Diffusion Tensor Imaging Along the Perivascular Space (DTI-ALPS) in Ischemic Stroke: A Systematic Review of Diagnostic and Prognostic Performance for Post-Stroke Cognitive Impairment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protocol and Registration
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Information Sources and Search Strategies
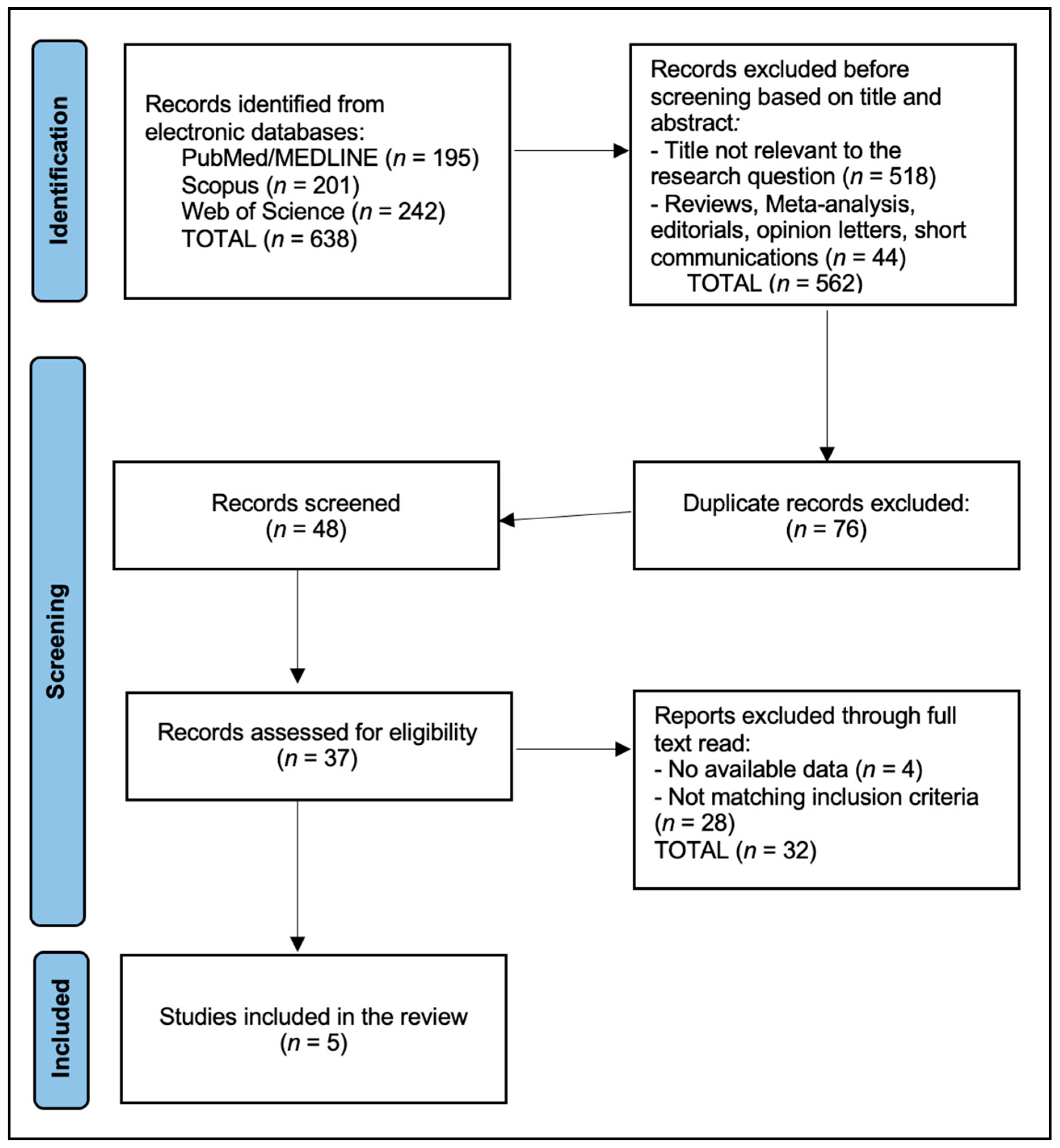
2.4. Selection Process
2.5. Risk of Bias
2.6. Synthesis Approach and Meta-Analysis Decision Rule
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Summary of Evidence
4.2. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Database/Platform | Search Date (Final Rerun) | Fields/Limits | Full Boolean Search String * |
|---|---|---|---|
| PubMed/MEDLINE | 24 August 2025 | Title/Abstract; Humans; English; Article; 1900–2025; Exclude reviews; “humans” filter active | (“DTI-ALPS”[tiab] OR “ALPS index”[tiab] OR “analysis along the perivascular space”[tiab] OR ((perivascular[tiab] OR “perivascular space”[tiab] OR “perivascular spaces”[tiab] OR “Virchow-Robin”[tiab]) AND (diffus *[tiab] OR tensor[tiab] OR DTI[tiab] OR “diffusion tensor imaging”[tiab] OR diffusivity[tiab] OR “fractional anisotropy”[tiab] OR “mean diffusivity”[tiab])) OR ((glymphatic[tiab] OR “glymphatic system”[tiab]) AND (diffus *[tiab] OR DTI[tiab] OR “diffusion tensor imaging”[tiab]))) AND (stroke[tiab] OR ischem *[tiab] OR ischaem *[tiab] OR infarct *[tiab] OR lacunar[tiab] OR “lacunar stroke”[tiab] OR “small vessel disease”[tiab] OR “small-vessel disease”[tiab] OR SVD[tiab] OR “transient ischemic attack”[tiab] OR TIA[tiab] OR lacune *[tiab] OR “subcortical infarct”[tiab] OR “subcortical infarcts”[tiab]) |
| Scopus (Elsevier) | 24 August 2025 | TITLE-ABS-KEY; Document type: Article; English; 1900–2025 | TITLE-ABS-KEY (“DTI-ALPS” OR “ALPS index” OR “analysis along the perivascular space” OR ((perivascular OR “perivascular space” OR “perivascular spaces” OR “Virchow-Robin”) AND (diffus * OR tensor OR DTI OR “diffusion tensor imaging” OR diffusivity OR “fractional anisotropy” OR “mean diffusivity”)) OR ((glymphatic OR “glymphatic system”) AND (diffus * OR DTI OR “diffusion tensor imaging”))) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY(stroke OR ischem * OR ischaem * OR infarct * OR lacunar OR “lacunar stroke” OR “small vessel disease” OR “small-vessel disease” OR SVD OR “transient ischemic attack” OR TIA OR lacune * OR “subcortical infarct” OR “subcortical infarcts”) |
| Web of Science Core Collection | 24 August 2025 | Topic (TS); Article; English; 1900–2025 | TS = ((“DTI-ALPS” OR “DTI ALPS” OR “ALPS index” OR “ALPS-index” OR “analysis along the perivascular space” OR ((perivascular OR “perivascular space” OR “perivascular spaces” OR “Virchow-Robin”) NEAR/3 (diffus * OR tensor OR DTI OR “diffusion tensor imaging” OR diffusivity OR “fractional anisotropy” OR “mean diffusivity”)) OR ((glymphatic OR “glymphatic system”) NEAR/3 (diffus * OR DTI OR “diffusion tensor imaging”))) AND (stroke OR ischem * OR ischaem * OR infarct * OR lacunar OR “lacunar stroke” OR “small vessel disease” OR “small-vessel disease” OR SVD OR “transient ischemic attack” OR TIA OR lacune * OR “subcortical infarct” OR “subcortical infarcts”)) |
| Reason for Exclusion at Full-Text Screening | n |
|---|---|
| Not ischemic stroke–specific ALPS (TIA-only or mixed cohorts without separable ischemic stroke results) | 12 |
| Wrong outcomes (no clinical, functional, cognitive, or longitudinal imaging endpoint relevant to PSCI) | 8 |
| Insufficient extractable ALPS numerical data (e.g., qualitative figures only) | 4 |
| Cohort or analysis overlap with a more complete dataset | 4 |
| Non-human or pediatric-only research | 4 |
| Total | 32 |
References
- Ma, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Huang, Y.; Nan, J.; Feng, J.; Yan, F.; Han, L. Prevalence and Risk Factors of Poststroke Cognitive Impairment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Public Health Nurs. 2025, 42, 1047–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iliff, J.J.; Wang, M.; Liao, Y.; Plogg, B.A.; Peng, W.; Gundersen, G.A.; Benveniste, H.; Vates, G.E.; Deane, R.; Goldman, S.A.; et al. A paravascular pathway facilitates CSF flow through the brain parenchyma and the clearance of interstitial solutes, including amyloid β. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 147ra111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Xie, L.; Kang, H.; Xu, Q.; Chen, M.J.; Liao, Y.; Thiyagarajan, M.; O’Donnell, J.; Christensen, D.J.; Nicholson, C.; Iliff, J.J.; et al. Sleep drives metabolite clearance from the adult brain. Science 2013, 342, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hablitz, L.M.; Plá, V.; Giannetto, M.; Vinitsky, H.S.; Stæger, F.F.; Metcalfe, T.; Nguyen, R.; Benrais, A.; Nedergaard, M. Circadian control of brain glymphatic and lymphatic fluid flow. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Li, C.; Lin, L.; Yin, L.; Li, J.; Ren, Y.; Tang, W.; Yang, Y. Cisternal Contrast-Enhanced MRI Reveals Post-Stroke Glymphatic Impairment and Compensatory Metabolic Waste Clearance via Microglia/Macrophages. Transl. Stroke Res. 2025, 16, 2106–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taoka, T.; Masutani, Y.; Kawai, H.; Nakane, T.; Matsuoka, K.; Yasuno, F.; Kishimoto, T.; Naganawa, S. Evaluation of glymphatic system activity with the diffusion MR technique: Diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space (DTI-ALPS) in Alzheimer’s disease cases. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2017, 35, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taoka, T.; Ito, R.; Nakamichi, R.; Kamagata, K.; Sakai, M.; Kawai, H.; Nakane, T.; Abe, T.; Ichikawa, K.; Kikuta, J.; et al. Reproducibility of diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space (DTI-ALPS) for evaluating interstitial fluid diffusivity and glymphatic function: Changes in Alps index on Multiple condition acquisition experiment (CHAMONIX) study. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2022, 40, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, Y.; Kamagata, K.; Andica, C.; Taoka, T.; Tuerxun, R.; Uchida, W.; Takabayashi, K.; Owaki, M.; Yoshida, S.; Yamazaki, K.; et al. Multisite harmonization of diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space using the Combined Association Test. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2023, 41, 1072–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Taoka, T.; Ito, R.; Nakamichi, R.; Nakane, T.; Kawai, H.; Naganawa, S. Diffusion Tensor Image Analysis Along the Perivascular Space (DTI-ALPS): Revisiting the Meaning and Significance of the Method. Magn. Reason. Med. Sci. 2024, 23, 268–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Georgiopoulos, C.; Werlin, A.; Lasic, S.; Hall, S.; van Westen, D.; Spotorno, N.; Hansson, O.; Nilsson, M. Diffusion tensor imaging along the perivascular space: The bias from crossing fibres. Brain Commun. 2024, 6, fcae421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Schirge, P.M.; Perneczky, R.; Taoka, T.; Ruiz-Rizzo, A.L.; Ersoezlue, E.; Forbrig, R.; Guersel, S.; Kurz, C.; Brendel, M.; Hellmann-Regen, J.; et al. Perivascular space and white matter hyperintensities in Alzheimer’s disease: Associations with disease progression and cognitive function. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2025, 17, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Șerban, M.; Toader, C.; Covache-Busuioc, R.A. The Collapse of Brain Clearance: Glymphatic-Venous Failure, Aquaporin-4 Breakdown, and AI-Empowered Precision Neurotherapeutics in Intracranial Hypertension. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mathias, K.; de Aguiar da Costa, M.; de Rezende, V.L.; Maragno, V.D.A.; Felipe, C.M.K.; da Rosa Dos Reis, L.; Gonçalves, C.L.; Petronilho, F. Impaired Flow: Glymphatic Dysfunction in Ischemic Stroke and the Influence of Sex. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2025, 75, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwan, J.; Hafdi, M.; Chiang, L.L.W.; Myint, P.K.; Wong, L.S.; Quinn, T.J. Antithrombotic therapy to prevent cognitive decline in people with small vessel disease on neuroimaging but without dementia. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2022, 7, CD012269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lin, B.; Leong, Y.Y.; Mohamad, M. Glymphatic system dysfunction in cerebral infarction: Advances and perspectives based on DTI-derived ALPS measures. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2025, 17, 1630–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 2021, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Toh, C.H.; Siow, T.Y. Glymphatic Dysfunction in Patients With Ischemic Stroke. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 756249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, M.; Zeng, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, W.; Wang, W.; Du, Y.; Ding, J.; Ding, X. Glymphatic dysfunction assessed by DTI-ALPS index predicts early cognitive impairment in acute subcortical infarcts: A prospective clinical cohort study. Front. Neurol. 2025, 16, 1605889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang, S.; Yu, W.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, S.; Zheng, J.; Yu, L.; Wang, P.; Geng, Y.; et al. Glymphatic dysfunction as a biomarker for post-stroke cognitive impairment. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 19382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Tozer, D.J.; Markus, H.S. Relationship of Perivascular Space Markers with Incident Dementia in Cerebral Small Vessel Disease. Stroke 2024, 55, 1032–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chen, Q.; Zhong, T.; Liu, J.; Yuan, B.; Gao, H. Chronic Glymphatic Dysfunction Modulates Domain-Specific Cognitive Recovery After Stroke: A DTI-ALPS Lesion Stratification Study. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2025, 31, e70512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhu, J.; Mo, J.; Liu, K.; Chen, Q.; Li, Z.; He, Y.; Chang, Y.; Lin, C.; Yu, M.; Xu, Y.; et al. Glymphatic System Impairment Contributes to the Formation of Brain Edema After Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2024, 55, 1393–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, T.; Manuello, J.; Premi, E.; Mattioli, I.; Lasagna, L.; Lahoz, C.B.; Cauda, F.; Duca, S.; Liloia, D. Evaluating the robustness of DTI-ALPS in clinical context: A meta-analytic parallel on Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 26381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Li, X.; Qiao, Y.; Zou, H.; Qian, Y.; Li, X.; Zhu, Y.; Huo, W.; Wang, L.; Zhang, M. DTI-ALPS: An MR biomarker for motor dysfunction in patients with subacute ischemic stroke. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1132393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wu, C.H.; Chen, S.P.; Chung, C.P.; Yu, K.W.; Lin, T.M.; Luo, C.B.; Lirng, J.F.; Lee, I.H.; Chang, F.C. Early Improvement in Interstitial Fluid Flow in Patients with Severe Carotid Stenosis After Angioplasty and Stenting. J. Stroke 2024, 26, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, H.; Jacob, M.A.; Cai, M.; Kessels, R.P.C.; Norris, D.G.; Duering, M.; De Leeuw, F.E.; Tuladhar, A.M. Perivascular Spaces, Diffusivity Along Perivascular Spaces, and Free Water in Cerebral Small Vessel Disease. Neurology 2024, 102, e209306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, Z.; Mo, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, D.; Huang, L.; Yang, Z.; Qin, R.; Mao, C.; Lv, W.; Huang, Y.; et al. Glymphatic Dysfunction Mediates the Influence of White Matter Hyperintensities on Episodic Memory in Cerebral Small Vessel Disease. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Satpathi, S.; Reid, R.I.; Przybelski, S.A.; Raghavan, S.; Cogswell, P.M.; Meyer, N.K.; Lowe, V.J.; Gunter, J.L.; Petersen, R.C.; Jack, C.R.; et al. Evaluation and interpretation of DTI-ALPS, a proposed surrogate marker for glymphatic clearance, in a large population-based sample. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2025, 17, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, O.; Delgado-Sanchez, A.; Cullell, N.; Correa, S.A.L.; Krupinski, J.; Ray, N. Diffusion tensor imaging analysis along the perivascular space in the UK biobank. Sleep Med. 2024, 119, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, H.; Wang, J.; Yu, Z.; Yu, H.; Li, X.; Bu, S.; Zhao, M.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Fan, G. Glymphatic function from diffusion-tensor MRI to predict conversion from mild cognitive impairment to dementia in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. 2024, 271, 5598–5609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ran, L.; Fang, Y.; Cheng, C.; He, Y.; Shao, Z.; Kong, Y.; Huang, H.; Xu, S.; Luo, X.; Wang, W.; et al. Genome-wide and phenome-wide studies provided insights into brain glymphatic system function and its clinical associations. Sci. Adv. 2025, 11, eadr4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
| Database/Platform | Search Field(s) and Coverage | Limits and Filters | Core Search Concepts and Representative Terms * |
|---|---|---|---|
| PubMed/MEDLINE | Title/Abstract ([tiab]) with database filters; coverage from 1900 to 24 August 2025 | Humans; English; Article-type; exclusion of reviews; date range 1900–2025; animals excluded except “humans” | DTI-ALPS/glymphatic/PVS block: “DTI-ALPS”, “ALPS index”, “analysis along the perivascular space”, “perivascular space(s)”, “Virchow-Robin” combined with diffus */tensor/DTI/“diffusion tensor imaging”/diffusivity/“fractional anisotropy”/“mean diffusivity”; “glymphatic”/“glymphatic system” combined with diffus */DTI. Stroke/cerebrovascular block: stroke, ischem *, ischaem *, infarct *, lacunar, “lacunar stroke”, “small vessel disease”, “small-vessel disease”, SVD, “transient ischemic attack”, TIA, lacune *, “subcortical infarct”, “subcortical infarcts”. |
| Scopus (Elsevier) | TITLE-ABS-KEY; coverage from 1900 to 24 August 2025 | Document type: Article; Language: English; Publication years >1900 and <2026 | Same concept blocks as PubMed, adapted to Scopus syntax: TITLE-ABS-KEY(“DTI-ALPS” OR “ALPS index” OR “analysis along the perivascular space” OR ((perivascular OR “perivascular space” OR “perivascular spaces” OR “Virchow-Robin”) AND (diffus * OR tensor OR DTI OR “diffusion tensor imaging” OR diffusivity OR “fractional anisotropy” OR “mean diffusivity”)) OR ((glymphatic OR “glymphatic system”) AND (diffus * OR DTI OR “diffusion tensor imaging”))) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY (stroke OR ischem * OR ischaem * OR infarct * OR lacunar OR “lacunar stroke” OR “small vessel disease” OR “small-vessel disease” OR SVD OR “transient ischemic attack” OR TIA OR lacune * OR “subcortical infarct” OR “subcortical infarcts”). |
| Web of Science Core Collection | Topic field (TS); coverage from 1900 to 24 August 2025 | Document type: Article; Language: English; Publication years 1900–2025 | TS = ((“DTI-ALPS” OR “DTI ALPS” OR “ALPS index” OR “ALPS-index” OR “analysis along the perivascular space” OR ((perivascular OR “perivascular space” OR “perivascular spaces” OR “Virchow-Robin”) NEAR/3 (diffus * OR tensor OR DTI OR “diffusion tensor imaging” OR diffusivity OR “fractional anisotropy” OR “mean diffusivity”)) OR ((glymphatic OR “glymphatic system”) NEAR/3 (diffus * OR DTI OR “diffusion tensor imaging”))) AND (stroke OR ischem * OR ischaem * OR infarct * OR lacunar OR “lacunar stroke” OR “small vessel disease” OR “small-vessel disease” OR SVD OR “transient ischemic attack” OR TIA OR lacune * OR “subcortical infarct” OR “subcortical infarcts”)). |
| Source | Records Retrieved (Initial + Rerun) | After Intra-Source Dedupe | Unique After Cross-Source Merge * |
|---|---|---|---|
| PubMed/MEDLINE | 195 | 195 | 22 |
| Scopus | 201 | 201 | 13 |
| Web of Science Core Collection | 242 | 242 | 13 |
| Total | 638 | 638 | 48 |
| First Author (Year) | Country/Setting | Design and Stroke Cohort | Imaging Timing vs. Stroke (Window) | Controls (n) | Scanner and DTI Parameters | ALPS ROI Method/Atlas | PSMD/WMH Covariates in ALPS Models |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toh (2021) [17] | Taiwan (single-center) | Retrospective; n = 50 ischemic stroke | 1–60 days post-onset (acute/subacute) | 44 | 3 T Siemens Tim Trio; b = 1000 s/mm2; 20 diffusion directions; 2 mm slices | Manual periventricular ROIs at lateral ventricle level; no atlas-based automation reported | PSMD and WMH not included; other covariates NR |
| Wang (2025) [18] | China (single-center) | Prospective acute subcortical infarcts; n = 29 | 7 and 90 days (acute and subacute) | 25 | 3 T Philips Ingenia; b = 1000 s/mm2; 32 diffusion directions; 2 mm isotropic voxels | Protocolized lesion and non-lesion ROIs following ALPS method; atlas use NR | Models did not include PSMD/WMH; limited clinical covariates reported; diffusion covariates NR |
| Zhang (2025) [19] | China (single-center) | Prospective; n = 51 ischemic stroke (plus HC and non-VCI comparators) | Time-1 pre-rehab (mostly subacute ≤ 90 days); Time-2 ≈ 30 days later (subacute/early-chronic) | 48 HC; 47 non-VCI | 3 T GE MR750; DTI parameters reported in supplement (b-value and directions NR in main text) | Side-specific ALPS with additional PVS/choroid-plexus metrics; ROI framework described; atlas type NR | Imaging covariates partially modeled; PSMD/WMH covariates NR |
| Hong (2024) [20] | UK (Cambridge) | Prospective lacunar SVD cohort; n = 120 | Baseline; annual MRI over 3 years; cognition over 5 years (chronic) | — | DTI acquired on 3 T scanners using a standardized pipeline; detailed b-values/directions NR in main text | Global ALPS derived from automated/standardized pipeline; ROIs based on white-matter skeleton and periventricular regions; specific atlas NR | PSMD and MD included as covariates; WMH burden incorporated in SVD characterization |
| Chen (2025) [21] | USA dataset; re-analysis in China | Retrospective chronic stroke; n = 51; HC n = 27 | 3 months and 12 months post-stroke (chronic) | 27 | 3 T Siemens Tim-Trio; multi-direction DTI; exact b-value and number of directions NR | Lesion-side and contralateral ROIs using an ALPS-type framework; atlas use NR | PSMD/WMH covariates not modeled; other covariates limited; details NR |
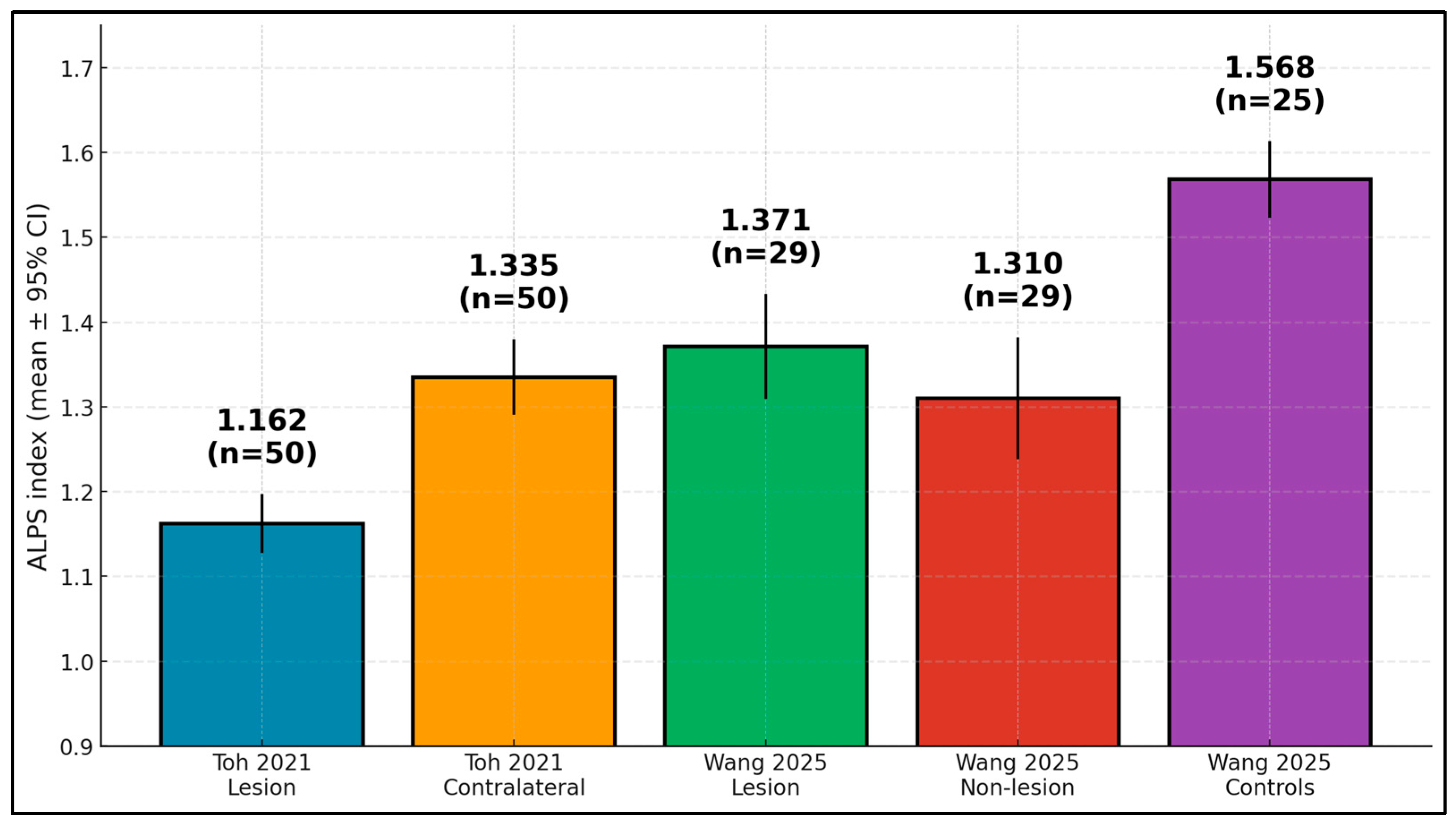
| Study | Group | Mean (SD) | n | 95% CI (Computed) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toh (2021) [17] | Lesion hemisphere | 1.162 (0.126) | 50 | 1.127–1.197 |
| Toh (2021) [17] | Contralateral | 1.335 (0.160) | 50 | 1.291–1.379 |
| Wang (2025) [18] | Lesion hemisphere | 1.371 (0.170) | 29 | 1.309–1.433 |
| Wang (2025) [18] | Non-lesion | 1.310 (0.198) | 29 | 1.238–1.382 |
| Wang (2025) [18] | Controls | 1.568 (0.115) | 25 | 1.523–1.613 |
| Study | Stroke vs. Controls | Lesion vs. Contralateral | Longitudinal Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zhang (2025) [19] | ↓ (stroke < controls) | ↓ at Time-1; partial ↑ at Time-2 | ↑ (partial recovery) |
| Hong (2024) [20] | NR | NR | ↓ (decline over 3 years) |
| Chen (2025) [21] | ↓ vs. controls (3 m and 12 m) | Lesion < contralateral at 3 months; ≈by 12 months | ≈symmetry by 12 months |
| Study | Cognitive Endpoints | Association Metrics | Prognostic Metrics | Other Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toh (2021) [17] | NR | ALPS ↑ with time since onset (β ≈ 0.79, p < 0.001) | NR | Hemispheric ALPS asymmetry early post-stroke |
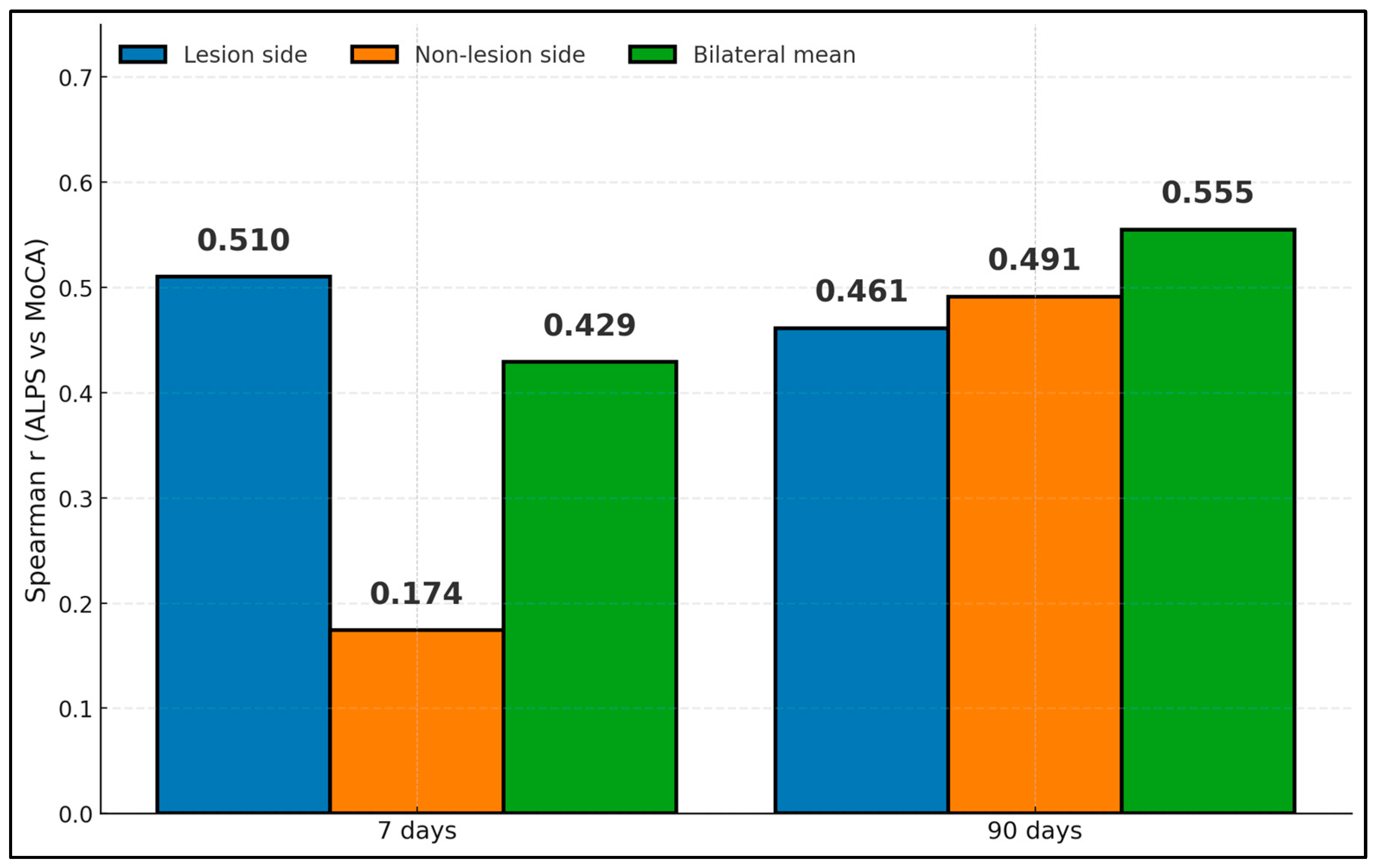
| Wang (2025) [18] | MoCA at 7 and 90 days | Lesion-side ALPS–MoCA r = 0.510 (7 days), r = 0.461 (90 days); mean bilateral r = 0.429 (7 days), 0.555 (90 days) | AUC 0.868 for early cognitive impairment (sensitivity 96%, specificity 66%) | NR |
| Zhang (2025) [19] | MMSE; PSCI at 6 months | Time-1 lesion ALPS associated with 6-month MMSE; bilateral WM-PVS also associated | Time-2 lesion ALPS AUC 0.786 for poor 6-month outcome (cutoff ~1.105) | Infarct-side ALPS improved over time |
| Hong (2024) [20] | Global, memory, executive, processing speed (5 years) | Baseline ALPS associated with change in global cognition and executive and long-term memory (β 0.142–0.287) | Incident dementia HR 0.328 per higher baseline ALPS; change in ALPS predicted dementia univariately but attenuated after PSMD/MD | PVS volume did not predict dementia |
| Chen (2025) [21] | Multidomain battery at 3 months and 1 year | Weak domain correlations at 3 months (uncorrected), not persisting at 1 year | NR | Hemispheric ALPS gap resolves by 1 year |
| Study | Stroke n (Controls) | Demographics | Imaging Timing | Scanner and DTI Basics | Cognitive Endpoint(s) and Timing |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toh (2021) [17] | 50 (44) | Age 56.7 ± 15.2 years; 60% male | MRI at 1–60 days post-onset; mean 17.1 ± 14.8 days | 3 T Siemens Tim Trio; b = 1000 s/mm2; 20 dirs; 2 mm slices | NR |
| Wang (2025) [18] | 29 (25) | Age 65.35 ± 11.11 years; 55.2% male | 7 and 90 days after subcortical infarct | 3 T Philips Ingenia; b = 1000; 32 dirs; 2 mm iso voxels | MoCA at 7 and 90 days |
| Zhang (2025) [19] | 51 (HC 48; n-VCI 47) | NR for stroke only (overall mean age across cohorts 63 years) | Time 1 (pre-rehab) and Time 2 (≈30 days later); onset-to-scan piecewise 42-day threshold | 3 T GE MR750; sequence parameters in supplement | MMSE at 6 months; PSCI at 6 months |
| Hong (2024) [20] | 120 (—) | Age 70.0 years; 65% male | Baseline; MRI annually 3 years; cognition annually 5 years | DTI pipeline with PSMD/MD adjustment; scanner NR | Global, executive, memory, processing speed; incident dementia |
| Chen (2025) [21] | 51 (27) | Age 53.25 ± 10.56 years; 28/51 male | 3 months and 1 year | 3 T Siemens Tim-Trio; controls matched; protocol detailed on PMC | Multidomain battery (language, memory, motor, attention) at both timepoints |
| Study (Year) | Design and n (Stroke/Controls) | Imaging Timing vs. Stroke | DTI Basics | ALPS ROI Method | Cognitive Endpoint(s) and Definition | Key Covariates/Adjustment | Notes Limiting Pooling |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toh (2021) [17] | Retrospective; 50/44 | 1–60 days (mean ~17 days) | 3T; b = 1000; ~20 dirs; ~2 mm | Manual periventricular ROIs; side-specific | None (temporal/asymmetry only) | None for diffusion confounds | No cognitive endpoint; manual ROI; variable timing |
| Wang (2025) [18] | Prospective subcortical; 29/25 | 7 days and 90 days | 3T; b = 1000; ~32 dirs; ~2 mm | Protocolized ALPS; lesion/non-lesion/bilateral | MoCA at 7 days and 90 days; early impairment per study | Limited adjustment (no PSMD/MD) | Acute/subacute only; impairment definition differs |
| Zhang (2025) [19] | Prospective; 51 stroke; HC 48; n-VCI 47 | Time-1 pre-rehab; Time-2 ~30 days later | 3T; params in supplement | Side-specific ALPS + PVS/CP metrics | 6-month MMSE; PSCI per study | Partial imaging covariates | Timing windows differ; some non-numeric reporting |
| Hong (2024) [20] | Prospective lacunar SVD; 120 | Baseline; MRI annually ×3; cognition ×5 years | Standardized DTI pipeline | Automated/standardized ALPS (global) | Global/executive/memory; incident dementia (adjudicated) | Adjusted for PSMD/MD; WMH | Outcome constructs differ; long-term SVD cohort |
| Chen (2025) [21] | Retrospective; 51/27 | 3 months and 12 months | 3T; multi-direction DTI | Lesion/contralateral ROIs | Multidomain battery at 3 months and 1 years | Limited covariate adjustment | Chronic window; asymmetry resolves by 12 months |
| Study | Assessment |
|---|---|
| Toh (2021) [17] | Retrospective convenience sample; manual periventricular ROIs; blinding of ALPS readers not reported; imaging acquired across a broad 1–60 day window |
| Wang (2025) [18] | Prospective subcortical stroke cohort with protocolized lesion/non-lesion ROIs; blinding of ALPS measurement to MoCA not explicitly stated; fixed 7- and 90-day imaging windows; MoCA-based impairment definition used as reference standard |
| Zhang (2025) [19] | Prospective design but recruitment procedures and exclusions not fully detailed; side-specific ALPS with unclear ROI blinding; MMSE-based PSCI definition acceptable but briefly described; partial reporting of numeric data across timepoints |
| Hong (2024) [20] | Lacunar SVD cohort not designed for diagnostic classification; global ALPS derived from a standardized diffusion pipeline; dementia outcomes adjudicated; QUADAS-2 domains largely not applicable for this prognostic design |
| Chen (2025) [21] | Chronic-phase stroke cohort focused on longitudinal recovery; no formal diagnostic reference standard; lesion/contralateral ROIs with unclear blinding; QUADAS-2 primarily not applicable |
| Study | Assessment |
|---|---|
| Wang (2025) [18] | Prospective, well-defined acute subcortical cohort with short follow-up; protocolized ALPS measurement but blinding unclear; MoCA outcomes at fixed timepoints; prognostic models did not incorporate PSMD/WMH; reporting of AUCs but not all CIs |
| Zhang (2025) [19] | Prospective stroke cohort with incomplete reporting of recruitment and attrition; side-specific ALPS ROIs; PSCI definition based on MMSE with limited detail; imaging confounders only partially adjusted; some outcomes presented graphically without full numeric statistics |
| Hong (2024) [20] | Lacunar SVD cohort with standardized diffusion pipeline; automated/global ALPS; adjudicated dementia endpoints; models adjusted for PSMD/MD and WMH; multi-year follow-up with expected attrition but appropriate longitudinal analyses |
| Chen (2025) [21] | Retrospective chronic-stroke sample; lesion/contralateral ALPS ROIs; multidomain cognitive battery with unclear blinding; limited covariate adjustment (no PSMD/WMH); statistical models described but sparsely reported |
| Toh (2021) [17] | Retrospective convenience sampling; manual ALPS ROIs without reported blinding; no prognostic clinical endpoint; no adjustment for diffusion or vascular confounders; therefore high concern in multiple QUIPS domains |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grigoras, M.L.; Bondar, A.-C.; Bratosin, F.; Bogdan, I.G.; Marc, F. Diffusion Tensor Imaging Along the Perivascular Space (DTI-ALPS) in Ischemic Stroke: A Systematic Review of Diagnostic and Prognostic Performance for Post-Stroke Cognitive Impairment. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2905. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15222905
Grigoras ML, Bondar A-C, Bratosin F, Bogdan IG, Marc F. Diffusion Tensor Imaging Along the Perivascular Space (DTI-ALPS) in Ischemic Stroke: A Systematic Review of Diagnostic and Prognostic Performance for Post-Stroke Cognitive Impairment. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(22):2905. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15222905
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrigoras, Mirela Loredana, Andrei-Cristian Bondar, Felix Bratosin, Iulia Georgiana Bogdan, and Felicia Marc. 2025. "Diffusion Tensor Imaging Along the Perivascular Space (DTI-ALPS) in Ischemic Stroke: A Systematic Review of Diagnostic and Prognostic Performance for Post-Stroke Cognitive Impairment" Diagnostics 15, no. 22: 2905. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15222905
APA StyleGrigoras, M. L., Bondar, A.-C., Bratosin, F., Bogdan, I. G., & Marc, F. (2025). Diffusion Tensor Imaging Along the Perivascular Space (DTI-ALPS) in Ischemic Stroke: A Systematic Review of Diagnostic and Prognostic Performance for Post-Stroke Cognitive Impairment. Diagnostics, 15(22), 2905. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15222905







