Predictive Impact of Hematological and Biochemical Parameters on the Clinical Course of Sarcoidosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analysis
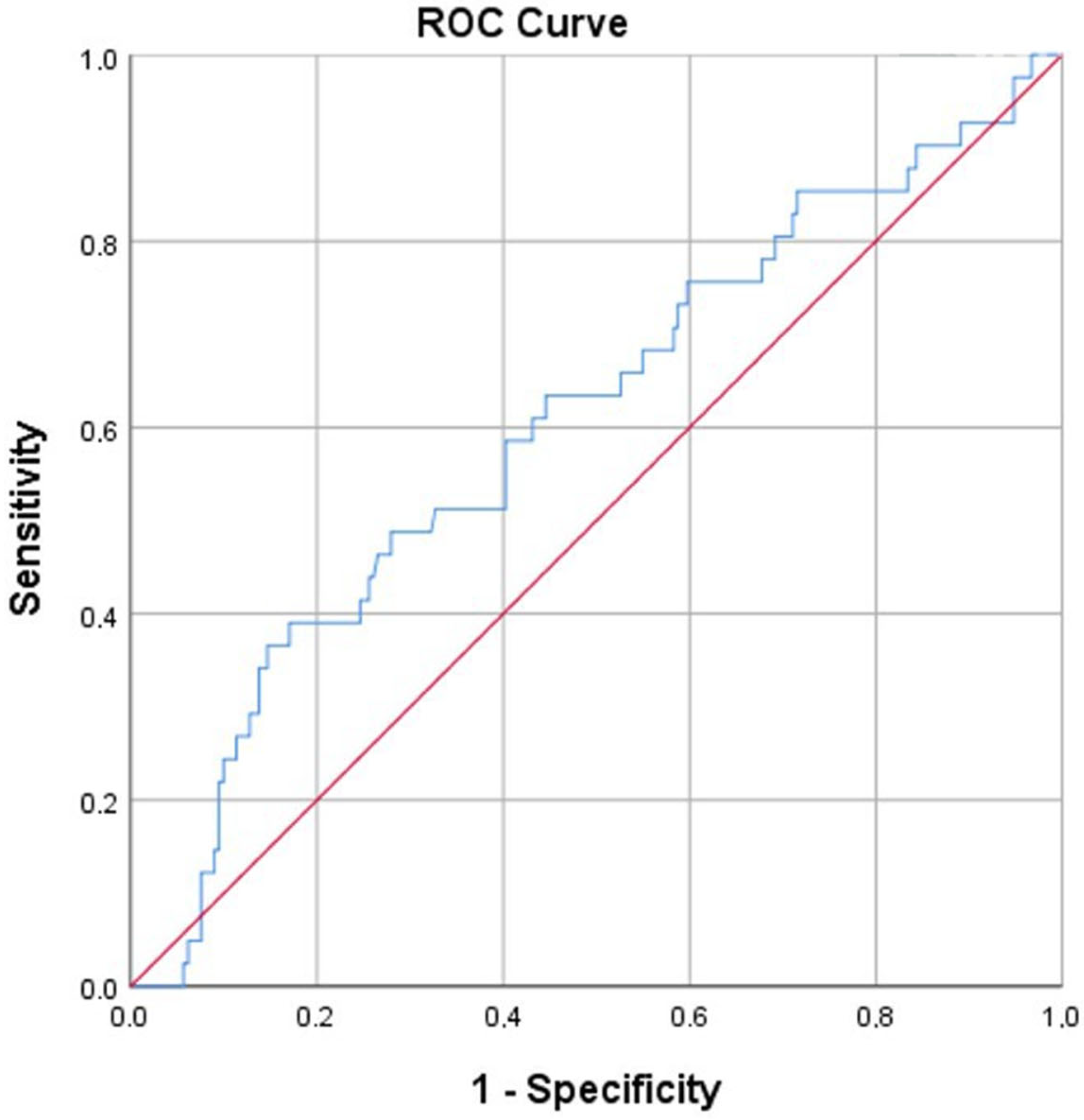
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramachandraiah, V.; Aronow, W.; Chandy, D. Pulmonary Sarcoidosis: An Update. Postgrad. Med. 2017, 129, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubrey, S.; Shah, S.; Hardman, T.; Sharma, R. Sarcoidosis: The Links between Epidemiology and Aetiology. Postgrad. Med. J. 2014, 90, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungprasert, P.; Ryu, J.H.; Matteson, E.L. Clinical Manifestations, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Sarcoidosis. Mayo Clin. Proc. Innov. Qual. Outcomes 2019, 3, 358–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patogenezden Tedaviye Her Yönüyle Sarkoidoz-2023 | Dergiler | Türkiye Klinikleri. Available online: https://www.turkiyeklinikleri.com/journal/gogus-hastaliklari-ozel-konular/88/issue/2023/16/1-0/patogenezden-tedaviye-her-yonuyle-sarkoidoz/tr-index.html (accessed on 30 April 2025).
- Baughman, R.P.; Valeyre, D.; Korsten, P.; Mathioudakis, A.G.; Wuyts, W.A.; Wells, A.; Rottoli, P.; Nunes, H.; Lower, E.E.; Judson, M.A.; et al. ERS Clinical Practice Guidelines on Treatment of Sarcoidosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 58, 2004079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahinoğlu, E.; Boyacı, H.; Kır, H.M.; Ilgazlı, A.H.; Başyiğit, İ.; Barış, S.A. An Important Question: Can Serum Chitotriosidase Enzyme Predict the Activity and Clinical Course of Sarcoidosis Disease? Thorac. Res. Pract. 2025, 26, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Casals, M.; Retamozo, S.; Sisó-Almirall, A.; Pérez-Alvarez, R.; Pallarés, L.; Brito-Zerón, P. Clinically-Useful Serum Biomarkers for Diagnosis and Prognosis of Sarcoidosis. Expert. Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 15, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonella, F.; Culver, D.A.; Israël-Biet, D. Sarcoidosis. In Sarcoidosis; European Respiratory Society: Sheffield, UK, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz, C.; Demircioglu, S. The Association of Neutrophil/Lymphocyte and Platelet/Lymphocyte Ratios and Hematological Parameters with Diagnosis, Stages, Extrapulmonary Involvement, Pulmonary Hypertension, Response to Treatment, and Prognosis in Patients with Sarcoidosis. Can. Respir. J. 2020, 2020, 1696450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosny Masoud, H.; Moustafa Ali, A.; AbdelWahab, F.; Abdel-Hamid, H.M. Novel Biomarkers for the Assessment of Disease Activity in Patients with Sarcoidosis: A Case-Control Study. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffus. Lung Dis. 2023, 40, e2023017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.Y.; Ryu, S.; Oh, S.-K.; Park, J.-S.; You, Y.-H.; Jeong, W.-J.; Cho, Y.-C.; Ahn, H.-J.; Kang, C.-S.; Kok, V.C. Lactate Dehydrogenase to Albumin Ratio as a Prognostic Factor for Patients with Severe Infection Requiring Intensive Care. Medicine 2021, 100, e27538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.-K.; Ryu, S.; Oh, S.-K.; Ahn, H.-J.; Jeon, S.-Y.; Jeong, W.-J.; Cho, Y.-C.; Park, J.-S.; You, Y.-H.; Kang, C.-S. Lactate Dehydrogenase to Albumin Ratio as a Prognostic Factor in Lower Respiratory Tract Infection Patients. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2022, 52, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouser, E.D.; Maier, L.A.; Wilson, K.C.; Bonham, C.A.; Morgenthau, A.S.; Patterson, K.C.; Abston, E.; Bernstein, R.C.; Blankstein, R.; Chen, E.S.; et al. Diagnosis and Detection of Sarcoidosis. An Official American Thoracic Society Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 201, e26–e51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, G.J.; Prescott, R.J.; Muers, M.F.; Middleton, W.G.; Mitchell, D.N.; Connolly, C.K.; Harrison, B.D. British Thoracic Society Sarcoidosis Study: Effects of Long Term Corticosteroid Treatment. Thorax 1996, 51, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fialek, B.; Pruc, M.; Smereka, J.; Jas, R.; Rahnama-Hezavah, M.; Denegri, A.; Szarpak, A.; Jaguszewski, M.J.; Peacock, F.W.; Szarpak, L. Diagnostic Value of Lactate Dehydrogenase in COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cardiol. J. 2022, 29, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drent, M.; Cobben, N.; Henderson, R.; Wouters, E.; van Dieijen-Visser, M. Usefulness of Lactate Dehydrogenase and Its Isoenzymes as Indicators of Lung Damage or Inflammation. Eur. Respir. J. 1996, 9, 1736–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, D.; Singh, M.; Rani, R. Role of LDH in Tumor Glycolysis: Regulation of LDHA by Small Molecules for Cancer Therapeutics. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 87, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, M.; Huiyin, L.; Shanglin, C.; Haiming, L.; Zhanyi, D.; Shuchun, W.; Meng, B.; Murong, L. Relationship between Human Serum Albumin and In-Hospital Mortality in Critical Care Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1109910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Su, Y.; Guo, C.; He, L.; Ding, N. Albumin Level Is Associated with Short-Term and Long-Term Outcomes in Sepsis Patients Admitted in the ICU: A Large Public Database Retrospective Research. Clin. Epidemiol. 2023, 15, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.-W.; Huang, S.-S.; Xu, Y.-H.; Chu, X.; Wang, L.; Mao, Y.-M.; Yuan, Y.-D.; Qiu, J.-Y. Lactate Dehydrogenase to Albumin Ratio and Prognosis in Patients with Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Retrospective Cohort Study. BMC Pulm. Med. 2025, 25, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, N.; Tabatabaei, F.-s.; Azimi, A.; Faraji, N.; Akbarpour, S.; Dianatkhah, M.; Moghaddas, A. Lactate Dehydrogenase to Albumin Ratio as a Predictive Factor of COVID-19 Patients’ Outcome; a Cross-Sectional Study. Arch. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2022, 10, e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Wei, Z.; Jiang, H.; Cheng, L.; Chen, Q.; Chen, M.; Yan, J.; Sun, Z. Lactate Dehydrogenase Is Associated with 28-Day Mortality in Patients with Sepsis: A Retrospective Observational Study. J. Surg. Res. 2018, 228, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekir, S.A.; Sonkaya, E.; Ozbaki, F.; Eroglu, S.A.; Sertcelik, L.; Duman, D.; Kavas, M.; Agca, M.; Erdem, I.; Ozmen, I.; et al. The Utility of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Determined at Initial Diagnosis in Predicting Disease Stage and Discriminating between Active and Stable Disease in Patients with Sarcoidosis: A Cross-Sectional Study. Postgrad. Med. 2022, 134, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekir, S.A.; Yalcinsoy, M.; Gungor, S.; Tuncay, E.; Akyil, F.T.; Sucu, P.; Yavuz, D.; Boga, S. Prognostic Value of Inflammatory Markers Determined during Diagnosis in Patients with Sarcoidosis: Chronic versus Remission. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2021, 67, 1575–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasempour Alamdari, M.; Kalami, N.; Shojaan, H.; Aminizadeh, S.; Ghaedi, A.; Bazrgar, A.; Khanzadeh, S. Systematic Review of the Diagnostic Role of Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio in Sarcoidosis. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffus. Lung Dis. 2023, 40, e2023008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemal, C.T.; Aylin, O.A.; Volkan, K.; Seda, M.; Recep, B.; Can, S. The Importance of PET/CT Findings and Hematological Parameters in Prediction of Progression in Sarcoidosis Cases. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffus. Lung Dis. 2017, 34, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Q.-Q.; Mo, Y.-J.; Zhu, K.-W.; Gao, F.; Huang, B.; Chen, P.; Jing, F.-T.; Jiang, X.; Xu, H.-Z.; Tang, Y.-F.; et al. Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (PLR), Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR), Monocyte-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (MLR), and Eosinophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (ELR) as Biomarkers in Patients with Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (AECOPD). Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2024, 19, 501–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.-Y.; Li, J.; Shao, X.-Y.; Zhang, C.-X. The Elevated NLR, PLR and PLT May Predict the Prognosis of Patients with Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 68837–68846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correlation Between NLR, PLR, and LMR and Disease Activity, Efficacy Assessment in Rheumatoid Arthritis-PMC. Available online: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8556079/ (accessed on 8 May 2025).
- Ozdemirel, T.S.; Özyürek, B.A.; Tatci, E.; Ertan, O.; Akkurt, E.S.; Senturk, A.; Ozmen, O. Relationships Between Systemic Inflammatory Markers and 18F-FDG PET/CT Imaging and Clinical Findings in Pulmonary Sarcoidosis. Cureus 2023, 15, e36521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| N (%) | ||
| Gender | Female | 268 (72.6) |
| Male | 101 (27.4) | |
| Age, years, Median/(25th–75th percentiles) | 52 (43–61) | |
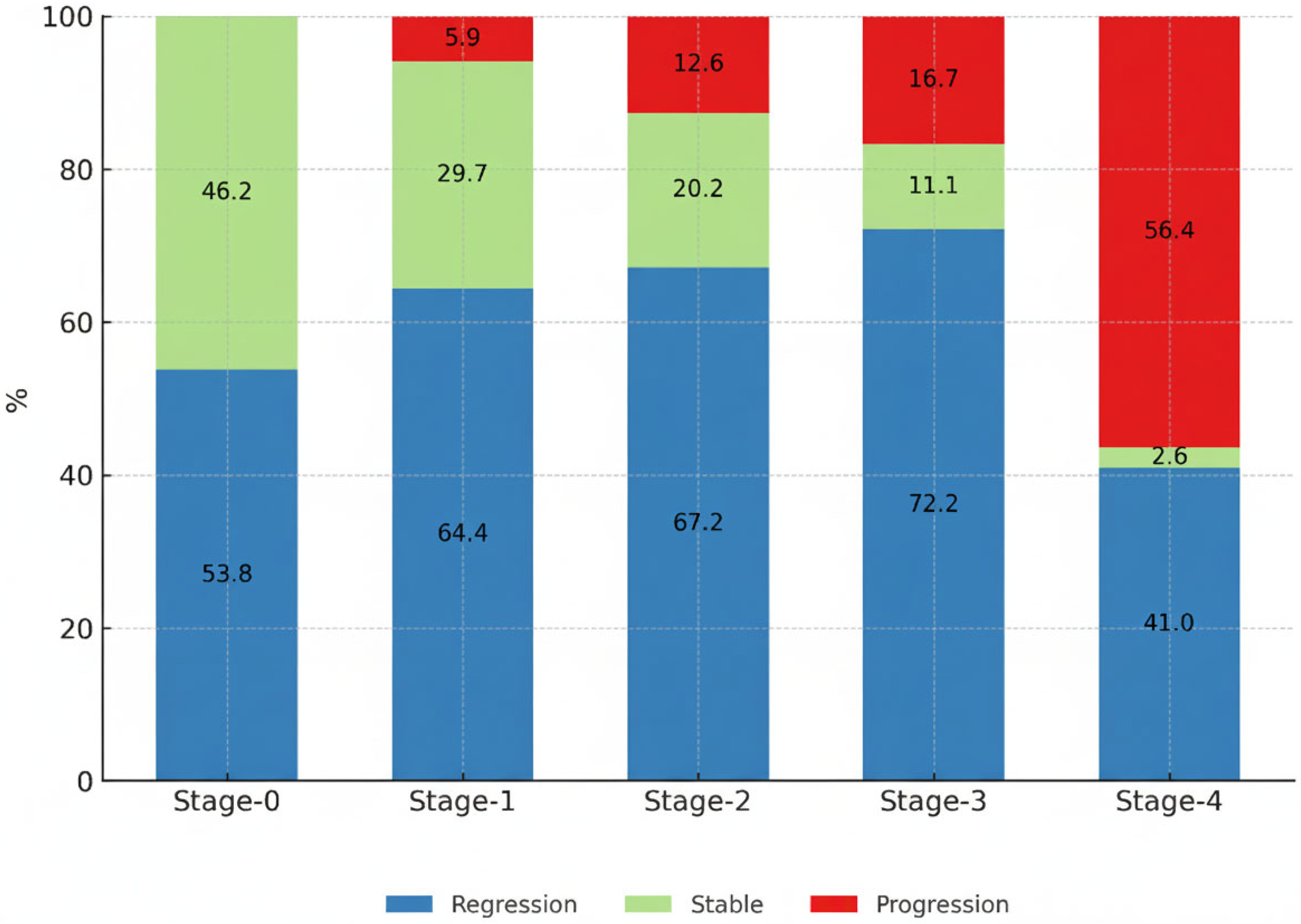
| Stage | 0 | 13 (3.5) |
| 1 | 101 (27.4) | |
| 2 | 198 (53.7) | |
| 3 | 18 (4.9) | |
| 4 | 39 (10.6) | |
| Treatment | Yes | 205 (55.6) |
| No | 164 (44.4) | |
| Clinical course of disease at 6th month | Regression | 234 (63.4) |
| Stable | 79 (21.4) | |
| Progression | 56 (15.2) | |
| Symptoms | Asymptomatic | 273 (74) |
| Weight loss | 19 (5.2) | |
| Fatigue | 82 (22.6) | |
| Loss of appetite | 4 (1.1) | |
| Fever | 3 (0.8) | |
| Respiratory Symptoms | 223 (60.4) | |
| Cough | 133 (36.5) | |
| Dyspnea | 142 (39) | |
| Chest pain | 50 (13.7) | |
| Hemoptysis | 2 (0.5) | |
| Smoking history | Nonsmoker | 166 (61.7) |
| Current Smoker | 57 (21.2) | |
| Former Smoker | 46 (17.1) | |
| Family History | Yes | 17 (8.5) |
| No | 182 (91.5) | |
| Physical examination | Normal | 295 (82.2) |
| Crackles | 38 (10.6) | |
| Rhonchi | 26 (7.2) | |
| Respiratory function test | Normal | 194 (79.2) |
| Obstructive | 28 (11.4) | |
| Restrictive | 14 (5.7) | |
| Mixed | 9 (3.7) | |
| Granuloma with FOB | Yes | 176 (74.6) |
| No | 60 (25.4) | |
| Extra pulmonary involvement | + | 145 (39.5) |
| Peripheral LAP | 49 (13.4) | |
| Skin | 69 (18.8) | |
| Eye | 21 (5.8) | |
| Cardiovascular | 3 (0.8) | |
| Neurological | 2 (0.5) | |
| Musculoskeletal | 19 (5.2) | |
| Gastro-urinary | 26 (7.1) | |
| Hematopoietic system | 5 (1.4) |
| Regression + Stable N:313 | Progression N:56 | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic characteristics | ||||
| Gender | Female | 230 (73.5%) | 38 (67.9%) | 0.39 |
| Male | 83 (26.5%) | 18 (32.1%) | ||
| Age, years | Median/(25th–75th percentiles) | 52 (43–60.5) | 56 (42.5–65) | 0.053 |
| Stage | 0 | 13 (4.2%) | 0 (0%) | 0.000 |
| 1 | 95 (30.4%) | 6 (10.7%) | ||
| 2 | 173 (55.3%) | 25 (44.6%) | ||
| 3 | 15 (4.8%) | 3 (5.4%) | ||
| 4 | 17 (5.4%) | 22 (39.3%) | ||
| Treatment | No | 152 (48.6%) | 12 (21.4%) | 0.000 |
| Yes | 161 (51.4%) | 44 (78.6%) | ||
| Symptoms | Asymptomatic | 241 (77%) | 32 (57.1%) | 0.002 |
| Weight loss | 17 (5.5%) | 2 (3.7%) | 0.58 | |
| Fatigue | 59 (19.1%) | 23 (42.6%) | 0.000 | |
| Loss of appetite | 4 (1.3%) | 0 | 0.4 | |
| Fever | 3 (1%) | 0 | 0.47 | |
| Respiratory Symptoms | 176 (56.2%) | 47 (83.9%) | 0.000 | |
| Cough | 102 (32.9%) | 31 (57.4%) | 0.001 | |
| Dyspnea | 106 (34.2%) | 36 (66.7%) | 0.001 | |
| Chest pain | 41 (13.2%) | 9 (16.7%) | 0.49 | |
| Hemoptysis | 1 (0.3%) | 1 (1.9%) | 0.16 | |
| Physical examination | Normal | 266 (86.6%) | 29 (55.8%) | 0.000 |
| Crackles | 20 (6.5%) | 18 (34.6%) | ||
| Rhonchi | 21 (6.8%) | 5 (9.6%) | ||
| Extra pulmonary involvement | + | 128 (41%) | 17 (30.9%) | 0.16 |
| Peripheral LAP | 43 (13.8%) | 6 (10.9%) | 0.56 | |
| Skin | 62 (19.9%) | 7 (12.7%) | 0.21 | |
| Eye | 19 (6.1%) | 2 (3.6%) | 0.46 | |
| Cardiovascular | 3 (1%) | 0 | 0.47 | |
| Neurological | 0 | 0 | NA | |
| Musculoskeletal | 18 (5.8%) | 1 (1.8%) | 0.22 | |
| Gastro-urinary | 23 (7.4%) | 3 (5.5%) | 0.61 | |
| Hematopoietic | 4 (1.3%) | 1 (1.8%) | 0.7 | |
| Laboratory tests at the time of diagnosis | ||||
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | Median/(25th–75th percentiles) | 0.7 (0.6–0.8) | 0.7 (0.6–0.8) | 0.176 |
| Calcium (mg/dL) | Median/(25th–75th percentiles) | 9.5 (9.1–9.8) | 9.6 (9.4–9.8) | 0.303 |
| 24 h urinary calcium (mg/day) | Median/(25th–75th percentiles) | 185 (106.5–265) | 168 (70–321) | 0.534 |
| Albumin (g/L) | Median/(25th–75th percentiles) | 42 (39–44.5) | 41.6 (37.5–44) | 0.138 |
| ACE (U/L) | Median/(25th–75th percentiles) | 71 (41–103) | 55 (30–81) | 0.161 |
| Neutrophil count, ×103 | Median/(25th–75th percentiles) | 4.206 (3.2–5.5) | 5.100 (3.7–6.9) | 0.021 |
| LDH (U/L) | Median/(25th–75th percentiles) | 189 (162–220) | 218 (179–272) | 0.058 |
| NLR | Median/(25th–75th percentiles) | 2.64 (1.9–3.5) | 3.09 (1.9–5) | 0.105 |
| PLR | Median/(25th–75th percentiles) | 172.1 (125.9–219.04) | 150.5 (120.7–202.5) | 0.368 |
| LMR | Median/(25th–75th percentiles) | 2.71 (2.08–3.75) | 2.69 (1.84–3.49) | 0.35 |
| LAR | Median/(25th–75th percentiles) | 4.59 (3.82–5.86) | 5.26 (4.21–7.76) | 0.033 |
| FEV1 | Median/(25th–75th percentiles) | 2.43 (2.05–2.88) | 2.32 (1.78–3.08) | 0.59 |
| FEV1 % | Median/(25th–75th percentiles) | 92 (79–102.3) | 78 (68.5–92.5) | 0.001 |
| FVC | Median/(25th–75th percentiles) | 3.0 (2.5–3.6) | 2.96 (2.15–3.82) | 0.62 |
| FVC % | Median/(25th–75th percentiles) | 94 (84–105) | 81 (73.5–94.5) | 0.001 |
| FEV1/FVC | Median/(25th–75th percentiles) | 82 (77–86) | 81 (75–84) | 0.812 |
| DLCO (mmol/kPa/min) | Median/(25th–75th percentiles) | 6.3 (5.4–9.8) | 5.1 (3.7–6.04) | 0.020 |
| DLCO % | Median/(25th–75th percentiles) | 75 (66–88) | 70 (62–83) | 0.046 |
| Variable | OR [95% CI] | p |
|---|---|---|
| Treatment | 1.398 [0.468–4.178] | 0.549 |
| Initial FVC % | 0.967 [0.937–0.998] | 0.036 |
| Initial Neutrophil count | 1.0 [1.0–1.01] | 0.751 |
| LDH/Albumin (LAR) | 0.972 [0.902–1.048] | 0.462 |
| Cough | 1.885 [0.754–4.713] | 0.175 |
| Dyspnea | 3.078 [1.117–8.484] | 0.03 |
| Fatigue | 1.433 [0.534–3.84] | 0.475 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Onyilmaz, T.; Argun Baris, S.; Kaya, H.; Pehlivan, A.Z.; Albayrak, H.; Aktoprak, S.N.; Boyaci, H.; Basyigit, I. Predictive Impact of Hematological and Biochemical Parameters on the Clinical Course of Sarcoidosis. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2501. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15192501
Onyilmaz T, Argun Baris S, Kaya H, Pehlivan AZ, Albayrak H, Aktoprak SN, Boyaci H, Basyigit I. Predictive Impact of Hematological and Biochemical Parameters on the Clinical Course of Sarcoidosis. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(19):2501. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15192501
Chicago/Turabian StyleOnyilmaz, Tugba, Serap Argun Baris, Huseyin Kaya, Ayse Zeynep Pehlivan, Hanife Albayrak, Sena Nur Aktoprak, Hasim Boyaci, and Ilknur Basyigit. 2025. "Predictive Impact of Hematological and Biochemical Parameters on the Clinical Course of Sarcoidosis" Diagnostics 15, no. 19: 2501. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15192501
APA StyleOnyilmaz, T., Argun Baris, S., Kaya, H., Pehlivan, A. Z., Albayrak, H., Aktoprak, S. N., Boyaci, H., & Basyigit, I. (2025). Predictive Impact of Hematological and Biochemical Parameters on the Clinical Course of Sarcoidosis. Diagnostics, 15(19), 2501. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15192501






