Functional and Anatomical Micro-Structural Recovery of Idiopathic Macular Holes Following the Inverted Internal Limiting Membrane Flap Technique: A Long-Term Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Inclusion Criteria and Exclusion Criteria
2.2. Primary Outcomes, Secondary Outcomes and Data Collections
2.3. Surgical Procedure
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. General Data Analysis and Primary Outcomes
3.2. Comparison of MHs of Different Sizes (<200 µm vs. ≥200 µm)
3.3. Secondary Outcomes: Functional Recovery
3.4. Secondary Outcomes: Micro-Structural Recovery
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Knapp, H. Ueber Isolirte zerreissungen der aderhaut infolge von traumen auf augapfel. Arch. Augenheilkd. 1869, 1, 6–29. [Google Scholar]
- Gass, J.D. Idiopathic senile macular hole. It’s early stages and pathogenesis. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1988, 106, 629–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gass, J.D.; Joondeph, B.C. Observations concerning patients with suspected impending macular holes. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1990, 109, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gass, J.D. Reappraisal of biomicroscopic classification of stages of development of a macular hole. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1995, 119, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonnell, P.J.; Fine, S.L.; Hillis, A.I. Clinical features of idiopathic macular cysts and holes. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1982, 93, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojtkowski, M.; Srinivasan, V.; Fujimoto, J.G.; Ko, T.; Schuman, J.S.; Kowalczyk, A.; Duker, J.S. Three-dimensional retinal imaging with high-speed ultrahigh-resolution optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology 2005, 112, 1734–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puliafito, C.A.; Hee, M.R.; Lin, C.P.; Reichel, E.; Schuman, J.S.; Duker, J.S.; Izatt, J.A.; Swanson, E.A.; Fujimoto, J.G. Imaging of macular diseases with optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology 1995, 102, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwa, T.; Terasaki, H.; Kondo, M.; Piao, C.-H.; Suzuki, T.; Miyake, Y. Function and morphology of macula before and after removal of idiopathic epiretinal membrane. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2003, 44, 1652–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The International Vitreomacular Traction Study Group. The role of vitreomacular adhesions and traction in macular hole formation and prognosis. Ophthalmology 2013, 120, 22–28. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, N.E.; Wendel, R.E. Vitreous surgery for idiopathic macular holes. Results of a pilot study. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1991, 109, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiteri, C.K.; Lois, N.; Scott, N.W.; Burr, J.; Cook, J.; Boachie, C.; Tadayoni, R.; la Cour, M.; Christensen, U.; Kwok, A.K. Vitrectomy with internal limiting membrane peeling versus no peeling for idiopathic full-thickness macular hole. Ophthalmology 2014, 121, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckardt, C.; Eckardt, U.; Groos, S.; Luciano, L.; Reale, E. Removal of the internal limiting membrane in macular holes. Clinical and morphological findings. Ophthalmologe 1997, 94, 545–551. (In German) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalewska, Z.; Michalewski, J.; Nawrocki, J. Macular hole closure after vitrectomy: The inverted flap technique. Retin. Today 2009, 3, 73–74. [Google Scholar]
- Michalewska, Z.; Michalewski, J.; Adelman, R.A.; Nawrocki, J. Inverted internal limiting membrane flap technique for large macular holes. Ophthalmology 2010, 117, 2018–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalewska, Z.; Michalewski, J.; Dulczewska-Cichecka, K.; Nawrocki, J. Inverted internal limiting membrane flap technique for surgical repair of myopic macular holes. Retina 2014, 34, 664–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frangieh, G.T.; Green, W.R.; Engel, H.M. A histopathologic study of macular cysts and holes. Retina 2005, 25, 311–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiode, Y.; Morizane, Y.; Matoba, R.; Hirano, M.; Doi, S.; Toshima, S.; Takahashi, K.; Araki, R.; Kanzaki, Y.; Hosogi, M.; et al. The role of inverted internal limiting membrane flap in macular hole closure. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2017, 58, 4847–4855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boninska, K.; Nawrocki, J.; Michalewska, Z. Mechanism of “flap closure” after the inverted internal limiting membrane flap technique. Retina 2018, 38, 2184–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, R.E.; Sousa, D.C.; Leal, I.; Faria, M.Y.; Marques-Neves, C. Complete ILM Peeling Versus Inverted Flap Technique for Macular Hole Surgery: A Meta-Analysis. Ophthalmic Surg. Lasers Imaging Retin. 2020, 51, 187-A2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalewska, Z.; Michalewski, J.; Dulczewska-Cichecka, K.; Adelman, R.A.; Nawrocki, J. Temporal inverted internal limiting membrane flap technique versus classic inverted internal limiting membrane flap technique: A comparative study. Retina 2015, 35, 1844–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casini, G.; Mura, M.; Figus, M.; Loiudice, P.; Peiretti, E.; De Cillà, S.; Fuentes, T.; Nasini, F. Inverted internal limiting membrane flap technique for macular hole surgery without extra manipulation of the flap. Retina 2017, 37, 2138–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, S.; Tartaro, R.; Barca, F.; Caporossi, T.; Bacherini, D.; Giansanti, F. Internal limiting membrane peeling versus inverted flap technique for treatment of full-thickness macular holes: A comparative study in a large series of patients. Retina 2018, 38, S73–S78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanan, R.; Singh, S.R.; Taylor, S.; Berrocal, M.H.; Chhablani, J.; Tyagi, M.; Ohno-Matsui, K.; Pappuru, R.R.; Apte, R.S. Surgical outcomes after inverted internal limiting membrane flap versus conventional peeling for very large macular holes. Retina 2019, 39, 1465–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, H.D.; Liu, L.; Wang, C.T.; Chen, K.J.; Wu, W.C.; Hwang, Y.S.; Chen, Y.P.; Kang, E.Y.C.; Chen, Y.H.; Yeung, L.; et al. Single-Layer Inverted Internal Limiting Membrane Flap Versus Conventional Peel for Small- or Medium-Sized Full-Thickness Macular Holes. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 235, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yang, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, Z.; Ke, B.; Zhang, K.; Wu, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, W. Differences in anatomical and visual outcomes among three internal limiting membrane techniques treating extra-large idiopathic macular holes. Retina 2023, 43, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumann, C.; Kaye, S.; Iannetta, D.; Sultan, Z.; Dwivedi, R.; Pearce, I. Effect of inverted internal limiting membrane flap on closure rate, postoperative visual acuity, and restoration of outer retinal layers in primary idiopathic macular hole surgery. Retina 2020, 40, 1955–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsui, M.-C.; Yang, C.-M. Early and late macular changes after the inverted internal limiting membrane flap technique for a full-thickness macular hole. Retina 2021, 41, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, C.; Dervenis, N.; Kirchmair, K.; Lohmann, C.P.; Kaye, S.B.; Sandinha, M.T. Functional and morphological outcomes of the inverted internal limiting membrane flap technique in small-sized and medium-sized macular holes <400 µm. Retina 2021, 41, 2073–2078. [Google Scholar]
- Iuliano, L.; Corbelli, E.; Bandello, F.; Codenotti, M. Inverted Internal Limiting Membrane Flap for Small-Sized (<250 µM) Full-Thickness Macular Hole: Anatomical and Functional Outcome. Retina 2023, 43, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuguchi, T.; Horiguchi, M.; Kakehi, S.; Ito, Y. Macular morphology after macular hole surgery using the inverted internal limiting membrane flap technique. Retina 2023, 43, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Lee, S.M.; Park, S.W.; Lee, J.E.; Byon, I. Comparative analysis of large macular hole surgery using an internal limiting membrane insertion versus inverted flap technique. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 103, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.-T.; Peng, K.-L. Treatment of persistent flap closure with fluid gas exchange after inverted internal limiting membrane flap technique for idiopathic macular hole. Medicine 2023, 102, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDonald, R.B.; Randlett, O.; Oswald, J.; Yoshimatsu, T.; Franze, K.; Harris, W.A. Müller glia provides essential tensile strength to the developing retina. J. Cell Biol. 2014, 210, 1075–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bringmann, A.; Duncker, T.; Jochmann, C.; Barth, T.; Duncker, G.I.; Wiedemann, P. Spontaneous closure of small full-thickness macular holes: Presumed role of Müller cells. Acta Ophthalmol. 2020, 98, e447–e456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichenbach, A.; Bringmann, A. Glia of the human retina. Glia 2020, 68, 768–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitao, M.; Wakabayashi, T.; Nishida, K.; Sakaguchi, H.; Nishida, K. Long-term reconstruction of foveal microstructure and visual acuity after idiopathic macular hole repair: Three-year follow-up study. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 103, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
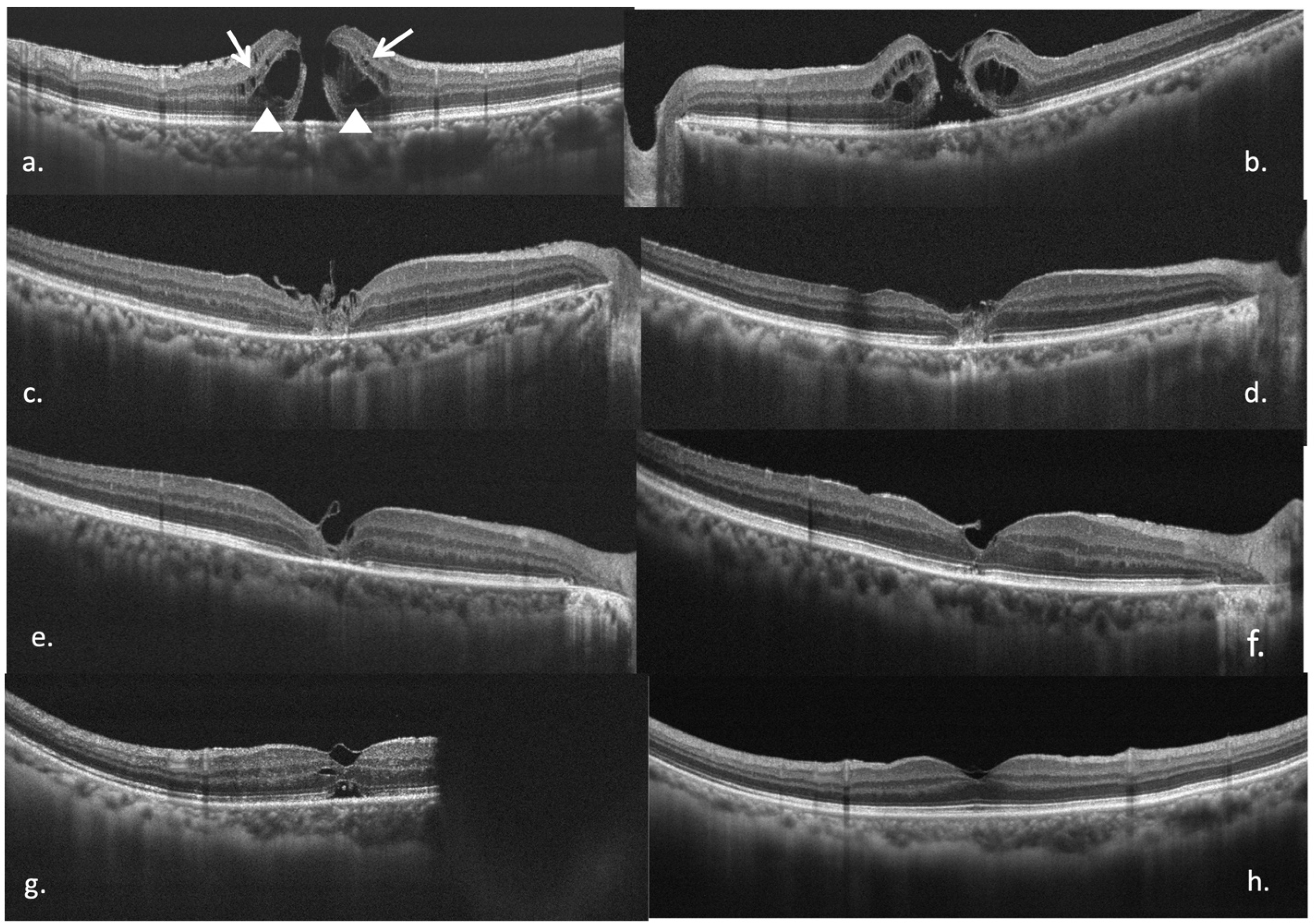
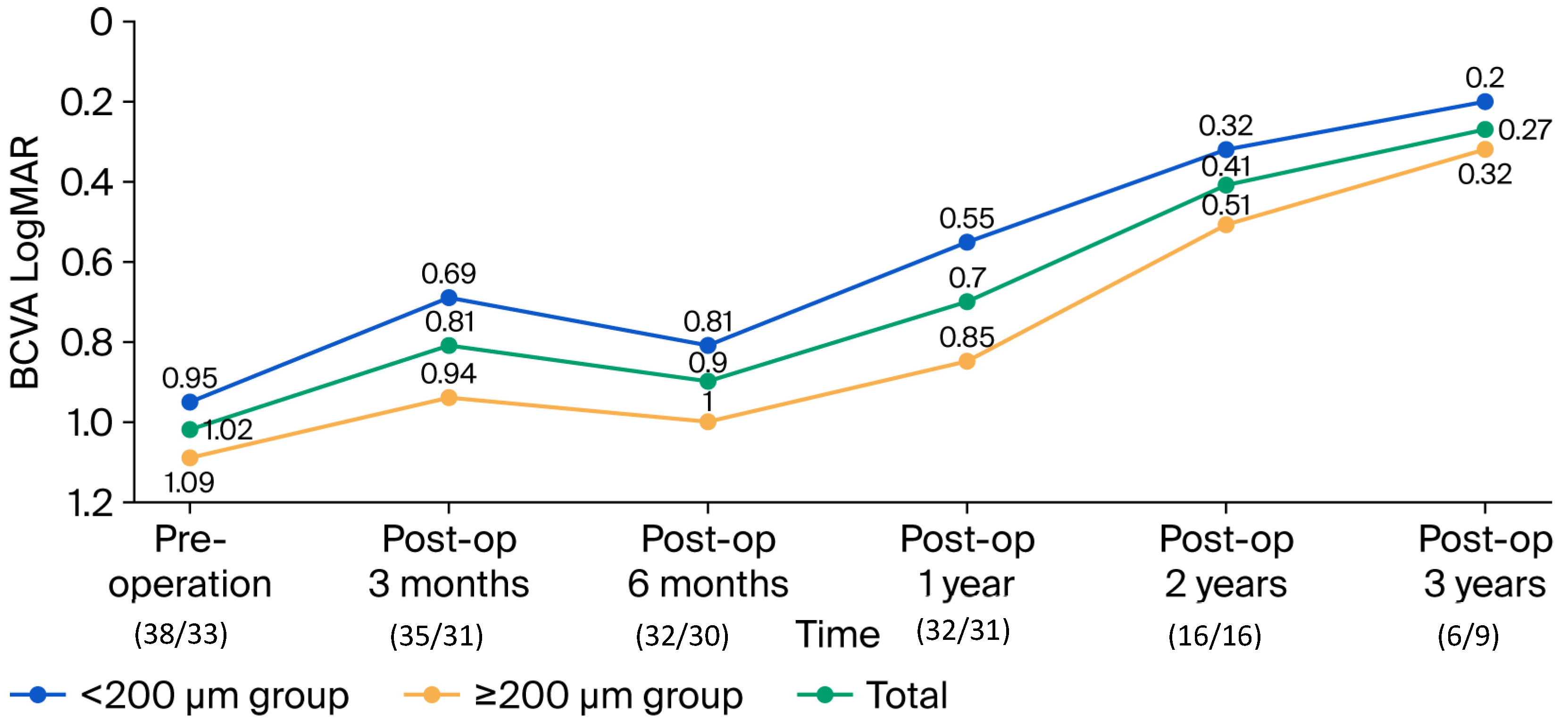
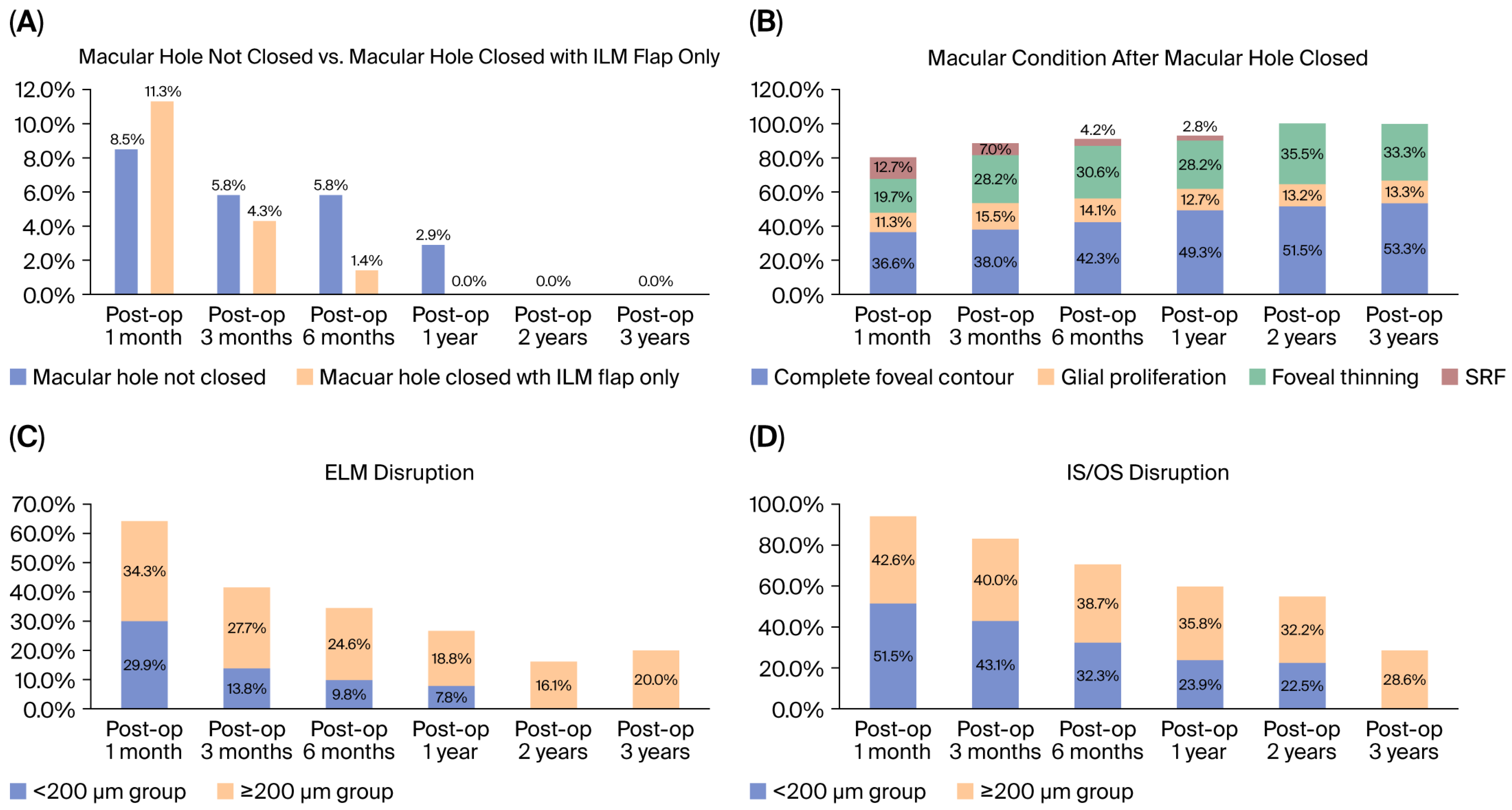
| Total (n = 71) | n (%)/Mean (SD) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years), mean (SD) | 62.38 (6.94) | 0.223 a | |
| Eye (OD), n (%) | 39 (54.93) | 0.427 b | |
| Sex (Male), n (%) | 14 (19.72) | 0.256 b | |
| Spherical equivalent (D), mean (SD) | −0.16 (0.28) | 0.376 a | |
| Axial length (mm), mean (SD) | 23.65 (0.98) | 0.177 a | |
| Lens status (phakia), n (%) | 65 (91.55) | 0.451 b | |
| Hole size (µm), mean (SD) | 184.36 (94.53) | <0.001 a,* | |
| Hole stage: | stage 1 and 2, n (%) | 24 (33.80) | 0.034 b,* |
| stage 3 and 4, n (%) | 47 (66.20) | ||
| Pre-op CFT (μm), mean (SD) | 393.54 (89.87) | 0.361 a | |
| Pre-op vision (logMAR), mean (SD) | 1.02 (0.40) | 0.002 a,* | |
| Outer retinal cysts, n (%) | 63 (88.73) | 0.355 b | |
| Inner retinal cysts, n (%) | 36 (50.70) | 0.291 b | |
| Drusen, n (%) | 23 (32.39) | 0.588 b | |
| Epiretinal membrane, n (%) | 18 (25.35) | 0.582 b | |
| Post-op 1-month ILMF trapped in MH or touched RPE, n (%) | 12 (16.90) | 0.022 b,* | |
| Post-op 1-month ILMF closure, n (%) | 8 (11.27) | 0.375 b | |
| Post-op 1-month SRF, n (%) | 9 (12.68) | 0.281 b | |
| Post-op 1-month MH non-closure, n (%) | 6 (8.45) | <0.001 b,* | |
| Final ELM (continuous), n (%) | 53 (74.65) | <0.001 b,* | |
| Final IS/OS (continuous), n (%) | 35 (49.30) | <0.001 b,* | |
| Final foveal contour (good), n (%) | 43 (62.30) | <0.001 b,* | |
| glial proliferation, n (%) | 11 (15.90) | <0.001 b,* | |
| foveal thinning, n (%) | 15 (21.70) | <0.001 b,* | |
| Final MH non-closure, n (%) | 2 (2.82) | 0.003 b,* | |
| Complications, n (%) | 0 (0.0) | ||
| Final CFT (µm), mean (SD) | 270.92 (47.97) | 0.064 a | |
| Final vision (logMAR), mean (SD) | 0.47 (0.39) | <0.001 c,* | |
| Follow-up time (month), mean (SD) | 20.59 (9.87) | <0.001 a,* | |
| Total: 71 Eyes | <200 µm Group | ≥200 µm Group | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | 38 (53.52) | 33 (46.47) | |
| Age (years), mean (SD) | 61.37 (6.29) | 63.55 (7.55) | 0.189 b |
| Eye (OD), n (%) | 21 (29.58) | 18 (25.35) | 0.388 d |
| Sex (Male), n (%) | 8 (11.27) | 6 (8.45) | 0.571 d |
| Spherical equivalent (D), mean (SD) | −0.38 (2.40) | +0.07 (2.21) | 0.195 b |
| Lens status (phakia), n (%) | 35 (49.30) | 30 (42.25) | 0.841 d |
| Hole stage (stage 1, 2), n (%) | 32 (28.83) | 8 (20.00) | 0.321 d |
| Hole size (µm), mean (SD) | 134.84 (59.79) | 304.19 (62.47) | <0.001 b,* |
| Pre-op CFT (µm), mean (SD) | 395.68 (101.59) | 390.90 (74.62) | 0.828 b |
| Pre-op vision (logMAR), mean (SD) | 0.95 (0.35) | 1.09 (0.44) | 0.122 b |
| Outer retinal cysts, n (%) | 31 (43.66) | 32 (45.07) | 0.060 d |
| Inner retinal cyst, n (%) | 16 (22.53) | 37 (28.17) | 0.155 d |
| Drusen, n (%) | 13 (18.31) | 10 (14.08) | 0.802 d |
| Epiretinal membrane, n (%) | 10 (14.08) | 8 (11.27) | 0.503 d |
| Post-op 1-month ILMF trapped in MH or touched RPE, n (%) | 3 (4.23) | 9 (12.68) | 0.022 d,* |
| Post-op 1-month ILM flap closure, n (%) | 2 (2.82) | 6 (8.45) | 0.026 d,* |
| Post-op 1-month SRF, n (%) | 8 (11.27) | 1 (1.41) | 0.066 d |
| Post-op 1-month MH non-closure, n (%) | 1 (1.41) | 5 (7.04) | 0.090 d |
| Final ELM (continuous), n (%) | 34 (49.30) | 19 (27.50) | 0.009 d,* |
| Final IS/OS (continuous), n (%) | 25 (36.20) | 10 (14.50) | 0.008 d,* |
| Final foveal contour (good), n (%) | 31 (44.90) | 12 (17.40) | <0.001 d,* |
| glial proliferation, n (%) | 3 (4.30) | 8 (11.60) | 0.001 d,* |
| foveal thinning, n (%) | 4 (5.80) | 11 (15.90) | 0.001 d,* |
| Final MH non-closure, n (%) | 0 (0.00) | 2 (2.82) | 0.212 d |
| Complications, n (%) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | |
| Final CFT (µm), mean (SD) | 278.58 (53.09) | 262.09 (40.30) | 0.150 b |
| Follow-up time (months), mean (SD) | 21.13 (10.50) | 19.97 (9.20) | 0.624 b |
| Final vision (logMAR), mean (SD) | 0.32 (0.30) | 0.64 (0.42) | <0.001 b,* |
| p | <0.001 c,* | 0.001 c,* |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, K.-L.; Kung, Y.-H.; Wu, T.-T. Functional and Anatomical Micro-Structural Recovery of Idiopathic Macular Holes Following the Inverted Internal Limiting Membrane Flap Technique: A Long-Term Study. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2961. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15232961
Peng K-L, Kung Y-H, Wu T-T. Functional and Anatomical Micro-Structural Recovery of Idiopathic Macular Holes Following the Inverted Internal Limiting Membrane Flap Technique: A Long-Term Study. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(23):2961. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15232961
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Kai-Ling, Ya-Hsin Kung, and Tsung-Tien Wu. 2025. "Functional and Anatomical Micro-Structural Recovery of Idiopathic Macular Holes Following the Inverted Internal Limiting Membrane Flap Technique: A Long-Term Study" Diagnostics 15, no. 23: 2961. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15232961
APA StylePeng, K.-L., Kung, Y.-H., & Wu, T.-T. (2025). Functional and Anatomical Micro-Structural Recovery of Idiopathic Macular Holes Following the Inverted Internal Limiting Membrane Flap Technique: A Long-Term Study. Diagnostics, 15(23), 2961. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15232961






