Reliability of Prediction Models for the Functional Classification of a Sinusoidal Intraocular Lens Depending on Pupil Diameter
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Intraocular Lens
2.2. Measurement Procedure
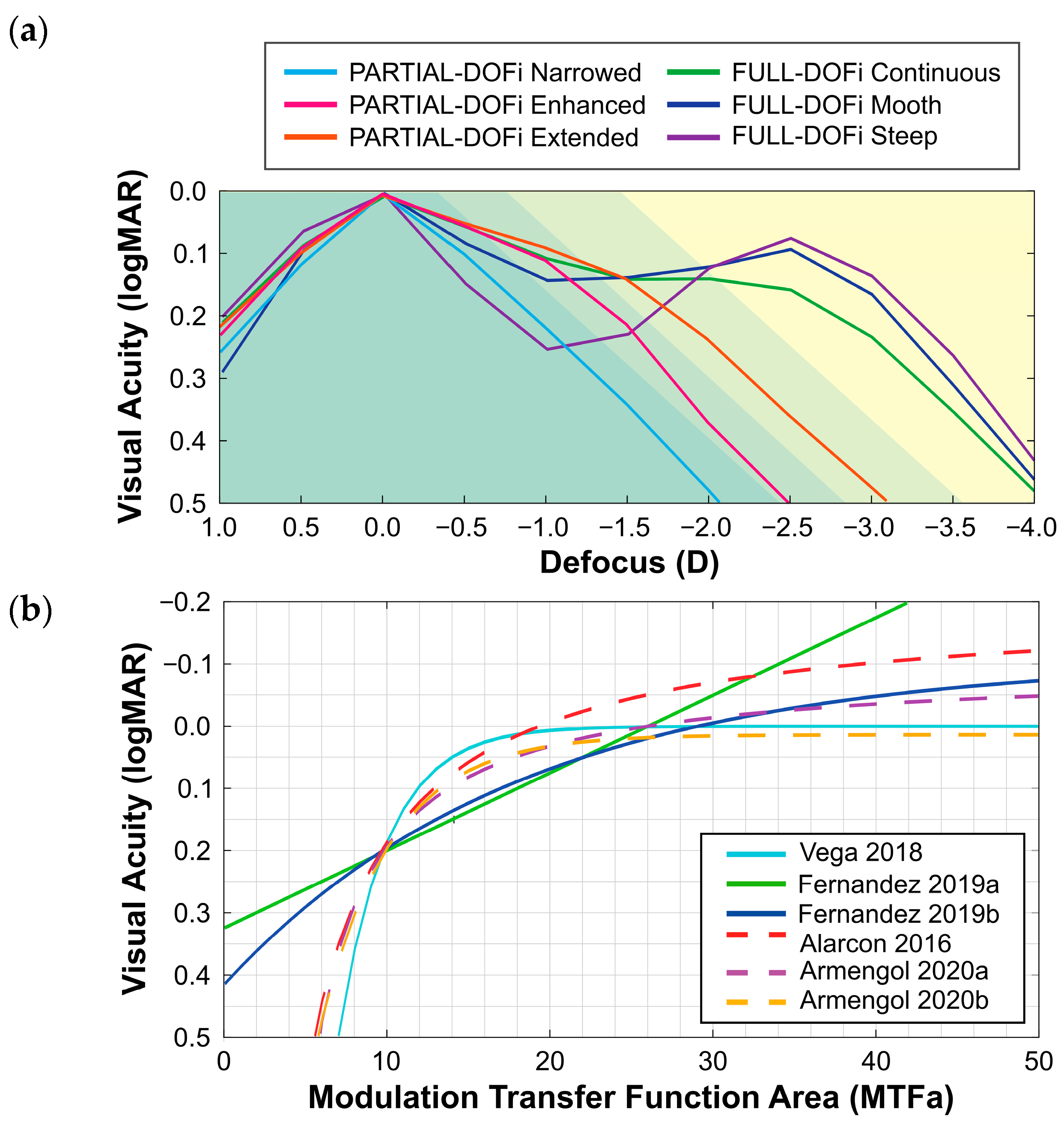
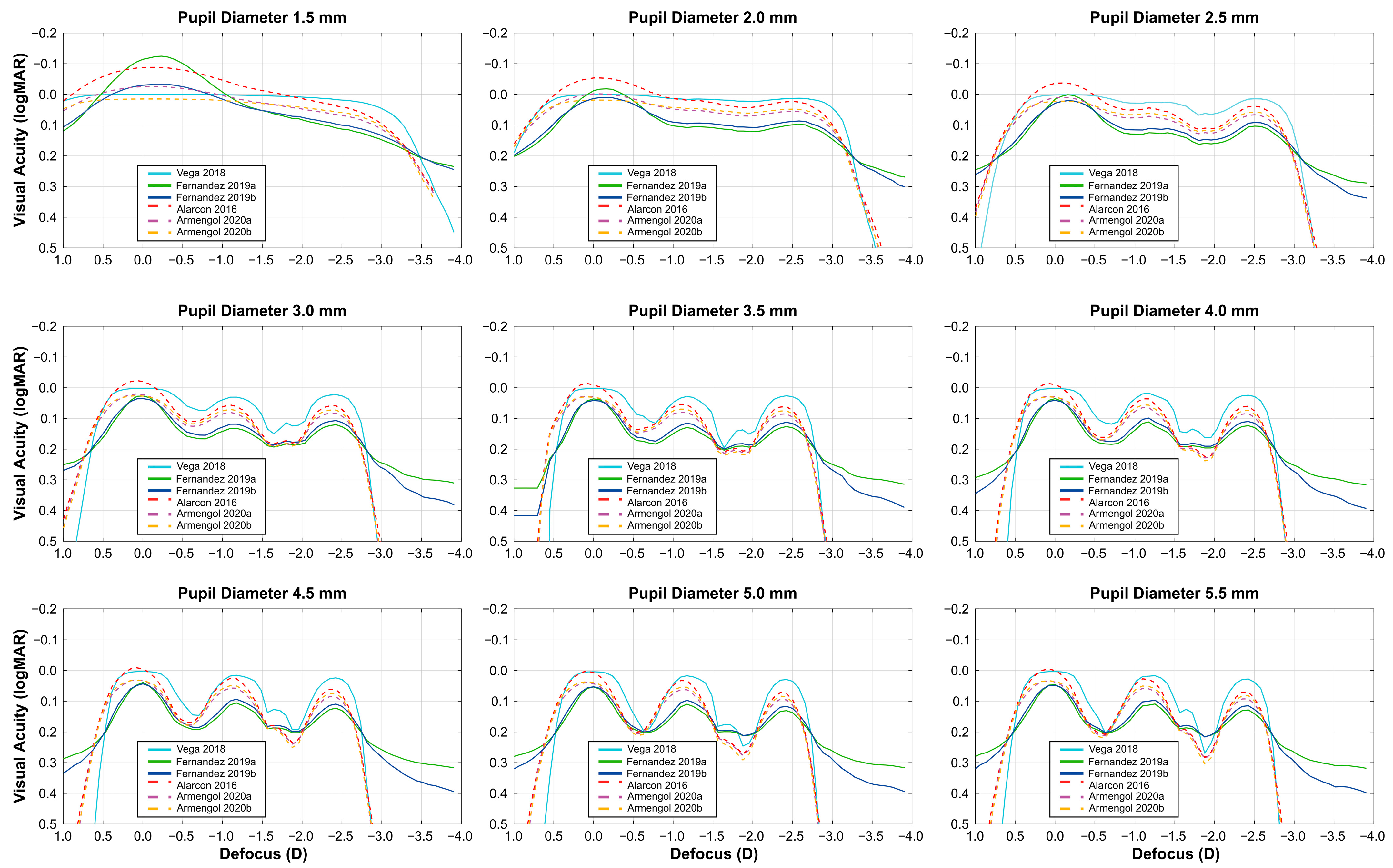
2.3. Prediction Models
- Vega et al. (2018) evaluated IOLs with a power of 20 D using an optical bench test under monochromatic green light. The MTF was measured using a four-slit pattern. A corneal model induced SA of +0.27 µm for a 6 mm of pupil diameter, while measurements were conducted with a 3 mm of pupil diameter at the IOL plane. The model, based on an exponential decay function for predicting monocular visual acuity, included both Full and Partial-DOFi IOLs [10].
- Fernández et al. (2019) conducted ray-tracing simulations under monochromatic green light using a single Full-DOFi IOL (21.5 D). A corneal model induced SA of +0.24 µm for a 6 mm optical surface. Simulations were performed for pupil diameters ranging from 2.5 mm to 4 mm in 0.5 mm increments. Their predictive models used both linear (2019a) and exponential decay (2019b) functions to estimate monocular visual acuity and contrast sensitivity defocus curves [11].
- Alarcon et al. (2016) obtained optical bench measurements of the MTF using the line spread function under polychromatic light for both Full and Partial-DOFi IOLs (20 D). An average corneal model was used to reproduce typical SA with a pupil diameter of 3 mm. The predictive model applied the MTFa raised to the power of −1. The model by Alarcon et al. differed from the others in predicting binocular rather than monocular visual acuity [12,22].
- Armengol et al. (2020) provided two predictive models under polychromatic light for estimating monocular visual acuity: the first utilized an inverse proportional function (Armengol 2020a), and the second applied an exponential decay function (Armengol 2020b). These models were developed using measurements from two Full and one Partial-DOFi IOLs (20 D) on an optical bench on which the MTF was measured using a four-slit pattern. A corneal model induced ±0.17 µm of SA for a 5 mm of pupil diameter, with measurements obtained for PDs of 3 mm and 4.5 mm [13].
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IOL | Intraocular Lens |
| VADC | Visual Acuity Defocus Curve |
| SVL | Simultaneous Vision Intraocular Lens |
| DOFi | Depth-of-Field |
| SA | Spherical Aberration |
| MTFa | Modulation Transfer Function area |
| MTF | Modulation Transfer Function |
| PSF | Point Spread Function |
Appendix A
|
Equations using Monochromatic Green Light Vega (2018) [10]: (A) Fernández (2019a) [11] (B) Fernández (2019b) [11] (C) Equations using Polychromatic light Alarcon (2016) [12]: (D) Armengol (2020a) [13]: (E) Armengol (2020b) [13]: (F) |
References
- Linebarger, E.J.; Hardten, D.R.; Shah, G.K.; Lindstrom, R.L. Phacoemulsification and Modern Cataract Surgery. Surv. Ophthalmol. 1999, 44, 123–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maxwell, W.A.; Waycaster, C.R.; D’Souza, A.O.; Meissner, B.L.; Hileman, K. A United States cost–benefit comparison of an apodized, diffractive, presbyopia-correcting, multifocal intraocular lens and a conventional monofocal lens. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2008, 34, 1855–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rampat, R.; Gatinel, D. Multifocal and Extended Depth-of-Focus Intraocular Lenses in 2020. Ophthalmology 2021, 128, e164–e185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Ciuffreda, K.J. Depth-of-Focus of the Human Eye: Theory and Clinical Implications. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2006, 51, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohnen, T.; Lemp-Hull, J.; Suryakumar, R. Defocus curves: Focusing on factors influencing assessment. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2022, 48, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, K.M.; Wendelstein, J.A.; Koch, D.D. Depth of field or depth of focus? J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2024, 50, 1291–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, F.; Dick, H.B.; Kohnen, T.; Findl, O.; Nuijts, R.; Cochener, B.; Fernández, J. Evidence-based functional classification of simultaneous vision intraocular lenses: Seeking a global consensus by the ESCRS Functional Vision Working Group. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2024, 50, 794–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, J.; Ribeiro, F.; Rocha-de-Lossada, C.; Rodríguez-Vallejo, M. Functional Classification of Intraocular Lenses Based on Defocus Curves: A Scoping Review and Cluster Analysis. J. Refract. Surg. 2024, 40, e108–e116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidova, P.; Kaiser, K.P.; Hemkeppler, E.; Böhm, M.; Kohnen, T. Effects of Pupil Size on Functional Outcomes of a Simultaneous Vision Intraocular Lens. J. Refract. Surg. 2025, 41, e645–e654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, F.; Millán, M.S.; Garzón, N.; Altemir, I.; Poyales, F.; Larrosa, J.M. Visual acuity of pseudophakic patients predicted from in-vitro measurements of intraocular lenses with different design. Biomed. Opt. Express 2018, 9, 4893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, J.; Rodríguez-Vallejo, M.; Martínez, J.; Burguera, N.; Piñero, D.P. Prediction of Visual Acuity and Contrast Sensitivity from Optical Simulations With Multifocal Intraocular Lenses. J. Refract. Surg. 2019, 35, 789–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcon, A.; Canovas, C.; Rosen, R.; Weeber, H.; Tsai, L.; Hileman, K.; Piers, P. Preclinical metrics to predict through-focus visual acuity for pseudophakic patients. Biomed. Opt. Express 2016, 7, 1877–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armengol, J.; Garzón, N.; Vega, F.; Altemir, I.; Millán, M.S. Equivalence of two optical quality metrics to predict the visual acuity of multifocal pseudophakic patients. Biomed. Opt. Express 2020, 11, 2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO-11979-7:2024; Ophthalmic Implants—Intraocular Lenses—Part 7: Clinical Investigations of Intraocular Lenses for the Correction of Aphakia. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024.
- Z80.35-2018; Ophthalmics—Extended Depth of Focus Intraocular Lenses for Presbyopia. ANSI: Washington, DC, USA, 2018.
- Simpson, M.J.; Gatinel, D.; Faria-Ribeiro, M.; Wei, X.; Yoon, G.; Liang, J.; Artal, P.; Marcos, S. Design concepts for advanced-technology intraocular lenses [Invited]. Biomed. Opt. Express 2024, 16, 334–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łabuz, G.; Yan, W.; Baur, I.D.; Khoramnia, R.; Auffarth, G.U. Chromatic aberration and spectral dependency of extended-range-of-vision intraocular lens technology. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 14781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can, E.; Senel, E.C.; Holmström, S.T.S.; Piñero, D.P. Comparison of the optical behaviour of five different multifocal diffractive intraocular lenses in a model eye. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 19646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montagud-Martínez, D.; Ferrando, V.; Martínez-Espert, A.; Garcia-Delpech, S.; Monsoriu, J.A.; Furlan, W.D. In Vitro Chromatic Performance of Three Presbyopia-Correcting Intraocular Lenses with Different Optical Designs. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remón, L.; García-Delpech, S.; Udaondo, P.; Ferrando, V.; Monsoriu, J.A.; Furlan, W.D. Fractal-structured multifocal intraocular lens. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO-11979-2 (2014); Ophthalmic Implants—Intraocular Lenses—Part 2: Optical Properties and Test Methods. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014.
- Alarcon, A.; Canovas, C.; Koopman, B.; Pande, M.V.; Koch, D.D.; Piers, P. Optical bench evaluation of the effect of pupil size in new generation monofocal intraocular lenses. BMC Ophthalmol. 2023, 23, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holladay, J.T.; van Dijk, H.; Lang, A.; Portney, V.; Willis, T.R.; Sun, R.; Oksman, H.C. Optical performance of multifocal intraocular lenses. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 1990, 16, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christie, B.; Nordan, L.; Chipman, R.; Gupta, A. Optical performance of an aspheric multifocal intraocular lens. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 1991, 17, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata-Díaz, J.F.; Rodríguez-Izquierdo, M.A.; Ould-Amer, N.; Lajara-Blesa, J.; López-Gil, N. Total Depth of Focus of Five Premium Multifocal Intraocular Lenses. J. Refract. Surg. 2020, 36, 578–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łabuz, G.; Khoramnia, R.; Yan, W.; van den Berg, T.J.P.; Auffarth, G.U.; Naujokaitis, T.; Tandogan, T. Characterizing glare effects associated with diffractive optics in presbyopia-correcting intraocular lenses. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2024, 50, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felipe, A.; Pastor, F.; Artigas, J.M.; Diez-Ajenjo, A.; Gené, A.; Menezo, J.L. Correlation between optics quality of multifocal intraocular lenses and visual acuity Tolerance to modulation transfer function decay. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2010, 36, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łabuz, G.; Yan, W.; Baur, I.D.; Khoramnia, R.; Auffarth, G.U. Comparison of Five Presbyopia-Correcting Intraocular Lenses: Optical-Bench Assessment with Visual-Quality Simulation. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Águila-Carrasco, A.J.D.; Alarcon, A.; Weeber, H.; Tsai, L.; Vilupuru, S.; Canovas, C.; Piers, P. Prediction of monocular defocus curves in pseudophakia with different pupil sizes. Biomed. Opt. Express 2025, 16, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vega, F.; Millán, M.S. Predicting visual acuity in pseudophakic eyes with pupil-dependent 2 extended depth of focus intraocular lenses. J. Refract. Surg. 2025, 41, e831–e838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruprecht, A.; Stauss, B.; Fuchs, C.; Krey, S. Physiological model eyes for advanced IOL characterization. Appl. Opt. 2025, 64, 2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, J.; Ribeiro, F.; Dick, H.B.; Rocha-de-Lossada, C.; Rodríguez-Vallejo, M. Navigating the Lens Labyrinth: A Practical Approach to Intraocular Lens Classification and Selection. Ophthalmol. Ther. 2025, 149, 2313–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Monochromatic Light Prediction Models | Polychromatic Light Prediction Models | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pupil (mm) | Vega 2018 | Fernández 2019a | Fernández 2019b | Alarcón 2016 | Armengol 2020a | Armengol 2020b |
| 1.5 | 0 a | 0 a | 0 a | 0 a | 0 a | 0 a |
| 2.0 | 0 a | 0 a | 0 a | 0 a | 0 a | 0 a |
| 2.5 | 0.04 a | 0.06 b | 0.06 b | 0.07 b | 0.06 b | 0.06 b |
| 3.0 | 0.13 b | 0.07 b | 0.07 b | 0.12 b | 0.11 b | 0.12 b |
| 3.5 | 0.17 c | 0.07 b | 0.09 b | 0.15 c | 0.13 b | 0.14 c |
| 4.0 | 0.14 c | 0.08 b | 0.08 b | 0.16 c | 0.15 c | 0.17 c |
| 4.5 | 0.17 c | 0.08 b | 0.09 b | 0.18 c | 0.16 c | 0.18 c |
| 5.0 | 0.21 c | 0.08 b | 0.09 b | 0.20 c | 0.18 c | 0.21 c |
| 5.5 | 0.24 c | 0.09 b | 0.10 b | 0.21 c | 0.20 c | 0.22 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Montagud-Martínez, D.; Furlan, W.D.; Ferrando, V.; Rodríguez-Vallejo, M.; Fernández, J. Reliability of Prediction Models for the Functional Classification of a Sinusoidal Intraocular Lens Depending on Pupil Diameter. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2446. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15192446
Montagud-Martínez D, Furlan WD, Ferrando V, Rodríguez-Vallejo M, Fernández J. Reliability of Prediction Models for the Functional Classification of a Sinusoidal Intraocular Lens Depending on Pupil Diameter. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(19):2446. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15192446
Chicago/Turabian StyleMontagud-Martínez, Diego, Walter D. Furlan, Vicente Ferrando, Manuel Rodríguez-Vallejo, and Joaquín Fernández. 2025. "Reliability of Prediction Models for the Functional Classification of a Sinusoidal Intraocular Lens Depending on Pupil Diameter" Diagnostics 15, no. 19: 2446. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15192446
APA StyleMontagud-Martínez, D., Furlan, W. D., Ferrando, V., Rodríguez-Vallejo, M., & Fernández, J. (2025). Reliability of Prediction Models for the Functional Classification of a Sinusoidal Intraocular Lens Depending on Pupil Diameter. Diagnostics, 15(19), 2446. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15192446









