Association of Hemoglobin to Red Blood Cell Distribution Width Ratio and Total Bone Mineral Density in U.S. Adolescents: The NHANES 2011–2018
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
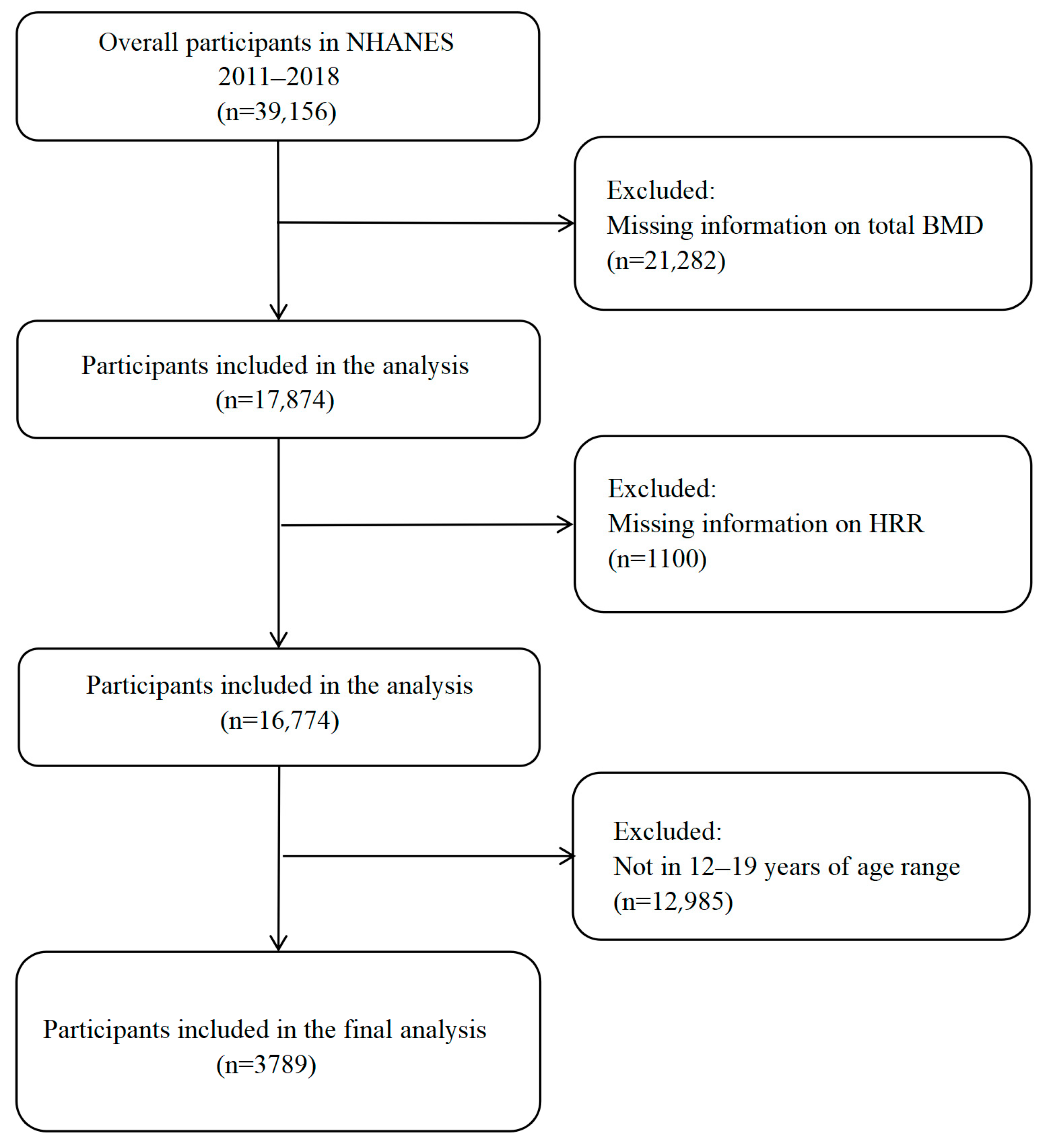
2.1. Data Source and Study Population
2.2. Study Variables
2.3. Covariates
2.4. Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Study Population Characteristics
3.2. Association Between RDW, HRR and BMD
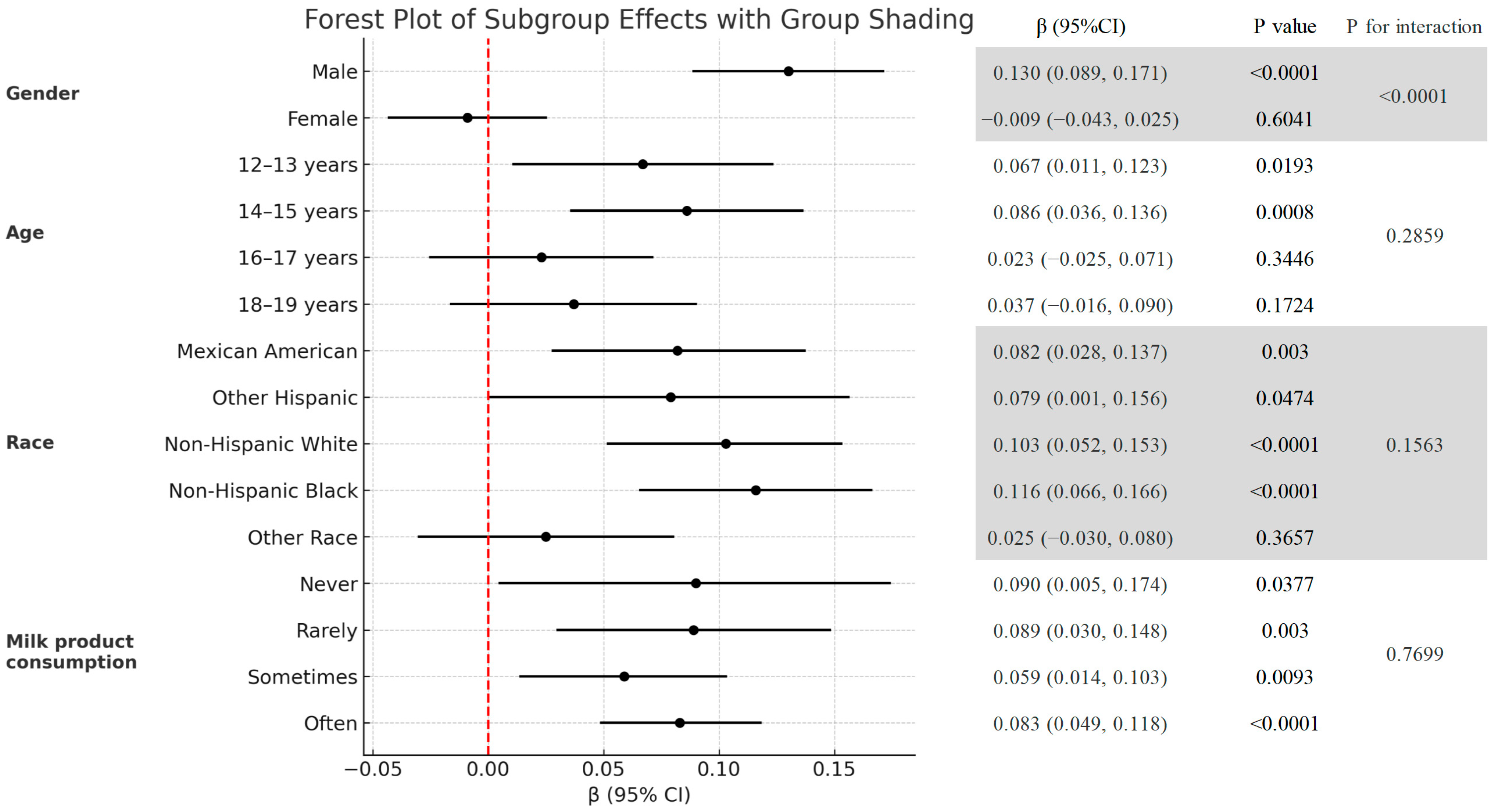
3.3. Subgroup Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Wojtys, E.M. Bone Health. Sports Health 2020, 12, 423–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, K.; Zhang, C.; Yao, X.; Zhu, Z. Association between dietary calcium intake and BMD in children and adolescents. Endocr. Connect. 2020, 9, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, A.; Xiao, P.; Fan, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhuang, Y. Associations between vitamin E status and bone mineral density in children and adolescents aged 8–19 years: Evidence based on NHANES 2005–2006, 2017–2018. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0283127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciaccio, C.; Coletta, A.; Coletta, M. Role of hemoglobin structural-functional relationships in oxygen transport. Mol. Asp. Med. 2022, 84, 101022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, M.A.; Melamed, M.L.; Kumar, J.; Roy, C.N.; Miller, E.R., 3rd; Furth, S.L.; Fadrowski, J.J. Vitamin D, race, and risk for anemia in children. J. Pediatr. 2014, 164, 153–158.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutten, E.P.; Franssen, F.M.; Spruit, M.A.; Wouters, E.F. Anemia is associated with bone mineral density in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. COPD J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2013, 10, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner, W.M.; Razo, C.; McHugh, T.A.; Hagins, H.; Vilchis-Tella, V.M.; Hennessy, C.; Taylor, H.J.; Perumal, N.; Fuller, K.; Cercy, K.M.; et al. Prevalence, years lived with disability, and trends in anaemia burden by severity and cause, 1990–2021: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Haematol. 2023, 10, e713–e734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, H.K.; Deepak, J.; Sachin, Y.; Kaverappa, V. Bone mineral density in patients with predialysis chronic kidney disease. Ren. Fail. 2013, 35, 1105–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.; Hou, X.; Liu, S.; Han, J.; Lv, H. Association of hemoglobin levels with bone mineral density for adults over 18 years of age: A cross-sectional study. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, B.; Huang, Z.; Xie, J.; Zhou, X.; Fan, C.; Chen, M.; Yan, L.; Shi, Z. Sex-specific association between platelet content and bone mineral density in adults: A cross-sectional study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2024, 25, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Yoo, D.M.; Min, C.; Choi, H.G. Association between Osteoporosis and Low Hemoglobin Levels: A Nested Case-Control Study Using a National Health Screening Cohort. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 11902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orhan, Ö.; Demir, H.; Talay, M.N.; Özgün, N.; Özbek, M.N. Evaluation of Children and Adolescents with Thalassemia Major in Terms of Osteoporosis: A Single-Centre Experience. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valderrábano, R.J.; Buzkova, P.; Chang, P.Y.; Zakai, N.A.; Fink, H.A.; Robbins, J.A.; Lee, J.S.; Wu, J.Y. Association of bone mineral density with hemoglobin and change in hemoglobin among older men and women: The Cardiovascular Health Study. Bone 2019, 120, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvagno, G.L.; Sanchis-Gomar, F.; Picanza, A.; Lippi, G. Red blood cell distribution width: A simple parameter with multiple clinical applications. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2015, 52, 86–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Sierra, M.; Romo-Cordero, A.; Quevedo-Abeledo, J.C.; Quevedo-Rodríguez, A.; Gómez-Bernal, F.; de Vera-González, A.; López-Mejías, R.; Martín-González, C.; González-Gay, M.; Ferraz-Amaro, I. Red Cell Distribution Width Association with Subclinical Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippi, G.; Turcato, G.; Cervellin, G.; Sanchis-Gomar, F. Red blood cell distribution width in heart failure: A narrative review. World J. Cardiol. 2018, 10, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, G.; Dai, C.; Xu, K.; Wu, M. Predictive value of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and red cell distribution width on death for ST segment elevation myocardial infarction. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, G.W.; Rossi, J.E.; Cannon, C.P. Acute myocardial infarction. Lancet 2017, 389, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.-D. Red blood cell distribution width: A promising index for estimating activity of autoimmune disease. J. Lab. Precis. Med. 2016, 1, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagnana, M.; Danese, E. Red cell distribution width and cancer. Ann. Transl. Med. 2016, 4, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xie, J.; Wang, P. Prognostic Value of the post-operative Red Blood Cell Distribution Width in rectal cancer patients with neoadjuvant chemoradiation followed surgery. Biosci. Rep. 2020, 40, BSR20201822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.M.; Lui, L.Y.; Cauley, J.A.; Ensrud, K.E.; Orwoll, E.S.; Schousboe, J.T.; Cummings, S.R. Red Cell Distribution Width Is a Risk Factor for Hip Fracture in Elderly Men Without Anemia. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2020, 35, 869–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z.; Yu, H.; Li, Q.; Ma, L.; Yang, Y. Red cell distribution width: A potential marker of reduced femoral neck bone mineral density in men and postmenopausal women. Endocrine 2025, 87, 1204–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Zhou, T.; Xue, M.; Sun, H.; Shen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Tang, L.; Qian, L.; You, J.; Yang, R.; et al. Correlation Analysis of Hemoglobin-to-Red Blood Cell Distribution Width Ratio and Frailty in Elderly Patients With Coronary Heart Disease. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 728800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, Y.; Fan, Z.; Xu, R. The Relationship between Red Blood Cell Distribution Width and Incident Diabetes in Chinese Adults: A Cohort Study. J. Diabetes Res. 2020, 2020, 1623247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.L.; Wu, J.N.; Lv, X.D.; Yang, Q.C.; Chen, J.R.; Zhang, D.M. The value of red blood cell distribution width, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, and hemoglobin-to-red blood cell distribution width ratio in the progression of non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Lu, B.; Han, R.; Tu, C. Exploring the hemoglobin-to-red blood cell distribution width ratio (HRR) to peripheral arterial disease nexus: A comprehensive analysis of NHANES data from 1999 to 2004. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1529155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, P.; Chen, S.; Lan, Z. Predictive role of red blood cell distribution width and hemoglobin-to-red blood cell distribution width ratio for mortality in patients with COPD: Evidence from NHANES 1999–2018. BMC Pulm. Med. 2024, 24, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salimi, M.; Karam, J.A.; Willman, M.; Willman, J.; Lucke-Wold, B.; Khanzadeh, S.; Mirghaderi, P.; Parvizi, J. Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio and Periprosthetic Joint Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Arthroplast. 2024, 39, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Zhang, F.; Chen, C.; Bi, X.; Yang, H.; An, X.; Wang, F.; Jiang, W. The ratio of hemoglobin to red cell distribution width as a novel prognostic parameter in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: A retrospective study from southern China. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 42650–42660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zhen, Z.; Dong, Y.; Liu, C.; Dong, B.; Xue, R. Hemoglobin to red cell distribution width ratio: A predictor of clinical outcome and diuretic response in patients with acute heart failure. Int. J. Cardiol. 2024, 394, 131368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Liao, N.; Lu, X.; Duan, X.; Zhou, Q.; Ge, L. Relationship Between the Hemoglobin-to-Red Cell Distribution Width Ratio and All-Cause Mortality in Ischemic Stroke Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: An Analysis from the MIMIC-IV Database. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2022, 18, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyiol, A.; Ertekin, B. The relationship between hemoglobin-to-red cell distribution width (RDW) ratio (HRR) and mortality in stroke patients. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2024, 28, 1504–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalamgari, A.; Valle, D.; Palau Villarreal, X.; Foreman, M.; Liu, A.; Patel, A.; Dave, A.; Lucke-Wold, B. Vertebral Primary Bone Lesions: Review of Management Options. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 3064–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehabeldin, M.; Gao, J.; Cho, Y.; Chong, R.; Tabib, T.; Li, L.; Smardz, M.; Gaffen, S.L.; Diaz, P.I.; Lafyatis, R.; et al. Therapeutic delivery of CCL2 modulates immune response and restores host-microbe homeostasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2400528121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Lan, Y.; Shen, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, W.; Mao, J.; Wu, Y.; Xie, Z.; Chen, Z. M2 macrophages secrete glutamate-containing extracellular vesicles to alleviate osteoporosis by reshaping osteoclast precursor fate. Mol. Ther. 2024, 32, 1158–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, L.; Fang, F.; Zhou, J.; Xu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, P.; Tu, J.; Sun, Q. Association of hemoglobin-to-red blood cell distribution width ratio and depression in older adults: A cross sectional study. J. Affect. Disord. 2024, 344, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiu, S.; Mu, Z.; Sun, L.; Zhao, L.; Fu, J. Hemoglobin level and osteoporosis in Chinese elders with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nutr. Diabetes 2022, 12, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Yang, Y.; Yue, R.; Su, C. Potential causal association between leisure sedentary behaviors, physical activity and musculoskeletal health: A Mendelian randomization study. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0283014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beydoun, M.A.; Hossain, S.; Beydoun, H.A.; Shaked, D.; Weiss, J.; Evans, M.K.; Zonderman, A.B. Red Cell Distribution Width Is Directly Associated with Poor Cognitive Performance among Nonanemic, Middle-Aged, Urban Adults. J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trevisani, L.F.M.; Kulcsar, I.F.; Kulcsar, M.A.V.; Dedivitis, R.A.; Kowalski, L.P.; Matos, L.L. Prognostic Value of Hematological Parameters in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2023, 15, 5245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Lan, Y.; Qi, B.; Shuai, P.; Hou, Q.; Liu, W.; Wang, Q. RDW-SD and PCT Are Potential Prognostic Factors for In-hospital Death in Patients With Stevens-Johnson Syndrome/Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2023, 15, 812–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamad, N.V.; Ima-Nirwana, S.; Chin, K.Y. Are Oxidative Stress and Inflammation Mediators of Bone Loss Due to Estrogen Deficiency? A Review of Current Evidence. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2020, 20, 1478–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, J.; Gong, Y.; Yan, L. The biomedical applications of nanozymes in orthopaedics based on regulating reactive oxygen species. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, H.; Luo, H.; Tan, W.; Zhong, J.; Xiong, J.; Liu, Z.; Wu, Q.; Lin, S.; Cao, K. Kurarinone Mitigates LPS-Induced Inflammatory Osteolysis by Inhibiting Osteoclastogenesis Through the Reduction of ROS Levels and Suppression of the PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway. Inflammation 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancera-Soto, E.; Ramos-Caballero, D.M.; Magalhaes, J.; Chaves Gomez, S.; Schmidt, W.F.J.; Cristancho-Mejía, E. Quantification of testosterone-dependent erythropoiesis during male puberty. Exp. Physiol. 2021, 106, 1470–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopiczko, A.; Łopuszańska-Dawid, M.; Gryko, K. Bone mineral density in young adults: The influence of vitamin D status, biochemical indicators, physical activity and body composition. Arch. Osteoporos. 2020, 15, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristic | Overall (n = 3789) | HRR Quartiles | SMD (Q1 vs. Q4) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q1 (n = 944) | Q2 (n = 948) | Q3 (n = 944) | Q4 (n = 953) | p Value | |||
| Age (years) | 15.406 ± 2.237 | 15.272 ± 2.252 | 14.932 ± 2.194 | 15.156 ± 2.210 | 16.129 ± 2.108 | <0.0001 | −0.438 |
| Gender (%) | <0.0001 | ||||||
| Male | 52.917 | 26.162 | 39.83 | 53.888 | 81.947 | −1.169 | |
| Female | 47.083 | 73.838 | 60.17 | 46.112 | 18.053 | 1.169 | |
| Race (%) | <0.0001 | ||||||
| Mexican American | 15.561 | 16.339 | 14.595 | 14.332 | 16.945 | −0.115 | |
| Other Hispanic | 7.68 | 10.655 | 8.375 | 7.411 | 5.25 | 0.132 | |
| Non-Hispanic White | 54.326 | 37.239 | 53.807 | 58.995 | 62.508 | −0.438 | |
| Non-Hispanic Black | 12.59 | 24.847 | 14.944 | 9.096 | 5.152 | 0.580 | |
| Other Race | 9.844 | 10.921 | 8.279 | 10.165 | 10.145 | −0.123 | |
| PIR | 2.418 ± 1.574 | 2.169 ± 1.530 | 2.434 ± 1.579 | 2.475 ± 1.557 | 2.526 ± 1.596 | <0.0001 | −0.213 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.965 ± 5.985 | 24.937 ± 6.796 | 24.027 ± 6.278 | 23.193 ± 5.727 | 23.926 ± 5.199 | <0.0001 | 0.170 |
| HDL-C (mmol/L) | 1.339 ± 0.306 | 1.398 ± 0.325 | 1.344 ± 0.309 | 1.357 ± 0.308 | 1.277 ± 0.275 | <0.0001 | 0.402 |
| BUN (mmol/L) | 4.037 ± 1.226 | 3.806 ± 1.110 | 4.015 ± 1.309 | 3.992 ± 1.143 | 4.258 ± 1.264 | <0.0001 | −0.364 |
| Total calcium (mmol/L) | 9.598 ± 0.297 | 9.468 ± 0.297 | 9.574 ± 0.299 | 9.618 ± 0.264 | 9.692 ± 0.286 | <0.0001 | −0.709 |
| Serum 25OHD (nmol/L) | 63.065 ± 22.329 | 58.228 ± 22.816 | 63.249 ± 22.773 | 64.898 ± 23.181 | 64.641 ± 20.239 | <0.0001 | −0.381 |
| Total BMD (g/cm2) | 1.030 ± 0.120 | 1.020 ± 0.114 | 1.008 ± 0.118 | 1.016 ± 0.126 | 1.068 ± 0.113 | <0.0001 | −0.411 |
| HGB (g/dL) | 14.042 ± 1.329 | 12.426 ± 0.986 | 13.525 ± 0.613 | 14.257 ± 0.692 | 15.421 ± 0.818 | <0.0001 | −3.324 |
| RDW (%) | 13.191 ± 1.076 | 14.429 ± 1.484 | 13.221 ± 0.590 | 12.892 ± 0.597 | 12.571 ± 0.552 | <0.0001 | 1.660 |
| HRR | 1.073 ± 0.141 | 0.870 ± 0.107 | 1.023 ± 0.026 | 1.106 ± 0.025 | 1.228 ± 0.060 | <0.0001 | −4.153 |
| Milk product consumption (%) | <0.0001 | ||||||
| Never | 6.816 | 7.483 | 7.869 | 6.656 | 5.589 | 0.187 | |
| Rarely (less than once a week) | 10.91 | 14.601 | 11.842 | 9.901 | 8.429 | 0.065 | |
| Sometimes (once a week or more, but less than once a day | 26.697 | 29.469 | 26.007 | 26.536 | 25.488 | −0.222 | |
| Often (once a day or more) | 55.577 | 48.448 | 54.283 | 56.907 | 60.493 | −0.038 | |
| Model 1 (Unadjusted) β (95% CI) p-Value | Model 2 (Age, Gender, Race Adjusted) β (95% CI) p-Value | Model 3 (Fully Adjusted) β (95% CI) p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HRR | 0.105 (0.079, 0.131) <0.0001 | 0.068 (0.043, 0.093) <0.0001 | 0.078 (0.053, 0.104) <0.0001 |
| Q1 | Reference | Reference | Reference |
| Q2 | −0.004 (−0.015, 0.007) 0.445 | 0.007 (−0.002, 0.016) 0.122 | 0.008 (−0.001, 0.017) 0.074 |
| Q3 | 0.004 (−0.007, 0.014) 0.505 | 0.011 (0.001, 0.020) 0.023 | 0.014 (0.005, 0.024) 0.003 |
| Q4 | 0.046 (0.036, 0.057) <0.0001 | 0.029 (0.019, 0.039) <0.0001 | 0.033 (0.022, 0.043) <0.0001 |
| p for trend | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Total BMD | Adjusted β (95% CI) p Value |
|---|---|
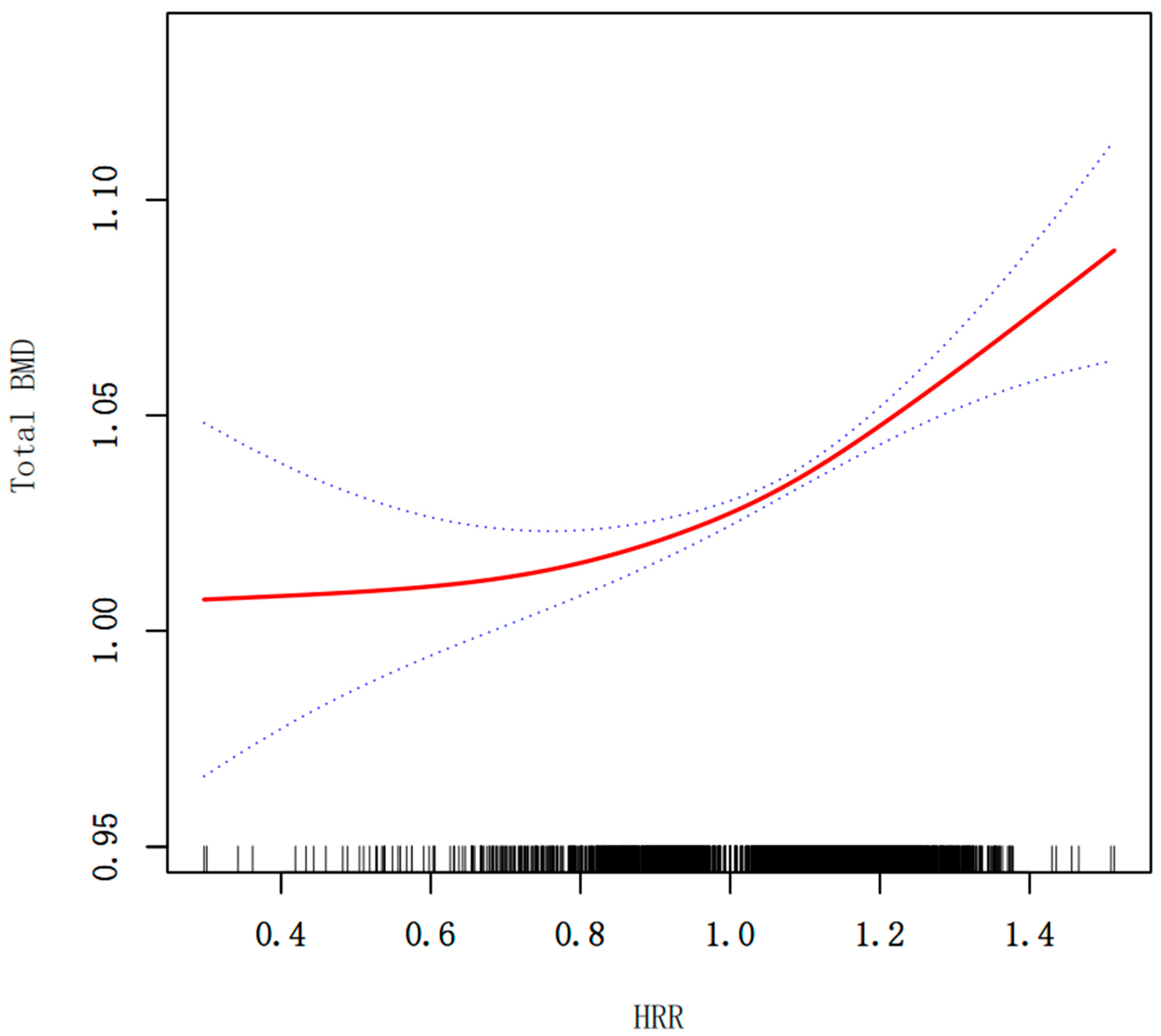
| Model I | |
| Fitting by the standard linear model | 0.079 (0.054, 0.105) <0.0001 |
| Model II | |
| Fitting by the standard linear model | |
| Inflection point (K) | 1.055 |
| HRR < K | 0.039 (0.002, 0.076) 0.041 |
| HRR > K | 0.143 (0.094, 0.193) <0.0001 |
| Log likelihood ratio | 0.003 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, T.; Xiao, J.; Yao, X.; Bai, J.; Yu, Y. Association of Hemoglobin to Red Blood Cell Distribution Width Ratio and Total Bone Mineral Density in U.S. Adolescents: The NHANES 2011–2018. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2567. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15202567
Guo T, Xiao J, Yao X, Bai J, Yu Y. Association of Hemoglobin to Red Blood Cell Distribution Width Ratio and Total Bone Mineral Density in U.S. Adolescents: The NHANES 2011–2018. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(20):2567. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15202567
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Tianhao, Jiheng Xiao, Xinjun Yao, Jiangbo Bai, and Yadong Yu. 2025. "Association of Hemoglobin to Red Blood Cell Distribution Width Ratio and Total Bone Mineral Density in U.S. Adolescents: The NHANES 2011–2018" Diagnostics 15, no. 20: 2567. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15202567
APA StyleGuo, T., Xiao, J., Yao, X., Bai, J., & Yu, Y. (2025). Association of Hemoglobin to Red Blood Cell Distribution Width Ratio and Total Bone Mineral Density in U.S. Adolescents: The NHANES 2011–2018. Diagnostics, 15(20), 2567. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15202567






