Diagnosis of Isolated Saccular Dysfunction Using Trapezius cVEMP: A Detailed Vestibular Assessment
Abstract
1. Introduction
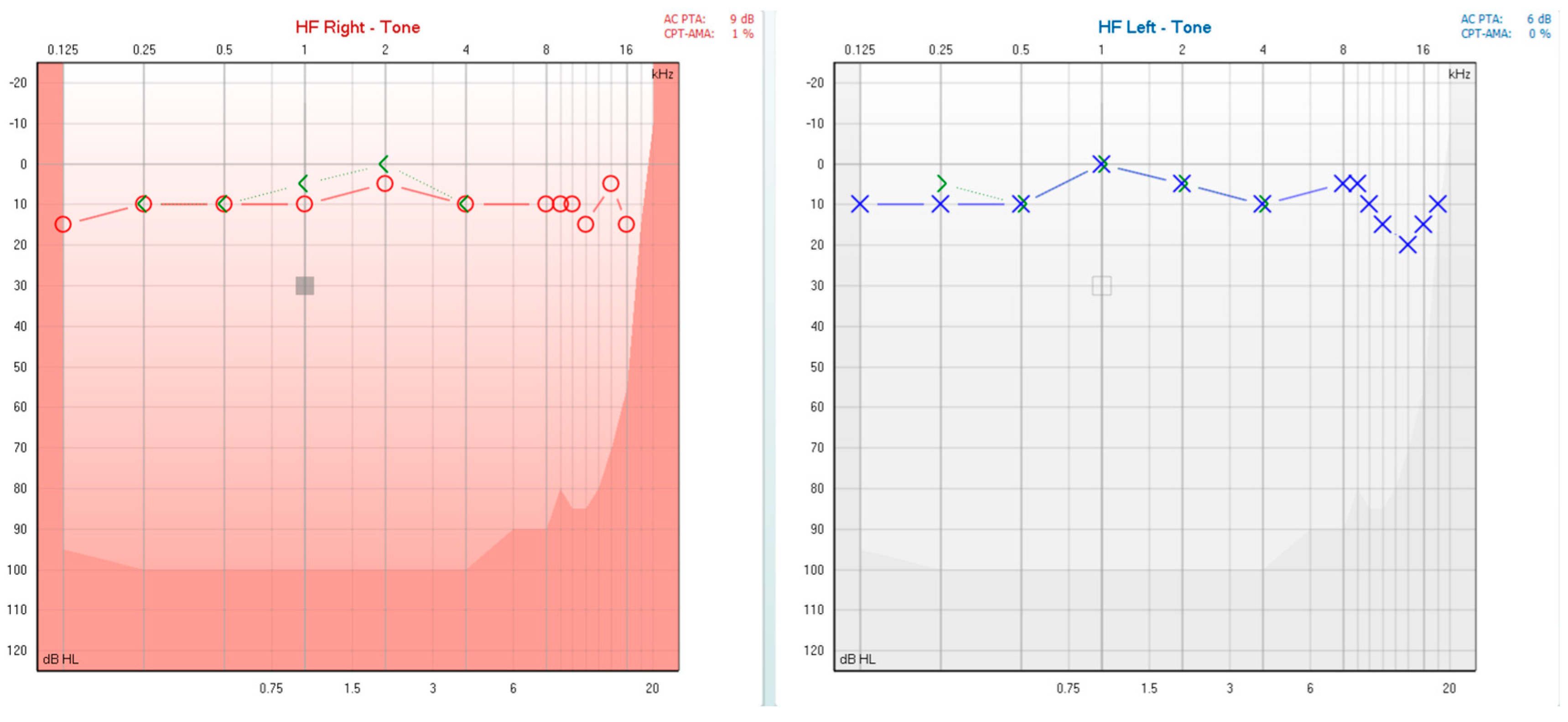
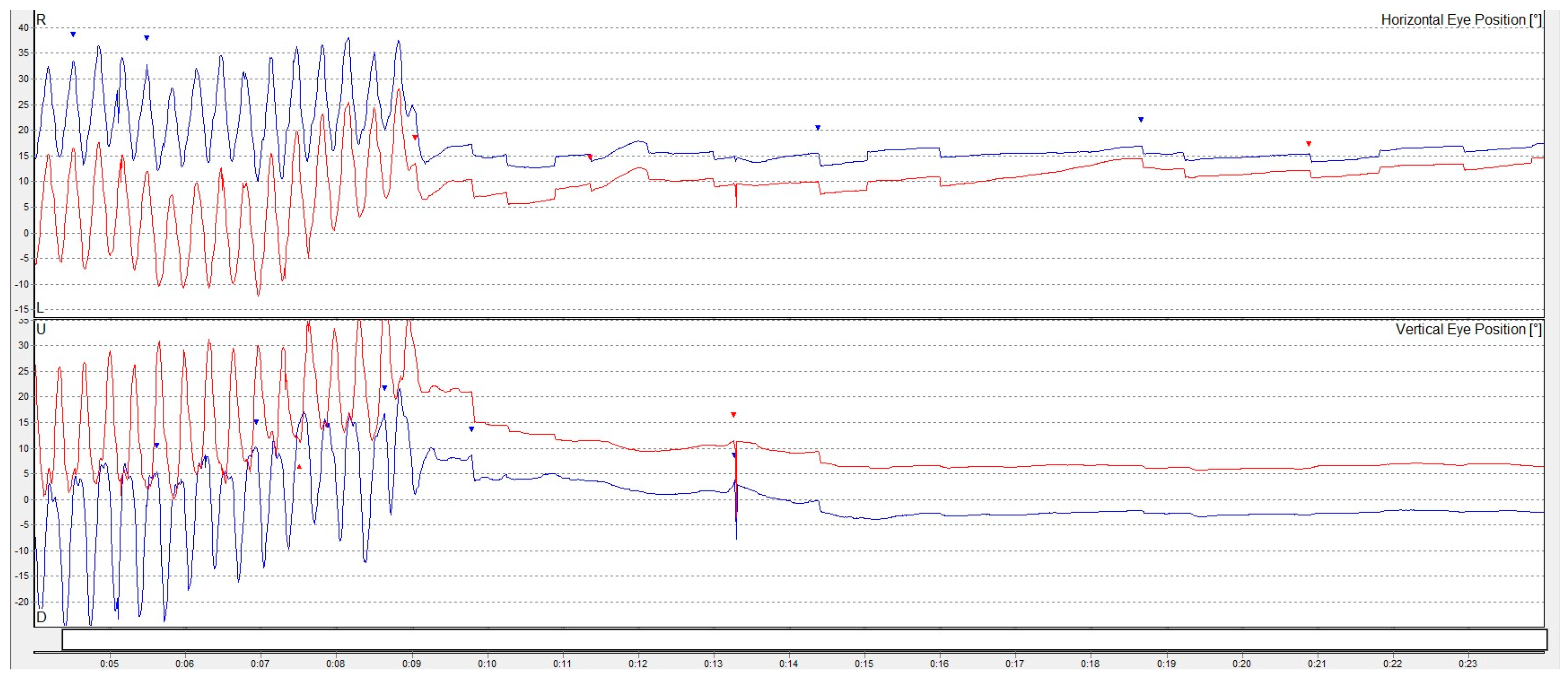
2. Detailed Case Presentation
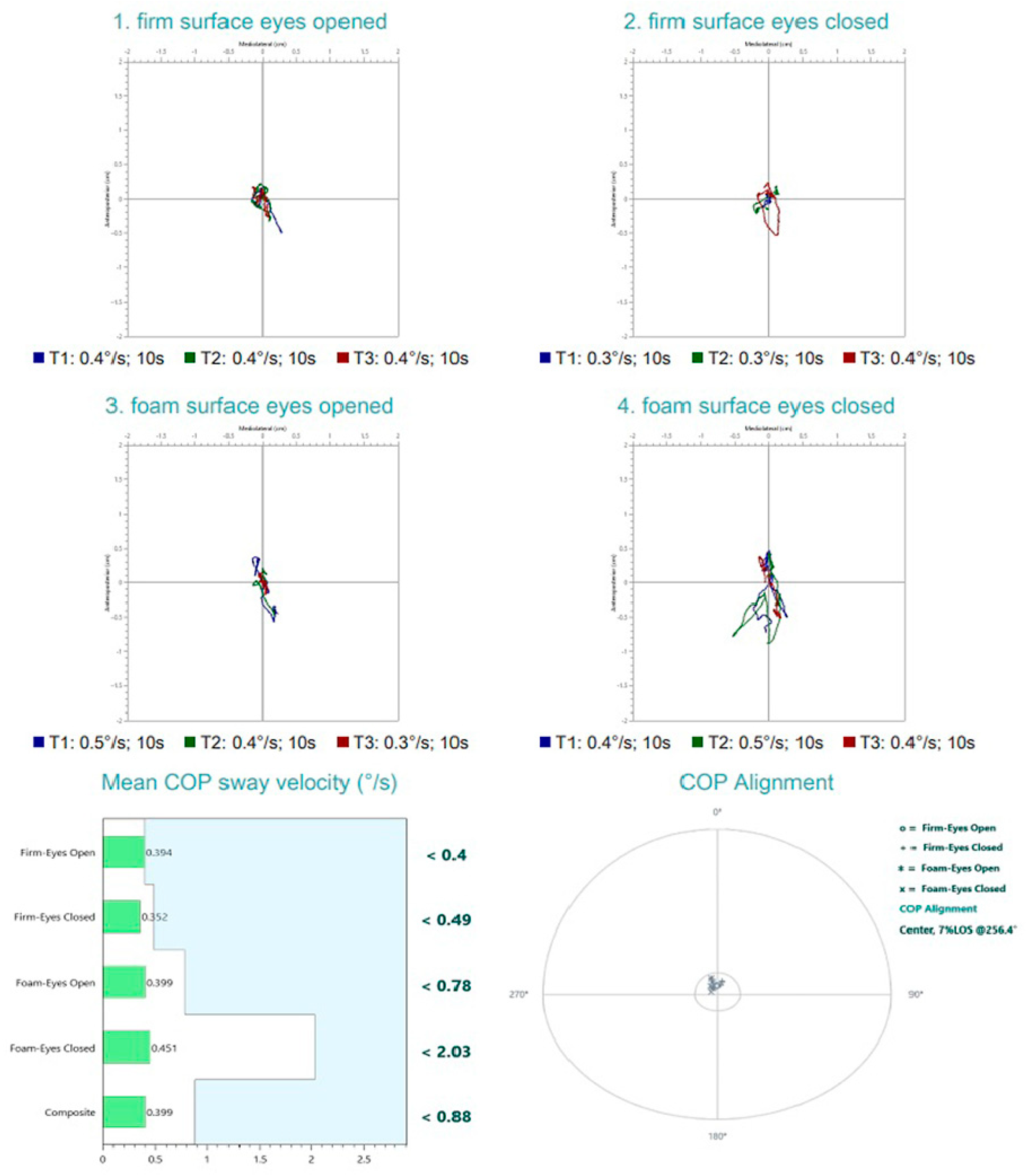
- Firm surface, eyes open—All sensory inputs available; baseline condition;
- Firm surface, eyes closed—Removes visual input; assesses somatosensory and vestibular reliance;
- Foam surface, eyes open—Somatosensory input is altered; evaluates ability to rely on visual and vestibular cues;
- Foam surface, eyes closed—Removes visual input and alters somatosensory cues; primarily assesses vestibular contribution.
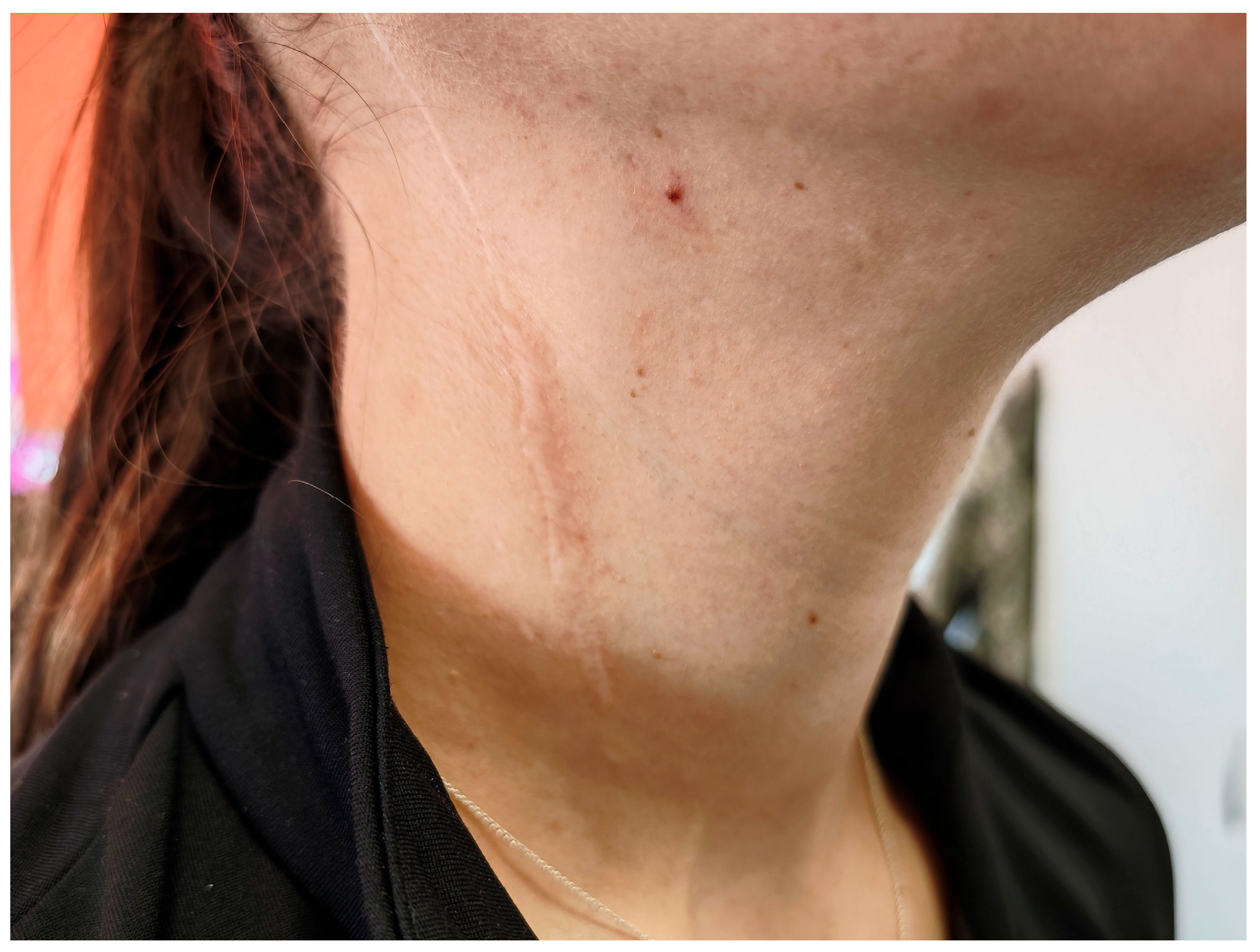
- Post-surgical cervical scarring and asymmetry with denervation and surgically absent SCM muscle fibers;
- Low-frequency vertical oscillations on a fitness ball;
- Higher-frequency bouncing on a trampoline;
- Speed-varied vertical movements on a rocker board.
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DHI | Dizziness Handicap Inventory |
| PTA | Pure Tone Audiometry |
| VNG | Videonistagmography |
| cVEMP | Cervical Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials |
| oVEMP | Ocular Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials |
| CDP | Computed Dynamic Posturography |
| MRI | Magnetic Resolution Imaging |
| MD | Ménière’s Disease |
| BPPV | Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo |
| SSCD | Superior Semicircular Canal Dehiscence |
| SSNHL | Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss |
| COP | Centre of Pressure |
| FLAIR | Fluid Attenuated Inversion Recovery |
| ENT | Otorhinolaryngology |
| SCM | Sternocleidomastoid |
| SVN | Superior Vestibular Nucleus |
| LVN | Lateral Vestibular Nucleus |
| MVN | Medial Vestibular Nucleus |
| IVN | Inferior Vestibular Nucleus |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| VR | Vestibular Rehabilitation |
References
- Strupp, M.; Brandt, T. Acute Unilateral Vestibulopathy (AUVP). In Oxford Textbook of Vertigo and Imbalance; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2025; p. 249. [Google Scholar]
- Dieterich, M.; Strupp, M.; Brandt, T. Bilateral Vestibulopathy. In Oxford Textbook of Vertigo and Imbalance; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2025; p. 331. [Google Scholar]
- Kudo, Y.; Johkura, K. Vertigo and Dizziness Due to Cerebrovascular Disease. Equilib. Res. 2023, 82, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos Carvalho, M.; Oliveira, A.C.; de Oliveira Almeida, B.M.; Chon, C.W.; de Alcantara Machado, D.A.; Neto, E.P.M.; Brazilian, F.S.; Chaves, F.N.R.; Centenaro, G.D.; Schug, G.H.; et al. Central and Peripheral Vertigo: Neurological and Otorhinolaryngological Approaches. In Challenges and Research in Health Sciences: A Multidisciplinary Approach; Seven Publicações Acadêmicas: São José dos Pinhais, Brazil, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitazawa, M.; Morita, Y.; Yagi, C.; Takahashi, K.; Ohshima, S.; Yamagishi, T.; Izumi, S.; Koizuka, I.; Horii, A. Test Batteries and the Diagnostic Algorithm for Chronic Vestibular Syndromes. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 768718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thömke, F. Acute Vestibular Syndrome: Clinical Examination Outperforms MRI in the Detection of Central Lesions. Nervenarzt 2018, 89, 1165–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattingly, J.K.; Riggs, W.J.; Adunka, O.F. Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials. In Diagnosis and Treatment of Vestibular Disorders; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 107–111. [Google Scholar]
- Bansal, S.; Sahni, S.; Sinha, S.K. Cervical and Ocular Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials in Individuals with Severe to Profound Hearing Loss. J. Hear. Sci. 2014, 3, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, T. Clinical Application of VEMP. Equilib. Res. 2017, 76, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, Y.-H. Potential Application of Ocular and Cervical Vestibular-Evoked Myogenic Potentials in Meniere’s Disease: A Review. Laryngoscope 2013, 123, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noij, K.; Rauch, S. Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potential (VEMP) Testing for Diagnosis of Superior Semicircular Canal Dehiscence. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murofushi, T.; Suh, M.-W.; Manzari, L. Editorial: Isolated Otolith Dysfunction and Vertigo. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 1030513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strupp, M.; Grimberg, J.; Teufel, J.; Laurell, G.; Kingma, H.; Grill, E. Worldwide Survey on Laboratory Testing of Vestibular Function. Neurol. Clin. Pract. 2020, 10, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magliulo, G.; Iannella, G.; Gagliardi, S.; Re, M. A 1-Year Follow-up Study with C-VEMPs, O-VEMPs and Video Head Impulse Testing in Vestibular Neuritis. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2015, 272, 3277–3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannigan, I.P.; Rosengren, S.M.; Young, A.S.; Bradshaw, A.P.; Calic, Z.; Kwok, B.; Alraddy, B.; Gibson, W.P.R.; Kong, J.; Flanagan, S.; et al. A Portrait of Menière’s Disease Using Contemporary Hearing and Balance Tests. Otol. Neurotol. 2022, 43, e489–e496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Xiao, H.; Lin, C.; Lin, J.; Cai, H.; Ke, X.; Lu, Y.; Ye, S. Differentiating Definite and Probable Ménière Disease: A Comprehensive Evaluation of Audio-Vestibular Function Testing Combined with Inner Ear MRI. Otol. Neurotol. 2024, 45, 925–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, X.; Yao, Q.; Feng, Y.; Huang, S.; Wang, H.; Yin, S. Contribution of Audiogram Classification in Evaluating Vestibular Dysfunction in Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss with Vertigo. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 667804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.G.; Park, J.W.; Han, S.Y.; Park, S.H.; Nam, S.I. The Role of Vestibular Function Tests in Patients with Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss Who Have Subclinical Vestibular Dysfunction. Korean J. Otorhinolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2013, 56, 700–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Bustamante, M.; Anderson, C.; Gutierrez, V. The Use of Posturography in Vestibular Evaluation of Neurodegenerative Disorders: Diagnostic and Rehabilitative Impacts. Cureus 2025, 17, e88752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janc, M.; Sliwinska-Kowalska, M.; Politański, P.; Kaminski, M.; Józefowicz-Korczyńska, M.; Zamyslowska-Szmytke, E. Posturography with Head Movements in the Assessment of Balance in Chronic Unilateral Vestibular Lesions. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strasilla, C.; Sychra, V. Imaging-Based Diagnosis of Vestibular Schwannoma. HNO 2017, 65, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benezech, L. The Hyperacute Vestibular Syndrome: Ear or Brain? Lancet Neurol. 2023, 22, 377–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Guo, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, D.; Tian, E.; Guo, J.; Kong, W.; Zhang, S. Vestibular Migraine or Meniere’s Disease: A Diagnostic Dilemma. J. Neurol. 2022, 270, 1955–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanspauwen, R.; Knoop, A.; Camp, S.; van Dinther, J.; Offeciers, F.E.; Somers, T.; Zarowski, A.; Blaivie, C. Outcome Evaluation of the Dizziness Handicap Inventory in an Outpatient Vestibular Clinic. J. Vestib. Res.-Equilib. Orientat. 2017, 26, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueß, D.; Vojacek, S.; Gungor, E.; Lüers, J.-C.; Hunsche, S.; Jabłońska, K.; Köcher, M.; Ruge, M.I. Longitudinal Evaluation of Vestibular Symptoms in Patients with Vestibular Schwannoma After Robotic-Guided Stereotactic Radiosurgery Using the Dizziness Handicap Inventory (DHI). Stomatology 2025, 14, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chari, D.A.; Liu, Y.-H.; Chung, J.J.; Rauch, S.D. Subjective Cognitive Symptoms and Dizziness Handicap Inventory (DHI) Performance in Patients with Vestibular Migraine and Menière’s Disease. Otol. Neurotol. 2021, 42, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Shin, S.; Kim, D.H. Optimal Trapezius Electrophysiological Recording Site. PM&R 2020, 12, 546–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strupp, M.; Brandt, T. Vestibular Neuritis. Semin. Neurol. 2009, 29, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.; Winnick, A.; Hsu, Y. The Bucket Test Differentiates Patients with MRI Confirmed Brainstem/Cerebellar Lesions from Patients Having Migraine and Dizziness Alone. BMC Neurol. 2019, 19, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, G.P.; Newman, C.W. The development of the Dizziness Handicap Inventory. Arch. Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 1990, 116, 424–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwislocki, J. Normal Function of the Middle Ear and Its Measurement. Audiology 1982, 21, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarou, I.; Sideris, G.; Papadimitriou, N.; Delides, A.; Korres, G. Third Window Syndrome: An Up-to-Date Systematic Review of Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment. J. Audiol. Otol. 2025, 29, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Striteska, M.; Valis, M.; Chrobok, V.; Profant, O.; Califano, L.; Syba, J.; Trnkova, K.; Kremlacek, J.; Chovanec, M. Head-Shaking-Induced Nystagmus Reflects Dynamic Vestibular Compensation: A 2-Year Follow-up Study. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 949696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botts, S.R.; Yang, S.; Mansour, M.; Kaye, A.M.; Kaye, A.D. Neck Anatomy. In Anatomy, Back, Trapezius; StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK518994/ (accessed on 25 October 2025).
- Singh, N.; Kadisonga, P.; Ashitha, P. Optimizing Stimulus Repetition Rate for Recording Ocular Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potential Elicited by Air-Conduction Tone Bursts of 500 Hz. Audiol. Res. 2014, 4, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosengren, S.; Colebatch, J. The Contributions of Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials and Acoustic Vestibular Stimulation to Our Understanding of the Vestibular System. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satar, B.; Karababa, E.; Karaçaylı, C. The Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials (VEMPs) Test over the Trapezius Muscle: Neurophysiological Grounds in Muscle Extensor and Flexor Conditions. J. Int. Adv. Otol. 2025, 21, 1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, C.; Wit, H. Asymmetric Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials in Unilateral Menière Patients. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2011, 268, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Interacoustics. cVEMP Testing with Eclipse. Available online: https://www.interacoustics.com/abr-equipment/eclipse/support/cvemp-testing-with-eclipse (accessed on 25 October 2025).
- Hall, C.D.; Herdman, S.J.; Whitney, S.L.; Cass, S.P.; Clendaniel, R.A.; Fife, T.D.; Furman, J.M.; Getchius, T.S.D.; Goebel, J.A.; Shepard, N.T.; et al. Vestibular Rehabilitation for Peripheral Vestibular Hypofunction: An Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Neurol. Phys. Ther. 2016, 40, 124–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Si, L.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, K.; Yang, X. Etiologic Distribution of Dizziness/Vertigo in a Neurological Outpatient Clinic According to the Criteria of the International Classification of Vestibular Disorders: A Single-Center Study. J. Neurol. 2024, 271, 2446–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Chong, Y.; Jiang, Z.D.; Liu, Z.L.; Ding, L.; Yang, S.L.; Wang, L.; Xiang, W. Etiological Analysis on Patients with Vertigo or Dizziness. Natl. Med. J. China 2018, 98, 1227–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strupp, M.; Feil, K.; Zwergal, A. Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosis of Peripheral and Central Vestibular Disorders. Laryngo-rhino-otologie 2021, 100, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzesiak, M.; Carender, W.J.; Basura, G.J. Posttraumatic Dizziness: Navigating the Maze Towards Accurate Vestibular Diagnosis and Treatment. Otol. Neurotol. 2020, 42, e573–e578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruthberg, J.S.; Rasendran, C.; Kocharyan, A.; Mowry, S.E.; Mowry, S.E.; Otteson, T.D.; Otteson, T.D. The Economic Burden of Vertigo and Dizziness in the United States. J. Vestib. Res.-Equilib. Orientat. 2021, 31, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saber Tehrani, A.S.; Coughlan, D.; Hsieh, Y.H.; Mantokoudis, G.; Korley, F.K.; Kerber, K.A.; Frick, K.D.; Newman-Toker, D.E. Rising Annual Costs of Dizziness Presentations to U.S. Emergency Departments. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2013, 20, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Strobl, R.; Holle, R.; Seidl, H.; Peters, A.; Grill, E. Vertigo and Dizziness Cause Considerable More Health Care Resource Use and Costs: Results from the KORA FF4 Study. J. Neurol. 2019, 266, 2120–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benecke, H.; Agus, S.; Kuessner, D.; Goodall, G.; Strupp, M. The Burden and Impact of Vertigo: Findings from the REVERT Patient Registry. Front. Neurol. 2013, 4, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, E.; Wang, X.; Grill, E. Economic Burden of Vertigo: A Systematic Review. Health Econ. Rev. 2019, 9, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinosa-Sanchez, J.M.; Lin, C.C. Vestibular migraine. Front. Neurol. 2025, 16, 1587097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrin, P.; Gimmon, Y. Reviews in neuro-otology: Highlighting recent advances in neuro-otology: New possibilities for future inquiries. Front. Neurol. 2025, 16, 1595204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimmo, Z.M.; Hwa, T.P.; Naples, J.G.; Shah, R.R.; Brant, J.A.; Eliades, S.J.; Bigelow, D.C.; Ruckenstein, M.J. Age-Related Patterns of Vestibular Dysfunction in Dizziness and Imbalance: A Review of Vestibular Testing Results Among 1,116 Patients. Otol. Neurotol. 2021, 42, 897–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, J.W.; Chang, M.Y.; Woo, S.-Y.; Kim, S.; Cho, Y.-S. Prevalence of Vestibular Dysfunction and Associated Factors in South Korea. BMJ Open 2015, 5, e008224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.P.; Zee, D.S.; Kheradmand, A. Technological Advances in Testing the Dizzy Patient: The Bedside Examination Is Still the Key to Successful Diagnosis. In Dizziness and Vertigo Across the Lifespan; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 9–30. [Google Scholar]
- Kamal, N.; Taha, H.; Galal, E. Office Vestibular Tests: A Battery Approach to Guide the Diagnosis of Dizzy Patients. Audiol. Med. 2011, 9, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maarsingh, O.R.; van Vugt, V.A. Ten Vestibular Tools for Primary Care. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 642137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Berg, R.; Rosengren, S.M.; Kingma, H. Laboratory Examinations for the Vestibular System. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2017, 31, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, J.S.; Sandhu, J.S.; Yung, M.; Parker-George, J.C.; Kearney, B.; Ray, J. Assessment of Vestibular Function in Patients with Chronic Middle Ear Disease Using the VHIT and VEMP Test. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2018, 43, 1179–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, E.A.; Stocker, C.; Kempton, C.M.; Dierking, D.M.; Fehlberg, H.E.; Adams, M.E. Vestibular Testing: Patient Perceptions, Morbidity, and Opportunity Costs. Otol. Neurotol. 2018, 39, 1222–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCaslin, D.L. Vestibular Testing: The Good, the Bad, and the Emesis Basin. Hear. J. 2008, 61, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gizzi, M.; Rosenberg, M.L. The Diagnostic Approach to the Dizzy Patient. Neurologist 1998, 4, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venhovens, J.; Meulstee, J.; Verhagen, W.I.M. Acute Vestibular Syndrome: A Critical Review and Diagnostic Algorithm Concerning the Clinical Differentiation of Peripheral versus Central Aetiologies in the Emergency Department. J. Neurol. 2016, 263, 2151–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, Z.; Ju, Y.; Zhao, X. Application of Bedside HINTS, ABCD2 Score and Truncal Ataxia to Differentiate Cerebellar-Brainstem Stroke from Vestibular Neuritis in the Emergency Room. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2024, 9, e002779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, J.S.; Newman, J.L. Quantifying the Direct Cost Benefits of Vestibular Telemetry Using the CAVA System to Diagnose the Causes of Dizziness. Cost Eff. Resour. Alloc. 2023, 21, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonenko, L.M.; Parfenov, V.A. A Specialized Approach to Diagnosing and Treating Vertigo. Neurol. Neuropsychiatry Psychosom. 2016, 8, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Futami, S.; Miwa, T. Comprehensive Equilibrium Function Tests for an Accurate Diagnosis in Vertigo: A Retrospective Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Waele, C.; Huy, P.; Diard, J.P.; Freyss, G.; Vidal, P.-P. Saccular Dysfunction in Meniere’s Disease. Am. J. Otol. 1999, 20, 223–232. [Google Scholar]
- Mucha, A.; Fedor, S.; DeMarco, D. Vestibular Dysfunction and Concussion. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2018, 158, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Legois, Q.; Marx, M.; Paul, A.; Giraudet, F. Vestibular evoked myogenic potentials beyond oVEMP and cVEMP: Exploring new recording sites. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2025, 55, 103115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lullo, F.; Piscosquito; Provitera, V.; Zamprotta, L.; Prisco, C.; Lanzillo, B.; Manganelli, F.; Santoro, L.; Nolano, M. Myogenic Vestibular-Evoked Potentials: An Extension of the Assessment Protocol. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2017, 128, e437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosengren, S.M.; Weber, K.P.; Govender, S.; Welgampola, M.S.; Dennis, D.L.; Colebatch, J.G. Sound-Evoked Vestibular Projections to the Splenius Capitis in Humans: Comparison with the Sternocleidomastoid Muscle. Appl. Physiol. 2019, 126, 1619–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hougaard, D.D.; Abrahamsen, E.R. Functional Testing of All Six Semicircular Canals with Video Head Impulse Test Systems. J. Vis. Exp. 2019, 146, e59012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albernaz, P.L.M.; Maia, F.Z.; Carmona, S.; Cal, R.; Zalazar, G. Clinical Evaluation of the Vestibular System: The Vestibular Laboratory Tests. In The New Neurotology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 65–77. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, E.; Li, F.; Liu, D.; Wang, J.; Guo, Z.; Chen, J.; Guo, J.; Zhang, S. Dispelling Mist That Obscures Positional Vertigo in Vestibular Migraine. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.G.; Lee, J.-H.; Oh, S.H.; Park, M.K.; Suh, M.-W. Proposal on the Diagnostic Criteria of Definite Isolated Otolith Dysfunction. J. Audiol. Otol. 2019, 23, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong Dinh, T.A.; Wittenborn, J.; Westhofen, M. The Dizziness Handicap Inventory for Quality Control in the Treatment of Vestibular Dysfunction. HNO 2021, 70, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawronska, A.; Rosiak, O.; Pajor, A.; Janc, M.; Kotas, R.; Kaminski, M.; Zamyslowska-Szmytke, E.; Jozefowicz-Korczynska, M. Instrumental and Non-Instrumental Measurements in Patients with Peripheral Vestibular Dysfunctions. Sensors 2023, 23, 1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furman, J.M. Posturography: Uses and Limitations. Baillière’s Clin. Neurol. 1994, 3, 501–513. [Google Scholar]
- Di Fabio, R.P. Meta-Analysis of the Sensitivity and Specificity of Platform Posturography. Arch. Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 1996, 122, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferber-Viart, C.; Duclaux, R.; Colleaux, B.; Dubreuil, C. Myogenic Vestibular-Evoked Potentials in Normal Subjects: A Comparison between Responses Obtained from Sternomastoid and Trapezius Muscles. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 1997, 117, 472–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comacchio, F.; Zattoni, G.; Di Pasquale Fiasca, V.M.; Magnavita, P.; Bellemo, B.; Fasanaro, E.; Poletto, E. Masseter Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials (M-VEMPs) in Vestibular Neuritis. Audiol. Res. 2025, 15, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jäger, L.; Strupp, M.; Brandt, T.; Reiser, M.F. Imaging of the Labyrinth and Vestibular Nerve. Clinical Significance for Differential Diagnosis of Vestibular Diseases. Nervenarzt 1997, 68, 443–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mafee, M.F. Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Evaluation of Otic Labyrinth Pathology. Top. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2000, 11, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.T.; Feng, Y.; Li, X.; Song, N.; Ma, X.; Sui, R. The Value of Postcontrast Delayed 3D Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery MRI in the Diagnosis of Unilateral Peripheral Vestibular Dysfunction. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2023, 3, 5072–5088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemps, G.; Mistry, J.; Connor, S.; Obholzer, R.; Ainsworth, C. Diagnosing Perilymphatic Fistula with 3D Flair MRI. Hear. Balance Commun. 2023, 21, 175–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wangaryattawanich, P.; Rutman, A.; Petcharunpaisan, S.; Mossa-Basha, M. Incidental Findings on Brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) in Adults: A Review of Imaging Spectrum, Clinical Significance, and Management. Br. J. Radiol. 2023, 96, 20220108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedeño-Vidal, A.; Hita-Contreras, F.; Montilla-Ibáñez, M.A. The Effects of Vestibular Rehabilitation and Manual Therapy on Patients with Unilateral Vestibular Dysfunction: A Randomized and Controlled Clinical Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 15080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese Geriatrics Society for Vestibular Disorders; Otolaryngology Expert Committee; National Health Commission Capacity Building and Continuing Education Center. Expert Consensus on Vestibular Rehabilitation in Vestibular Disorders. Natl. Med. J. China 2024, 104, 1097–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyahya, D. A Systematic Review of Effectiveness of Vestibular Rehabilitation on Improving Balance in Patients with Different Conditions. Int. J. Physiother. 2022, 9, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferri, N.; Morone, G.; Piermaria, J.; Manzari, L.; Turolla, A.; De Tanti, A.; Ciancarelli, I.; Pillastrini, P.; Tramontano, M. Knowledge, Barriers, and Future Directions of Vestibular Rehabilitation Practice in Neurorehabilitation: An Italian Survey. Healthcare 2025, 13, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tramontano, M.; Haijoub, S.; Lacour, M.; Manzari, L. Updated Views on Vestibular Physical Therapy for Patients with Vestibular Disorders. Healthcare 2025, 13, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ALShammari, M.; ALSharif, D.S.; Aldaihan, M.M.; Whitney, S.L. Vestibular Rehabilitation in Saudi Arabia: Practice, Knowledge, and Beliefs of Physical Therapists. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gameiro, B.; Fonseca, A.C.; Guimarães, B.S.C. Betahistine in the Treatment of Peripheral Vertigo: An Evidence-Based Review. Egypt. J. Otolaryngol. 2024, 40, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Vanegas, G.; Castro-Moreno, C.A.; Buitrago, D. Betahistine in the Treatment of Peripheral Vestibular Vertigo: Results of a Real-Life Study in Primary Care. Ear Nose Throat J. 2020, 99, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parfenov, V.A.; Zamergrad, M.V.; Kazei, D.V.; Nauta, J. A Study of the Efficacy and Safety of a New Modified-Release Betahistine Formulation in the Treatment of Vestibular Vertigo and Meniere’s Disease. S.S. Korsakov J. Neurol. Psychiatry 2020, 120, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajenaru, O.; Roceanu, A.; Albu, S.; Zainea, V.; Pascu, A.; Georgescu, M.; Cozma, S.; Marceanu, L.G.; Muresanu, D.F. Effects and Tolerability of Betahistine in Patients with Vestibular Vertigo: Results from the Romanian Contingent of the OSVaLD Study. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2014, 7, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabaya, K.; Tamai, H.; Okajima, A.; Minakata, T.; Kondo, M.; Nakayama, M.; Iwasaki, S. Presence of Exacerbating Factors of Persistent Perceptual-postural Dizziness in Patients with Vestibular Symptoms at Initial Presentation. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2022, 7, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
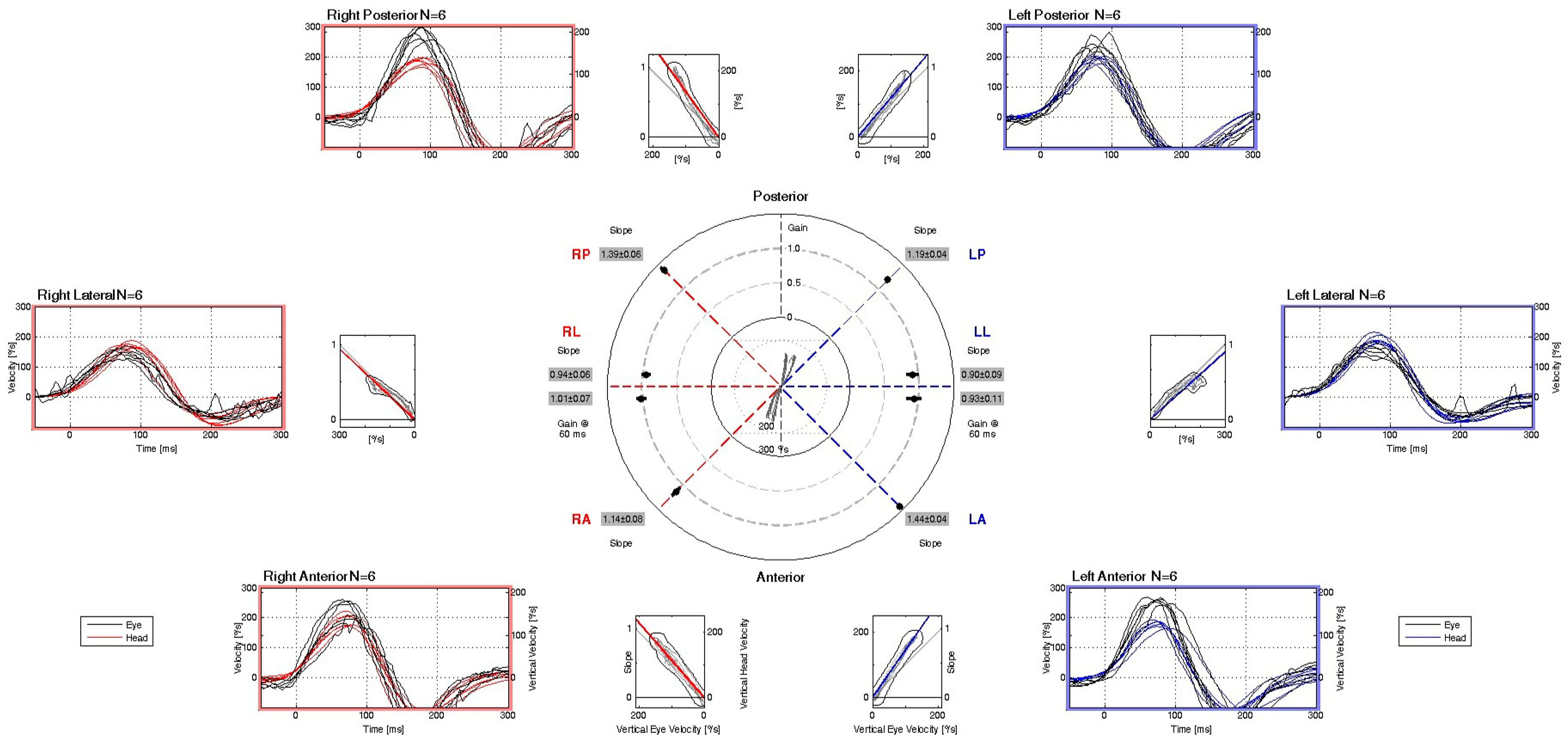
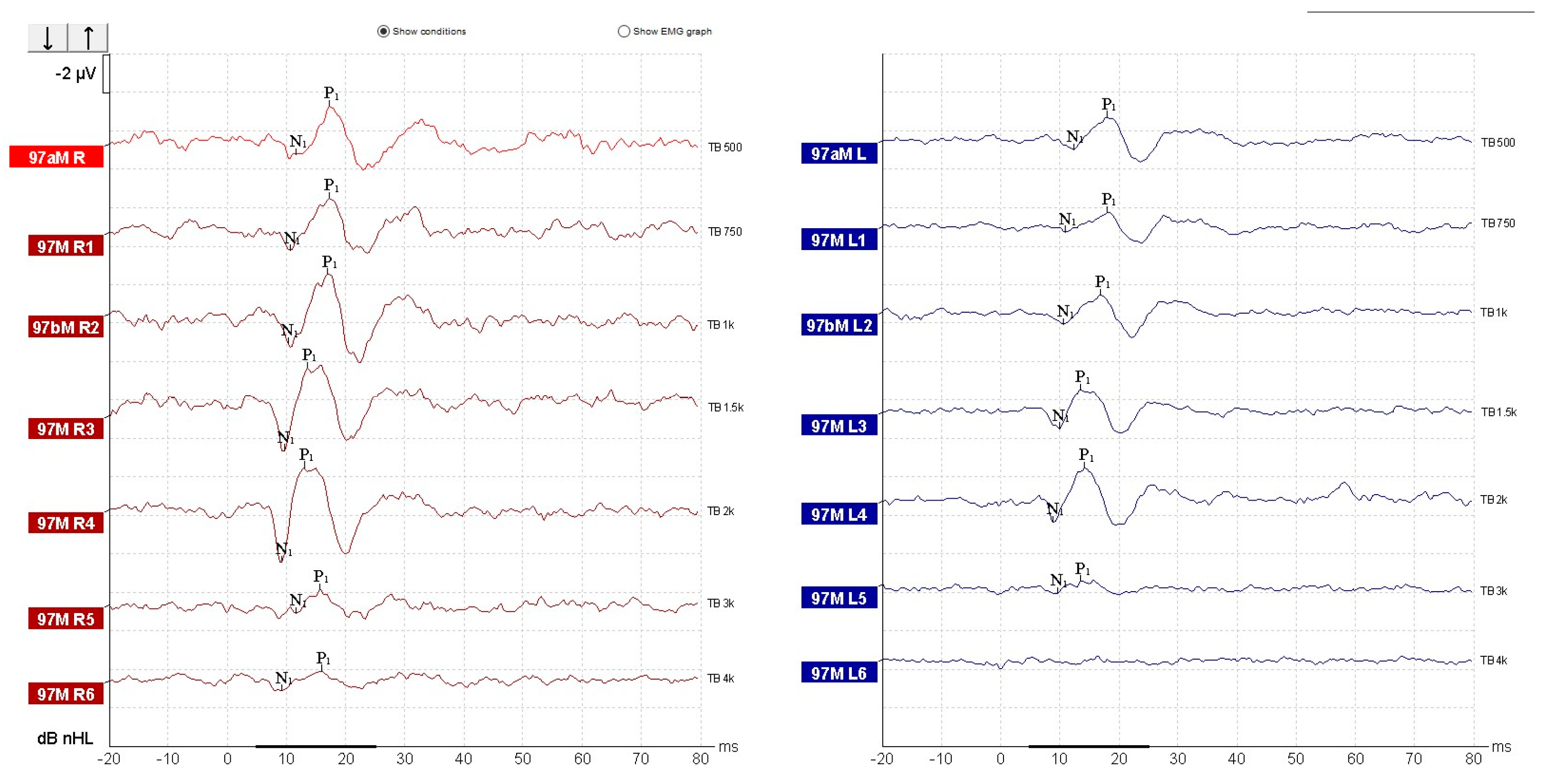
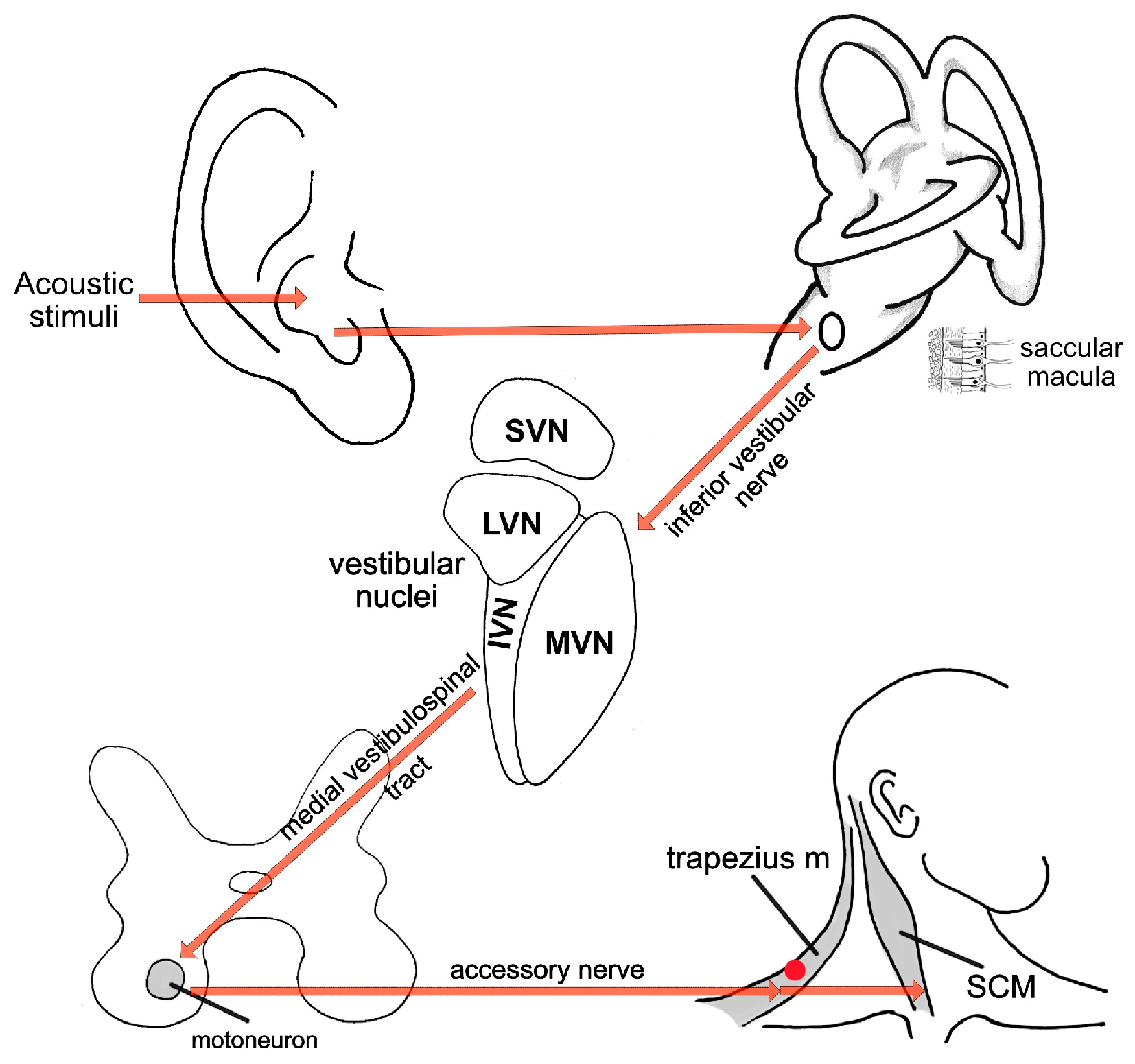
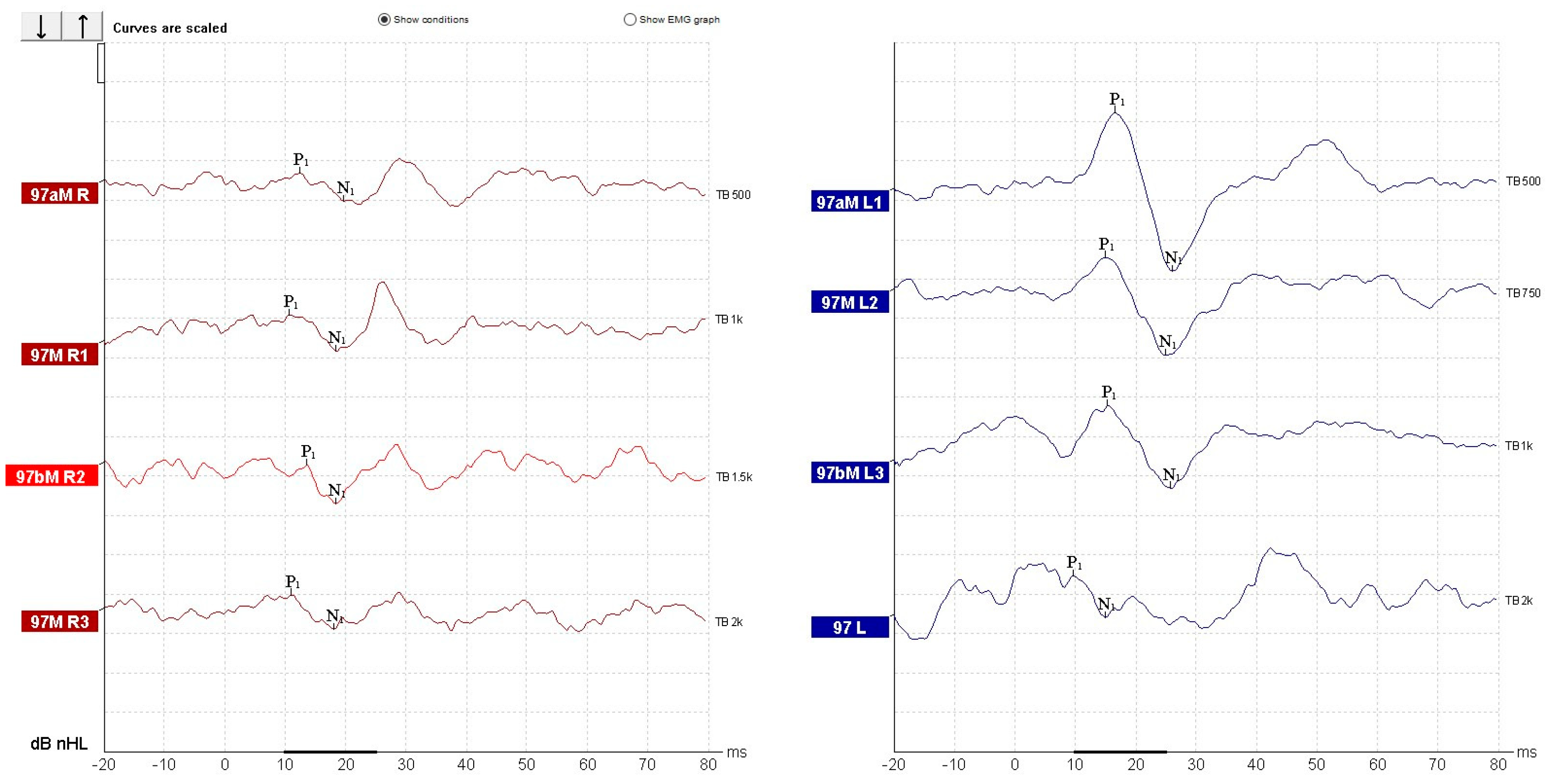
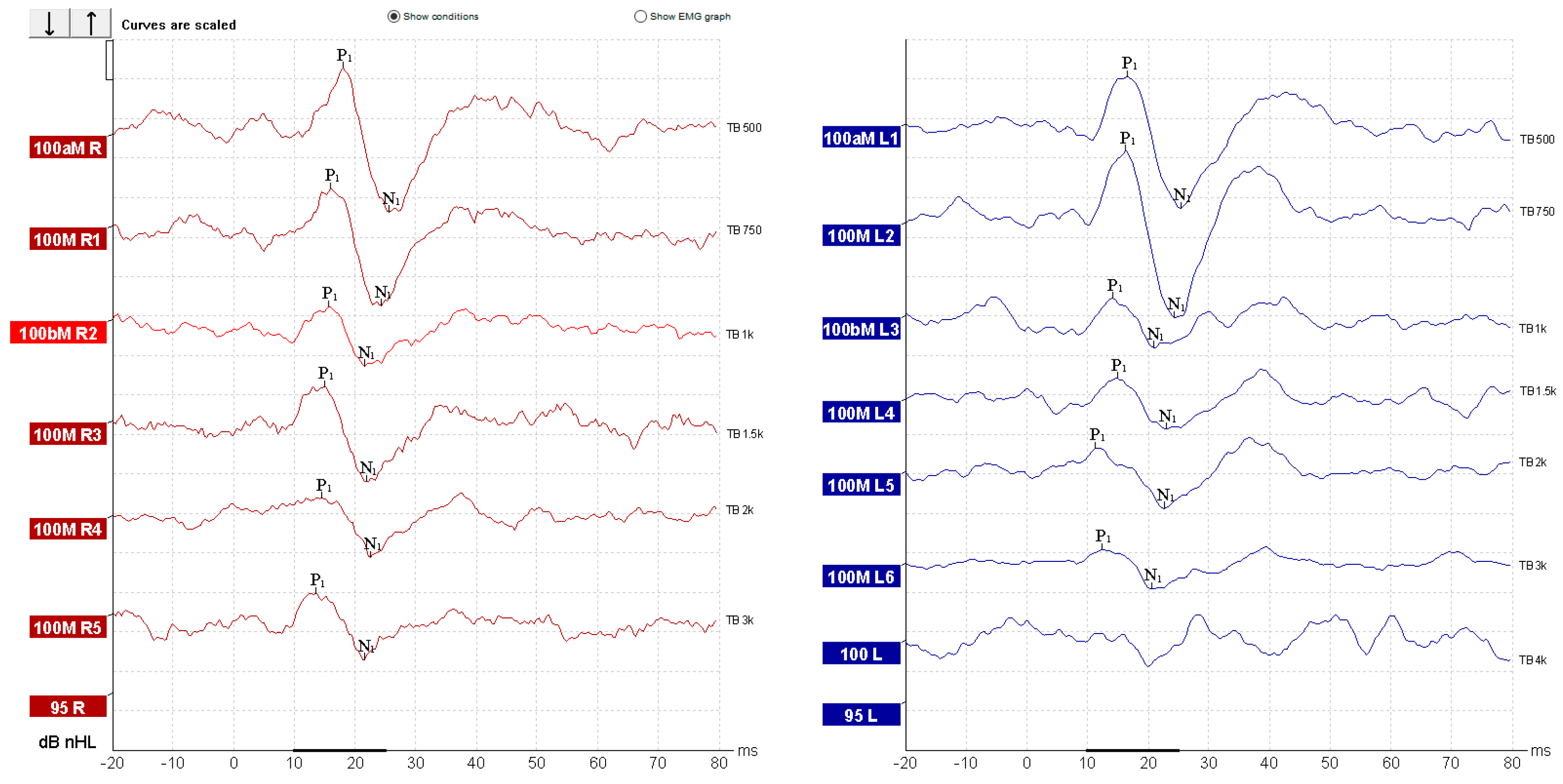
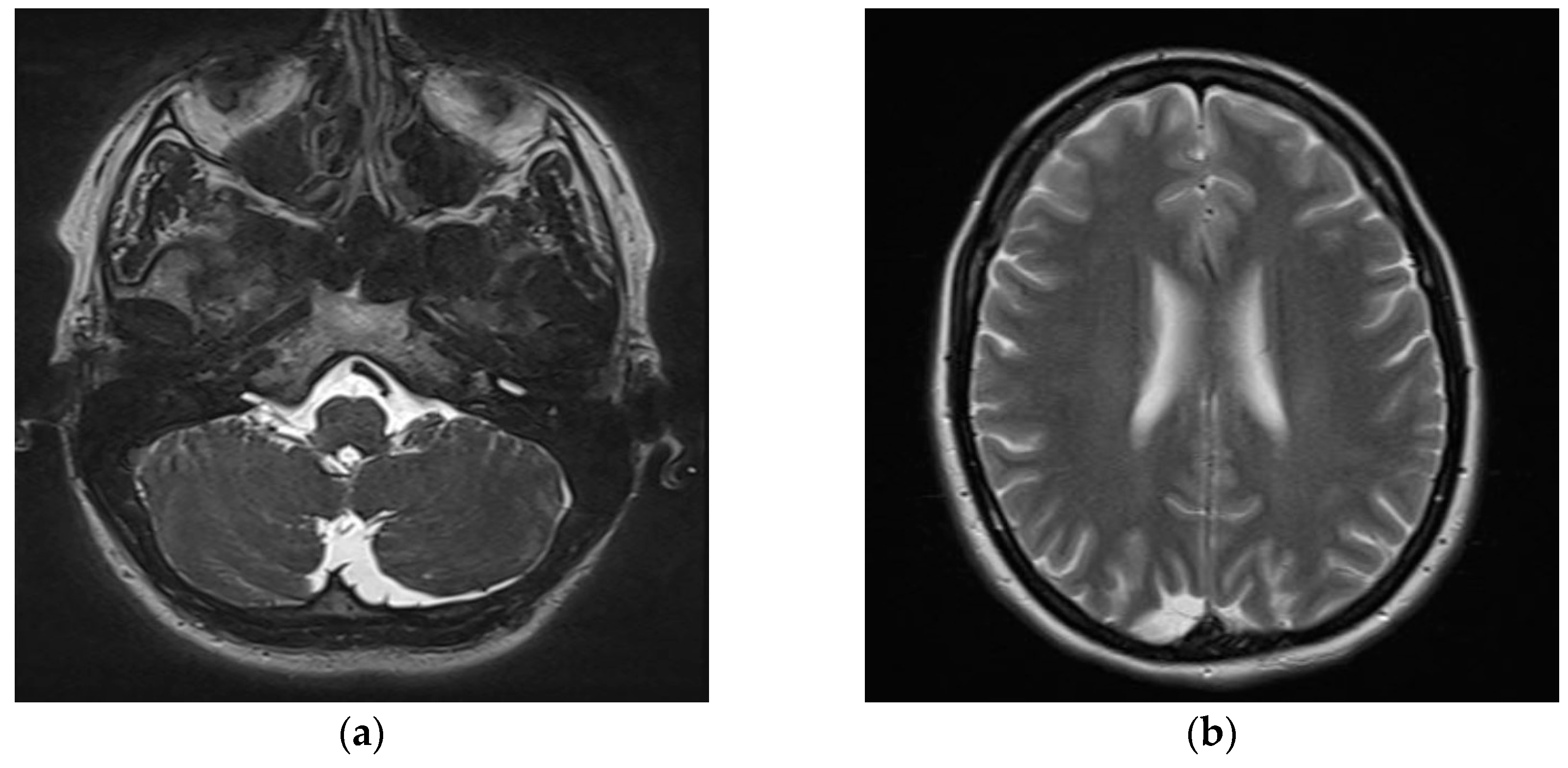
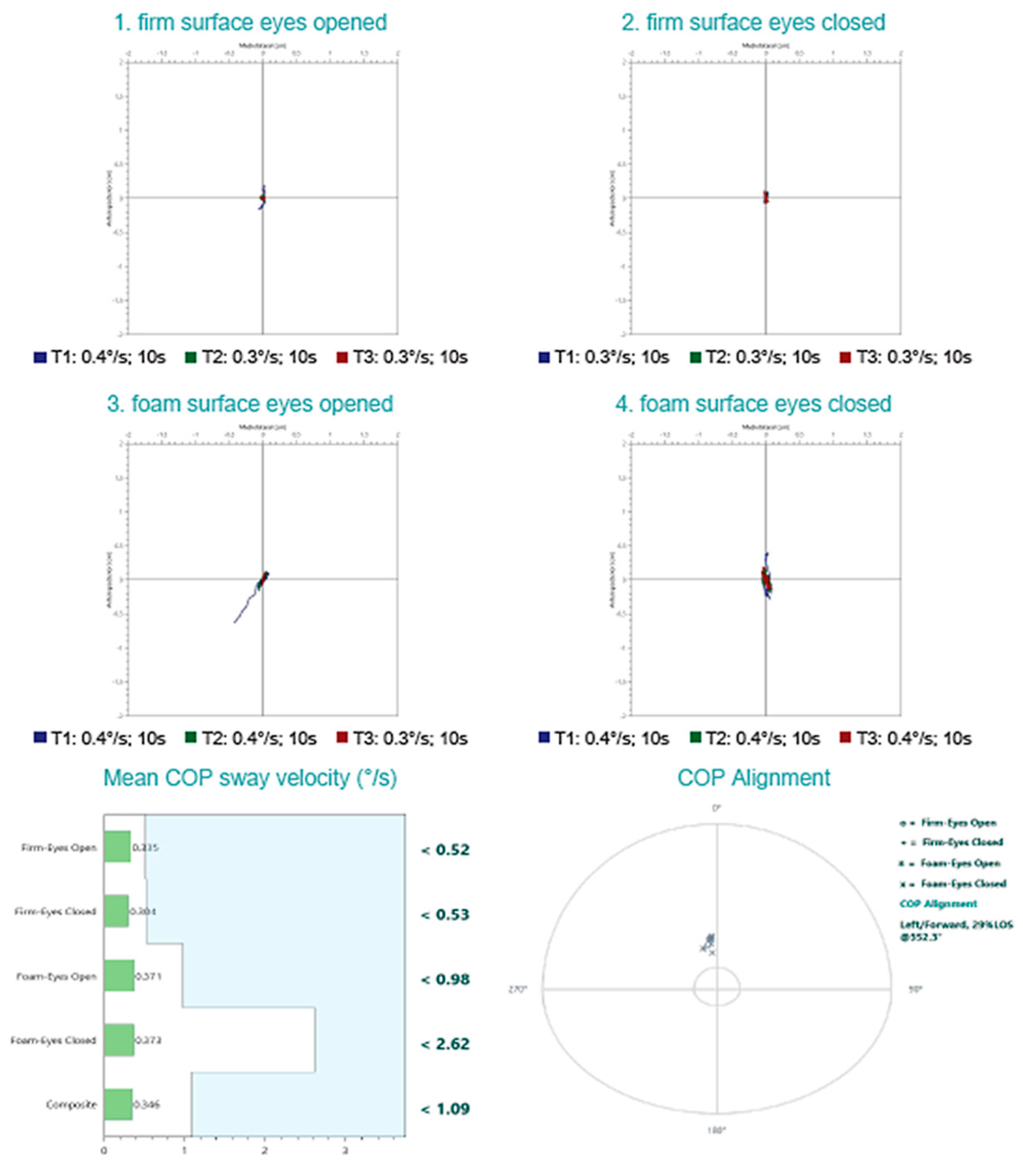
| Parameter | cVEMP | oVEMP |
|---|---|---|
| Stimulus type | Tone Burst | Tone Burst |
| Stimuli per second | 5.1/s | 5.1/s |
| Polarity | Rarefaction | Rarefaction |
| Test frequency | 500 Hz (optional: 250, 750, 1000 Hz) | 500 Hz (optional: 250, 750, 1000 Hz) |
| Rise/Fall time | 2 cycles (4.0 ms) | 2 cycles (4.0 ms) |
| Plateau | 2 cycles (4.0 ms) | 2 cycles (4.0 ms) |
| Stimulus transducer | Insert earphones (ER-3A or equivalent) | Insert earphones (ER-3A or equivalent) |
| Stimulus ear | Ipsilateral | Ipsilateral |
| Masking | Off | Off |
| Recording site | Trapezius muscle (ipsilateral) | Inferior oblique muscle (contralateral) |
| Patient position | Supine with head inclined ipsilaterally | Reclined with upward gaze |
| Intensity | 97 dB nHL and descend | 97 dB nHL and descend |
| Recording window | −20 ms to 80 ms | −20 ms to 80 ms |
| Number of stimuli | 200 | 500 |
| Filter settings | Low pass: 1000 Hz; High pass: 10 Hz (6 dB/oct) | Low pass: 1000 Hz; High pass: 10 Hz (6 dB/oct) |
| Rejection level | ±800 µV (66 dB) | ±400 µV (72 dB) |
| Display scale | 20 µV/div | 10 µV/div |
| Rejection level | ±800 µV (66 dB) | ±400 µV (72 dB) |
| Display scale | 20 µV/div | 10 µV/div |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Georgescu, M.; Popa, O.I.; Ștefănescu, H.; Necula, V.; Maniu, A.; Enache, I.; Osman, A. Diagnosis of Isolated Saccular Dysfunction Using Trapezius cVEMP: A Detailed Vestibular Assessment. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2988. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15232988
Georgescu M, Popa OI, Ștefănescu H, Necula V, Maniu A, Enache I, Osman A. Diagnosis of Isolated Saccular Dysfunction Using Trapezius cVEMP: A Detailed Vestibular Assessment. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(23):2988. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15232988
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeorgescu, Mădălina, Oana Irina Popa, Horațiu Ștefănescu, Violeta Necula, Alma Maniu, Irina Enache, and Andrei Osman. 2025. "Diagnosis of Isolated Saccular Dysfunction Using Trapezius cVEMP: A Detailed Vestibular Assessment" Diagnostics 15, no. 23: 2988. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15232988
APA StyleGeorgescu, M., Popa, O. I., Ștefănescu, H., Necula, V., Maniu, A., Enache, I., & Osman, A. (2025). Diagnosis of Isolated Saccular Dysfunction Using Trapezius cVEMP: A Detailed Vestibular Assessment. Diagnostics, 15(23), 2988. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15232988







