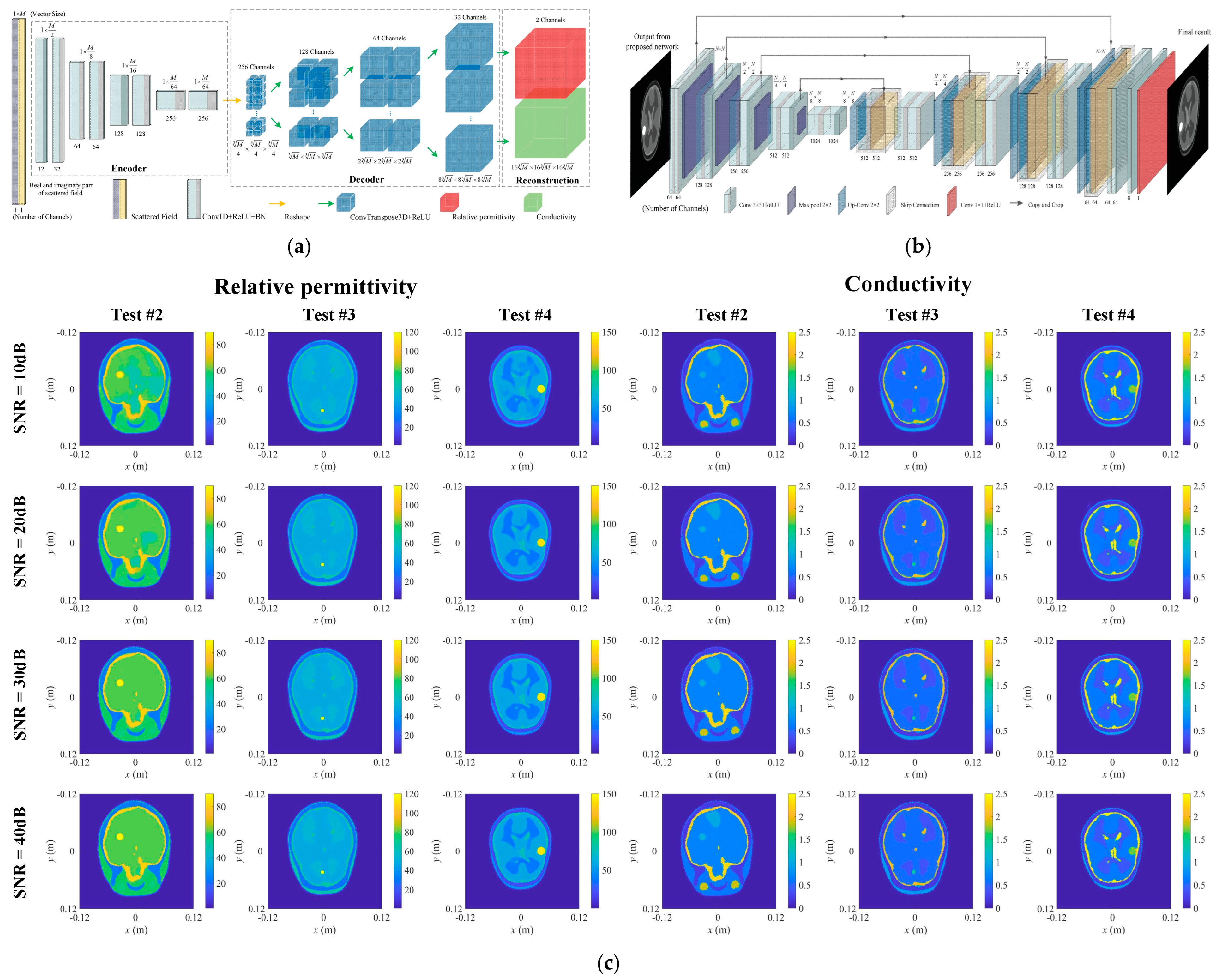
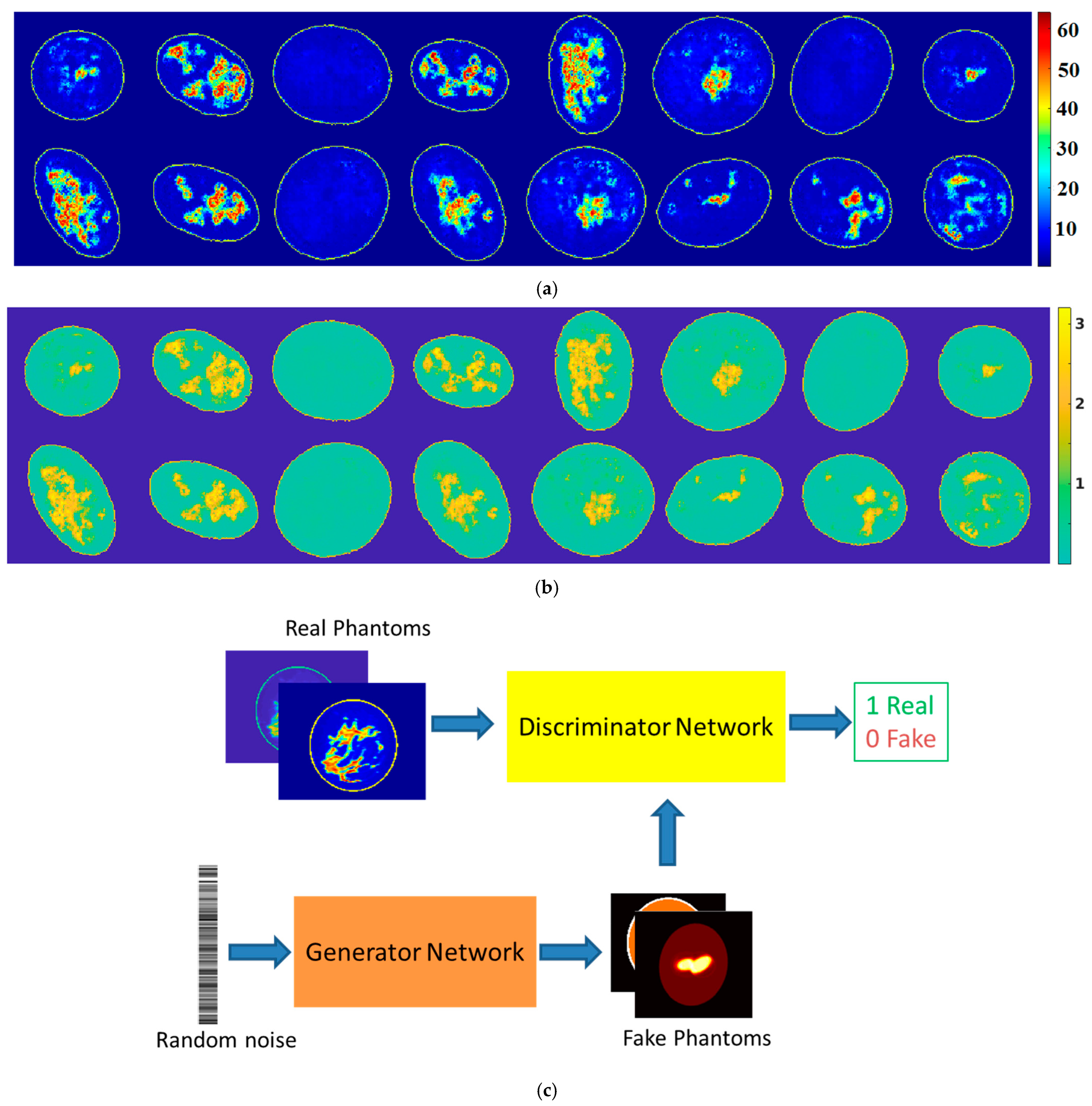
| Developers | Application | Algorithm | Accuracy | Training Data Resource |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hossain [24] | Brain | CNN | 96.97% | Experiment |
| Gong [26] | Brain | DT | 90% | Experiment |
| Singh [27] | Brain | Multiple | 94% | Simulation |
| Ullah [28] | Brain | CNN | 87% | Simulation |
| El-Shenawee [29] | Breast | NN | 96.24% | Simulation |
| Franceschini [30] | Breast | CNN | 96% | Simulation |
| Reimer [31] | Breast | CNN | 73% | Experiment |
| Oliveira [33] | Breast | RF | unclear | Simulation |
| Mojabi [35] | Breast | CNN | Not apply | Simulation |
| Wang [36] | Breast | CNN | 96.84% | Simulation |
| Rana [41] | Breast | SVM | 91% | Simulation |
| Li [42] | Breast | CNN | 93.2% | Experiment |
| Ozsobaci [43] | Breast | SVM | 94.4% | Experiment |
| Geng [44] | Cold Pain | RF | 93.75% | Experiment |
| Ruiz [45] | Neck | CNN | 90% | Simulation |
| Cataldo [46] | Skin Cancer | CNN | unclear | Experiment |
| Developers | Application | Main NN Features | Training Data Resource |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cheng [55] | Brain | An NN for coarse reconstruction followed by a U-net for image quality improvement | Simulation |
| Abbosh [56] | Brain | A pretrained U-Net fine-tuned through transfer learning | Simulation |
| Kidera [63] | Breast | An encoding–decoding model with a two-step training procedure | Simulation |
| Baselice [66] | Breast | A fully connected NN trained by synthetic phantoms | Simulation |
| Bicer [70] | Breast | A fully connected NN followed by a U-net | Experimental scan |
| Dachena [71] | Neck | Fully connected NN | Simulation |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shao, W. Machine Learning in Microwave Medical Imaging and Lesion Detection. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 986. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15080986
Shao W. Machine Learning in Microwave Medical Imaging and Lesion Detection. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(8):986. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15080986
Chicago/Turabian StyleShao, Wenyi. 2025. "Machine Learning in Microwave Medical Imaging and Lesion Detection" Diagnostics 15, no. 8: 986. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15080986
APA StyleShao, W. (2025). Machine Learning in Microwave Medical Imaging and Lesion Detection. Diagnostics, 15(8), 986. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15080986






