Is Digital Maxillary Model Scanning Reliable in Individuals with Unilateral Cleft Lip and Palate?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- ·
- Not having any kind of syndrome;
- ·
- Not having any kind of neurological or mental problem;
- ·
- Being in the permanent dentition period;
- ·
- Having unilateral cleft lip and palate;
- ·
- Not having received orthodontic treatment;
- ·
- Not having different ethnic origins.
- ·
- Not having any syndrome, craniofacial anomaly, or cleft lip and palate;
- ·
- No history of head–face trauma or any surgical operation in the facial area;
- ·
- Not having any kind of neurologic or mental problem;
- ·
- Having Angle Class I canine and molar relationships;
- ·
- Being in the permanent dentition period;
- ·
- Not having received orthodontic treatment;
- ·
- Having a similar chronological age to the CLP group;
- ·
- Having a similar gender distribution as the CLP group;
- ·
- Not having different ethnic origins and racial characteristics.
2.1. Study Design
2.1.1. Preparation of Orthodontic Models
2.1.2. Transferring Orthodontic Models to 3D Digital Models and Performing Applications
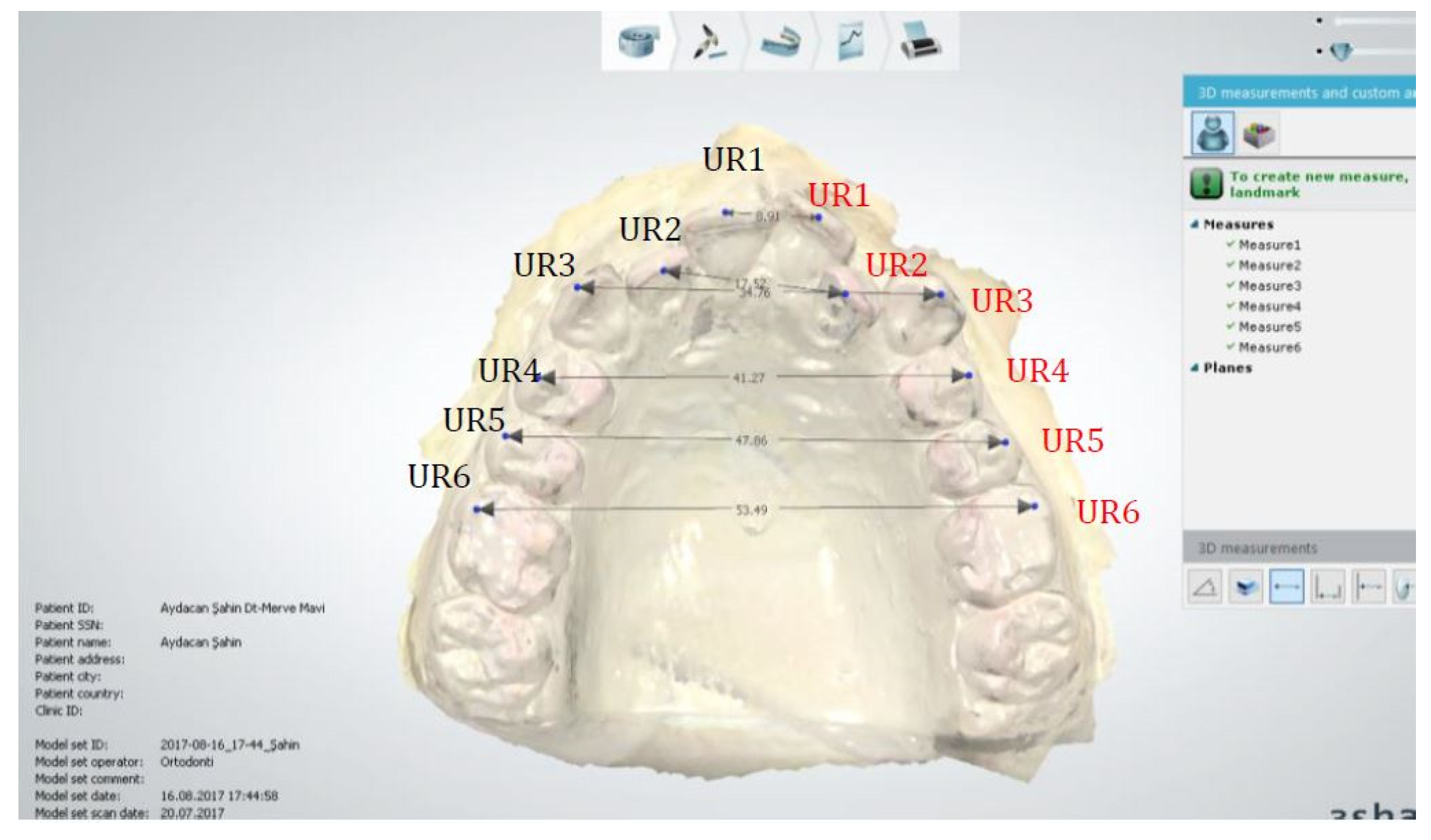
2.1.3. Anatomical Reference Points (Figure 3)
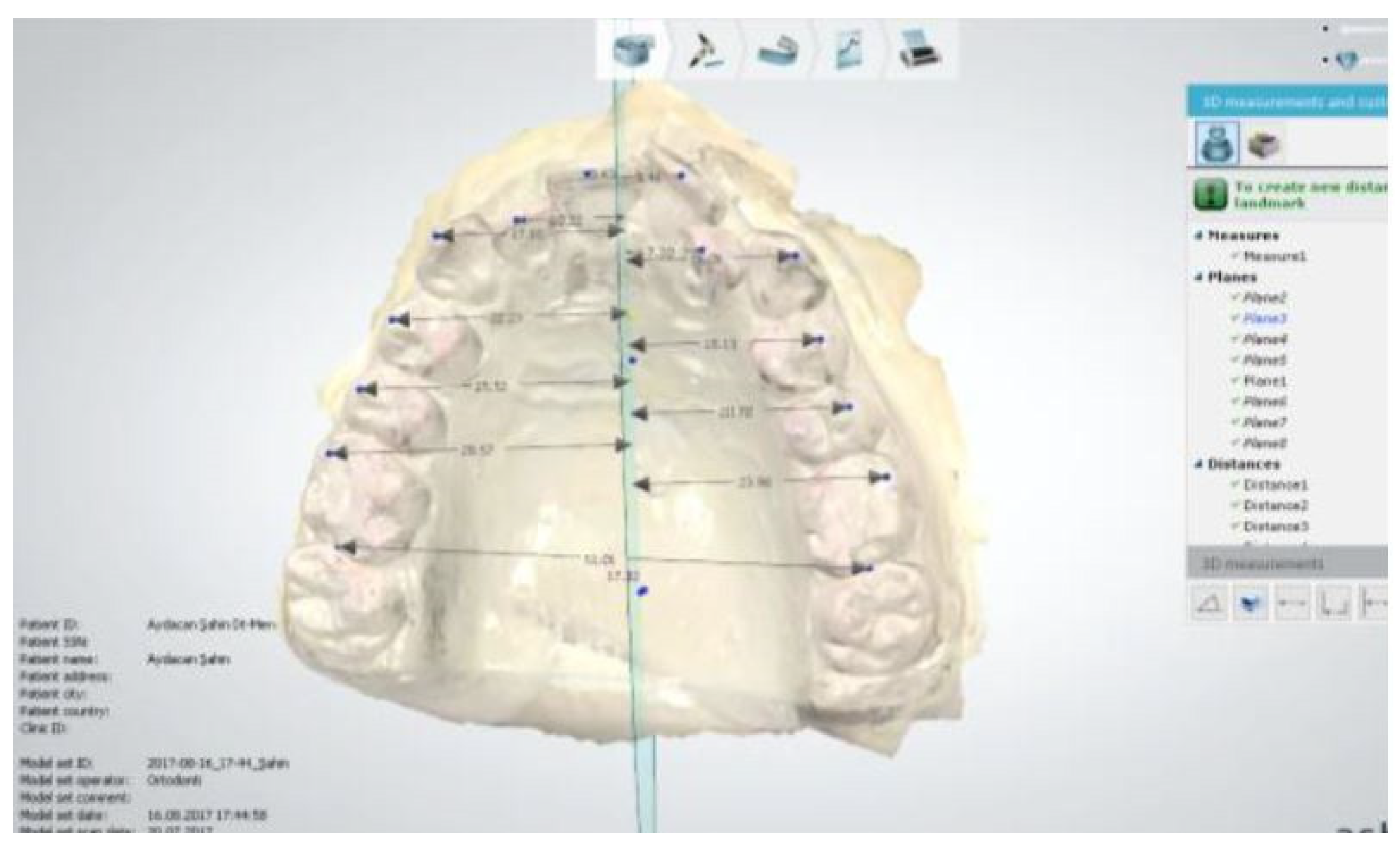
2.1.4. Reference Planes
2.1.5. Transversal Dimension Parameters
2.2. Statistical Analysis
2.3. Method Error
3. Results
3.1. Intra-Observer Reliability
3.2. Comparison of Two Methods
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- *
- For all parameters, smaller values were obtained in the CLP group compared with the control group in both measurement modalities.
- *
- A statistically significant difference was found in the comparison of right–left asymmetry in the CLP group.
- *
- Statistically significant differences were found between the CLP and control groups for all parameters.
- *
- When comparing the two measurement modalities with Student’s t-tests in the CLP and control groups, all parameters were found to be similar and only the difference between the right and left central incisors was found to be statistically significant. Although this difference was found to be statistically significant for both groups, it remained within clinically acceptable limits (0.60–0.61 mm).
- *
- The ICCs were found to be high for values obtained with both measurement methods in the CLP and control groups; therefore, both measurement modalities can be considered reliable.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yagcı, A.; Uysal, T. Tek taraflı dudak-damak yarığına sahip bebeklerde nazoalveolar şekillendirme yönteminin yarık segmentler ve alveol genişlikleri üzerine etkilerinin değerlendirilmesi. Sağlık Bilim. Dergisi. 2007, 16, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Burston, W.R. The early orthodontic treatment of cleft palate conditions. Dent. Prac. 1958, 9, 41–52. [Google Scholar]
- Villoria, E.M.; Souki, B.Q.; Antunes, F.L.; Assis, M.A.L.; Andrade Júnior, I.; Oliveira, D.D.; Soares, R.V. Craniofacial morphology of patients with unilateral cleft lip and palate at two stages of skeletal maturation. Braz. Oral. Res. 2023, 6, 37–49. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, J.; Tanikawa, C.; Kogo, M.; Yamashiro, T. Prognostic Factors for Orthognathic Surgery in Children with Cleft Lip and/or Palate: Dentition and Palatal Morphology. Cleft Palate Craniofacial J. 2023, 60, 1556–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Normandro, A.D.C.; Da Silva Filho, O.G.; Filho, L.C. Influence of surgery on maxillary growth in cleft lip and palate patients. J. Cranio-Maxillo-Facial Surg. 1992, 20, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Filho, O.G.; Ramos, A.L.; Abdo, R.C.C. The influence of unilateral cleft lip and palate on maxillary dental arch morphology. Angle Orthod. 1992, 62, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ball, J.V.; Dibiase, D.; Sommerland, B.C. Transverse maxillary arch changes with the use of preoperative orthopedics in unilateral cleft lip and palate infants. Cleft Palate Craniofacial J. 1995, 32, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidelbuchel, K.L.W.M.; Kuijpers-Jagtman, A.M.; Kramer, G.; Andersen, P. Maxillary arch dimensions in bilateral cleft lip and palate from birth until four years of age. Cleft Palate Craniofacial J. 1998, 35, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huddart, A.G.; Bodenham, R.S. Evaluation of arch form and occlusion in unilateral cleft lip and palate subjects. Cleft Palate J. 1972, 9, 194–209. [Google Scholar]
- Parveen, S.; Husain, A.; Johns, G.; Mascarenhas, R.; Reddy, S.G. Three-Dimensional Analysis of Craniofacial Structures of Individuals with Nonsyndromic Unilateral Complete Cleft Lip and Palate. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2021, 32, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltomaki, T.; Vendittelli, B.L.; Grayson, B.H.; Cutting, C.B.; Brecht, L.E. Assosiations between severity of clefting and maxillary growth in patients with unilateral cleft lip and palate treated with infant orthopedics. Cleft Palate Craniofacial J. 2001, 38, 582–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harding, R.L.; Mazaheri, M. Growth and spatial changes in the arch form in bilateral cleft lip and palate patients. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1972, 50, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruzansky, S.; Aduss, H. Prevelance of arch collapse and malocclusion in complete unilateral cleft lip and palate. Proc. Eur. Orthod. Soc. 1967, 43, 365–382. [Google Scholar]
- Maulina, I.; Priede, D.; Linkeviciene, L.; Akota, I. The influence of early orthopedic treatment on the growth of craniofacial complex in deciduous occlusion of unilateral cleft lip and palate patients. Stomatol. Balt. Dent. Maxillofac. J. 2007, 9, 91–96. [Google Scholar]
- Pruzansky, S.; Aduss, H. Arch form and deciduous occlusion in complete unilateral clefts. Cleft Palate J. 1964, 1, 411–418. [Google Scholar]
- Pruzansky, S. Factors determing arch form in clefts of the lip and palate. Am. J. Orthod. 1955, 41, 827–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rheude, B.; Sadowsky, P.L.; Ferriera, A.; Jacobson, A. An evaluation of the use of digital study models in orthodontic diagnosis and treatment planning. Angle Orthod. 2005, 75, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peluso, M.J.; Josell, S.D.; Levine, S.W.; Lorei, B.J. Digital models: An introduction. Semin. Orthod. 2004, 10, 226–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung-Hwa, L.; Ji-man, P.; Minji, K.; Seong-Joo, H.; Ji-yun, M. Comparison of digital intraoral scanner reproducibility and image trueness considering repetitive experience. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2017, 118, 36–42. [Google Scholar]
- Nedelcu, R.; Olsson, P.; Nyström, I.; Ryden, J.; Thor, A. Accuracy and precision of 3 intraoral scanners and accuracy of conventional impressions: A novel in vivo analysis method. J. Dent. 2018, 69, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vögltin, C.; Schulz, G.; Jager, K.; Müller, B. Comparing the accuracy of master models based on digital intra-oral scanners with conventional plaster casts. Phys. Med. 2016, 1, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anh, J.; Park, J.-M.; Chun, Y.-S.; Kim, M.; Kim, M. A comparison of the precision of three-dimensional images acquired by 2 digital intraoral scanners: Effects of tooth irregularity and scanning direction. Korean J. Orthod. 2016, 46, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camardella, L.T.; Breuning, H.; de Vasconcellos, V. Accuracy and reproducibility of measurements on plaster models and digital models created using an intraoral scanner. J. Orofac. Orthop. 2017, 78, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerman, M.; Koller, C.; Rumetsch, M.; Ender, A.; Mehl, A. Precision of guided scanning procedures for full-arch digital impressions in vivo. J. Orofac. Orthop. 2017, 78, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiranto, M.G.; Engelbrecht, W.P.; Nolthenius, H.E.T. Validity, reliability, and reproducibility of linear measurements on digital models obtained from intraoral and cone-beam computed tomography scans of alginate impressions. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2013, 143, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leenarts, C.M.; Bartzela, T.N.; Bronkhorst, E.M.; Semb, G.; Shaw, W.C.; Katsaros, C.; Kuijpers-Jagtman, A.M. Photographs of dental casts or digital models: Rating dental arch relationships in bilateral cleft lip and palate. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2012, 41, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalmers, E.V.; Mıntyre, G.T.; Wang, W.; Gillgrass, T.; Martin, C.B.; Mossey, P.A. Intraoral 3D Scanning or Dental Impressions for the Assessment of Dental Arch Relationships in Cleft Care: Which is Superior? Cleft Palate Craniofacial J. 2016, 53, 568–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashquith, J.A.; Mcıntyre, G.T. Dental arch relationships on three-dimensional digital study models and conventional plaster study models for patients with unilateral cleft lip and palate. Cleft Palate Craniofacial J. 2012, 49, 530–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Zhao, J.; Zheng, J.; Yu, Q. A Digital Assessment of the Maxillary Deformity Correction in Infants with Bilateral Cleft Lip and Palate Using Computer-Aided Nasoalveolar Molding. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2017, 28, 1543–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.; Yao, C.A.; Magee, W., 3rd; Chai, G.; Zhang, Y. Presurgical nasoalveolar molding for cleft lip and palate: The application of digitally designed molds. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2015, 135, 1007e–1015e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, F.X.; Gull, F.D.; Roth, M.; Ritschl, L.M.; Rau, A.; Gau, D.; Gruber, M.; Eblenkamp, M.; Hilmer, B.; Wolff, K.D.; et al. A prospective longitudinal study of postnatal dentoalveolar and palatal growth: The anatomical basis for CAD/CAM-assisted production of cleft-lip-palate feeding plates. Clin. Anat. 2017, 30, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gary, D.H.; Sebastian, B.; Patzel, M. Evaluation of the Accuracy of Six Intraoral Scanning Devices: An in-vitro Investigation. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2015, 10, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Antonarakis, G.S.; Adibfar, A.; Tompson, B.D.; Paedo, D.; Daskalogiannakis, J.; Fisher, D.M. Presurgical cleft lip anthropometrics and dental arch relationships in patients with complete unilateral cleft lip and palate. Cleft Palate Craniofacial J. 2015, 52, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassi, D.; Blasio, A.D.; Gandolfinini, M.; Magnifico, M.; Pellegrino, F.; Piancino, M.G. Dentoalveolar Effects of Early Orthodontic Treatment in Patients with Cleft Lip and Palate. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2017, 28, 2021–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, S.; Alam, M.K.; Khamis, M.F. The effect of various factors on the dental arch relationship in non-syndromic unilateral cleft lip and palate children assessed by new approach: A retrospective study. BMC Pediatr. 2017, 17, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, G.V.; Rani, S.A.; Mohd Sharab, N.F.; Mohamed, H.Y. Facial profile and maxillary arch dimensions in unilateral cleft lip and palate children in the mixed dentition stage. Eur. J. Dent. 2017, 10, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Disthaporn, S.; Suri, S.; Ross, B.; Tompson, B.; Baena, A.D.; Fisher, D.; Lou, W. Incisor and molar overjet, arch contraction, and molar relationship in the mixed dentition in repaired complete unilateral cleft lip and palate: A qualitative and quantitative appraisal. Angle Orthod. 2017, 87, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suri, S.; Utreja, A.; Khandelwal, N.; Mago, S.K. Craniofacial Computerized Tomography Analysis of the midface of patients with repaired complete unilateral cleft lip and palate. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2008, 3, 418–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranta, R. A review of tooth formation in children with cleft lip/palate. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1986, 90, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vichy, M.; Franchi, L. Abnormalities of the f the maxillary incisors in children with cleft lip and palate. ASDC J. Dent. Child. 1995, 62, 412–417. [Google Scholar]
- Tortora, C.; Meazzini, M.C.; Garattini, G.; Brusati, R. Prevalence of abnormalities in dental structure, position, and eruption pattern in a population of unilateral and bilateral cleft lip and palate patients. Cleft Palate Craniofacial J. 2008, 45, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, M.; Hajdarević, A.; Čirgić, E.; Sabel, N. Validity of digital analysis versus manual analysis on orthodontic casts. J. World Fed. Orthod. 2024, 13, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unnikrishnan, J.; Bakr, M.; Love, R.; Idris, G. Enhancing Effective Scanning Techniques for Digital Impression in Neonates with Cleft Lip and/or Palate: A Laboratory Study Investigating the Impact of Different Scanners, Scanning Tip Sizes, and Strategies. Children 2024, 11, 1435. [Google Scholar]
- Okazaki, T.; Kawanabe, H.; Fukui, K. Comparison of conventional impression making and intraoral scanning for the study of unilateral cleft lip and palate. Congenit. Anom. 2023, 63, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| CLP Group | t-Test | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Mean | Median | Minimum | Maximum | ss | t | p | ||
| U1-MRP | Right | 42 | 4.16 | 3.34 | 1.31 | 14.69 | 2.87 | −5.4 | 0.0001 |
| Left | 42 | 7.45 | 8.25 | 1.07 | 10.59 | 2.69 | |||
| U2-MRP | Right | 22 | 3.21 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 12.39 | 4.58 | 2.09 | 0.043 |
| Left | 22 | 1.08 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 3.38 | 1.40 | |||
| U3-MRP | Right | 42 | 12.80 | 13.36 | 5.24 | 20.01 | 4.95 | 2.24 | 0.028 |
| Left | 42 | 10.21 | 7.53 | 3.09 | 19.82 | 5.62 | |||
| U4-MRP | Right | 42 | 12.22 | 11.00 | 0.00 | 25.24 | 6.56 | −2.2 | 0.031 |
| Left | 42 | 15.59 | 16.85 | 0.00 | 29.01 | 7.43 | |||
| U5-MRP | Right | 42 | 11.17 | 10.40 | 0.00 | 26.96 | 5.88 | −6.5 | 0.0001 |
| Left | 42 | 21.49 | 24.89 | 0.00 | 29.76 | 8.44 | |||
| U6-MRP | Right | 42 | 21.76 | 20.31 | 10.49 | 29.95 | 6.62 | 2.29 | 0.024 |
| Left | 42 | 18.30 | 17.06 | 3.60 | 29.90 | 7.19 | |||
| Control Group | t-Test | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Mean | Median | Minimum | Maximum | sd | t | p | ||
| U1-MRP | Right | 43 | 5.31 | 5.05 | 3.64 | 7.95 | 1.01 | 0.04 | 0.968 |
| Left | 43 | 5.30 | 5.21 | 3.98 | 7.21 | 0.92 | |||
| U2-MRP | Right | 43 | 12.60 | 12.24 | 10.37 | 15.86 | 1.38 | 1.14 | 0.256 |
| Left | 43 | 12.28 | 12.16 | 10.27 | 15.89 | 1.21 | |||
| U3-MRP | Right | 43 | 17.69 | 17.81 | 15.06 | 22.37 | 1.36 | 0.5 | 0.617 |
| Left | 43 | 17.54 | 17.46 | 15.23 | 22.34 | 1.33 | |||
| U4-MRP | Right | 43 | 22.29 | 22.08 | 19.37 | 26.33 | 1.32 | −0.2 | 0.838 |
| Left | 43 | 22.35 | 22.12 | 19.09 | 26.76 | 1.34 | |||
| U5-MRP | Right | 43 | 25.39 | 25.46 | 22.09 | 29.06 | 1.41 | −0.03 | 0.971 |
| Left | 43 | 25.40 | 25.39 | 22.47 | 29.09 | 1.35 | |||
| U6-MRP | Right | 43 | 27.17 | 26.88 | 23.14 | 30.59 | 1.67 | −0.09 | 0.924 |
| Left | 43 | 27.20 | 27.12 | 23.17 | 30.89 | 1.67 | |||
| CLP Group | t-Test | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Mean | Median | Minimum | Maximum | sd | t | p | ||
| U1-MRP (right) | CLP | 42 | 4.16 | 3.34 | 1.31 | 14.69 | 2.87 | −2.7 | 0.015 |
| Control | 43 | 5.31 | 5.05 | 3.64 | 7.95 | 1.01 | |||
| U1-MRP (left) | CLP | 42 | 7.45 | 8.25 | 1.07 | 10.59 | 2.69 | 4.9 | 0.0001 |
| Control | 43 | 5.30 | 5.21 | 3.98 | 7.21 | 0.92 | |||
| U2-MRP (right) | CLP | 22 | 3.21 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 12.39 | 4.58 | −12.4 | 0.0001 |
| Control | 43 | 12.60 | 12.24 | 10.37 | 15.86 | 1.38 | |||
| U2-MRP (left) | CLP | 22 | 1.08 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 3.38 | 1.40 | −33.4 | 0.0001 |
| Control | 43 | 12.28 | 12.16 | 10.27 | 15.89 | 1.21 | |||
| U3-MRP (right) | CLP | 42 | 12.80 | 13.36 | 5.24 | 20.01 | 4.95 | −6.2 | 0.0001 |
| Control | 43 | 17.69 | 17.81 | 15.06 | 22.37 | 1.36 | |||
| U3-MRP (left) | CLP | 42 | 10.21 | 7.53 | 3.09 | 19.82 | 5.62 | −8.3 | 0.0001 |
| Control | 43 | 17.54 | 17.46 | 15.23 | 22.34 | 1.33 | |||
| U4-MRP (right) | CLP | 42 | 12.22 | 11.00 | 0.00 | 25.24 | 6.56 | −9.8 | 0.0001 |
| Control | 43 | 22.29 | 22.08 | 19.37 | 26.33 | 1.32 | |||
| U4-MRP (left) | CLP | 42 | 15.59 | 16.85 | 0.00 | 29.01 | 7.43 | −5.8 | 0.0001 |
| Control | 43 | 22.35 | 22.12 | 19.09 | 26.76 | 1.34 | |||
| U5-MRP (right) | CLP | 42 | 11.17 | 10.40 | 0.00 | 26.96 | 5.88 | −15.4 | 0.0001 |
| Control | 43 | 25.39 | 25.46 | 22.09 | 29.06 | 1.41 | |||
| U5-MRP (left) | CLP | 42 | 21.49 | 24.89 | 0.00 | 29.76 | 8.44 | −3.1 | 0.004 |
| Control | 43 | 25.40 | 25.39 | 22.47 | 29.09 | 1.35 | |||
| U6-MRP (right) | CLP | 42 | 21.76 | 20.31 | 10.49 | 29.95 | 6.62 | −5.1 | 0.0001 |
| Control | 43 | 27.17 | 26.88 | 23.14 | 30.59 | 1.67 | |||
| U6-MRP (left) | CLP | 42 | 18.30 | 17.06 | 3.60 | 29.90 | 7.19 | −7.9 | 0.0001 |
| Control | 43 | 27.20 | 27.12 | 23.17 | 30.89 | 1.67 | |||
| CLP Group | t-Test | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Mean | Median | Minimum | Maximum | sd | t | p | ||
| UR1- MRP | 3Shape | 42 | 4.18 | 4.30 | 2.18 | 6.55 | 1.00 | 0.065 | 0.948 |
| Caliper | 42 | 4.17 | 4.28 | 2.15 | 6.53 | 1.00 | |||
| UR2- MRP | 3Shape | 42 | 9.37 | 10.15 | 2.54 | 11.76 | 2.33 | 0.024 | 0.981 |
| Caliper | 42 | 9.35 | 10.13 | 2.50 | 11.75 | 2.34 | |||
| UR3- MRP | 3Shape | 42 | 12.17 | 12.33 | 3.64 | 19.01 | 3.48 | 0.008 | 0.994 |
| Caliper | 42 | 12.17 | 12.32 | 3.64 | 19.03 | 3.48 | |||
| UR4- MRP | 3Shape | 42 | 17.04 | 17.57 | 7.37 | 22.98 | 3.04 | 0.018 | 0.986 |
| Caliper | 42 | 17.03 | 17.55 | 7.37 | 22.95 | 3.04 | |||
| UR5- MRP | 3Shape | 42 | 20.12 | 20.61 | 11.44 | 27.83 | 3.80 | 0.018 | 0.985 |
| Caliper | 42 | 20.10 | 20.59 | 11.45 | 27.85 | 3.81 | |||
| UR6- MRP | 3Shape | 42 | 23.62 | 23.94 | 16.79 | 27.58 | 2.51 | 0.023 | 0.981 |
| Caliper | 42 | 23.61 | 23.94 | 16.78 | 27.59 | 2.51 | |||
| UL1- MRP | 3Shape | 42 | 4.33 | 4.32 | 1.23 | 7.33 | 1.58 | 0.041 | 0.967 |
| Caliper | 42 | 4.31 | 4.30 | 1.21 | 7.29 | 1.58 | |||
| UL2- MRP | 3Shape | 42 | 9.09 | 9.08 | 2.33 | 12.51 | 2.53 | 0.011 | 0.992 |
| Caliper | 42 | 9.08 | 9.07 | 2.30 | 12.49 | 2.53 | |||
| UL3- MRP | 3Shape | 42 | 13.28 | 13.00 | 5.40 | 19.70 | 3.65 | 0.013 | 0.991 |
| Caliper | 42 | 13.27 | 13.00 | 5.36 | 19.68 | 3.65 | |||
| UL4- MRP | 3Shape | 42 | 18.39 | 18.46 | 11.47 | 25.93 | 3.19 | 0.026 | 0.981 |
| Caliper | 42 | 18.37 | 18.45 | 11.45 | 25.94 | 3.19 | |||
| UL5- MRP | 3Shape | 42 | 20.78 | 21.39 | 10.63 | 29.52 | 3.83 | 0.025 | 0.981 |
| Caliper | 42 | 20.76 | 21.37 | 10.61 | 29.51 | 3.84 | |||
| UL6-MRP | 3Shape | 42 | 22.41 | 22.88 | 15.81 | 29.90 | 3.28 | 0.049 | 0.961 |
| Caliper | 42 | 22.38 | 22.86 | 15.80 | 29.60 | 3.30 | |||
| UR1-UL1 | 3Shape | 42 | 9.31 | 9.12 | 5.30 | 12.20 | 1.61 | 2.15 | 0.034 |
| Caliper | 42 | 8.69 | 8.88 | 5.97 | 10.99 | 0.96 | |||
| UR3-UL3 | 3Shape | 42 | 26.11 | 25.89 | 16.14 | 37.23 | 5.41 | 0.236 | 0.814 |
| Caliper | 42 | 25.83 | 25.60 | 16.14 | 35.43 | 5.16 | |||
| UR4-UL4 | 3Shape | 42 | 36.71 | 35.95 | 28.64 | 47.29 | 4.32 | 0.305 | 0.761 |
| Caliper | 42 | 36.42 | 35.84 | 26.27 | 47.25 | 4.57 | |||
| UR5-UL5 | 3Shape | 42 | 41.65 | 42.55 | 21.03 | 51.86 | 7.00 | 0.017 | 0.986 |
| Caliper | 42 | 41.63 | 42.51 | 21.01 | 51.82 | 6.99 | |||
| UR6-UL6 | 3Shape | 42 | 49.06 | 49.98 | 33.62 | 55.72 | 4.06 | 1.26 | 0.211 |
| Caliper | 42 | 46.89 | 49.74 | 1.03 | 55.69 | 10.41 | |||
| Control Group | t-Test | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Mean | Median | Minimum | Maximum | sd | t | p | ||
| UR1-MRP | 3Shape | 43 | 5.26 | 5.03 | 3.64 | 7.95 | 1.04 | 0.012 | 0.991 |
| Caliper | 43 | 5.26 | 5.05 | 3.65 | 7.94 | 1.04 | |||
| UR2-MRP | 3Shape | 43 | 12.34 | 12.11 | 10.14 | 15.86 | 1.50 | 0.049 | 0.961 |
| Caliper | 43 | 12.33 | 12.08 | 10.12 | 15.86 | 1.51 | |||
| UR3-MRP | 3Shape | 43 | 17.55 | 17.69 | 15.53 | 21.37 | 1.14 | 0.057 | 0.955 |
| Caliper | 43 | 17.53 | 17.54 | 15.56 | 21.37 | 1.14 | |||
| UR4-MRP | 3Shape | 43 | 21.22 | 21.08 | 16.64 | 24.33 | 1.45 | 0.047 | 0.962 |
| Caliper | 43 | 21.20 | 21.06 | 16.62 | 24.31 | 1.45 | |||
| UR5-MRP | 3Shape | 43 | 24.17 | 24.20 | 21.22 | 28.01 | 1.36 | 0.053 | 0.958 |
| Caliper | 43 | 24.15 | 24.18 | 21.20 | 28.02 | 1.37 | |||
| UR6-MRP | 3Shape | 43 | 26.62 | 26.54 | 22.70 | 30.59 | 1.74 | 0.032 | 0.975 |
| Caliper | 43 | 26.61 | 26.51 | 22.69 | 30.58 | 1.74 | |||
| UL1-MRP | 3Shape | 43 | 4.75 | 5.02 | 3.04 | 6.09 | 0.79 | 0.067 | 0.947 |
| Caliper | 43 | 4.74 | 5.00 | 3.03 | 6.07 | 0.79 | |||
| UL2-MRP | 3Shape | 43 | 11.65 | 11.56 | 10.12 | 13.67 | 0.97 | 0.071 | 0.944 |
| Caliper | 43 | 11.63 | 11.57 | 10.00 | 13.65 | 0.98 | |||
| UL3-MRP | 3Shape | 43 | 18.19 | 18.09 | 14.67 | 22.34 | 1.47 | 0.039 | 0.969 |
| Caliper | 43 | 18.18 | 18.08 | 14.66 | 22.33 | 1.47 | |||
| UL4-MRP | 3Shape | 43 | 22.29 | 22.09 | 19.45 | 26.76 | 1.39 | 0.051 | 0.959 |
| Caliper | 43 | 22.28 | 22.07 | 19.43 | 26.75 | 1.39 | |||
| UL5-MRP | 3Shape | 43 | 25.62 | 25.52 | 22.67 | 29.09 | 1.31 | 0.04 | 0.968 |
| Caliper | 43 | 25.61 | 25.51 | 22.64 | 29.06 | 1.32 | |||
| UL6-MRP | 3Shape | 43 | 26.48 | 26.78 | 22.14 | 30.76 | 1.99 | 0.034 | 0.973 |
| Caliper | 43 | 26.46 | 26.77 | 22.13 | 30.75 | 1.99 | |||
| UR1-UL1 | 3Shape | 43 | 8.70 | 8.90 | 5.97 | 10.99 | 0.96 | −2.14 | 0.034 |
| Caliper | 43 | 9.31 | 9.19 | 5.30 | 12.20 | 1.59 | |||
| UR3-UL3 | 3Shape | 43 | 34.87 | 35.38 | 31.58 | 39.04 | 1.94 | −0.002 | 0.997 |
| Caliper | 43 | 34.87 | 35.35 | 31.55 | 39.00 | 1.95 | |||
| UR4-UL4 | 3Shape | 43 | 41.99 | 42.57 | 34.23 | 45.98 | 2.73 | −0.07 | 0.944 |
| Caliper | 43 | 42.04 | 42.79 | 34.20 | 45.95 | 2.78 | |||
| UR5-UL5 | 3Shape | 43 | 47.63 | 48.05 | 39.38 | 52.09 | 2.63 | 0.086 | 0.932 |
| Caliper | 43 | 47.59 | 48.01 | 39.35 | 52.05 | 2.65 | |||
| UR6-UL6 | 3Shape | 43 | 50.55 | 51.82 | 36.50 | 56.55 | 4.40 | 0.033 | 0.994 |
| Caliper | 43 | 50.52 | 51.81 | 36.48 | 56.52 | 4.40 | |||
| ICC (Intraclass Correlation Coefficient) | ICC | |
|---|---|---|
| UR1-MRP | CLP | 1 |
| Control | 1 | |
| UR2-MRP | CLP | 1 |
| Control | 1 | |
| UR3-MRP | CLP | 1 |
| Control | 0.999 | |
| UR4-MRP | CLP | 1 |
| Control | 1 | |
| UR5-MRP | CLP | 1 |
| Control | 1 | |
| UR6-MRP | CLP | 1 |
| Control | 1 | |
| UL1-MRP | CLP | 1 |
| Control | 1 | |
| UL2-MRP | CLP | 1 |
| Control | 1 | |
| UL3-MRP | CLP | 1 |
| Control | 1 | |
| UL4-MRP | CLP | 1 |
| Control | 1 | |
| UL5-MRP | CLP | 1 |
| Control | 1 | |
| UL6-MRP | CLP | 0.999 |
| Control | 1 | |
| UR1-UL1 | CLP | 0.995 |
| Control | 0.999 | |
| UR3-UL3 | CLP | 0.82 |
| Control | 0.999 | |
| UR4-UL4 | CLP | 0.967 |
| Control | 0.998 | |
| UR5-UL5 | CLP | 1 |
| Control | 0.991 | |
| UR6-UL6 | CLP | 1 |
| Control | 0.991 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mavi, E.M.; Uslu-Akcam, O.; Akcam, M.O. Is Digital Maxillary Model Scanning Reliable in Individuals with Unilateral Cleft Lip and Palate? Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2553. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15202553
Mavi EM, Uslu-Akcam O, Akcam MO. Is Digital Maxillary Model Scanning Reliable in Individuals with Unilateral Cleft Lip and Palate? Diagnostics. 2025; 15(20):2553. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15202553
Chicago/Turabian StyleMavi, Elif Merve, Ozge Uslu-Akcam, and Mehmet Okan Akcam. 2025. "Is Digital Maxillary Model Scanning Reliable in Individuals with Unilateral Cleft Lip and Palate?" Diagnostics 15, no. 20: 2553. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15202553
APA StyleMavi, E. M., Uslu-Akcam, O., & Akcam, M. O. (2025). Is Digital Maxillary Model Scanning Reliable in Individuals with Unilateral Cleft Lip and Palate? Diagnostics, 15(20), 2553. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15202553







