Prevalence of Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra Trace Call Results and Associated Risk Factors During Active Tuberculosis Case Finding in Viet Nam: A Programmatic Evaluation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design
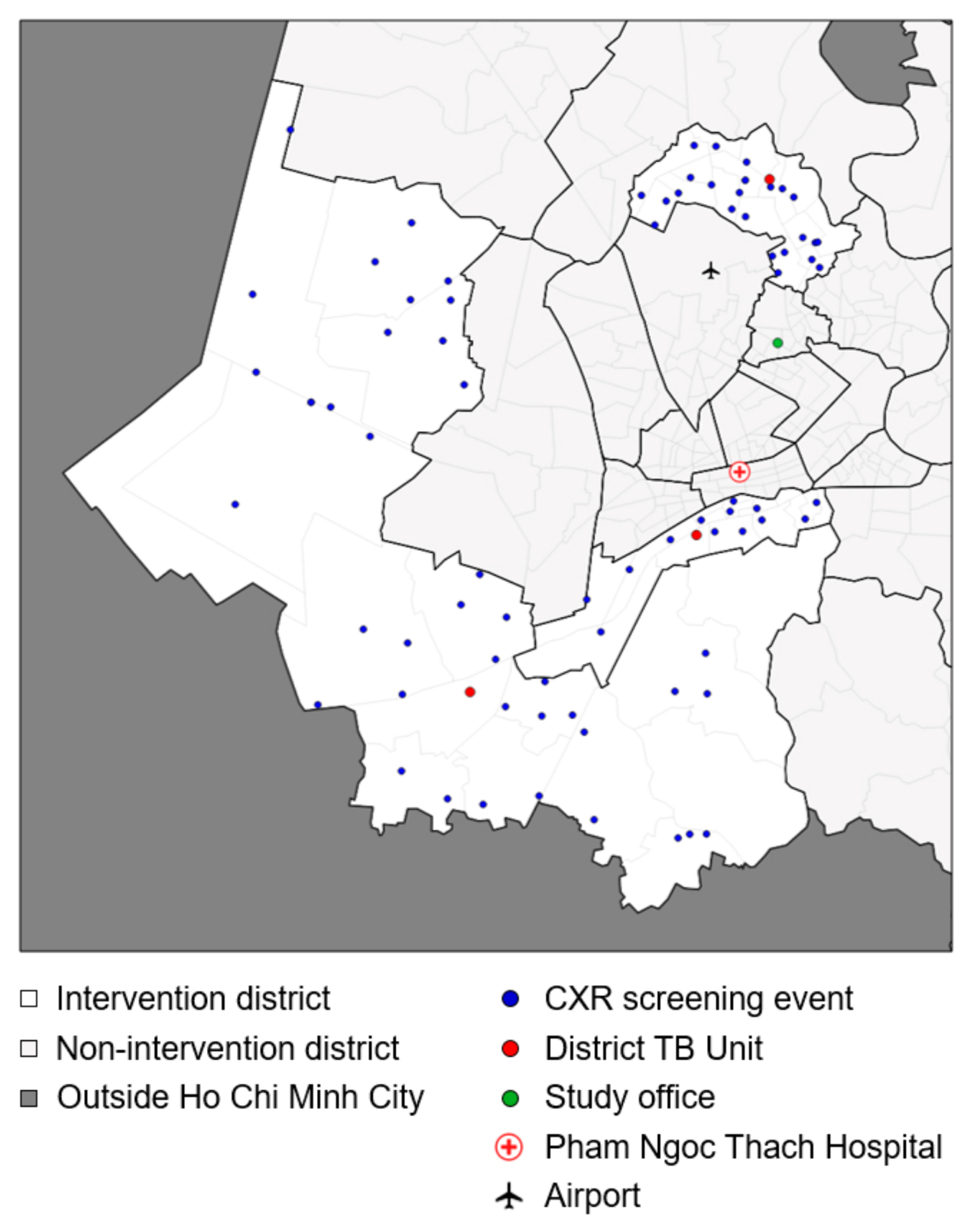
2.2. Setting
2.3. Target Population
2.4. Mobilization
2.5. Screening and Testing
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACF | Active Case Finding |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| CAD | Computer-aided Detection |
| CXR | Chest X-ray |
| HCMC | Ho Chi Minh City |
| NTP | National TB Control Programme |
| (a)OR | (adjusted) Odds Ratio |
| TB | Tuberculosis |
| Ultra | Second-generation Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra assay |
| Xpert | First-generation Xpert MTB/RIF assay |
References
- World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report 2024; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024; Available online: https://www.who.int/teams/global-programme-on-tuberculosis-and-lung-health/tb-reports/global-tuberculosis-report-2024 (accessed on 11 April 2025).
- Burke, R.M.; Nliwasa, M.; Feasey, H.R.A.; Chaisson, L.H.; Golub, J.E.; Naufal, F.; Shapiro, A.E.; Ruperez, M.; Telisinghe, L.; Ayles, H.; et al. Community-Based Active Case-Finding Interventions for Tuberculosis: A Systematic Review. Lancet Public Health 2021, 6, e283–e299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Xpert MTB/RIF Implementation Manual: Technical and Operational ‘How-To’; Practical Considerations; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; ISBN 9789241506700. [Google Scholar]
- Steingart, K.R.; Schiller, I.; Horne, D.J.; Pai, M.; Boehme, C.C.; Dendukuri, N. Xpert ® MTB/RIF Assay for Pulmonary Tuberculosis and Rifampicin Resistance in Adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, 2014, CD009593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahrin, M.; Rahman, A.; Uddin, M.K.M.; Kabir, S.N.; Kabir, S.; Houpt, E.; Banu, S. Discordance in Xpert ® MTB/RIF Assay Results among Low Bacterial Load Clinical Specimens in Bangladesh. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2018, 22, 1056–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cepheid. Xpert ® MTB/RIF Ultra Package Insert; Cepheid: Sunnyvale, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chakravorty, S.; Simmons, A.M.; Rowneki, M.; Parmar, H.; Cao, Y.; Ryan, J.; Banada, P.P.; Deshpande, S.; Shenai, S.; Gall, A.; et al. The New Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra: Improving Detection of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis and Resistance to Rifampin in an Assay Suitable for Point-of-Care Testing. mBio 2017, 8, e00812-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorman, S.E.; Schumacher, S.G.; Alland, D.; Nabeta, P.; Armstrong, D.T.; King, B.; Hall, S.L.; Chakravorty, S.; Cirillo, D.M.; Tukvadze, N.; et al. Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra for Detection of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis and Rifampicin Resistance: A Prospective Multicentre Diagnostic Accuracy Study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilukutu, L.; Mwanza, W.; Kerkhoff, A.D.; Somwe, P.; Kagujje, M.; Muyoyeta, M. Prevalence and Interpretation of Xpert ® Ultra Trace Results among Presumptive TB Patients. Public Health Action 2022, 12, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Meeting Report of a Technical Expert Consultation: Non-Inferiority Analysis of Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra Compared to Xpert MTB/RIF; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report 2024—Country Profile: Viet Nam; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024; Available online: https://worldhealthorg.shinyapps.io/tb_profiles/?_inputs_&tab=%22charts%22&lan=%22EN%22&iso2=%22VN%22&entity_type=%22country%22 (accessed on 11 April 2025).
- Central Coordinating Committee. Proceedings on the Increase of the Protection, Care and Improvement of Population Health in the New Situation; Central Coordinating Committee: Hanoi, Vietnam, 2017. (In Vietnamese) [Google Scholar]
- Office of the Prime Minister. Approval of the National Strategy for TB Prevention and Control until 2020 with Vision to 2030; Office of the Prime Minister: Hanoi, Vietnam, 2014. (In Vietnamese) [Google Scholar]
- Vietnam Ministry of Health. Guidelines on the Diagnosis, Treatment and Prevention of Tuberculosis; Vietnam Ministry of Health: Hanoi, Vietnam, 2020. (In Vietnamese) [Google Scholar]
- Vietnam Ministry of Health. Guidelines on the Diagnosis, Treatment and Prevention of Tuberculosis; Vietnam Ministry of Health: Hanoi, Vietnam, 2024. (In Vietnamese) [Google Scholar]
- Zifodya, J.S.; Kreniske, J.S.; Schiller, I.; Kohli, M.; Dendukuri, N.; Schumacher, S.G.; Ochodo, E.A.; Haraka, F.; Zwerling, A.A.; Pai, M.; et al. Xpert Ultra versus Xpert MTB/RIF for Pulmonary Tuberculosis and Rifampicin Resistance in Adults with Presumptive Pulmonary Tuberculosis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 2021, CD009593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saavedra, B.; Mambuque, E.; Nguenha, D.; Gomes, N.; Munguambe, S.; García, J.I.; Izco, S.; Acacio, S.; Murias-Closas, A.; Cossa, M.; et al. Performance of Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra for Tuberculosis Diagnosis in the Context of Passive and Active Case Finding. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 58, 2100257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.; Uddin, M.K.M.; Paul, K.K.; Ather, M.F.; Ahmed, S.; Nasrin, R.; Kabir, S.; Heysell, S.K.; Banu, S. Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra Assay for the Detection of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis in People with Negative Conventional Xpert MTB/RIF but Chest Imaging Suggestive of Tuberculosis in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 114, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, M.P.; Cassim, N.; Ndlovu, S.; Marokane, P.S.; Radebe, M.; Shapiro, A.; Scott, L.E.; Stevens, W.S. More Than a Decade of GeneXpert® Mycobacterium Tuberculosis/Rifampicin (Ultra) Testing in South Africa: Laboratory Insights from Twenty-Three Million Tests. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iem, V.; Chittamany, P.; Suthepmany, S.; Siphanthong, S.; Siphanthong, P.; Somphavong, S.; Kontogianni, K.; Dodd, J.; Khan, J.A.M.; Dominguez, J.; et al. Pooled Testing of Sputum with Xpert MTB/RIF and Xpert Ultra during Tuberculosis Active Case Finding Campaigns in Lao People’s Democratic Republic. BMJ Glob. Health 2022, 7, e007592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vo, L.N.Q.; Codlin, A.J.; Forse, R.J.; Nguyen, N.T.; Vu, T.N.; Le, G.T.; Van Truong, V.; Do, G.C.; Dang, H.M.; Nguyen, L.H.; et al. Evaluating the Yield of Systematic Screening for Tuberculosis among Three Priority Groups in Ho Chi Minh City, Viet Nam. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2020, 9, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mac, T.H.; Phan, T.H.; Nguyen, V.V.; Dong, T.T.T.; Le, H.V.; Nguyen, Q.D.; Nguyen, T.D.; Codlin, A.J.; Mai, T.D.T.; Forse, R.J.; et al. Optimizing Active Tuberculosis Case Finding: Evaluating the Impact of Community Referral for Chest X-Ray Screening and Xpert Testing on Case Notifications in Two Cities in Viet Nam. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2020, 5, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creswell, J.; Vo, L.N.Q.; Qin, Z.Z.; Muyoyeta, M.; Tovar, M.; Wong, E.B.; Ahmed, S.; Vijayan, S.; John, S.; Maniar, R.; et al. Early User Perspectives on Using Computer-Aided Detection Software for Interpreting Chest X-Ray Images to Enhance Access and Quality of Care for Persons with Tuberculosis. BMC Glob. Public Health 2023, 1, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.H.; Codlin, A.J.; Vo, L.N.Q.; Dao, T.; Tran, D.; Forse, R.J.; Vu, T.N.; Le, G.T.; Luu, T.; Do, G.C.; et al. An Evaluation of Programmatic Community-Based Chest X-Ray Screening for Tuberculosis in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2020, 5, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, M.; Lowbridge, C.; du Cros, P.; Marais, B.J. Community-Wide Active Case Finding for Tuberculosis: Time to Use the Evidence We Have. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2024, 9, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpagama, S.G.; Msaji, K.S.; Kaswaga, O.; Zurba, L.J.; Mbelele, P.M.; Allwood, B.W.; Ngungwa, B.; Kisonga, R.M.; Lesosky, M.; Rylance, J.; et al. The Burden and Determinants of Post-TB Lung Disease. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2021, 25, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Early Detection of Tuberculosis. An Overview of Approaches, Guidelines and Tools; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ayabina, D.V.; Gomes, M.G.M.; Nguyen, N.V.; Vo, L.; Shreshta, S.; Thapa, A.; Codlin, A.J.; Mishra, G.; Caws, M. The Impact of Active Case Finding on Transmission Dynamics of Tuberculosis: A Modelling Study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0257242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, G.B.; Nguyen, N.V.; Nguyen, P.T.B.; Nguyen, T.A.; Nguyen, H.B.; Tran, K.H.; Nguyen, S.V.; Luu, K.B.; Tran, D.T.T.; Vo, Q.T.N.; et al. Community-Wide Screening for Tuberculosis in a High-Prevalence Setting. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1347–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frascella, B.; Richards, A.S.; Sossen, B.; Emery, J.C.; Odone, A.; Law, I.; Onozaki, I.; Esmail, H.; Houben, R.M.G.J. Subclinical Tuberculosis Disease—A Review and Analysis of Prevalence Surveys to Inform Definitions, Burden, Associations, and Screening Methodology. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, e830–e841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falzon, D.; Miller, C.; Law, I.; Floyd, K.; Arinaminpathy, N.; Zignol, M.; Kasaeva, T. Managing Tuberculosis before the Onset of Symptoms. Lancet Respir. Med. 2024, 2600, 11–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Chest Radiography in Tuberculosis Detection—Summary of Current WHO Recommendations and Guidance on Programmatic Approaches; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016; ISBN 9789241511506. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.; Zhang, L.; Li, S.; Shang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xue, Z.; Shu, W.; Sun, Y.; Gao, X.; Liu, Y.; et al. Pooled Sputum Testing by Xpert® MTB/RIF Ultra for Active Tuberculosis Case Finding among High-Risk Groups in a Low-Incidence Area: A Prospective Study. Infect. Dis. 2024, 56, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Codlin, A.J.; Vo, L.N.Q.; Garg, T.; Banu, S.; Ahmed, S.; John, S.; Abdulkarim, S.; Muyoyeta, M.; Sanjase, N.; Wingfield, T.; et al. Expanding Molecular Diagnostic Coverage for Tuberculosis by Combining Computer-Aided Chest Radiography and Sputum Specimen Pooling: A Modeling Study from Four High-Burden Countries. BMC Glob. Public Health 2024, 2, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Binh Chanh | District 8 | Go Vap | Total | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % 1 | N | % 1 | N | % 1 | N | % 1 | |
| Days of community screening | 24 | 8 | 24 | 56 | ||||
| Unique ACF event locations | 40 | 14 | 25 | 79 | ||||
| Verbally screened | 6212 | 3661 | 7147 | 17,020 | ||||
| Screened by CXR | 6139 | 98.8% | 3599 | 98.3% | 6960 | 97.4% | 16,698 | 98.1% |
| Abnormal CXR | 958 | 15.6% | 527 | 14.6% | 457 | 6.6% | 1942 | 11.6% |
| Tested with Ultra (total) | 774 | 12.6% | 545 | 15.1% | 410 | 5.9% | 1729 | 10.4% |
| Tested with Ultra after abnormal CXR | 693 | 89.5% | 387 | 71.0% | 402 | 98.0% | 1482 | 85.7% |
| Tested with Ultra without abnormal CXR | 81 | 10.5% | 158 | 29.0% | 8 | 2.0% | 247 | 14.3% |
| Ultra-positive test results 2 | 76 | 9.8% | 65 | 11.9% | 44 | 10.7% | 185 | 10.7% |
| Very Low, Low, Medium or High test results | 46 | 60.5% | 35 | 53.8% | 33 | 75.0% | 114 | 61.6% |
| Trace Call test results | 30 | 39.5% | 30 | 46.2% | 11 | 25.0% | 71 | 38.4% |
| Retesting of Trace Call test results | 27 | 90.0% | 25 | 83.3% | 9 | 81.8% | 61 | 85.9% |
| Ultra-positive retest results 2 | 15 | 55.6% | 11 | 44.0% | 2 | 22.2% | 28 | 45.9% |
| Ultra Trace Call retest results | 2 | 13.3% | 2 | 18.2% | 1 | 50.0% | 5 | 17.9% |
| Total confirmed TB diagnoses | 61 | 1.0% | 46 | 1.3% | 35 | 0.5% | 142 | 0.9% |
| Initial Ultra-Positive | Retest | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total (N = 185) | Positive 1 (n = 114) | Trace Call (n = 71) | p-Value 2 | Total (N = 61) | Positive 3 (n = 28) | Negative (n = 33) | p-Value 2 | |||||||
| N | % | N | % | n | % | N | % | n | % | n | % | |||
| Sex | ||||||||||||||
| Male | 149 | 80.5% | 95 | 83.3% | 54 | 76.1% | 0.224 | 45 | 73.8% | 21 | 75.0% | 24 | 72.7% | 0.841 |
| Female | 36 | 19.5% | 19 | 16.7% | 17 | 23.9% | 16 | 26.2% | 7 | 25.0% | 9 | 27.3% | ||
| Age | ||||||||||||||
| 15–39 years | 8 | 4.3% | 4 | 3.5% | 4 | 5.6% | 0.479 | 3 | 4.9% | 1 | 3.6% | 2 | 6.1% | 1.000 |
| 40–64 years | 106 | 57.3% | 69 | 60.5% | 37 | 52.1% | 30 | 49.2% | 14 | 50.0% | 16 | 48.5% | ||
| ≥65 years | 71 | 38.4% | 41 | 36.0% | 30 | 42.3% | 28 | 45.9% | 13 | 46.4% | 15 | 45.5% | ||
| District | ||||||||||||||
| District 8 | 44 | 23.8% | 33 | 29.0% | 11 | 15.5% | 0.081 | 9 | 14.8% | 2 | 7.1% | 7 | 21.2% | 0.250 |
| Binh Chanh | 65 | 35.1% | 35 | 30.7% | 30 | 42.3% | 25 | 41.0% | 11 | 39.3% | 14 | 42.4% | ||
| Go Vap | 76 | 41.1% | 46 | 40.4% | 30 | 42.3% | 27 | 44.3% | 15 | 53.6% | 12 | 36.4% | ||
| W4SS | ||||||||||||||
| No | 106 | 57.3% | 63 | 55.3% | 43 | 60.6% | 0.478 | 35 | 57.4% | 15 | 53.6% | 20 | 60.6% | 0.580 |
| Yes | 79 | 42.7% | 51 | 44.7% | 28 | 39.4% | 26 | 42.6% | 13 | 46.4% | 13 | 39.4% | ||
| Any comorbidity 4 | ||||||||||||||
| No | 158 | 85.4% | 97 | 85.1% | 61 | 85.9% | 0.877 | 53 | 86.9% | 24 | 85.7% | 29 | 87.9% | 1.000 |
| Yes | 27 | 14.6% | 17 | 14.9% | 10 | 14.1% | 8 | 13.1% | 4 | 14.3% | 4 | 12.1% | ||
| History of TB | ||||||||||||||
| No | 105 | 56.8% | 74 | 64.9% | 31 | 43.7% | 0.011 | 27 | 44.3% | 13 | 46.4% | 14 | 42.4% | 0.818 |
| 0–5 years | 58 | 31.4% | 27 | 23.7% | 31 | 43.7% | 27 | 44.3% | 11 | 39.3% | 16 | 48.5% | ||
| >5 years | 22 | 11.9% | 13 | 11.4% | 9 | 12.7% | 7 | 11.5% | 4 | 14.3% | 3 | 9.1% | ||
| TB contact | ||||||||||||||
| No | 168 | 90.8% | 104 | 91.2% | 64 | 90.1% | 0.803 | 54 | 88.5% | 25 | 89.3% | 29 | 87.9% | 1.000 |
| Yes | 17 | 9.2% | 10 | 8.8% | 7 | 9.9% | 7 | 11.5% | 3 | 10.7% | 4 | 12.1% | ||
| qXR score | ||||||||||||||
| ≥0.50 | 160 | 86.5% | 106 | 93.0% | 54 | 76.1% | 0.001 | 44 | 72.1% | 20 | 71.4% | 24 | 72.7% | 0.910 |
| <0.50 | 25 | 13.5% | 8 | 7.0% | 17 | 23.9% | 17 | 27.9% | 8 | 28.6% | 9 | 27.3% | ||
| Initial Ultra | Retest | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| aOR (95% CI) | p-Value 1 | aOR (95% CI) | p-Value 1 | |
| Sex | ||||
| Male | ref | ref | ||
| Female | 1.44 [0.62, 3.31] | 0.396 | 1.27 [0.35, 4.65] | 0.713 |
| Age | ||||
| 15–54 years | ref | ref | ||
| 55–74 years | 0.72 [0.14, 3.66] | 0.694 | 0.59 [0.04, 9.27] | 0.706 |
| ≥75 years | 0.99 [0.18, 5.26] | 0.987 | 0.63 [0.04, 11.35] | 0.757 |
| W4SS | ||||
| No | ref | ref | ||
| Yes | 0.85 [0.44, 1.64] | 0.632 | 0.73 [0.25, 2.13] | 0.563 |
| Any comorbidity | ||||
| No | ref | ref | ||
| Yes | 0.86 [0.33, 2.20] | 0.750 | 0.94 [0.17, 5.04] | 0.942 |
| History of TB | ||||
| No | ref | ref | ||
| 0–5 years | 3.53 [1.69, 7.35] | 0.001 | 1.32 [0.40, 4.39] | 0.646 |
| >5 years | 2.31 [0.84, 6.39] | 0.106 | 0.76 [0.11, 5.44] | 0.787 |
| TB contact | ||||
| No | ref | ref | ||
| Yes | 1.00 [0.31, 3.28] | 0.998 | 1.19 [0.19, 7.52] | 0.852 |
| qXR score | ||||
| ≥0.50 | ref | ref | ||
| <0.50 | 4.97 [1.88, 13.14] | 0.001 | 0.93 [0.25, 3.49] | 0.917 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Van Dinh, L.; Tran, K.T.; Codlin, A.J.; Vo, L.N.Q.; Nguyen, N.T.T.; Nguyen, L.P.; Forse, R.; Nguyen, H.T.; Dang, T.M.H.; Nguyen, L.H.; et al. Prevalence of Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra Trace Call Results and Associated Risk Factors During Active Tuberculosis Case Finding in Viet Nam: A Programmatic Evaluation. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15081006
Van Dinh L, Tran KT, Codlin AJ, Vo LNQ, Nguyen NTT, Nguyen LP, Forse R, Nguyen HT, Dang TMH, Nguyen LH, et al. Prevalence of Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra Trace Call Results and Associated Risk Factors During Active Tuberculosis Case Finding in Viet Nam: A Programmatic Evaluation. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(8):1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15081006
Chicago/Turabian StyleVan Dinh, Luong, Khoa Tu Tran, Andrew James Codlin, Luan Nguyen Quang Vo, Nga Thuy Thi Nguyen, Lan Phuong Nguyen, Rachel Forse, Han Thi Nguyen, Thi Minh Ha Dang, Lan Huu Nguyen, and et al. 2025. "Prevalence of Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra Trace Call Results and Associated Risk Factors During Active Tuberculosis Case Finding in Viet Nam: A Programmatic Evaluation" Diagnostics 15, no. 8: 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15081006
APA StyleVan Dinh, L., Tran, K. T., Codlin, A. J., Vo, L. N. Q., Nguyen, N. T. T., Nguyen, L. P., Forse, R., Nguyen, H. T., Dang, T. M. H., Nguyen, L. H., Nguyen, H. B., & Creswell, J. (2025). Prevalence of Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra Trace Call Results and Associated Risk Factors During Active Tuberculosis Case Finding in Viet Nam: A Programmatic Evaluation. Diagnostics, 15(8), 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15081006






