The Evaluation of a Rapid Syndromic Multiplex Meningitis/Encephalitis RT-qPCR MX-17 Panel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
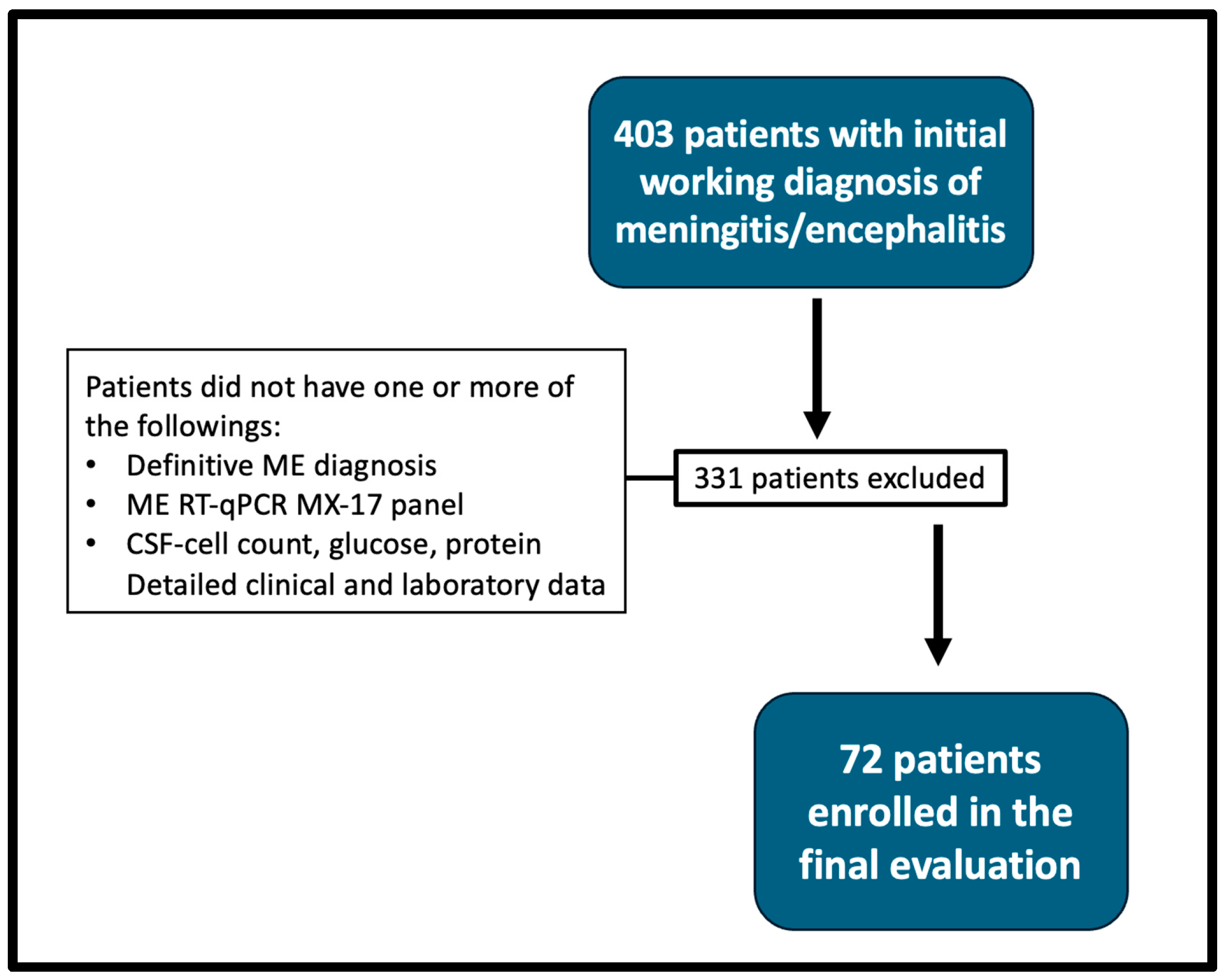
2.1. Selection of Participants
2.2. Cerebrospinal Fluid Culture
2.3. Biochemical Analysis
2.4. Bio-Speedy Meningitis/Encephalitis RT-qPCR MX-17 Panel
2.5. Analysis
3. Results
| Bio-Speedy® ME RT-qPCR | CSF Culture | Blood Culture | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viral pathogens | Total: 28 | - | - | Coinfected patients |
| Herpes simplex virus 1 | 5 | N/A | N/A | |
| Human Herpesvirus 6 | 11 | N/A | N/A | 1 patient coinfected with Enterovirus |
| Human Herpesvirus 8 | 1 | N/A | N/A | |
| Varicella Zoster virus | 3 | N/A | N/A | |
| Enterovirus | 7 | N/A | N/A | 1 patient coinfected with HHV-6 |
| Cytomegalovirus | 1 | N/A | N/A | |
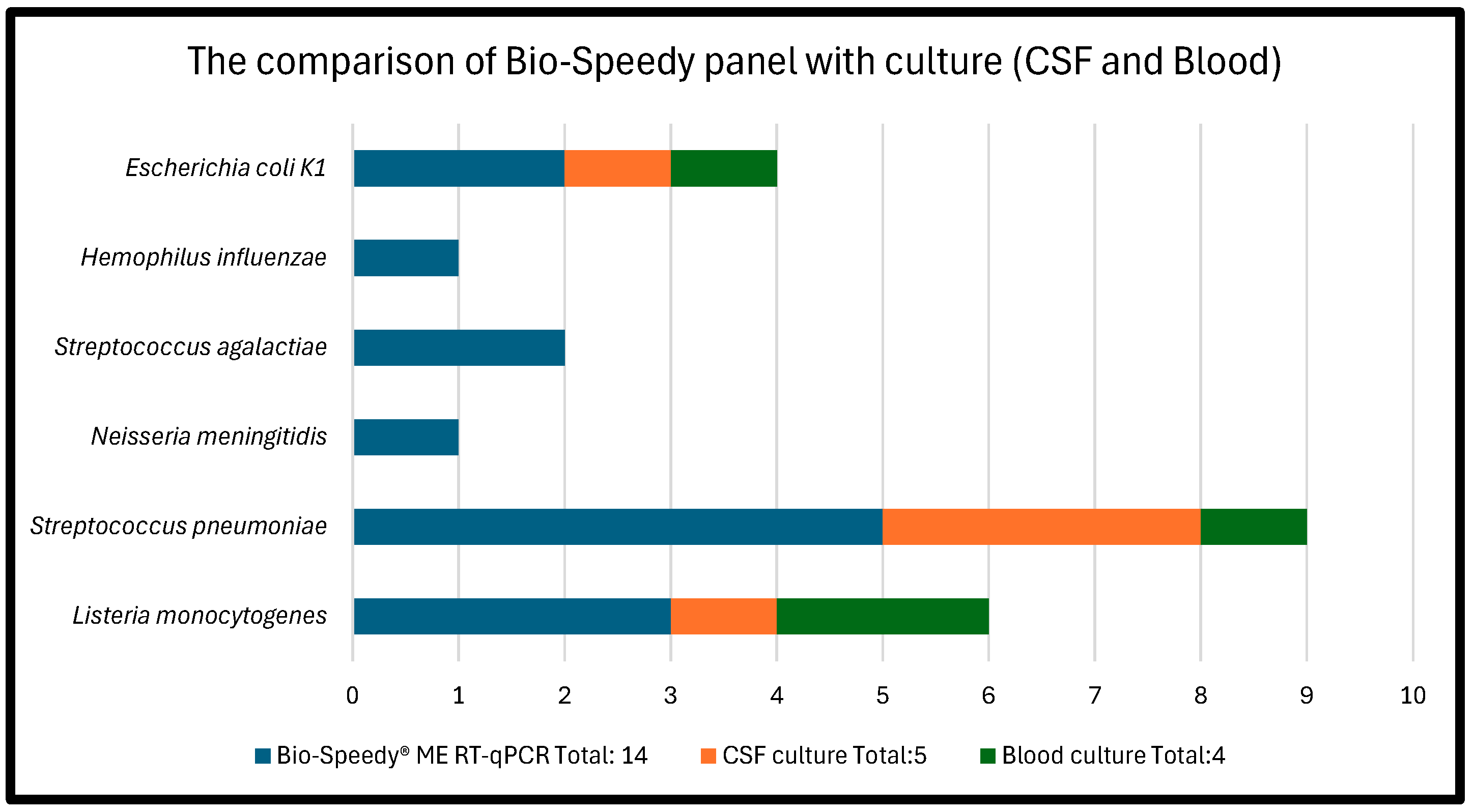
| Bacterial pathogens | Total: 14 | Total: 5 | Total: 4 | Coinfected patients |
| Listeria monocytogenes | 3 | 1 | 2 | |
| Streptococcus pneumoniae | 5 | 3 | 1 | 1 patient coinfected with H. influenzae |
| Neisseria meningitidis | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| Streptococcus agalactiae | 2 | 0 | 0 | |
| Hemophilus influenzae | 1 | 0 | 0 | Only detected in 1 coinfection with S. pneumoniae |
| Escherichia coli K1 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Viral | Bacterial | Aseptic Meningitis | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multiplex PCR analysis of 72 patients | ||||
| Patients (n) | 28 | 14 | 30 | |
| Age, median (IQR*) | 19 (0–81) | 4 (0–74) | 10 (0–72) | |
| Gender (%) | 0.79 | |||
| ● Female | 41.4 | 6 (46.2) | 6 (20) | |
| ● Male | 58.6 | 7 (53.8) | 24 (80) | 0.200 |
| Laboratory Findings: | ||||
| CSF WBC | ||||
| ● ≤5n | 11 | 1 | 0 | |
| ● >5n | 17 | 12 | 30 | |
| Mean | 424.8 ± 889.4 | 1903.6 ± 3960 | 1259.6 ± 4618.2 | 0.101 |
| Median (IQR*) | 66 (1–4221) | 315 (4–14,963) | 30.5 (9–25,085) | |
| CSF glucose level | 0.189 | |||
| ● <50 mg/dL | 9 | 8 | 8 | |
| ● 50–75 mg/dL | 13 | 2 | 13 | |
| ● >75 mg/dL | 6 | 3 | 9 | |
| Mean | 66.8 ± 29.3 | 42.8 ± 43.7 | 61.7 ± 30.1 | |
| Median (IQR*) | 56.8 (33.9–165) | 29.9 (0.083–157) | 62.8 (0.123–140) | |
| CSF protein level | 69 ± 50 | 228.3 ± 224.6 | 162.6 ± 300 | 0.282 |
| Median (IQR*) | 55.5 (14.2–200) | 143.9 (35.2–531) | 59.5 (16.8–887.3) | |
| CRP level | 46.2 ± 77.5 | 137.2 ± 136 | 35.8 ± 70.9 | 0.391 |
| Median (IQR*) | 15.2 (0.142–329.5) | 85 (6.18–41.3) | 12.45 (0.20–83.8) | |
| Clinical Features: | ||||
| Fever (Mean ± SD (°C)) | 37.22 ± 0.9 | 37.6 ± 1.3 | 37.3 ± 0.8 | 0.95 |
| Impaired consciousness n (%) | 9 (32.14) | 10 (76.9) | 21 (70) | 0.004 |
| Neck stiffness n (%) | 6 (21.43) | 4 (30.8) | 2 (6.6) | 0.113 |
| Headache n (%) | 11 (39.3) | 1 (7.1) | 4 (13.3) | 0.017 |
| Outcomes: | ||||
| Prolonged stay in the hospital (>7 days) n (%) | 13 (46.4) | 6 (46) | 6(20) | 0.067 |
| Among prolonged stays: | ||||
| Patients age n (%) | ||||
| ● <1 year | 4 (30.8) | 2 (33.3) | - | |
| ● 1–17 year | 4 (30.8) | 2 (33.3) | 4 (66.6) | |
| ● 18–64 year | 3 (23) | - | 2 (33.3) | |
| ● 65 or older | 2 (15.4) | 2 (33.3) | - | |
| Underlying condition other than ME** n (%) | 8 (28.5) | 2 (14.2) | 1 (3.3) | |
| 30-day survival n (%) | 26 (92.8) | 12 (85.7) | 28 (93.3) | 0.594 |
| Method | Positive Cases, n (%) | Viral, n (%) | Bacterial, n (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bio-Speedy PCR (n = 72) | 41 (56.9) | 28 (38.9) | 14 (19.4) |
| CSF culture (n = 66) | 5 (7.5) | - | 6 (9.1) |
| Blood culture (n = 72) | 4 (5.5) | - | 4 (5.5) |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roos, K.L.; Greenlee, J.E. Meningitis and Encephalitis. Contin. Lifelong Learn. Neurol. 2011, 17, 1010–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, J.; Luintel, A.; Chandna, A.; Heyderman, R.S. Community-acquired acute bacterial meningitis in adults: A clinical update. Br. Med. Bull. 2019, 131, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitch, M.T.; Abrahamian, F.M.; Moran, G.J.; Talan, D.A. Emergency Department Management of Meningitis and Encephalitis. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2008, 22, 33–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bystritsky, R.J.; Chow, F.C. Infectious Meningitis and Encephalitis. Neurol. Clin. 2022, 40, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasbun, R. Progress and Challenges in Bacterial Meningitis: A Review. JAMA 2022, 328, 2147–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiess, N.; Groce, N.E.; Dua, T. The Impact and Burden of Neurological Sequelae Following Bacterial Meningitis: A Narrative Review. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thy, M.; de Montmollin, E.; Bouadma, L.; Timsit, J.F.; Sonneville, R. Severe meningoencephalitis: Epidemiology and outcomes. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2023, 29, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costerus, J.M.; Brouwer, M.C.; Bijlsma, M.W.; van de Beek, D. Community-acquired bacterial meningitis. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 30, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzulli, T. Laboratory Diagnosis of Infection Due to Viruses, Chlamydia, Chlamydophila, and Mycoplasma. In Principles and Practice of Pediatric Infectious Diseases; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; p. e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poplin, V.; Boulware, D.R.; Bahr, N.C. Methods for rapid diagnosis of meningitis etiology in adults. Biomark Med. 2020, 14, 459–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanan, P.; Bryson, A.L.; Binnicker, M.J.; Pritt, B.S.; Patel, R. Syndromic Panel-Based Testing in Clinical Microbiology. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 31, e00024-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, M.; Kilic, S.; Bayrakdar, F.; Otgun, S.N.; Tosun, A.I.; Zeybek, U.; Celik, F.; Aygun, G.; Safak, B.; Mahroum, N. Syndromic Testing-The Evaluation of Four Novel Multiplex Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction Panels. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leber, A.L. (Ed.) Clinical Microbiology Procedures Handbook; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bio-Eksen Molecular Diagnostics. Bio-Speedy® Meningitis/Encephalitis RT-qPCR MX-17 Panel. Available online: https://www.bioeksen.com/human-health/ce-ivd/central-nervous-system-infectio/meningitis%2Fencephalitis-rt-qpcr-mx-17-panel (accessed on 5 December 2023).
- Koster-Rasmussen, R.; Korshin, A.; Meyer, C.N. Antibiotic treatment delay and outcome in acute bacterial meningitis. J. Infect. 2008, 57, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunkel, A.R.; Hasbun, R.; Bhimraj, A.; Byers, K.; Kaplan, S.L.; Scheld, W.M.; van de Beek, D.; Bleck, T.P.; Garton, H.J.L.; Zunt, J.R. 2017 Infectious Diseases Society of America’s Clinical Practice Guidelines for Healthcare-Associated Ventriculitis and Meningitis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 64, e34–e65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Sánchez, C.; Bloise, I.; García-Rodríguez, J.; Cendejas-Bueno, E. Are cerebrospinal fluid biochemical parameters valid to predict positive results in microbiological molecular diagnostic platforms? A 4-year experience with the FilmArray® Panel Meningitis/Encephalitis for detection of community-acquired bacterial meningitis. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2023, 107, 116031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mount, H.R.; Boyle, S.D. Aseptic and Bacterial Meningitis: Evaluation, Treatment, and Prevention. Am. Fam. Physician 2017, 96, 314–322. [Google Scholar]
- Saxena, S.; Kaur, R.; Randhawa, V.S. Microbial Etiology of Community Acquired Meningoencephalitis in Adults: A Retrospective Review. J. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 11, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tansarli, G.S.; Chapin, K.C. Diagnostic test accuracy of the BioFire® FilmArray® meningitis/encephalitis panel: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. Viral Meningitis. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK545217/ (accessed on 10 February 2025).
- Steiner, I.; Budka, H.; Chaudhuri, A.; Koskiniemi, M.; Sainio, K.; Salonen, O.; Kennedy, P.G. Viral meningoencephalitis: A review of diagnostic methods and guidelines for management. Eur. J. Neurol. 2010, 17, 999-e57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.F.; Li, W.; Li, K. Acute encephalopathy and encephalitis caused by influenza virus infection. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2010, 23, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.; He, W.; Guo, S.; Wang, X.; Tang, M.; Ying, B.; Wang, M. Multiplex detection of meningitis and encephalitis pathogens: A study from laboratory to clinic. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 1054071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapra, H. Managing Meningoencephalitis in Indian ICU. Indian J. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 23 (Suppl. 2), 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, K.E.; Slechta, E.S.; Killpack, J.A.; Heyrend, C.; Lunt, T.; Daly, J.A.; Hemmert, A.C.; Blaschke, A.J. Preclinical Assessment of a Fully Automated Multiplex PCR Panel for Detection of Central Nervous System Pathogens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 785–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Beek, D.; Brouwer, M.; Hasbun, R.; Koedel, U.; Whitney, C.G.; Wijdicks, E. Community-acquired bacterial meningitis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mańdziuk, J.; Kuchar, E.P. Streptococcal Meningitis. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554448 (accessed on 10 February 2025).
- Hall, C.B.; Long, C.E.; Schnabel, K.C.; Caserta, M.T.; McIntyre, K.M.; Costanzo, M.A.; Knott, A.; Dewhurst, S.; Insel, R.A.; Epstein, L.G. Human Herpesvirus-6 Infection in Children—A Prospective Study of Complications and Reactivation. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994, 331, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dockrell, D.H.; Smith, T.F.; Paya, C.V. Human Herpesvirus 6. Mayo Clin. Proc. 1999, 74, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berzero, G.; Campanini, G.; Vegezzi, E.; Paoletti, M.; Pichiecchio, A.; Simoncelli, A.M.; Colombo, A.A.; Bernasconi, P.; Borsani, O.; Di Matteo, A.; et al. Human Herpesvirus 6 Encephalitis in Immunocompetent and Immunocompromised Hosts. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 8, e942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leber, A.L.; Everhart, K.; Balada-Llasat, J.-M.; Cullison, J.; Daly, J.; Holt, S.; Lephart, P.; Salimnia, H.; Schreckenberger, P.C.; DesJarlais, S.; et al. Multicenter Evaluation of BioFire FilmArray Meningitis/Encephalitis Panel for Detection of Bacteria, Viruses, and Yeast in Cerebrospinal Fluid Specimens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 2251–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, H.; Ozturk-Engin, D.; Cag, Y.; Senbayrak, S.; Inan, A.; Kazak, E.; Savasci, U.; Elaldi, N.; Vahaboglu, H.; Hasbun, R. Central nervous system infections in the absence of cerebrospinal fluid pleocytosis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 65, 107–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyayula, S. 1823. Incidence of Meningoencephalitis in the Absence of CSF Pleocytosis. Open Forum. Infect. Dis. 2019, 6 (Suppl. 2), S39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Østergaard, A.A.; Sydenham, T.V.; Nybo, M.; Andersen, Å.B. Cerebrospinal fluid pleocytosis level as a diagnostic predictor? A cross-sectional study. BMC Clin. Pathol. 2017, 17, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadwick, D.R. Viral meningitis. Br. Med. Bull. 2005, 75, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, R.G.; Herrera, T.I. When to Perform Lumbar Puncture in Infants at Risk for Meningitis in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. In Infectious Disease and Pharmacology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Precit, M.R.; Yee, R.; Pandey, U.; Fahit, M.; Pool, C.; Naccache, S.N.; Dien Bard, J. Cerebrospinal Fluid Findings Are Poor Predictors of Appropriate FilmArray Meningitis/Encephalitis Panel Utilization in Pediatric Patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, 10-1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benninger, F.; Steiner, I. CSF in acute and chronic infectious diseases. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; American Psychiatric Publishing: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.J.; Westblade, L.F.; Gottesdiener, L.S.; Liang, K.; A Li, H.; Wehmeyer, G.T.; Glesby, M.J.; Simon, M.S. Impact of a Multiplex Polymerase Chain Reaction Panel on Duration of Empiric Antibiotic Therapy in Suspected Bacterial Meningitis. Open Forum. Infect. Dis. 2021, 8, ofab467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cailleaux, M.; Pilmis, B.; Mizrahi, A.; Lourtet-Hascoet, J.; Van, J.-C.N.; Alix, L.; Couzigou, C.; Vidal, B.; Tattevin, P.; Le Monnier, A. Impact of a multiplex PCR assay (FilmArray®) on the management of patients with suspected central nervous system infections. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 39, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahraman, H.; Tünger, A.; Şenol, Ş.; Gazi, H.; Avci, M.; Örmen, B.; Türker, N.; Atalay, S.; Köse, Ş.; Ulusoy, S.; et al. Toplum Kökenli Santral Sinir Sistemi Enfeksiyonlarında Bakteriyel ve Viral Etiyolojinin Moleküler Yöntemlerle Değerlendirilmesi. Mikrobiyoloji Bul. 2017, 51, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niyas, V.K.; Sasidharan, A.; Chandran, S.; Chandran, S. Clinical Performance of FilmArray Meningitis/Encephalitis Multiplex Polymerase Chain Reaction Panel in Central Nervous System Infections. Indian J. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 26, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldriweesh, M.A.; Shafaay, E.A.; Alwatban, S.M.; Alkethami, O.M.; Aljuraisi, F.N.; Bosaeed, M.; Alharbi, N.K. Viruses Causing Aseptic Meningitis: A Tertiary Medical Center Experience With a Multiplex PCR Assay. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 602267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, B.S.W.; Kennedy, K.J. Comparison of a commercial real-time PCR panel to routine laboratory methods for the diagnosis of meningitis–encephalitis. Pathology 2021, 53, 635–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mahroum, N.; Yashar, M.; Ugur, F.N.; Oz, N.Z.; Ulfer, G.; Tosun, A.I.; Yilmaz, M. The Evaluation of a Rapid Syndromic Multiplex Meningitis/Encephalitis RT-qPCR MX-17 Panel. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2629. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15202629
Mahroum N, Yashar M, Ugur FN, Oz NZ, Ulfer G, Tosun AI, Yilmaz M. The Evaluation of a Rapid Syndromic Multiplex Meningitis/Encephalitis RT-qPCR MX-17 Panel. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(20):2629. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15202629
Chicago/Turabian StyleMahroum, Naim, Meltem Yashar, Feyza Nihal Ugur, Nefise Zulal Oz, Gozde Ulfer, Ayse Istanbullu Tosun, and Mesut Yilmaz. 2025. "The Evaluation of a Rapid Syndromic Multiplex Meningitis/Encephalitis RT-qPCR MX-17 Panel" Diagnostics 15, no. 20: 2629. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15202629
APA StyleMahroum, N., Yashar, M., Ugur, F. N., Oz, N. Z., Ulfer, G., Tosun, A. I., & Yilmaz, M. (2025). The Evaluation of a Rapid Syndromic Multiplex Meningitis/Encephalitis RT-qPCR MX-17 Panel. Diagnostics, 15(20), 2629. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15202629






