MRI Detection of Unknown Primary Tumours in the Head and Neck: What Is the Expected Normal Asymmetry in the Size of the Palatine Tonsils?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Patients
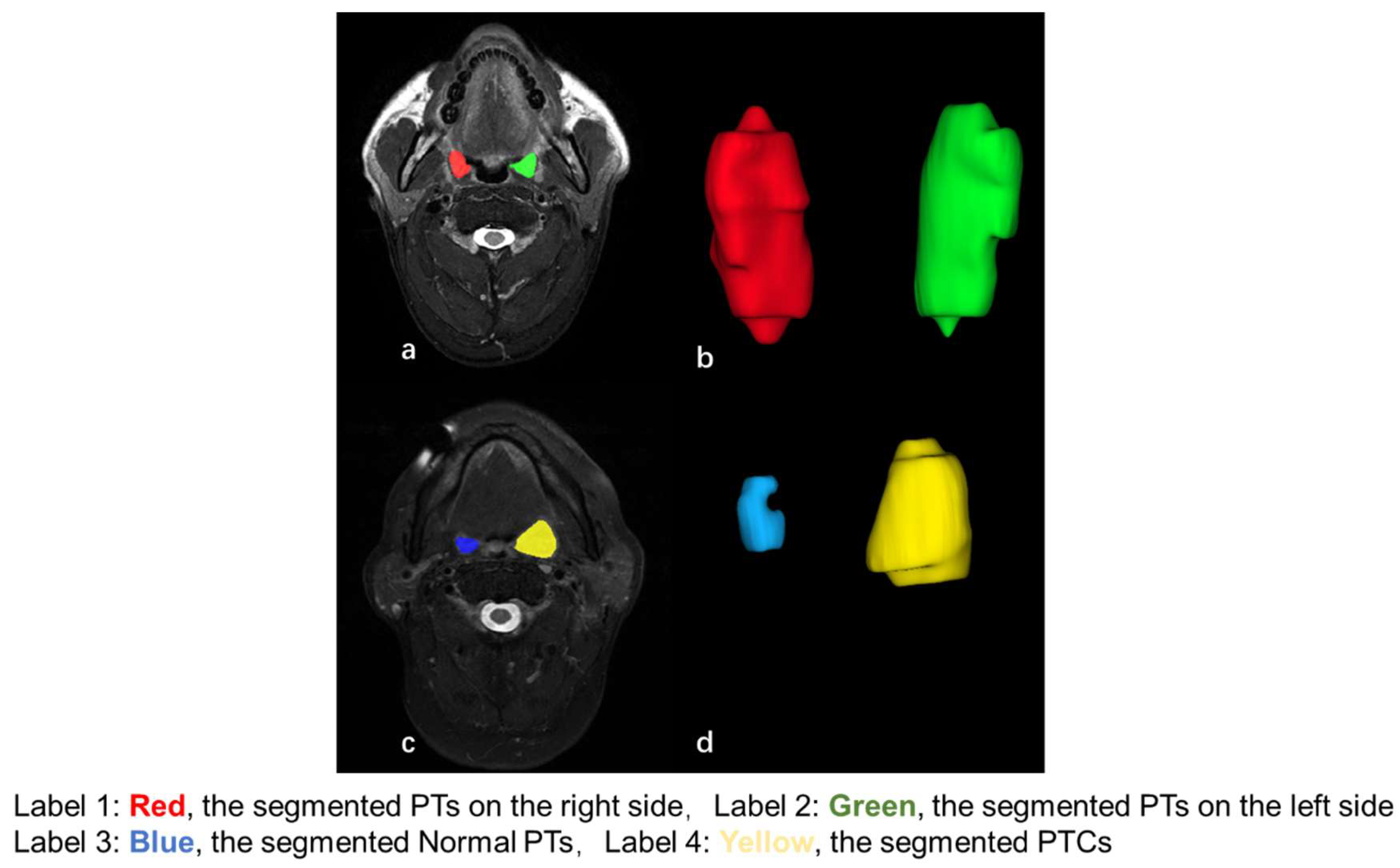
2.2. MRI Acquisition and Analysis
2.3. Node Size
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients
3.2. Sizes of the PTs in Patients Without PTC
3.3. Differences in Size Between Normal PTs and PTs with PTC
3.4. Association Between the Size of PTs with the Size of Ipsilateral Nodes, Age, and Cigarette Consumption in Patients Without PTC
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EBV | Epstein–Barr Virus |
| FDG | 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose |
| ICCs | Intra-class correlation coefficients |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| PET/CT | Positron emission tomography–computed tomography |
| PTCs | Palatine tonsillar cancers |
| PTs | Palatine tonsils |
| ROI | Region of interest |
| SAD | Short axial diameter |
| SCC | Squamous cell carcinoma |
References
- Johnson, D.E.; Burtness, B.; Leemans, C.R.; Lui, V.W.Y.; Bauman, J.E.; Grandis, J.R. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marur, S.; Forastiere, A.A. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Update on epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2016, 91, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mody, M.D.; Rocco, J.W.; Yom, S.S.; Haddad, R.I.; Saba, N.F. Head and neck cancer. Lancet 2021, 398, 2289–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosway, B.; Drinnan, M.; Paleri, V. Narrow band imaging for the diagnosis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A systematic review. Head Neck 2016, 38, E2358–E2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Economopoulou, P.; De Bree, R.; Kotsantis, I.; Psyrri, A. Diagnostic tumor markers in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) in the clinical setting. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, E.J.; Kim, D.H.; Ahn, J.Y.; Choi, K.-S.; Jung, K.W.; Lee, J.H.; Choi, K.D.; Song, H.J.; Lee, G.H.; Jung, H.-Y. Routine endoscopic screening for synchronous esophageal neoplasm in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A prospective study. Dis. Esophagus 2016, 29, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.D.; Thoeny, H.C. Functional MRI for the prediction of treatment response in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Potential and limitations. Cancer Imaging 2016, 16, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, M.; Zaidi, H. Imaging in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: The potential role of PET/MRI. Br. J. Radiol. 2014, 87, 20130677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.I.; Guenette, J.P.; Suh, C.H.; Hanna, G.J.; Chung, S.R.; Baek, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Choi, Y.J. The diagnostic performance of CT and MRI for detecting extranodal extension in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A systematic review and diagnostic meta-analysis. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 2048–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genden, E.M.; Ferlito, A.; Scully, C.; Shaha, A.R.; Higgins, K.; Rinaldo, A. Current management of tonsillar cancer. Oral Oncol. 2003, 39, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syrjänen, S. HPV infections and tonsillar carcinoma. J. Clin. Pathol. 2004, 57, 449. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ballin, A.C.; Koerner, H.N.; Ballin, C.H.; Pereira, R.; Alcântara, L.J.L.; Taques, G.R.; Mocellin, M. Palatine tonsils asymmetry: 10 years experience of the Otorhinolaryngology service of the clinical hospital of the Federal University of Paraná. Arq. Int. Otorrinolaringol. 2011, 15, 067–071. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez, S.T.; Asenjo, V.P.; Perera, M.B.; Hernández, I.P.; Giner, A.R.; García, V.P. Clinical significance of unilateral tonsillar enlargement. Acta Otorrinolaringol. Engl. Ed. 2009, 60, 194–198. [Google Scholar]
- Cinar, F. Significance of asymptomatic tonsil asymmetry. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2004, 131, 101–103. [Google Scholar]
- Harley, E.H. Asymmetric tonsil size in children. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2002, 128, 767–769. [Google Scholar]
- King, A.; Vlantis, A.; Tsang, R.; Gary, T.; Au, A.; Chan, C.; Kok, S.; Kwok, W.; Lui, H.; Ahuja, A. Magnetic resonance imaging for the detection of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2006, 27, 1288–1291. [Google Scholar]
- King, A.; Woo, J.; Ai, Q.; Chan, J.; Lam, W.; Tse, I.; Bhatia, K.; Zee, B.; Hui, E.; Ma, B. Complementary roles of MRI and endoscopic examination in the early detection of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 977–982. [Google Scholar]
- Ai, Q.Y.H.; So, T.Y.; Hung, K.F.; King, A.D. Normal size of benign upper neck nodes on MRI: Parotid, submandibular, occipital, facial, retroauricular and level IIb nodal groups. Cancer Imaging 2022, 22, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Hardman, J.C.; Constable, J.; Williamson, A.; Dobbs, S.; Hogan, C.; Hulse, K.; Khosla, S.; Milinis, K.; Tudor-Green, B.; Paleri, V. Investigations for suspected head and neck squamous cell carcinoma of unknown primary (HNSCCUP): A national cohort study. In Clinical Otolaryngology; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, H.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Jeong, S.H. Normative values for tonsils in pediatric populations based on ultrasonography. J. Ultrasound Med. 2018, 37, 1657–1663. [Google Scholar]
- Bozbeyoğlu, S.G.; Dogan, M.B. A Tissue Ignored In Cervical Ultrasound: Relationship of Palatine Tonsil Size with Age, Sex, Body Mass Index, and Body Surface Area in the Pediatric Population. Cerrahpaşa Med. J. 2023, 47, 302–305. [Google Scholar]
- Aydin, S.; Uner, C. Normal palatine tonsil size in healthy children: A sonographic study. Radiol. Med. 2020, 125, 864–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogler, R.; Ii, F.W.; Pilgram, T. Age-specific size of the normal adenoid pad on magnetic resonance imaging. Clin. Otolaryngol. Allied Sci. 2000, 25, 392–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surov, A.; Ryl, I.; Bartel-Friedrich, S.; Wienke, A.; Kösling, S. MRI of nasopharyngeal adenoid hypertrophy. Neuroradiol. J. 2016, 29, 408–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, K.C.; Vasilyeva, D.; Bansal, T.; Moonis, G. Adenoidal-Nasopharyngeal Ratio in Healthy Adults on Cone Beam Computed Tomography. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2022, 46, 836–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahali, M.B.; de Paula Soares, C.F.; da Silva Dantas, D.A.; Formigoni, G.G.S. Tonsil volume, tonsil grade and obstructive sleep apnea: Is there any meaningful correlation? Clinics 2011, 66, 1347–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahne, A.; El-Haddad, G.; Alavi, A.; Houseni, M.; Moonis, G.; Mong, A.; Hernandez-Pampaloni, M.; Torigian, D.A. Assessment of age-related morphological and functional changes of selected structures of the head and neck by computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, and positron emission tomography. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2007, 37, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grégoire, V.; Ang, K.; Budach, W.; Grau, C.; Hamoir, M.; Langendijk, J.A.; Lee, A.; Le, Q.-T.; Maingon, P.; Nutting, C. Delineation of the neck node levels for head and neck tumors: A 2013 update. DAHANCA, EORTC, HKNPCSG, NCIC CTG, NCRI, RTOG, TROG consensus guidelines. Radiother. Oncol. 2014, 110, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Overall a | Left a | Right a | Left vs. Right p-Value | ΔV% b | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients without PTCs (cm3) (n = 250) | 3.0 ± 1.7 (0.1–13.5) | 2.9 ± 1.7 (0.1–13.5) | 3.1 ± 1.7 (0.1–12.2) | <0.01 | 11.6% (0.1–79.0%) |
| Overall a | Normal PTs a | PTCs a | Normal PT vs. PTCs p-value | ΔV% b | |
| Patients with PTCs (cm3) (n = 29) | - | 1.8 ± 1.2 (0.8–6.9) | 5.0 ± 3.4 (1.5–12.9) | <0.01 | 132.9% (8.5–863.2%) |
| ≤5% | >5%, ≤10% | >10%, ≤15% | >15%, ≤20% | >20%, ≤25% | >25%, ≤30% | >30%, ≤40% | >40%, ≤50% | >50% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients without PTCs | 62 (24.8%) | 51 (20.4%) | 41 (16.4%) | 37 (14.8%) | 26 (10.4%) | 14 (5.6%) | 7 (2.8%) | 2 (0.8%) | 10 (4.0%) |
| Patients with PTCs | 0 (0%) | 2 (6.9%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (3.4%) | 0 (0%) | 2 (6.9%) | 24 (82.8%) |
| Retropharyngeal a | Submandibular a | Jugulodigastric a | Level IIa a | Level IIb a | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAD (mm) | Right | 3.7 ± 1.2 (2.0–9.0) | 5.0 ± 1.5 (2.3–8.7) | 6.8 ± 1.9 (2.5–11.9) | 4.3 ± 1.5 (2.1–11.9) | 4.0 ± 1.1 (2.1–7.5) |
| Left | 3.8 ± 1.1 (2.1–7.9) | 4.9 ± 1.3 (2.7–9.3) | 6.8 ± 2.0 (3.0–12.6) | 4.5 ± 1.5 (2.1–9.4) | 3.9 ± 1.1 (2.0–7.6) | |
| Retropharyngeal | Submandibular | Jugulodigastric | Level IIa | Level IIb | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | p-Value | R | p-Value | R | p-Value | R | p-Value | R | p-Value | ||
| Palatine Tonsils | Right | 0.22 | <0.01 | 0.27 | <0.01 | 0.34 | <0.01 | 0.32 | <0.01 | 0.26 | <0.01 |
| Left | 0.24 | <0.01 | 0.15 | 0.02 | 0.46 | <0.01 | 0.29 | <0.01 | 0.20 | 0.02 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mao, K.; Ai, Q.Y.H.; Hung, K.F.; Tse, I.O.L.; Leung, H.S.; Liang, Y.Y.; Chen, Y.; Wong, L.M.; Lam, W.K.J.; King, A.D. MRI Detection of Unknown Primary Tumours in the Head and Neck: What Is the Expected Normal Asymmetry in the Size of the Palatine Tonsils? Diagnostics 2025, 15, 788. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15060788
Mao K, Ai QYH, Hung KF, Tse IOL, Leung HS, Liang YY, Chen Y, Wong LM, Lam WKJ, King AD. MRI Detection of Unknown Primary Tumours in the Head and Neck: What Is the Expected Normal Asymmetry in the Size of the Palatine Tonsils? Diagnostics. 2025; 15(6):788. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15060788
Chicago/Turabian StyleMao, Kaijing, Qi Yong H. Ai, Kuo Feng Hung, Irene O. L. Tse, Ho Sang Leung, Yannis Yan Liang, Yu Chen, Lun M. Wong, W. K. Jacky Lam, and Ann D. King. 2025. "MRI Detection of Unknown Primary Tumours in the Head and Neck: What Is the Expected Normal Asymmetry in the Size of the Palatine Tonsils?" Diagnostics 15, no. 6: 788. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15060788
APA StyleMao, K., Ai, Q. Y. H., Hung, K. F., Tse, I. O. L., Leung, H. S., Liang, Y. Y., Chen, Y., Wong, L. M., Lam, W. K. J., & King, A. D. (2025). MRI Detection of Unknown Primary Tumours in the Head and Neck: What Is the Expected Normal Asymmetry in the Size of the Palatine Tonsils? Diagnostics, 15(6), 788. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15060788









