Accuracy of Artificial Intelligence Models in Detecting Peri-Implant Bone Loss: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Article Selection Criteria
2.2. Exposure and Outcome
2.3. Search Design, Selection of Studies, and Extraction of Pertinent Data
2.4. Quality Assessment of Included Studies
3. Results
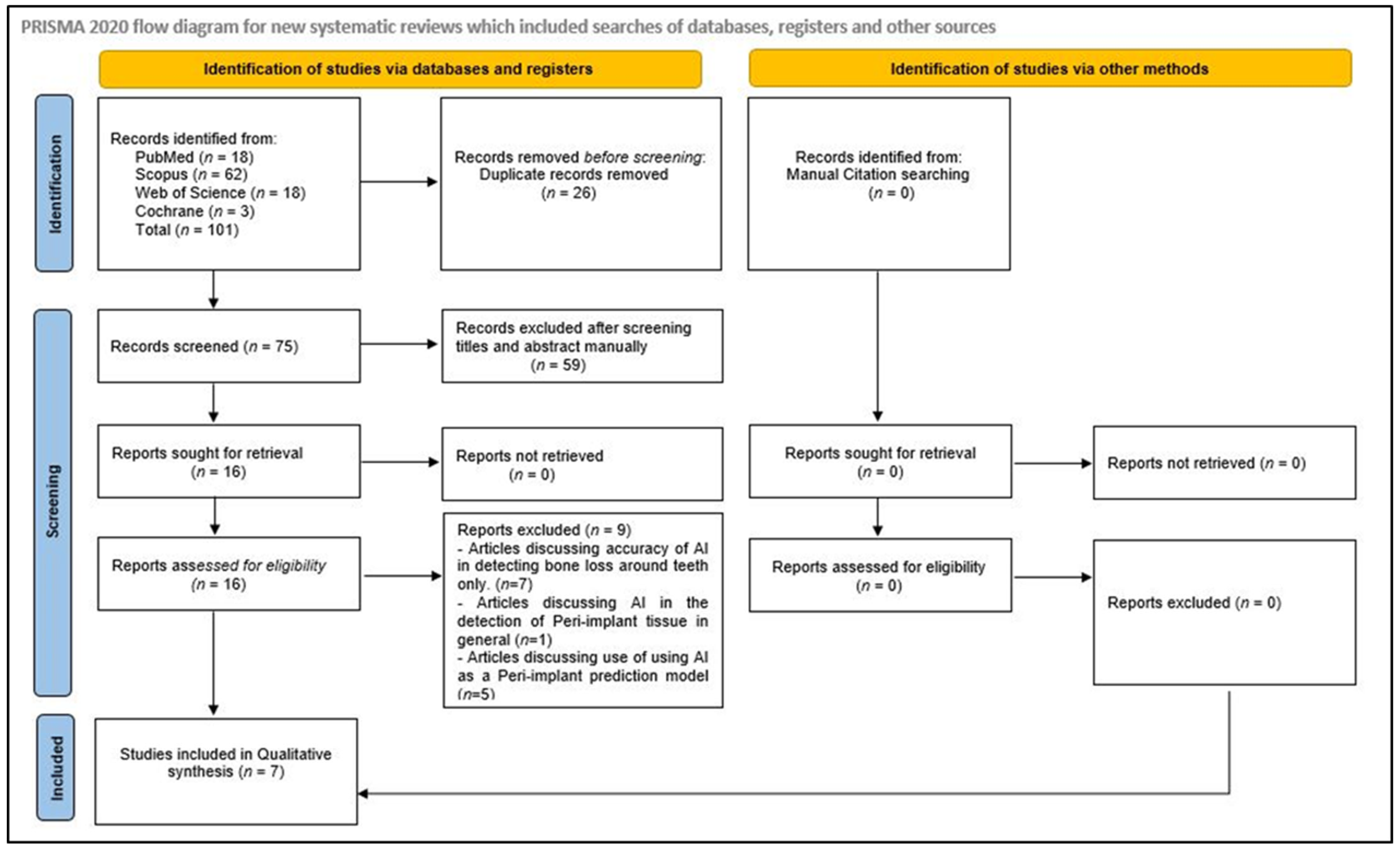
3.1. Identification and Screening
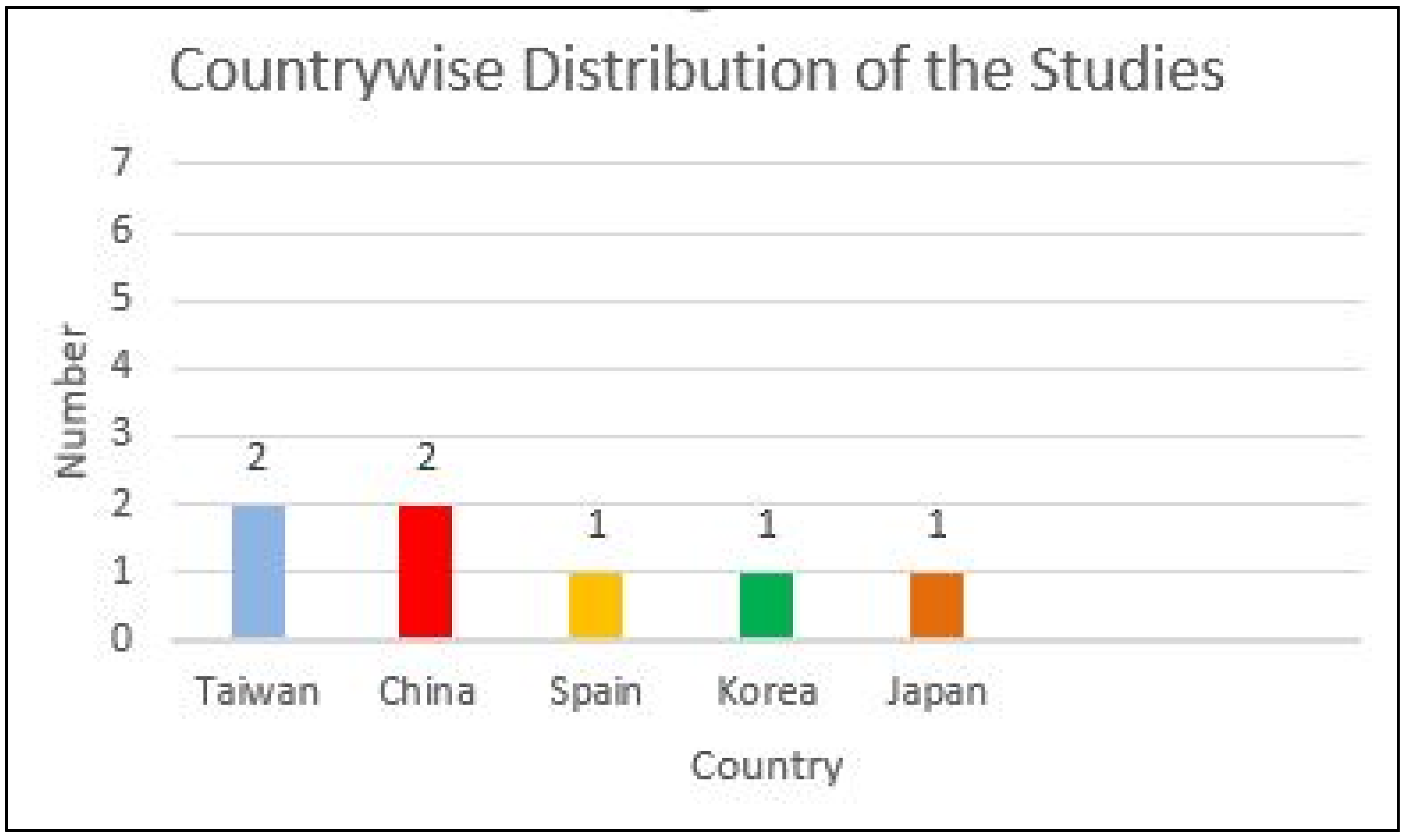
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. Assessment of Strength of Evidence
3.4. Accuracy Assessment/Features of the Included Studies
3.5. Risk of Bias Assessment and Applicability Concern
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations and Strengths
4.2. Challenges and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Davidowitz, G.; Kotick, P.G. The use of CAD/CAM in dentistry. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2011, 55, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alghazzawi, T.F. Advancements in CAD/CAM technology: Options for practical implementation. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2016, 60, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turkyilmaz, I.; Wilkins, G.N. 3D printing in dentistry-Exploring the new horizons. J. Dent. Sci. 2021, 16, 1037–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Ku, H.-M.; Jun, M.-K. Clinical Application of Intraoral Scanners in Dentistry: A Narrative Review. Oral 2024, 4, 639–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Watanabe, M.; Ichikawa, T. Robotics in Dentistry: A Narrative Review. Dent. J. 2023, 11, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Sayed, M.E.; Ibraheem, W.I.; Ageeli, A.A.; Gandhi, S.; Jokhadar, H.F.; AlResayes, S.S.; Alqarni, H.; Alshehri, A.H.; Huthan, H.M.; et al. Accuracy Comparison between Robot-Assisted Dental Implant Placement and Static/Dynamic Computer-Assisted Implant Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of In Vitro Studies. Medicina 2024, 60, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amornvit, P.; Rokaya, D.; Sanohkan, S. Comparison of Accuracy of Current Ten Intraoral Scanners. Biomed. Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 2673040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshni, A.A.; Jain, S.; Osaysi, H.N.M.; Hezam, K.N.; Adlan, S.S.G. The Comparison of Accuracy of Post Space Digital Impressions Made by Three Different Intraoral Scanners: An In Vitro Study. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akst, J. A primer: Artificial intelligence versus neural networks. In Inspiring Innovation: The Scientist Exploring Life; LabX Media Group: Midland, Canada, 2019; p. 65802. [Google Scholar]
- Kozan, N.M.; Kotsyubynska, Y.Z.; Zelenchuk, G.M. Using the artificial neural networks for identification unknown person. IOSR J. Dent. Med. Sci. 2017, 1, 107–113. [Google Scholar]
- Khanagar, S.B.; Al-ehaideb, A.; Maganur, P.C.; Vishwanathaiah, S.; Patil, S.; Baeshen, H.A.; Sarode, S.C.; Bhandi, S. Developments, application, and performance of artificial intelligence in dentistry—A systematic review. J. Dent. Sci. 2021, 16, 508–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, J.A.; Krois, J.; Schwendicke, F. Demystifying artificial intelligence and deep learning in dentistry. Braz. Oral Res. 2021, 35, e094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallineni, S.K.; Sethi, M.; Punugoti, D.; Kotha, S.B.; Alkhayal, Z.; Mubaraki, S.; Almotawah, F.N.; Kotha, S.L.; Sajja, R.; Nettam, V.; et al. Artificial Intelligence in Dentistry: A Descriptive Review. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiraiwa, T.; Ariji, Y.; Fukuda, M.; Kise, Y.; Nakata, K.; Katsumata, A.; Fujita, H.; Ariji, E. A deep-learning artificial intelligence system for assessment of root morphology of the mandibular first molar on panoramic radiography. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2019, 48, 20180218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgir, E.; Bayrakdar, İ.Ş.; Çelik, Ö.; Orhan, K.; Akkoca, F.; Sağlam, H.; Odabaş, A.; Aslan, A.F.; Ozcetin, C.; Kıllı, M.; et al. An artifıcial ıntelligence approach to automatic tooth detection and numbering in panoramic radiographs. BMC Med. Imaging 2021, 21, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kılıc, M.C.; Bayrakdar, I.S.; Çelik, Ö.; Bilgir, E.; Orhan, K.; Aydın, O.B.; Kaplan, F.A.; Sağlam, H.; Odabaş, A.; Aslan, A.F.; et al. Artificial intelligence system for automatic deciduous tooth detection and numbering in panoramic radiographs. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2021, 50, 20200172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.W.; Fan, J.; Zhao, F.B.; Ma, B.; Shen, X.Q.; Geng, Y.M. Diagnostic accuracy of artificial intelligence-assisted caries detection: A clinical evaluation. BMC Oral Health 2024, 24, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, J.; Jaber, M.; Rifai, I.; Mozdziak, P.; Kempisty, B.; Dyszkiewicz-Konwińska, M. Diagnostic Test Accuracy of Artificial Intelligence in Detecting Periapical Periodontitis on Two-Dimensional Radiographs: A Retrospective Study and Literature Review. Medicina 2023, 59, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rawi, N.; Sultan, A.; Rajai, B.; Shuaeeb, H.; Alnajjar, M.; Alketbi, M.; Mohammad, Y.; Shetty, S.R.; Mashrah, M.A. The Effectiveness of Artificial Intelligence in Detection of Oral Cancer. Int. Dent. J. 2022, 72, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurt-Bayrakdar, S.; Bayrakdar, İ.Ş.; Yavuz, M.B.; Sali, N.; Çelik, Ö.; Köse, O.; Uzun Saylan, B.C.; Kuleli, B.; Jagtap, R.; Orhan, K. Detection of periodontal bone loss patterns and furcation defects from panoramic radiographs using deep learning algorithm: A retrospective study. BMC Oral Health 2024, 24, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, R.S.S.; Kumar, H.S.K.; Sekhar, A.; Nadakkavukaran, D.; Feroz, S.M.A.; Gangadharappa, P. Evaluating the Role of AI in Predicting the Success of Dental Implants Based on Preoperative CBCT Images: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2024, 16 (Suppl. S1), S886–S888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgarba, B.M.; Fontenele, R.C.; Tarce, M.; Jacobs, R. Artificial intelligence serving pre-surgical digital implant planning: A scoping review. J. Dent. 2024, 143, 104862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vodanović, M.; Subašić, M.; Milošević, D.P.; Galić, I.; Brkić, H. Artificial intelligence in forensic medicine and forensic dentistry. J. Forensic Odontostomatol. 2023, 41, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thorat, V.; Rao, P.; Joshi, N.; Talreja, P.; Shetty, A.R. Role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Patient Education and Communication in Dentistry. Cureus 2024, 16, e59799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alowais, S.A.; Alghamdi, S.S.; Alsuhebany, N.; Alqahtani, T.; Alshaya, A.I.; Almohareb, S.N.; Aldairem, A.; Alrashed, M.; Bin Saleh, K.; Badreldin, H.A.; et al. Revolutionizing healthcare: The role of artificial intelligence in clinical practice. BMC Med. Educ. 2023, 23, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boven, G.C.; Raghoebar, G.M.; Vissink, A.; Meijer, H.J. Improving masticatory performance, bite force, nutritional state and patient’s satisfaction with implant overdentures: A systematic review of the literature. J. Oral Rehabil. 2015, 42, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehira, Y.; Arai, K.; Kanehira, T.; Nagahisa, K.; Baba, S. Oral health-related quality of life in patients with implant treatment. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2017, 9, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raikar, S.; Talukdar, P.; Kumari, S.; Panda, S.K.; Oommen, V.M.; Prasad, A. Factors Affecting the Survival Rate of Dental Implants: A Retrospective Study. J. Int. Soc. Prev. Community Dent. 2017, 7, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S. Efficacy of Various Implant Abutment Screw Access Channel Sealing Materials in Preventing Microleakage: A Systematic Review. J. Oral Implantol. 2022, 48, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, F.; Derks, J.; Monje, A.; Wang, H.L. Peri-implantitis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018, 45 (Suppl. S20), S246–S266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darby, I. Risk factors for periodontitis & peri-implantitis. Periodontology 2000 2022, 90, 9–12. [Google Scholar]
- Albrektsson, T.; Buser, D.; Chen, S.T.; Cochran, D.; DeBruyn, H.; Jemt, T.; Koka, S.; Nevins, M.; Sennerby, L.; Simion, M.; et al. Statements from the Estepona consensus meeting on peri-implantitis, February 2–4, 2012. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2012, 14, 781–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalago, H.R.; Schuldt Filho, G.; Rodrigues, M.A.; Renvert, S.; Bianchini, M.A. Risk indicators for Peri-implantitis. A cross-sectional study with 916 implants. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2017, 28, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albrektsson, T.; Canullo, L.; Cochran, D.; De Bruyn, H. “Peri-Implantitis”: A Complication of a Foreign Body or a Man-Made “Disease”. Facts and Fiction. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2016, 18, 840–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Larrivee, N.; Lee, A.; Bilaniuk, O.; Durand, R. Use of artificial intelligence in dentistry: Current clinical trends and research advances. J. Can. Dent. Assoc. 2021, 87, l7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Dental Association Council on Scientific Affairs. The use of dental radiographs: Update and recommendations. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2006, 137, 1304–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, M.; Gómez-Silva, M.J.; Vera, V.; López-González, C.I.; Aliaga, I.; Gascó, E.; Vera-González, V.; Pedrera-Canal, M.; Besada-Portas, E.; Pajares, G. Artificial Intelligence Techniques for Automatic Detection of Peri-implant Marginal Bone Remodeling in Intraoral Radiographs. J. Digit. Imaging 2023, 36, 2259–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-C.; Chen, M.-Y.; Chen, T.-Y.; Chan, M.-L.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Liu, Y.-L.; Lee, P.-T.; Lin, G.-J.; Li, T.-F.; Chen, C.-A.; et al. Improving Dental Implant Outcomes: CNN-Based System Accurately Measures Degree of Peri-Implantitis Damage on Periapical Film. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.-F.; Day, M.-Y.; Fang, C.-Y.; Nataraj, V.; Wen, S.-C.; Chang, W.-J.; Teng, N.-C. Establishing a novel deep learning model for detecting peri-implantitis. J. Dent. Sci. 2024, 19, 1165–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, S.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y. A pilot study of a deep learning approach to detect marginal bone loss around implants. BMC Oral Health 2022, 22, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, J.Y.; Yoon, H.I.; Yeo, I.S.; Huh, K.H.; Han, J.S. Peri-Implant Bone Loss Measurement Using a Region-Based Convolutional Neural Network on Dental Periapical Radiographs. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mameno, T.; Wada, M.; Nozaki, K.; Takahashi, T.; Tsujioka, Y.; Akema, S.; Hasegawa, D.; Ikebe, K. Predictive modeling for peri-implantitis by using machine learning techniques. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Shan, J.; Zhang, P.; Chen, X.; Jiang, H. Trabeculae microstructure parameters serve as effective predictors for marginal bone loss of dental implant in the mandible. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeflang, M.M.; Davenport, C.; Bossuyt, P.M. Chapter 5: Defining the review question. In Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Diagnostic Test Accuracy; Deeks, J.J., Bossuyt, P.M., Leeflang, M.M., Takwoingi, Y., Eds.; Version 2.0 (Updated July 2023); Cochrane: London, UK, 2023; Available online: https://training.cochrane.org/handbook-diagnostic-test-accuracy/current (accessed on 12 January 2025).
- Whiting, P.F.; Rutjes, A.W.; Westwood, M.E.; Mallett, S.; Deeks, J.J.; Reitsma, J.B.; Leeflang, M.M.; Sterne, J.A.; Bossuyt, P.M.; QUADAS-2 Group. QUADAS-2: A revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann. Intern. Med. 2011, 155, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiting, P.; Rutjes, A.W.; Reitsma, J.B.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Kleijnen, J. The development of QUADAS: A tool for the quality assessment of studies of diagnostic accuracy included in systematic reviews. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2003, 3, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guler Ayyildiz, B.; Karakis, R.; Terzioglu, B.; Ozdemir, D. Comparison of deep learning methods for the radiographic detection of patients with different periodontitis stages. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2024, 53, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krois, J.; Ekert, T.; Meinhold, L.; Golla, T.; Kharbot, B.; Wittemeier, A.; Dorfer, C.; Schwendicke, F. Deep Learning for the Radiographic Detection of Periodontal Bone Loss. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danks, R.P.; Bano, S.; Orishko, A.; Tan, H.J.; Moreno Sancho, F.; D’Aiuto, F.; Stoyanov, D. Automating Periodontal bone loss measurement via dental landmark localisation. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2021, 16, 1189–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, T.; Chen, L.; Sun, Q. Deep learning method to automatically diagnose periodontal bone loss and periodontitis stage in dental panoramic radiograph. J. Dent. 2024, 150, 105373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, G.; Awawdeh, M.; Farook, F.F.; Aljohani, M.; Aldhafiri, R.M.; Aldhoayan, M. Artificial intelligence (AI) diagnostic tools: Utilizing a convolutional neural network (CNN) to assess periodontal bone level radiographically-a retrospective study. BMC Oral Health 2022, 22, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.J.; Lee, S.J.; Yong, T.H.; Shin, N.Y.; Jang, B.G.; Kim, J.E.; Huh, K.H.; Lee, S.S.; Heo, M.S.; Choi, S.C.; et al. Deep Learning Hybrid Method to Automatically Diagnose Periodontal Bone Loss and Stage Periodontitis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, W.S.; Kim, S.; Yun, P.S.; Jang, H.S.; Seong, Y.W.; Yang, H.S.; Chang, J.S. Accurate detection for dental implant and peri-implant tissue by transfer learning of faster R-CNN: A diagnostic accuracy study. BMC Oral Health 2022, 22, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rekawek, P.; Herbst, E.A.; Suri, A.; Ford, B.P.; Rajapakse, C.S.; Panchal, N. Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence: A Web-Based Implant Failure and Peri-implantitis Prediction Model for Clinicians. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2023, 38, 576–582b. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, V.; Wilkins, R.C. A comprehensive review of the literature on the biological effects from dental x-ray exposures. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2019, 95, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourcade, A.; Khonsari, R.H. Deep learning in medical image analysis: A third eye for doctors. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 120, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yüksel, A.E.; Gültekin, S.; Simsar, E.; Özdemir, Ş.D.; Gündoğar, M.; Tokgöz, S.B.; Hamamcı, İ.E. Dental enumeration and multiple treatment detection on panoramic X-rays using deep learning. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granholm, A.; Alhazzani, W.; Møller, M.H. Use of the GRADE approach in systematic reviews and guidelines. Br. J. Anaesth. 2019, 123, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2017 Oral Disorders Collaborators; Bernabe, E.; Marcenes, W.; Hernandez, C.R.; Bailey, J.; Abreu, L.G.; Alipour, V.; Amini, S.; Arabloo, J.; Arefi, Z.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Levels and Trends in Burden of Oral Conditions from 1990 to 2017: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease 2017 Study. J. Dent. Res. 2020, 99, 362–373. [Google Scholar]

| Inclusion Criteria | Exclusion Criteria |
|---|---|
| Studies published in the English language | Studies published in languages other than English |
| Studies published from January 2000 to December 2024. | Studies published prior to January 2000 |
| Human clinical and in vitro studies | Studies conducted on animals |
| Studies evaluating the diagnostic accuracy of artificial intelligence models in detecting peri-implant bone loss in human X-ray images. | Studies evaluating the accuracy of AI in detecting bone loss around the tooth rather than around dental implants. |
| Studies utilizing AI for implant detection | |
| Studies employing AI in implant planning and assessing the prognosis of implant therapy | |
| Studies lacking statistical analysis | |
| Case reports, chapters in books, editorials, letters to the editor, dissertations, commentaries, opinions, reviews, unpublished studies, incomplete trials, and review articles. |
| Database | Combination of Search Terms and Strategy | Number of Titles |
|---|---|---|
| PubMed | (((“peri implantitis” [MeSH Terms] OR “dental implants” [MeSH Terms] OR “bone resorption” [MeSH Terms] OR “marginal bone loss” [All Fields] OR “peri implant bone levels” [All Fields] AND (“artificial intelligence” [MeSH Terms] OR “machine learning” [MeSH Terms] OR “convolutional neural network*” OR “deep learning” OR “Deep Neural Network*” OR “Transfer Learning” OR CNN AND (“Dental X-ray” [All Fields] OR radiography [MeSH Terms] OR “Image processing” [All Fields] OR “smart diagnosis” [All Fields] OR “keypoint detection” [All Fields] OR “Computer vision” [All Fields] OR “computer-aided diagnosis” [All Fields] OR “dental diagnostic imaging” [All Fields] OR “Panoramic image*” [All Fields] OR OPG [All Fields] OR “Periapical images” [All Fields] OR “dental Digital radiograph” [All Fields] AND (Accuracy [All Fields] OR Precision [All Fields] OR sensitivity [All Fields] OR specificity [All Fields] AND ((humans[Filter]) AND (2000/1/1:2024/12/31[pdat]) AND (english[Filter]))) Filters: English, Humans, from 1 January 2000–31 December 2024 | 18 |
| Cochrane | #1: MeSH descriptor: [Peri-Implantitis] explode all trees; #2: MeSH descriptor: [Dental Implants] explode all trees; #3: MeSH descriptor: [Bone Resorption] explode all tree; #4; (marginal bone loss):ti,ab,kw; #5: (peri implant bone levels):ti,ab,kw; #6: MeSH descriptor: [Artificial Intelligence] explode all trees; #7: MeSH descriptor: [Machine Learning] explode all trees; #8: (convolutional neural network):ti,ab,kw; #9: (deep learning): ti,ab,kw; #10: (Deep Neural Network): ti,ab,kw; #11: (Transfer Learning): ti,ab,kw; #12: (CNN): ti,ab,kw; #13: (Dental X-ray): ti,ab,kw; #14: MeSH descriptor: [Radiography] explode all trees; #15: (image processing):ti,ab,kw; #16: (smart diagnosis): ti,ab,kw; #17: (keypoint detection): ti,ab,kw; #18: (Computer vision): ti,ab,kw; #19: (computer aided diagnosis): ti,ab,kw; #20: (dental diagnostic imaging): ti,ab,kw; #21:(Panoramic image): ti,ab,kw; #22: (OPG): ti,ab,kw; #23: (Periapical images): ti,ab,kw; #24: (dental Digital radiograph): ti,ab,kw; #25: (accuracy): ti,ab,kw; #26: (Precision): ti,ab,kw; #27: (sensitivity): ti,ab,kw; #28: (specificity): ti,ab,kw; #29: #1 OR #2 OR #3 OR #4 OR #5; #30: #6 OR #7 OR #8 OR #9 OR #10 OR #11 OR #12; #31: #13 OR #14 OR #15 OR #16 OR #17 OR #18 OR #19 OR #20 OR #21 OR #22 OR #23 OR #24; #32: #25 OR #26 OR #27 OR #28; #33: #29 AND #30 AND #31 AND #32; [Custom year range: 2000–2024; Language: English] | 3 |
| Scopus | (“peri implantitis” OR “dental implants” OR “bone resorption” OR “marginal bone loss” OR “peri implant bone levels”) AND (“artificial intelligence” OR “machine learning” OR “convolutional neural network” OR “deep learning” OR “Deep Neural Network*” OR “Transfer Learning” OR CNN) AND (“Dental X-ray” OR radiography OR “Image processing” OR “smart diagnosis” OR “key point detection” OR “Computer vision” OR “computer-aided diagnosis” OR “dental diagnostic imaging” OR “Panoramic image” OR OPG OR “Periapical images” OR “dental Digital radiograph”) AND (Accuracy OR Precision OR sensitivity OR specificity) AND PUBYEAR > 2000 AND PUBYEAR < 2024 AND (LIMIT-TO (SUBJAREA, “DENT”)) AND (LIMIT-TO (DOCTYPE, “ar”)) AND (LIMIT-TO (LANGUAGE, “English”)) AND (LIMIT-TO (SRCTYPE, “j”)) | 62 |
| Web of Science (core Collection) | #1 (TS = (“peri implantitis” OR “dental implants” OR “bone resorption” OR “marginal bone loss” OR “peri implant bone levels”)) AND #2 TS = (“artificial intelligence” OR “machine learning” OR “convolutional neural network” OR “deep learning” OR “Deep Neural Network*” OR “Transfer Learning” OR CNN)) AND #3 TS = (“Dental X-ray” OR radiography OR “Image processing” OR “smart diagnosis” OR “keypoint detection” OR “Computer vision” OR “computer-aided diagnosis” OR “dental diagnostic imaging” OR “Panoramic image” OR OPG OR “Periapical images” OR “dental Digital radiograph”)) AND #4 TS = (Accuracy OR Precision OR sensitivity OR specificity) #4 AND #3 AND #2 AND #1 Indexes = SCI-EXPANDED, SSCI, A&HCI, CPCI-S, CPCI-SSH, ESCI, CCR-EXPANDED, Timespan: 2000-01-01 to 2024-07-31 and English (Languages) | 18 |
| Author, Year, and Country | Algorithm Network Architecture and Name | Architecture Depth (Number of Layers), Number of Training Epochs, and Learning Rate | Modality | Patient Data Collection/X-Ray Collection Duration | Number of X-Rays/Areas Evaluated (N) Test Group and Training/Validation Number and Ratio | Annotation Performed By | Comparator |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vera et al., 2023, Spain [37] | Two ML models used:
| NM | Intraoral radiographs [IOPAR (85%) and bitewing (15%)] | NM | 2920 radiographic images (lower jaw) Training: 1460 Test: 1394 | Specialist Dentist | EORS |
| Chen et al., 2023, Taiwan [38] | Two ML models used:
|
| IOPAR | NM | 406 radiographic images Training: 80% Testing: 20% | Three physicians with at least 5 years of experience | EORS |
| Lee et al., 2024, Taiwan [39] | YOLOv7 deep learning network: DL object detector with high speed and accuracy compared to previous versions. |
| IOPAR | November 2016 to June 2021 | 800 peri apical images Training: 600 Validation & Testing: 200 | Specialist Dentist | EORS |
| Liu et al., 2022, China [40] | Inception Resnet v2 (Atrous version) (Region-based convolutional neural networks: R-CNNs): object detector |
| IOPAR | NM | 1670 PA images Training: 1370 Validation: 150 Test: 150 | One experienced dentist (>5 years of clinical experience and one oral and maxillofacial radiologist) | 2 Dentist (Dentist 1: resident dentist, Dentist 2: MD dentist with 2 years of clinical experience, Reference standard: Senior dentist (with more than 5 years of clinical experience) |
| Cha et al., 2021, Korea [41] | 2 ML models used:
|
| IOPAR | December 2018 to June 2020 | 708 PA images (upper: 366; Lower: 342) Training: 508 (upper: 266; Lower: 242) Validation: 100 (upper: 50; Lower: 50) Test: 100 (upper: 50; Lower: 50) | 2 Dentist (general practitioner and maxillofacial radiologist) | 1 Dentist |
| Mameno et al., 2021, Japan [42] | Three ML models:
| NM | IOPAR | November 1996 to December 2012 | 254 radiographic images Training: 70% Testing: 30% | One Specialist Dentist | EORS |
| Zhang et al., 2020, China [43] | Four ML models based on the R Programming Language were used:
| NM | CBCT | January 2016 to March 2019 | 81 radiographic images Training: 70% Testing: 30% | Two Specialist Dentist | EORS |
| Author, Year, and Country | Evaluation of peri-implant bone loss/resorption | Results (+)effective, (−)non effective (N) neutral | Outcome | Inference/ Author’s suggestions/Conclusions | |||
| Vera et al., 2023, Spain [37] | Error: Mean: 2.63 pixels Standard deviation: 1.28 pixels Average p value: 0.0213 (p < 0.05 is significant) | (+)effective | As the average p-value is less than 0.05, the test is statistically significant. From a clinical point of view: AI is able to accurately detect bone loss due to peri-implantitis. | AI methods can detect bone loss in intraoral radiographs and can assist dental specialists in diagnosing peri-implantitis. | |||
| Chen et al., 2023, Taiwan [38] | Accuracy rate of AlexNet damage detection model: 90.45% | (+)effective | CNN has the ability to determine bone loss around implants with high accuracy. | The CNN model has the potential to improve patient outcomes. | |||
| Lee et al., 2024, Taiwan [39] | Values for recognizing peri-implantitis: Accuracy: Overall: 94.74%; Bone loss: 96.18%; Non-bone loss: 93.42% Precision: Overall: 100%; Bone loss: 100%; Non-bone loss: 100% Sensitivity: Overall: 94.44%; Bone loss: 95.83%; Non-bone loss: 93.06% Specificity: Overall: 100%; Bone loss: 100%; Non-bone loss: 100% F1-Score: Overall: 97.10%; Bone loss: 97.86%; Non-bone loss: 96.43% | (+)effective | CNN model can facilitate the detection of marginal bone loss around dental implant. | AI can help dentists effectively and accurately monitor the condition of patients | |||
| Liu et al., 2022, China [40] | Bone loss around implants: Sensitivity: AI: 67%; Dentist 1: 93%; Dentist 2: 62% Specificity: AI: 87%; Dentist 1: 64%; Dentist 2: 77% Mistake diagnostic rate: AI: 13%; Dentist 1: 36%; Dentist 2: 23% Omission diagnostic rate: AI: 33%; Dentist 1: 7%; Dentist 2: 38% Positive predictive value: AI: 81%; Dentist 1: 69%; Dentist 2: 70% Inter observer agreement (k): AI vs. RS: 0.568 (moderate) Dentist 1 vs. RS: 0.544 (moderate) Dentist 2 vs. RS: 0.383 (fair) | (+)effective | CNN model performance is similar to the resident dentist, but less well than the experienced dentist. | CNN model may facilitate the detection of marginal bone loss around implants. | |||
| Cha et al., 2021, Korea [41] | Mean OKS (object keypoint similarity) CNN: Upper: 0.8748; Lower: 0.9029; Total dataset: 0.8885 Dentist: 0.9012 | (+)effective | CNN’s ability to determine the extent of bone loss on IOPA for periimplantitis diagnosis is comparable to dentist | CNN can be used to assist the dentist in diagnosing and categorizing peri-implantitis | |||
| Mameno et al., 2021, Japan [42] | AUC: SVM: 0.64 +_ 0.05; RF: 0.71+_ 0.04; LR: 0.63 +_ 0.05 Accuracy: SVM: 0.63 #; RF: 0.70; LR: 0.62 # Precision: SVM: 0.64 #; RF: 0.72; LR: 0.63 # Recall: SVM: 0.62 #; RF: 0.66; LR:0.61 # f1 score: SVM: 0.618 #; RF: 0.69; LR: 0.612 # | (+)effective | MBL prediction performance: RF > SVM > LR | ML methods have higher accuracy in predicting the onset of peri-implantitis. | |||
| Zhang et al., 2020, China [43] | AUC: SVM: 0.967; ANN: 0.928; LR: 0.906; RF: 0.842 Sensitivity: SVM: 91.67%; ANN: 91.67%; LR: 91.67%; RF: 75% Specificity: SVM: 100%; ANN: 93.33%; LR: 93.33%; RF: 86.67% | (+)effective | MBL prediction performance: SVM > ANN > LR > RF | ML algorithms that utilize the morphological variation in trabecular bone can be used to successfully predict MBL. ML models perform better when compared to the single predictor in predicting the MBL of mandibular implant | |||
| Outcome | AI Application in Detecting Peri-Implant Bone Loss in Peri-Apical Images [37,38,39,40,41,42] | AI Application in Detecting Peri-Implant Bone Loss in CBCT Images [43] |
|---|---|---|
| Inconsistency | Not present | Not present |
| Indirectness | Not present | Not present |
| Imprecision | Not present | Not present |
| Risk of Bias | Present | Not present |
| Publication Bias | Not present | Not present |
| Strength of Evidence |  |  |
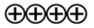 —High evidence
—High evidence 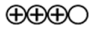 —Moderate evidence.
—Moderate evidence.Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mugri, M.H. Accuracy of Artificial Intelligence Models in Detecting Peri-Implant Bone Loss: A Systematic Review. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 655. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15060655
Mugri MH. Accuracy of Artificial Intelligence Models in Detecting Peri-Implant Bone Loss: A Systematic Review. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(6):655. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15060655
Chicago/Turabian StyleMugri, Maryam H. 2025. "Accuracy of Artificial Intelligence Models in Detecting Peri-Implant Bone Loss: A Systematic Review" Diagnostics 15, no. 6: 655. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15060655
APA StyleMugri, M. H. (2025). Accuracy of Artificial Intelligence Models in Detecting Peri-Implant Bone Loss: A Systematic Review. Diagnostics, 15(6), 655. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15060655





