Confirmation of Large Language Models in Head and Neck Cancer Staging
Abstract
1. Introduction
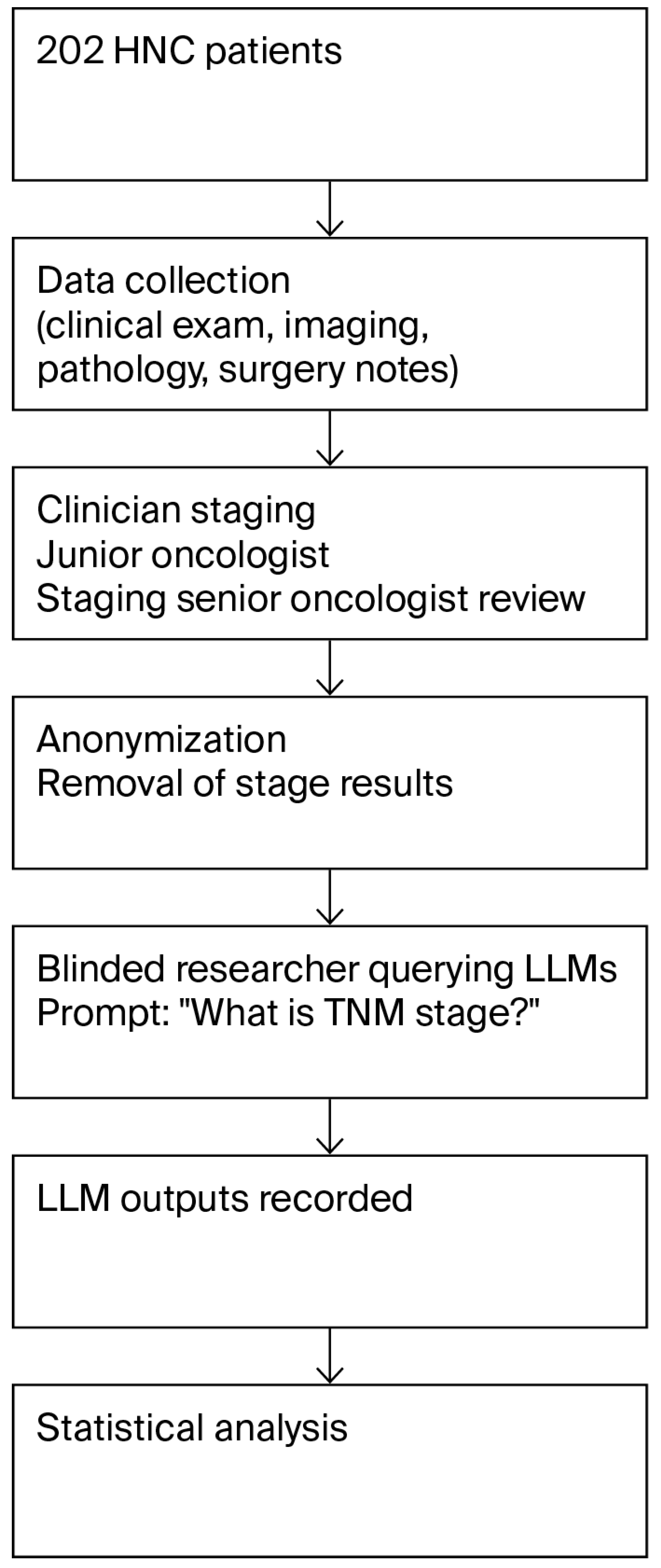
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Group
2.2. Staging by Clinicians
2.3. LLM-Based Cancer Staging
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Ethical Approval and Informed Consent
3. Results
3.1. Demographics and Patient Characteristics
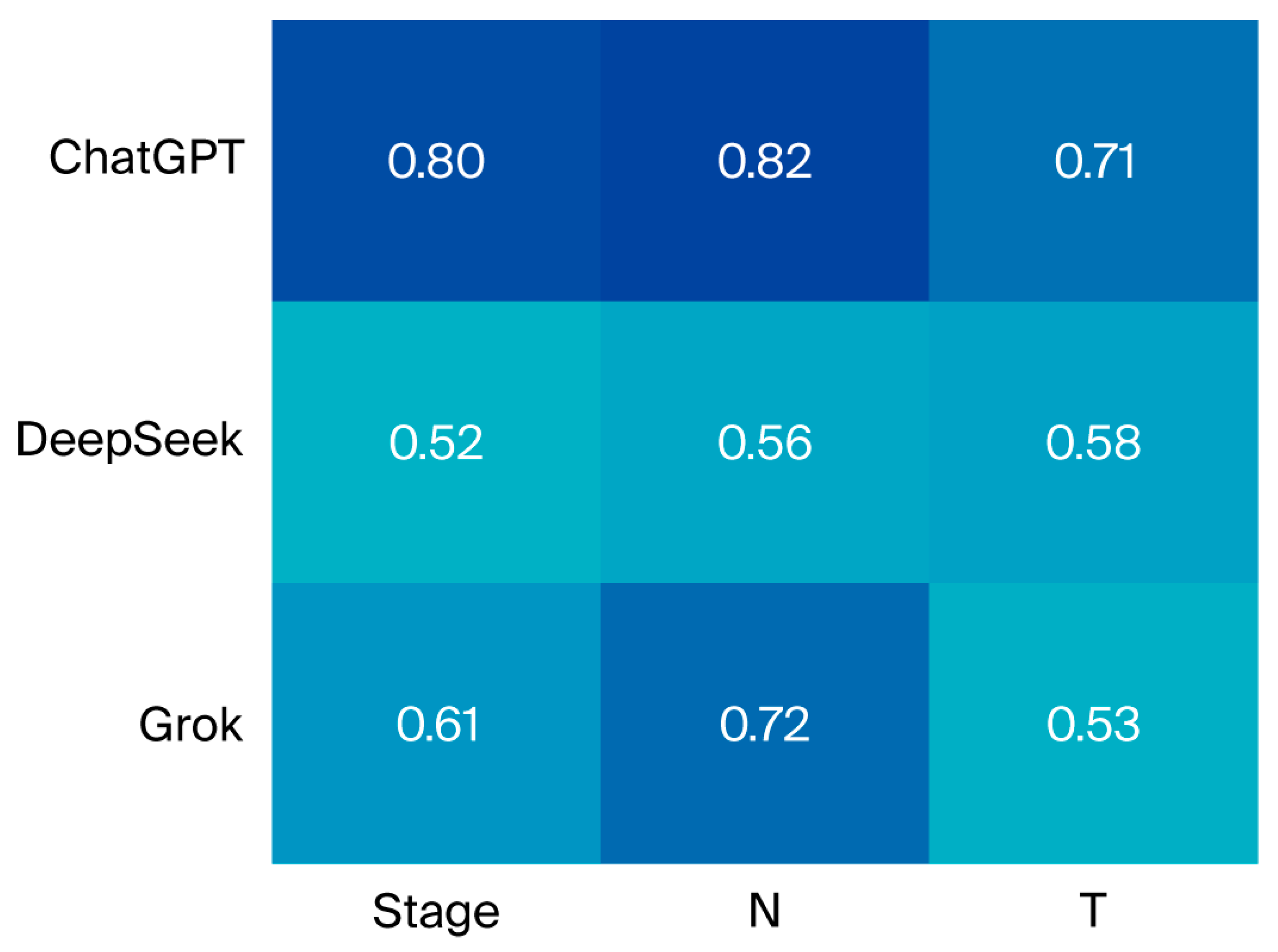
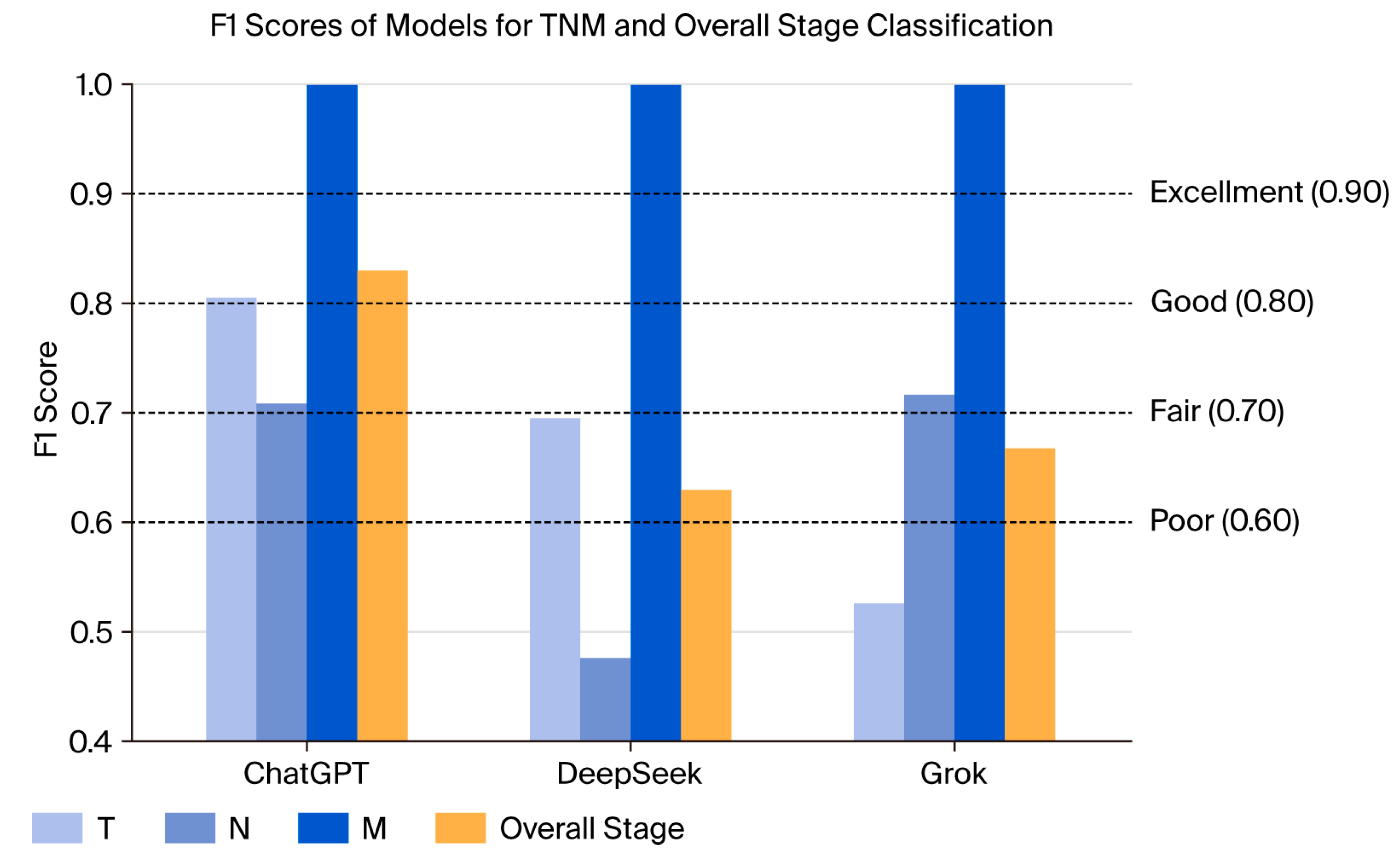
3.2. Staging Results by Clinicians and Large Language Models
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LLM | Large language model |
| HNC | Head and neck cancer |
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machiels, J.P.; Leemans, C.R.; Golusinski, W.; Grau, C.; Licitra, L.; Gregoire, V. Squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity, larynx, oropharynx and hypopharynx: EHNS-ESMO-ESTRO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1462–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poon, C.S.; Stenson, K.M. Overview of the Diagnosis and Staging of Head and Neck Cancer. UptoDate (online), Fev, 2012. Available online: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/overview-of-the-diagnosis-and-staging-of-head-and-neck-cancer (accessed on 12 September 2025).
- Amin, M.B.; Edge, S.B.; Greene, F.L.; Byrd, D.R.; Brookland, R.K.; Washington, M.K.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Compton, C.C.; Hess, K.R.; Sullivan, D.C.; et al. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; Volume 1024. [Google Scholar]
- Naveed, H.; Khan, A.U.; Qiu, S.; Saqib, M.; Anwar, S.; Usman, M.; Akhtar, N.; Barnes, N.; Mian, A. A Comprehensive Overview of Large Language Models. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2023, 16, 1–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, N.Q.K. Leveraging transformers-based language models in proteome bioinformatics. Proteomics 2023, 23, 2300011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.-O.; Le, N.Q.K. Sa-TTCA: An SVM-based approach for tumor T-cell antigen classification using features extracted from biological sequencing and natural language processing. Comput. Biol. Med. 2024, 174, 108408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibney, E. Scientists flock to DeepSeek: How they’re using the blockbuster AI model. Nature 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clusmann, J.; Kolbinger, F.R.; Muti, H.S.; Carrero, Z.I.; Eckardt, J.-N.; Laleh, N.G.; Löffler, C.M.L.; Schwarzkopf, S.-C.; Unger, M.; Veldhuizen, G.P.; et al. The future landscape of large language models in medicine. Commun. Med. 2023, 3, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carl, N.; Schramm, F.; Haggenmüller, S.; Kather, J.N.; Hetz, M.J.; Wies, C.; Michel, M.S.; Wessels, F.; Brinker, T.J. Large language model use in clinical oncology. npj Precis. Oncol. 2024, 8, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chizhikova, M.; López-Úbeda, P.; Martín-Noguerol, T.; Díaz-Galiano, M.C.; Ureña-López, L.A.; Luna, A.; Martín-Valdivia, M.T. Automatic TNM staging of colorectal cancer radiology reports using pre-trained language models. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2025, 259, 108515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baran, E.; Lee, M.; Aviv, S.; Weiss, J.; Pettengell, C.; Karam, I.; Bayley, A.; Poon, I.; Chan, K.K.W.; Parmar, A.; et al. Oropharyngeal Cancer Staging Health Record Extraction Using Artificial Intelligence. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2024, 150, 1051–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidl, B.; Hütten, T.; Pigorsch, S.; Stögbauer, F.; Hoch, C.C.; Hussain, T.; Wollenberg, B.; Wirth, M. Assessing the use of the novel tool Claude 3 in comparison to ChatGPT 4.0 as an artificial intelligence tool in the diagnosis and therapy of primary head and neck cancer cases. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2024, 281, 6099–6109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozuka, R.; Johno, H.; Amakawa, A.; Sato, J.; Muto, M.; Seki, S.; Komaba, A.; Onishi, H. Application of NotebookLM, a large language model with retrieval-augmented generation, for lung cancer staging. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2025, 43, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OpenAi, ChatGPT (GPT-4O). 2024. Available online: www.chatgpt.com (accessed on 12 September 2025).
- DeepSeek. DeepSeek-V3: An Advanced AI Language Model; DeepSeek: Hangzhou, China, 2023; Available online: https://www.deepseek.com/ (accessed on 12 September 2025).
- xAi. Grok 3 Beta—The Age of Reasoning Agents. 2025. Available online: www.grok.com (accessed on 12 September 2025).
- IBM Corp. IBM SPSS Statistics; IBM Corp.: Armonk, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kolla, L.; Parikh, R.B. Uses and Limitations of Artificial Intelligence for Oncology. Cancer 2024, 130, 2101–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.A.; Yaramis, I.; Roy, T.D. Creating trustworthy llms: Dealing with hallucinations in healthcare ai. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2311.01463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benary, M.; Wang, X.D.; Schmidt, M.; Soll, D.; Hilfenhaus, G.; Nassir, M.; Sigler, C.; Knödler, M.; Keller, U.; Beule, D.; et al. Leveraging Large Language Models for Decision Support in Personalized Oncology. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2343689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, K.; Fritz, C.; Rajasekaran, K. Answering head and neck cancer questions: An assessment of ChatGPT responses. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2024, 45, 104085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchi, F.; Bellini, E.; Iandelli, A.; Sampieri, C.; Peretti, G. Exploring the landscape of AI-assisted decision-making in head and neck cancer treatment: A comparative analysis of NCCN guidelines and ChatGPT responses. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2024, 281, 2123–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechien, J.R.; Chiesa-Estomba, C.-M.; Baudouin, R.; Hans, S. Accuracy of ChatGPT in head and neck oncological board decisions: Preliminary findings. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2024, 281, 2105–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.J.; Ayo-Ajibola, O.; Lin, M.E.; Swanson, M.S.; Chambers, T.N.; Kwon, D.I.; Kokot, N.C. Evaluation of Oropharyngeal Cancer Information from Revolutionary Artificial Intelligence Chatbot. Laryngoscope 2024, 134, 2252–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Kim, J.W.; Lee, Y.S.; Tae, J.H.; Choi, S.Y.; Chang, I.H.; Kim, J.H. Availability of ChatGPT to provide medical information for patients with kidney cancer. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdat, E.C.; Kavak, E.E. Benchmarking LLM chatbots’ oncological knowledge with the Turkish Society of Medical Oncology’s annual board examination questions. BMC Cancer 2025, 25, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology: Head and Neck Cancers (Version 2.2025); National Comprehensive Cancer Network: Montgomery, PA, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Bossi, P.; Chan, A.; Licitra, L.; Trama, A.; Orlandi, E.; Hui, E.; Halámková, J.; Mattheis, S.; Baujat, B.; Hardillo, J.; et al. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: ESMO-EURACAN Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up(†). Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 452–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Change, C.-H.; Lucas, M.M.; Lu-Yao, G.; Yang, C.C. Classifying cancer stage with open-source clinical large language models. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 12th International Conference on Healthcare Informatics (ICHI), Orlando, FL, USA, 3–6 June 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.E.; Park, K.-S.; Kim, Y.-H.; Song, H.-C.; Park, B.; Jeong, Y.J. Lung Cancer Staging Using Chest CT and FDG PET/CT Free-Text Reports: Comparison Among Three ChatGPT Large Language Models and Six Human Readers of Varying Experience. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2024, 223, e2431696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Yang, D.M.; Rong, R.; Nezafati, K.; Treager, C.; Chi, Z.; Wang, S.; Cheng, X.; Guo, Y.; Klesse, L.J.; et al. A critical assessment of using ChatGPT for extracting structured data from clinical notes. npj Digit. Med. 2024, 7, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, Y.; Liao, L.; Li, M.; Che, W.; Yu, P.S. A survey of multilingual large language models. Patterns 2025, 6, 101118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables | N (%) |
|---|---|
| Gender | |
| Male | 151 (74.8) |
| Female | 51 (25.2) |
| Smoking | |
| Active | 75 (37.1) |
| Exsmoker | 73 (36.1) |
| Never | 51 (25.2) |
| Age, years (median) | Median (SD) |
| Total | 58.35 (14.35) |
| Male | 59.37 (13.16) |
| Female | 52.86(15.67) |
| Smoking Status | |
| Never | 54 (26.7) |
| Current | 75 (37.1) |
| Ex | 73 (36.1) |
| Localization | |
| Larynx | 92 (45.5) |
| Hypopharynx | 13 (6.4) |
| Oral Cavity/Oropharynx | 46 (22.8) |
| Nasopharynx | 43 (21.3) |
| Salivary | 1 (0.5) |
| Nasal cavity and sinuses | 7 (3.5) |
| Definitive Surgery | |
| Performed | 80 (39.6) |
| Not Performed | 122 (60.4) |
| Diagnostic Method | |
| Imaging Only | 49 (24.3) |
| Pathology Only | 3 (1.5) |
| Clinical Examination Note | 1 (0.5) |
| All Methods Combined | 149 (73.8) |
| Stages | |
| 1 | 11 (5.4) |
| 2 | 23 (11.4) |
| 3 | 58 (28.7) |
| 4 | 110 (54.4) |
| LLM | T Stage n (%) | N Stage n (%) | M Stage n (%) | TNM Stagen (%) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ChatGPT | 159 (78.7) | 176 (87.1) | 202 (100) | 173 (85.6) | p1 < 0.001 p2 = 0.077 p3 = 0.009 p4 < 0.001 |
| DeepSeek | 139 (68.8) | 135 (66.8) | 202(100) | 136 (67.3) | |
| Grok | 130 (64.4) | 162 (80.2) | 202 (100) | 152 (75.2) |
| LLM | Larynx n (%) κ (sd) | Hypopharynx n (%) κ (sd) | Oral Cavity/Oropharynx n (%) κ (sd) | Nasopharynx n (%) κ (sd) | Salivary n (%) κ (sd) | Nasal Cavity and Sinuses n (%) κ (sd) | Overall n (%) κ (sd) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ChatGPT | 77 (83.7) | 11 (84.6) | 41 (89.1) | 38 (88.4) | 1 (100) | 5 (71.4) | 173 (85.6) |
| 0.778 (0.06) | 0.743 (0.19) | 0.852 (0.07) | 0.791 (0.09) | - | 0.553 (0.34) | 0.797 (0.04) | |
| DeepSeek | 60 (65.2) | 8 (61.5) | 32 (69.6) | 29 (67.4) | 1 (100) | 6 (85.7) | 136 (67.3) |
| 0.518 (0.09) | 0.268 (0.27) | 0.580 (0.12) | 0.580 (0.12) | - | 0.611 (0.32) | 0.522 (0.06) | |
| Grok | 67 (72.8) | 12 (93.1) | 35 (76.1) | 32 (74.4) | 1 (100) | 5 (71.4) | 152 (75.2) |
| 0.596 (0.08) | 0.687 (0.21) | 0.671 (0.11) | 0.497 (0.13) | - | - | 0.614 (0.05) |
| Study (Year) | Cancer Type/Setting | LLM Evaluated | Task | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tozuka et al., 2025 [14] | Lung cancer (fictional cases, n = 100) | NotebookLM (RAG-enhanced) | TNM staging | Accuracy of ~76–86%, demonstrated feasibility of staging from reports |
| Chizhikova et al., 2025 [11] | Colorectal cancer | Pre-trained LLMs (BERT, RoBERTa) | Radiology report TNM extraction | Macro F1 scores of 0.7464, 0.8792, and 0.6776 for T, N, and M staging, respectively |
| Baran et al., 2024 [12] | Oropharyngeal cancer | AI-based NLP (health record extraction) | Automated staging | T: 55.9%, N: 56.0%, M: 87.6%, and p16: 92.1%; local vs. advanced: 80.7% |
| Schmidl et al., 2024 [13] | Head and neck cancer (n = 50) | Claude vs. ChatGPT | Diagnosis, therapy recommendations | OPSCC surgery: ChatGPT: 72.2% vs Claude: 27.8% |
| Lee et al., 2024 [31] | Lung cancer | ChatGPT (3 versions) | Staging using CT/PET reports | GPT-4o: 74.1%; GPT-4: 70.1%; and GPT-3.5: 57.4% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kayaalp, M.; Bölek, H.; Yaşar, H.A. Confirmation of Large Language Models in Head and Neck Cancer Staging. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2375. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15182375
Kayaalp M, Bölek H, Yaşar HA. Confirmation of Large Language Models in Head and Neck Cancer Staging. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(18):2375. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15182375
Chicago/Turabian StyleKayaalp, Mehmet, Hatice Bölek, and Hatime Arzu Yaşar. 2025. "Confirmation of Large Language Models in Head and Neck Cancer Staging" Diagnostics 15, no. 18: 2375. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15182375
APA StyleKayaalp, M., Bölek, H., & Yaşar, H. A. (2025). Confirmation of Large Language Models in Head and Neck Cancer Staging. Diagnostics, 15(18), 2375. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15182375





