The Effect of Lumen-Apposing Metal Stent (LAMS) in Acute Cholecystitis Unfit for Surgery: Good Tidings
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Indications for Gallbladder Drainage and Definition of “Unfit for Surgery”
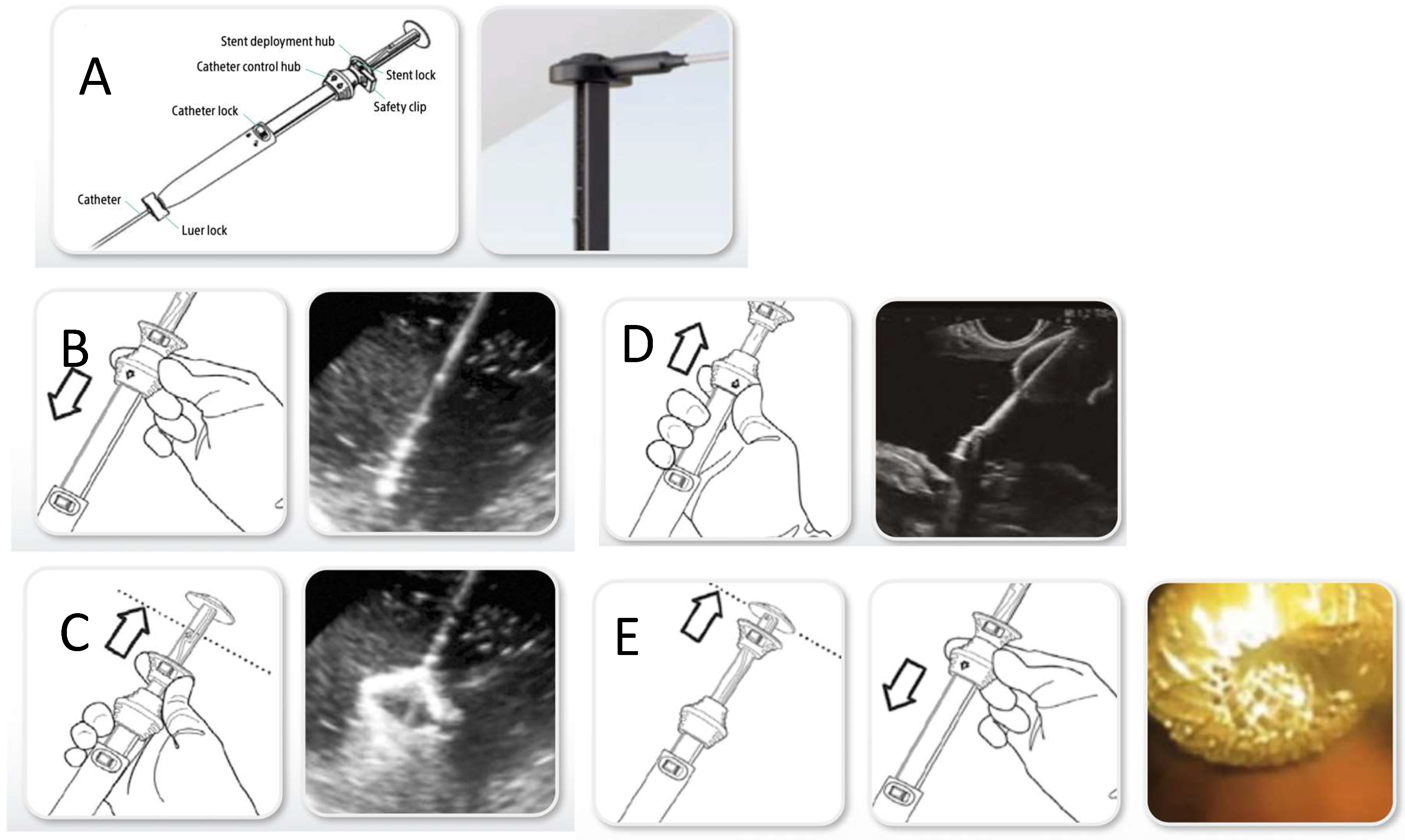
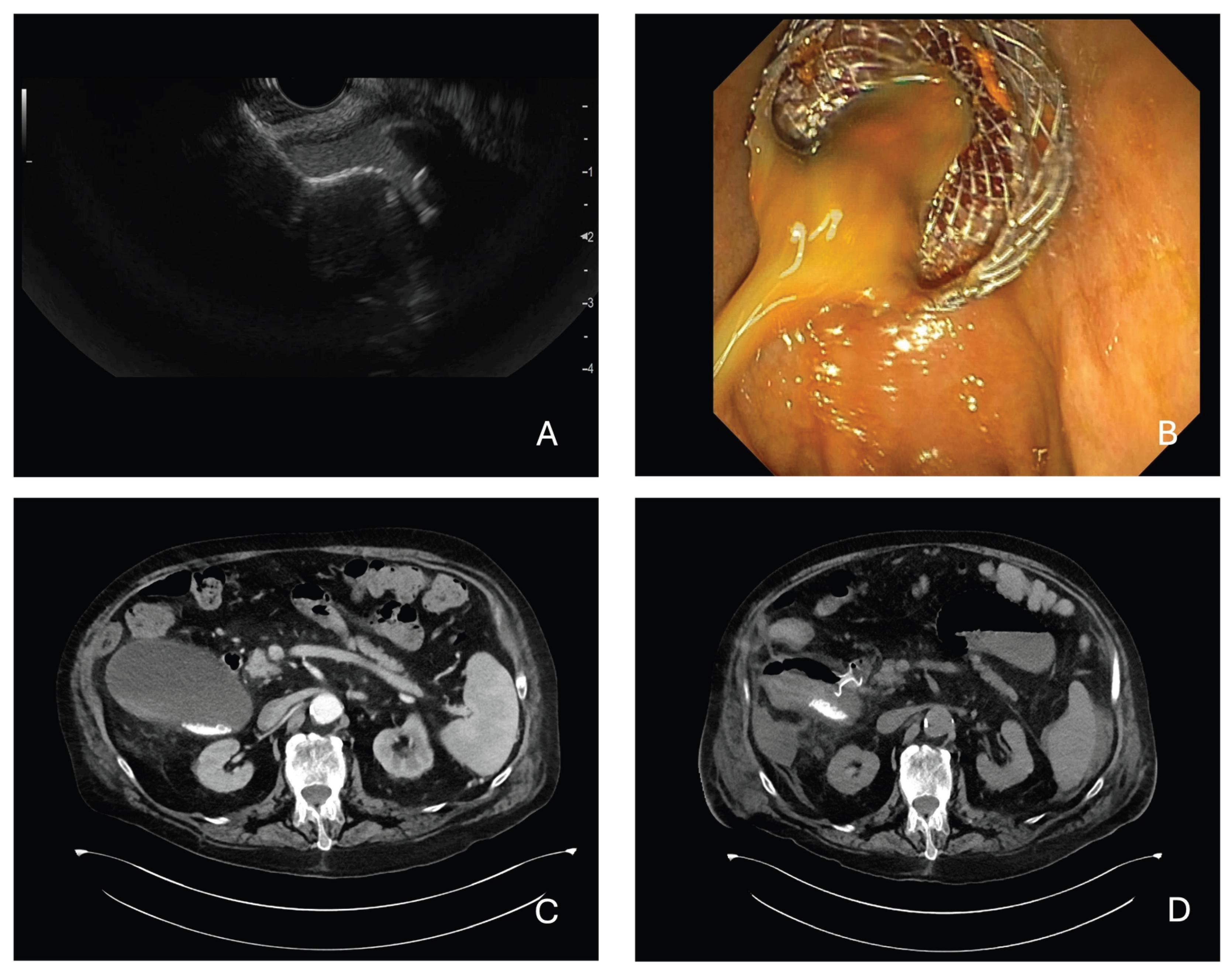
1.2. Technical Aspects
- AXIOS (Boston Scientific, Marlborough, MA, USA): introduced in 2012 is a fully covered nitinol with a dumbbell (“yo-yo”) shape that prevents migration.
- Hot-AXIOS (Boston Scientific, USA) is the most widely used cautery-enhanced LAMS system worldwide and is available in lumen diameters of 6, 8, 10, 15, 20 mm and lengths of 10–15 mm body. FDA-approved in the USA for pancreatic pseudocysts, Walled-Off Necrosis (WON), EUS-GBD in high-risk cholecystitis, and biliary drainage post-ERCP failure.
- Spaxus (Taewoong Medical, Goyang-si, South Korea) is a fully covered nitinol LAMS with bilateral flanges; designed for pseudocyst drainage, EUS-GBD, EUS-guided biliary drainage (EUS-BD).
- Hot-Spaxus (Taewoong Medical, South Korea): added electrocautery tip to permit single-step deployment; not yet available worldwide (e.g., limited in the USA).
- Hanaro/Hanarostent (M.I.Tech, Pyeongtaek-si, South Korea): covered nitinol stent with flanges; provides approximation but may be less effective at full lumen apposition; used in pseudocysts, WON, and EUS-GBD.
1.3. Contraindications
1.4. Stent Removal
1.5. Comparison with PT-GBD and ETP-GBD
1.6. Technical and Operational Requirements
2. Materials and Methods
- Population: Adult patients with a diagnosis of acute cholecystitis at high surgical risk or deemed unfit for cholecystectomy;
- Intervention: Endoscopic ultrasound-guided gallbladder drainage using LAMS;
- Outcomes: Technical and clinical success rates, procedure-related adverse events, procedure-related mortality, and need for reintervention or additional procedures.
- non-English language studies;
- single case reports or case series with fewer than three patients;
- narrative reviews, editorials, or letters without original patient data;
3. Results
3.1. Technical Success
3.2. Clinical Success
3.3. Adverse Events, Reintervention and Readmission
4. Discussion
4.1. Benefits and Outcomes: Point of View of the Clinician/Endoscopist
4.2. Benefits and Outcomes: Point of View of Surgeon
4.3. Benefits and Outcomes: Point of View of Patients
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AC | Acute Cholecystitis |
| AEs | Adverse Event |
| EUS | Endoscopic Ultrasound |
| EUS-GBD | Endoscopic Ultrasound Gallbladder Drainage |
| EUS-BD | Endoscopic Ultrasound Biliary Drainage |
| ETP-GBD | Endoscopic Transpapillary Gallbladder Drainage |
| LAMS | Lumen-Apposing Metal Stent |
| LOS | Length Of Stay |
| PT-GBD | Percutaneous Transhepatic Gallbladder Drainage |
| PTC | Percutaneous Transhepatic Cholecystotomy |
| WON | Walled-Off Necrosis |
References
- Mori, Y.; Itoi, T.; Baron, T.H.; Takada, T.; Strasberg, S.M.; Pitt, H.A.; Ukai, T.; Shikata, S.; Noguchi, Y.; Teoh, A.Y.B.; et al. Tokyo Guidelines 2018: Management strategies for gallbladder drainage in patients with acute cholecystitis (with videos). J. Hepato-Biliary-Pancreat. Sci. 2018, 25, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mencarini, L.; Vestito, A.; Zagari, R.M.; Montagnani, M. The Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Cholecystitis: A Comprehensive Narrative Review for a Practical Approach. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisano, M.; Allievi, N.; Gurusamy, K.; Borzellino, G.; Cimbanassi, S.; Boerna, D.; Coccolini, F.; Tufo, A.; Di Martino, M.; Leung, J.; et al. 2020 World Society of Emergency Surgery updated guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute calculus cholecystitis. World J. Emerg. Surg. 2020, 15, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, K.; Suzuki, K.; Takada, T.; Strasberg, S.M.; Asbun, H.J.; Endo, I.; Iwashita, Y.; Hibi, T.; Pitt, H.A.; Umezawa, A.; et al. Tokyo Guidelines 2018: Flowchart for the management of acute cholecystitis. J. Hepato-Biliary-Pancreat. Sci. 2018, 25, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurusamy, K.S.; Davidson, C.; Gluud, C.; Davidson, B.R. Early versus delayed laparoscopic cholecystectomy for people with acute cholecystitis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoe, M.; Hata, J.; Takada, T.; Strasberg, S.M.; Asbun, H.J.; Wakabayashi, G.; Kozaka, K.; Endo, I.; Deziel, D.J.; Miura, F.; et al. Tokyo Guidelines 2018: Diagnostic criteria and severity grading of acute cholecystitis (with videos). J. Hepato-Biliary-Pancreat. Sci. 2018, 25, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coccolini, F.; Catena, F.; Pisano, M.; Gheza, F.; Fagiuoli, S.; Di Saverio, S.; Leandro, G.; Montori, G.; Ceresoli, M.; Corbella, D.; et al. Open versus laparoscopic cholecystectomy in acute cholecystitis. Systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Surg. 2015, 18, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fugazza, A.; Colombo, M.; Repici, A.; Anderloni, A. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided gallbladder drainage: Current perspectives. Clin. Exp. Gastroenterol. 2020, 13, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Y.; Li, T.; Wang, B.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhao, S. Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Gallbladder Drainage Versus Percutaneous Transhepatic Gallbladder Drainage for Acute Cholecystitis with High Surgical Risk: An Up-to-Date Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. J. Laparoendosc. Adv. Surg. Tech. 2021, 31, 1232–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boregowda, U.; Umapathy, C.; Nanjappa, A.; Wong, H.; Desai, M.; Roytman, M.; Theethira, T.; Saligram, S. Endoscopic ultrasound guided gallbladder drainage—Is it ready for prime time? World J. Gastrointest. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 9, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Merwe, S.W.; Van Wanrooij, R.L.J.; Bronswijk, M.; Everett, S.; Lakhtakia, S.; Rimbas, M.; Hucl, T.; Kunda, R.; Badaoui, A.; Law, R.; et al. Therapeutic endoscopic ultrasound: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Guideline. Endoscopy 2022, 54, 185–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimbaş, M.; Tripodi, G.; Rizzatti, G.; Larghi, A. Endoscopic ultrasound in the management of acute cholecystitis: Practical review. Dig. Endosc. 2023, 35, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemerly, M.C.; de Moura, D.T.H.; do Monte Junior, E.S.; Proença, I.M.; Ribeiro, I.B.; Yvamoto, E.Y.; Ribas, P.H.B.V.; Sánchez-Luna, S.A.; Bernardo, W.M.; de Moura, E.G.H. Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)-guided cholecystostomy versus percutaneous cholecystostomy (PTC) in the management of acute cholecystitis in patients unfit for surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg. Endosc. 2023, 37, 2421–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.J.; Park, D.H.; Eum, J.B.; Moon, S.H.; Lee, S.S.; Seo, D.W.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, M.-H. EUS-guided cholecystoenterostomy with single-step placement of a 7F double-pigtail plastic stent in patients who are unsuitable for cholecystectomy: A pilot study (with video). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2010, 71, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwan, V.; Eisendrath, P.; Antaki, F.; Moine OLe Devière, J. EUS-guided cholecystenterostomy: A new technique (with videos). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2007, 66, 582–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.S.; Park, D.H.; Hwang, C.Y.; Ahn, C.S.; Lee, T.Y.; Seo, D.W.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, M.-W. EUS-guided transmural cholecystostomy as rescue management for acute cholecystitis in elderly or high-risk patients: A prospective feasibility study. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2007, 66, 1008–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Yoshida, M.; Naitoh, I.; Okumura, F.; Kitano, R.; Haneda, K.; Hayashi, K.; Yoneda, M. Long-Term Impact of Endoscopic Gallbladder Stenting for Calculous Cholecystitis in Poor Surgical Candidates: A Multi-center Comparative Study. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2023, 68, 1529–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozakai, F.; Kanno, Y.; Ito, K.; Koshita, S.; Ogawa, T.; Kusunose, H.; Masu, K.; Sakai, T.; Murabayashi, T.; Yonamine, K.; et al. Endoscopic ultrasonography-guided gallbladder drainage as a treatment option for acute cholecystitis after metal stent placement in malignant biliary strictures. Clin. Endosc. 2019, 52, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, H.; Kitano, M.; Omoto, S.; Kadosaka, K.; Kamata, K.; Miyata, T.; Yamao, K.; Sakamoto, H.; Harwani, Y.; Kudo, M. EUS-guided gallbladder drainage for rescue treatment of malignant distal biliary obstruction after unsuccessful ERCP. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2016, 84, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, A.; Tarantino, I.; Facciorusso, A.; Binda, C.; Crinò, S.F.; Fugazza, A.; Forti, E.; Petrone, M.C.; Di Mitri, R.; Macchiarelli, R.; et al. Real-life multicentre study of lumen-Apposing metal stent for EUS-guided drainage of pancreatic fluid collections. Gut 2022, 71, 1050–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanovic, S.; Adler, D.G.; Arlt, A.; Baron, T.H.; Binmoeller, K.F.; Bronswijk, M.; Bruno, M.J.; Chevaux, J.-B.; Crinò, S.F.; Degroote, H.; et al. International Consensus Recommendations for Safe Use of LAMS for On- and Off-Label Indications Using a Modified Delphi Process. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 119, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troncone, E.; Fugazza, A.; Cappello, A.; Blanco, G.D.V.; Monteleone, G.; Repici, A.; Teoh, A.Y.B.; Anderloni, A. Malignant gastric outlet obstruction: Which is the best therapeutic option? World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 1847–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderloni, A.; Troncone, E.; Fugazza, A.; Cappello, A.; Blanco, G.D.V.; Monteleone, G.; Repici, A. Lumen-apposing metal stents for malignant biliary obstruction: Is this the ultimate horizon of our experience? World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 3857–3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dollhopf, M.; Larghi, A.; Will, U.; Rimbaş, M.; Anderloni, A.; Sanchez-Yague, A.; Teoh, A.Y.B.; Kunda, R. EUS-guided gallbladder drainage in patients with acute cholecystitis and high surgical risk using an electrocautery-enhanced lumen-apposing metal stent device. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2017, 86, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.W.; Lee, S.S.; Park, D.H.; Seo, D.W.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, M.H. Feasibility and safety of EUS-guided transgastric/transduodenal gallbladder drainage with single-step placement of a modified covered self-expandable metal stent in patients unsuitable for cholecystectomy. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2011, 74, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, D.; Song, T.J.; Cho, D.H.; Park, D.H.; Seo, D.W.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, M.-H.; Lee, S.S. EUS-guided cholecystostomy versus endoscopic transpapillary cholecystostomy for acute cholecystitis in high-risk surgical patients. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2019, 89, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irani, S.; Kozarek, R.A. The buried lumen-apposing metal stent: Is this a stent problem, a location problem, or both? VideoGIE 2016, 1, 25–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teoh, A.Y.B.; Serna, C.; Penas, I.; Chong, C.C.N.; Perez-Miranda, M.; Ng, E.K.W.; Lau, J.Y.W. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided gallbladder drainage reduces adverse events compared with percutaneous cholecystostomy in patients who are unfit for cholecystectomy. Endoscopy 2017, 49, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.W.; Lee, S.S. Current status of endoscopic management of cholecystitis. Dig. Endosc. 2022, 34, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderloni, A.; Buda, A.; Vieceli, F.; Khashab, M.A.; Hassan, C.; Repici, A. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided transmural stenting for gallbladder drainage in high-risk patients with acute cholecystitis: A systematic review and pooled analysis. Surg. Endosc. 2016, 30, 5200–5208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teoh, A.Y.; Perez-Miranda, M.; Kunda, R.; Lee, S.S.; Irani, S.; Yeaton, P.; Sun, S.; Baron, T.H.; Moon, J.H.; Holt, B.; et al. Outcomes of an international multicenter registry on EUS-guided gallbladder drainage in patients at high risk for cholecystectomy. Endosc. Int. Open 2019, 7, E964–E973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beunon, C.; Debourdeau, A.; Schaefer, M.; Wallenhorst, T.; Perez-Cuadrado-Robles, E.; Belle, A.; Gonzalez, J.-M.; Duboc, M.C.; Caillol, F.; Toudic, H.-P.; et al. Technical failure of endoscopic ultrasound-guided choledochoduodenostomy: Multicenter study on rescue techniques, consequences, and risk factors. Endoscopy 2025, 57, 990–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troncone, E.; Amendola, R.; Moscardelli, A.; De Cristofaro, E.; De Vico, P.; Paoluzi, O.A.; Monteleone, G.; Perez-Miranda, M.; Blanco, G.D.V. Endoscopic Gallbladder Drainage: A Comprehensive Review on Indications, Techniques, and Future Perspectives. Medicina 2024, 60, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Suresh Kumar, V.C.; Aswath, G.; Akbar Khan, H.M.; Sapkota, B.; Vinayek, R.; Dutta, S.; Dahiya, D.S.; Inamdar, S.; Mohan, B.P.; et al. Indirect comparison of various lumen-apposing metal stents for EUS-guided biliary and gallbladder drainage: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2024, 100, 829–839.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binda, C.; Anderloni, A.; Forti, E.; Fusaroli, P.; Macchiarelli, R.; Manno, M.; Fugazza, A.; Redaelli, A.; Aragona, G.; Lovera, M.; et al. EUS-Guided Gallbladder Drainage Using a Lumen-Apposing Metal Stent for Acute Cholecystitis: Results of a Nationwide Study with Long-Term Follow-Up. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabbani, T.; Bonura, G.F.; Biancheri, P.; Soriani, P.; Manno, M. Endoscopic lithotripsy of a gallstone impacted in lumen-apposing metal stent positioned for cholecysto-gastrostomy. VideoGIE 2023, 8, 286–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higa, J.T.; Irani, S.S. Endoscopic Methods for Gallbladder Drainage. Curr. Treat. Options Gastroenterol. 2019, 17, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teoh, A.Y.B.; Leung, C.H.; Tam, P.T.H.; Au Yeung, K.K.Y.; Mok, R.C.Y.; Chan, D.L.; Chan, S.M.; Yip, H.C.; Chiu, P.W.Y.; Ng, E.K.W. EUS-guided gallbladder drainage versus laparoscopic cholecystectomy for acute cholecystitis: A propensity score analysis with 1-year follow-up data. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2021, 93, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.M.; Teoh, A.Y.B.; Yip, H.C.; Wong, V.W.Y.; Chiu, P.W.Y.; Ng, E.K.W. Feasibility of per-oral cholecystoscopy and advanced gallbladder interventions after EUS-guided gallbladder stenting (with video). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2017, 85, 1225–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisotti, A. Endoscopic ultrasound gallbladder drainage (EUS-GBD) with LAMS: While we know how to drain we are still questioning who to drain. Endosc. Int. Open 2025, 13, a24877723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irani, S.S.; Sharma, N.R.; Storm, A.C.; Shah, R.J.; Chahal, P.; Willingham, F.F.; Swanstrom, L.; Baron, T.; Shlomovitz, E.; Kozarek, R.A.; et al. Endoscopic Ultrasound-guided Transluminal Gallbladder Drainage in Patients with Acute Cholecystitis: A Prospective Multicenter Trial. Ann. Surg. 2023, 278, E556–E562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facciorusso, A.; Binda, C.; Crinò, S.F.; Lisotti, A.; Spadaccini, M.; Amato, A.; Carrozza, L.; Catena, F.; Cobianchi, L. The i-EUS consensus on EUS-guided gallbladder drainage: A 3-step modified Delphi approach. Endosc. Ultrasound 2025, 14, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, J.Y.; Arnoletti, J.P.; Wagner, A.; Varadarajulu, S. EUS-guided gallbladder drainage in acute cholecystitis: Long-term problems with surgical approach. Gut 2023, 73, 395–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaura, K.; Bazerbachi, F.; Sawas, T.; Levy, M.J.; Martin, J.A.; Storm, A.C.; Wise, K.B.; Reisenauer, C.J. Surgical outcomes of ERCP-guided transpapillary gallbladder drainage versus percutaneous cholecystostomy as bridging therapies for acute cholecystitis followed by interval cholecystectomy. HPB 2020, 22, 996–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saumoy, M.; Tyberg, A.; Brown, E.; Eachempati, S.R.; Lieberman, M.; Afaneh, C.; Kunda, R.; Cosgrove, N.; Siddiqui, A.; Gaidhane, M.; et al. Successful Cholecystectomy after Endoscopic Ultrasound Gallbladder Drainage Compared with Percutaneous Cholecystostomy, Can it Be Done? J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2019, 53, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazaga, S.; García-Alonso, F.J.; Aparicio Tormo, J.R.; Martinez Moreno, B.; Sanchiz, V.; Gornals, J.B. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided gallbladder drainage with long-term lumen-apposing metal stent indwell: 1-year results from a prospective nationwide observational study. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 39, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irani, S.S.; Sharzehi, K.; Siddiqui, U.D. AGA Clinical Practice Update on Role of EUS-Guided Gallbladder Drainage in Acute Cholecystitis: Commentary. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 21, 1141–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, S.S. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided gallbladder drainage: A technical review. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2021, 34, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Rana, S.S.; Bhasin, D.K. Endoscopic ultrasound guided interventional procedures. World J. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2015, 7, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobani, Z.A.; Ling, C.; Rustagi, T. Endoscopic Transpapillary Gallbladder Drainage for Acute Cholecystitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2021, 66, 1425–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Takano, Y.; Kigawa, G.; Shiozawa, T.; Takahashi, Y.; Nagahama, M. Percutaneous transhepatic gallbladder drainage versus endoscopic gallbladder stenting for managing acute cholecystitis until laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Asian J. Endosc. Surg. 2024, 17, e13253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winbladh, A.; Gullstrand, P.; Svanvik, J.; Sandström, P. Systematic review of cholecystostomy as a treatment option in acute cholecystitis. HPB 2009, 11, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podboy, A.; Yuan, J.; Stave, C.D.; Chan, S.M.; Hwang, J.H.; Teoh, A.Y.B. Comparison of EUS-guided endoscopic transpapillary and percutaneous gallbladder drainage for acute cholecystitis: A systematic review with network meta-analysis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2021, 93, 797–804.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayat, U.; Al Shabeeb, R.; Perez, P.; Hensien, J.; Dwivedi, A.; Sakhawat, U.; Ahmad, O.; Haseeb, M.; Siddiqui, A.A.; Adler, D.G. Safety and adverse events of EUS-guided gallbladder drainage using lumen-apposing metal stents and percutaneous cholecystostomy tubes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2024, 99, 444–448.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irani, S.; Ngamruengphong, S.; Teoh, A.; Will, U.; Nieto, J.; Dayyeh, B.K.A.; Gan, S.I.; Larsen, M.; Yip, H.C.; Topazian, M.D.; et al. Similar Efficacies of Endoscopic Ultrasound Gallbladder Drainage with a Lumen-Apposing Metal Stent Versus Percutaneous Transhepatic Gallbladder Drainage for Acute Cholecystitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 15, 738–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyberg, A.; Saumoy, M.; Sequeiros, E.V.; Giovannini, M.; Artifon, E.; Teoh, A. EUS-guided Versus Percutaneous Gallbladder Drainage: Isn’t It Time to Convert? J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2016, 52, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, B.P.; Khan, S.R.; Trakroo, S.; Ponnada, S.; Jayaraj, M.; Asokkumar, R.; Adler, D.G. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided gallbladder drainage, transpapillary drainage, or percutaneous drainage in high risk acute cholecystitis patients: A systematic review and comparative meta-analysis. Vol. 52, Endoscopy. Endoscopy 2020, 52, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luk, S.W.Y.; Irani, S.; Krishnamoorthi, R.; Wong Lau, J.Y.; Wai Ng, E.K.; Teoh, A.Y.B. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided gallbladder drainage versus percutaneous cholecystostomy for high risk surgical patients with acute cholecystitis: A systematic review and meta-Analysis. Endoscopy 2019, 51, 722–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamoorthi, R.; Jayaraj, M.; Thoguluva Chandrasekar, V.; Singh, D.; Law, J.; Larsen, M.; Ross, A.; Kozarek, R.; Irani, S. EUS-guided versus endoscopic transpapillary gallbladder drainage in high-risk surgical patients with acute cholecystitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg. Endosc. 2020, 34, 1904–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarty, T.R.; Hathorn, K.E.; Bazarbashi, A.N.; Jajoo, K.; Ryou, M.; Thompson, C.C. Endoscopic gallbladder drainage for symptomatic gallbladder disease: A cumulative systematic review meta-analysis. Surg. Endosc. 2021, 35, 4964–4985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, J.Y.; Varadarajulu, S. Management of walled-off necrosis using the multiple transluminal gateway technique with the Hot AXIOS System. Dig. Endosc. 2016, 28, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fok, J.C.Y.; Teoh, A.Y.B.; Chan, S.M. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided gallbladder drainage for acute cholecystitis. Dig. Endosc. 2024, 37, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, N.; Coelho-Prabhu, N.; Al-Haddad, M.A.; Kwon, R.S.; Amateau, S.K.; Buxbaum, J.L.; Calderwood, A.H.; Elhanafi, S.E.; Fujii-Lau, L.L.; Kohli, D.R.; et al. Adverse events associated with EUS and EUS-guided procedures. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2022, 95, 16–26.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goonawardena, J.; Gunnarsson, R.; De Costa, A. Predicting conversion from laparoscopic to open cholecystectomy presented as a probability nomogram based on preoperative patient risk factors. Am. J. Surg. 2015, 210, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, Y.; Kakked, G.; Confer, B.; Shah, R.; Khara, H.; Diehl, D.L.; Krafft, M.R.; Shah-Khan, S.M.; Nasr, J.Y.; Benias, P.; et al. US multicenter outcomes of endoscopic ultrasound-guided gallbladder drainage with lumen-apposing metal stents for acute cholecystitis. Endosc. Int. Open 2025, 13, a24955542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boregowda, U.; Chen, M.; Saligram, S. Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Gallbladder Drainage versus Percutaneous Gallbladder Drainage for Acute Cholecystitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Early AEs | Late AEs | Mortality Rate (30-Day) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| EUS-GBD with LAMS | Dislodgement: 2.5% | Migration: 0.8% | 19.8% |
| Bleeding: 1.7% | Perforation: 0.8% | ||
| Perforation: 0.8% | Buried stent: 0.8% | ||
| Malpositioning: 0.8% | AC recurrence: 0.8% | ||
| PT-GBD | Dislodgement: 8.6% | Infections: 6.2% | 15.4% |
| AC recurrence: 9% | |||
| Obstruction: 4–15% |
| Clinical Success | Technical Success | AEs | Re-Intervention Rate | External Device | Anesthesia | Hospital LOS | Resource Utilization | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EUS-GBD with LAMS | High | High | Low | Low | No | Deep sedation, General | Shorter | Endoscopy service, anesthesiologist |
| PT-GBD | High | High | High | High | Yes | Minimal or Local | Prolonged | Interventional Radiology |
| ETP-GBD | Low | Low | High | Low | No | Deep sedation, General | Prolonged | Endoscopy service, anesthesiologist |
| Study (Author, Year) | N. Studies Included | Comparison | Technical Success | Clinical Success | Adverse Event | Reintervention | Readmission |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hemerly et al., 2023 [13] | 11 (4 EUS-GBD with LAMS) | EUS-GBD vs. PT-GBD | ≈ | ≈ | ↓ EUS-GBD with LAMS | ↓ EUS-GBD with LAMS | ↓ EUS-GBD with LAMS |
| Luk et al., 2019 [58] | 5 (3 EUS-GBD with LAMS) | EUS-GBD vs. PT-GBD | ≈ | ≈ | ≈ | ↓ EUS-GBD with LAMS | ↓ EUS-GBD with LAMS |
| Hayat et al., 2024 [54] | 6 (all EUS-GBD with LAMS) | EUS-GBD vs. PT-GBD | N/S | N/S | ↓ EUS-GBD with LAMS | ↓ EUS-GBD with LAMS | ↓ EUS-GBD with LAMS |
| Krishnamoorthi et al., 2020 [59] | 5 (3 EUS-GBD with LAMS) | EUS-GBD vs. ETP-GBD | ↑ EUS-GBD with LAMS | ↑ EUS-GBD with LAMS | ≈ | N/S | N/S |
| McCarty et al., 2021 [60] | 36 (11 EUS-GBD with LAMS) | Endoscopic GBD (ERCP vs. EUS) | ↑ EUS-GBD with LAMS | ↑ EUS-GBD with LAMS | ≈ | ↓ EUS-GBD with LAMS | N/S |
| Study (Author, Year) | Mean Age | Comorbidities | AC Grade (Tokyo Criteria) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hemerly et al., 2023 [13] | 73 ± 12 | ASA ≥ III | Grade II/III |
| CCI ≥ 4 | |||
| Luk et al., 2019 [58] | 73.9 ± 7.5 | ASA ≥ IV | Grade II/III |
| CCI ≥ 4 (mean 5.6) | |||
| Hayat et al., 2024 [54] | 73.78 ± 8.01 | ASA ≥ III | Grade II/III |
| CCI ≥ 4 | |||
| Krishnamoorthi et al., 2020 [59] | 70.5 ± 8.2 | ASA ≥ III | Grade II/III |
| McCarty et al., 2021 [60] | 72.4 ± 5.4 | ASA ≥ III | Grade II/III |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zadro, V.; Bertoncini, G.; Bonura, G.F.; Cortegoso Valdivia, P.; Gualandi, N.; Soriani, P.; Gabbani, T.; Manno, M. The Effect of Lumen-Apposing Metal Stent (LAMS) in Acute Cholecystitis Unfit for Surgery: Good Tidings. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2835. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15222835
Zadro V, Bertoncini G, Bonura GF, Cortegoso Valdivia P, Gualandi N, Soriani P, Gabbani T, Manno M. The Effect of Lumen-Apposing Metal Stent (LAMS) in Acute Cholecystitis Unfit for Surgery: Good Tidings. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(22):2835. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15222835
Chicago/Turabian StyleZadro, Valentina, Giulia Bertoncini, Giuliano Francesco Bonura, Pablo Cortegoso Valdivia, Noemi Gualandi, Paola Soriani, Tommaso Gabbani, and Mauro Manno. 2025. "The Effect of Lumen-Apposing Metal Stent (LAMS) in Acute Cholecystitis Unfit for Surgery: Good Tidings" Diagnostics 15, no. 22: 2835. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15222835
APA StyleZadro, V., Bertoncini, G., Bonura, G. F., Cortegoso Valdivia, P., Gualandi, N., Soriani, P., Gabbani, T., & Manno, M. (2025). The Effect of Lumen-Apposing Metal Stent (LAMS) in Acute Cholecystitis Unfit for Surgery: Good Tidings. Diagnostics, 15(22), 2835. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15222835






