Navigating Biopsy Safety: Complication Rates Under Ultrasound and CT Guidance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Data Collection
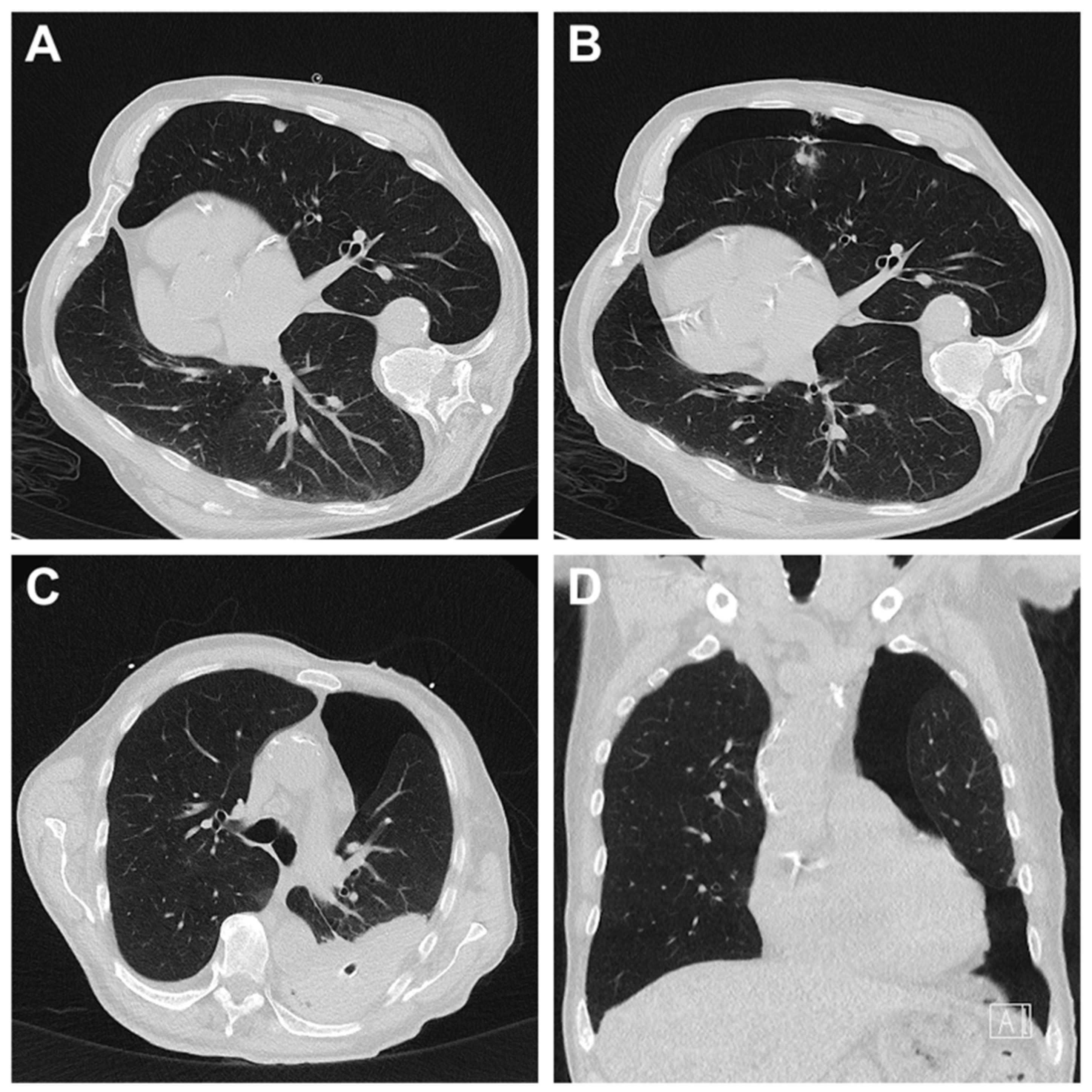
2.3. Biopsy Procedure
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Age, Sex and Time
3.2. Biopsied Organs
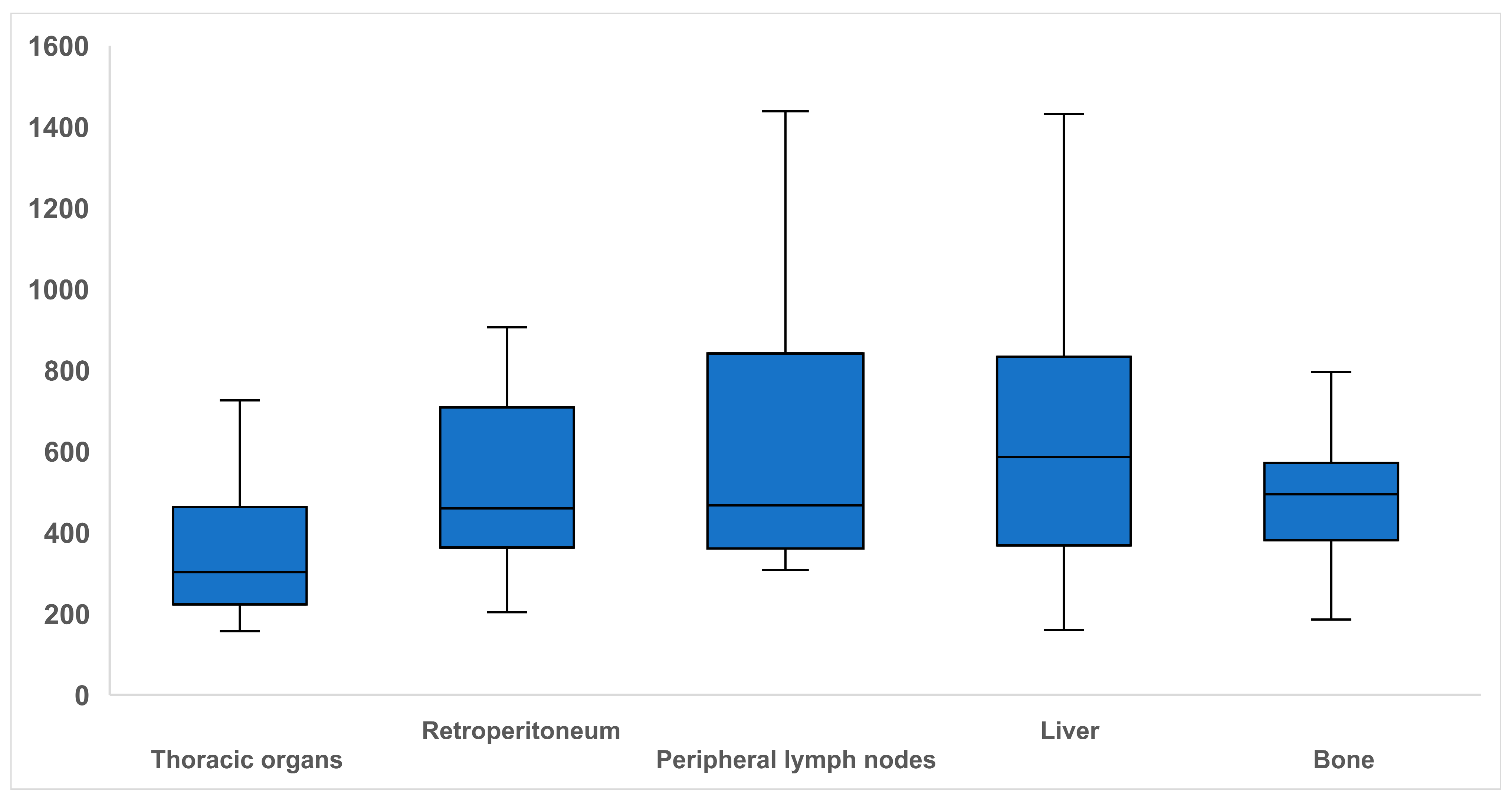
3.3. Radiation Dose for CT-Guided Biopsies
3.4. Complications
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DLP | dose-length product |
| IQR | interquartile range |
References
- Katoh, M. Outpatient Treatment in Radiology. RöFo 2024, 196, 661–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.; Lee, M.K. Diagnostic Performance and Safety of Ultrasound-Guided Core Needle Biopsy for Diagnosing Lymphoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancer Med. 2025, 14, e70414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Poorten, D.; Kwok, A.; Lam, T.; Ridley, L.; Jones, D.B.; Ngu, M.C.; Lee, A.U. Twenty-Year Audit of Percutaneous Liver Biopsy in a Major Australian Teaching Hospital. Intern. Med. J. 2006, 36, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tselikas, L.; Sun, R.; Ammari, S.; Dercle, L.; Yevich, S.; Hollebecque, A.; Ngo-Camus, M.; Nicotra, C.; Deutsch, E.; Deschamps, F.; et al. Role of Image-Guided Biopsy and Radiomics in the Age of Precision Medicine. Chin. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 8, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerci, J.J.; Bogoni, M.; Delbeke, D. History of Image-Guided Biopsy. In Oncological PET/CT with Histological Confirmation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahnken, A.H.; Thomas, C. Interventionelle Radiologie, 1st ed.; Wilhelm, K., Ed.; Thieme: Stuttgart, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Alfidi, R.J.; Haaga, J.; Meaney, T.F.; MacIntyre, W.J.; Gonzalez, L.; Tarar, R.; Zelch, M.G.; Boller, M.; Cook, S.A.; Jelden, G. Computed Tomography of the Thorax and Abdomen; a Preliminary Report. Radiology 1975, 117, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manhire, A.; Charig, M.; Clelland, C.; Gleeson, F.; Miller, R.; Moss, H.; Pointon, K.; Richardson, C.; Sawicka, E. Guidelines for Radiologically Guided Lung Biopsy. Thorax 2003, 58, 920–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lal, H.; Neyaz, Z.; Nath, A.; Borah, S. CT-Guided Percutaneous Biopsy of Intrathoracic Lesions. Korean J. Radiol. 2012, 13, 210–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Ramm, O.T.; Smith, S.W. Prospects and Limitations of Diagnostic Ultrasound. In Recent and Future Developments in Medical Imaging II; Society of Photo Optical Instrumentation Engineers: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1979; Volume 206, pp. 6–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinand, J.T.; du Pisanie, L.; Ngeve, S.; Commander, C.; Yu, H. Pneumothorax after Computed Tomography-Guided Lung Biopsy: Utility of Immediate Post-Procedure Computed Tomography and One-Hour Delayed Chest Radiography. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0284145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messersmith, R.N.; Cronan, J.; Esparza, A.R. Computed Tomography-Guided Percutaneous Biopsy: A Combined Approach to the Retroperitoneum. Neurosurgery 1984, 14, 218–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, C.; Shamimi-Noori, S. Ultrasound and CT-Directed Liver Biopsy. Clin. Liver Dis. 2014, 4, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavon, L.H.D.O.; Tyng, C.J.; Travesso, D.J.; Rocha, R.D.; Schiavon, A.C.S.A.; Bitencourt, A.G.V. Computed Tomography-Guided Percutaneous Biopsy of Abdominal Lesions: Indications, Techniques, Results, and Complications. Radiol. Bras. 2018, 51, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uppot, R.N.; Sahani, D.V.; Hahn, P.F.; Gervais, D.; Mueller, P.R. Impact of Obesity on Medical Imaging and Image-Guided Intervention. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2007, 188, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rechl, H.; Kirchhoff, C.; Wörtler, K.; Lenze, U.; Töpfer, A.; Von Eisenhart-Rothe, R. Diagnosis of Malignant Bone and Soft Tissue Tumors. Orthopade 2011, 40, 931–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gala, K.B.; Chandra, D.; Shetty, N.S.; Agarwal, U.; Bansal, H.; Shariq, M.; Pendse, H.A.; Janu, A.; Mandava, R.; Kulkarni, S.S. Imaging Recommendations for Image-Guided Biopsy in Oncology. J. Med. Paediatr. Oncol. 2023, 44, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Zhao, R.; Wang, W.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Wen, C.; Ren, Y. The Accuracy of Ultrasound-Guided Fine-Needle Aspiration and Core Needle Biopsy in Diagnosing Axillary Lymph Nodes in Women with Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1166035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, M.; Choi, J.; El-Haddad, G.; Sweeney, J.; Biebel, B.; Robinson, L.; Antonia, S.; Kumar, A.; Kis, B. Retrospective Analysis of Technical Success Rate and Procedure-Related Complications of 867 Percutaneous CT-Guided Needle Biopsies of Lung Lesions. Clin. Radiol. 2017, 72, 1038–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalilzadeh, O.; Baerlocher, M.O.; Shyn, P.B.; Connolly, B.L.; Devane, A.M.; Morris, C.S.; Cohen, A.M.; Midia, M.; Thornton, R.H.; Gross, K.; et al. Proposal of a New Adverse Event Classification by the Society of Interventional Radiology Standards of Practice Committee. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2017, 28, 1432–1437.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgio, A.; Tarantino, L.; De Stefano, G.; Francica, G.; Esposito, F.; Perrotta, A.; Aloisio, V.; Farella, N.; Mariniello, N.; Coppola, C.; et al. Complications after Interventional Sonography of Focal Liver Lesions: A 22-Year Single-Center Experience. J. Ultrasound Med. 2003, 22, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tárnoki, D.L.; Karlinger, K.; Ridge, C.A.; Kiss, F.J.; Györke, T.; Grabczak, E.M.; Tárnoki, Á.D. Lung Imaging Methods: Indications, Strengths and Limitations. Breathe 2024, 20, 230127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, E.M.; Lubner, M.G.; Pickhardt, P.J.; Hartung, M.P. Ultrasound-Guided Biopsy of Challenging Abdominopelvic Targets. Abdom. Radiol. 2022, 47, 2567–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kloeckner, R.; Dos Santos, D.P.; Schneider, J.; Kara, L.; Dueber, C.; Pitton, M.B. Radiation Exposure in CT-Guided Interventions. Eur. J. Radiol. 2013, 82, 2253–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerber, B.; Ensle, F.; Kroschke, J.; Strappa, C.; Stolzmann-Hinzpeter, R.; Blüthgen, C.; Marty, M.; Larici, A.R.; Frauenfelder, T.; Jungblut, L. The Effect of X-Ray Dose Photon-Counting Detector Computed Tomography on Nodule Properties in a Lung Cancer Screening Cohort: A Prospective Study. Investig. Radiol. 2025, 60, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liu, B.; Meng, H.; Lv, W.; Jia, H. Efficacy and Radiation Exposure of Ultra-Low-Dose Chest CT at 100 KVp with Tin Filtration in CT-Guided Percutaneous Core Needle Biopsy for Small Pulmonary Lesions Using a Third-Generation Dual-Source CT Scanner. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 30, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokop, M. Optimizing Dosage in Thoracic Computerized Tomography. Radiologe 2001, 41, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwell, T.D.; Smith, R.L.; Hesley, G.K.; Callstrom, M.R.; Schleck, C.D.; Harmsen, W.S.; Charboneau, J.W.; Welch, T.J. Incidence of Bleeding after 15,181 Percutaneous Biopsies and the Role of Aspirin. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2010, 194, 784–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrish, A.E. Complications of Percutaneous Renal Biopsy: A Review of 37 Years’ Experience. Clin. Nephrol. 1992, 38, 135–141. [Google Scholar]
- Piccinino, F.; Sagnelli, E.; Pasquale, G.; Giusti, G.; Battocchia, A.; Bernardi, M.; Bertolazzi, R.; Bianchi, F.B.; Brunelli, E.; Budillon, G.; et al. Complications Following Percutaneous Liver Biopsy. A Multicentre Retrospective Study on 68,276 Biopsies. J. Hepatol. 1986, 2, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGill, D.B.; Rakela, J.; Zinsmeister, A.R.; Ott, B.J. A 21-Year Experience with Major Hemorrhage after Percutaneous Liver Biopsy. Gastroenterology 1990, 99, 1396–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomiyama, N.; Yasuhara, Y.; Nakajima, Y.; Adachi, S.; Arai, Y.; Kusumoto, M.; Eguchi, K.; Kuriyama, K.; Sakai, F.; Noguchi, M.; et al. CT-Guided Needle Biopsy of Lung Lesions: A Survey of Severe Complication Based on 9783 Biopsies in Japan. Eur. J. Radiol. 2006, 59, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.; Park, S.; Kim, J.H.; Hwang, J.H.; Park, C.; Park, S. Percutaneous Core Needle Biopsy of 566 Peripheral Lung Lesions: Analysis of Factors Associated with Biopsy Failure and Postprocedural Pneumothorax. Clin. Radiol. 2025, 85, 106911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.Y.; Sun, J.S.; Kim, E.Y.; Park, K.J.; You, S. Diagnostic Accuracy and Safety of CT-Guided Percutaneous Lung Biopsy with a Coaxial Cutting Needle for the Diagnosis of Lung Cancer in Patients with UIP Pattern. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.R.; Chan, M.V.; Habib, A.R.; Lui, I.; Ridley, L. Pneumothorax Rates in CT-Guided Lung Biopsies: A Comprehensive Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Risk Factors. Br. J. Radiol. 2020, 93, 20190866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, W.; Yoon, S.H.; Goo, J.M.; Park, C.M. Cone-Beam CT-Guided Percutaneous Transthoracic Needle Lung Biopsy of Juxtaphrenic Lesions: Diagnostic Accuracy and Complications. Korean J. Radiol. 2021, 22, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otto, S.; Mensel, B.; Friedrich, N.; Schäfer, S.; Mahlke, C.; Von Bernstorff, W.; Bock, K.; Hosten, N.; Kühn, J.P. Predictors of Technical Success and Rate of Complications of Image-Guided Percutaneous Transthoracic Lung Needle Biopsy of Pulmonary Tumors. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolderman, N.C.; Cheti, D.R.; Hasbrook, C.D.; Forsyth, A.J.; Coffey, M.P.; Nair, G.B.; Al-Katib, S.A. Pneumothorax Rate and Diagnostic Adequacy of Computed Tomography-Guided Lung Nodule Biopsies Performed With 18 G Versus 20 G Needles: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Thorac. Imaging 2020, 35, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.M.; Park, C.M.; Lee, K.H.; Bahn, Y.E.; Kim, J.I.; Goo, J.M. C-Arm Cone-Beam CT-Guided Percutaneous Transthoracic Needle Biopsy of Lung Nodules: Clinical Experience in 1108 Patients. Radiology 2014, 271, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Huang, M.; Weng, H.H.; Hsu, S.L.; Hsu, L.S.; Lin, W.M.; Chen, C.W.; Tsai, Y.H. Accuracy and Complications of CT-Guided Pulmonary Core Biopsy in Small Nodules: A Single-Center Experience. Cancer Imaging 2019, 19, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, F.; Kato, T.; Sugiura, K.; Nishimura, M.; Kinoshita, T.; Hashimoto, M.; Kaminoh, T.; Ogawa, T. CT-Guided Transthoracic Needle Biopsy Using a Puncture Site-down Positioning Technique. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2006, 187, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, A.C.; McCarthy, C.; Ridge, C.A.; Mitchell, P.; Hanrahan, E.; Butler, M.; Keane, M.P.; Dodd, J.D. Rapid Needle-out Patient-Rollover Time after Percutaneous CT-Guided Transthoracic Biopsy of Lung Nodules: Effect on Pneumothorax Rate. Radiology 2012, 262, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Du, Y.; Luo, T.Y.; Yang, H.F.; Yu, J.H.; Xu, X.X.; Zheng, H.J.; Li, B. Usefulness of Normal Saline for Sealing the Needle Track after CT-Guided Lung Biopsy. Clin. Radiol. 2015, 70, 1192–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renier, H.; Gérard, L.; Lamborelle, P.; Cousin, F. Efficacy of the Tract Embolization Technique with Gelatin Sponge Slurry to Reduce Pneumothorax and Chest Tube Placement after Percutaneous CT-Guided Lung Biopsy. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2020, 43, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heerink, W.J.; de Bock, G.H.; de Jonge, G.J.; Groen, H.J.M.; Vliegenthart, R.; Oudkerk, M. Complication Rates of CT-Guided Transthoracic Lung Biopsy: Meta-Analysis. Eur. Radiol. 2017, 27, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birchard, K.R. Transthoracic Needle Biopsy. Semin. Intervent. Radiol. 2011, 28, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheth, R.A.; Baerlocher, M.O.; Connolly, B.L.; Dariushnia, S.R.; Shyn, P.B.; Vatsky, S.; Tam, A.L.; Gupta, S. Society of Interventional Radiology Quality Improvement Standards on Percutaneous Needle Biopsy in Adult and Pediatric Patients. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2020, 31, 1840–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomozawa, Y.; Inaba, Y.; Yamaura, H.; Sato, Y.; Kato, M.; Kanamoto, T.; Sakane, M. Clinical Value of CT-Guided Needle Biopsy for Retroperitoneal Lesions. Korean J. Radiol. 2011, 12, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ah-Lan, K.C.; Nakhaei, M.; Camacho, A.; Appel, E.; Siewert, B.; Ahmed, M.; Brook, O.R. Safely Shortening the Observation Time After CT-Guided Lung Procedures. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2021, 18, 1118–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.M.; Um, S.W.; Yoo, C.G.; Young, W.K.; Sung, K.H.; Shim, Y.S.; Lee, C.T. Incidence and Risk Factors of Delayed Pneumothorax after Transthoracic Needle Biopsy of the Lung. Chest 2004, 126, 1516–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Patient and Procedure Data | Gender | male | female | |||
| Age (years) | ||||||
| Imaging Modality | CT (incl. DLP) | ultrasound | ||||
| Organ | liver | thoracic organs (lung, lymph nodes mediastinal) | Retroperitoneum (kidney, retroperitoneal space, paraaortic lymph nodes) | Peripheral lymph nodes (axillary, iliac, inguinal, pelvic, cervical) | bone | |
| Duration of the Intervention (min) | ||||||
| Technical Success | yes | no | ||||
| Complications | Complications | yes | no | |||
| Type | bleeding | pneumothorax | ||||
| Time | 0–4 h | 4–12 h | 12–24 h | >24 h | ||
| Severity | mild | moderate | severe | life-threatening or disabling | patient death or unexpected pregnancy abortion | |
| Treatment | no specific therapy | conservative or symptom-oriented treatment | radiological-interventional treatment | surgical treatment |
| Part A (Adverse Event Description) | ||
| A (description narrative of adverse event) | ||
| B (assessment of adverse event) | ||
| 1. Mild | e.g., minimal venous bleeding from the access channel (treatment with gel foam particles if necessary). Minimal free fluid or hematomas, e.g., adjacent to the needle, subcutaneous, intercostal, retrosternal, perirenal, perihepatic, in the lung parenchyma, extradural. Minimal mediastinal emphysema or discrete pleural effusion/pneumothorax (up to 1.5 cm), adjacent hypoventilation | |
| 2. Moderate | e.g., relevant bleeding or pneumothorax (>1.5 cm) with treatment (e.g., chest drainage) if necessary. | |
| 3. Severe | e.g., cardiac and pulmonary complications, significant drop in oxygen saturation, major bleeding, surgical intervention (e.g., hematoma evacuation). | |
| 4. Life-threatening or disabling event | e.g., cardiopulmonary arrest, shock, organ failure | |
| 5. Patient death or unexpected pregnancy abortion | ||
| Part B (Adverse Event Analysis) | ||
| A (Causality of adverse event) | ||
| Category 1 | AE not caused by the procedure | |
| Category 2 | Unknown whether AE was caused by the procedure | |
| Category 3 | AE caused by the procedure | |
| Liver | Thoracic Organs | Retroperitoneum | Peripheral Lymph Nodes | Bone | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ultrasound | 87 (73.7%/76.3%) | 0 (0.0%/0.0%) | 4 (3.4%/11.8%) | 23 (19.5%/74.2%) | 4 (3.4%/12.1%) | 118 (100%/47.2%) |
| CT | 27 (20.5%/23.7%) | 38 (28.8%/100.0%) | 30 (22.7%/88.2%) | 8 (6.1%/25.8%) | 29 (22.0%/87.9%) | 132 (100%/52.8%) |
| Total | 114 (45.6%/100%) | 38 (15.2%/100%) | 34 (13.6%/100%) | 31 (12.4%/100%) | 33 (13.2%/100%) | 250 (100%) |
| No complication | 103 (51.2%/90.4%) | 13 (6.5%/34.2%) | 27 (13.4%/79.4%) | 28 (13.9%/90.3%) | 30 (14.9%/90.9%) | 201 (100%/80.4%) |
| Complication | 11 (22.4%/9.6%) | 25 (51.0%/65.8%) | 7 (14.3%/20.6%) | 3 (6.1%/9.7%) | 3 (6.1%/9.1%) | 49 (100%/19.6%) |
| Total | 114 (45.6%/100%) | 38 (15.2%/100%) | 34 (13.6%/100%) | 31 (12.4%/100%) | 33 (13.2%/100%) | 250 (100%) |
| Type of Complications | Severity of Complications | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bleeding | Pneumothorax | Mild | Moderate | Severe | Total | |
| Ultrasound | 9 (100%/32.1%) | 0 (0.0%/0.0%) | 9 (100%/21.4%) | 0 (0.0%/0.0%) | 0 (0.0%/0.0%) | 9 (100%) |
| CT | 19 (47.5%/67.9%) | 21 (52.5%/100%) | 33 (82.5%/78.6%) | 5 (12.5%/100%) | 2 (5%/100%) | 40 (100%) |
| Total | 28 (57.0%/100%) | 21 (42.9%/100%) | 42 (85.7%/100%) | 5 (10.2%/100%) | 2 (4.1%/100%) | 49 (100%) |
| Bleeding | Mild | 26 (92.9%) |
| Moderate | 2 (7.1%) | |
| Severe | 0 (0.0%) | |
| Pneumothorax | Mild | 16 (76.2%) |
| Moderate | 3 (14.3%) | |
| Severe | 2 (9.5%) |
| Timing of Complications | Treatment of Complications | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–4 h | 4–12 h | 12–24 h | >24 h | No | Conservative or Symptom-Oriented | Radiological-Interventional | Surgical | |
| Ultrasound | 9 (100%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 5 (55.6%) | 4 (44.4%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) |
| CT | 37 (92.5%) | 1 (2.5%) | 1 (2.5%) | 1 (2.5%) | 20 (50.0%) | 14 (35.0%) | 5 (12.5%) | 1 (2.5%) |
| total | 46 (93.9%) | 1 (2.0%) | 1 (2.0%) | 1 (2.0%) | 25 (51.0%) | 18 (36.7%) | 5 (10.2%) | 1 (2.0%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Patzer, T.S.; Müller, F.; Meir, M.; Huflage, H.; Müller, L.; Bley, T.A.; Grunz, J.-P.; Kunz, A.S. Navigating Biopsy Safety: Complication Rates Under Ultrasound and CT Guidance. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2641. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15202641
Patzer TS, Müller F, Meir M, Huflage H, Müller L, Bley TA, Grunz J-P, Kunz AS. Navigating Biopsy Safety: Complication Rates Under Ultrasound and CT Guidance. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(20):2641. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15202641
Chicago/Turabian StylePatzer, Theresa Sophie, Franziska Müller, Michael Meir, Henner Huflage, Lukas Müller, Thorsten Alexander Bley, Jan-Peter Grunz, and Andreas Steven Kunz. 2025. "Navigating Biopsy Safety: Complication Rates Under Ultrasound and CT Guidance" Diagnostics 15, no. 20: 2641. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15202641
APA StylePatzer, T. S., Müller, F., Meir, M., Huflage, H., Müller, L., Bley, T. A., Grunz, J.-P., & Kunz, A. S. (2025). Navigating Biopsy Safety: Complication Rates Under Ultrasound and CT Guidance. Diagnostics, 15(20), 2641. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15202641






