An Emerging Trend of At-Home Uroflowmetry—Designing a New Vibration-Based Uroflowmeter with Artificial Intelligence Pattern Recognition of Uroflow Curves and Comparing with Other Technologies
Abstract
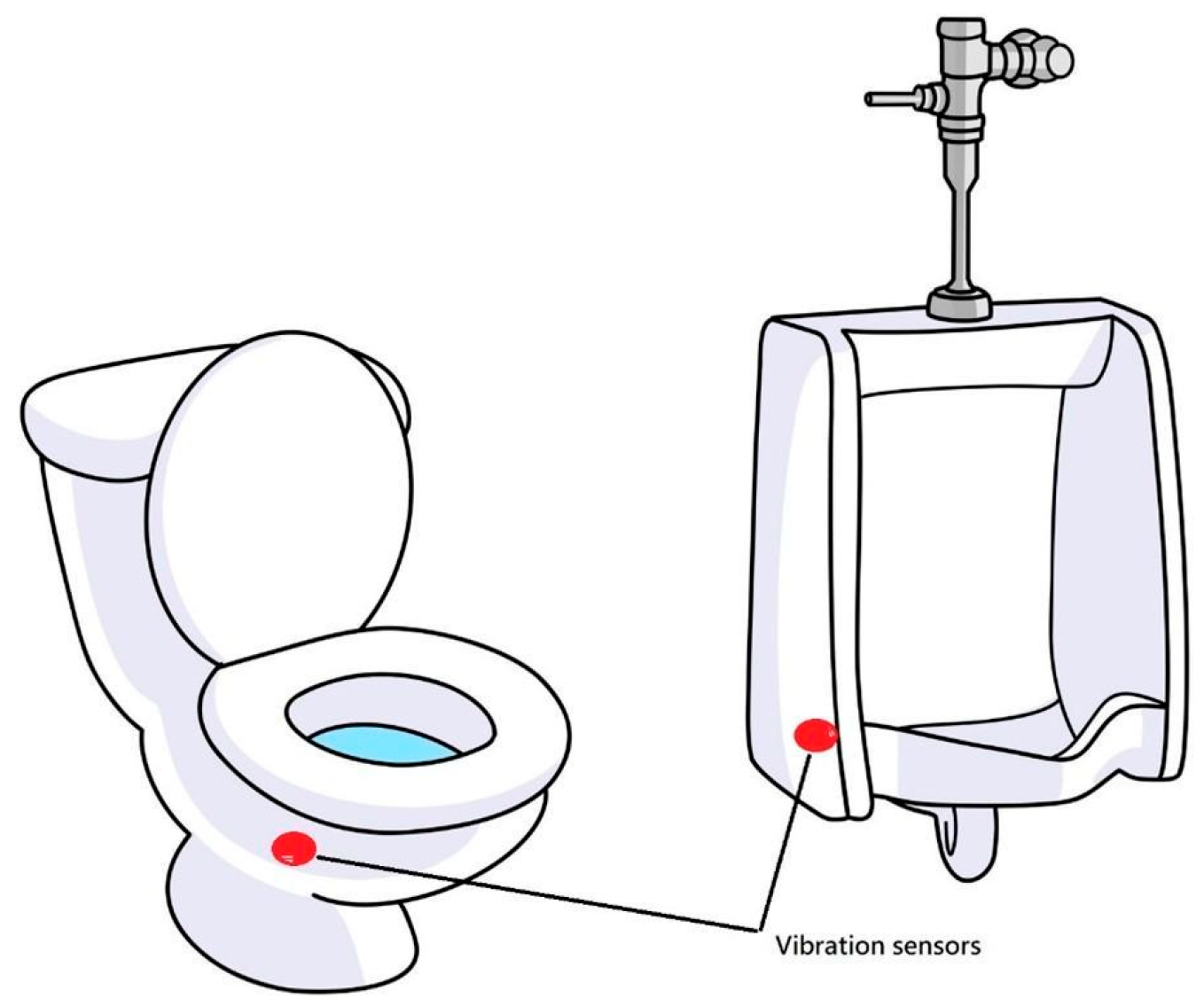
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations
4.2. AI Applications in Home UFM and Urology
4.3. Big Data and Repeated Measurements in Home UFM
4.4. Home UFM of Different Technologies
4.5. An Ideal Model for Home UFM
| Features\Technologies | Weighing (Gravimetric) | Height Sensor Stream Dx | Sound | Vibration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | FDA approved [22] | Non inferior to existing methods [26] | Correlation with office UFM (R = 0.91) [16]; Prediction rate of 99% [18] | Uroflow curve pattern recognition accuracy > 0.98 [12] |
| Vulnerability to the surrounding interferences | X | X | V [17] | X |
| Uroflow curve pattern recognition | X | X | V [18] | V |
| AI algorithm/model | X | X | V [17,18] | V |
| Contact-free (no need for installation/cleaning) | X | X | V | V |
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | artificial intelligence |
| ANN | general neural network |
| AUA | American Urological Association |
| BD | bladder diary |
| BMI | body mass index |
| CNN | convolution neural network |
| EAU | European Association of Urology |
| LSTM | long short-term memory |
| LUT | lower urinary tract |
| LUTS | lower urinary tract symptoms |
| MFCC | mel-frequency cepstrum coefficient |
| Mmax | maximal amplitude |
| Qmax | maximal flow rate |
| RMS | root mean square |
| UFM | uroflowmetry |
| UMAP | uniform manifold approximation and projection |
References
- Kuo, H.C. Interpreting the Voiding Diary of Patients with Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms. Incont. Pelvic Floor Dysfunct. 2010, 4, 105–110. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, S.; Geng, B.; Xu, X.; Harmanli, O. Current state of bladder diary: A survey and review of the literature. Int. Urogynecol. J. 2023, 34, 809–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EAU Guidelines. EAU-Non-Neurogenic Female LUTS Guidelines. In Proceedings of the EAU Annual Congress, Paris, France, 5–8 April 2024; ISBN 978-94-92671-23-3. [Google Scholar]
- EAU Guidelines. EAU-Non Neurogenic Male LUTS Guidelines. In Proceedings of the EAU Annual Congress, Paris, France, 5–8 April 2024; ISBN 978-94-92671-23-3. [Google Scholar]
- Committee on Practice Bulletins—Gynecology; American Urogynecologic Society. ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 155: Urinary Incontinence in Women. Obstet. Gynecol. 2015, 126, e66–e81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosier, P.; Schaefer, W.; Lose, G.; Goldman, H.B.; Guralnick, M.; Eustice, S.; Dickinson, T.; Hashim, H. International Continence Society Good Urodynamic Practices and Terms 2016: Urodynamics, Uroflowmetry, Cystometry, and Pressure-Flow Study. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2017, 36, 1243–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandhu, J.S.; Bixler, B.R.; Dahm, P.; Goueli, R.; Kirkby, E.; Stoffel, J.T.; Wilt, T.J. Management of lower urinary tract symptoms attributed to benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH): AUA Guideline amendment 2023. J. Urol. 2023, 211, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woerl, A.C.; Eckstein, M.; Geiger, J.; Wagner, D.C.; Daher, T.; Stenzel, P.; Fernandez, A.; Hartmann, A.; Wand, M.; Roth, W.; et al. Deep Learning Predicts Molecular Subtype of Muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer from Conventional Histopathological Slides. Eur. Urol. 2020, 78, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nojima, S.; Terayama, K.; Shimoura, S.; Hijiki, S.; Nonomura, N.; Morii, E.; Okuno, Y.; Fujita, K. A deep learning system to diagnose the malignant potential of urothelial carcinoma cells in cytology specimens. Cancer Cytopathol. 2021, 129, 984–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hameed, B.M.Z.; AVL, S.D.; Raza, S.Z.; Karimi, H.; Khanuja, H.S.; Shetty, D.K.; Ibrahim, S.; Shah, M.J.; Naik, N.; Paul, R.; et al. Artificial Intelligence and Its Impact on Urological Diseases and Management: A Comprehensive Review of the Literature. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eun, S.J.; Kim, J.; Kim, K.H. Applications of artificial intelligence in urological setting: A hopeful path to improved care. J. Exerc. Rehabil. 2021, 17, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pong, Y.H.; Tsai, V.F.S.; Hsu, Y.H.; Lee, C.H.; Wang, K.C.; Tsai, Y.-T. Application of a Deep Learning Neural Network for Voiding Dysfunction Diagnosis Using a Vibration Sensor. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakhaie Jazar, G.; Alkhatib, R.; Golnaraghi, M.F. Root mean square optimization criterion for vibration behaviour of linear quarter car using analytical methods. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2006, 44, 477–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, V.F.S.; Pong, Y.H.; Zheng, Z.W.; Tsai, Y.-T. MP59-15 Application of artificial intelligence (deep learning neural network) for assisting diagnosis of voiding dysfunction by using an accelerometer—AI voiding diary. J. Urol. 2024, 211, e963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaivas, J.; Benedon, M.; Weinberger, J.; Rozenberg, Y.; Ravid, L.; Vapnek, J. PD21-11 The dynamic urine vibration halter: A new outpatient device for remote patient monitoring of uroflow. J. Urol. 2015, 193, e475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, R.E. Smartphone App for In-home Uroflowmetry. Urol. Pract. 2022, 9, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.J.; Kim, M.M.; Song, S.H.; Lee, S. A Novel Mobile Acoustic Uroflowmetry: Comparison with Contemporary Uroflowmetry. Int. Neurourol. J. 2021, 25, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.; Chung, Y.; Kim, W.; Heo, Y.; Jeon, J.; Hoh, J.; Park, J.; Jo, J. Classification of Bladder Emptying Patterns by LSTM Neural Network Trained Using Acoustic Signatures. Sensors 2021, 21, 5328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rickey, L.M.; Mueller, E.R.; Newman, D.K.; Markland, A.D.; Falke, C.; Rudser, K.; Lukacz, E.S. MP37-13 Inter-rater and intra-rater reliability of uroflowmetry interpretation in adult women. J. Urol. 2023, 209, e519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, A.; Mathur, A.; Alshiek, J.; Shobeiri, S.A.; Wei, Q. Utilization of Artificial Intelligence for Diagnosis and Management of Urinary Incontinence in Women Residing in Areas with Low Resources: An Overview. Open J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2021, 11, 403–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Kumar, M. MP09-09 Mobile app-based versus conventional uroflowmetry: Is your home toilet the new uroflowmetry lab? J. Urol. 2024, 211, e129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, E.V.B.; Peters, M.; Pauwels, J.; Vermandel, A.; Wachter, S.D.; Bladt, L.; Win, G.D. MP75-13 Digital health solutions create opportunities for home uroflowmetry. J. Urol. 2024, 211, e1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.H.; Park, J.H.; Park, H.J.; Jeong, Y.; Ryu, H.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, S. MP09-12 A prospective multicenter clinical trial for efficacy of mobile uroflowmetry in treatment-naive benign prostatic hyperplasia undergoing medical therapy: Interim results. J. Urol. 2024, 211, e131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summers, S.J.; Armstrong, J.M.; Kaplan, S.A.; Te, A.E.; Le, A.; Heiner, S.M.; Presson, A.P.; Wei, G.; Hotaling, J.M. Male Voiding Behavior: Insight from 19,824 At-Home Uroflow Profiles. J. Urol. 2021, 205, 1126–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, S.; Pastore, S.; Piloni, L.; Mangiulli, M.; Esposito, Y.; Pierella, F.; Galani, A.; Pintus, G.; Mastroluca, D.; Shahabadi, H.; et al. Chronic kidney disease and urological disorders: Systematic use of uroflowmetry in nephropathic patients. Clin. Kidney J. 2019, 12, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, D.; Ogden, K.; Anderl, W.; Mastrangelo, S.; Le, A.; Hotaling, J.; Summers, S. PD50-07 Non-inferiority of a novel capacitance fluid height design compared to rotating disc and weight transducer designs for home uroflowmetry applications. J. Urol. 2018, 199, e972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
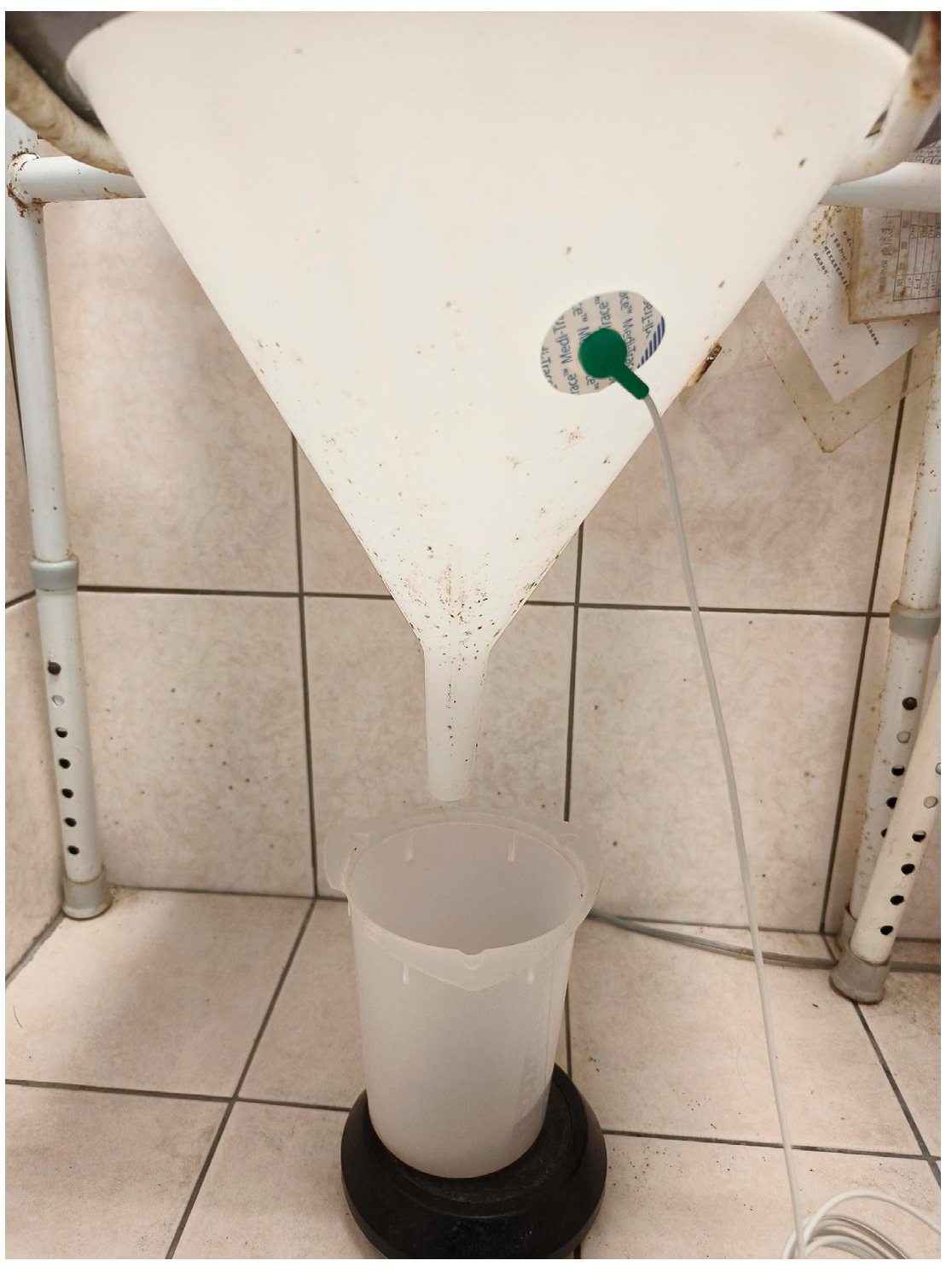



| Patients (n = 76) | Data |
| Age (years) | 51.01 ± 14.54 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.24 ± 3.67 |
| Median voided volume (mL) | 160 [70.00,212.50] |
| Average Qmax (mL/s) | 16.22 ± 10.68 |
| Average voiding time (s) | 21.91 ± 12.98 |
| Average time to Qmax (s) | 6.26 ± 5.68 |
| Uroflow patterns | Numbers of patients |
| Normal (label 0) | 18 |
| Decreased flow (label 1) | 38 |
| Flattened flow (label 2) | 4 |
| Intermittent flow (label 3) | 5 |
| Sawtooth flow (label 4) | 9 |
| Tall and peak flow (label 5) | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsai, V.F.S.; Tsai, Y.-C.; Yang, S.S.D.; Li, M.-W.; Pong, Y.-H.; Tsai, Y.-T. An Emerging Trend of At-Home Uroflowmetry—Designing a New Vibration-Based Uroflowmeter with Artificial Intelligence Pattern Recognition of Uroflow Curves and Comparing with Other Technologies. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1832. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15141832
Tsai VFS, Tsai Y-C, Yang SSD, Li M-W, Pong Y-H, Tsai Y-T. An Emerging Trend of At-Home Uroflowmetry—Designing a New Vibration-Based Uroflowmeter with Artificial Intelligence Pattern Recognition of Uroflow Curves and Comparing with Other Technologies. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(14):1832. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15141832
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsai, Vincent F. S., Yao-Chou Tsai, Stephen S. D. Yang, Ming-Wei Li, Yuan-Hung Pong, and Yu-Ting Tsai. 2025. "An Emerging Trend of At-Home Uroflowmetry—Designing a New Vibration-Based Uroflowmeter with Artificial Intelligence Pattern Recognition of Uroflow Curves and Comparing with Other Technologies" Diagnostics 15, no. 14: 1832. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15141832
APA StyleTsai, V. F. S., Tsai, Y.-C., Yang, S. S. D., Li, M.-W., Pong, Y.-H., & Tsai, Y.-T. (2025). An Emerging Trend of At-Home Uroflowmetry—Designing a New Vibration-Based Uroflowmeter with Artificial Intelligence Pattern Recognition of Uroflow Curves and Comparing with Other Technologies. Diagnostics, 15(14), 1832. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15141832







