Dysregulation of miRNAs in Sicilian Patients with Huntington’s Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. RNA Extraction
2.3. RNA Sequencing and Data Analysis
3. Results
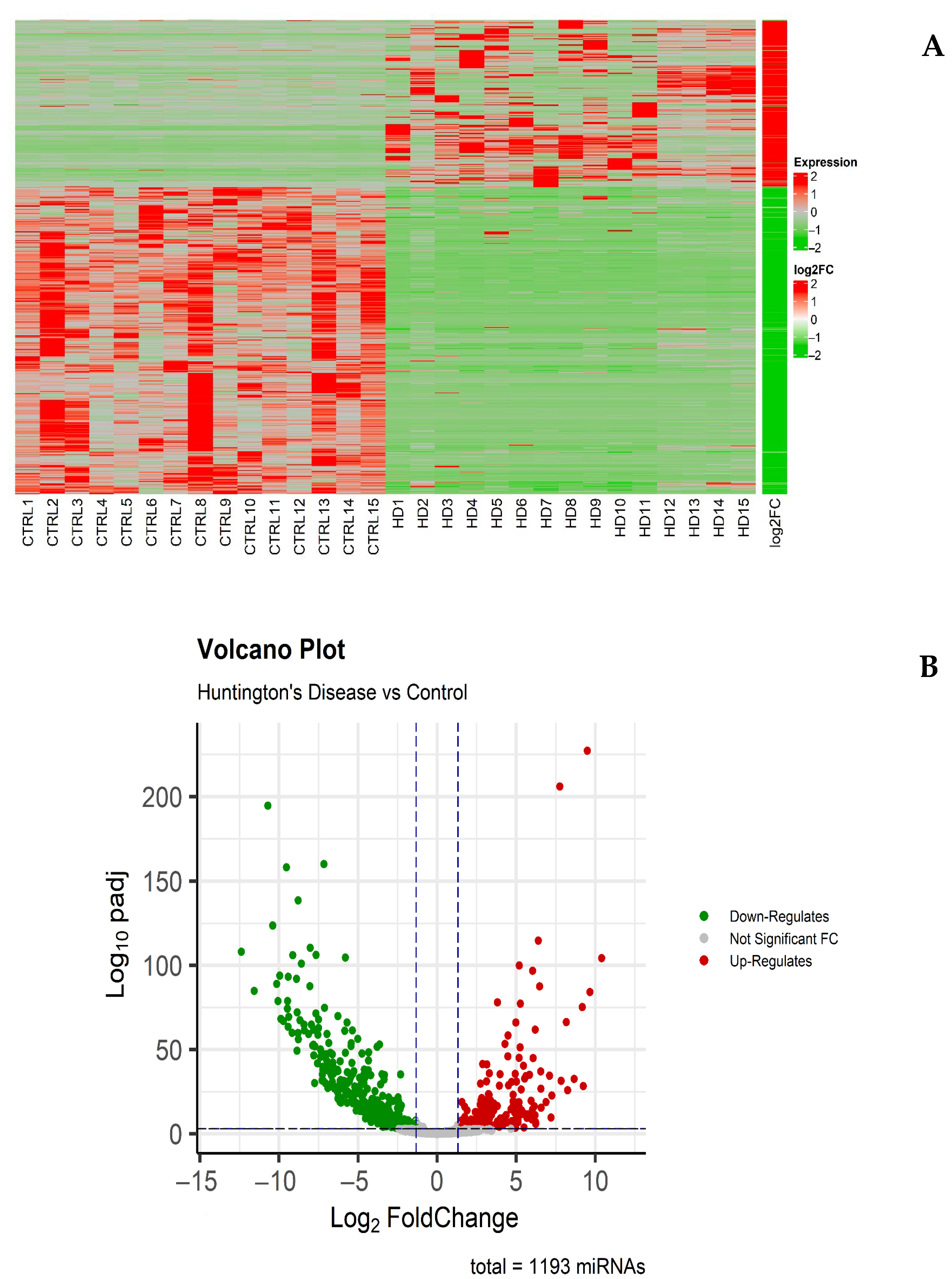
3.1. Analysis of Differentially Expressed miRNAs
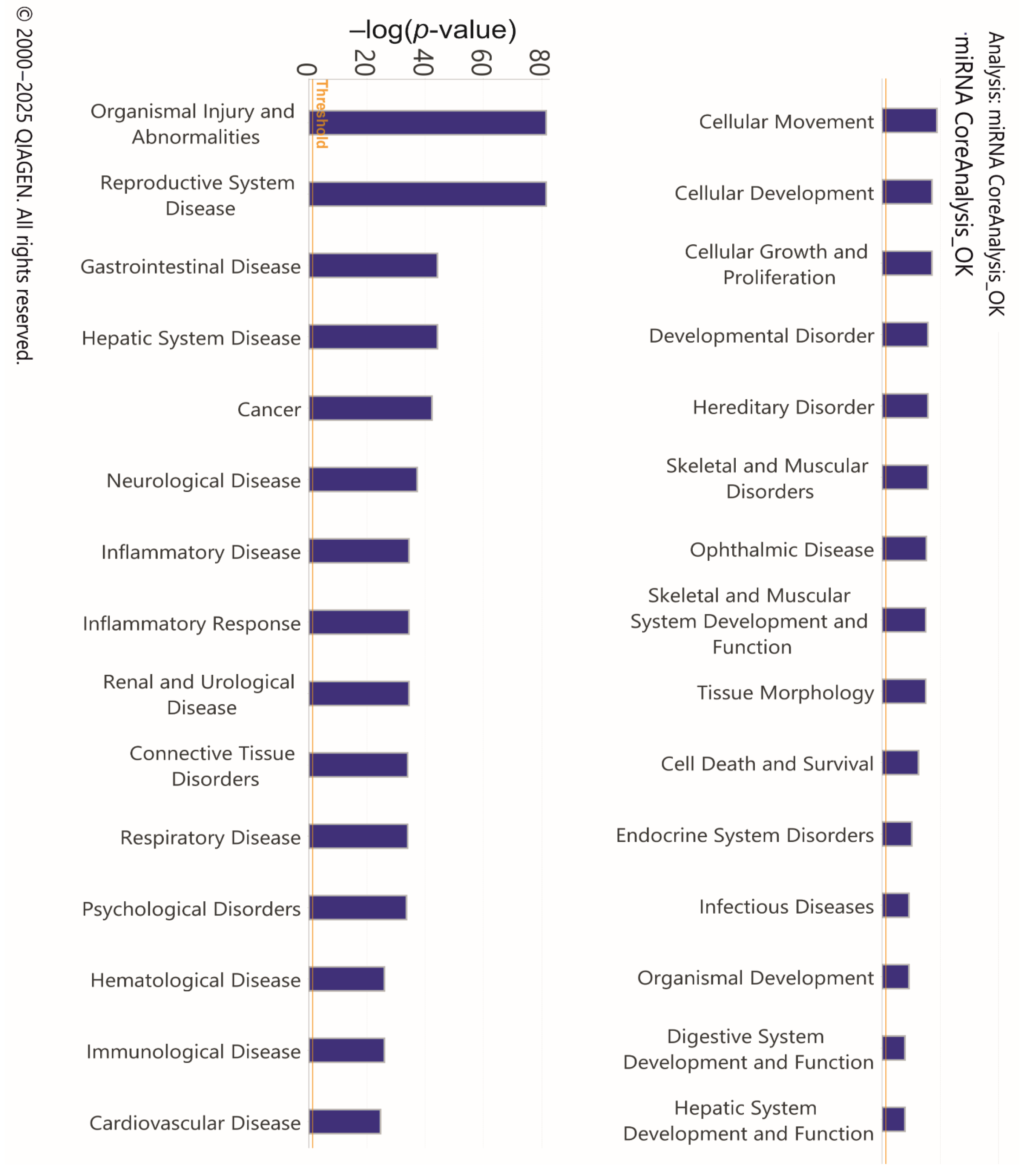
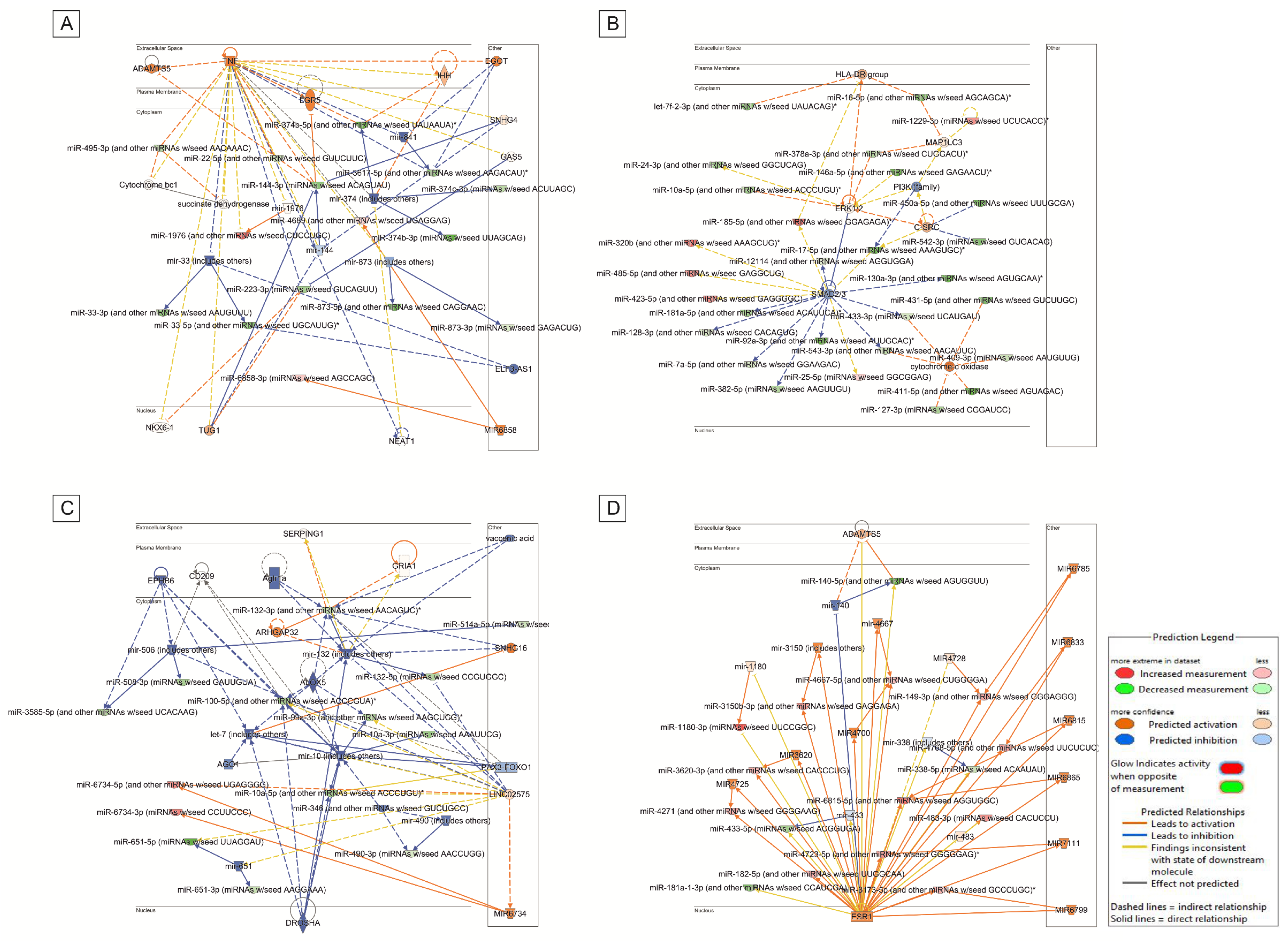
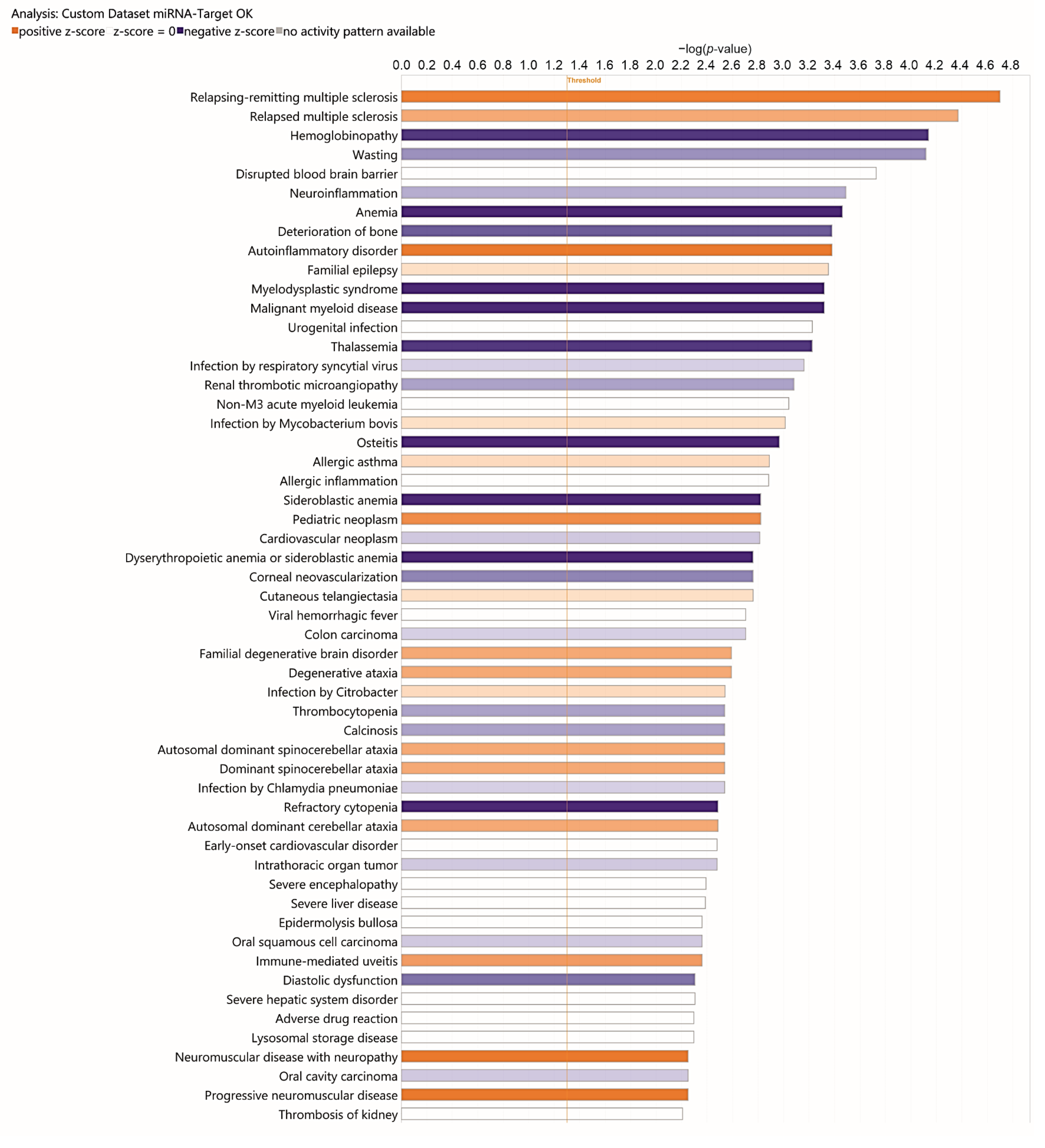
3.2. Analysis of Target Genes of Differentially Expressed miRNAs
4. Discussion
4.1. Main Findings
4.2. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Bates, G.P.; Dorsey, R.; Gusella, J.F.; Hayden, M.R.; Kay, C.; Leavitt, B.R.; Nance, M.; Ross, C.A.; Scahill, R.I.; Wetzel, R.; et al. Huntington Disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2015, 1, 15005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, R.H. Huntington’s Disease Genetics. NeuroRx 2004, 1, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finkbeiner, S. Huntington’s Disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a007476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, G. Huntingtin Aggregation and Toxicity in Huntington’s Disease. Lancet 2003, 361, 1642–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, C.-W.; Huang, P.-Y.; Chan, S.C.; Cheng, P.-H.; Yang, S.-H. The Regulatory Roles of microRNAs toward Pathogenesis and Treatments in Huntington’s Disease. J. Biomed. Sci. 2021, 28, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-T.; Chu, K.; Im, W.-S.; Yoon, H.-J.; Im, J.-Y.; Park, J.-E.; Park, K.-H.; Jung, K.-H.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, M.; et al. Altered microRNA Regulation in Huntington’s Disease Models. Exp. Neurol. 2011, 227, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.; Zuccato, C.; Belyaev, N.D.; Guest, D.J.; Cattaneo, E.; Buckley, N.J. A microRNA-Based Gene Dysregulation Pathway in Huntington’s Disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2008, 29, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Cong, S. MicroRNAs in Huntington’s Disease: Diagnostic Biomarkers or Therapeutic Agents? Front. Cell Neurosci. 2021, 15, 705348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salemi, M.; Lanza, G.; Mogavero, M.P.; Cosentino, F.I.I.; Borgione, E.; Iorio, R.; Ventola, G.M.; Marchese, G.; Salluzzo, M.G.; Ravo, M.; et al. A Transcriptome Analysis of mRNAs and Long Non-Coding RNAs in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salemi, M.; Marchese, G.; Lanza, G.; Cosentino, F.I.I.; Salluzzo, M.G.; Schillaci, F.A.; Ventola, G.M.; Cordella, A.; Ravo, M.; Ferri, R. Role and Dysregulation of miRNA in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Xu, Y.; Quan, Z.; Chen, Z.; Sun, Z.; Qing, H. Dysregulated microRNAs in Neural System: Implication in Pathogenesis and Biomarker Development in Parkinson’s Disease. Neuroscience 2017, 365, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hébert, S.S.; Papadopoulou, A.S.; Smith, P.; Galas, M.-C.; Planel, E.; Silahtaroglu, A.N.; Sergeant, N.; Buée, L.; De Strooper, B. Genetic Ablation of Dicer in Adult Forebrain Neurons Results in Abnormal Tau Hyperphosphorylation and Neurodegeneration. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2010, 19, 3959–3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, J.; Wu, H.; Lin, Q.; Wei, W.; Lu, X.-H.; Cantle, J.P.; Ao, Y.; Olsen, R.W.; Yang, X.W.; Mody, I.; et al. Deletion of Astroglial Dicer Causes Non-Cell-Autonomous Neuronal Dysfunction and Degeneration. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 8306–8319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuccato, C.; Tartari, M.; Crotti, A.; Goffredo, D.; Valenza, M.; Conti, L.; Cataudella, T.; Leavitt, B.R.; Hayden, M.R.; Timmusk, T.; et al. Huntingtin Interacts with REST/NRSF to Modulate the Transcription of NRSE-Controlled Neuronal Genes. Nat. Genet. 2003, 35, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ooi, L.; Wood, I.C. Chromatin Crosstalk in Development and Disease: Lessons from REST. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007, 8, 544–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez-Planelles, C.; Sánchez-Lozano, P.; Crespo, M.C.; Gil-Zamorano, J.; Ribacoba, R.; González, N.; Suárez, E.; Martínez-Descals, A.; Martínez-Camblor, P.; Álvarez, V.; et al. Circulating microRNAs in Huntington’s Disease: Emerging Mediators in Metabolic Impairment. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 108, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, E.R.; Latourelle, J.C.; Bockholt, J.H.; Bregu, J.; Smock, J.; Paulsen, J.S.; Myers, R.H. PREDICT-HD CSF ancillary study investigators MicroRNAs in CSF as Prodromal Biomarkers for Huntington Disease in the PREDICT-HD Study. Neurology 2018, 90, e264–e272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salemi, M.; Di Stefano, V.; Schillaci, F.A.; Marchese, G.; Salluzzo, M.G.; Cordella, A.; De Leo, I.; Perrotta, C.S.; Nibali, G.; Lanza, G.; et al. Transcriptome Study in Sicilian Patients with Huntington’s Disease. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickers, K.C.; Palmisano, B.T.; Shoucri, B.M.; Shamburek, R.D.; Remaley, A.T. MicroRNAs Are Transported in Plasma and Delivered to Recipient Cells by High-Density Lipoproteins. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-Y.; Hsu, Y.-H.; Lin, M.-H.; Yang, T.-H.; Chen, H.-M.; Chen, Y.-C.; Hsiao, H.-Y.; Chen, C.-C.; Chern, Y.; Chang, C. Neurovascular Abnormalities in Humans and Mice with Huntington’s Disease. Exp. Neurol. 2013, 250, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.J.; Salat, D.H.; Rosas, H.D. Complex Relationships between Cerebral Blood Flow and Brain Atrophy in Early Huntington’s Disease. Neuroimage 2012, 59, 1043–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielcarek, M.; Inuabasi, L.; Bondulich, M.K.; Muller, T.; Osborne, G.F.; Franklin, S.A.; Smith, D.L.; Neueder, A.; Rosinski, J.; Rattray, I.; et al. Dysfunction of the CNS-Heart Axis in Mouse Models of Huntington’s Disease. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihm, M.J.; Amann, D.M.; Schanbacher, B.L.; Altschuld, R.A.; Bauer, J.A.; Hoyt, K.R. Cardiac Dysfunction in the R6/2 Mouse Model of Huntington’s Disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2007, 25, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephen, C.; Hersch, S.; Rosas, H. Huntington’s Disease and the Heart: Electrocardiogram Abnormalities Suggest Cardiac Involvement (P5.294). Neurology 2015, 84, P5.294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cankar, K.; Melik, Z.; Kobal, J.; Starc, V. Evidence of Cardiac Electrical Remodeling in Patients with Huntington Disease. Brain Behav. 2018, 8, e01077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj, K.; Manickam, N.; Kumaran, E.; Thangadurai, K.; Elumalai, G.; Sekar, A.; Radhakrishnan, R.K.; Kandasamy, M. Deterioration of Neuroregenerative Plasticity in Association with Testicular Atrophy and Dysregulation of the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Gonadal (HPG) Axis in Huntington’s Disease: A Putative Role of the Huntingtin Gene in Steroidogenesis. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2020, 197, 105526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Pang, T.Y.; Mo, C.; Renoir, T.; Wright, D.J.; Hannan, A.J. The Influence of the HPG Axis on Stress Response and Depressive-like Behaviour in a Transgenic Mouse Model of Huntington’s Disease. Exp. Neurol. 2015, 263, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Raamsdonk, J.M.; Murphy, Z.; Selva, D.M.; Hamidizadeh, R.; Pearson, J.; Petersén, A.; Björkqvist, M.; Muir, C.; Mackenzie, I.R.; Hammond, G.L.; et al. Testicular Degeneration in Huntington Disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2007, 26, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papalexi, E.; Persson, A.; Björkqvist, M.; Petersén, A.; Woodman, B.; Bates, G.P.; Sundler, F.; Mulder, H.; Brundin, P.; Popovic, N. Reduction of GnRH and Infertility in the R6/2 Mouse Model of Huntington’s Disease. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2005, 22, 1541–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Burg, J.M.M.; Winqvist, A.; Aziz, N.A.; Maat-Schieman, M.L.C.; Roos, R.A.C.; Bates, G.P.; Brundin, P.; Björkqvist, M.; Wierup, N. Gastrointestinal Dysfunction Contributes to Weight Loss in Huntington’s Disease Mice. Neurobiol. Dis. 2011, 44, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, N.A.; van der Burg, J.M.M.; Landwehrmeyer, G.B.; Brundin, P.; Stijnen, T.; EHDI Study Group; Roos, R.A.C. Weight Loss in Huntington Disease Increases with Higher CAG Repeat Number. Neurology 2008, 71, 1506–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Burg, J.M.M.; Gardiner, S.L.; Ludolph, A.C.; Landwehrmeyer, G.B.; Roos, R.A.C.; Aziz, N.A. Body Weight Is a Robust Predictor of Clinical Progression in Huntington Disease. Ann. Neurol. 2017, 82, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciacca, S.; Favellato, M.; Madonna, M.; Metro, D.; Marano, M.; Squitieri, F. Early Enteric Neuron Dysfunction in Mouse and Human Huntington Disease. Park. Relat. Disord. 2017, 34, 73–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasser, C.I.; Mercieca, E.-C.; Kong, G.; Hannan, A.J.; McKeown, S.J.; Glikmann-Johnston, Y.; Stout, J.C. Gut Dysbiosis in Huntington’s Disease: Associations among Gut Microbiota, Cognitive Performance and Clinical Outcomes. Brain Commun. 2020, 2, fcaa110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekwudo, M.N.; Gubert, C.; Hannan, A.J. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Huntington’s Disease: Pathogenic Mechanisms and Therapeutic Targets. FEBS J. 2025, 292, 1282–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasser, C.I.; Mercieca, E.-C.; Kong, G.; Hannan, A.J.; Allford, B.; McKeown, S.J.; Stout, J.C.; Glikmann-Johnston, Y. A Randomized Controlled Trial of Probiotics Targeting Gut Dysbiosis in Huntington’s Disease. J. Huntingtons Dis. 2023, 12, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podolsky, S.; Leopold, N.A.; Sax, D.S. Increased Frequency of Diabetes Mellitus in Patients with Huntington’s Chorea. Lancet 1972, 1, 1356–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menkes, J.H.; Stein, N. Fibroblast Cultures in Huntington’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1973, 288, 856–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stüwe, S.H.; Goetze, O.; Lukas, C.; Klotz, P.; Hoffmann, R.; Banasch, M.; Orth, M.; Schmidt, W.E.; Gold, R.; Saft, C. Hepatic Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Manifest and Premanifest Huntington Disease. Neurology 2013, 80, 743–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, M.-C.; Chern, Y.; Juo, C.-G. The Dysfunction of Hepatic Transcriptional Factors in Mice with Huntington’s Disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1812, 1111–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpuj, M.V.; Becher, M.W.; Springer, J.E.; Chabas, D.; Youssef, S.; Pedotti, R.; Mitchell, D.; Steinman, L. Prolonged Survival and Decreased Abnormal Movements in Transgenic Model of Huntington Disease, with Administration of the Transglutaminase Inhibitor Cystamine. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathasivam, K.; Hobbs, C.; Turmaine, M.; Mangiarini, L.; Mahal, A.; Bertaux, F.; Wanker, E.E.; Doherty, P.; Davies, S.W.; Bates, G.P. Formation of Polyglutamine Inclusions in Non-CNS Tissue. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1999, 8, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, S.M.B.; Vinther-Jensen, T.; Nielsen, J.E.; Nørremølle, A.; Hasholt, L.; Hjermind, L.E.; Josefsen, K. Liver Function in Huntington’s Disease Assessed by Blood Biochemical Analyses in a Clinical Setting. J. Neurol. Sci. 2016, 362, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, E.; Mackay, I.R.; Bhathal, P.B. Hepatic Morphology in Huntington’s Chorea. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1975, 38, 1000–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- MacDonald, M.E.; Ambrose, C.M.; Duyao, M.P.; Myers, R.H.; Lin, C.; Srinidhi, L.; Barnes, G.; Taylor, S.A.; James, M.; Groot, N.; et al. A Novel Gene Containing a Trinucleotide Repeat That Is Expanded and Unstable on Huntington’s Disease Chromosomes. The Huntington’s Disease Collaborative Research Group. Cell 1993, 72, 971–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warby, S.C.; Montpetit, A.; Hayden, A.R.; Carroll, J.B.; Butland, S.L.; Visscher, H.; Collins, J.A.; Semaka, A.; Hudson, T.J.; Hayden, M.R. CAG Expansion in the Huntington Disease Gene Is Associated with a Specific and Targetable Predisposing Haplogroup. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 84, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazeki, N.; Nakamura, K.; Goto, J.; Kanazawa, I. Rapid Aggregate Formation of the Huntingtin N-Terminal Fragment Carrying an Expanded Polyglutamine Tract. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 256, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charig, M.J.; Hindley, A.C.; Lloyd, K.; Golding, S.J. “Watch Policy” in Patients with Suspected Stage I Testicular Seminoma: CT as a Sole Staging and Surveillance Technique. Clin. Radiol. 1990, 42, 40–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kettenmann, H.; Hanisch, U.-K.; Noda, M.; Verkhratsky, A. Physiology of Microglia. Physiol. Rev. 2011, 91, 461–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garaschuk, O.; Verkhratsky, A. Physiology of Microglia. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 2034, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickman, S.; Izzy, S.; Sen, P.; Morsett, L.; El Khoury, J. Microglia in Neurodegeneration. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 1359–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, C.A.; Popescu, A.S.; Kitchener, E.J.A.; Allendorf, D.H.; Puigdellívol, M.; Brown, G.C. Microglial Phagocytosis of Neurons in Neurodegeneration, and Its Regulation. J. Neurochem. 2021, 158, 621–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cserép, C.; Pósfai, B.; Lénárt, N.; Fekete, R.; László, Z.I.; Lele, Z.; Orsolits, B.; Molnár, G.; Heindl, S.; Schwarcz, A.D.; et al. Microglia Monitor and Protect Neuronal Function through Specialized Somatic Purinergic Junctions. Science 2020, 367, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lively, S.; Schlichter, L.C. Microglia Responses to Pro-Inflammatory Stimuli (LPS, IFNγ+TNFα) and Reprogramming by Resolving Cytokines (IL-4, IL-10). Front. Cell Neurosci. 2018, 12, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politis, M.; Lahiri, N.; Niccolini, F.; Su, P.; Wu, K.; Giannetti, P.; Scahill, R.I.; Turkheimer, F.E.; Tabrizi, S.J.; Piccini, P. Increased Central Microglial Activation Associated with Peripheral Cytokine Levels in Premanifest Huntington’s Disease Gene Carriers. Neurobiol. Dis. 2015, 83, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, Y.F.; Pavese, N.; Gerhard, A.; Tabrizi, S.J.; Barker, R.A.; Brooks, D.J.; Piccini, P. Imaging Microglial Activation in Huntington’s Disease. Brain Res. Bull. 2007, 72, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavese, N.; Gerhard, A.; Tai, Y.F.; Ho, A.K.; Turkheimer, F.; Barker, R.A.; Brooks, D.J.; Piccini, P. Microglial Activation Correlates with Severity in Huntington Disease: A Clinical and PET Study. Neurology 2006, 66, 1638–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, N.; Galleguillos, D.; Zaidi, A.; Horkey, M.; Sipione, S. Naïve Huntington’s Disease Microglia Mount a Normal Response to Inflammatory Stimuli but Display a Partially Impaired Development of Innate Immune Tolerance That Can Be Counteracted by Ganglioside GM1. J. Neuroinflamm. 2023, 20, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvan, R.; Becker, V.; Hosseinpour, M.; Moradi, Y.; Louch, W.E.; Cataliotti, A.; Devaux, Y.; Frisk, M.; Silva, G.J.J. AtheroNET COST Action CA21153 Prognostic and Predictive microRNA Panels for Heart Failure Patients with Reduced or Preserved Ejection Fraction: A Meta-Analysis of Kaplan-Meier-Based Individual Patient Data. BMC Med. 2025, 23, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabeti Touchaei, A.; Vahidi, S.; Samadani, A.A. The Practical Landscape of Cytokine-Targeted miRNAs to Enhance NK Cell Function in Cancer Immunotherapy: A Bioinformatic Analysis. Cancer Rep. 2025, 8, e70192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, M.; Darroudi, M.; Musavi, M.; Momtazi-Borojeni, A.A. Prediction of Age-Related MicroRNA Signature in Mesenchymal Stem Cells by Using Computational Methods. Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2025, 20, 464–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Sheng, W.; Jia, C.; Tang, J.; Dong, M. Hsa-MiR-590-3p Promotes the Malignancy Progression of Pancreatic Ductal Carcinoma by Inhibiting the Expression of P27 and PPP2R2A via G1/S Cell Cycle Pathway. Onco Targets Ther. 2020, 13, 11045–11058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salemi, M.; Mogavero, M.P.; Lanza, G.; Mongioì, L.M.; Calogero, A.E.; Ferri, R. Examples of Inverse Comorbidity between Cancer and Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Possible Role for Noncoding RNA. Cells 2022, 11, 1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.R.; Tareq, M.M.I.; Biswas, P.; Tauhida, S.J.; Bibi, S.; Zilani, M.N.H.; Albadrani, G.M.; Al-Ghadi, M.Q.; Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Hasan, M.N. Identification of Molecular Targets and Small Drug Candidates for Huntington’s Disease via Bioinformatics and a Network-Based Screening Approach. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2024, 28, e18588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, P.M.; Afonso, M.B.; Simão, A.L.; Islam, T.; Gaspar, M.M.; O’Rourke, C.J.; Lewinska, M.; Andersen, J.B.; Arretxe, E.; Alonso, C.; et al. miR-21-5p Promotes NASH-Related Hepatocarcinogenesis. Liver Int. 2023, 43, 2256–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Lv, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Liang, C.; Liao, X.; Liang, R.; Lin, Y.; Li, Y. Identification and Validation of a Four-miRNA (miRNA-21-5p, miRNA-9-5p, miR-149-5p, and miRNA-30b-5p) Prognosis Signature in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 5759–5766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, K.; Zhang, X.; Lin, T.; Liu, T.; Wang, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhou, L.; Wei, J.; Chang, H.; Li, K.; et al. Circulating miRNA-21-5p as a Diagnostic Biomarker for Pancreatic Cancer: Evidence from Comprehensive miRNA Expression Profiling Analysis and Clinical Validation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badacz, R.; Kleczyński, P.; Legutko, J.; Żmudka, K.; Gacoń, J.; Przewłocki, T.; Kabłak-Ziembicka, A. Expression of miR-1-3p, miR-16-5p and miR-122-5p as Possible Risk Factors of Secondary Cardiovascular Events. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalá-López, F.; Suárez-Pinilla, M.; Suárez-Pinilla, P.; Valderas, J.M.; Gómez-Beneyto, M.; Martinez, S.; Balanzá-Martínez, V.; Climent, J.; Valencia, A.; McGrath, J.; et al. Inverse and Direct Cancer Comorbidity in People with Central Nervous System Disorders: A Meta-Analysis of Cancer Incidence in 577,013 Participants of 50 Observational Studies. Psychother. Psychosom. 2014, 83, 89–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gijsen, R.; Hoeymans, N.; Schellevis, F.G.; Ruwaard, D.; Satariano, W.A.; van den Bos, G.A. Causes and Consequences of Comorbidity: A Review. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2001, 54, 661–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Sánchez, R.; Gómez-Ferrer, M.; Reinal, I.; Buigues, M.; Villanueva-Bádenas, E.; Ontoria-Oviedo, I.; Hernándiz, A.; González-King, H.; Peiró-Molina, E.; Dorronsoro, A.; et al. miR-4732-3p in Extracellular Vesicles from Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Is Cardioprotective During Myocardial Ischemia. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 734143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, W.; Liu, C.; Hong, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, M.; Tang, H.; Zhao, L.; Huang, Z.; Tu, M.; Yu, L.; et al. Tumor-Suppressive miR-4732-3p Is Sorted into Fucosylated Exosome by hnRNPK to Avoid the Inhibition of Lung Cancer Progression. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 43, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melas, K.; Talevi, V.; Imtiaz, M.A.; Etteldorf, R.; Estrada, S.; Krüger, D.M.; Pena-Centeno, T.; Aziz, N.A.; Fischer, A.; Breteler, M.M.B. Blood-Derived microRNAs Are Related to Cognitive Domains in the General Population. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2024, 20, 7138–7159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salemi, M.; Schillaci, F.A.; Salluzzo, M.G.; Marchese, G.; Ventola, G.M.; Perrotta, C.S.; Di Stefano, V.; Lanza, G.; Ferri, R. Dysregulation of miRNAs in Sicilian Patients with Huntington’s Disease. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2454. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15192454
Salemi M, Schillaci FA, Salluzzo MG, Marchese G, Ventola GM, Perrotta CS, Di Stefano V, Lanza G, Ferri R. Dysregulation of miRNAs in Sicilian Patients with Huntington’s Disease. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(19):2454. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15192454
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalemi, Michele, Francesca Antonia Schillaci, Maria Grazia Salluzzo, Giovanna Marchese, Giovanna Maria Ventola, Concetta Simona Perrotta, Vincenzo Di Stefano, Giuseppe Lanza, and Raffaele Ferri. 2025. "Dysregulation of miRNAs in Sicilian Patients with Huntington’s Disease" Diagnostics 15, no. 19: 2454. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15192454
APA StyleSalemi, M., Schillaci, F. A., Salluzzo, M. G., Marchese, G., Ventola, G. M., Perrotta, C. S., Di Stefano, V., Lanza, G., & Ferri, R. (2025). Dysregulation of miRNAs in Sicilian Patients with Huntington’s Disease. Diagnostics, 15(19), 2454. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15192454








