Automatic Diagnosis, Classification, and Segmentation of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm and Dissection from Computed Tomography Images
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. The Main Contributions
- A novel deep CNN model is proposed for the classification and segmentation of the CT images. The proposed model might allow for the early diagnosis and treatment of AAAs and AADs.
- A unique CNN model is proposed in terms of the sequence of convolutional, pooling, activation, dropout, fully connected (FC), and classifier layers. It is best known in the study, and this model is highly successful in diagnosing both AAA and AAD.
- A real dataset obtained from the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Turkey was used. The dataset consists of non-disease, AAA, and AAD abdominal CT images in Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) format.
- The results of the experiments note that the proposed method is better than ResDenseUNet, INet, and C-Net.
1.2. Paper Organization
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The CNN Architecture of the Proposed Scheme
2.2. Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA) Detection
| Algorithm 1: Hough circle transform method for aorta diameter calculation |
| 1: Start the accumulator (H[a,b,r]) to all zeros |
| 2: Detect the edge image using Canny edge detector |
| 3: for each edge pixel(x,y) in the abdomen image then |
| 4: for = 0 to 360 then |
| 5: a = x-r*cosθ |
| 6: b = y-r*sinθ |
| 7: H[a,b,r] = H[a,b,r] + 1 |
| 8: Determine the [a,b,r] values, where H[a,b,r] is above an appropriate threshold value |
| 9: end for |
| 10: end for |
2.3. Abdominal Aortic Dissection (AAD) Detection
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Dataset
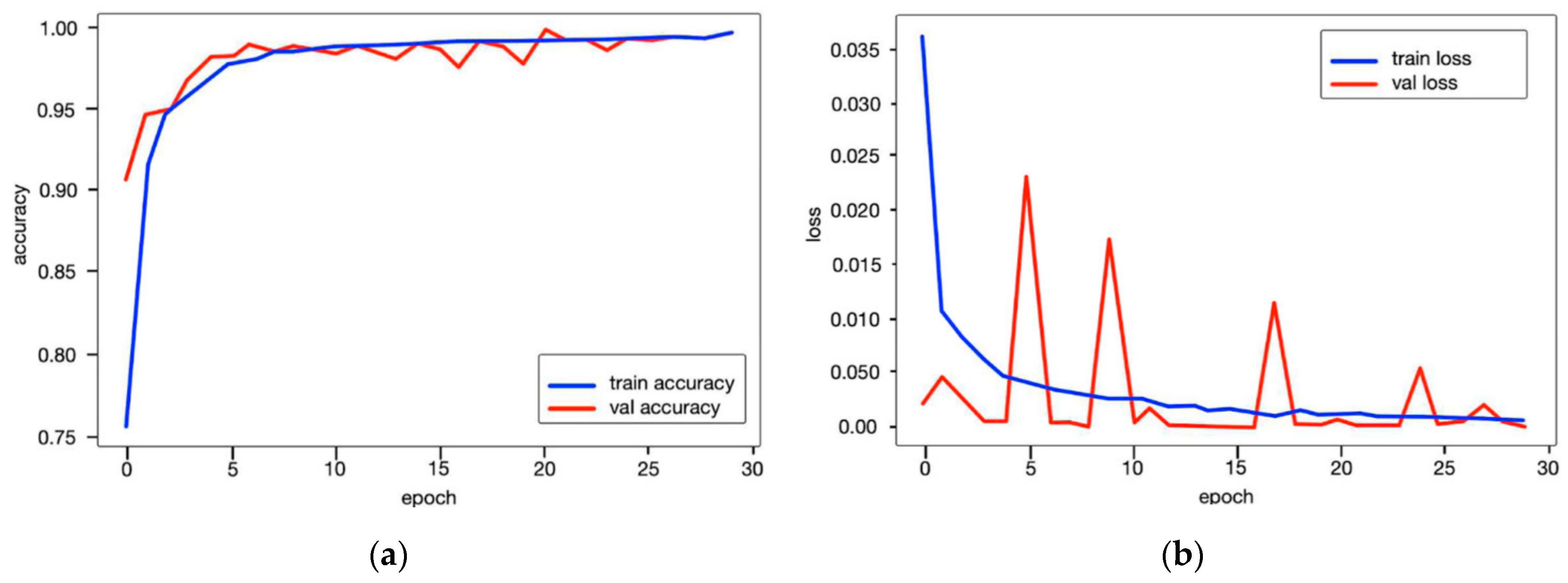
3.2. Experimental Setup
3.3. The Performance Results of the AAA and AAD Diagnosis and Classification
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Selvaraj, J.; Prabha, T.; Kumar, T.D.A.; Palaniappan, S. Artificial Intelligence in Biomedical Image Processing. In Machine Learning and Systems Biology in Genomics and Health; Singh, S., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Devi, K.G.; Balasubramanian, K. Machine Learning and Deep Learning Techniques for Medical Science; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022; 412p. [Google Scholar]
- Payal, M.; Kumar, K.S.; Kumar, T.A. Recent advances of Machine Learning Techniques in Biomedicine. Int. J. Multidiscip. Res. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2022, 5, 772–779. [Google Scholar]
- Das, A.; Mohapatra, S.K.; Mohanty, M.N. Design of deep ensemble classifier with fuzzy decision method for biomedical image classification. Appl. Soft Comput. 2022, 115, 108178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Velden, B.H.M.; Kuijf, H.J.; Gilhuijs, K.G.A.; Viergever, M.A. Explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) in deep learning-based medical image analysis. Med. Image Anal. 2022, 79, 102470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimzadeh, M.; Attar, A. A modified deep convolutional neural network for detecting COVID-19 and pneumonia from chest X-ray images based on the concatenation of Xception and ResNet50V2. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2020, 19, 100360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.-C.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Rethinking Atrous Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.05587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumara, K.S.A.; Prasad, A.Y.; Metan, J. A hybrid deep CNN-Cov-19-Res-Net Transfer learning architype for an enhanced Brain tumor Detection and Classification scheme in medical image processing. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2022, 76, 103631. [Google Scholar]
- Nisha, J.S.; Varun PGopi Palanisamy, P. Automated colorectal polyp detection based on image enhancement and dual-path CNN architecture. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2022, 73, 103465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Ren, H.; Zhou, W.; Liu, Z. ISANET: Non-small cell lung cancer classification and detection based on CNN and attention mechanism. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2022, 77, 103773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Shang, L.; Tang, J.; Bao, Y.; Fu, J.; Yin, J. Classifying breast cancer tissue by Raman spectroscopy with one-dimensional convolutional neural network. Spectrochim. Acta 2021, 256, 119732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalçın, S.; Herdem, M.S. A CNN-ABC model for estimation and optimization of heat generation rate and voltage distributions of lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2022, 199, 123486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Ruan, S.; Canu, S. A review: Deep learning for medical image segmentation using multi-modality fusion. Array 2019, 3, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, R.F.; Alfar, N.M.; Abdel-Khalek, S.; Abdelhaq, M.; Saeed, R.A.; Alsaqour, R. Optimal deep learning based fusion model for biomedical image classification. Expert Syst. 2021, 39, e12764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punn, N.S.; Agarwal, S. Modality specific U-Net variants for biomedical image segmentation: A survey. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2022, 55, 5845–5889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Faraji, M.; Basu, A. Robust segmentation of arterial walls in intravascular ultrasound images using dual path u-net. Ultrasonics 2019, 96, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xie, S.; Lin, L.; Iwamoto, Y.; Han, X.H.; Chen, Y.W.; Tong, R. Mixed transformer u-net for medical image segmentation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.04734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Ma, M.; Li, H.; Song, S. Mc-net: Multi-scale context-attention network for medical CT image segmentation. Appl. Intell. 2022, 52, 1508–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. Segnet: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y. Road extraction by deep residual UNet. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 749–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, W.; Zhu, X. INet: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 16591–16603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khened, M.; Kollerathu, V.A.; Krishnamurthi, G. Fully convolutional multi-scale residual DenseNets for cardiac segmentation and automated cardiac diagnosis using ensemble of classifiers. Med. Image Anal. 2019, 51, 21–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzekar, H.; Yu, Z. C-Net: A reliable convolutional neural network for biomedical image classification. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 187, 116003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artzner, C.; Bongers, M.N.; Kärgel, R.; Faby, S.; Hefferman, G.; Herrmann, J.; Nopper, S.L.; Perl, R.M.; Walter, S.S. Assessing the Accuracy of an Artificial Intelligence-Based Segmentation Algorithm for the Thoracic Aorta in Computed Tomography Applications. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Secchi, F.; Interlenghi, M.; Alì, M.; Schiavon, E.; Monti, C.B.; Capra, D.; Salvatore, C.; Castiglioni, I.; Papa, S.; Sardanelli, F.; et al. A Combined Deep Learning System for Automatic Detection of “Bovine” Aortic Arch on Computed Tomography Scans. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, F.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, K.; Zhou, M.; Zhao, H.; Zhu, S.; Chen, J.; Li, P.; et al. Artificial Intelligence Uncovers Natural MMP Inhibitor Crocin as a Potential Treatment of Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm and Dissection. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 871486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Shi, D.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang Xueli Tang, S.; Shang, X.; Li, C.; He, M. Retinal vascular features as new biomarkers for aortic aneurysms and aortic dissections. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2022, 63, 2666. [Google Scholar]
- Fanga, Z.M.; Feng, X.; Chen, Y.; Luo, H.; Jiang, D.S.; Yi, X. Targeting autophagy in aortic aneurysm and dissection. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 153, 113547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golledge, J. Abdominal aortic aneurysm: Update on pathogenesis and medical treatments. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2019, 16, 225–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffort, J.; Adam, C.; Carrier, M.; Ballaith, A.; Coscas, R.; Jean-Baptiste, E.; Hassen-Khodja, R.; Chakfé, N.; Lareyre, F. Artificial intelligence in abdominal aortic aneurysm. J. Vasc. Surg. 2020, 72, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criado, F.J. Aortic dissection: A 250-year perspective. Tex. Heart Inst. J. 2011, 38, 694. [Google Scholar]
- White, A.; Broder, J.; Mando-Vandrick, J.; Wendell, J.; Crowe, J. Acute aortic emergencies—Part 2 aortic dissections. Adv. Emerg. Nurs. J. 2013, 35, 28–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borioni, R.; Garofalo, M.; De Paulis, R.; Nardi, P.; Scaffa, R.; Chiariello, L. Abdominal Aortic dissections: Anatomic and clinical features and therapeutic options. Tex. Heart Inst. J. 2005, 32, 70–73. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.T.; Tsai, Y.S.; Liou, C.F.; Lee, T.H.; Kuo, P.T.P.; Huang, H.S.; Wang, C.K. Automated Stanford classification of aortic dissection using a 2-step hierarchical neural network at computed tomography angiography. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 2277–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yan, S.; Xie, M.; Huang, J. Application of cascaded GAN based on CT scan in the diagnosis of aortic dissection. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2022, 226, 107130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Wei, J.; Liao, F.; Xiao, Q.; Zhang, J.; Yin, W.; Lu, B. A Three-Dimensional Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Automatic Segmentation and Diameter Measurement of Type B Aortic Dissection. Korean J. Radiol. 2021, 22, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, R.J.; Kim, S.; Lohr, J.; Towey, S.; Velichkovich, Z.; Kabachenko, T.; Driscoll, I.; Baker, B. Classification of Aortic Dissection and Rupture on Post-contrast CT Images Using a Convolutional Neural Network. J. Digit. Imaging 2019, 32, 939–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonechi, S.; Andreini, P.; Mecocci, A.; Giannelli, N.; Scarselli, F.; Neri, E.; Bianchini, M.; Dimitri, G.M. Segmentation of Aorta 3D CT Images Based on 2D Convolutional Neural Networks. Electronics 2021, 10, 2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, S.; Mohammadi, M.; Dehlaghi, V.; Ahmadi, A. Automatic Segmentation, Detection, and Diagnosis of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA) Using Convolutional Neural Networks and Hough Circles Algorithm. Cardiovasc. Eng. Technol. 2019, 10, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camara, J.R.; Tomihama, R.T.; Pop, A.; Shedd, M.P.; Dobrowski, B.S.; Knox, C.J.; Abou-Zamzam, A.M.; Kiang, S.C. Development of a convolutional neural network to detect abdominal aortic aneurysms. J. Vasc. Surg. Cases Innov. Tech. 2022, 8, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, T.; Yang, G.; Zhao, X.; Shu, H.; Luo, L.; Chen, D.; Xiong, J.; Yang, J.; Li, S.; Coatrieux, J.L.; et al. Dissected aorta segmentation using convolutional neural networks. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 211, 106417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comelli, A.; Dahiya, N.; Stefano, A.; Benfante, V.; Gentile, G.; Agnese, V.; Raffa, G.M.; Pilato, M.; Yezzi, A.; Petrucc, G.; et al. Deep learning approach for the segmentation of aneurysmal ascending aorta. Biomed. Eng. Lett. 2021, 11, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, J.; Cao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Xia, W. Differentiation of Cerebral Dissecting Aneurysm from Hemorrhagic Saccular Aneurysm by Machine-Learning Based on Vessel Wall MRI: A Multicenter Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chhabra, M.; Ravulakollu, K.K.; Kumar, M.; Sharma, A.; Nayyar, A. Improving automated latent fingerprint detection and segmentation using deep convolutional neural network. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 35, 6471–6497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhu, G.; Govardhan, A.; Ravi, V.; Kautish, S.; Srinivas, B.S.; Chaudhary, T.; Kumar, M. DSCN-net: A deep Siamese capsule neural network model for automatic diagnosis of malaria parasites detection. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 34105–34127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhu, G.; Kautish, S.; Gupta, Y.; Nagachandrika, G.; Biju, S.M.; Kumar, M. XCovNet: An optimized xception convolutional neural network for classification of COVID-19 from point-of-care lung ultrasound images. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 33653–33674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wei, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, D.; Tian, X.; Jiang, W.; Li, Z. Hemodynamic Analysis of Stanford Type B Aortic Dissection Based on Computational Fluid Dynamics. J. Med. Biomech. 2018, 33, 490–495. [Google Scholar]
- Polanczyk, A.; Piechota-Polanczyk, A.; Huk, I.; Neumayer, C.; Balcer, J.; Strzelecki, M. Computational Fluid Dynamic Technique for Assessment of How Changing Character of Blood Flow and Different Value of Hct Influence Blood Hemodynamic in Dissected Aorta. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddqi, Z.F. Computational Fluid Dynamics: Modeling and Analysis of Blood Flow in Arteries. In Motion Analysis of Biological Systems; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 89–121. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, S.; Tu, Z. Holistically-nested edge detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Washington, DC, USA, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1395–1403. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.Y.; Xie, S.; Gallagher, P.; Zhang, Z.; Tu, Z. Deeply-supervised nets. In Proceedings of the Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, San Diego, CA, USA, 9–12 May 2015; pp. 562–570. [Google Scholar]
- TR_Abdomen Rad_Emergency Data Set. Available online: https://acikveri.saglik.gov.tr/Home/DataSetDetail/2 (accessed on 10 January 2025).
- Koç, U.; Sezer, E.A.; Özkaya, Y.A.; Yarbay, Y.; Beşler, M.S.; Taydaş, O.; Yalçın, A.; Evrimler, Ş.; Kızıloğlu, H.A.; Kesimal, U.; et al. Elevating healthcare through artificial intelligence: Analyzing the abdominal emergencies data set (TR_ABDOMEN_RAD_EMERGENCY) at TEKNOFEST-2022. Eur. Radiol. 2024, 34, 3588–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chollet, F. Keras. 2015. Available online: https://github.com/fchollet/keras (accessed on 5 July 2025).
- Abadi, M.; Barham, P.; Chen, J.; Chen, Z.; Davis, A.; Dean, J.; Devin, M.; Ghemawat, S.; Irving, G.; Isard, M.; et al. Tensorflow: A system for large-scale machine learning. In Proceedings of the 12th USENIX Symposium on Operating Systems Design and Implementation (OSDI 16), Berkeley, CA, USA, 2–4 November 2016; pp. 265–283. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Zhang, X.; Mei, Y.; Liao, F.; Xu, H.; Li, Z.; Xiao, Q.; Guo, W.; Zhang, H.; Yan, T.; et al. Multi-stage learning for segmentation of aortic dissections using a prior aortic anatomy simplification. Med. Image Anal. 2021, 69, 101931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackstein, U.; Krüger, T.; Mair, A.; Degünther, C.; Krickl, S.; Schlensak, C.; Bernhard, S. Early diagnosis of aortic aneurysms based on the classification of transfer function parameters estimated from two photoplethysmographic signals. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2021, 25, 100652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

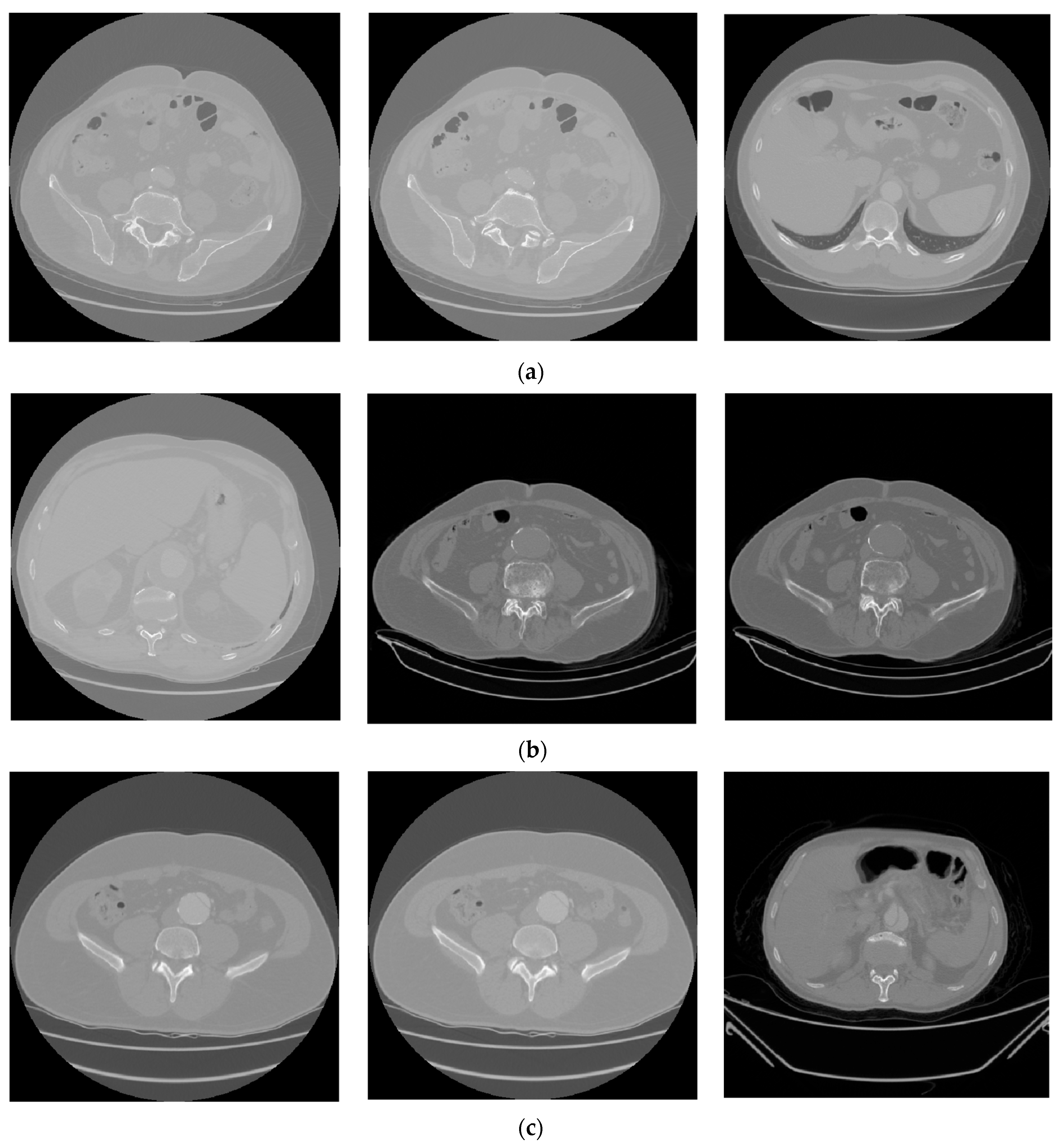


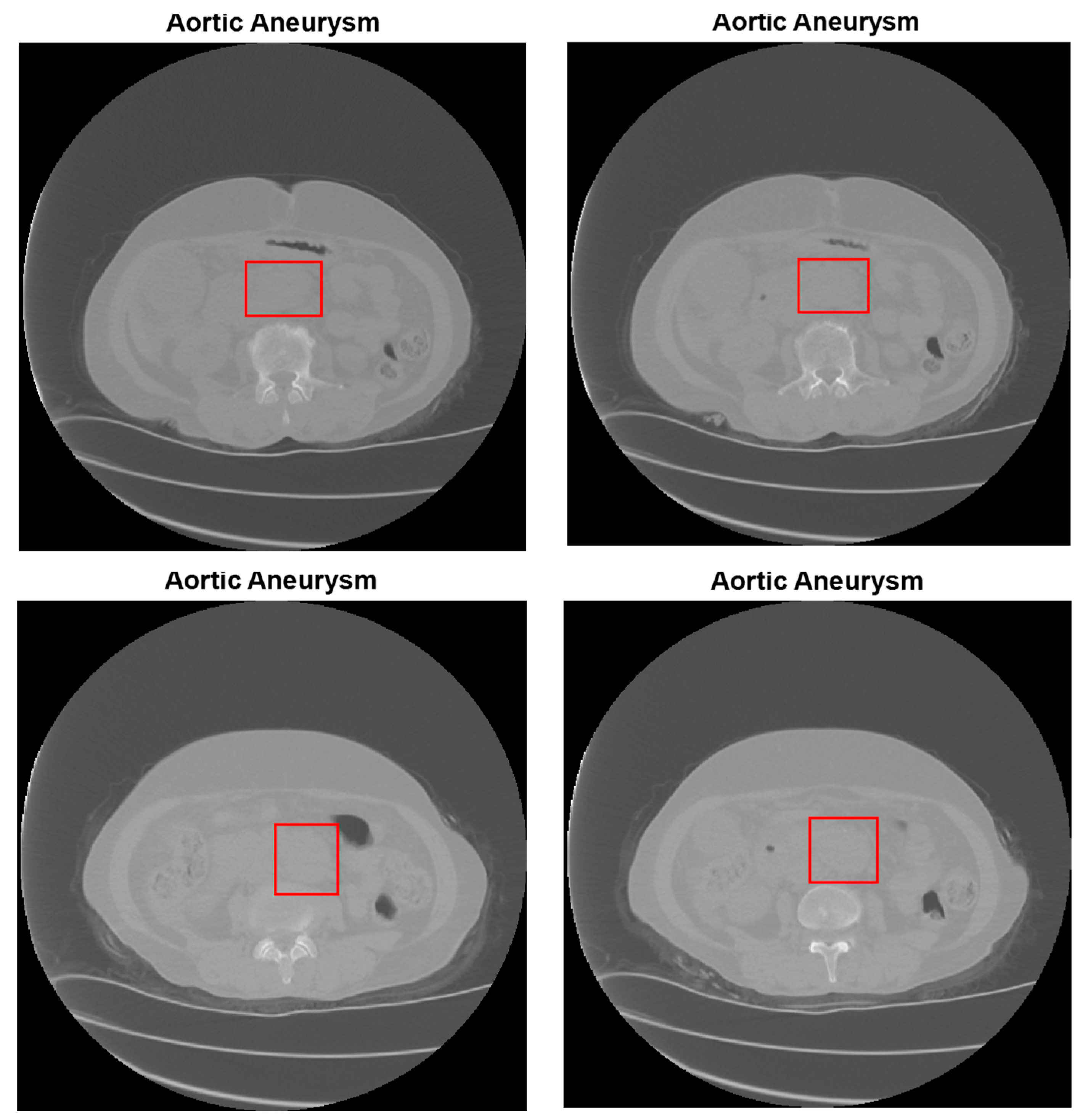
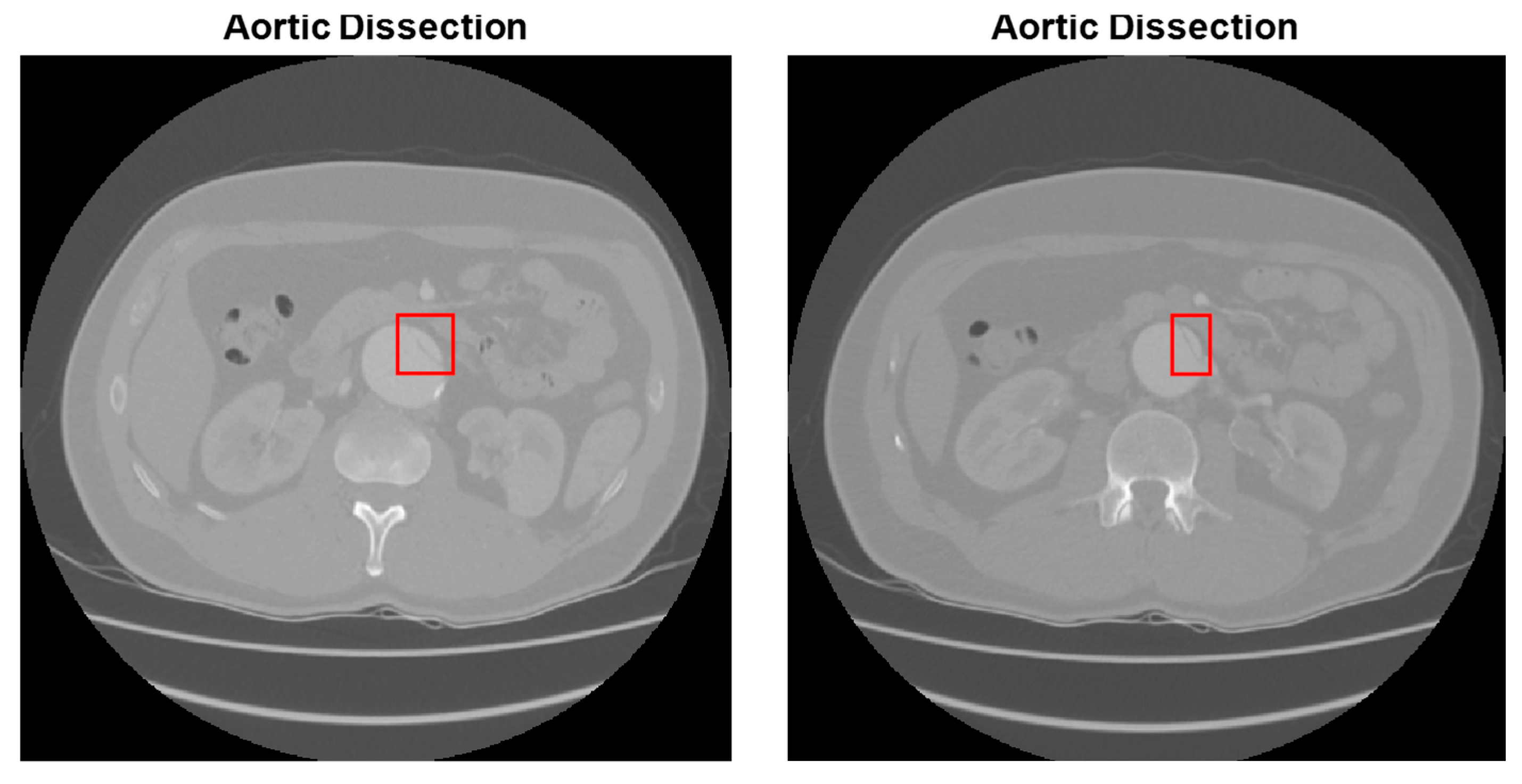
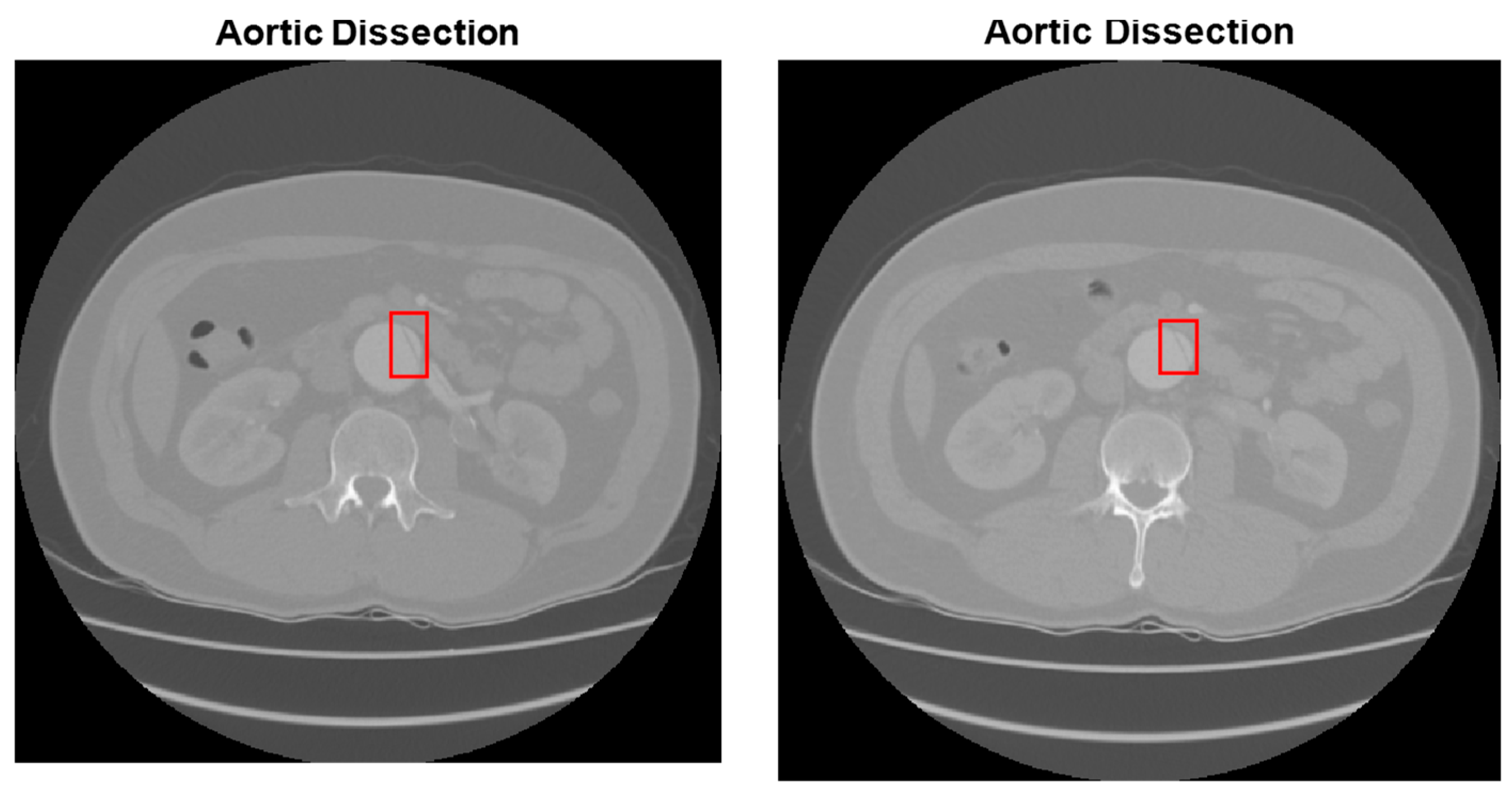
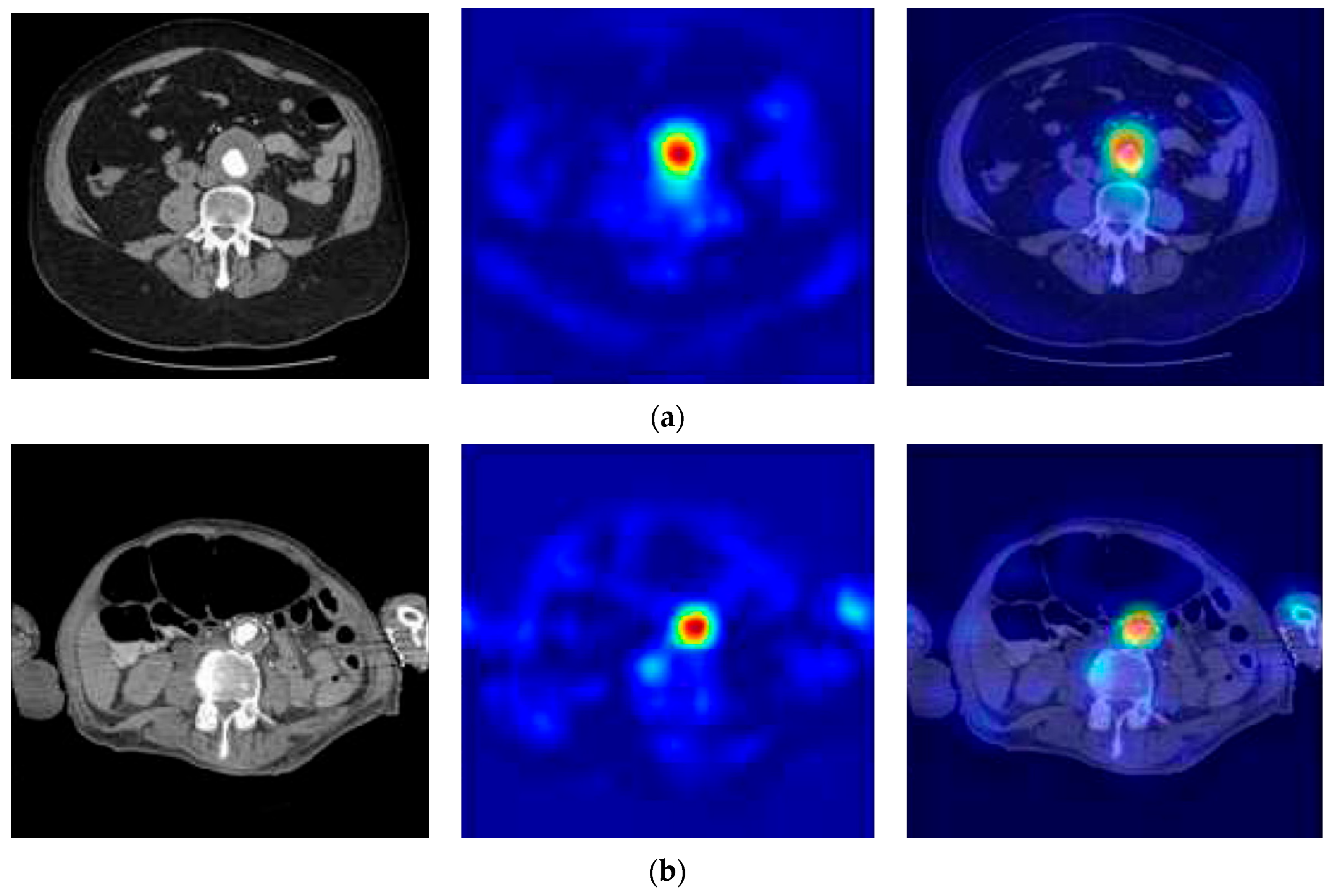


| Type of Phase | No Disease | Abdominal Aortic Disease | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aneurysm | Dissection | ||
| Training | 3428 | 3603 | 3603 |
| Test | 430 | 450 | 450 |
| Validation | 428 | 451 | 451 |
| Parameters | Definition |
|---|---|
| Hardware | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090 |
| Software | Python 3.8, TensorFlow 2.5, CUDA 11.4 |
| Data preprocessing | Image normalization to a range of 0–1, and random cropping and rotation for data augmentation |
| Evaluation metrics | Accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, F1-score, and dice coefficient |
| Convolution layer kernel size | (3 × 3) kernel size is used |
| Output nodes | 3 classes classification (no disease, aneurysm, or dissection) |
| Learning rate | 0.001 |
| Optimization method | Adam |
| Batch size | 32 |
| Number of epochs | 50 |
| Dropout | 0.5 |
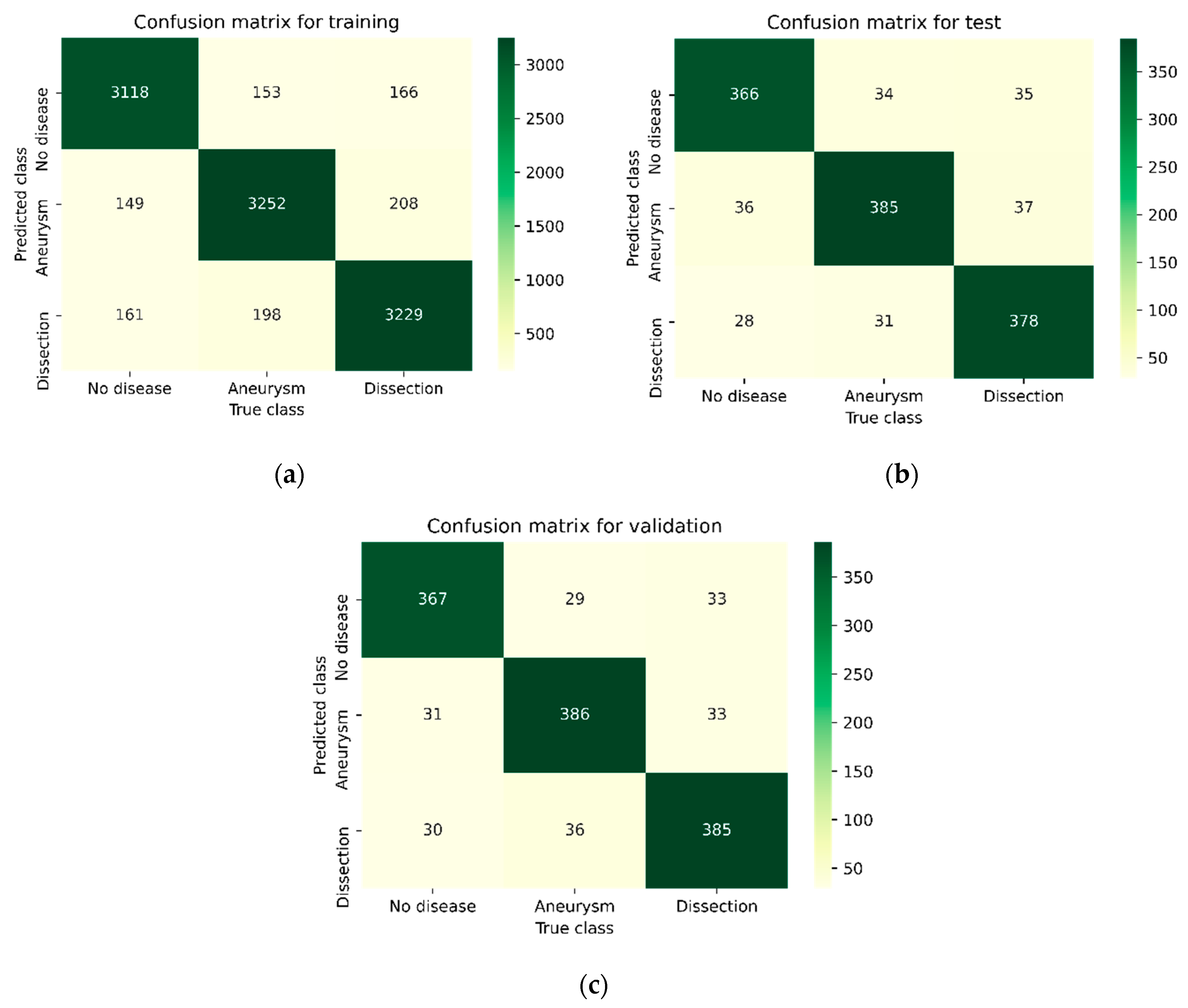
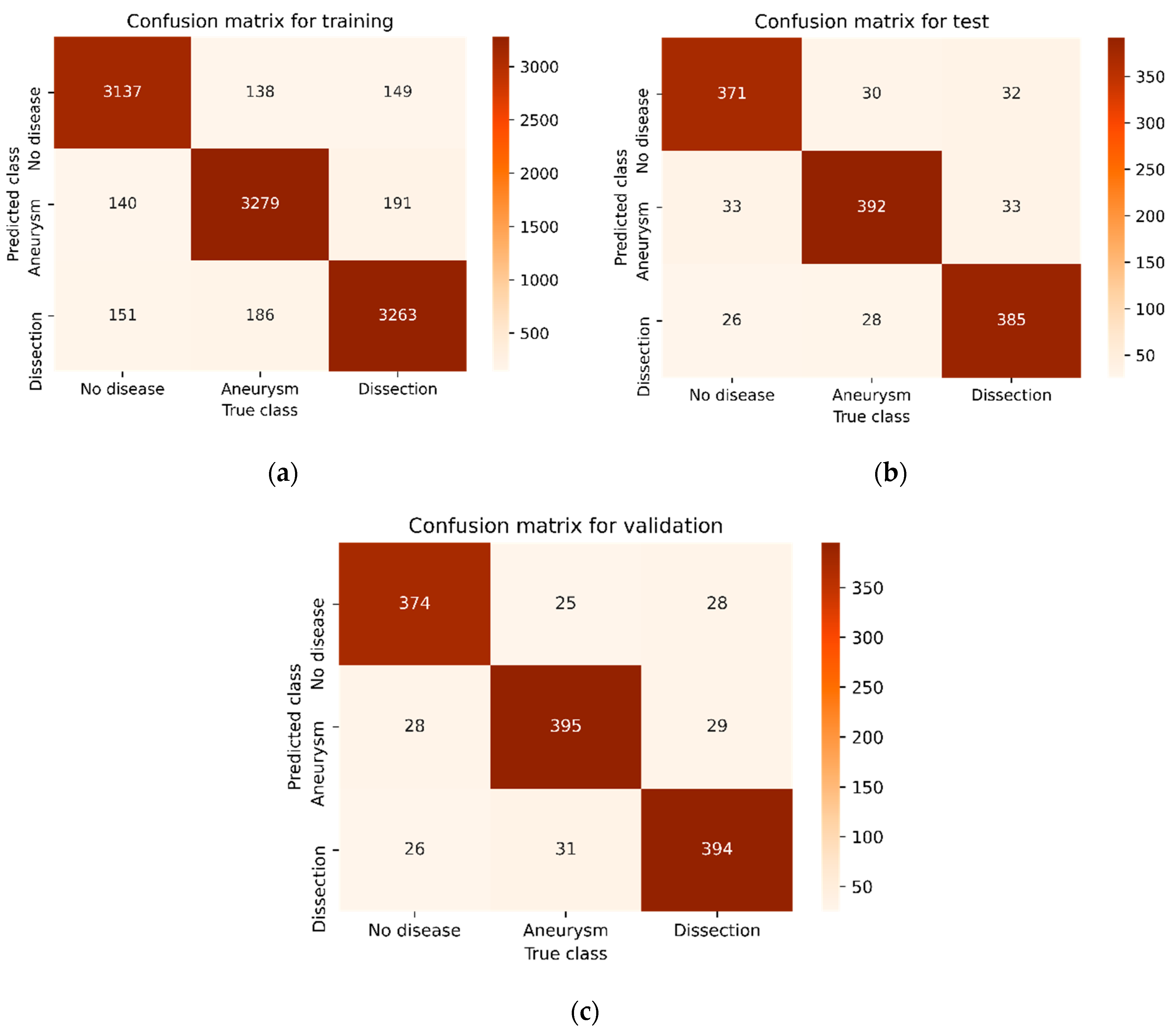
| Methods | Phase | Disease Type | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ResDenseUNet | Training | No | 0.8997 | 0.9022 | 0.9009 | 0.8949 |
| Aneurysm | 0.8931 | 0.8956 | 0.8944 | |||
| Dissection | 0.8922 | 0.8873 | 0.8897 | |||
| Test | No | 0.7904 | 0.8069 | 0.7986 | 0.8000 | |
| Aneurysm | 0.7951 | 0.8022 | 0.7986 | |||
| Dissection | 0.8146 | 0.7911 | 0.8027 | |||
| Validation | No | 0.8098 | 0.8060 | 0.8079 | 0.8097 | |
| Aneurysm | 0.8151 | 0.8115 | 0.8133 | |||
| Dissection | 0.8043 | 0.8115 | 0.8079 | |||
| INet | Training | No | 0.9071 | 0.9095 | 0.9083 | 0.9026 |
| Aneurysm | 0.9010 | 0.9025 | 0.9018 | |||
| Dissection | 0.8999 | 0.8961 | 0.8980 | |||
| Test | No | 0.8413 | 0.8511 | 0.8462 | 0.8488 | |
| Aneurysm | 0.8406 | 0.8555 | 0.8480 | |||
| Dissection | 0.8649 | 0.8400 | 0.8523 | |||
| Validation | No | 0.8554 | 0.8574 | 0.8564 | 0.8556 | |
| Aneurysm | 0.8577 | 0.8558 | 0.8568 | |||
| Dissection | 0.8536 | 0.8536 | 0.8536 | |||
| C-Net | Training | No | 0.9161 | 0.9151 | 0.9156 | 0.9101 |
| Aneurysm | 0.9083 | 0.9100 | 0.9091 | |||
| Dissection | 0.9063 | 0.9056 | 0.9060 | |||
| Test | No | 0.8568 | 0.8627 | 0.8597 | 0.8631 | |
| Aneurysm | 0.8558 | 0.8711 | 0.8634 | |||
| Dissection | 0.8769 | 0.8555 | 0.8661 | |||
| Validation | No | 0.8758 | 0.8738 | 0.8748 | 0.8744 | |
| Aneurysm | 0.8738 | 0.8758 | 0.8748 | |||
| Dissection | 0.8736 | 0.8736 | 0.8736 | |||
| Proposed CNN | Training | No | 0.9234 | 0.9189 | 0.9211 | 0.9163 |
| Aneurysm | 0.9137 | 0.9172 | 0.9155 | |||
| Dissection | 0.9120 | 0.9128 | 0.9124 | |||
| Test | No | 0.8778 | 0.8860 | 0.8819 | 0.8872 | |
| Aneurysm | 0.8793 | 0.8717 | 0.8755 | |||
| Dissection | 0.9004 | 0.8844 | 0.8923 | |||
| Validation | No | 0.8839 | 0.8901 | 0.8870 | 0.8857 | |
| Aneurysm | 0.8847 | 0.8847 | 0.8847 | |||
| Dissection | 0.8883 | 0.8824 | 0.8854 |
| Authors | Publication Year | Method | Intersection-over-Union (IoU) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Khened et al. [23] | 2019 | ResDenseUNet | 0.7924 |
| Weng and Zhu [22] | 2021 | INet | 0.8163 |
| Barzekar and Yu [24] | 2022 | C-Net | 0.8248 |
| Chen et al. [57] | 2021 | Cascaded neural networks | 0.8251 |
| Hackstein et al. [58] | 2021 | Naive Bayes and K-Nearest-Neighbor | 0.8328 |
| Proposed | Proposed CNN method | 0.8376 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baltaci, H.; Yalcin, S.; Yildirim, M.; Bingol, H. Automatic Diagnosis, Classification, and Segmentation of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm and Dissection from Computed Tomography Images. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2476. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15192476
Baltaci H, Yalcin S, Yildirim M, Bingol H. Automatic Diagnosis, Classification, and Segmentation of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm and Dissection from Computed Tomography Images. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(19):2476. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15192476
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaltaci, Hakan, Sercan Yalcin, Muhammed Yildirim, and Harun Bingol. 2025. "Automatic Diagnosis, Classification, and Segmentation of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm and Dissection from Computed Tomography Images" Diagnostics 15, no. 19: 2476. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15192476
APA StyleBaltaci, H., Yalcin, S., Yildirim, M., & Bingol, H. (2025). Automatic Diagnosis, Classification, and Segmentation of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm and Dissection from Computed Tomography Images. Diagnostics, 15(19), 2476. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15192476






