Special Considerations in Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease Pathology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Classification
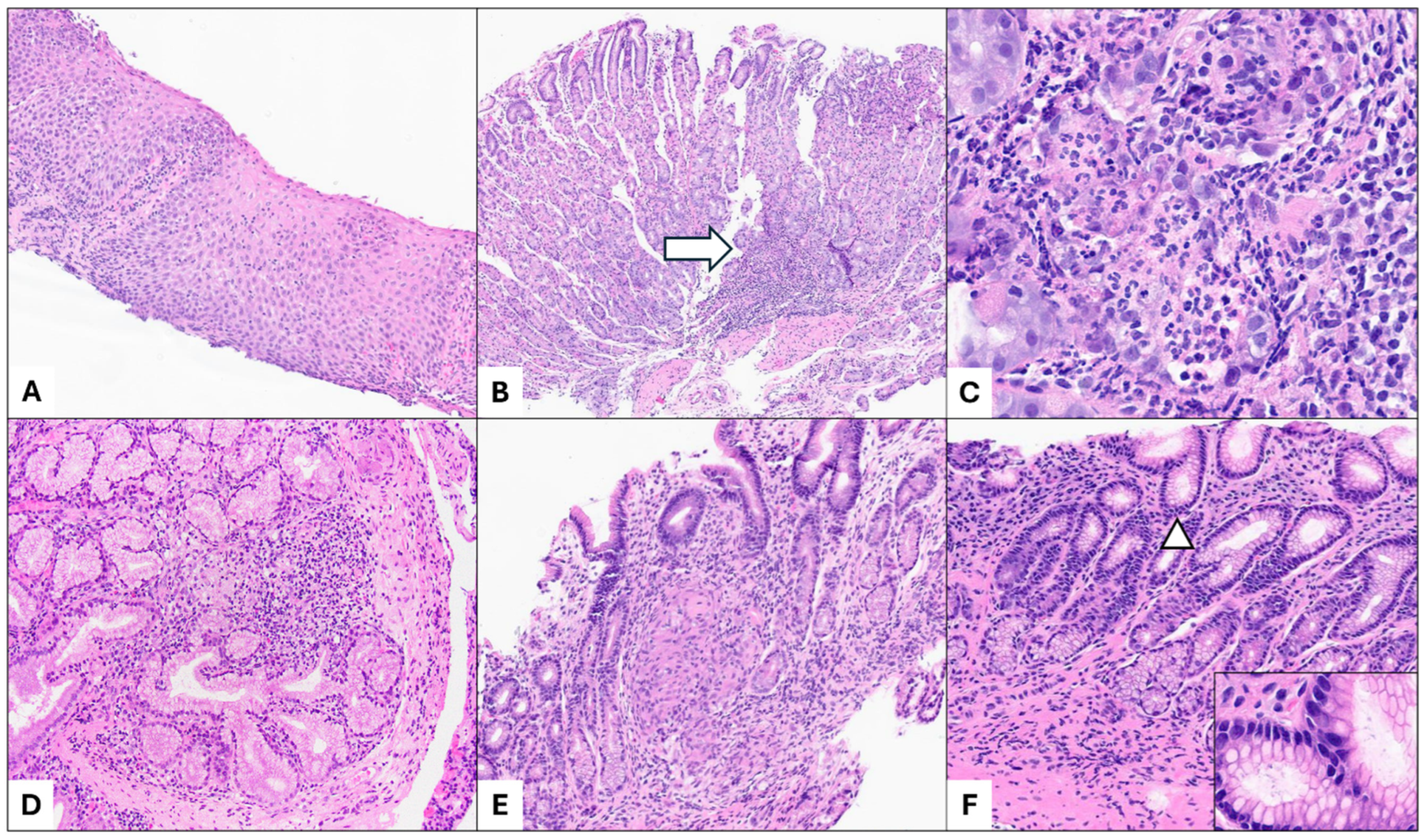
3. Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Involvement in Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease
4. Inflammatory Bowel Disease with Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC-IBD)
5. Monogenic Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
5.1. IL-10R/R
5.2. XIAP
5.3. CYBB
5.4. LRBA
5.5. TTC7A
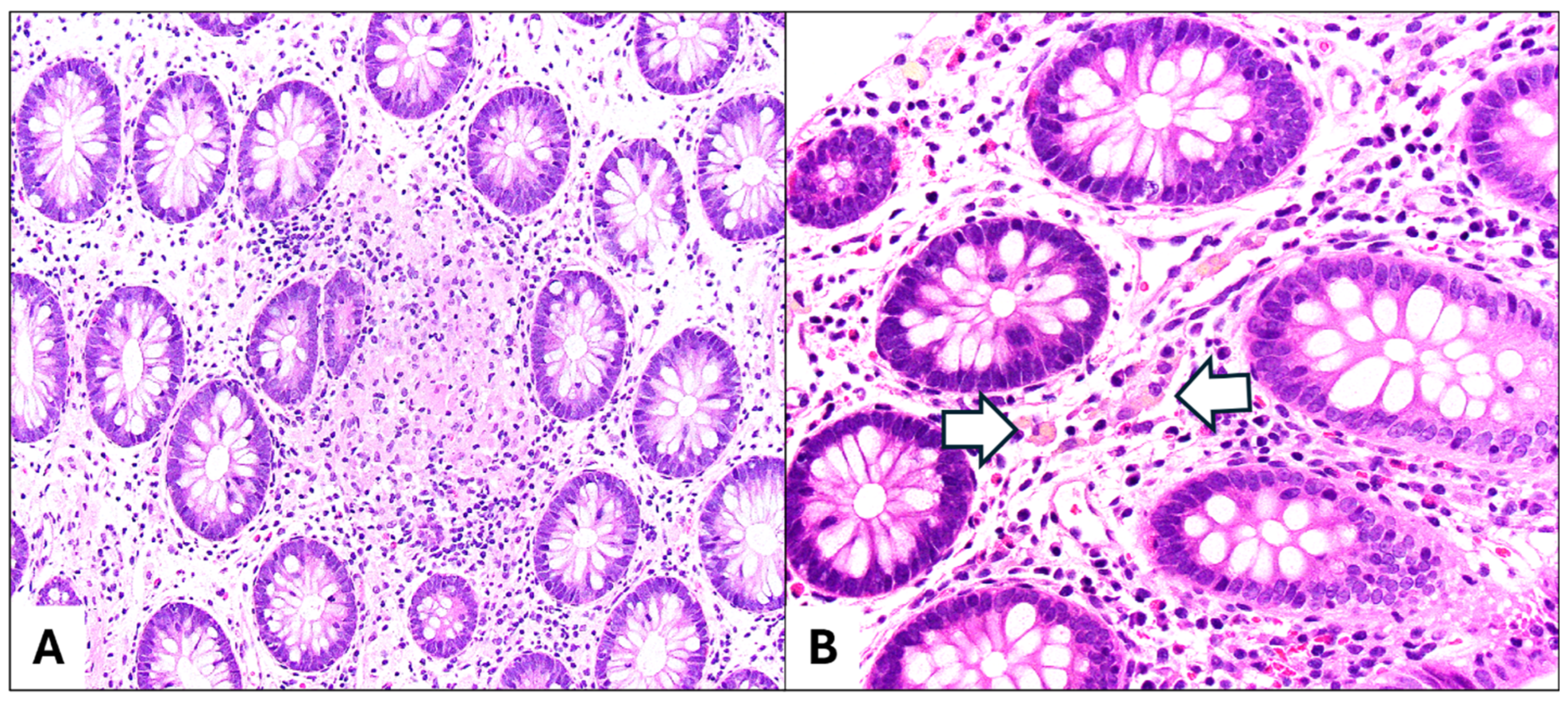
6. Differential Diagnosis
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bouhuys, M.; Lexmond, W.S.; van Rheenen, P.F. Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Pediatrics 2023, 151, e2022058037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuenzig, M.E.; Fung, S.G.; Marderfeld, L.; Mak, J.W.Y.; Kaplan, G.G.; Ng, S.C.; Wilson, D.C.; Cameron, F.; Henderson, P.; Kotze, P.G.; et al. Twenty-First Century Trends in the Global Epidemiology of Pediatric-Onset Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Systematic Review. Gastroenterology 2022, 162, 1147–1159.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuijk, S.A.; Camman, A.E.; de Ridder, L. Considerations in Paediatric and Adolescent Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Crohns Colitis 2024, 18 (Suppl. S2), ii31–ii45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzog, D.; Fournier, N.; Buehr, P.; Rueger, V.; Koller, R.; Heyland, K.; Nydegger, A.; Braegger, C.P.; Swiss IBD Cohort Study Group. Prevalence of Intestinal Complications in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Comparison between Paediatric-Onset and Adult-Onset Patients. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 29, 926–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakobsen, C.; Bartek, J.; Wewer, V.; Vind, I.; Munkholm, P.; Groen, R.; Paerregaard, A. Differences in Phenotype and Disease Course in Adult and Paediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease—A Population-Based Study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 34, 1217–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, A.; Koletzko, S.; Turner, D.; Escher, J.C.; Cucchiara, S.; de Ridder, L.; Kolho, K.-L.; Veres, G.; Russell, R.K.; Paerregaard, A.; et al. ESPGHAN Revised Porto Criteria for the Diagnosis of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Children and Adolescents. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2014, 58, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinawi, F.; Assa, A.; Eliakim, R.; Mozer-Glassberg, Y.; Nachmias Friedler, V.; Niv, Y.; Rosenbach, Y.; Silbermintz, A.; Zevit, N.; Shamir, R. The Natural History of Pediatric-Onset IBD-Unclassified and Prediction of Crohn’s Disease Reclassification: A 27-Year Study. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 52, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaty, H.M.; Mehta, S.; Abraham, B.; Garnett, E.A.; Ferry, G.D. The Natural Course of Inflammatory Bowel Disease-Indeterminate from Childhood to Adulthood: Within a 25 Year Period. Clin. Exp. Gastroenterol. 2013, 6, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satsangi, J.; Silverberg, M.S.; Vermeire, S.; Colombel, J.-F. The Montreal Classification of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Controversies, Consensus, and Implications. Gut 2006, 55, 749–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birimberg-Schwartz, L.; Zucker, D.M.; Akriv, A.; Cucchiara, S.; Cameron, F.L.; Wilson, D.C.; Lazowska, I.; Yianni, L.; Paul, S.P.; Romano, C.; et al. Development and Validation of Diagnostic Criteria for IBD Subtypes Including IBD-Unclassified in Children: A Multicentre Study From the Pediatric IBD Porto Group of ESPGHAN. J. Crohns Colitis 2017, 11, 1078–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledder, O.; Sonnino, M.; Birimberg-Schwartz, L.; Escher, J.C.; Russell, R.K.; Orlanski-Meyer, E.; Matar, M.; Assa, A.; Tzion, R.L.; Shteyer, E.; et al. Appraisal of the PIBD-Classes Criteria: A Multicentre Validation. J. Crohns Colitis 2020, 14, 1672–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, Y.; Hagiwara, S.-I.; Hizuka, K.; Saura, R.; Hata, A.; Maeyama, T.; Etani, Y. Validation of the Simplified PIBD-Classes Criteria: A Single-Center Retrospective Study. Pediatr. Int. Off. J. Jpn. Pediatr. Soc. 2024, 66, e15846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhaliwal, J.; Erdman, L.; Drysdale, E.; Rinawi, F.; Muir, J.; Walters, T.D.; Siddiqui, I.; Griffiths, A.M.; Church, P.C. Accurate Classification of Pediatric Colonic Inflammatory Bowel Disease Subtype Using a Random Forest Machine Learning Classifier. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2021, 72, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, N.; Sohrabi, K.; Schneider, H.; Zimmer, K.-P.; Fischer, P.; de Laffolie, J.; CEDATA-GPGE Study Group. Machine Learning Classification of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Children Based on a Large Real-World Pediatric Cohort CEDATA-GPGE® Registry. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 666190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mossotto, E.; Ashton, J.J.; Coelho, T.; Beattie, R.M.; MacArthur, B.D.; Ennis, S. Classification of Paediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease Using Machine Learning. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlig, H.H.; Schwerd, T.; Koletzko, S.; Shah, N.; Kammermeier, J.; Elkadri, A.; Ouahed, J.; Wilson, D.C.; Travis, S.P.; Turner, D.; et al. The Diagnostic Approach to Monogenic Very Early Onset Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 990–1007.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jevon, G.P.; Madhur, R. Endoscopic and Histologic Findings in Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 6, 174–180. [Google Scholar]
- Abuquteish, D.; Putra, J. Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Involvement of Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Pathological Review. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 1928–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repo, M.; Pessi, J.; Wirtanen, E.; Hiltunen, P.; Huhtala, H.; Kivelä, L.; Kurppa, K. Frequency and Clinical Significance of Histologic Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Findings in Children with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 57, 1046–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.B.; Hamilton, Z.; Hasosah, M.; Zetler, P.; Popescu, O.; Bush, J.; Katz, R.; Smyth, M.; Jacobson, K. The Role of Upper Gastrointestinal Endoscopy in the Diagnosis of Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2024, 162, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, C.A.; Sjödahl, K.; Lagergren, J. Lymphocytic Esophagitis: A Histologic Subset of Chronic Esophagitis. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2006, 125, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Coady, L.C.; Sheahan, K.; Brown, I.S.; Carneiro, F.; Gill, A.J.; Kumarasinghe, P.; Kushima, R.; Lauwers, G.Y.; Pai, R.K.; Shepherd, N.A.; et al. Esophageal Lymphocytosis: Exploring the Knowns and Unknowns of This Pattern of Esophageal Injury. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 18, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebach, D.R.; Vanderheyden, A.D.; Ellison, J.M.; Jensen, C.S. Lymphocytic Esophagitis: A Possible Manifestation of Pediatric Upper Gastrointestinal Crohn’s Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2011, 17, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, L.M.; Heintz, D.D.; Patel, A.S.; Weinberg, A.G. Lymphocytic Esophagitis in Children. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2014, 20, 1324–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spasic, S.; Pankaj, A.; Kaplan, J.L.; Patil, D.; Moran, C.J.; Deshpande, V. Paediatric Crohn’s Disease: Histologic Findings at Initial Presentation. J. Clin. Pathol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittman, M.E. Lymphocytic Esophagitis: Current Understanding and Controversy. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2022, 46, e55–e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, I.W.; Atkinson, A.E.; Liu, X.; Suriawinata, A.A.; Lefferts, J.A.; Lisovsky, M. Mucosal Inflammation in Candida Esophagitis Has Distinctive Features That May Be Helpful Diagnostically. Mod. Pathol. 2018, 31, 1653–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuquteish, D.; Siddiqui, I.; Putra, J. Lymphocytic Esophagitis: Inflammatory Pattern of Candida Esophagitis in a Patient with Ulcerative Colitis. Int. J. Surg. Pathol. 2019, 27, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, J.; Ornvold, K. Focally Enhanced Gastritis in Children with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Clinicopathological Correlation. Pathology 2017, 49, 808–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, J.B.; Gopal, P.; Greenson, J.K. The Clinical Significance of Focally Enhanced Gastritis in Children. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2013, 37, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kővári, B.; Pai, R.K. Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Involvement in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: Histologic Clues and Pitfalls. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2022, 29, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ushiku, T.; Moran, C.J.; Lauwers, G.Y. Focally Enhanced Gastritis in Newly Diagnosed Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2013, 37, 1882–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roka, K.; Roma, E.; Stefanaki, K.; Panayotou, I.; Kopsidas, G.; Chouliaras, G. The Value of Focally Enhanced Gastritis in the Diagnosis of Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. J. Crohns Colitis 2013, 7, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbdullGaffar, B.; Quraishi, H. Histopathologic Manifestations of Crohn Disease in Duodenal Endoscopy Biopsy: The Value of Different Patterns of Involvement of Brunner Glands. Int. J. Surg. Pathol. 2021, 29, 710–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Matos, V.; Russo, P.A.; Cohen, A.B.; Mamula, P.; Baldassano, R.N.; Piccoli, D.A. Frequency and Clinical Correlations of Granulomas in Children with Crohn Disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2008, 46, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putniković, D.; Jevtić, J.; Ristić, N.; Milovanovich, I.D.; Đuknić, M.; Radusinović, M.; Popovac, N.; Đorđić, I.; Leković, Z.; Janković, R. Pediatric Crohn’s Disease in the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract: Clinical, Laboratory, Endoscopic, and Histopathological Analysis. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queliza, K.; Ihekweazu, F.D.; Schady, D.; Jensen, C.; Kellermayer, R. Granulomatous Upper Gastrointestinal Inflammation in Pediatric Ulcerative Colitis. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2018, 66, 620–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilaghi, E.; Felici, E.; Lahner, E.; Pilozzi, E.; Furio, S.; Lucchini, L.; Quatrale, G.; Piccirillo, M.; Parisi, P.; Curto, S.; et al. Helicobacter Pylori Infection in Children with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Prospective Multicenter Study. BMC Pediatr. 2024, 24, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roka, K.; Roubani, A.; Stefanaki, K.; Panayotou, I.; Roma, E.; Chouliaras, G. The Prevalence of Helicobacter Pylori Gastritis in Newly Diagnosed Children with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Helicobacter 2014, 19, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirzad-Aski, H.; Besharat, S.; Kienesberger, S.; Sohrabi, A.; Roshandel, G.; Amiriani, T.; Norouzi, A.; Keshtkar, A. Association Between Helicobacter Pylori Colonization and Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2021, 55, 380–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalba-Davila, P.; Aronson, S.; Lat, J.; Charles, C.; Schroeder, B.; Pittman, M.; Tang, V.; Wallach, T. Helicobacter Pylori Infection Is Associated with Significant Elevations to Fecal Calprotectin, Systemic Inflammatory Markers. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putra, J.; Goldsmith, J.D. Daily Dilemmas in Pediatric Gastrointestinal Pathology. Surg. Pathol. Clin. 2020, 13, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto-Sanchez, M.I.; Seiler, C.L.; Santesso, N.; Alaedini, A.; Semrad, C.; Lee, A.R.; Bercik, P.; Lebwohl, B.; Leffler, D.A.; Kelly, C.P.; et al. Association Between Inflammatory Bowel Diseases and Celiac Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 884–903.e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kori, M.; Zamir, Y.; Yermiyahu, S.O.; Ainbinder, I.; Daichman, S.; Pinto, G.D.; Loewenberg Weisband, Y.; Greenfeld, S.; Kariv, R.; Lederman, N.; et al. The Association of Inflammatory Bowel Disease with Coeliac Disease and Coeliac Autoimmunity in Children and Adults: A Nationwide Study from the Epi-IIRN. J. Crohns Colitis 2023, 17, 700–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Karlsen, T.H. Genetics of Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Pathophysiological Implications. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 279–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quraishi, M.N.; Acharjee, A.; Beggs, A.D.; Horniblow, R.; Tselepis, C.; Gkoutos, G.; Ghosh, S.; Rossiter, A.E.; Loman, N.; van Schaik, W.; et al. A Pilot Integrative Analysis of Colonic Gene Expression, Gut Microbiota, and Immune Infiltration in Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis-Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Association of Disease with Bile Acid Pathways. J. Crohns Colitis 2020, 14, 935–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciuto, A.; Hansen, B.E.; Ngo, B.; Aloi, M.; Walters, T.D.; Church, P.C.; Mazurek, A.; Khan, M.; Carman, N.; Siddiqui, I.; et al. Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis in Children with Inflammatory Bowel Diseases Is Associated with Milder Clinical Activity But More Frequent Subclinical Inflammation and Growth Impairment. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Off. Clin. Pract. J. Am. Gastroenterol. Assoc. 2020, 18, 1509–1517.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, R.; Putra, J.; Kamath, B.M.; Griffiths, A.M.; Ricciuto, A.; Siddiqui, I. Intestinal Histopathology in Pediatric PSC-IBD: Characterization of Phenotype and Assessment of the Nancy Index. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2024, 80, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catassi, G.; D’Arcangelo, G.; Norsa, L.; Bramuzzo, M.; Hojsak, I.; Kolho, K.-L.; Romano, C.; Gasparetto, M.; Di Giorgio, A.; Hussey, S.; et al. Outcome of Very Early Onset Inflammatory Bowel Disease Associated With Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis: A Multicenter Study From the Pediatric IBD Porto Group of ESPGHAN. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2024, 30, 1662–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vries, A.B.; Janse, M.; Blokzijl, H.; Weersma, R.K. Distinctive Inflammatory Bowel Disease Phenotype in Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 1956–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Lauwers, G.Y.; Choi, W.-T. Increased Risk of Non-Conventional and Invisible Dysplasias in Patients with Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Crohns Colitis 2022, 16, 1825–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubin, D.T.; Ananthakrishnan, A.N.; Siegel, C.A.; Sauer, B.G.; Long, M.D. ACG Clinical Guideline: Ulcerative Colitis in Adults. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 114, 384–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nambu, R.; Warner, N.; Mulder, D.J.; Kotlarz, D.; McGovern, D.P.B.; Cho, J.; Klein, C.; Snapper, S.B.; Griffiths, A.M.; Iwama, I.; et al. A Systematic Review of Monogenic Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Off. Clin. Pract. J. Am. Gastroenterol. Assoc. 2022, 20, e653–e663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glocker, E.-O.; Kotlarz, D.; Boztug, K.; Gertz, E.M.; Schäffer, A.A.; Noyan, F.; Perro, M.; Diestelhorst, J.; Allroth, A.; Murugan, D.; et al. Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Mutations Affecting the Interleukin-10 Receptor. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 2033–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlig, H.H.; Charbit-Henrion, F.; Kotlarz, D.; Shouval, D.S.; Schwerd, T.; Strisciuglio, C.; de Ridder, L.; van Limbergen, J.; Macchi, M.; Snapper, S.B.; et al. Clinical Genomics for the Diagnosis of Monogenic Forms of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Position Paper From the Paediatric IBD Porto Group of European Society of Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2021, 72, 456–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, E.; Warner, N.; Pan, J.; Khalouei, S.; Elkadri, A.; Fiedler, K.; Foong, J.; Turinsky, A.L.; Bronte-Tinkew, D.; Zhang, S.; et al. Prevalence and Clinical Features of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases Associated with Monogenic Variants, Identified by Whole-Exome Sequencing in 1000 Children at a Single Center. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 2208–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolton, C.; Smillie, C.S.; Pandey, S.; Elmentaite, R.; Wei, G.; Argmann, C.; Aschenbrenner, D.; James, K.R.; McGovern, D.P.B.; Macchi, M.; et al. An Integrated Taxonomy for Monogenic Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterology 2022, 162, 859–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, B.J.; Kelsen, J.R.; Conrad, M.A. A Pattern-Based Pathology Approach to Very Early-Onset Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Thinking Beyond Crohn Disease and Ulcerative Colitis. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2022, 29, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlig, H.H.; Booth, C.; Cho, J.; Dubinsky, M.; Griffiths, A.M.; Grimbacher, B.; Hambleton, S.; Huang, Y.; Jones, K.; Kammermeier, J.; et al. Precision Medicine in Monogenic Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Proposed mIBD REPORT Standards. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 20, 810–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotlarz, D.; Beier, R.; Murugan, D.; Diestelhorst, J.; Jensen, O.; Boztug, K.; Pfeifer, D.; Kreipe, H.; Pfister, E.; Baumann, U.; et al. Loss of Interleukin-10 Signaling and Infantile Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Implications for Diagnosis and Therapy. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelsen, J.R.; Dawany, N.; Martinez, A.; Grochowski, C.M.; Maurer, K.; Rappaport, E.; Piccoli, D.A.; Baldassano, R.N.; Mamula, P.; Sullivan, K.E.; et al. A de Novo Whole Gene Deletion of XIAP Detected by Exome Sequencing Analysis in Very Early Onset Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Case Report. BMC Gastroenterol. 2015, 15, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekbua, A.; Ouahed, J.; O’Connell, A.E.; Kahn, S.A.; Goldsmith, J.D.; Imamura, T.; Duncan, C.N.; Kelsen, J.R.; Worthey, E.; Snapper, S.B.; et al. Risk-Factors Associated with Poor Outcomes in VEO-IBD Secondary to XIAP Deficiency: A Case Report and Literature Review. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2019, 69, e13–e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zurro, N.B.; Tavares de Albuquerque, J.A.; França, T.T.; Vendramini, P.; Arslanian, C.; Tavares-Scancetti, F.; Condino-Neto, A. A Novel Mutation in CYBB Gene in a Patient with Chronic Colitis and Recurrent Pneumonia Due to X-Linked Chronic Granulomatous Disease. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2018, 65, e27382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Chen, H.; Feng, X.; Ruan, Y.; Yang, M. Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for CYBB Heterozygous Mutation Resulting in Very Early Onset Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Children: A Case Report. BMC Pediatr. 2023, 23, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Wong, A.; Sutton, K.; Gondim, M.J.B.; Samson, C. Very-Early Onset Chronic Active Colitis with Heterozygous Variants in LRBA1 and CARD11, a Case of “Immune TOR-Opathies”. Fetal Pediatr. Pathol. 2023, 42, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okur, F.V.; Kuskonmaz, B.; Cagdas, D.; Tezcan, I.; Uckan-Cetinkaya, D. Bone Marrow Transplantation with Favorable Outcome in Three Patients with LPS-Responsive Beige-like Anchor (LRBA) Deficiency. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 203, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, R.; Lin, Y.-F.; Lai, M.-W.; Weng, H.-Y.; Wu, R.-C.; Jaing, T.-H.; Huang, J.-L.; Tsai, S.-F.; Lee, W.-I. Novel Mutations of the Tetratricopeptide Repeat Domain 7A Gene and Phenotype/Genotype Comparison. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avitzur, Y.; Guo, C.; Mastropaolo, L.A.; Bahrami, E.; Chen, H.; Zhao, Z.; Elkadri, A.; Dhillon, S.; Murchie, R.; Fattouh, R.; et al. Mutations in Tetratricopeptide Repeat Domain 7A Result in a Severe Form of Very Early Onset Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 1028–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dannheim, K.; Ouahed, J.; Field, M.; Snapper, S.; Raphael, B.P.; Glover, S.C.; Bishop, P.R.; Bhesania, N.; Kamin, D.; Thiagarajah, J.; et al. Pediatric Gastrointestinal Histopathology in Patients with Tetratricopeptide Repeat Domain 7A (TTC7A) Germline Mutations: A Rare Condition Leading to Multiple Intestinal Atresias, Severe Combined Immunodeficiency, and Congenital Enteropathy. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2022, 46, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feakins, R.; Torres, J.; Borralho-Nunes, P.; Burisch, J.; Cúrdia Gonçalves, T.; De Ridder, L.; Driessen, A.; Lobatón, T.; Menchén, L.; Mookhoek, A.; et al. ECCO Topical Review on Clinicopathological Spectrum and Differential Diagnosis of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Crohns Colitis 2022, 16, 343–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panarelli, N.C. Infectious Mimics of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Mod. Pathol. 2023, 36, 100210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voltaggio, L.; Montgomery, E.A.; Ali, M.A.; Singhi, A.D.; Arnold, C.A. Sex, Lies, and Gastrointestinal Tract Biopsies: A Review of Selected Sexually Transmitted Proctocolitides. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2014, 21, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herlihy, N.; Feakins, R. Gut Inflammation Induced by Drugs: Can Pathology Help to Differentiate from Inflammatory Bowel Disease? United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2022, 10, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reggiani Bonetti, L.; Leoncini, G.; Daperno, M.; Principi, M.B.; Baronchelli, C.; Manenti, S.; Caprioli, F.; Armuzzi, A.; Caputo, A.; Parente, P.; et al. Histopathology of Non-IBD Colitis Practical Recommendations from Pathologists of IG-IBD Group. Dig. Liver Dis. Off. J. Ital. Soc. Gastroenterol. Ital. Assoc. Study Liver 2021, 53, 950–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Class 1 (features incompatible with UC)
|
Class 2 (features rarely found in UC)
|
Class 3 (features uncommon in UC)
|
| Monogenic Disorder | Genes | IBD Type Reported | Extraintestinal Associations (in Order of Relative Frequency) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agammaglobulinemia | BTK, PIK3CD, PIK3R1 | CD/CD-like, IBD, UC/UC-like | Autoimmunity, infection |
| Chronic enteropathy associated with SLCO2A1 gene | SLCO2A1 | IBD, CD/CD-like | Autoimmunity |
| Chronic granulomatous disease | CYBA, CYBB, NCF1, NCF2, NCF4 | Granulomatous colitis, IBD, CD/CD-like, UC/UC-like, IBD-U/IC | Autoimmunity, infection, HLH, malignancy |
| CHAPLE syndrome | CD55 | ND | Autoimmunity, infection, malignancy |
| DOCK8 syndrome | DOCK8 | UC/UC-like, CD/CD-like, IBD | Autoimmunity, infection |
| Familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis 4 | STXBP2 | ND | Autoimmunity, infection, HLH |
| Glycogen storage disease type 1B | SLC37A4 | IBD, CD/CD-like | Infection, hematolymphoid involvement, metabolic disease |
| Familial GUCY2C diarrhea syndrome | GUCY2C | CD/CD-like, IBD | |
| G6PC3 deficiency | G6PC3 | CD/CD-like, IBD | Infection, dysmorphic features |
| Haploinsufficiency of A20 | TNFAIP3 | Intestinal BD, CD/CD-like, IBD | Autoimmunity, infection |
| Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome | HPS1, HPS4, HPS6 | CD/CD-like, IBD, UC/UC-like | Autoimmunity |
| Hoyeraal-Hreidarsson Syndrome | DKC1, RTEL1 | UC/UC-like, CD/CD-like | Dysmorphic features, infection |
| IL-10 and IL-10-receptor associated colitis | IL-10, IL-10RA, IL-10RB | IBD, CD/CD-like, IBD-U/IC | Autoimmunity, infection, HLH |
| Immunodysregulation polyendocrinopathy enteropathy X-linked syndrome (IPEX) | FOXP3 | IBD, CD/CD-like, UC/UC-like, IBD-U/IC | Autoimmunity, infection |
| Immunodysregulation polyendocrinopathy enteropathy X-linked-like syndrome (IPEX-like) | STAT1, STAT3, CTLA4, LRBA, IL21, IL2RA, IL2RB, MALT1 | IBD, CD/CD-like, UC/UC-like, IBD-U | Autoimmunity, infection, malignancy, hematolymphoid involvement |
| Kindler syndrome | FERMT1 | UC/UC-like, CD/CD-like | |
| Leukocyte adhesion deficiency | ITGB2 | ND | Infection |
| Loeys-Dietz syndrome | TGFBR1, TGFBR2 | UC/UC-like, CD/CD-like, IBD | Dysmorphic features, infection |
| Mevalonate kinase deficiency | MVK | ND | Autoimmunity |
| Nuclear factor-kappa B Essential Modulator deficiency (NEMO) | IKBKG | IBD, CD/CD-like, intestinal BD | Dysmorphic features, infection |
| NLRC4-macrophage activating syndrome | NLRC4 | ND | Autoimmunity, infection, HLH |
| Niemann-Pick disease type C | NPC1 | CD/CD-like, IBD-U/IC | Metabolic disease |
| RIPK1 deficiency | RIPK1 | IBD | Autoimmunity, infection |
| Severe combined immunodeficiency | CD3G, DCLRE1C, IL2RG, LIG4, RAG1 | IBD, CD/CD-like | Infection |
| Trichohepatoenteric syndrome | SKIV2L, TTC37 | IBD-U/IC, IBD, CD/CD-like | Dysmorphic features, infection |
| TTC7A deficiency | TTC7A | IBD, IBD-U/IC, CD/CD-like | Autoimmunity, infection, dysmorphic features, malignancy |
| TRIM22 deficiency | TRIM22 | ND | Autoimmunity, infection |
| Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome/Wiskott-Aldrich-like syndrome (WAS/WAS-like) | WAS, ARPC1B | IBD, CD/CD-like, UC/UC-like | Autoimmunity, infection |
| XIAP deficiency | XIAP | CD/CD-like, IBD, UC/UC-like, IBD-U/IC | Autoimmunity, infection, HLH, hematolymphoid involvement, malignancy |
| Pattern | Key Findings | Associated Monogenic Disorders | Other Causes of Pattern |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chronic active enteritis | Active inflammation (neutrophilic cryptitis and crypt abscesses) Chronic mucosal changes (architectural changes and cellular metaplasia) | IL-10/R; CGD; XIAP; GUCY2C; familial Mediterranean fever; HPS types 1, 4, 6; GSD1; WAS; CVID; TTC7A | Polygenic IBD |
| Apoptosis/Epithelial injury pattern | Epithelial injury or apoptosis out of proportion to inflammatory activity | Disorders resulting in B and T cell deficiency/dysregulation; SCID; Omenn syndrome; IPEX; TTC7A; dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa; mevalonate kinase deficiency; disorders of telomere maintenance | GvHD; antimetabolite immunosuppression, especially mycophenolate mofetil; acute GI transplant rejection; viral infection |
| Eosinophil-rich pattern | Clusters of eosinophils in the lamina propria and eosinophilic infiltration of surface and crypt epithelium | Omenn syndrome | Non-monogenic IBD; non-IBD etiologies for GI eosinophilia (e.g., allergy, parasitic infection, Langerhans cell histiocytosis) |
| Lymphocytic patterns | Lymphocytosis and nodular lymphoid hyperplasia OR Lymphocyte or plasma cell depletion AND Lack of active inflammation and chronic mucosal changes | Lymphocytosis: CVID; IgA deficiency; CTLA4-related disorders; T cell regulatory disorders; IPEX Lymphocyte or plasma cell depletion: CVID; hypogammaglobulinemia; X-linked lymphoproliferative disorder type 1; SCID | Lymphocytosis: celiac disease; post-infectious enteritis (can be secondary to immunodeficiency), medication effect (especially NSAIDs); bacterial overgrowth Lymphoid depletion: medical therapy (e.g., conditioning chemotherapy prior to bone marrow transplant); artifactual due to mucosal edema |
| Granulomatous pattern | Non-necrotizing granulomas | CGD; IL-10/R; HPS types 1, 4, 6 | Misidentification of cryptolytic granuloma/germinal center; infectious granulomas (mycobacterial/fungal, usually necrotizing); or very rarely sarcoidosis |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Andrews, A.R.; Putra, J. Special Considerations in Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease Pathology. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 831. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15070831
Andrews AR, Putra J. Special Considerations in Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease Pathology. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(7):831. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15070831
Chicago/Turabian StyleAndrews, Alicia R., and Juan Putra. 2025. "Special Considerations in Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease Pathology" Diagnostics 15, no. 7: 831. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15070831
APA StyleAndrews, A. R., & Putra, J. (2025). Special Considerations in Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease Pathology. Diagnostics, 15(7), 831. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15070831






