Multimodal Deep Learning-Based Classification of Breast Non-Mass Lesions Using Gray Scale and Color Doppler Ultrasound
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Ultrasound Examination
2.2. NML BUS Dataset Construction and Image Preprocessing
2.3. Partition of Training and Testing Sets
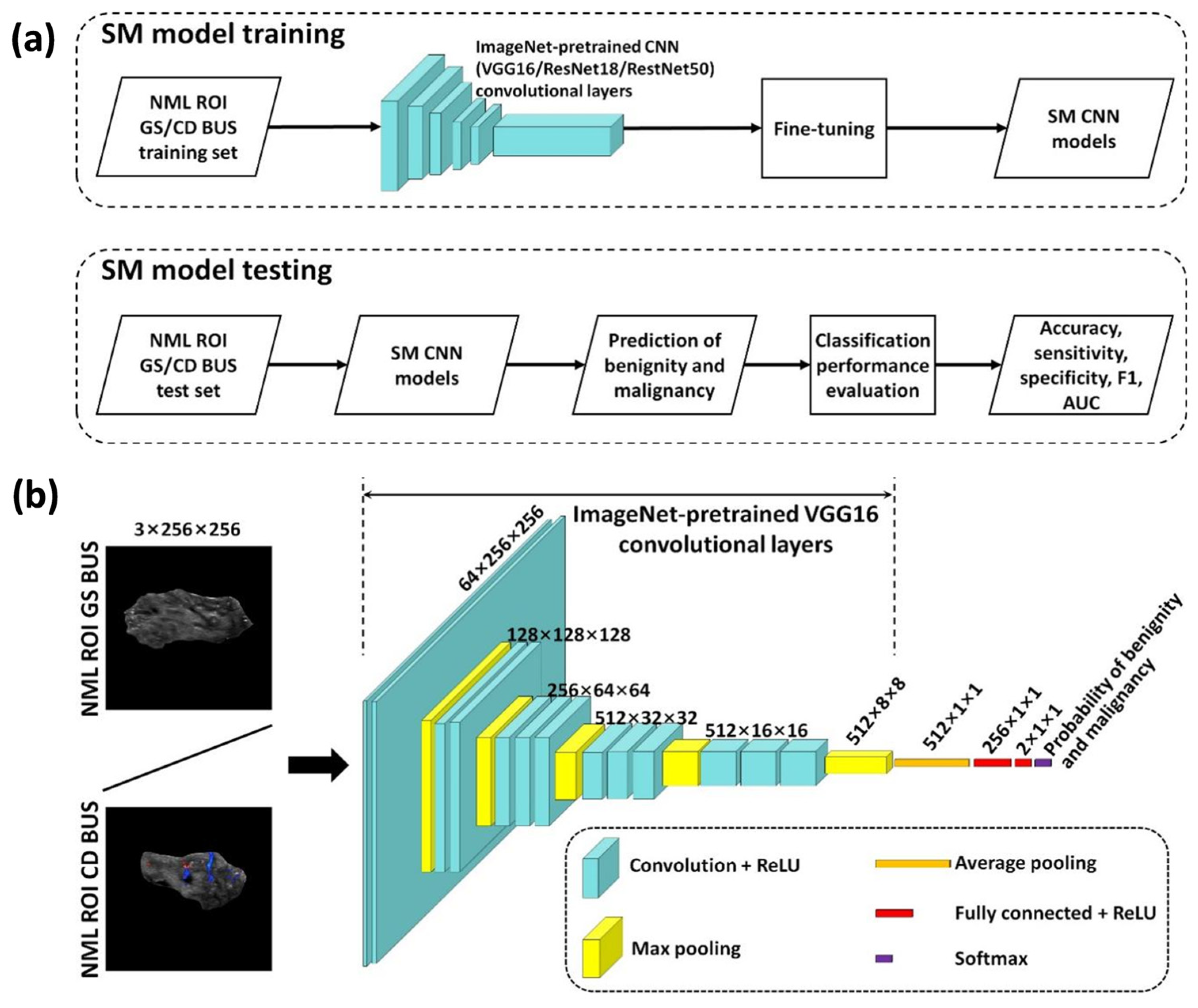
2.4. Single-Modality Deep Learning-Based NML Classification
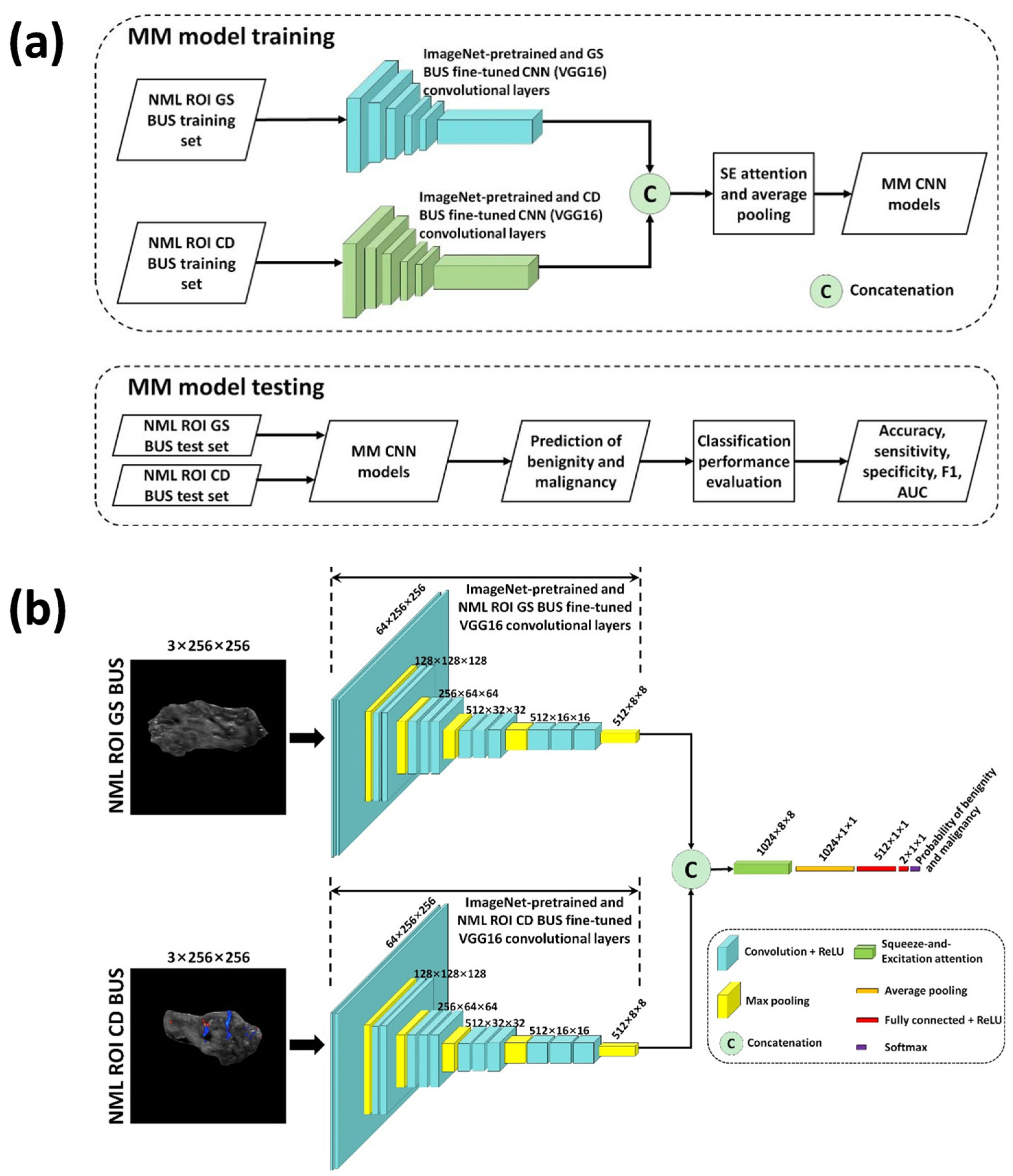
2.5. Multimodal Deep Learning-Based NML Classification
2.6. Experimental Setup
2.7. Classification Performance Evaluation
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
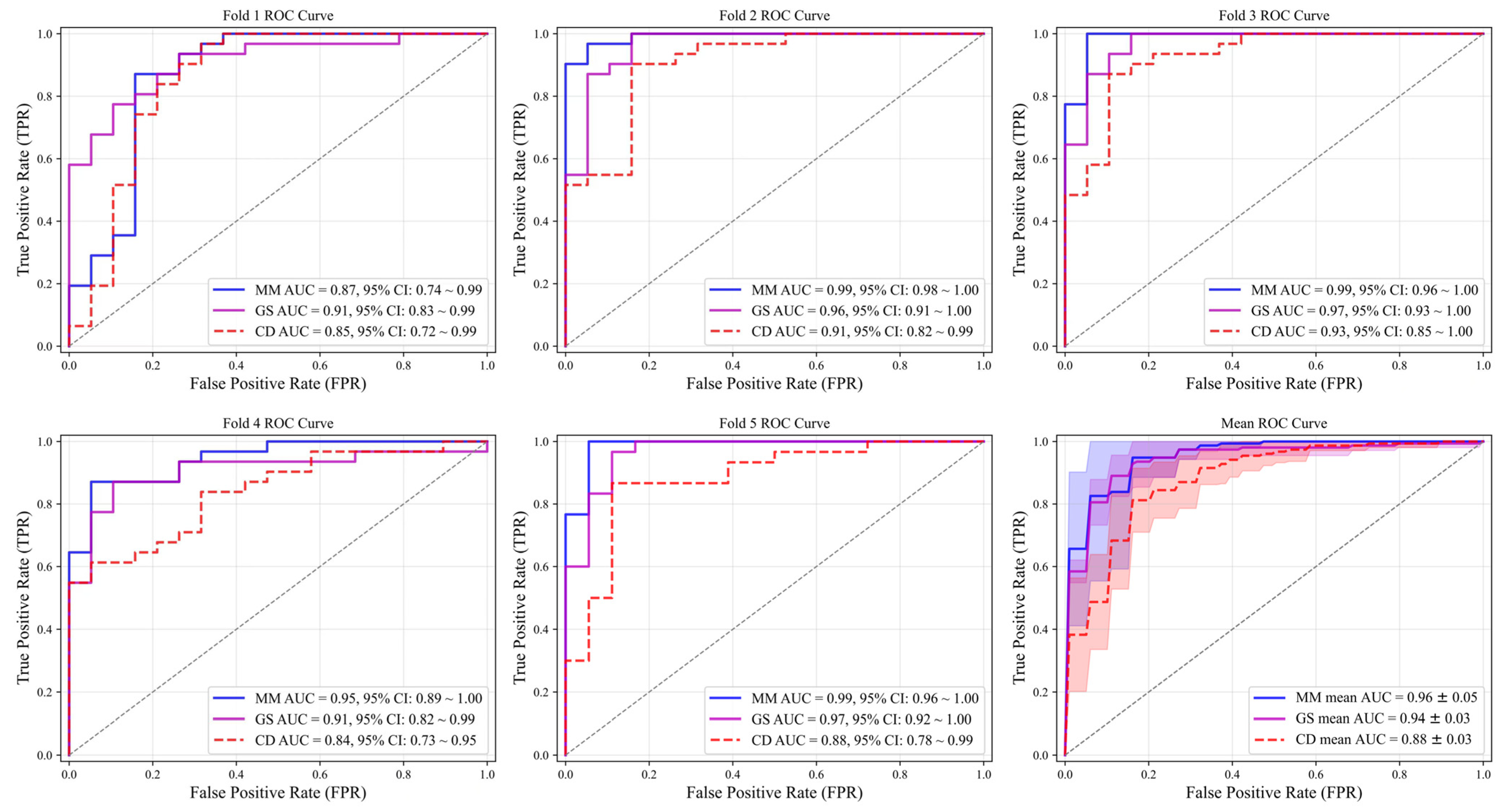
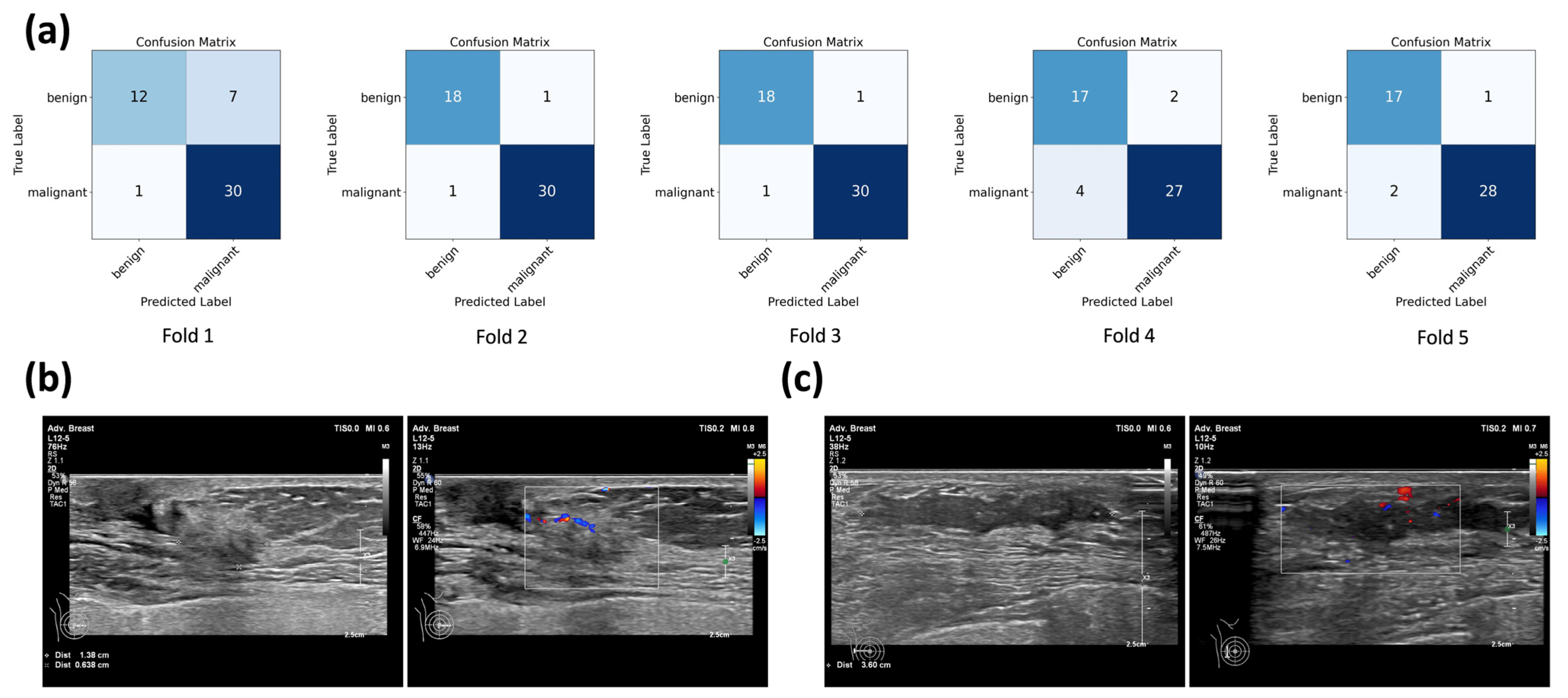
3.2. Performance of Single-Modality and Multimodal CNN Models
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BUS | Breast ultrasound |
| ACR | American College of Radiology |
| BI-RADS® | Breast imaging and reporting system |
| NML | Non-mass lesion |
| AI | Artificial intelligence |
| CNN | Convolutional neural network |
| LAP | Linear-array probe |
| ROI | Region of interest |
| ReLU | Rectified linear unit |
| GS | Grayscale |
| CD | Color Doppler |
| MM | Multimodal |
| SGDM | Stochastic gradient descent with momentum |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| CAD | Computer-aided diagnosis |
| SE | Strain elastography |
| CEUS | Contrast-enhanced ultrasound |
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.S.; Tsunoda, H.; Moon, W.K. Nonmass Lesions on Breast US: An International Perspective on Clinical Use and Outcomes. J. Breast Imaging 2024, 6, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, R.; Rositch, A.F.; Shakoor, D.; Ambinder, E.; Pool, K.L.; Pollack, E.; Mollura, D.J.; Mullen, L.A.; Harvey, S.C. Ultrasound for Breast Cancer Detection Globally: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Glob. Oncol. 2019, 5, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Li, N.; Li, M.; Wan, W.B. Non-mass-like lesions on breast ultrasound: Classification and correlation with histology. Radiol. Med. 2015, 120, 905–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, R.; Watanabe, H.; Mihara, Y.; Yamaguchi, M.; Tanaka, M. Histopathology of non-mass-like breast lesions on ultrasound. J. Med. Ultrason. 2023, 50, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunoda, H.; Moon, W.K. Beyond BI-RADS: Nonmass Abnormalities on Breast Ultrasound. Korean J. Radiol. 2024, 25, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibusawa, M.; Nakayama, R.; Okanami, Y.; Kashikura, Y.; Imai, N.; Nakamura, T.; Kimura, H.; Yamashita, M.; Hanamura, N.; Ogawa, T. The usefulness of a computer-aided diagnosis scheme for improving the performance of clinicians to diagnose non-mass lesions on breast ultrasonographic images. J. Med. Ultrason. 2016, 43, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xiao, X.; Xu, X.; Liang, M.; Wu, H.; Ruan, J.; Luo, B. Non-Mass Breast Lesions on Ultrasound: Feature Exploration and Multimode Ultrasonic Diagnosis. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2018, 44, 1703–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Tian, H.; Wu, H.; Huang, Z.; Yang, K.; Li, J.; Luo, Y.; Shi, S.; Cui, C.; Xu, J.; et al. Artificial intelligence for non-mass breast lesions detection and classification on ultrasound images: A comparative study. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2023, 23, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gökmen Inan, N.; Kocadağlı, O.; Yıldırım, D.; Meşe, İ.; Kovan, Ö. Multi-class classification of thyroid nodules from automatic segmented ultrasound images: Hybrid ResNet based UNet convolutional neural network approach. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2024, 243, 107921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Qu, S.; Wang, Z.; Li, L.; An, X.; Cong, Z. The study on ultrasound image classification using a dual-branch model based on Resnet50 guided by U-net segmentation results. BMC Med. Imaging 2024, 24, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.C.; Jin, P.F.; Bao, J.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, X. Thyroid ultrasound image classification using a convolutional neural network. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaivas, M.; Blaivas, L. Are All Deep Learning Architectures Alike for Point-of-Care Ultrasound?: Evidence From a Cardiac Image Classification Model Suggests Otherwise. J. Ultrasound Med. 2020, 39, 1187–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.J.; Kai, L.; Li, F.-F. ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Obuchowski, N.A.; Bullen, J.A. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves: Review of methods with applications in diagnostic medicine. Phys. Med. Biol. 2018, 63, 07tr01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.W.; Park, S.; Shon, I.; Kim, M.J.; Han, B.K.; Ko, E.Y.; Ko, E.S.; Shin, J.H.; Kwon, M.R.; Choi, J.S. Non-mass lesions detected by breast US: Stratification of cancer risk for clinical management. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 1693–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, S.M.; Choi, W.J.; Han, B.K.; Kim, H.H.; Moon, W.K.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, K.; Yoen, H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, H.; et al. Assessment of Nonmass Lesions Detected with Screening Breast US Based on Mammographic Findings. Radiology 2024, 313, e240043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.M.; Cha, J.H.; Kim, H.H.; Shin, H.J.; Chae, E.Y.; Choi, W.J.; Eom, H.J.; Kim, H.J. Prevalence and outcomes of nonmass lesions detected on screening breast ultrasound based on ultrasound features. J. Ultrasound 2025, 28, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Kong, P.; Liu, D.; He, S.; Zhang, X. Non-mass-type ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast on ultrasound: Features and pathological analysis. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2024, 20, 665–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elayat, G.; Selim, A. Angiogenesis in breast cancer: Insights and innovations. Clin. Exp. Med. 2024, 24, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, W.; Sun, N.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Q. Diagnostic value of multimodal ultrasound strategies in the differentiation of non-mass-like breast lesions. J. Clin. Ultrasound 2023, 51, 848–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Wang, T.; Li, F.; Jia, C.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, X.; Bai, M. Non-mass Breast Lesions: Could Multimodal Ultrasound Imaging Be Helpful for Their Diagnosis? Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, X.; Hao, S.; Yao, J.; Zhong, W.; Zhi, H. B-Mode Ultrasound Combined with Color Doppler and Strain Elastography in the Diagnosis of Non-mass Breast Lesions: A Prospective Study. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2017, 43, 2582–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, L.; Xu, S. Incremental Value of Shear Wave Elastography and Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound in the Differential Diagnosis of Breast Non-Mass-Like Lesions. Int. J. Womens Health 2024, 16, 2221–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuno, T.; Watanabe, T.; Yamaguchi, T.; Konno, S.; Takaki, R.; Watanabe, R.; Ban, K.; Hirokaga, K.; Tsuruoka, M.; Morita, T. Usefulness of color Doppler and strain elastography adjunctive to B-mode ultrasonography in the diagnosis of non-mass abnormalities of the breast: Results of the BC-07 multicenter study of 385 cases. J. Med. Ultrason. 2025, 52, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.X.; Song, Y.; Zhang, Y.H.; Qing, H.M. Value of Ultrasonic Elastography and Conventional Ultrasonography in the Differential Diagnosis of Non-Mass-like Breast Lesions. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2019, 45, 1358–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.S.; Han, B.K.; Ko, E.Y.; Ko, E.S.; Shin, J.H.; Kim, G.R. Additional diagnostic value of shear-wave elastography and color Doppler US for evaluation of breast non-mass lesions detected at B-mode US. Eur. Radiol. 2016, 26, 3542–3549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurt, S.A.; Taskin, F.; Kayadibi, Y.; Ozturk, T.; Adaletli, İ.; Icten, G.E. Role of Combining Grayscale Findings With Superb Microvascular Imaging and Shear Wave Elastography in Standardization and Management of NON-MASS Breast Lesions. Ultrasound Q. 2024, 40, e00689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, K.H.; Jung, H.K.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, H.; Yoon, J.H. Potential role of shear-wave ultrasound elastography for the differential diagnosis of breast non-mass lesions: Preliminary report. Eur. Radiol. 2014, 24, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Li, Y.; Wan, W.B.; Li, N.; Tang, J. Shear-Wave Elastography: Could it be Helpful for the Diagnosis of Non-Mass-Like Breast Lesions? Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2017, 43, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, H.; Pourbagher, A.; Ozen, M. The role of Shear-Wave elastography in the differentiation of benign and malign non-mass lesions of the breast. Ann. Ital. Chir. 2018, 89, 385–391. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.Y.; Choi, J.S.; Han, B.K.; Ko, E.Y.; Ko, E.S. Shear wave elastography in the diagnosis of breast non-mass lesions: Factors associated with false negative and false positive results. Eur. Radiol. 2017, 27, 3788–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.; Li, W.; Gao, W.; Liu, M.; Song, D.; Dong, Y.; Xu, J.; Dong, F. Diagnostic performance of elastography for breast non-mass lesions: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Radiol. 2021, 144, 109991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Jin, L.; Li, G.; Jia, C.; Shi, Q.; Du, L.; Wu, R. The role of contrast-enhanced ultrasound in the diagnosis of malignant non-mass breast lesions and exploration of diagnostic criteria. Br. J. Radiol. 2021, 94, 20200880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.Y.; Du, Y.C.; Zhao, L.; Hu, W.J.; Bai, Y.; Chen, A.; Du, L.F.; Li, F. The kinetic quantitative characteristics of non-mass breast lesions with contrast-enhanced ultrasound: A prospective study. Br. J. Radiol. 2023, 96, 20221002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Fold | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | F1 | ROC | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GS | CD | GS | CD | GS | CD | GS | CD | GS | CD | |
| ResNet50 | ||||||||||
| 1 | 85.99% | 71.99% | 93.54% | 83.87% | 73.68% | 52.63% | 0.89 | 0.79 | 0.94 | 0.74 |
| 2 | 89.99% | 65.99% | 96.77% | 77.41% | 78.94% | 47.36% | 0.92 | 0.74 | 0.95 | 0.71 |
| 3 | 83.99% | 69.99% | 83.87% | 70.96% | 84.21% | 68.42% | 0.87 | 0.75 | 0.95 | 0.75 |
| 4 | 71.99% | 68.00% | 67.74% | 74.19% | 78.94% | 57.89% | 0.75 | 0.74 | 0.82 | 0.66 |
| 5 | 79.16% | 58.33% | 76.66% | 53.33% | 83.33% | 66.66% | 0.82 | 0.62 | 0.93 | 0.66 |
| Mean | 82.23% | 66.86% | 83.72% | 71.95% | 79.82% | 58.59% | 0.85 | 0.73 | 0.93 | 0.70 |
| ResNet18 | ||||||||||
| 1 | 85.99% | 65.99% | 96.77% | 77.41% | 68.42% | 47.36% | 0.90 | 0.74 | 0.94 | 0.75 |
| 2 | 89.99% | 68.00% | 93.54% | 83.87% | 84.21% | 42.10% | 0.92 | 0.76 | 0.96 | 0.77 |
| 3 | 81.99% | 77.99% | 77.41% | 93.54% | 89.47% | 52.63% | 0.84 | 0.84 | 0.93 | 0.87 |
| 4 | 81.99% | 69.99% | 87.09% | 83.87% | 73.68% | 47.36% | 0.86 | 0.78 | 0.86 | 0.77 |
| 5 | 85.41% | 72.91% | 83.33% | 83.33% | 88.88% | 55.55% | 0.88 | 0.79 | 0.96 | 0.84 |
| Mean | 85.08% | 70.98% | 87.63% | 84.40% | 80.93% | 49.00% | 0.88 | 0.78 | 0.93 | 0.80 |
| VGG16 | ||||||||||
| 1 | 81.99% | 79.99% | 93.54% | 83.87% | 63.15% | 73.68% | 0.87 | 0.84 | 0.91 | 0.85 |
| 2 | 91.99% | 83.99% | 96.77% | 93.54% | 84.21% | 68.42% | 0.94 | 0.88 | 0.96 | 0.91 |
| 3 | 94.00% | 85.99% | 100.00% | 87.09% | 84.21% | 84.21% | 0.95 | 0.89 | 0.97 | 0.93 |
| 4 | 83.99% | 75.99% | 87.09% | 87.09% | 78.94% | 57.89% | 0.87 | 0.82 | 0.91 | 0.84 |
| 5 | 93.75% | 85.41% | 96.66% | 83.33% | 88.88% | 88.88% | 0.95 | 0.88 | 0.97 | 0.88 |
| Mean | 89.14% | 82.28% | 94.81% | 86.98% | 79.88% | 74.61% | 0.92 | 0.86 | 0.94 | 0.88 |
| Benign | Malignant | Total | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | 94 | 154 | 248 | |||
| Age | 44.6 ± 9.5 (95%CI: 42.7—46.6) | 49.9 ± 12.1 (95%CI: 48.0—51.9) | 47.9 ± 11.5 | <0.001 | ||
| ≤40 years | 36 (38.3%) | 34 (22.1%) | 70 (28.2%) | 0.006 | ||
| >40 years | 58 (61.7%) | 120 (77.9%) | 178 (71.8%) | |||
| Clinical symptoms | ||||||
| Mass | 16 (17.0%) | 50 (32.5%) | 66 (26.6%) | 0.008 | ||
| Pain | 5 (5.3%) | 12 (7.8%) | 17 (6.9%) | 0.455 | ||
| Nipple discharge | 5 (5.3%) | 24 (15.6%) | 29 (11.7%) | 0.015 | ||
| Nipple retraction | 0 (0%) | 4 (2.6%) | 4 (1.6%) | 0.291 | ||
| Skin redness | 1 (1.1%) | 4 (2.6%) | 5 (2.0%) | 0.713 | ||
| Asymptomatic | 68 (72.3%) | 78 (50.6%) | 146 (58.9%) | 0.001 | ||
| NML size (cm) | 2.1 ± 1.1 | 3.2 ± 1.7 | 2.8 ± 1.6 | <0.001 | ||
| Laterality | 0.314 | |||||
| Right | 39 (41.5%) | 74 (48.1%) | 113 (45.6%) | |||
| Left | 55 (58.5%) | 80 (51.9%) | 135 (54.4%) | |||
| Location | 0.929 | |||||
| UIQ | 13 (13.8%) | 22 (14.3%) | 35 (14.1%) | |||
| LIQ | 6 (6.4%) | 9 (5.8%) | 15 (6.0%) | |||
| UOQ | 39 (41.5%) | 57 (37.0%) | 96 (38.7%) | |||
| LOQ | 10 (10.6%) | 24 (15.6%) | 34 (13.7%) | |||
| UOQ-UIQ | 12 (12.8%) | 16 (10.4%) | 28 (11.3%) | |||
| UOQ-LOQ | 10 (10.6%) | 15 (9.7%) | 25 (10.1%) | |||
| LOQ-LIQ | 1 (1.1%) | 1 (0.6%) | 2 (0.8%) | |||
| UIQ–LIQ | 2 (2.1%) | 6 (3.9%) | 8 (3.2%) | |||
| CZ | 1 (1.1%) | 4 (2.6%) | 5 (2.0%) | |||
| Pathological type | ||||||
| Glandular disease | 48 (51.1%) | DCIS | 57 (37.0%) | |||
| Intraductal papilloma | 16 (17.0%) | DCIS with microinvasion | 39 (25.3%) | |||
| Fibroadenoma | 15 (16.0%) | Invasive ductal carcinoma | 49 (31.8%) | |||
| Mammary tissue | 12 (12.8%) | Lobular carcinoma in situ | 1 (0.6%) | |||
| Fibrocystic disease | 2 (2.1%) | Invasive lobular carcinoma | 8 (5.2%) | |||
| Hamartoma | 1 (1.1%) | |||||
| Fold | Model | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | F1 | AUC (95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 83.99% | 96.77% | 63.15% | 0.88 | 0.87 (0.74–0.99) | |
| 2 | 95.99% | 96.77% | 94.73% | 0.97 | 0.99 (0.98–1.00) | |
| 3 | 95.99% | 96.77% | 94.73% | 0.97 | 0.99 (0.96–1.00) | |
| 4 | 88.00% | 87.09% | 89.47% | 0.90 | 0.95 (0.89–1.00) | |
| 5 | 93.75% | 93.33% | 94.44% | 0.95 | 0.99 (0.96–1.00) | |
| Mean | to | 91.54% | 94.15% | 87.30% | 0.93 | 0.96 ± 0.05 |
| Model | Mean Accuracy | Mean Sensitivity | Mean Specificity | Mean F1 | Mean AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| to | 89.14% | 94.81% | 79.88% | 0.92 | 0.94 |
| to | 82.28% | 86.98% | 74.61% | 0.86 | 0.88 |
| to | 91.54% | 94.15% | 87.30% | 0.93 | 0.96 |
| Study | Year | Method | Modality | Patients Number | With Cross-Validations | NML Classification Performance | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | ||||||
| Shibusawa et al. [7] | 2016 | SM ML | GS | 97 | No | 0.78 | NR | NR | NR |
| Zhang et al. [8] | 2018 | MM ML | GS + CD + SE + CEUS | 71 | No | NR | 87.3% | 95.0% | 77.4% |
| Li et al. [9] | 2023 | SM DL | GS | 228 | No | 0.84 | 70.5% | 80.3% | 74.6% |
| This study | 2025 | MM DL | GS + CD | 248 | Yes | 0.96 | 91.5% | 94.2% | 87.3% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, T.; Zhu, Q.; Yu, T.; Leonov, D.; Shi, X.; Zhou, Z.; Lv, K.; Xiao, M.; Li, J. Multimodal Deep Learning-Based Classification of Breast Non-Mass Lesions Using Gray Scale and Color Doppler Ultrasound. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2967. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15232967
Wang T, Zhu Q, Yu T, Leonov D, Shi X, Zhou Z, Lv K, Xiao M, Li J. Multimodal Deep Learning-Based Classification of Breast Non-Mass Lesions Using Gray Scale and Color Doppler Ultrasound. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(23):2967. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15232967
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Tianjiao, Qingli Zhu, Tianxiang Yu, Denis Leonov, Xinran Shi, Zhuhuang Zhou, Ke Lv, Mengsu Xiao, and Jianchu Li. 2025. "Multimodal Deep Learning-Based Classification of Breast Non-Mass Lesions Using Gray Scale and Color Doppler Ultrasound" Diagnostics 15, no. 23: 2967. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15232967
APA StyleWang, T., Zhu, Q., Yu, T., Leonov, D., Shi, X., Zhou, Z., Lv, K., Xiao, M., & Li, J. (2025). Multimodal Deep Learning-Based Classification of Breast Non-Mass Lesions Using Gray Scale and Color Doppler Ultrasound. Diagnostics, 15(23), 2967. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15232967








