Superiority of 3D-DIR over 3D-FLAIR in the Detection of Cortical Lesions and Correlation with Disability in Multiple Sclerosis: A Multicenter Study
Abstract
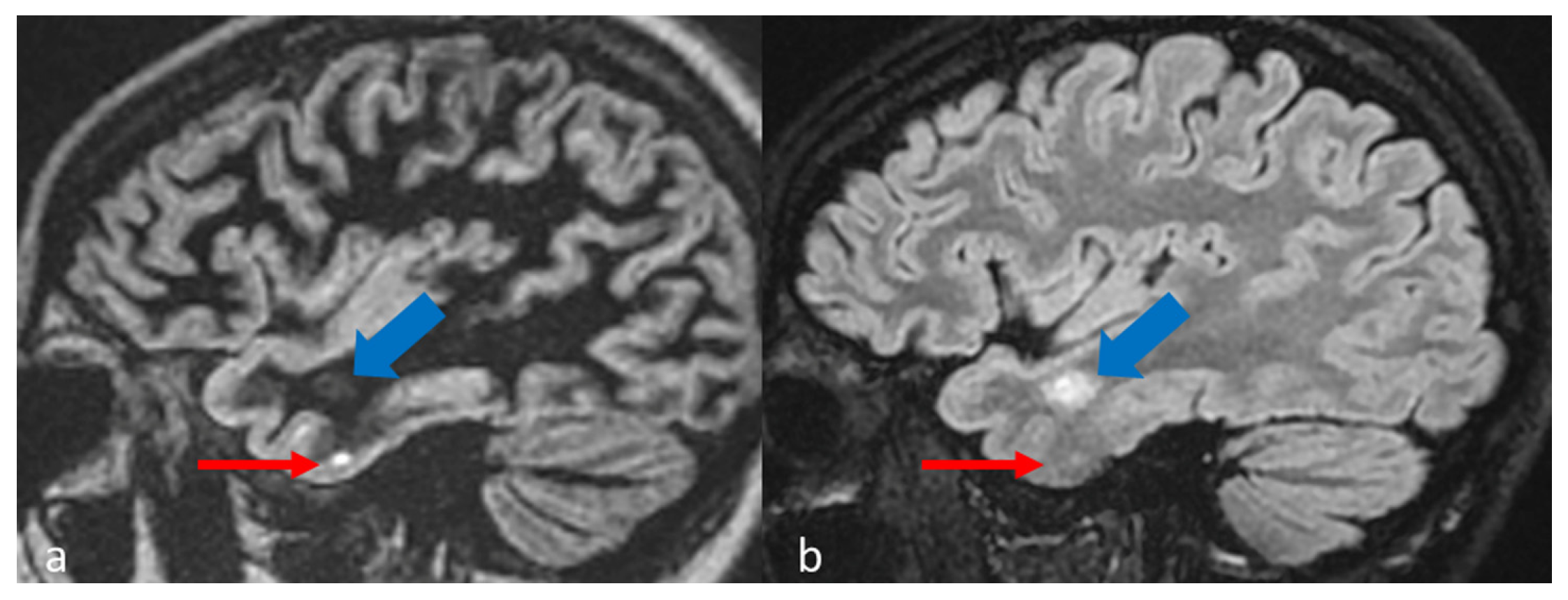
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Population
2.2. MR Imaging Acquisition
- (a)
- Conventional imaging: axial T1-weighted, obtained pre- and post-intravenous injection of 0.1 mmol/kg of gadolinium-based contrast agents, axial T2WI and axial DWI.
- (b)
- Sagittal 3D-DIR and sagittal 3D-FLAIR, obtained with identical anatomic position in each scanner and patient.
- On GE scanner: acquisition plane 3D Sagittal, TR 6800 ms, TE 112 ms, TI 1 2650 ms, TI 2 445 ms, Refocusing Flip Angle (variable), acquisition matrix 256 × 256, reconstruction matrix 256 × 256, FOV 225, slice number 96, acquisition slice thickness 1.8, reconstruction slice thickness 1 mm, gap 0, NEX 1, parallel imaging: Autocalibrating Reconstruction for Cartesian Imaging (ARC) with acceleration factor 2; acquisition time 6 min 11 s.
- On Siemens scanner: acquisition plane 3D Sagittal, TR 7500 ms, TE 310 ms, TI 1 3000 ms, TI 2 450 ms, Refocusing Flip Angle (variable), acquisition matrix 192 × 192, reconstruction matrix 192 × 192, FOV 280, slice number 128, acquisition slice thickness 1.5 mm, reconstruction slice thickness 1 mm, gap 0, NSA 1, parallel imaging: integrated Parallel Acquisition Techniques (iPAT) Mode GeneRalized Autocalibrating Partial Parallel Acquisition (GRAPPA) with acceleration factor 2; acquisition time 5 min 39 s.
- On GE scanner: acquisition plane 3D Sagittal, TR 6000 ms, TE 105, TI 1908 ms, Refocusing Flip Angle (variable), acquisition matrix 256 × 256, reconstruction matrix ZIP 512, FOV 256, slice number 96, acquisition slice thickness 1.8 mm, reconstruction slice thickness 1 mm, gap 0, NEX 1, parallel imaging: ARC with acceleration factor 2; acquisition time 7 min 09 s.
- On Siemens scanner: acquisition plane 3D Sagittal, TR 10,000 ms, TE 372 ms, TI 2500, Refocusing Flip Angle (variable), acquisition matrix 179 × 256, reconstruction matrix 256 × 256, FOV 256, slice number 144, acquisition slice thickness 1 mm, reconstruction slice thickness 1 mm, gap 0, NSA 1, parallel imaging: iPAT Mode GRAPPA with acceleration factor 4; acquisition time 6 min 10 s.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
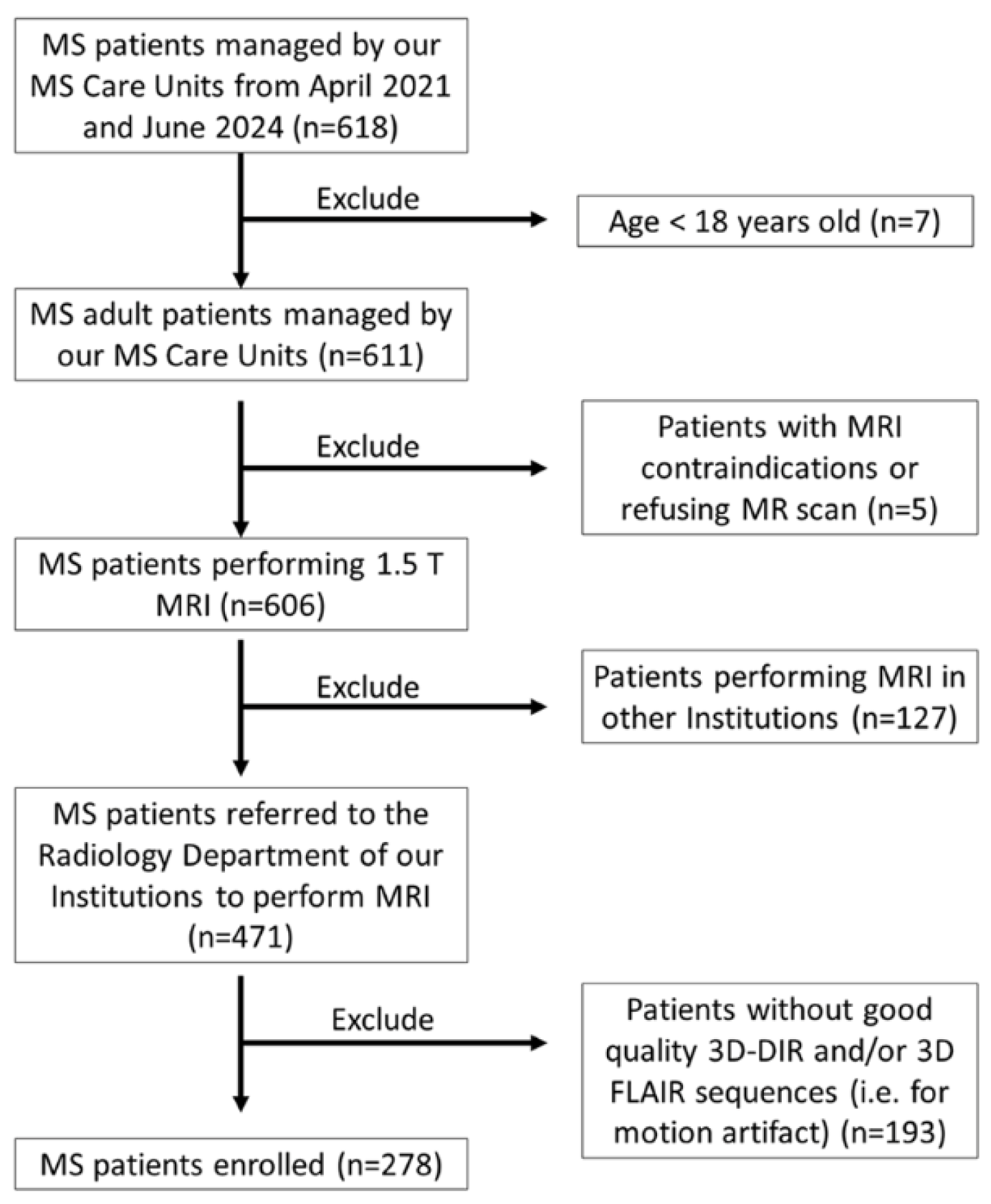
3.1. Final Study Population
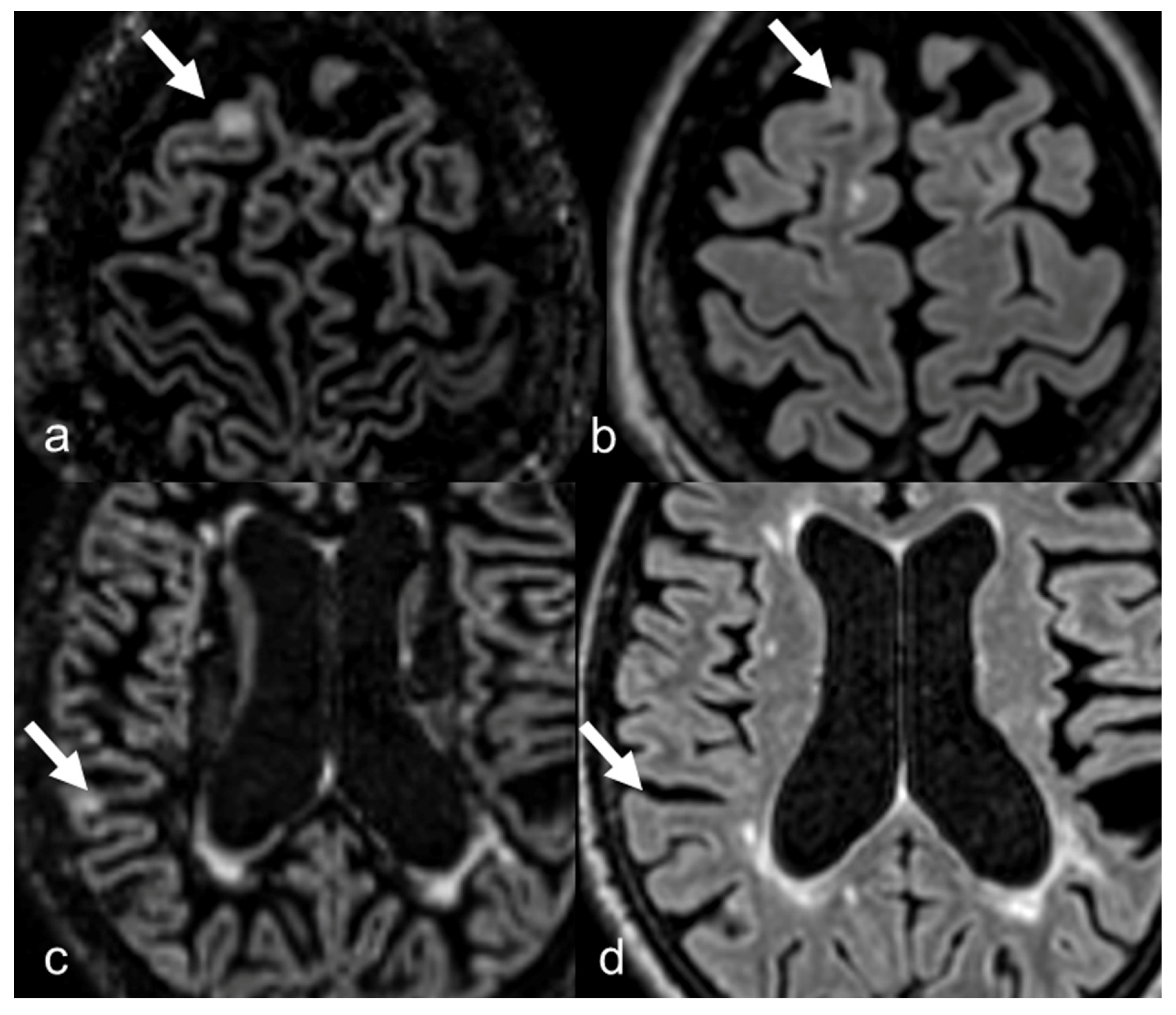
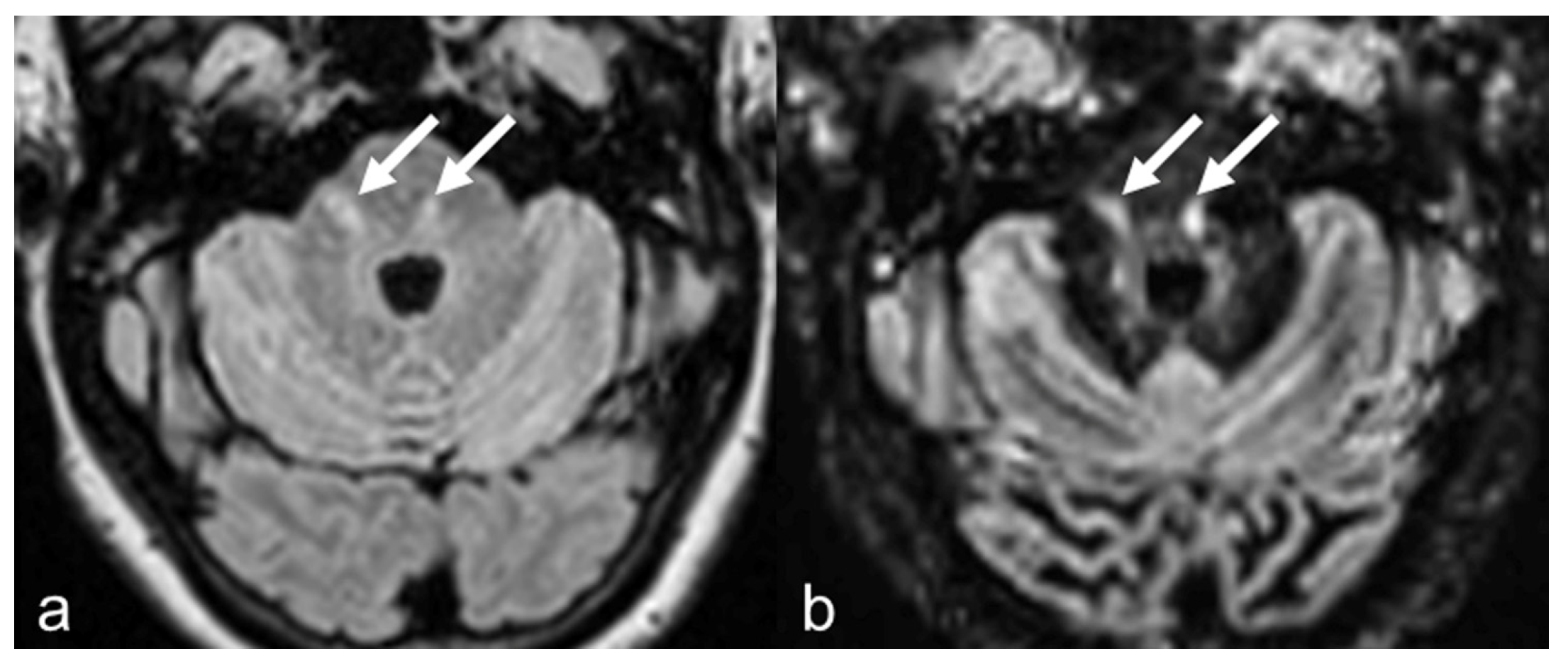
3.2. Lesion Count
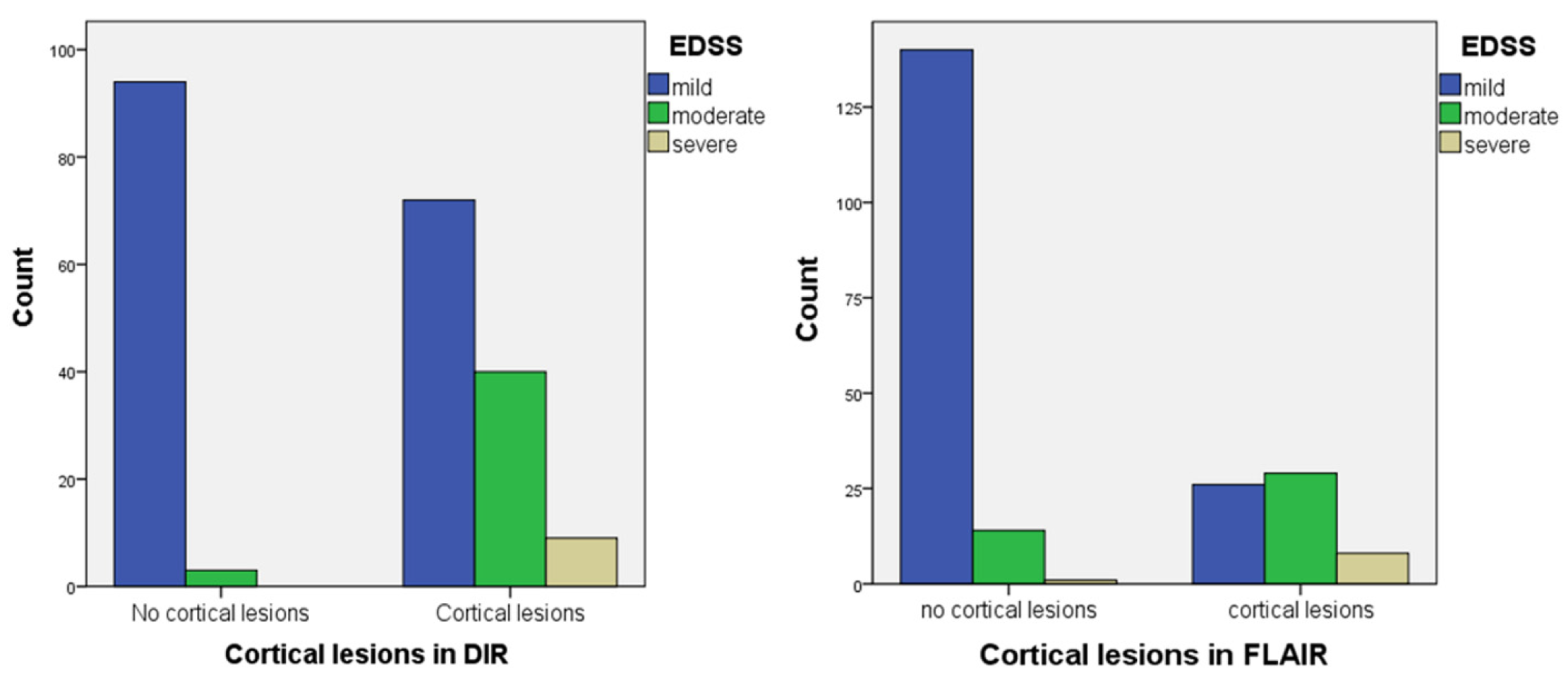
3.3. Correlation with Clinical Score
4. Discussion
| Practical Recommendation |
| In MS protocol, attention has to be paid to perform DIR before contrast-administration, as post-contrast DIR may suppress active subcortical lesions. |
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Compston, A.; Coles, A. Multiple sclerosis. Lancet 2008, 372, 1502–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reich, D.S.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; Calabresi, P.A. Multiple Sclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geurts, J.J.; Barkhof, F. Grey matter pathology in multiple sclerosis. Lancet Neurol. 2008, 7, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herranz, E.; Giannì, C.; Louapre, C.; Treaba, C.A.; Govindarajan, S.T.; Ouellette, R.; Loggia, M.L.; Sloane, J.A.; Madigan, N.; Izquierdo-Garcia, D.; et al. Neuroinflammatory component of gray matter pathology in multiple sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2016, 80, 776–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, M.; Agosta, F.; Rinaldi, F.; Mattisi, I.; Grossi, P.; Favaretto, A.; Atzori, M.; Bernardi, V.; Barachino, L.; Rinaldi, L.; et al. Cortical lesions and atrophy associated with cognitive impairment in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Arch. Neurol. 2009, 66, 1144–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippi, M.; Preziosa, P.; Banwell, B.L.; Barkhof, F.; Ciccarelli, O.; De Stefano, N.; Geurts, J.J.G.; Paul, F.; Reich, D.S.; Toosy, A.T.; et al. Assessment of lesions on magnetic resonance imaging in multiple sclerosis: Practical guidelines. Brain 2019, 142, 1858–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnekeidy, A.M.; Kamal, M.A.; Elfatatry, A.M.; Elskeikh, M.L. Added value of double inversion recovery magnetic resonance sequence in detection of cortical and white matter brain lesions in multiple sclerosis. Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med. 2014, 45, 1193–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treaba, C.A.; Granberg, T.E.; Sormani, M.P.; Herranz, E.; Ouellette, R.A.; Louapre, C.; Sloane, J.A.; Kinkel, R.P.; Mainero, C. Longitudinal Characterization of Cortical Lesion Development and Evolution in Multiple Sclerosis with 7.0-T MRI. Radiology 2019, 291, 740–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, M.; Filippi, M.; Gallo, P. Cortical lesions in multiple sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2010, 6, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, A.J.; Banwell, B.L.; Barkhof, F.; Carroll, W.M.; Coetzee, T.; Comi, G.; Correale, J.; Fazekas, F.; Filippi, M.; Freedman, M.S.; et al. Diagnosis of multiple sclerosis: 2017 revisions of the McDonald criteria. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abidi, Z.; Faeghi, F.; Mardanshahi, Z.; Mortazavi, H. Assessment of the diagnostic accuracy of double inversion recovery sequence compared with FLAIR and T2W_TSE in detection of cerebral multiple sclerosis lesions. Electron. Physician 2017, 9, 4162–4170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seewann, A.; Vrenken, H.; Kooi, E.J.; van der Valk, P.; Knol, D.L.; Polman, C.H.; Pouwels, P.J.; Barkhof, F.; Geurts, J.J. Imaging the tip of the iceberg: Visualization of cortical lesions in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. 2011, 17, 1202–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vural, G.; Keklikoğlu, H.D.; Temel, Ş.; Deniz, O.; Ercan, K. Comparison of double inversion recovery and conventional magnetic resonance brain imaging in patients with multiple sclerosis and relations with disease disability. Neuroradiol. J. 2013, 26, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouman, P.M.; Strijbis, V.I.; Jonkman, L.E.; Hulst, H.E.; Geurts, J.J.; Steenwijk, M.D. Artificial double inversion recovery images for (juxta)cortical lesion visualization in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. 2022, 28, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redpath, T.W.; Smith, F.W. Technical note: Use of a double inversion recovery pulse sequence to image selectively grey or white brain matter. Br. J. Radiol. 1994, 67, 1258–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedell, B.J.; Narayana, P.A. Implementation and evaluation of a new pulse sequence for rapid acquisition of double inversion recovery images for simultaneous suppression of white matter and CSF. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 1998, 8, 544–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, A.S.; Khater, N.; Barakat, M.M.K. Diagnostic utility of 3D DIR MRI in the estimation of MS lesions overall load with special emphasis on cortical subtypes. Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med. 2022, 53, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolber, P.; Montag, S.; Fleischer, V.; Luessi, F.; Wilting, J.; Gawehn, J.; Gröger, A.; Zipp, F. Identification of cortical lesions using DIR and FLAIR in early stages of multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. 2015, 262, 1473–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabrese, M.; De Stefano, N.; Atzori, M.; Bernardi, V.; Mattisi, I.; Barachino, L.; Morra, A.; Rinaldi, L.; Romualdi, C.; Perini, P.; et al. Detection of cortical inflammatory lesions by double inversion recovery magnetic resonance imaging in patients with multiple sclerosis. Arch. Neurol. 2007, 64, 1416–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, F.; Poonawalla, A.H.; Hou, P.; Huang, F.; Wolinsky, J.; Narayana, P. Improved identification of intracortical lesions in multiple sclerosis with phase-sensitive inversion recovery in combination with fast double inversion recovery MR imaging. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2007, 28, 1645–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattjes, M.P.; Lutterbey, G.G.; Gieseke, J.; Träber, F.; Klotz, L.; Schmidt, S.; Schild, H.H. Double inversion recovery brain imaging at 3T: Diagnostic value in the detection of multiple sclerosis lesions. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2007, 28, 54–59. [Google Scholar]
- Hamed, W.; Fathi, W.; Mahmoud, W.; Elhawary, G. Diagnostic accuracy of double inversion recovery in delineation of multiple sclerosis lesions and its clinical correlation with expanded disability scoring system. Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med. 2019, 50, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattjes, M.P.; Ciccarelli, O.; Reich, D.S.; Banwell, B.; de Stefano, N.; Enzinger, C.; Fazekas, F.; Filippi, M.; Frederiksen, J.; Gasperini, C.; et al. 2021 MAGNIMS-CMSC-NAIMS consensus recommendations on the use of MRI in patients with multiple sclerosis. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 653–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, F.; Poonawalla, A.; Hou, P.; Wolinsky, J.S.; Narayana, P.A. 3D MPRAGE improves classification of cortical lesions in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. 2008, 14, 1214–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, F.; Poonawalla, A.; Datta, S.; Wolinsky, J.; Narayana, P. Is 3D MPRAGE better than the combination DIR/PSIR for cortical lesion detection at 3T MRI? Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2014, 3, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favaretto, A.; Poggiali, D.; Lazzarotto, A.; Rolma, G.; Causin, F.; Gallo, P. The Parallel Analysis of Phase Sensitive Inversion Recovery (PSIR) and Double Inversion Recovery (DIR) Images Significantly Improves the Detection of Cortical Lesions in Multiple Sclerosis (MS) since Clinical Onset. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forslin, Y.; Bergendal, Å.; Hashim, F.; Martola, J.; Shams, S.; Wiberg, M.K.; Fredrikson, S.; Granberg, T. Detection of Leukocortical Lesions in Multiple Sclerosis and Their Association with Physical and Cognitive Impairment: A Comparison of Conventional and Synthetic Phase-Sensitive Inversion Recovery MRI. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2018, 39, 1995–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkholy, S.F.; Sabet, M.A.; Mohammad, M.E.; Edward, R.; Asaad, I. Comparative study between double inversion recovery (DIR) and fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) MRI sequences for detection of cerebral lesions in multiple sclerosis. Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med. 2020, 51, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertan, G.; Ozge, A.; Ulus, S.; Metin, B. Efficiency of double inversion recovery (DIR) sequence in the evaluation of supratentorial cortical lesions in multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroquantol. 2018, 16, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearney, H.; Altmann, D.R.; Samson, R.S.; Yiannakas, M.C.; Wheeler-Kingshott, C.A.; Ciccarelli, O.; Miller, D.H. Cervical cord lesion load is associated with disability independently from atrophy in MS. Neurology 2015, 84, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauerer, M.; McGinnis, J.; Bussas, M.; El Husseini, M.; Pongratz, V.; Engl, C.; Wuschek, A.; Berthele, A.; Riederer, I.; Kirschke, J.S.; et al. Prognostic value of spinal cord lesion measures in early relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2024, 95, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichinger, P.; Kirschke, J.S.; Hoshi, M.M.; Zimmer, C.; Mühlau, M.; Riederer, I. Pre- and Postcontrast 3D Double Inversion Recovery Sequence in Multiple Sclerosis: A Simple and Effective MR Imaging Protocol. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2017, 38, 1941–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lespagnol, M.; Massire, A.; Megdiche, I.; Lespagnol, F.; Brugières, P.; Créange, A.; Stemmer, A.; Bapst, B. Improved detection of juxtacortical lesions using highly accelerated double inversion-recovery MRI in patients with multiple sclerosis. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2023, 104, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichinger, P.; Hock, A.; Schön, S.; Preibisch, C.; Kirschke, J.S.; Mühlau, M.; Zimmer, C.; Wiestler, B. Acceleration of Double Inversion Recovery Sequences in Multiple Sclerosis With Compressed Sensing. Investig. Radiol. 2019, 54, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonacchi, R.; Filippi, M.; Rocca, M.A. Role of artificial intelligence in MS clinical practice. Neuroimage Clin. 2022, 35, 103065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finck, T.; Li, H.; Grundl, L.; Eichinger, P.; Bussas, M.; Mühlau, M.; Menze, B.; Wiestler, B. Deep-learning generated synthetic double inversion recovery images improve multiple sclerosis lesion detection. Investig. Radiol. 2020, 55, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Poirion, E.; Bodini, B.; Durrleman, S.; Colliot, O.; Stankoff, B.; Ayache, N. Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery MRI synthesis from multisequence MRI using three-dimensional fully convolutional networks for multiple sclerosis. J. Med. Imaging 2019, 6, 014005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouman, P.M.; Noteboom, S.; Nobrega Santos, F.A.; Beck, E.S.; Bliault, G.; Castellaro, M.; Calabrese, M.; Chard, D.T.; Eichinger, P.; Filippi, M.; et al. Multicenter Evaluation of AI-generated DIR and PSIR for Cortical and Juxtacortical Multiple Sclerosis Lesion Detection. Radiology 2023, 307, e221425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Lorenzo, D.; Francis, S.; Narayanan, S.; Arnold, D.L.; Collins, D.L. Review of automatic segmentation methods of multiple sclerosis white matter lesions on conventional magnetic resonance imaging. Med. Image Anal. 2013, 17, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, H.M.R.; Luo, S.; Ramadan, S.; Lechner-Scott, J. The emerging role of artificial intelligence in multiple sclerosis imaging. Mult. Scler. 2020, 28, 849–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danelakis, A.; Theoharis, T.; Verganelakis, D.A. Survey of automated multiple sclerosis lesion segmentation techniques on magnetic resonance imaging. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2018, 70, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Repetition Time (ms) | 7500 | 6800 | 10,000 | 6000 |
| Echo Time (ms) | 310 | 112 | 372 | 105 |
| Inversion Time 1/2 (ms) | 3000/450 | 2650/445 | 2500 | 1908 |
| Flip Angle | Variable | Variable | Variable | Variable |
| Acquisition Matrix | 192 × 192 | 256 × 256 | 179 × 256 | 256 × 256 |
| Reconstruction Matrix | 192 × 192 | 256 × 256 | 256 × 256 | ZIP 512 |
| FOV (mm) | 280 | 225 | 256 | 256 |
| Slice Number | 128 | 96 | 144 | 96 |
| Acquisition Slice Thickness (mm) | 1.5 | 1.8 | 1 | 1.8 |
| Reconstruction Slice Thickness (mm) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Gap | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Number of Signals Averaged | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Parallel Imaging | GRAPPA (iPAT: 2) | ARC | GRAPPA (iPAT: 4) | ARC |
| Acquisition Time | 5 min 39 s | 6 min 11 s | 6 min 10 s | 7 min 9 s |
| Parameters | 3D DIR Siemens | 3D DIR GE | 3D FLAIR Siemens | 3D FLAIR GE |
| Number of Patients | 278 |
| Age (years) 1 | 47.01 ± 12.668 (18–75) |
| Gender 2 | |
| Female | 201 (72.3%) |
| Male | 77 (27.7%) |
| EDSS 1 | 1.18 ± 1.687 (0–8) |
| Region | FLAIR | DIR | Z | p Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Mean | SD | No. | Mean | SD | |||
| Overall burden | 6484 | 23.32 | 15.200 | 6601 | 23.74 | 16.503 | −4089 b | <0.001 * |
| Infratentorial | 543 | 1.95 | 2.192 | 546 | 1.96 | 2.198 | −0.056 c | 0.955 |
| Periventricular WM | 2600 | 9.35 | 6.196 | 2610 | 9.39 | 6.329 | −1.772 c | 0.076 |
| Juxtacortical | 586 | 2.11 | 2.472 | 613 | 2.21 | 2.635 | −1.599 b | 0.110 |
| Subcortical WM | 2596 | 9.34 | 8.633 | 2485 | 8.94 | 8.415 | –5.814 c | <0.001 * |
| Cortical | 144 | 0.52 | 1.029 | 435 | 1.56 | 2.767 | –9.502 b | <0.001 * |
| EDSS | Cortical Lesion n (%) | No Cortical Lesion n (%) | χ2 | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DIR | ||||
| Mild | 90 (59.60%) | 123 (96.85%) | 41.615 | <0.001 |
| Moderate | 50 (33.10%) | 4 (3.15%) | ||
| Severe | 11 (7.30%) | 0 (0.0%) | ||
| FLAIR | ||||
| Mild | 33 (41.25%) | 179 (90.40%) | 61.006 | <0.001 |
| Moderate | 37 (46.25%) | 18 (9.10%) | ||
| Severe | 10 (12.50%) | 1 (0.50%) |
| MS Plaques | EDSS Score | |
|---|---|---|
| Correlation coefficient 1 | p value (two-tailed) | |
| Cortical lesions in 3D-FLAIR | 0.662 ** | 0.001 |
| Cortical lesions in 3D-DIR | 0.874 ** | 0.000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grazzini, I.; Del Roscio, D.; Cirinei, M.; Calchetti, B.; Grammatico, M.; Spossati, G.; Malatesti, L.; De Stefano, T.; Cuneo, A.; Leonini, S.; et al. Superiority of 3D-DIR over 3D-FLAIR in the Detection of Cortical Lesions and Correlation with Disability in Multiple Sclerosis: A Multicenter Study. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 3103. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15243103
Grazzini I, Del Roscio D, Cirinei M, Calchetti B, Grammatico M, Spossati G, Malatesti L, De Stefano T, Cuneo A, Leonini S, et al. Superiority of 3D-DIR over 3D-FLAIR in the Detection of Cortical Lesions and Correlation with Disability in Multiple Sclerosis: A Multicenter Study. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(24):3103. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15243103
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrazzini, Irene, Davide Del Roscio, Marco Cirinei, Benedetta Calchetti, Matteo Grammatico, Giulia Spossati, Lorenzo Malatesti, Teresa De Stefano, Andrea Cuneo, Sara Leonini, and et al. 2025. "Superiority of 3D-DIR over 3D-FLAIR in the Detection of Cortical Lesions and Correlation with Disability in Multiple Sclerosis: A Multicenter Study" Diagnostics 15, no. 24: 3103. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15243103
APA StyleGrazzini, I., Del Roscio, D., Cirinei, M., Calchetti, B., Grammatico, M., Spossati, G., Malatesti, L., De Stefano, T., Cuneo, A., Leonini, S., Piane, E., & Testaverde, L. (2025). Superiority of 3D-DIR over 3D-FLAIR in the Detection of Cortical Lesions and Correlation with Disability in Multiple Sclerosis: A Multicenter Study. Diagnostics, 15(24), 3103. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15243103








