Codify and Localize Lesions on a Coronary Acoustic Map: Scientific Rationale, Trial Design and Artificial Intelligence Algorithm Protocols
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Investigations for a Scientific Basis
2.1. Classifications
2.2. Mechanical Stress Due to Repetitive Bending at a Hinge Location
- Mechanics Perspective:
- Hinge Movement in Coronary Arteries:
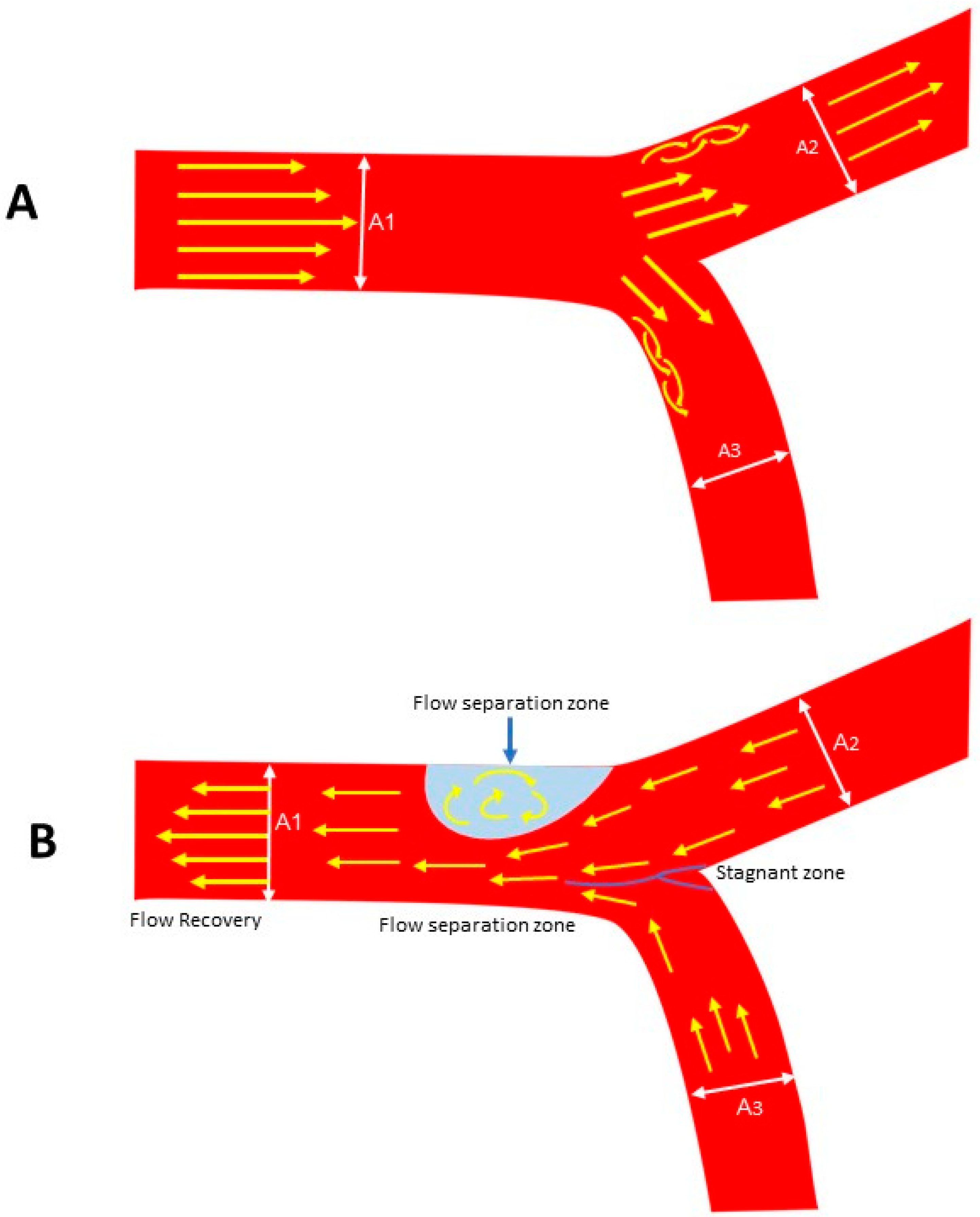
2.3. Local Intimal Ischemia Due to Thick Boundary Layer
- Fluid Mechanics Perspective:
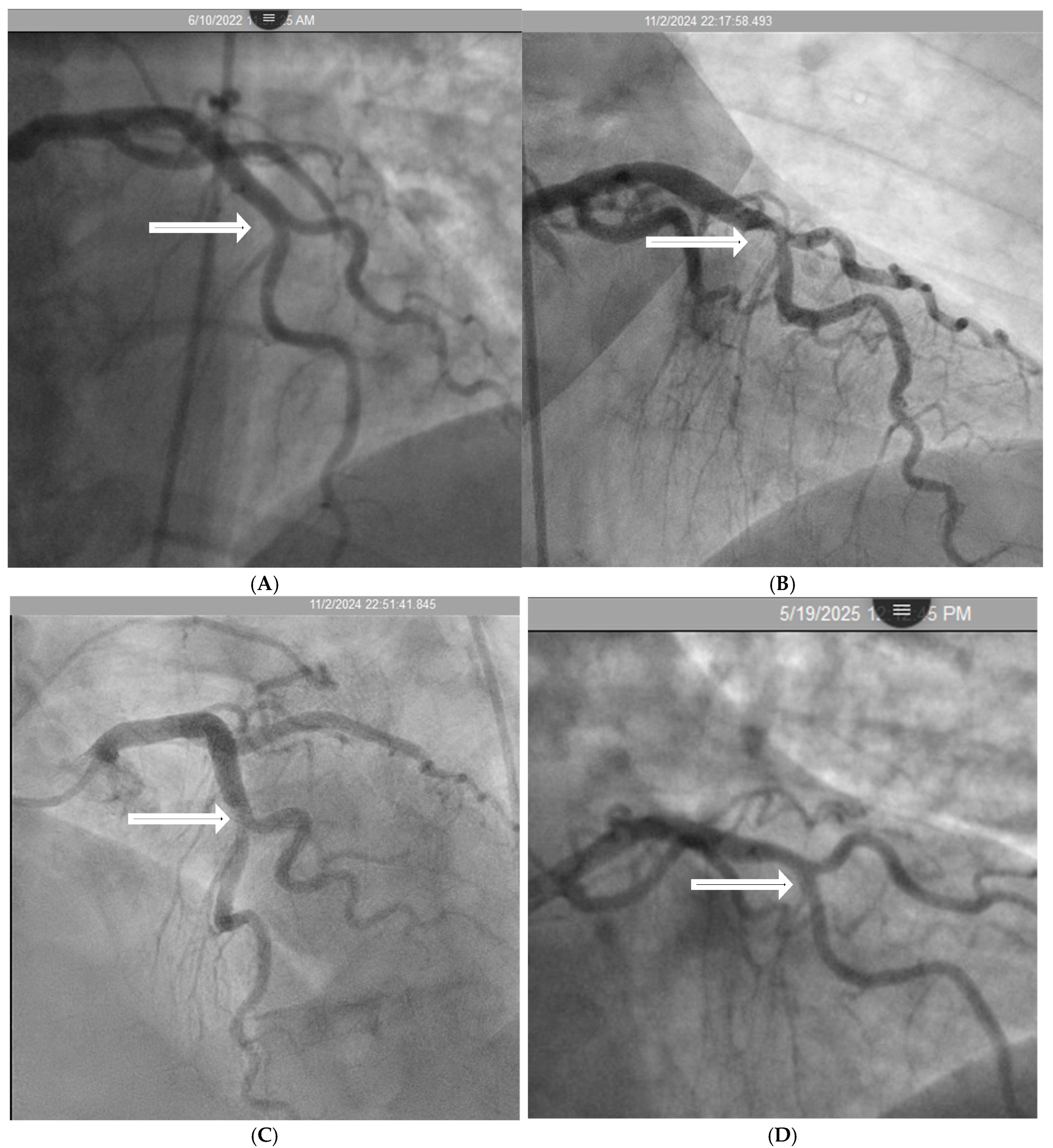
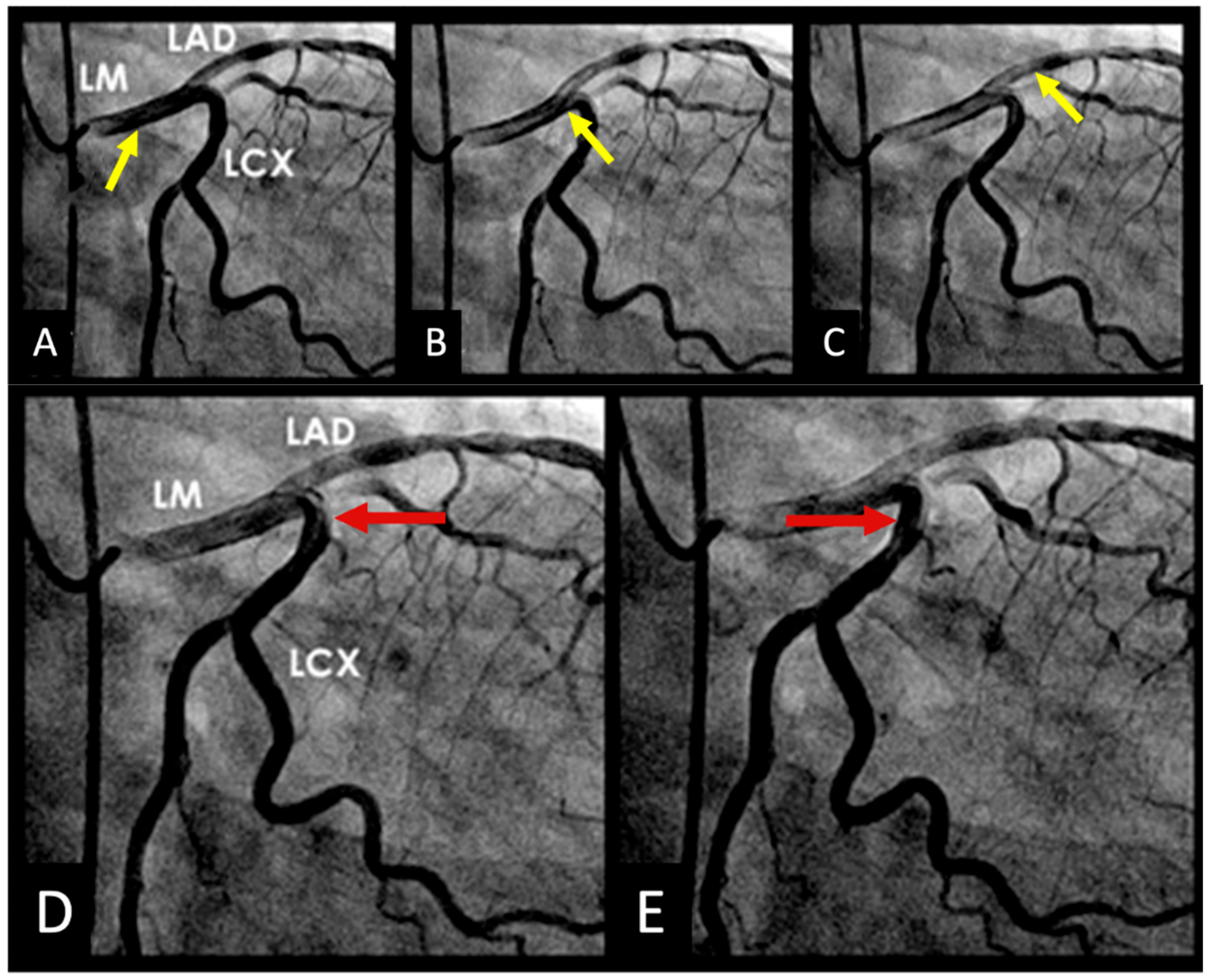
- Coronary Angiographic Perspective:
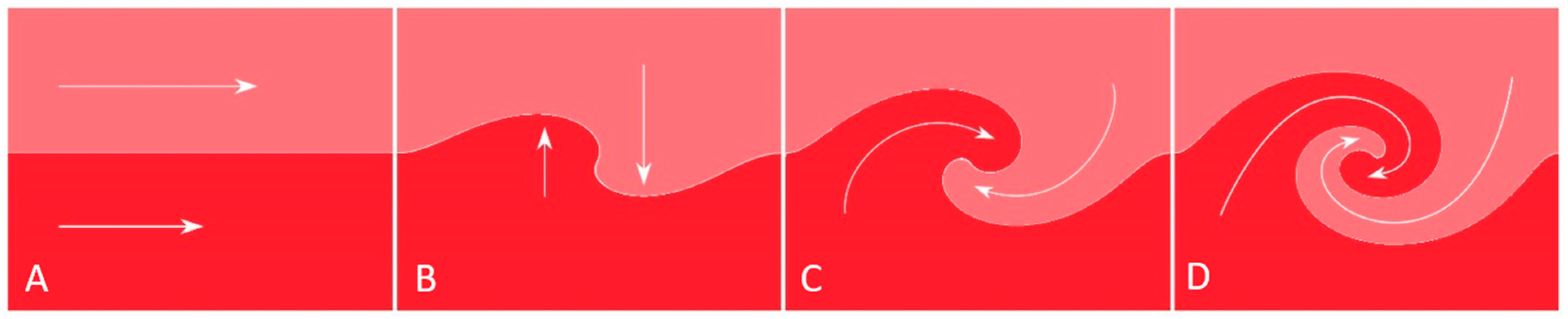
2.4. Recirculating Flow
- Fluid Mechanics Perspective:
- Coronary Angiographic Perspective:
2.5. Collision Secondary to Water Hammer Shock
- Fluid Mechanics Perspective:
- Coronary Dynamics Perspective:
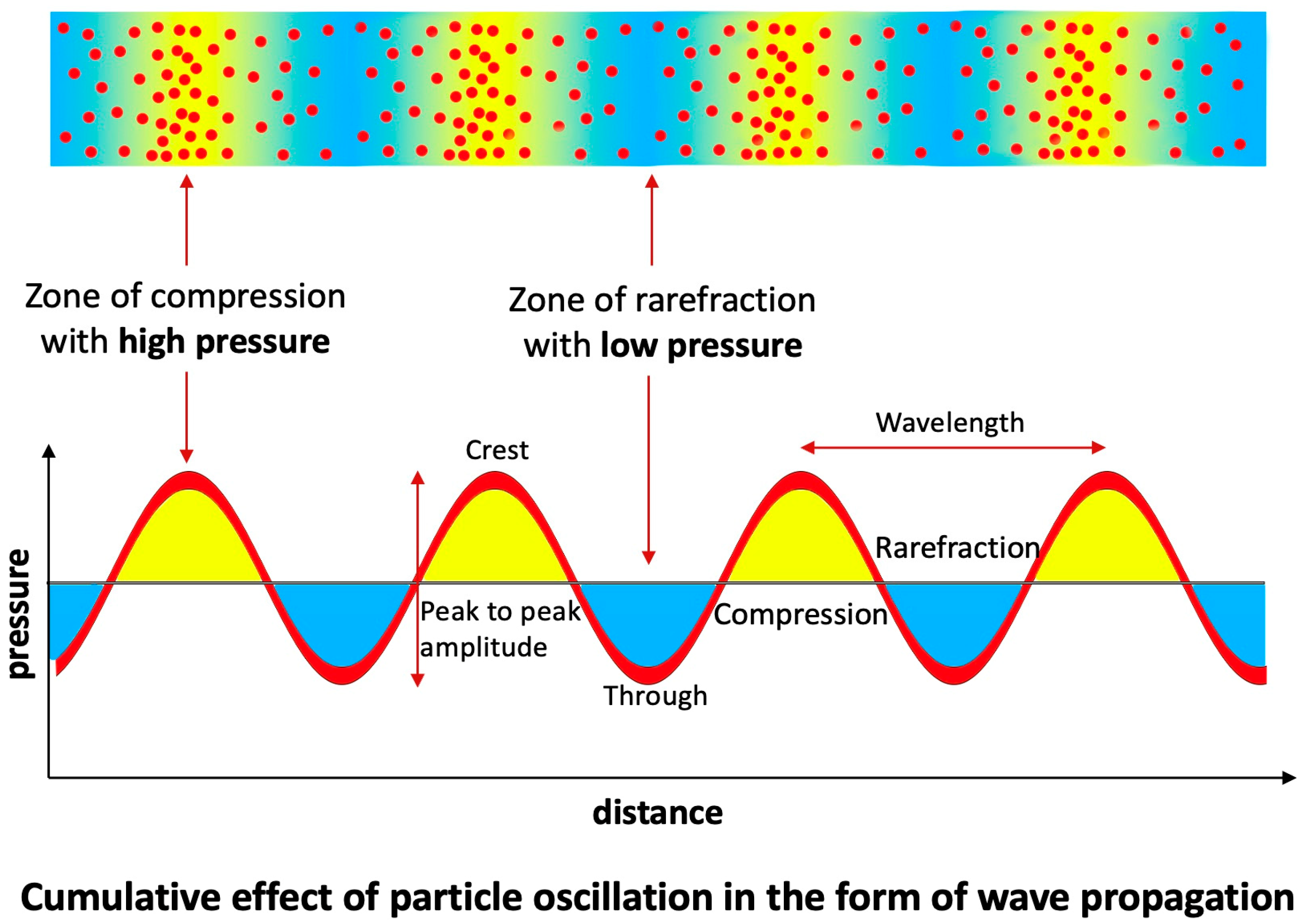
- Acoustics Analysis of In Vitro Studies:
- Acoustic Analysis of Coronary Angiographic Flow:
- Acoustic Mechanisms of Coronary Injuries:
2.6. Codification of Lesions and Creation of a Coronary Acoustic Map
3. Study Design and Protocol
- Goals and Challenges:
- Methodology: Theoretical Basis of Contrast as Acoustic Signals:
- Inclusion criteria:
- Exclusion criteria:
- New dynamic angiographic recording technique:
- Protocol of angiographic frame to frame analysis:
- Data Collection:
- Statistical analysis:
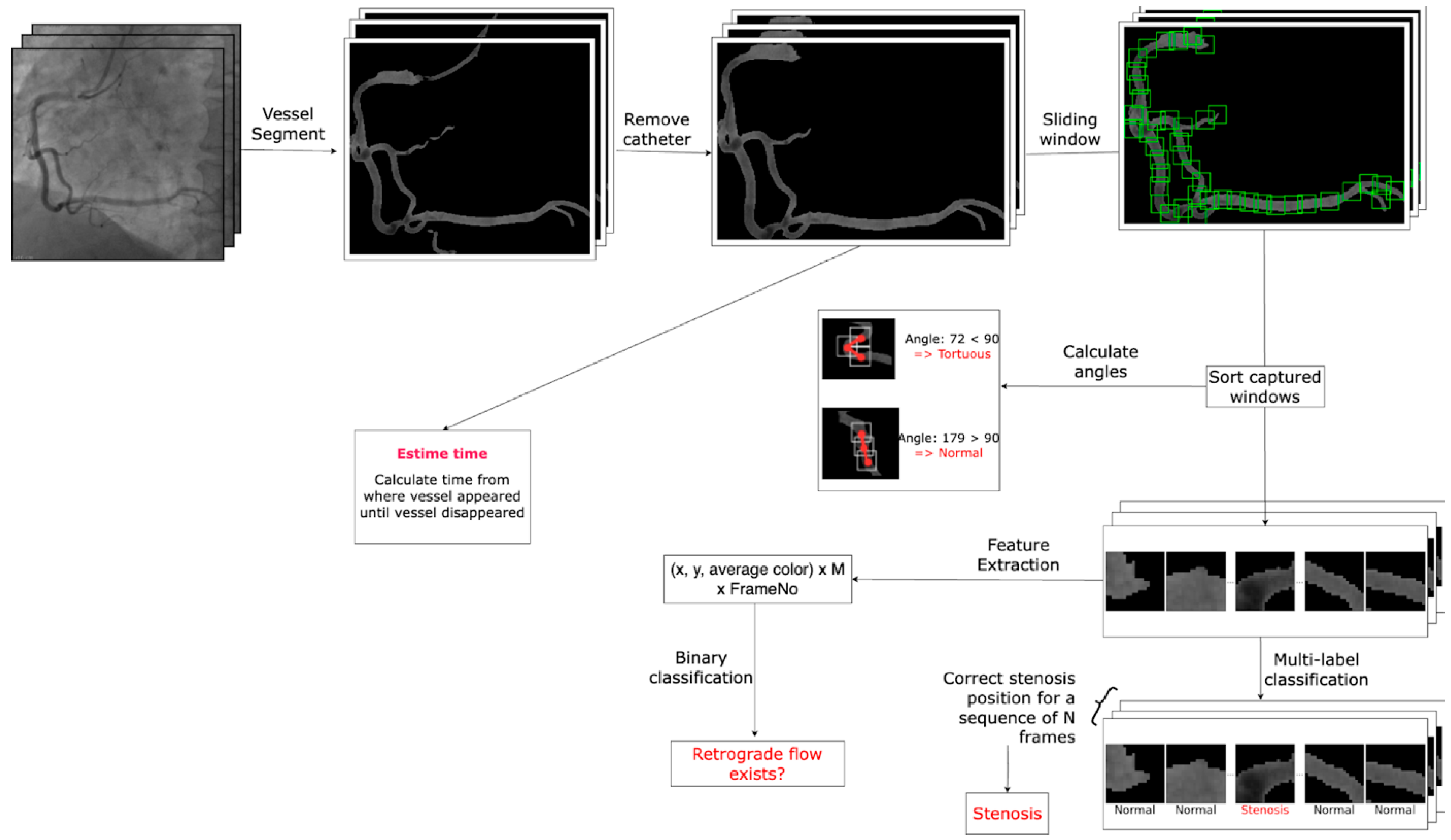
- Artificial Intelligence Algorithm:
- General Workflow:
- Dataset Preparation:
- Data Preprocessing:
- Model Architectures:
- Training and Evaluation:
4. Conclusions
- Limitations:
- Future Plan:
5. Perspective
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hashim, M.J.; Mustafa, H.; Baniyas, M.Y.; Al Suwaidi, S.K.B.M.; AlKatheeri, R.; Alblooshi, F.M.K.; Almatrooshi, M.E.A.H.; Alzaabi, M.E.H.; Al Darmaki, R.S.; Lootah, S.N.A.H. Global Epidemiology of Ischemic Heart Disease: Results from the Global Burden of Disease Study. Cureus 2020, 12, e9349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jebari-Benslaiman, S.; Galicia-García, U.; Larrea-Sebal, A.; Olaetxea, J.R.; Alloza, I.; Vandenbroeck, K.; Benito-Vicente, A.; Martín, C. Pathophysiology of Atherosclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Ngo, K.; Vu, T.L.; Nguyen, H.Q.; Pham, D.H.; Kodenchery, M.; Zuin, M.; Rigatelli, G.; Nanjundappa, A.; Gibson, M. Introducing a Novel Innovative Technique for the Recording and Interpretation of Dynamic Coronary Angiography. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Texon, M. A hemodynamic concept of atherosclerosis, with particular reference to coronary occlusion. AMA Arch. Intern. Med. 1957, 99, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caro, C.G.; Fitz-Gerald, J.M.; Schroter, R.C. Arterial wall shear and distribution of early atheroma in man. Nature 1969, 223, 1159–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.R.; Maffessanti, F.; Patel, M.B.; Kebed, K.; Narang, A.; Singh, A.; Medvedofsky, D.; Zaidi, S.J.; Mediratta, A.; Goyal, N.; et al. Hemodynamic impact of coronary stenosis using computed tomography: Comparison between noninvasive fractional flow reserve and 3D fusion of coronary angiography with stress myocardial perfusion. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 35, 1733–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doucette, J.W.; Corl, P.D.; Payne, H.M.; Flynn, A.E.; Goto, M.; Nassi, M.; Segal, J. Validation of a Doppler guide wire for intravascular measurement of coronary artery flow velocity. Circulation 1992, 85, 1899–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parviz, Y.; Shlofmitz, E.; Fall, K.N.; Konigstein, M.; Maehara, A.; Jeremias, A.; Shlofmitz, R.A.; Mintz, G.S.; Ali, Z.A. Utility of intracoronary imaging in the cardiac catheterization laboratory: Comprehensive evaluation with intravascular ultrasound and optical coherence tomography. Br. Med. Bull. 2018, 125, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prati, F.; Cera, M.; Ramazzotti, V.; Imola, F.; Giudice, R.; Giudice, M.; De Propris, S.; Albertucci, M. From bench to bedside: A novel technique of acquiring OCT images. Circ. J. 2008, 72, 839–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obisesan, O.H.; Osei, A.D.; Uddin, S.M.I.; Dzaye, O.; Blaha, M.J. An Update on Coronary Artery Calcium Interpretation at Chest and Cardiac CT. Radiol. Cardiothorac. Imaging 2021, 3, e200484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigatelli, G.; Zuin, M.; Dell’Avvocata, F.; Vassilev, D.; Daggubati, R.; Nguyen, T.; Thang, N.V.V.; Foinh, N. Evaluation of coronary flow conditions in complex coronary artery bifurcations stenting using computational fluid dynamics: Impact of final proximal optimization technique on different double-stent techniques. Cardiovasc. Revasc. Med. 2017, 18, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, K.D.; Nguyen, T.; Pham, H.D.; Tran, H.; Ha, D.Q.; Dinh, T.S.; Mihas, I.; Kodenchery, M.; Gibson, C.M.; Nguyen, H.Q.; et al. Water Hammer Phenomenon in Coronary Arteries: Scientific Basis for Diagnostic and Predictive Modeling with Acoustic Action Mapping. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desyatova, A.; MacTaggart, J.; Romarowski, R.; Poulson, W.; Conti, M.; Kamenskiy, A. Effect of aging on mechanical stresses, deformations, and hemodynamics in human femoropopliteal artery due to limb flexion. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 2018, 17, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michiels, C.; Arnould, T.; Remacle, J. Endothelial cell responses to hypoxia: Initiation of a cascade of cellular interactions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Res. 2000, 1497, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Song, Y.; Mu, X. The Role of Fluid Mechanics in Coronary Atherosclerotic Plaques: An Up-to-Date Review Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2024, 25, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgardner, J. Numerical Modeling of the Large-Scale Erosion, Sediment Transport, and Deposition Processes of the Genesis Flood (Revised). Answ. Res. J. 2018, 11, 149–170. Available online: https://answersresearchjournal.org/numerical-modeling-genesis-flood-2/ (accessed on 10 June 2025).
- Choo, Y.-M.; Kim, J.-G.; Park, S.-H. A Study on the Friction Factor and Reynolds Number Relationship for Flow in Smooth and Rough Channels. Water 2021, 13, 1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, K.; Wu, R. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Regulates Endothelial Metabolism in Cardiovascular Disease. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 670653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Lu, W.H.; Ai, R.; Yang, J.H.; Chen, F.; Tang, Z.Z. The relationship between serum hypoxia-inducible factor 1α and coronary artery calcification in asymptomatic type 2 diabetic patients. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2014, 13, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, D.; Xu, R.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y. The Physiological Functions and Therapeutic Potential of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α in Vascular Calcification. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, K.; Philip, J.; de Silva, C.M.; Hutchins, N.; Marusic, I. The turbulent/non-turbulent interface and entrainment in a boundary layer. J. Fluid. Mech. 2014, 742, 119151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanckaert, K.; Graf, W.L. Flow in meander bends with recirculation at the inner bank. Water Resour. Res. 2003, 39, 1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghidaoui, M.; Zhao, M.; McInnis, D.; Axworthy, D. A Review of Water Hammer Theory and Practice. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2005, 58, 49–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mynard, J.P.; Kondiboyina, A.; Kowalski, R.; Cheung, M.M.H.; Smolich, J.J. Measurement, Analysis and Interpretation of Pressure/Flow Waves in Blood Vessels. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nguyen, T.; Nguyen, H.D.; Dinh, H.V.K.; Dinh, T.H.T.; Ngo, K.; Truong, H.H.; Nguyen, H.Q.; Loc, V.T.; Le, T.; Vo, N.; et al. Preliminary Results in the Investigation of In Vivo Iliac and Coronary Flow Collision, Vortex Formation, and Disorganized Flow Degeneration: Insights from Invasive Cardiology Based on Fluid Mechanics Principles and Practices. Fluids 2024, 9, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, L. Croxford A, Drinkwater B, Dynamic patterning of microparticles with acoustic impulse control. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AKhorram, A.; Ramazani, S.A.; Jamshidi, S.; Kariman, A. Modeling and Simulation of Oil Well Stimulation by High Power Ultrasonic Irradiation. Acta Acust. United Acust. 2017, 103, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imashiro, C.; Kang, B.; Lee, Y.; Hwang, Y.H.; Im, S.; Kim, D.E.; Takemura, K.; Lee, H. Propagating acoustic waves on a culture substrate regulate the directional collective cell migration. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2021, 7, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrett, S.L. Reflection, Transmission, and Refraction. In Understanding Acoustics; Graduate Texts in Physics; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
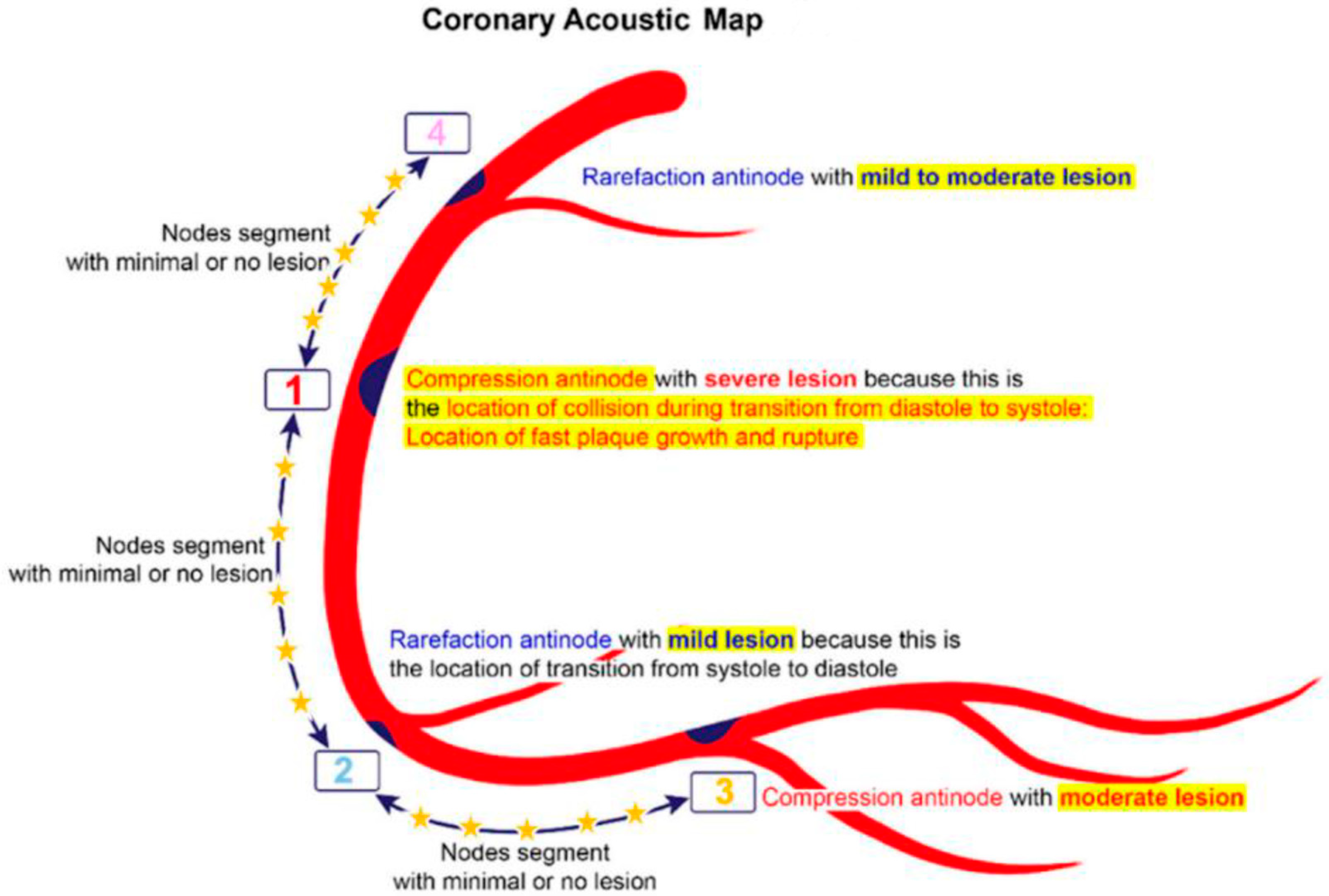






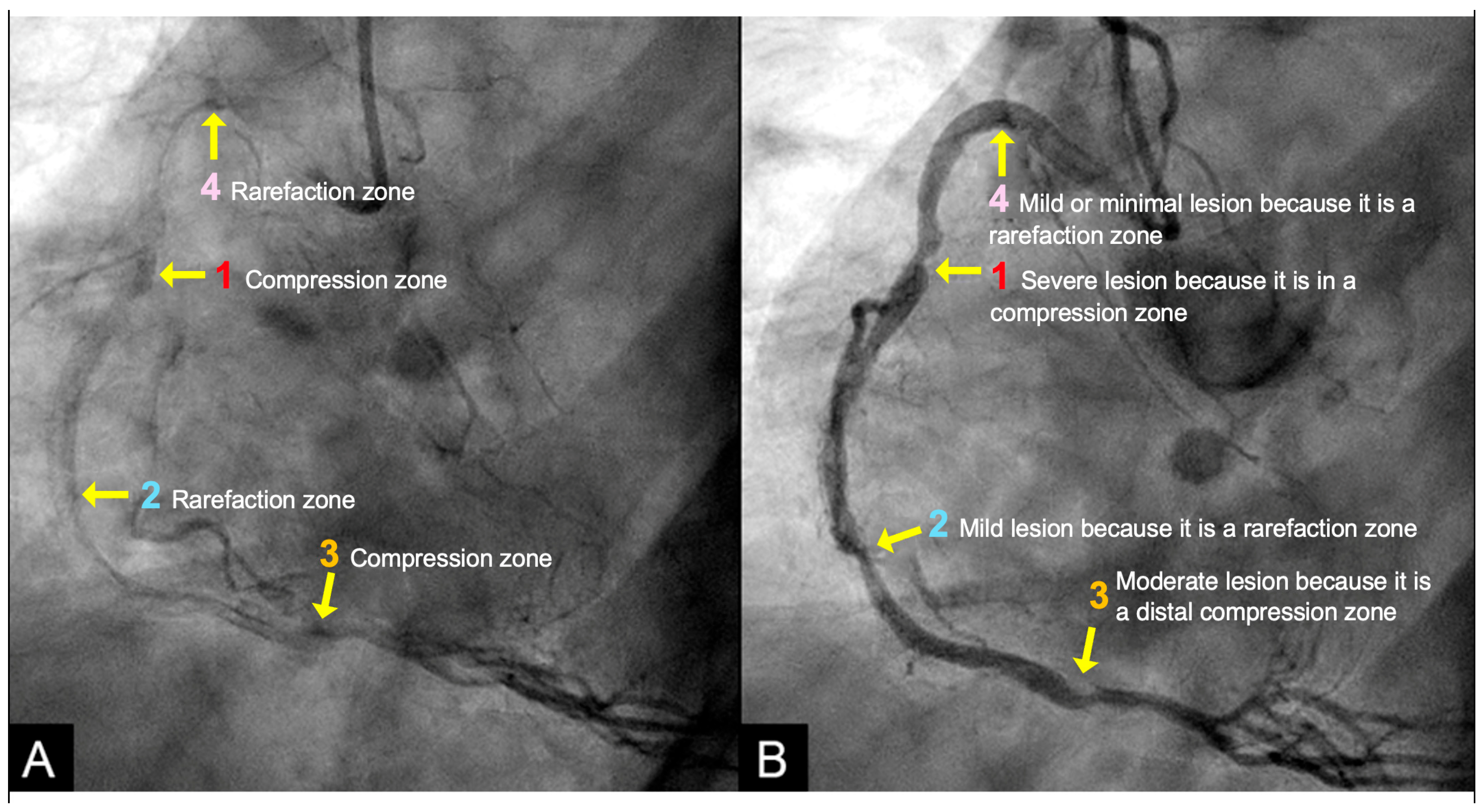
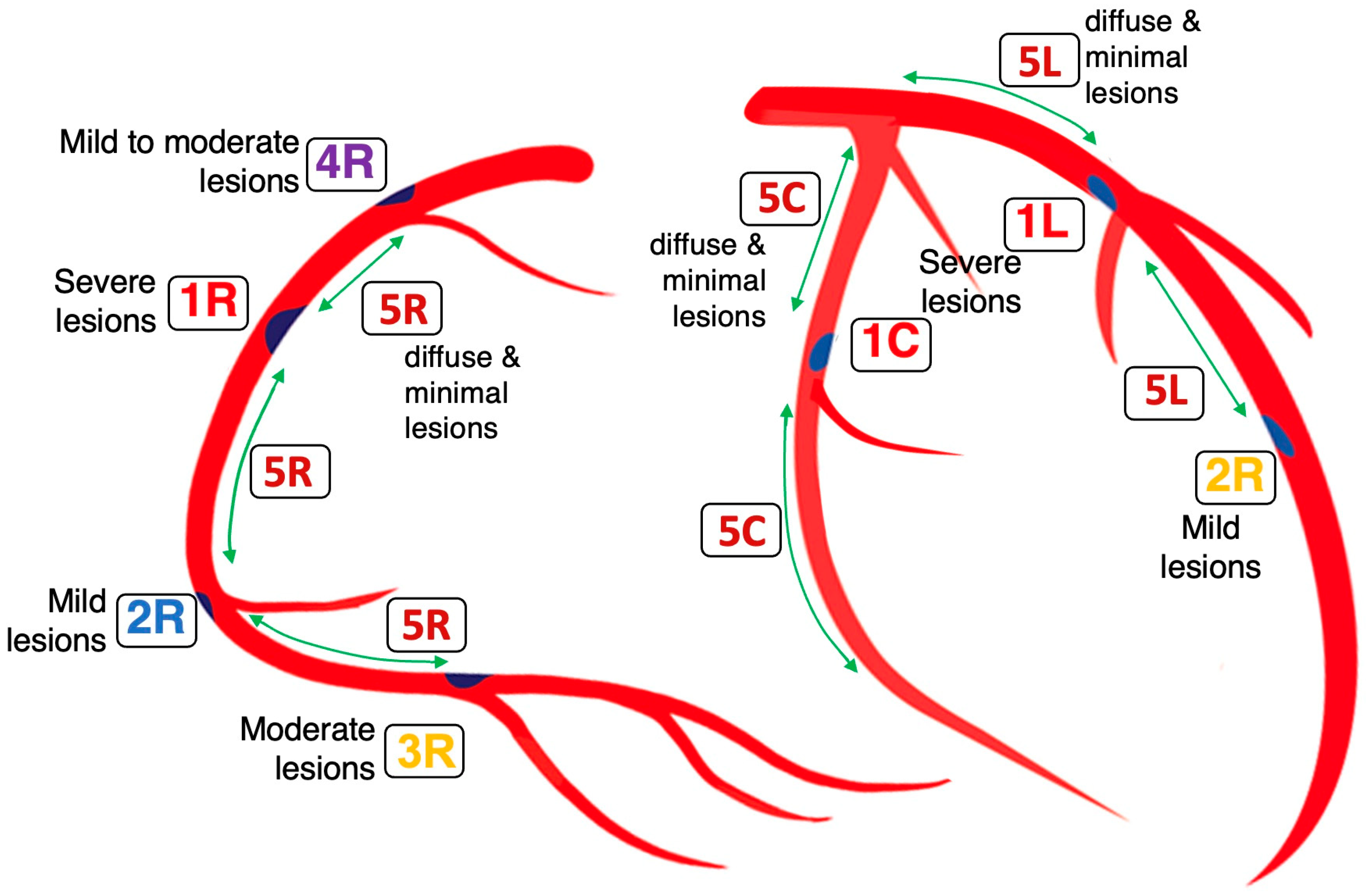
| 1. | Mechanical stress due to repetitive flexion and extension at a hinge location |
| 2. | Local intimal ischemia due to thick boundary layers |
| 3. | Recirculating flow at an exit curve of a bifurcation |
| 4. | Excessive pressure fluctuation at compression nodes generated by collision with a retrograde pressure wave |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, T.; Ngo, K.; Tien, H.A.; Ho, D.T.; Nguyen, C.D.; Vu, L.T.; Kodenchery, M.; Hung, H.; Huynh, V.X.; Nanjundappa, A.; et al. Codify and Localize Lesions on a Coronary Acoustic Map: Scientific Rationale, Trial Design and Artificial Intelligence Algorithm Protocols. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2994. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15232994
Nguyen T, Ngo K, Tien HA, Ho DT, Nguyen CD, Vu LT, Kodenchery M, Hung H, Huynh VX, Nanjundappa A, et al. Codify and Localize Lesions on a Coronary Acoustic Map: Scientific Rationale, Trial Design and Artificial Intelligence Algorithm Protocols. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(23):2994. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15232994
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Thach, Khiem Ngo, Hoang Anh Tien, Dzung T. Ho, Chinh D. Nguyen, Loc T. Vu, Mihas Kodenchery, Huynh Hung, Vinh X. Huynh, Aravinda Nanjundappa, and et al. 2025. "Codify and Localize Lesions on a Coronary Acoustic Map: Scientific Rationale, Trial Design and Artificial Intelligence Algorithm Protocols" Diagnostics 15, no. 23: 2994. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15232994
APA StyleNguyen, T., Ngo, K., Tien, H. A., Ho, D. T., Nguyen, C. D., Vu, L. T., Kodenchery, M., Hung, H., Huynh, V. X., Nanjundappa, A., & Gibson, M. (2025). Codify and Localize Lesions on a Coronary Acoustic Map: Scientific Rationale, Trial Design and Artificial Intelligence Algorithm Protocols. Diagnostics, 15(23), 2994. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15232994









