Advanced Assessment of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Military Personnel: Development of a Novel IIRPM Score Using Artificial Intelligence
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
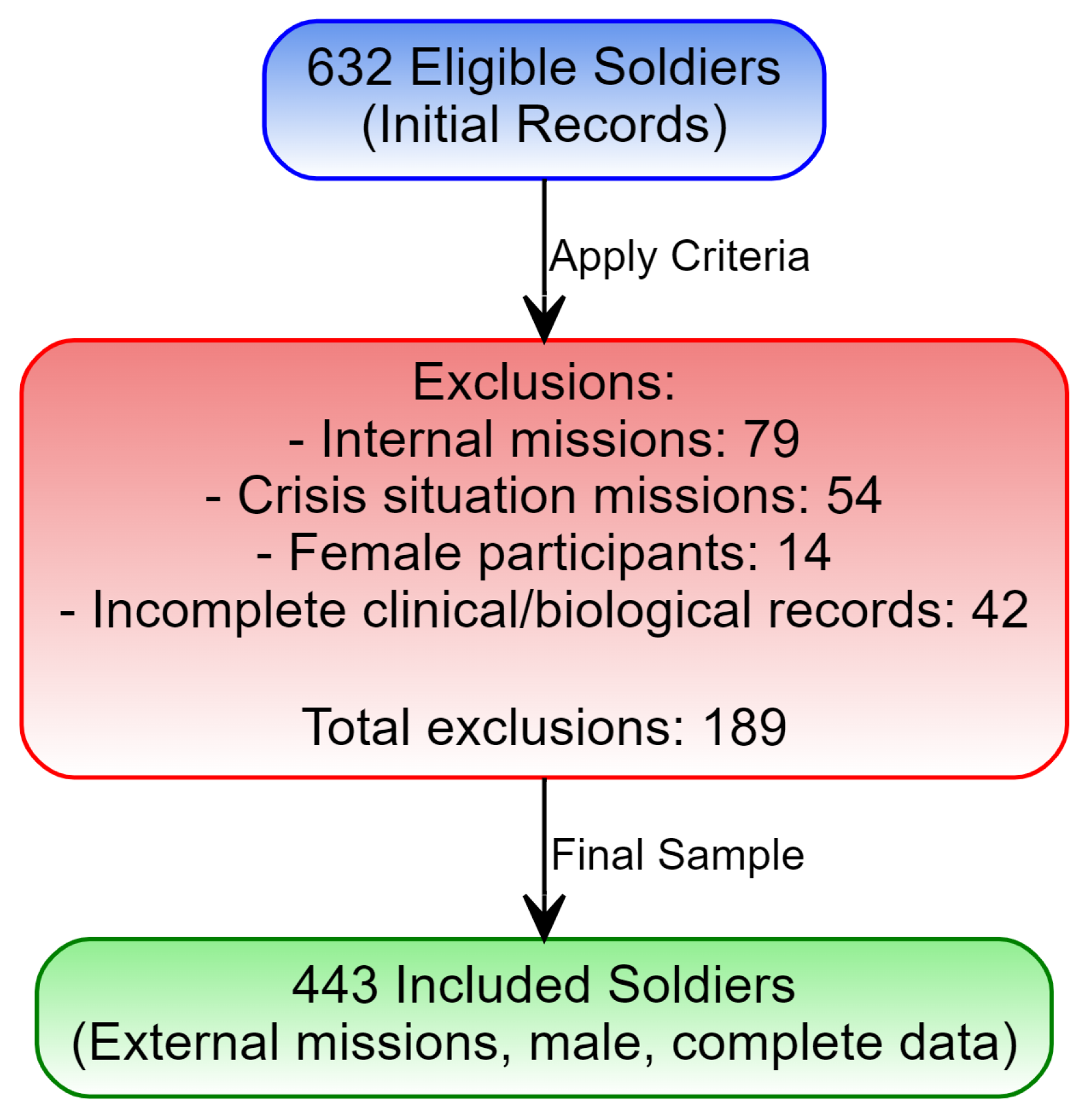
2.2. Inclusion Criteria
2.3. Exclusion Criteria
2.4. Data Collection
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.5.1. Data Preprocessing
2.5.2. Data Augmentation and Balancing
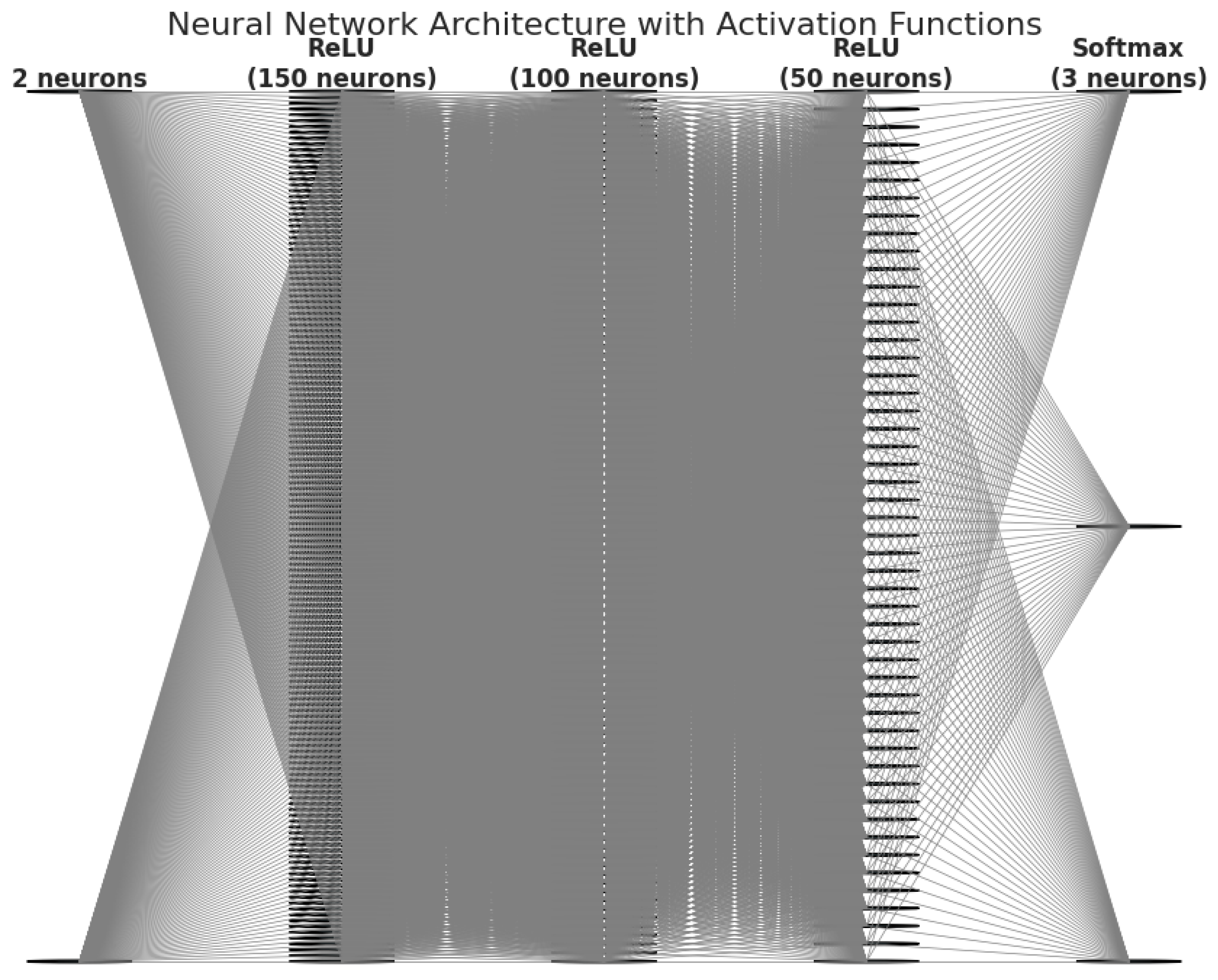
2.5.3. Neural Network Model
2.5.4. Model Validation
2.5.5. Capturing Variable Interactions
2.5.6. Advanced Clustering for Profile Identification
2.5.7. Calculation of the Post-Mission Integrated Risk Index (IIRPM)
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Analysis of Hematological and Biochemical Parameters
3.2. Selection of the Inflammatory Marker and Development of the NLR-Based Risk Score
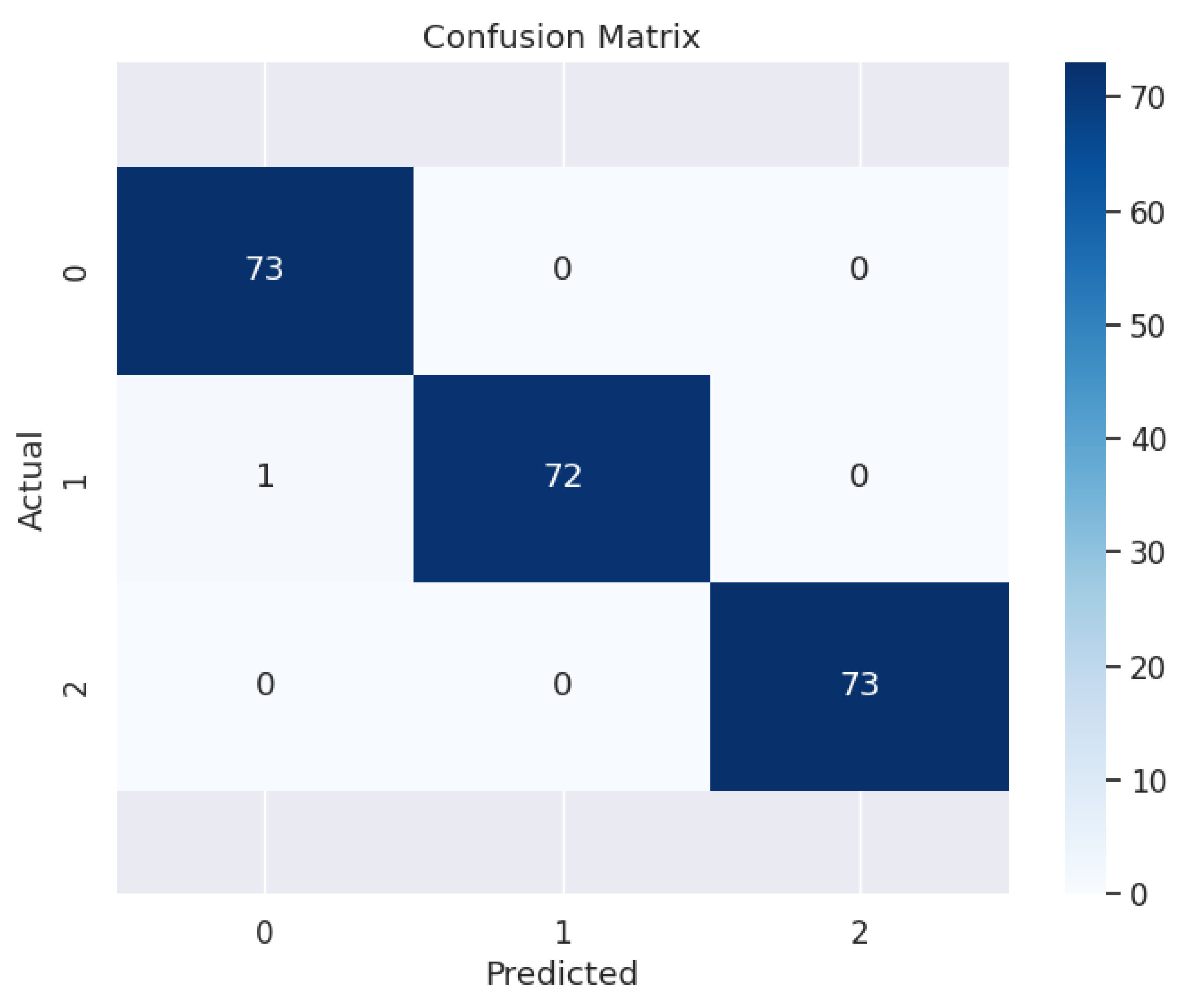
3.3. Evaluation of Model Performance
3.4. Performance on the Test Set
3.5. Learning Curve and Training Stability
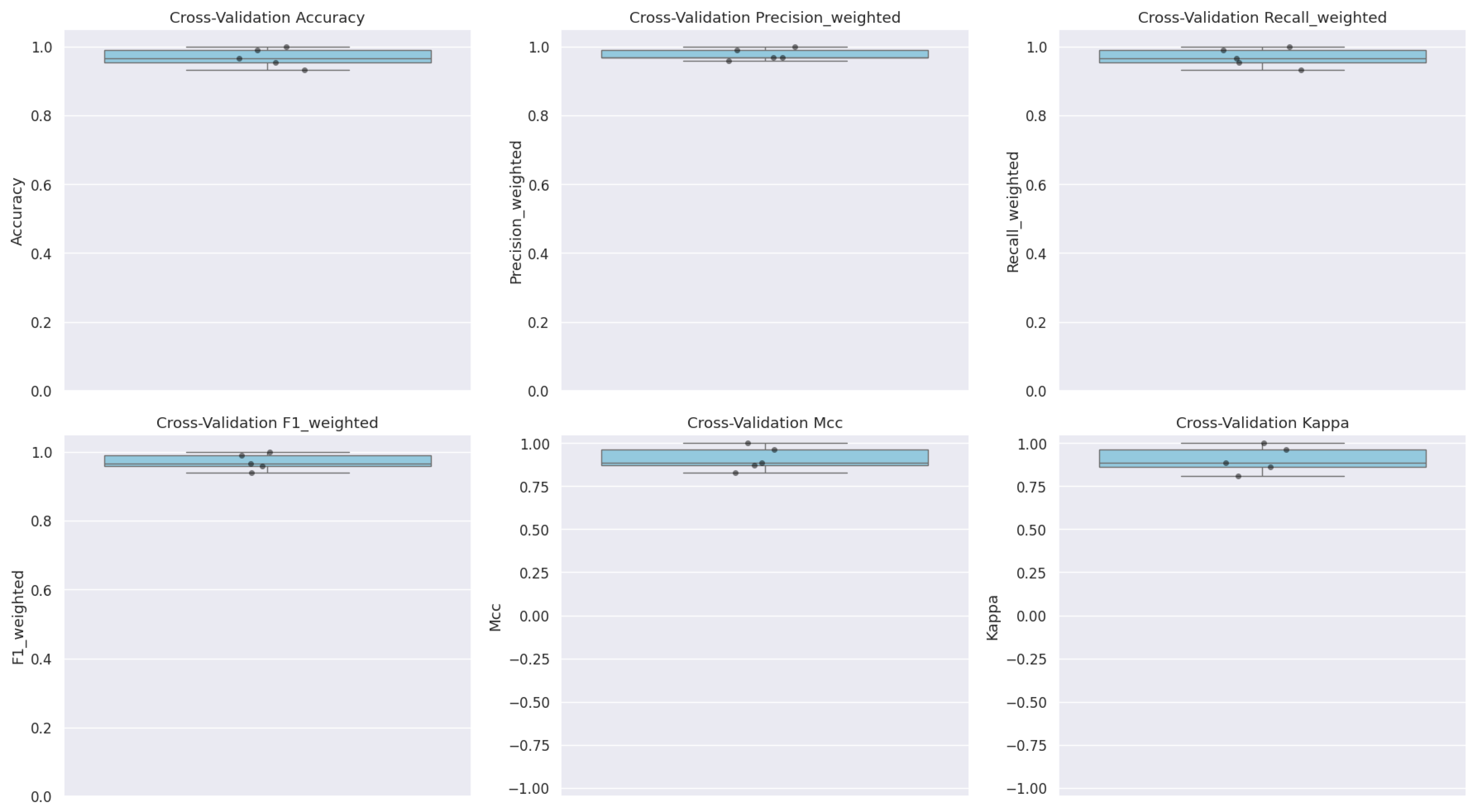
3.6. Model Validation via Cross-Validation
4. Discussion
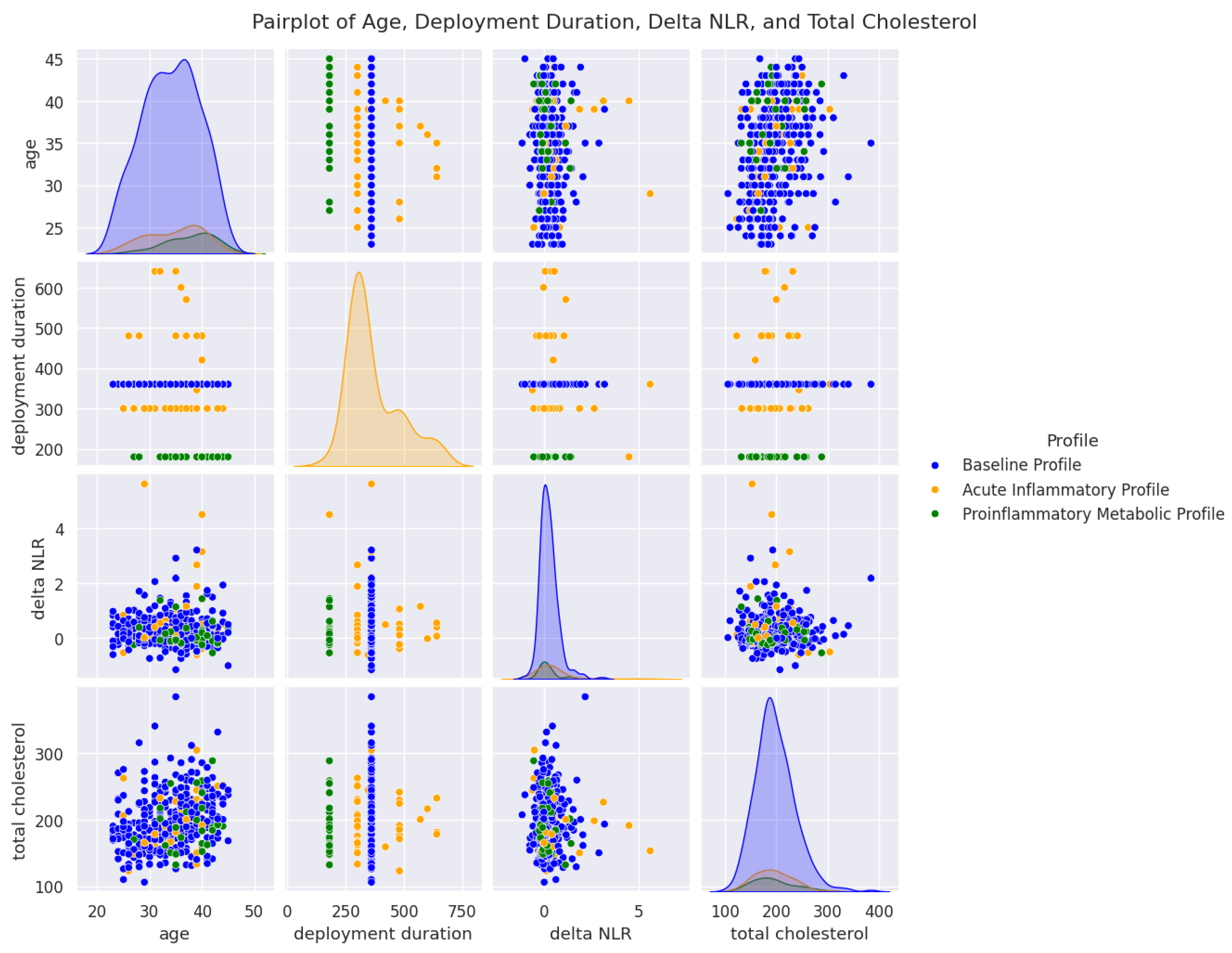
4.1. Cluster Segmentation and Biological Significance
4.2. Relevance of ΔNLR and Its Correlation with the Cumulative Inflammatory Index
4.3. Predictive Model and the Role of Artificial Intelligence
4.4. Age, Mission Duration, and Cholesterol: Foundations of the IIRPM
4.5. Clinical Implications and Operational Context
4.6. Influence of Environmental and Psychological Factors
4.7. Study Limitations
4.8. Implications and Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kargl, C.K.; Gage, C.R.; Forse, J.N.; Koltun, K.J.; Bird, M.B.; Lovalekar, M.; Martin, B.J.; Nindl, B.C. Inflammatory and Oxidant Responses to Arduous Military Training: Associations with Stress, Sleep, and Performance. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2024, 56, 2315–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Rawish, E.; Nording, H.M.; Langer, H.F. Inflammation in Metabolic and Cardiovascular Disorders—Role of Oxidative Stress. Life 2021, 11, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firment, J.; Hulin, I. Zahorec index or Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, valid biomarker of inflammation and immune response to infection, cancer and surgery. Bratisl. Lek. Listy. 2024, 125, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Cao, T.; Ji, T.; Luo, Y.; Huang, J.; Ma, K. Predictive value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in the prognosis and risk of death for adult sepsis patients: A meta-analysis. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1336456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamstein, N.H.; Ridker, P.M. The neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio: Considerations for clinical application. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 2216–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Q.Q.; Mo, Y.J.; Zhu, K.W.; Gao, F.; Huang, B.; Chen, P.; Jing, F.T.; Jiang, X.; Xu, H.Z.; Tang, Y.F.; et al. Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (PLR), Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR), Monocyte-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (MLR), and Eosinophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (ELR) as Biomarkers in Patients with Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (AECOPD). Int. J. Chron. Obstruct. Pulmon. Dis. 2024, 19, 501–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Zhan, F.; Wang, Y. Evaluation of monocyte-to-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio in ischemic stroke. J. Int. Med. Res. 2020, 48, 300060520933806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pritzker, K.P.H. Blood-based biomarkers of chronic inflammation. Expert. Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2023, 23, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmeister, A.; Rothenbacher, D.; Kunze, M.; Brenner, H.; Koenig, W. Prognostic value of inflammatory markers alone and in combination with blood lipids in patients with stable coronary artery disease. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2005, 16, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrisette-Thomas, V.; Cohen, A.A.; Fülöp, T.; Riesco, É.; Legault, V.; Li, Q.; Milot, E.; Dusseault-Bélanger, F.; Ferrucci, L. Inflamm-aging does not simply reflect increases in pro-inflammatory markers. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2014, 139, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulusoy, C.O.; Kurt, A.; Seyhanli, Z.; Hizli, B.; Bucak, M.; Agaoglu, R.T.; Oguz, Y.; Yucel, K.Y. Role of Inflammatory Markers and Doppler Parameters in Late-Onset Fetal Growth Restriction: A Machine-Learning Approach. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2024, 92, e70004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Zeng, L.; Yuan, S.; Shang, Y.; Zhuang, W.; Chen, Z.; Lyu, J. Machine learning for the prediction of cognitive impairment in older adults. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1158141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radulescu, D.; Mihai, F.D.; Trasca, M.E.; Caluianu, E.I.; Calafeteanu, C.D.M.; Radulescu, P.M.; Mercut, R.; Ciupeanu-Calugaru, E.D.; Marinescu, G.A.; Siloşi, C.A.; et al. Oxidative Stress in Military Missions-Impact and Management Strategies: A Narrative Analysis. Life 2024, 14, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holliday, S.B.; DeSantis, A.; Germain, A.; Buysse, D.J.; Matthews, K.A.; Troxel, W.M. Deployment Length, Inflammatory Markers, and Ambulatory Blood Pressure in Military Couples. Mil. Med. 2017, 182, e1892–e1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almer, A.; Weber, A.; Haid, F.; Paletta, L.; Schneeberger, M.; Ladstätter, S.; Wallner, D.; Glanz, P.; Klöckl, P.; Eder, D.; et al. Real-time remote stress monitoring based on specific stress modelling considering load characteristics of different military forces. In Cognitive Computing and Internet of Things; Paletta, L., Ayaz, H., Asgher, U., Eds.; AHFE (2023) International Conference; AHFE Open Access; AHFE International: Orlando, FL, USA, 2023; Volume 73. [Google Scholar]
- Beckner, M.E.; Main, L.; Tait, J.L.; Martin, B.J.; Conkright, W.R.; Nindl, B.C. Circulating biomarkers associated with performance and resilience during military operational stress. Eur. J. Sport. Sci. 2022, 22, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daoub, M.; Mustafa, A. The Neutrophil Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR); recycled as Predictor of Angiographic Coronary Artery Disease Severity in stable Ischaemic Heart Disease. J. Clin. Cardiol. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2022, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tait, J.L.; Bulmer, S.; Drain, J.R.; Main, L.C. Associations between inflammatory markers and well-being during 12 weeks of basic military training. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2021, 121, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizuti, M.R.; Meneghel, D.; Schwede ED, C.; Jost, L.N. Physical Exercise As a Modulator of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Atherosclerotic Plaque. J. Adv. Med. Med. Res. 2020, 32, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, R.; Ielapi, N.; Licastro, N.; Provenzano, M.; Andreucci, M.; Bracale, U.M.; Jiritano, F.; de Franciscis, S.; Mastroroberto, P.; Serraino, G.F. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte Ratio and Platelet-to-lymphocyte Ratio as Biomarkers for Cardiovascular Surgery Procedures: A Literature Review. Rev. Recent. Clin. Trials. 2021, 16, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aljuraiban, G.S.; Alharbi, F.J.; Aljohi, A.O.; Almeshari, A.Z.; Alsahli, A.S.; Alotaibi, B.S.; Abudawood, M.; Alfawaz, W.; Abulmeaty, M. Systemic immune-inflammation index and its relation to blood pressure and dyslipidemia in adults: A retrospective study. Medicine 2024, 103, e38810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridker, P.M.; Lei, L.; Louie, M.J.; Haddad, T.; Nicholls, S.J.; Lincoff, A.M.; Libby, P.; Nissen, S.E.; CLEAR Outcomes Investigators. Inflammation and Cholesterol as Predictors of Cardiovascular Events Among 13,970 Contemporary High-Risk Patients With Statin Intolerance. Circulation 2024, 149, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Church, M.C.; Workman, J.L.; Suganuma, T. Macrophages, Metabolites, and Nucleosomes: Chromatin at the Intersection between Aging and Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, N.; Lawrence-Wood, E.; McFarlane, A. Is inflammatory change associated with psychological risk and resilience in high-risk military personnel? BMJ Mil. Health. 2024, 170, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radulescu, P.M.; Davitoiu, D.V.; Baleanu, V.D.; Padureanu, V.; Ramboiu, D.S.; Surlin, M.V.; Bratiloveanu, T.C.; Georgescu, E.F.; Streba, C.T.; Mercut, R.; et al. Has COVID-19 Modified the Weight of Known Systemic Inflammation Indexes and the New Ones (MCVL and IIC) in the Assessment as Predictive Factors of Complications and Mortality in Acute Pancreatitis? Diagnostics 2022, 12, 3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.R.; Habib, M.A.; Lia, F.A.; Noor Islam, L. Role of oxidase and antioxidant enzymes in neutrophils and blood circulation in patients with acute coronary syndrome. J. Blood Biol. Disord. 2023, 8, 020890351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.T.; Chen, B.W.; Cao, Y.J.; Zhou, C.; Li, H.B.; Wang, D.H. Enhanced oxidative stress is associated with tissue neutrophilia and poor steroid response in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. World J. Otorhinolaryngol. Head. Neck Surg. 2023, 9, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zendelovska, D.; Petrushevska, M.; Atanasovska, E.; Spasovska, K.; Gjorgjievska, K.; Pavlovska, K.; Grozdanovski, K. COVID-19 disease induced alteration of oxidative stress and clinical laboratory parameters in moderate and severe patients. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 26, 5611–5617. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Somani, A.; Singh, A.K.; Gupta, B.; Nagarkoti, S.; Dalal, P.K.; Dikshit, M. Oxidative and Nitrosative Stress in Major Depressive Disorder: A Case Control Study. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercuţ, R.; Ciurea, M.E.; Traşcă, E.T.; Ionescu, M.; Mercuţ, M.F.; Rădulescu, P.M.; Călăraşu, C.; Streba, L.; Ionescu, A.G.; Rădulescu, D. Applying Neural Networks to Analyse Inflammatory, Sociodemographic, and Psychological Factors in Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer and Colon Cancer: A Statistical and Artificial Intelligence Approach. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buican, I.L.; Gheorman, V.; Udriştoiu, I.; Olteanu, M.; Rădulescu, D.; Calafeteanu, D.M.; Nemeş, A.F.; Călăraşu, C.; Rădulescu, P.M.; Streba, C.T. Interactions between Cognitive, Affective, and Respiratory Profiles in Chronic Respiratory Disorders: A Cluster Analysis Approach. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moshtagh, M.; Moodi, M.; Moezi, S.A.; Sharifi, F.; Khazdair, M.R. Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Biomarkers in the Elderly, the Birjand Longitudinal Aging Study. Biomed. Res. Int. 2023, 2023, 4683542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babcock, M.C.; DuBose, L.E.; Witten, T.L.; Stauffer, B.L.; Hildreth, K.L.; Schwartz, R.S.; Kohrt, W.M.; Moreau, K.L. Oxidative Stress and Inflammation Are Associated With Age-Related Endothelial Dysfunction in Men With Low Testosterone. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, e500–e514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, H.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhen, X.; Yan, N. The Effect of Cholesterol Efflux on Endothelial Dysfunction Caused by Oxidative Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachmann, M.C.; Bellalta, S.; Basoalto, R.; Gómez-Valenzuela, F.; Jalil, Y.; Lépez, M.; Matamoros, A.; von Bernhardi, R. The Challenge by Multiple Environmental and Biological Factors Induce Inflammation in Aging: Their Role in the Promotion of Chronic Disease. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 570083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, J. The interplay between aging and inflammation and its role in chronic disease development. Theor. Nat. Sci. 2024, 48, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekhar, R.; Taffet, G.; Kumar, P. Glynac supplementation in older adults protects from meal driven oxidative stress and inflammation: Results of a rct. Innov. Aging 2022, 6 (Suppl. S1), 814–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prata, C.; Angeloni, C.; Maraldi, T. Strategies to Counteract Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Chronic-Degenerative Diseases 2.0. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blagov, A.V.; Summerhill, V.I.; Sukhorukov, V.N.; Zhigmitova, E.B.; Postnov, A.Y.; Orekhov, A.N. Potential use of antioxidants for the treatment of chronic inflammatory diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1378335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Şahin, F.; Koşar, A.F.; Aslan, A.F.; Yiğitbaş, B.; Uslu, B. Serum biomarkers in patients with stable and acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A comparative study. J. Med. Biochem. 2019, 38, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sipahi, H.; Mat, A.F.; Ozhan, Y.; Aydin, A. The Interrelation between Oxidative Stress, Depression and Inflammation through the Kynurenine Pathway. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2023, 23, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.; Kim, J. Abstract LB144: The short-term associations of air pollutants with inflammation and oxidative stress markers in the Korean population. Cancer Res. 2024, 84, LB144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahoon, D.S.; Rabin, B.M.; Fisher, D.R.; Shukitt-Hale, B. Effects of HZE-Particle Exposure Location and Energy on Brain Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Rats. Radiat. Res. 2023, 200, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olaniyan, M.F.; Muhibi, M.A.; Olaniyan, T.B. Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Response Interplay. J. Prev. Diagn. Treat. Strateg. Med. 2023, 2, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Biological Parameter | Mean ± SD (Pre-Mission) | Mean ± SD (Post-Mission) | p-Value (t-Test) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basophils (×103/µL) | 0.03 ± 0.02 | 0.03 ± 0.02 | 0.4311 |
| Total Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 194.69 ± 37.16 | 196.69 ± 38.25 | 0.4275 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.92 ± 0.18 | 0.91 ± 0.15 | 0.8151 |
| Eosinophils (×103/µL) | 0.29 ± 2.18 | 0.19 ± 0.12 | 0.3613 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 96.51 ± 8.62 | 96.69 ± 8.12 | 0.7446 |
| Neutrophils (×103/µL) | 3.61 ± 1.11 | 4.29 ± 1.57 | <0.0001 * |
| Hematocrit (%) | 44.74 ± 3.94 | 44.20 ± 2.46 | 0.0136 * |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 15.33 ± 1.70 | 15.43 ± 0.95 | 0.2705 |
| Lymphocytes (×103/µL) | 2.51 ± 4.03 | 2.37 ± 0.62 | 0.4668 |
| MCH (pg) | 30.00 ± 2.49 | 30.19 ± 1.51 | 0.1824 |
| MCHC (g/dL) | 34.24 ± 2.76 | 34.92 ± 0.91 | <0.0001 * |
| MCV (fL) | 88.09 ± 8.24 | 86.47 ± 4.01 | 0.0002 * |
| Monocytes (×103/µL) | 1.30 ± 14.72 | 0.66 ± 0.19 | 0.3637 |
| MPV (fL) | 10.82 ± 1.21 | 10.67 ± 0.92 | 0.0433 * |
| PCT (%) | 0.28 ± 0.61 | 0.24 ± 0.05 | 0.2709 |
| Platelets (×103/µL) | 232.72 ± 55.13 | 231.59 ± 50.56 | 0.7495 |
| RBC (×10⁶/µL) | 5.20 ± 2.10 | 5.12 ± 0.37 | 0.4241 |
| RDW (%) | 13.14 ± 3.59 | 13.05 ± 0.84 | 0.6034 |
| AST (U/L) | 24.69 ± 7.75 | 23.05 ± 8.63 | 0.0029 * |
| ALT (U/L) | 29.28 ± 13.45 | 27.43 ± 13.65 | 0.0416 * |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 121.96 ± 63.27 | 150.15 ± 107.00 | <0.0001 * |
| ESR (mm/hr) | 8.02 ± 5.12 | 7.33 ± 5.01 | 0.0444 * |
| WBC (×103/µL) | 6.74 ± 1.57 | 7.54 ± 1.96 | <0.0001 * |
| Inflammatory Marker | Mean ± SD (Pre-Mission) | Mean ± SD (Post-Mission) | p-Value (t-Test) |
|---|---|---|---|
| NLR | 1.62 ± 0.54 | 1.90 ± 0.80 | <0.0001 * |
| PLR | 105.14 ± 30.98 | 103.46 ± 32.80 | 0.4336 |
| MLR | 0.27 ± 0.18 | 0.29 ± 0.09 | 0.0853 |
| SIRI | 0.99 ± 0.54 | 1.28 ± 0.72 | <0.0001 * |
| SII | 377.79 ± 163.92 | 443.79 ± 234.42 | <0.0001 * |
| IIC | 1.86 ± 0.72 | 2.14 ± 0.94 | <0.0001 * |
| Marker | Pearson Correlation (r) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| NLR2—NLR3 | 0.6299 | p < 0.0001 (11.43 × 10−50) |
| SIRI2—SIRI3 | 0.4938 | p < 0.0001 (9.87 × 10−29) |
| SII2—SII3 | 0.7094 | p < 0.0001 (2.67 × 10−69) |
| IIC2—IIC3 | 0.5747 | p < 0.0001 (1.79 × 10−40) |
| Variable | Coefficient (β) | Standard Error | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | −1.20 | 0.33 | <0.001 * |
| ΔNLR | 2.05 | 0.42 | <0.001 * |
| Age (years) | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.005 * |
| Mission Duration (days) | 0.0048 | 0.0018 | 0.017 * |
| Post-Mission Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 0.011 | 0.003 | 0.004 * |
| Parameter | Cluster 0 (n = 354) | Cluster 1 (n = 58) | Cluster 2 (n = 31) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 34.00 ± 5.4 | 34.60 ± 5.3 | 37.80 ± 4.5 | 0.0003 |
| Mission Duration (days) | 360.00 ± 0.7 | 369.80 ± 98.6 | 180.00 (fix) | <0.0001 |
| NLR (post-deployment) | 1.80 ± 0.57 | 2.53 ± 1.31 | 1.76 ± 1.12 | <0.0001 |
| ΔNLR | 0.21 ± 0.44 | 0.70 ± 1.07 | 0.31 ± 0.90 | <0.0001 |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 196.50 ± 39.3 | 210.30 ± 40.8 | 225.60 ± 46.6 | <0.0001 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 140.30 ± 86.5 | 158.20 ± 68.1 | 176.70 ± 78.5 | <0.0001 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 96.80 ± 8.12 | 98.30 ± 8.62 | 100.50 ± 9.0 | <0.0001 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.91 ± 0.14 | 0.93 ± 0.11 | 0.95 ± 0.15 | 0.0080 |
| Hematocrit (%) | 44.20 ± 2.46 | 43.70 ± 2.50 | 44.00 ± 2.45 | 0.0020 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 15.40 ± 0.95 | 15.20 ± 1.00 | 15.30 ± 0.98 | 0.1250 |
| Platelets (103/µL) | 231.60 ± 50.56 | 228.10 ± 48.98 | 230.90 ± 51.20 | 0.0007 |
| Leukocytes (103/µL) | 7.54 ± 1.96 | 8.62 ± 2.00 | 7.12 ± 1.75 | <0.0001 |
| Parameter | Interval/Values | Assigned Score |
|---|---|---|
| ΔNLR (Delta NLR) | <0.2 | 0 |
| 0.2–0.5 | 1 | |
| ≥0.5 | 2 | |
| Age (years) | <35 | 0 |
| 35–40 | 1 | |
| >40 | 2 | |
| Mission Duration (days) | <300 | 0 |
| 300–360 | 1 | |
| ≥360 | 2 | |
| Post-Mission Cholesterol (mg/dL) | <190 | 0 |
| 190–220 | 1 | |
| >220 | 2 |
| Total Score | Risk Level | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| <2 points | Low | Minimal risk; no significant concerns. |
| 3–4 points | Moderate | Present risk; warrants monitoring. |
| ≥5 points | High | Elevated risk; requires enhanced monitoring and potential clinical intervention. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mihai, F.-D.; Trasca, E.-T.; Radulescu, P.-M.; Mercut, R.; Caluianu, E.-I.; Ciupeanu-Calugaru, E.D.; Calafeteanu, D.M.; Marinescu, G.-A.; Danoiu, S.; Radulescu, D. Advanced Assessment of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Military Personnel: Development of a Novel IIRPM Score Using Artificial Intelligence. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15070832
Mihai F-D, Trasca E-T, Radulescu P-M, Mercut R, Caluianu E-I, Ciupeanu-Calugaru ED, Calafeteanu DM, Marinescu G-A, Danoiu S, Radulescu D. Advanced Assessment of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Military Personnel: Development of a Novel IIRPM Score Using Artificial Intelligence. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(7):832. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15070832
Chicago/Turabian StyleMihai, Florina-Diana, Emil-Tiberius Trasca, Patricia-Mihaela Radulescu, Razvan Mercut, Elena-Irina Caluianu, Eleonora Daniela Ciupeanu-Calugaru, Dan Marian Calafeteanu, Georgiana-Andreea Marinescu, Suzana Danoiu, and Dumitru Radulescu. 2025. "Advanced Assessment of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Military Personnel: Development of a Novel IIRPM Score Using Artificial Intelligence" Diagnostics 15, no. 7: 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15070832
APA StyleMihai, F.-D., Trasca, E.-T., Radulescu, P.-M., Mercut, R., Caluianu, E.-I., Ciupeanu-Calugaru, E. D., Calafeteanu, D. M., Marinescu, G.-A., Danoiu, S., & Radulescu, D. (2025). Advanced Assessment of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Military Personnel: Development of a Novel IIRPM Score Using Artificial Intelligence. Diagnostics, 15(7), 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15070832






