Dangerous Alarming Diameter Assessment (DADA Index) in Which the Ratio of Iris Surface/Pupil Surface Size Is More Reliable than Pupil Diameter Measurement in Comatose Patients After Subarachnoid Haemorrhage: An Experimental Rabbit Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Histological and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Larson, M.D.; Muhiudeen, I. Pupillometric Analysis of the “Absent Light Reflex”. JAMA Neurol. 1995, 52, 369–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeker, M.; Du, R.; Bacchetti, P.; Privitera, C.M.; Larson, M.D.; Holland, M.C.; Manley, G. Pupil Examination: Validity and Clinical Utility of an Automated Pupillometer. J. Neurosci. Nurs. 2005, 37, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couret, D.; Boumaza, D.; Grisotto, C.; Triglia, T.; Pellegrini, L.; Ocquidant, P.; Bruder, N.J.; Velly, L.J. Reliability of Standard Pupillometry Practice in Neurocritical Care: An Observational, Double-Blinded Study. Crit. Care 2016, 20, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Roux, P.; Menon, D.K.; Citerio, G.; Vespa, P.; Bader, M.K.; Brophy, G.M.; Diringer, M.N.; Stocchetti, N.; Videtta, W.; Armonda, R.; et al. Consensus Summary Statement of the International Multidisciplinary Consensus Conference on Multimodality Monitoring in Neurocritical Care: A Statement for Healthcare Professionals from the Neurocritical Care Society and the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Neurocrit. Care 2014, 21, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Gombart, Z.; Rogers, S.; Gardiner, S.; Cecil, S.; Bullock, R. Pupillary Reactivity as an Early Indicator of Increased Intracranial Pressure: The Introduction of the Neurological Pupil Index. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2011, 2, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, W.R.; Chen, J.W.; Meltzer, H.; Gennarelli, T.A.; Kelbch, C.; Knowlton, S.; Richardson, J.; Lutch, M.J.; Farin, A.; Hults, K.N.; et al. Quantitative Pupillometry, a New Technology: Normative Data and Preliminary Observations in Patients with Acute Head Injury—Technical Note. J. Neurosurg. 2003, 98, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, D.M.; Stutzman, S.E.; Atem, F.; Kincaide, J.D.; Ho, T.T.; Carlisle, B.A.; Aiyagari, V. Establishing Normative Data for Pupillometer Assessment in Neuroscience Intensive Care: The “END-PANIC” Registry. J. Neurosci. Nurs. 2017, 49, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, S.S.; Mueller, C.M.; Nogueira, R.G.; Khalifa, Y.M. A Systematic Review Assessing the Current State of Automated Pupillometry in the NeuroICU. Neurocrit. Care 2019, 31, 142–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, P.J.; Reiner, A.; Gamlin, P.D. Autonomic Regulation of the Eye. In Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Neuroscience; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, J.W.; Skrobik, Y.; Gélinas, C.; Needham, D.M.; Slooter, A.J.C.; Pandharipande, P.P.; Watson, P.L.; Weinhouse, G.L.; Nunnally, M.E.; Rochwerg, B.; et al. Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Prevention and Management of Pain, Agitation/Sedation, Delirium, Immobility, and Sleep Disruption in Adult Patients in the ICU. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 46, E825–E873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadade, R.; Harde, M.; Nadkar, M.; Tiwasker, M.; Vora, A.; Saraf, A.; Pal, J.; Joshi, S.; Sreenivasmurthy; de Souza, R. Clinical Practice Guidelines for Management of Pain, Agitation, Delirium, Immobility, and Sleep Disturbance in the Intensive Care Unit: The ABCDEF Bundle. J. Assoc. Physicians India 2023, 71, 11–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biçer, G.Y.; Zor, K.R.; Küçük, E. Do Static and Dynamic Pupillary Parameters Differ According to Childhood, Adulthood, and Old Age? A Quantitative Study in Healthy Volunteers. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 70, 3575–3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayraktar, S.; Hondur, G.; Şekeroǧlu, M.A.; Şen, E. Evaluation of Static and Dynamic Pupillary Functions in Early Stage Primary Open Angle Glaucoma. J. Glaucoma 2023, 32, e90–e94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kızıltoprak, H.; Tekin, K.; Sekeroglu, M.A.; Yetkin, E.; Doguizi, S.; Yilmazbas, P. Static and Dynamic Pupillary Responses in Patients with Different Stages of Diabetic Retinopathy. Neuro-Ophthalmology 2020, 44, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lussier, B.L.; Olson, D.W.M.; Aiyagari, V. Automated Pupillometry in Neurocritical Care: Research and Practice. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2019, 19, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, C.J. The Prognostic Potential of Pupillometry in Patients with Acute Brain Injury. Lancet Neurol. 2023, 22, 876–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.; Lefering, R.; Rueger, J.M.; Kolb, J.P.; Izbicki, J.R.; Ruecker, A.H.; Rupprecht, M.; Lehmann, W. Pupil Evaluation in Addition to Glasgow Coma Scale Components in Prediction of Traumatic Brain Injury and Mortality. Br. J. Surg. 2012, 99, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koirala, P.; Shrestha, D.; Phuyal, S.; Sharma, M.R. Comparision between the Glasgow Coma Scale and Glasgow Coma Scale Pupil Reactivity Score in Predicting Mortality in Traumatic Brain Injury Patients. Nepal J. Neurosci. 2022, 19, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majdan, M.; Steyerberg, E.W.; Nieboer, D.; Mauritz, W.; Rusnak, M.; Lingsma, H.F. Glasgow Coma Scale Motor Score and Pupillary Reaction to Predict Six-Month Mortality in Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury: Comparison of Field and Admission Assessment. J. Neurotrauma 2015, 32, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlamäki, K.; Rautalin, I.; Korja, M. Supplementary Material for: Case Fatality Rates of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Are Decreasing with Substantial between-Country Variation: A Systematic Review of Population-Based Studies between 1980 and 2020. Neuroepidemiology 2022, 56, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwkamp, D.J.; Setz, L.E.; Algra, A.; Linn, F.H.; de Rooij, N.K.; Rinkel, G.J. Changes in Case Fatality of Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Haemorrhage over Time, According to Age, Sex, and Region: A Meta-Analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2009, 8, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, M.D.; Behrends, M. Portable Infrared Pupillometry: A Review. Anesth. Analg. 2015, 120, 1242–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morelli, P.; Oddo, M.; Ben-Hamouda, N. Role of Automated Pupillometry in Critically Ill Patients. Minerva Anestesiol. 2019, 85, 995–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banco, P.; Taccone, F.S.; Sourd, D.; Privitera, C.; Bosson, J.L.; Teixeira, T.L.; Adolle, A.; Payen, J.F.; Bouzat, P.; Gauss, T. Prediction of Neurocritical Care Intensity through Automated Infrared Pupillometry and Transcranial Doppler in Blunt Traumatic Brain Injury: The NOPE Study. Eur. J. Trauma Emerg. Surg. 2024, 50, 1209–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oddo, M.; Taccone, F.S.; Petrosino, M.; Badenes, R.; Blandino-Ortiz, A.; Bouzat, P.; Caricato, A.; Chesnut, R.M.; Feyling, A.C.; Ben-Hamouda, N.; et al. The Neurological Pupil Index for Outcome Prognostication in People with Acute Brain Injury (ORANGE): A Prospective, Observational, Multicentre Cohort Study. Lancet Neurol. 2023, 22, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghauri, M.S.; Ueno, A.; Mohammed, S.; Miulli, D.E.; Siddiqi, J. Evaluating the Reliability of Neurological Pupillary Index as a Prognostic Measurement of Neurological Function in Critical Care Patients. Cureus 2022, 14, e28901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortube, M.C.; Kiderman, A.; Eydelman, Y.; Yu, F.; Aguilar, N.; Nusinowitz, S.; Gorin, M.B. Comparative Regional Pupillography as a Noninvasive Biosensor Screening Method for Diabetic Retinopathy. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurgel Lopes, C. Cerebral State Index and Brain Death. In Proceedings of the ESA 2016, London, UK, 28–30 May 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mader, M.M.; Piffko, A.; Dengler, N.F.; Ricklefs, F.L.; Dührsen, L.; Schmidt, N.O.; Regelsberger, J.; Westphal, M.; Wolf, S.; Czorlich, P. Initial Pupil Status Is a Strong Predictor for In-Hospital Mortality after Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobata, H.; Ikawa, F.; Sato, A.; Kato, Y.; Sano, H. Significance of Pupillary Findings in Decision Making and Outcomes of World Federation of Neurological Societies Grade V Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 2023, 93, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahns, F.P.; Miroz, J.P.; Messerer, M.; Daniel, R.T.; Taccone, F.S.; Eckert, P.; Oddo, M. Quantitative Pupillometry for the Monitoring of Intracranial Hypertension in Patients with Severe Traumatic Brain Injury. Crit. Care 2019, 23, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.A.; Garza, P.S.; Biousse, V.; Samuels, O.B.; Newman, N.J.; Bruce, B.B.; Fraser, C.; Mollan, S. Prognostic Value of the Neurological Pupil Index in Patients With Acute Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. J. Neuro-Ophthalmol. 2022, 42, 256–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerapaneni, D.; Arunachalam Sakthiyendran, N.; Du, Y.; Mallinger, L.A.; Reinert, A.; Yeon Kim, S.; Nguyen, C.; Daneshmand, A.; Abdalkader, M.; Mohammed, S.; et al. Early Pupil Abnormality Frequency Predicts Poor Outcomes and Enhances International Mission for Prognosis and Analysis of Clinical Trials in Traumatic Brain Injury (IMPACT) Model Prognostication in Traumatic Brain Injury. Crit. Care Explor. 2025, 7, e1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scala, I.; Miccoli, M.; Di Giovanni, J.; Cerulli, F.; Rizzo, P.A.; Bellavia, S.; Vitali, F.; Colò, F.; Abruzzese, S.; Della Marca, G.; et al. Automated Pupillometry Is a Predictor of Outcome of Stroke Patients: An Observational, Prospective, Cohort Study. Brain Commun. 2025, 7, fcaf079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, C.; Moreno, J.H.; Marshall, J.L.; Olson, D.M.; Aiyagari, V. Neuroradiological Correlates of Abnormal Pupillary Light Reflex Findings among Patients in the Neuroscience Intensive Care Unit. J. Neurosci. Nurs. 2025, 57, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Perez, S.; Shoyombo, I.; Aiyagari, V.; Atem, F.; Hill, M.; Stutzman, S.E.; Olson, D.W.M. Pupillary Light Reflex Variability as a Predictor of Clinical Outcomes in Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. J. Neurosci. Nurs. 2019, 51, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, S.A.; Noble, J.; Wong, A.M.F. Examining the Pupils. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2013, 185, E424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hernández-Sierra, J.F.; Tellez-Quijada, F.; Hernández Gómez, C.A.; Hernández-Gómez, J.F.; Fonseca Leal, P. Estimation and Interrater Reliability of Pupillography by Digital Mobile App: Digital Movil Pupillography App Validity. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 31, 1779–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekonnen, T.; Zevallos Delgado, C.; Safa, B.N.; Singh, M.; Aglyamov, S.R.; Ethier, C.R.; Larin, K.V. Characterizing Regional Biomechanical Properties of the Porcine Iris Using Optical Coherence Elastography. Opt. Elastography Tissue Biomech. X 2023, 12381, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appenzeller, O.; Lamotte, G.J.; Coon, E.A. The Pupil. In Introduction to Clinical Aspects of the Autonomic Nervous System; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 45–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skalicky, S.E. The Iris and Pupil. In Ocular and Visual Physiology; Springer: Singapore, 2016; pp. 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, H. Ocular Autonomic Nervous System: An Update from Anatomy to Physiological Functions. Vision 2022, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafar, S.F.; Suarez, J.I. Automated Pupillometer for Monitoring the Critically Ill Patient: A Critical Appraisal. J. Crit. Care 2014, 29, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litvan, I.; Saposnik, G.; Mauriño, J.; Gonzalez, L.; Saizar, R.; Sica, R.E.P.; Bartko, J.J. Pupillary Diameter Assessment: Need for a Graded Scale. Neurology 2000, 54, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blini, E.; Arrighi, R.; Anobile, G. Pupillary Manifolds: Uncovering the Latent Geometrical Structures behind Phasic Changes in Pupil Size. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 27306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peinkhofer, C.; Knudsen, G.M.; Moretti, R.; Kondziella, D. Cortical Modulation of Pupillary Function: Systematic Review. PeerJ 2019, 7, e6882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maddess, T. Pupil Dynamics and Response Amplitude: Only Size Matters. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 7644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bremner, F.D. Pupillometric Evaluation of the Dynamics of the Pupillary Response to a Brief Light Stimulus in Healthy Subjects. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 7343–7347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozicz, T.; Bittencourt, J.C.; May, P.J.; Reiner, A.; Gamlin, P.D.R.; Palkovits, M.; Horn, A.K.E.; Toledo, C.A.B.; Ryabinin, A.E. The Edinger-Westphal Nucleus: A Historical, Structural, and Functional Perspective on a Dichotomous Terminology. J. Comp. Neurol. 2011, 519, 1413–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Whang, M. Infrared Camera-Based Non-Contact Measurement of Brain Activity From Pupillary Rhythms. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.H.; Kuo, L.T. Application of Pupillometry in Neurocritical Patients. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDougal, D.H.; Gamlin, P.D. Autonomic Control of the Eye. Compr. Physiol. 2015, 5, 439–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabadi, E. Functional Organization of the Sympathetic Pathways Controlling the Pupil: Light-Inhibited and Light-Stimulated Pathways. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Ricarte, F.; Castro, A.; Poca, M.A.; Sahuquillo, J.; Expósito, L.; Arribas, M.; Aparicio, J. Pupilometría por Infrarrojos. Descripción y Fundamentos de La Técnica y su Aplicación en la Monitorización No Invasiva del Paciente Neurocrítico. Neurologia 2013, 28, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bower, M.M.; Sweidan, A.J.; Xu, J.C.; Stern-Neze, S.; Yu, W.; Groysman, L.I. Quantitative Pupillometry in the Intensive Care Unit. J. Intensive Care Med. 2021, 36, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opic, P.; Rüegg, S.; Marsch, S.; Gut, S.S.; Sutter, R. Automated Quantitative Pupillometry in the Critically Ill: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Neurology 2021, 97, E629–E642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, D.W.M.; Stutzman, S.; Saju, C.; Wilson, M.; Zhao, W.; Aiyagari, V. Interrater Reliability of Pupillary Assessments. Neurocrit. Care 2016, 24, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulter, J.H.; Shields, M.M.; Meister, M.R.; Murtha, G.; Curry, B.P.; Dengler, B.A. The Expanding Role of Quantitative Pupillometry in the Evaluation and Management of Traumatic Brain Injury. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 685313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, C.S. Performance of the Quantitative Pupillary Light Reflex and Neurological Pupil Index for Predicting Neurological Outcomes in Cardiac Arrest Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medicine 2025, 104, e41314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijdicks, E.F.M.; Varelas, P.N.; Gronseth, G.S.; Greer, D.M. Evidence-Based Guideline Update: Determining Brain Death in Adults: Report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 2010, 74, 1911–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khandelwal, A.; Mishra, R.K.; Singh, S.; Singh, S.; Rath, G.P. Dilated Pupil as a Diagnostic Component of Brain Death-Does It Really Matter? J. Neurosurg. Anesthesiol. 2018, 31, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenga, P.; Kühlwein, D.; Schönenberger, S.; Neumann, J.O.; Unterberg, A.W.; Beynon, C. The Use of Quantitative Pupillometry in Brain Death Determination: Preliminary Findings. Neurol. Sci. 2024, 45, 2165–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Bansal, R.; Sharma, A.; Kapil, A. Pupillary Signs. In Ophthalmic Signs in Practice of Medicine; Springer: Singapore, 2023; pp. 475–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, C.A.; Chilcott, R.P. Eyeing up the Future of the Pupillary Light Reflex in Neurodiagnostics. Diagnostics 2018, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
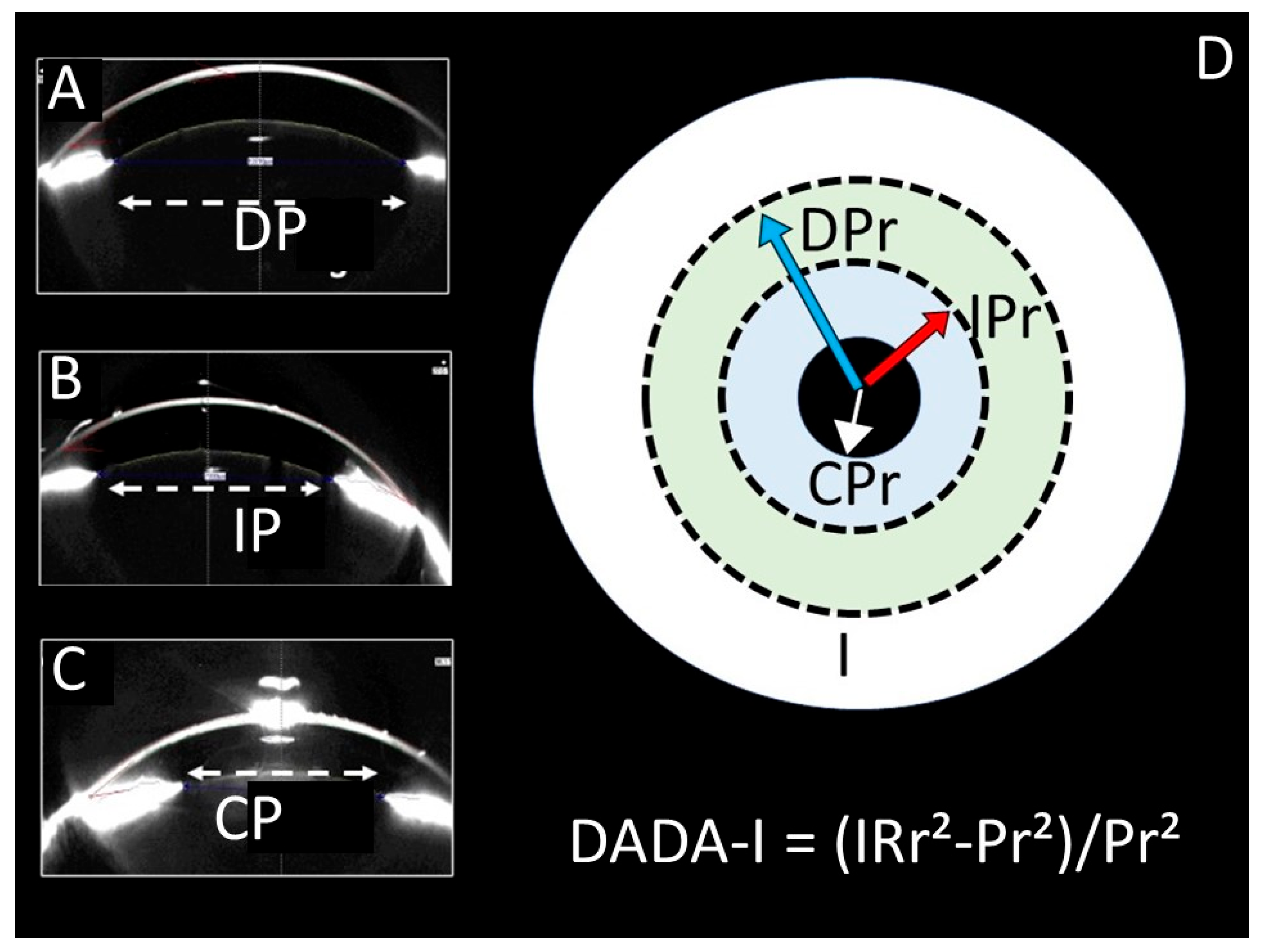
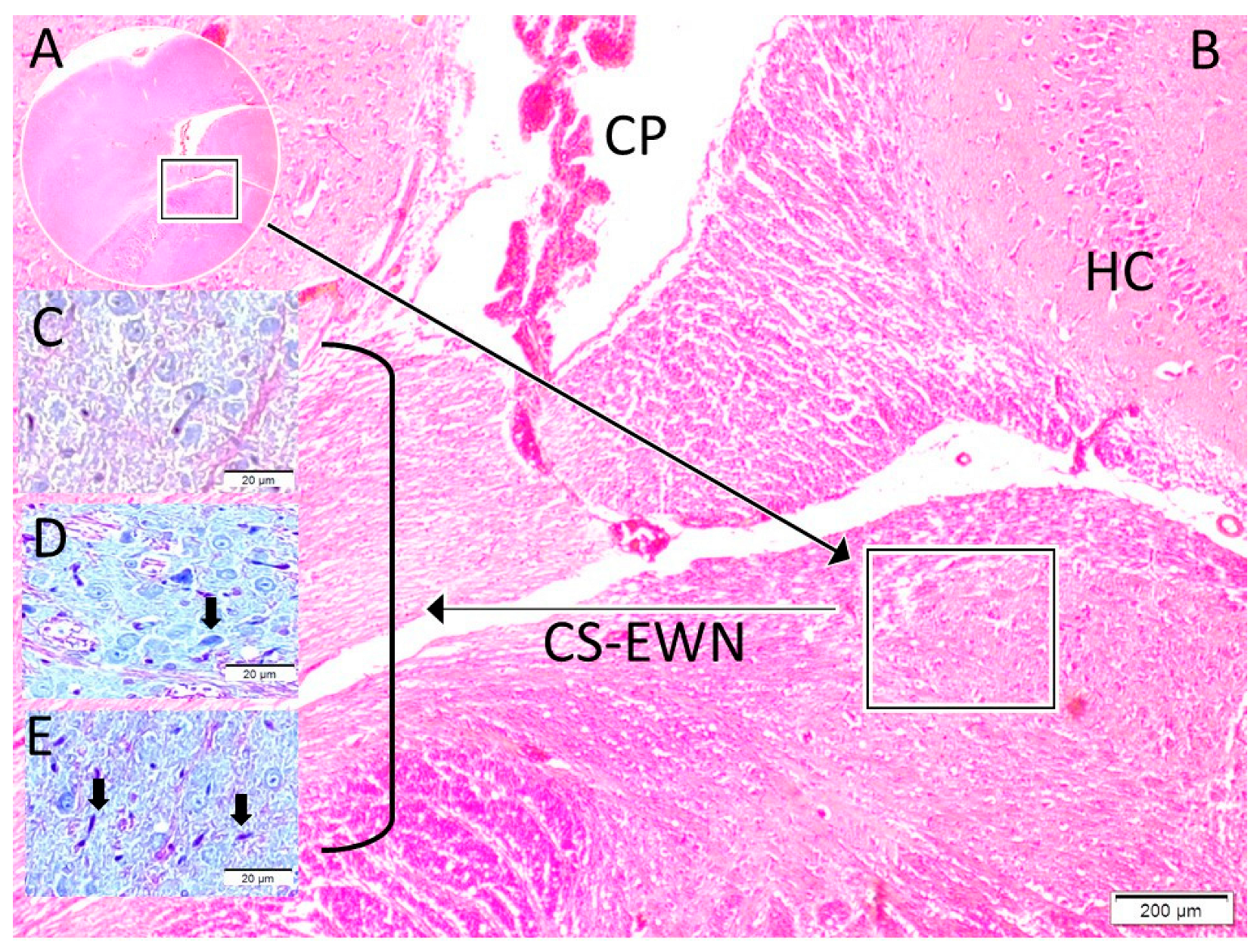
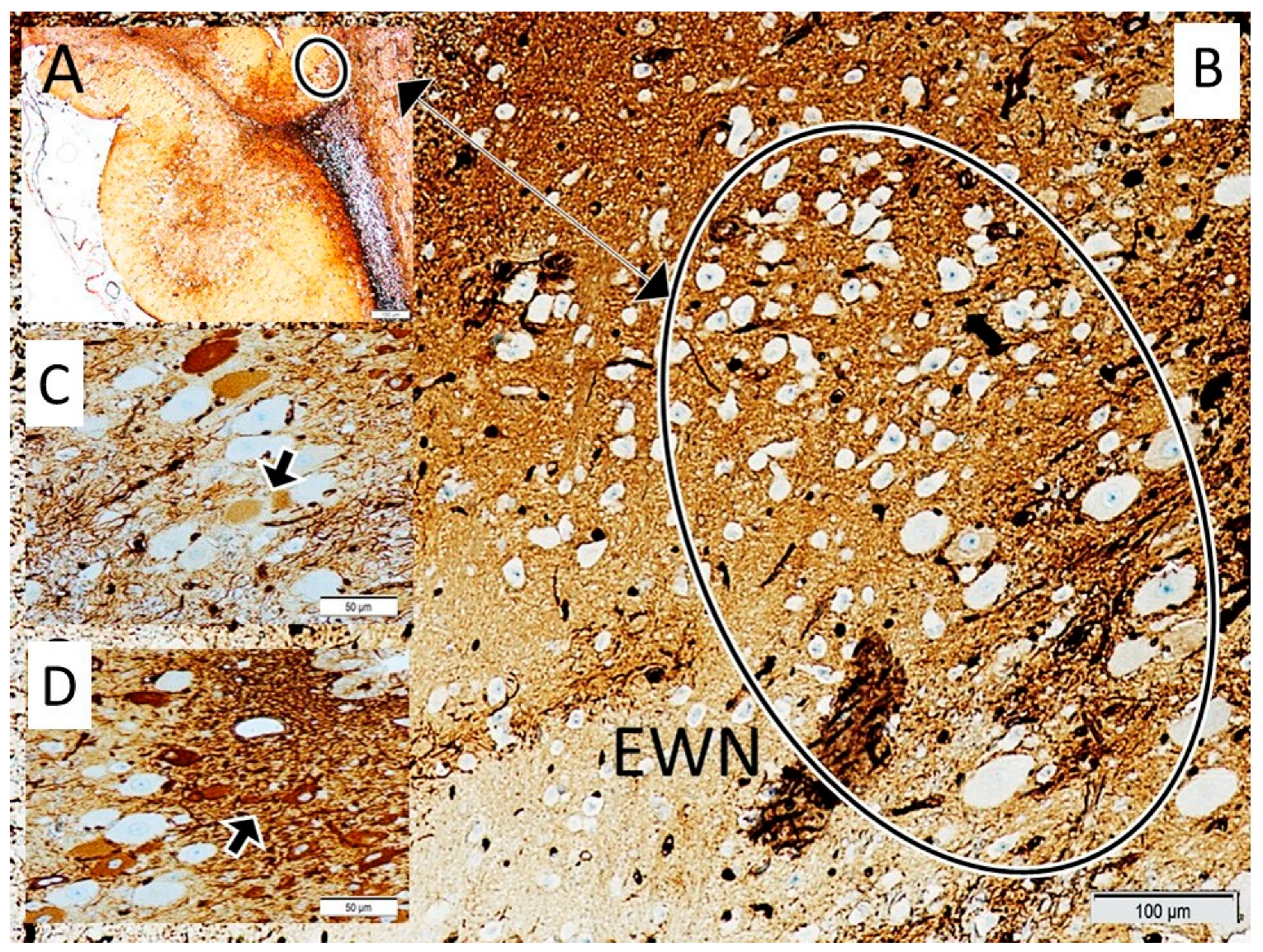
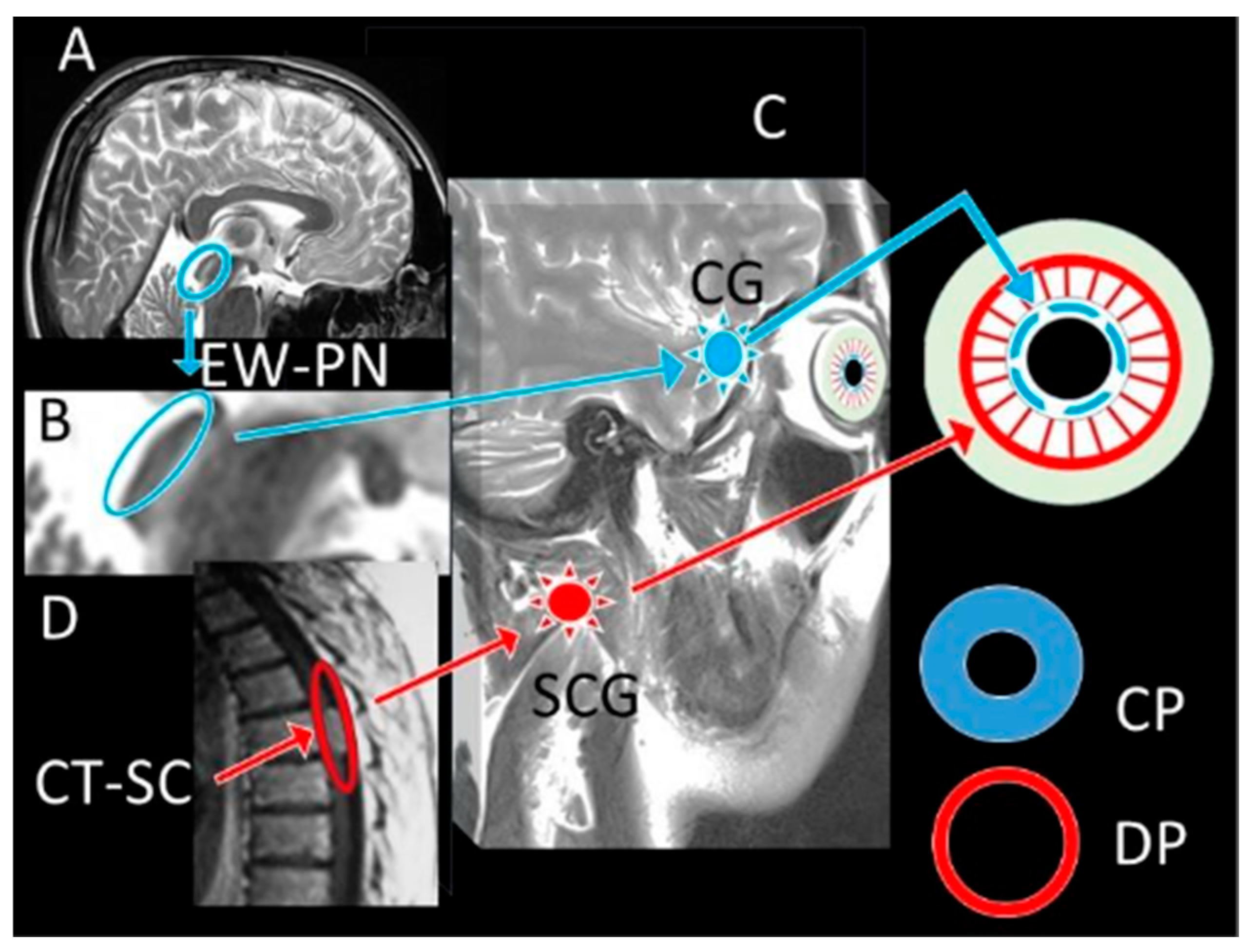
| Control (1) | SHAM (2) | STUDY (3) | p (1–2) | p (1–3) | p (2–3) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pupil Diameter | Mean ± SS | 5900.00 ± 546.32 | 6310.00 ± 533.35 | 9989.50 ± 747.12 | |||
| Median (Min–Max) | 5900.00 (5200.00–6600.00) | 6340.00 (5452.00–6850.00) | 10,039.00 (8780.00–11,138.00) | 0.602 | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | |
| DADA Index | Mean ± SS | 2.32 ± 0.43 | 1.95 ± 0.37 | 1.06 ± 0.31 | |||
| Median (Min–Max) | 2.32 (1.78–2.90) | 1.95 (1.47–2.41) | 1.04 (0.58–1.65) | 0.444 | 0.003 * | 0.008 * | |
| Degeneration Neuron | Mean ± SS | 3.00 ± 0.95 | 12.00 ± 2.92 | 18.00 ± 4.00 | |||
| Median (Min–Max) | 3.00 (1.80–4.20) | 12.00 (8.20–15.80) | 18.00 (11.00–25.00) | 0.004 * | <0.001 * | 0.018 * |
| Pupil Diameter | Degeneration Neuron | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Dada Index | r | −0.972 ** | −0.977 ** |
| p | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| N | 12 | 12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Findik, H.; Aydın, M.D.; Uzun, F.; Kaim, M.; Kanat, A.; Keleş, O.N.; Kadıoğlu, H.H.; Akyüz, M.E.; Zeynal, M. Dangerous Alarming Diameter Assessment (DADA Index) in Which the Ratio of Iris Surface/Pupil Surface Size Is More Reliable than Pupil Diameter Measurement in Comatose Patients After Subarachnoid Haemorrhage: An Experimental Rabbit Model. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2696. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15212696
Findik H, Aydın MD, Uzun F, Kaim M, Kanat A, Keleş ON, Kadıoğlu HH, Akyüz ME, Zeynal M. Dangerous Alarming Diameter Assessment (DADA Index) in Which the Ratio of Iris Surface/Pupil Surface Size Is More Reliable than Pupil Diameter Measurement in Comatose Patients After Subarachnoid Haemorrhage: An Experimental Rabbit Model. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(21):2696. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15212696
Chicago/Turabian StyleFindik, Hüseyin, Mehmet Dumlu Aydın, Feyzahan Uzun, Muhammet Kaim, Ayhan Kanat, Osman Nuri Keleş, Hakan Hadi Kadıoğlu, Mehmet Emin Akyüz, and Mete Zeynal. 2025. "Dangerous Alarming Diameter Assessment (DADA Index) in Which the Ratio of Iris Surface/Pupil Surface Size Is More Reliable than Pupil Diameter Measurement in Comatose Patients After Subarachnoid Haemorrhage: An Experimental Rabbit Model" Diagnostics 15, no. 21: 2696. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15212696
APA StyleFindik, H., Aydın, M. D., Uzun, F., Kaim, M., Kanat, A., Keleş, O. N., Kadıoğlu, H. H., Akyüz, M. E., & Zeynal, M. (2025). Dangerous Alarming Diameter Assessment (DADA Index) in Which the Ratio of Iris Surface/Pupil Surface Size Is More Reliable than Pupil Diameter Measurement in Comatose Patients After Subarachnoid Haemorrhage: An Experimental Rabbit Model. Diagnostics, 15(21), 2696. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15212696






