Clinicopathological Pearls and Diagnostic Pitfalls in IgG4-Related Disease: Challenging Case Series and Literature Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
- pancreato-biliary disease, 31% of the patients;
- retroperitoneal-aortitis, 24% of the patients;
- head and neck disease without other features, 24% of the patients;
- head and neck disease with extra-glandular involvement, 22% of the patients.
2. Case Presentation
2.1. Case 1
2.1.1. Clinical Presentation
2.1.2. Investigation
2.1.3. Histopathology
2.1.4. Treatment
2.1.5. Outcome
2.2. Case 2
2.3. Case 3
3. Case Series Discussion and Literature Review
3.1. Case 1
3.1.1. IgG4 Related Gastroenteric Disease (GE-IgG4-RD)
3.1.2. IgG4-Related Sclerosing Mesenteritis (SM-IgG4-RD)
3.1.3. IgG4-Related Orbital Disease (O-IgG4-RD)
3.1.4. IgG4 Related Neurological Involvement
3.2. Case 2
IgG4 Related Sclerosing Cholangitis (SC-IgG4-RD)
- Type 1, intrapancreatic disease.
- Type 2, diffuse extrahepatic and intrahepatic disease, with (type 2a) or without (type 2b) pre-stenotic dilatation of bile duct.
- Type 3, hilar stenosis associated with distal stenosis.
- Type 4, hilar only stenosis.
3.3. Case 3
IgG4 Related Sialadenitis (S-IgG4-RD)
4. Therapy
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 18FDG | 18Fluorodeoxyglucose |
| AIP1 | Autoimmune pancreatitis type 1 |
| ANA | Anti-nuclear antibodies |
| BMB | Bone marrow biopsy |
| CCa | Cholangiocarcinoma |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal fluid |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| DMARD | Disease-modifying antirheumatic drug |
| EGDS | Esophagogastroduodenoscopy |
| ENA | Extractable nuclear antigens |
| EOM | Extraocular muscles |
| ERCP | Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography |
| EULAR | European league against rheumatism |
| EUS | Endoscopic ultrasound |
| FNB | Fine needle biopsy |
| GE-IgG4-RD | Gastroenteric IgG4 related disease |
| HPF | High-power field corresponding to a magnification of 40× |
| IBD | Inflammatory bowel disease |
| IDUS | Intraductal ultrasound |
| IgG4-RD | IgG4 related disease |
| IV | Intravenous |
| MRCP | Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| O-IgG4-RD | Orbital IgG4 related disease |
| PET | Positron emission tomography |
| PSC | Primitive sclerosing cholangitis |
| rDSAbs | Rheumatic disease-specific antibodies |
| RF | Rheumatoid factor |
| S-IgG4-RD | Salivary gland IgG4 related disease |
| SC-IgG4-RD | IgG4 related sclerosing cholangitis |
| SG | Salivary glands |
| SM-IgG4-RD | IgG4 related sclerosing mesenteritis |
| US | Ultrasound |
References
- Wallace, Z.S.; Miles, G.; Smolkina, E.; Petruski-Ivleva, N.; Madziva, D.; Cook, C.; Fu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Stone, J.H.; Choi, H.K. Incidence, prevalence and mortality of IgG4-related disease in the USA: A claims-based analysis of commercially insured adults. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 82, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, Z.S.; Naden, R.P.; Chari, S.; Choi, H.K.; Della-Torre, E.; Dicaire, J.-F.; Hart, P.A.; Inoue, D.; Kawano, M.; Khosroshahi, A.; et al. The 2019 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism classification criteria for IgG4-related disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, J.H.; Zen, Y.; Deshpande, V. Mechanisms of disease: IgG4-related disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, Z.S.; Zhang, Y.; Perugino, C.A.; Naden, R.; Choi, H.K.; Stone, J.H. Clinical phenotypes of IgG4-related disease: An analysis of two international cross-sectional cohorts. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noda, J.; Takano, Y.; Yamawaki, M.; Azami, T.; Niiya, F.; Maruoka, N.; Ohike, N.; Nagahama, M. A case of synchronous IgG4-associated pleuritis and type 1 autoimmune pancreatitis. Clin. J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 16, 925–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukoyama, H.; Murakami, K.; Onizawa, H.; Shirakashi, M.; Hiwa, R.; Tsuji, H.; Kitagori, K.; Akizuki, S.; Nakashima, R.; Onishi, A.; et al. A case of atypical IgG4-related disease presenting hypereosinophilia, polyneuropathy, and liver dysfunction. Mod. Rheumatol. Case Rep. 2023, 8, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Elsayes, K.M.; Waranch, C.; Abdelaziz, A.; Menias, C.O.; Sandrasegaran, K.; Shaaban, A.M.; Gaballah, A.H. IgG4-related disease in the abdomen and pelvis: Atypical findings, pitfalls, and mimics. Abdom. Radiol. 2020, 45, 2485–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Almudaires, A.; Alzahrani, M.; Qumosani, K.; Chakrabarti, S. IgG4-related disease as a rare cause of gastric outlet obstruction: A case report and literature review. BMC Gastroenterol. 2021, 21, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilani, S.I.; Buglioni, A.; Cornell, L.D. IgG4-related kidney disease: Clinicopathologic features, differential diagnosis, and mimics. Semin. Diagn. Pathol. 2024, 41, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maritati, F.; Peyronel, F.; Vaglio, A. IgG4-related disease: A clinical perspective. Rheumatology 2020, 59 (Suppl. S3), iii123–iii131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weindorf, S.C.; Frederiksen, J.K. IgG4-Related Disease: A Reminder for Practicing Pathologists. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2017, 141, 1476–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carruthers, M.N.; Khosroshahi, A.; Augustin, T.; Deshpande, V.; Stone, J.H. The diagnostic utility of serum IgG4 concentrations in IgG4-related disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akahoshi, K.; Kanno, A.; Miwata, T.; Nagai, H.; Yokoyama, K.; Ikeda, E.; Ando, K.; Tamada, K.; Fukushima, N.; Lefor, A.K.; et al. Cholangiocarcinoma Resembling IgG4-related Sclerosing Cholangitis. Intern. Med. 2023, 62, 3495–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löhr, J.-M.; Beuers, U.; Vujasinovic, M.; Alvaro, D.; Frøkjær, J.B.; Buttgereit, F.; Capurso, G.; Culver, E.L.; de-Madaria, E.; Della-Torre, E.; et al. European Guideline on IgG4-related digestive disease—UEG and SGF evidence-based recommendations. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2020, 8, 637–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ming, B.; Zhong, J.; Dong, L. Role of eosinophilia in IgG4-related disease. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2022, 40, 1038–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, Z.S.; Mattoo, H.; Carruthers, M.; Mahajan, V.S.; Della Torre, E.; Lee, H.; Kulikova, M.; Deshpande, V.; Pillai, S.; Stone, J.H. Plasmablasts as a biomarker for IgG4-related disease, independent of serum IgG4 concentrations. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccocioppo, R.; De Marchi, G.; Zuliani, V.; Adamo, A.; Amodio, A.; Campagnola, P.; Gabrieletto, E.M.; de Pretis, N.; Ugel, S.; Delfino, P.; et al. Circulating IgG4+ Plasmablast Count as a Diagnostic Tool in Autoimmune Pancreatitis. Gastro Hep Adv. 2022, 1, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floreani, A.; Okazaki, K.; Uchida, K.; Gershwin, M.E. IgG4-related disease: Changing epidemiology and new thoughts on a multisystem disease. J. Transl. Autoimmun. 2021, 4, 100074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamisawa, T.; Zen, Y.; Pillai, S.; Stone, J.H. IgG4-related disease. Lancet 2015, 385, 1460–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, V.; Zen, Y.; Chan, J.K.; Yi, E.E.; Sato, Y.; Yoshino, T.; Klöppel, G.; Heathcote, J.G.; Khosroshahi, A.; Ferry, J.A.; et al. Consensus statement on the pathology of IgG4-related disease. Mod. Pathol. 2012, 25, 1181–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Wang, H. IgG4-related digestive diseases: Diagnosis and treatment. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1278332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della-Torre, E.; Mancuso, G.; Lanzillotta, M.; Ramirez, G.A.; Arcidiacono, P.G.; Capurso, G.; Falconi, M.; Dagna, L. Urgent manifestations of immunoglobulin G(4)-related disease. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2021, 50, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Codina, A.; Martínez-Valle, F.; Pinilla, B.; López, C.; DeTorres, I.; Solans-Laqué, R.; Fraile-Rodríguez, G.; Casanovas-Martínez, A.; López-Dupla, M.; Robles-Marhuenda, Á.; et al. IgG4-Related Disease: Results From a Multicenter Spanish Registry. Medicine 2015, 94, e1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandelwal, A.; Inoue, D.; Takahashi, N. Autoimmune pancreatitis: An update. Abdom. Radiol. 2020, 45, 1359–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nista, E.C.; De Lucia, S.S.; Manilla, V.; Schepis, T.; Pellegrino, A.; Ojetti, V.; Pignataro, G.; Zileri dal Verme, L.; Franceschi, F.; Gasbarrini, A.; et al. Autoimmune Pancreatitis: From Pathogenesis to Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, C.; Dispinzieri, G.; Zucchini, N.; Invernizzi, P.; Massironi, S. Autoimmune pancreatitis: Cornerstones and future perspectives. World J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 30, 817–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheuk, W.; Bledsoe, J.R. IgG4-related lymphadenopathy. Semin. Diagn. Pathol. 2024, 41, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takanashi, S.; Kikuchi, J.; Sasaki, T.; Akiyama, M.; Yasuoka, H.; Yoshimoto, K.; Seki, N.; Sugahara, K.; Chiba, K.; Kaneko, Y.; et al. Lymphadenopathy in IgG4-related disease: A phenotype of severe activity and poor prognosis, with eotaxin-3 as a new biomarker. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 967–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzillotta, M.; Mancuso, G.; Della-Torre, E. Advances in the diagnosis and management of IgG4 related disease. BMJ 2020, 369, m1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löhr, J.-M.; Vujasinovic, M.; Rosendahl, J.; Stone, J.H.; Beuers, U. IgG4-related diseases of the digestive tract. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 19, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, H.; Mori, N.; Sato, S.; Mugikura, S.; Masamune, A.; Takase, K. American College of Rheumatology and the European League Against Rheumatism classification criteria for IgG4-related disease: An update for radiologists. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2022, 40, 876–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, Q.; Yang, F.; Gao, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, K.; Ren, L.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Clinical features of IgG4-related retroperitoneal fibrosis among 407 patients with IgG4-related disease: A retrospective study. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 767–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, M.; Kaneko, Y.; Takeuchi, T. Characteristics and prognosis of IgG4-related periaortitis/periarteritis: A systematic literature review. Autoimmun. Rev. 2019, 18, 102354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakazawa, T.; Kamisawa, T.; Okazaki, K.; Kawa, S.; Tazuma, S.; Nishino, T.; Inoue, D.; Naitoh, I.; Watanabe, T.; Notohara, K.; et al. Clinical diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis 2020: (Revision of the clinical diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis 2012). J. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Sci. 2021, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yata, M.; Suzuki, K.; Furuhashi, N.; Kawakami, K.; Kawai, Y.; Naganawa, S. Comparison of the multidetector-row computed tomography findings of IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis and extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Clin. Radiol. 2016, 71, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Nares, E.; Ángeles-Ángeles, A.; Hernandez-Molina, G. Major salivary gland enlargement in IgG4-related disease is associated with multiorgan involvement and higher basal disease activity. Mod. Rheumatol. 2020, 30, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xue, M.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, Q.; Ren, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Shen, D.; Xia, C.; et al. Salivary gland involvement disparities in clinical characteristics of IgG4-related disease: A retrospective study of 428 patients. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czarnywojtek, A.; Agaimy, A.; Pietrończyk, K.; Nixon, I.J.; Vander Poorten, V.; Mäkitie, A.A.; Zafereo, M.; Florek, E.; Sawicka-Gutaj, N.; Ruchała, M.; et al. IgG4-related disease: An update on pathology and diagnostic criteria with a focus on salivary gland manifestations. Virchows Arch. 2024, 484, 381–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Chen, Y.; Sun, Z.-P.; Cai, Z.-G.; Li, T.-T.; Zhang, L.; Huang, M.-X.; Hua, H.; Li, M.; Hong, X.; et al. Clinicopathological characteristics of immunoglobulin G4-related sialadenitis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.; Andrew, N.H.; McNab, A.A.; Selva, D. IgG4-Related Ophthalmic Disease: Pooling of Published Cases and Literature Review. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2015, 15, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, Z.S.; Deshpande, V.; Stone, J.H. Ophthalmic manifestations of IgG4-related disease: Single-center experience and literature review. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2014, 43, 806–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, H.K.; Lee, Y.S.; Yang, S.-W.; Lee, J.; Kwok, S.-K.; Ju, J.H.; Kim, W.-U.; Park, S.-H. Clinical outcomes and pathological characteristics of immunoglobulin G4-related ophthalmic disease versus orbital inflammatory pseudotumor. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2019, 34, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogabe, Y.; Ohshima, K.; Azumi, A.; Takahira, M.; Kase, S.; Tsuji, H.; Yoshikawa, H.; Nakamura, T. Location and frequency of lesions in patients with IgG4-related ophthalmic diseases. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2014, 252, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyoda, K.; Oba, H.; Kutomi, K.; Furui, S.; Oohara, A.; Mori, H.; Sakurai, K.; Tsuchiya, K.; Kan, S.; Numaguchi, Y. MR imaging of IgG4-related disease in the head and neck and brain. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2012, 33, 2136–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginat, D.T.; Freitag, S.K.; Kieff, D.; Grove, A.; Fay, A.; Cunnane, M.; Moonis, G. Radiographic Patterns of Orbital Involvement in IgG4-Related Disease. Ophthal. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2013, 29, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Jin, X.; Guan, L.; Lin, X.; Li, X.; Li, Y. IgG4-Related Disease With Gastrointestinal Involvement: Case Reports and Literature Review. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 816830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.X.; Della-Torre, E.; Stone, J.H.; Clark, S.W. IgG4-related hypertrophic pachymeningitis: Clinical features, diagnostic criteria, and treatment. JAMA Neurol. 2014, 71, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melenotte, C.; Seguier, J.; Ebbo, M.; Kaphan, E.; Bernit, E.; Saillier, L.; Audoin, B.; Feyeux, D.; Daniel, L.; Roche, P.-H.; et al. Clinical presentation, treatment and outcome of IgG4-related pachymeningitis: From a national case registry and literature review. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2019, 49, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapkota, B.; Rampure, R.; Gokden, M.; Kanuru, S. IgG4-Related Disease Presenting as Hypertrophic Pachymeningitis. Cureus 2022, 14, e21850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della-Torre, E.; Passerini, G.; Furlan, R.; Roveri, L.; Chieffo, R.; Anzalone, N.; Doglioni, C.; Zardini, E.; Sabbadini, M.G.; Franciotta, D. Cerebrospinal fluid analysis in immunoglobulin G4-related hypertrophic pachymeningitis. J. Rheumatol. 2013, 40, 1927–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, Y.; Aoe, K.; Mimura, Y. Pleural effusion related to IgG4. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2019, 25, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, R.; Ebbo, M.; Habert, P.; Daniel, L.; Briantais, A.; Chanez, P.; Gaubert, J.Y.; Schleinitz, N. Thoracic manifestations of IgG4-related disease. Respirology 2023, 28, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, K.; Saleh, M.; Kakakhel, M.; Yasin, H.; Ali, Y.; Rehman, H.U.; Saeed, U. Diagnostic Dilemma: IgG4-Related Sclerosing Mesenteritis Mimicking an Abdominal Malignancy Enveloping the Superior Mesenteric Artery. Cureus 2024, 16, e58480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danford, C.J.; Lin, S.C.; Wolf, J.L. Sclerosing Mesenteritis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 114, 867–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minato, H.; Shimizu, J.; Arano, Y.; Saito, K.; Masunaga, T.; Sakashita, T.; Nojima, T. IgG4-related sclerosing mesenteritis: A rare mesenteric disease of unknown etiology. Pathol. Int. 2012, 62, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoni, M.; Giani, A.; Tozzini, S.; Di Natale, M.E. Sclerosing Mesenteritis as an Uncommon Site of Involvement of IgG4-Related Disease: A Case Report With an Updated Review of the Literature. Cureus 2022, 14, e25041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, A.; Manabe, T.; Takizawa, N.; Ueki, T.; Yamada, D.; Nagayoshi, K.; Sadakari, Y.; Fujita, H.; Nagai, S.; Yamamoto, H.; et al. IgG4-related sclerosing mesenteritis causing bowel obstruction: A case report. Surg. Case Rep. 2016, 2, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.-W.; Sultan, K.S. Sclerosing Mesenteritis Causing Chylous Ascites and Small Bowel Perforation. Am. J. Case Rep. 2017, 18, 696–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyronel, F.; Vaglio, A. IgG4-Related Kidney Disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2023, 18, 994–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katerji, R.; Smoller, B.R. Immunoglobulin-G4–related skin disease. Clin. Dermatol. 2021, 39, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernia, F.; Cirella, L.; Calvisi, G.; Viscido, A.; Latella, G. Immunoglobulin G4-Related Disease of the Intestine: A Clinicopathological Entity to Be Considered. Medicina 2024, 60, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccone, F.; Ciccone, A.; Di Ruscio, M.; Vernia, F.; Cipolloni, G.; Coletti, G.; Calvisi, G.; Frieri, G.; Latella, G. IgG4-Related Disease Mimicking Crohn’s Disease: A Case Report and Review of Literature. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2018, 63, 1072–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minaga, K.; Watanabe, T.; Chung, H.; Kudo, M. Autoimmune hepatitis and IgG4-related disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 2308–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arase, Y.; Matsumoto, K.; Anzai, K.; Tsuruya, K.; Sugiyama, S.; Yoshihara, S.; Hirose, S.; Uojima, H.; Hidaka, H.; Nakazawa, T.; et al. Clinicopathological Features of Autoimmune Hepatitis with IgG4-Positive Plasma Cell Infiltration. Dig. Dis. 2020, 39, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, L. IgG4-related autoimmune hepatitis: A case report. J. Int. Med. Res. 2023, 51, 03000605231164003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashi, B.; Khosroshahi, A. IgG4-Related Disease with Emphasis on Its Gastrointestinal Manifestation. Gastroenterol. Clin. North Am. 2019, 48, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyabe, K.; Zen, Y.; Cornell, L.D.; Rajagopalan, G.; Chowdhary, V.R.; Roberts, L.R.; Chari, S.T. Gastrointestinal and Extra-Intestinal Manifestations of IgG4–Related Disease. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 990–1003.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawada, H.; Czech, T.; Silangcruz, K.; Kozai, L.; Obeidat, A.; Wien, E.A.; Nishimura, M.F.; Nishikori, A.; Sato, Y.; Nishimura, Y. Clinicopathological characteristics of gastric IgG4-related disease: Systematic scoping review. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 37, 1865–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masterman, B.; Zhang, Y.; Pauling, J.D.; Zeino, Z. IgG4-related disease presenting with gastric outlet obstruction. BMJ Case Rep. 2024, 17, e259997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ino, K.; Arinuma, Y.; Akiya, M.; Kajita, S.; Okina, S.; Sakamoto, J.; Tanaka, T.; Matsueda, Y.; Wada, T.; Tanaka, S.; et al. IgG4-related disease complicated with diffuse and chronic gastrointestinal inflammation leading to small intestinal perforation. Mod. Rheumatol. Case Rep. 2024, 8, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, C.; Sun, R.; Zhang, W.; Peng, Y. Gastrointestinal: A case of IgG4-related disease involving intestinal tract and orbital cavity. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 38, 1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshidome, Y.; Mizoguchi, A.; Narimatsu, K.; Takahashi, S.; Hirata, D.; Ono, S.; Onoyama, Y.; Suzuki, S.; Horiuchi, T.; Chiya, N.; et al. Immunoglobulin G4-related disease accompanying a small intestinal ulcer: A case. DEN Open 2022, 2, e76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skorus, U.; Kenig, J.; Mastalerz, K. IgG4-related disease manifesting as an isolated gastric lesion- a literature review. Pol. Przegl. Chir. 2018, 90, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.X.; De Petris, G.; Nguyen, B.D. Usefulness of PET/CT imaging in systemic IgG4-related sclerosing disease. A report of three cases. JOP 2011, 12, 297–305. [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka, R.; Kano, M.; Hayashi, H.; Hanari, N.; Gunji, H.; Hayano, K.; Matsubara, H. Probable IgG4-related sclerosing disease presenting as a gastric submucosal tumor with an intense tracer uptake on PET/CT: A case report. Surg. Case Rep. 2016, 2, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadi, S.K.; Parihar, A.S.; Kumar, R.; Singh, H.; Mittal, B.R.; Bal, A.; Sinha, S.K. IgG4-Related Disease Simulating Carcinoma Colon With Diffuse Peritoneal Carcinomatosis on 18F-FDG PET/CT. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2018, 43, e247–e249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazale, A.; Chari, S.T.; Zhang, L.; Smyrk, T.C.; Takahashi, N.; Levy, M.J.; Topazian, M.D.; Clain, J.E.; Pearson, R.K.; Petersen, B.T.; et al. Immunoglobulin G4-associated cholangitis: Clinical profile and response to therapy. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.S.; Montgomery, E.A. Are tumefactive lesions classified as sclerosing mesenteritis a subset of IgG4-related sclerosing disorders? J. Clin. Pathol. 2008, 61, 1093–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archer, S.; Pereira-Guedes, T.; Fonseca, T.; Carvalho Sá, D.; Pedroto, I. A Rare Cause of Abdominal Pain: IgG4-Related Sclerosing Mesenteritis. J. Gastrointest. Liver Dis. 2023, 32, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de los Angeles Mejías Manzano, M.; Trigo Salado, C.; Serrano Jiménez, M.; Parada Blázquez, M.J.; Leo Carnerero, E. IgG4-related sclerosing mesenteritis, a rare condition that causes abdominal pain. Rev. Esp. Enferm. Dig. 2018, 110, 201–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozono, M.; Tanoue, S.; Kiyama, K.; Jikuya, K.; Kawahira, M.; Hinokuchi, M.; Iwaya, H.; Arima, S.; Hashimoto, S.; Hiwatashi, K.; et al. A case of immunoglobulin G4-related sclerosing mesenteritis without other organ involvement. Clin. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 14, 1411–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitakis, G.; Chwalisz, B.K. The neurology of IGG4-related disease. J. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 424, 117420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryasit, O.; Tiraset, N.; Preechawai, P.; Kayasut, K.; Sanghan, N.; Sittivarakul, W. IgG4-related disease in patients with idiopathic orbital inflammation. BMC Ophthalmol. 2021, 21, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, K.; Yajima, R.; Seki, N.; Abe, A.; Yamamoto, M.; Takahashi, H.; Himi, T. A study of infraorbital nerve swelling associated with immunoglobulin G4 Mikulicz’s disease. Mod. Rheumatol. 2014, 24, 798–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, G.; Wang, M.; Tian, Y.; Chen, F.; Chen, B.; Wu, H. Novel Advances in the Study of IgG4-Related Disease in the Eye and Ocular Adnexa. Ophthalmic Res. 2022, 65, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrew, N.; Kearney, D.; Selva, D. IgG4-related orbital disease: A meta-analysis and review. Acta Ophthalmol. 2013, 91, 694–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, H.; Takahira, M.; Azumi, A.; Japanese Study Group for IgG4-Related Ophthalmic Disease. Diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related ophthalmic disease. Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 59, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersten, R.; Trampert, D.C.; Herta, T.; Hubers, L.M.; Maillette de Buy Wenniger, L.J.; Verheij, J.; van de Graaf, S.F.J.; Beuers, U. IgG4-related cholangitis—A mimicker of fibrosing and malignant cholangiopathies. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 1502–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, A.; Tazuma, S.; Okazaki, K.; Nakazawa, T.; Inui, K.; Chiba, T.; Takikawa, H. Clinical Features, Response to Treatment, and Outcomes of IgG4-Related Sclerosing Cholangitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 15, 920–926.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazawa, T.; Ohara, H.; Sano, H.; Ando, T.; Joh, T. Schematic classification of sclerosing cholangitis with autoimmune pancreatitis by cholangiography. Pancreas 2006, 32, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, K.; Tada, M.; Isayama, H.; Yamamoto, K.; Mizuno, S.; Yagioka, H.; Yashima, Y.; Sasaki, T.; Kogure, H.; Togawa, O.; et al. Endoscopic evaluation of factors contributing to intrapancreatic biliary stricture in autoimmune pancreatitis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2010, 71, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naitoh, I.; Kamisawa, T.; Tanaka, A.; Nakazawa, T.; Kubota, K.; Takikawa, H.; Unno, M.; Masamune, A.; Kawa, S.; Nakamura, S.; et al. Clinical characteristics of immunoglobulin IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis: Comparison of cases with and without autoimmune pancreatitis in a large cohort. Dig. Liver Dis. 2021, 53, 1308–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naitoh, I.; Nakazawa, T. Classification and Diagnostic Criteria for IgG4-Related Sclerosing Cholangitis. Gut Liver 2022, 16, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, W.R.; Lau, N.-S.; Fadia, M.; Gananadha, S. IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis mimicking cholangiocarcinoma. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2023, 2023, rjad621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh Thong, P.; Dang Luu, V.; Tra My, T.-T.; Xuan Hien, N.; Anh Tuan, T.; Minh Duc, N. IgG4-Related Sclerosing Cholangitis Mimicking Cholangiocarcinoma. Case Rep. Oncol. 2021, 14, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, H.K.; Bhat, S.J.; Panigrahi, M.K.; Chouhan, I.; Kumar, C.; Samal, S.C. IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis— A great mimicker. Indian J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 39, 614–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonstra, K.; Culver, E.L.; de Buy Wenniger, L.M.; van Heerde, M.J.; van Erpecum, K.J.; Poen, A.C.; van Nieuwkerk, K.M.J.; Spanier, B.W.M.; Witteman, B.J.M.; Tuynman, H.A.R.E.; et al. Serum immunoglobulin G4 and immunoglobulin G1 for distinguishing immunoglobulin G4-associated cholangitis from primary sclerosing cholangitis. Hepatology 2014, 59, 1954–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccagno, A.; Grosser, B.; Füzesi, L.; Konukiewitz, B.; Vlasenko, D.; Weckermann, D.; Raab, S.; Zenk, J.; Agaimy, A.; Märkl, B. IgG4-related pseudotumours: A series of 12 cases and a review of the literature. Pathology 2022, 54, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velegraki, M.; Vardas, E.; Dervenis, C.; Fragaki, M.; Nikolaou, P.; Mpitouli, A.; Kazamias, G.; Sepsa, A.; Giannikaki, E.; Paspatis, G.A. IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis: Not always an obvious entity. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2021, 34, 594–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Cheng, F. IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis: A case report. Asian J. Surg. 2023, 46, 2878–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazale, A.; Chari, S.T.; Smyrk, T.C.; Levy, M.J.; Topazian, M.D.; Takahashi, N.; Clain, J.E.; Pearson, R.K.; Pelaez-Luna, M.; Petersen, B.T.; et al. Value of serum IgG4 in the diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis and in distinguishing it from pancreatic cancer. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 102, 1646–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vosskuhl, K.; Negm, A.A.; Framke, T.; Weismüller, T.; Manns, M.P.; Wedemeyer, H.; Plentz, R.R.; Wedemeyer, J.; Lankisch, T.O. Measurement of IgG4 in bile: A new approach for the diagnosis of IgG4-associated cholangiopathy. Endoscopy 2012, 44, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meena, B.L.; Verma, N.; De, A.; Taneja, S.; Singh, V. IgG4-Related Sclerosing Cholangitis with Cholecystitis Mimicking Cholangiocarcinoma: A Case Report. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2022, 12, 1012–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granito, A.; Muratori, P.; Quarneti, C.; Pappas, G.; Cicola, R.; Muratori, L. Antinuclear antibodies as ancillary markers in primary biliary cirrhosis. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2012, 12, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, S.-W.; Fan, C.-S.; Yen, H.-H.; Huang, S.-P.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Su, P.-Y. A retrospective study of prevalence and pattern of international consensus on ANA patterns among patients with hepatitis C virus infection. PeerJ 2022, 10, e14200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Hu, T.; Song, X.; Nie, H.; Chen, M.; Chen, W.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, D.; Hu, H.; Hu, P.; et al. Production of Autoantibodies in Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection Is Associated with the Augmented Function of Blood CXCR5+CD4+ T Cells. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itazaki, Y.; Einama, T.; Konno, F.; Fujinuma, I.; Takihata, Y.; Iwasaki, T.; Ogata, S.; Tsujimoto, H.; Ueno, H.; Kishi, Y. IgG4-related hepatic inflammatory pseudotumor mimicking cholangiolocellular carcinoma. Clin. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 14, 1733–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motor, J.; Gajewska, A.; Cienkowski, K.; Langner, S.; Durko, Ł.; Malecka-Wojciesko, E. IgG4-related disease—Focus on digestive system involvement. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1584107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokala, A.; Khalili, K.; Menezes, R.; Hirschfield, G.; Jhaveri, K.S. Comparative MRI Analysis of Morphologic Patterns of Bile Duct Disease in IgG4-Related Systemic Disease Versus Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2014, 202, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlachou, P.A.; Khalili, K.; Jang, H.-J.; Fischer, S.; Hirschfield, G.M.; Kim, T.K. IgG4-related sclerosing disease: Autoimmune pancreatitis and extrapancreatic manifestations. Radiographics 2011, 31, 1379–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazawa, T.; Ohara, H.; Sano, H.; Aoki, S.; Kobayashi, S.; Okamoto, T.; Imai, H.; Nomura, T.; Joh, T.; Itoh, M. Cholangiography can discriminate sclerosing cholangitis with autoimmune pancreatitis from primary sclerosing cholangitis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2004, 60, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zheng, Z.; Wu, X.; Guo, T.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Wu, D.; Yang, A. Biliary inflammation scoring for immunoglobulin G4-related sclerosing cholangitis: An endoscopic approach with endoscopic ultrasound. Surg. Endosc. 2021, 35, 7068–7073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Moura, D.T.H.; Ryou, M.; de Moura, E.G.H.; Ribeiro, I.B.; Bernardo, W.M.; Thompson, C.C. Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration and Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography-Based Tissue Sampling in Suspected Malignant Biliary Strictures: A Meta-Analysis of Same-Session Procedures. Clin. Endosc. 2020, 53, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakazawa, T.; Naitoh, I.; Hayashi, K. Usefulness of Intraductal Ultrasonography in the Diagnosis of Cholangiocarcinoma and IgG4-Related Sclerosing Cholangitis. Clin. Endosc. 2012, 45, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barresi, L.; Tacelli, M.; Crinò, S.F.; Attili, F.; Petrone, M.C.; De Nucci, G.; Carrara, S.; Manfredi, G.; Capurso, G.; De Angelis, C.G.; et al. Multicentric Italian survey on daily practice for autoimmune pancreatitis: Clinical data, diagnosis, treatment, and evolution toward pancreatic insufficiency. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2020, 8, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurram, S.A.; Fernando, M.; Smith, A.T.; Hunter, K.D. IgG4-related sclerosing disease clinically mimicking oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2013, 115, e48–e51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Li, W.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Gao, Y.; Sun, Z.-P.; Peng, X.; Su, J.-Z.; et al. Treatment of immunoglobulin G4-related sialadenitis: Outcomes of glucocorticoid therapy combined with steroid-sparing agents. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2018, 20, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Feng, R.; Chen, Y.; Duan, M.; Wang, M.; Jin, Z.; Rumboldt, Z.; Zhang, Z. CT features and pathologic characteristics of IgG4-related systemic disease of submandibular gland. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 16111–16116. [Google Scholar]
- Marcus, K.S.; Hoffman, H.T.; Rajan KD, A. Not All Küttner Tumors Are IgG4-Related Disease (IgG4-RD). Head Neck Pathol. 2021, 15, 1322–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinnon, T.; Randazzo, W.T.; Kim, B.D.; Biddinger, P.; Forseen, S. IgG4-Related Disease Presenting as a Solitary Neck Mass. J. Radiol. Case Rep. 2015, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, H.; Kanematsu, M.; Watanabe, H.; Mizuta, K.; Aoki, M. Salivary gland tumors of the parotid gland: CT and MR imaging findings with emphasis on intratumoral cystic components. Neuroradiology 2014, 56, 789–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawano, M. IgG4-related Disease: Recent Topics on Immunological Aspects of This Disorder and Their Application in New Treatment Strategies. Intern. Med. 2025, 64, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puxeddu, I.; Capecchi, R.; Carta, F.; Tavoni, A.G.; Migliorini, P.; Puxeddu, R. Salivary Gland Pathology in IgG4-Related Disease: A Comprehensive Review. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 6936727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshifuji, H.; Umehara, H. Glucocorticoids in the treatment of IgG4-related disease—Prospects for new international treatment guidelines. Mod. Rheumatol. 2023, 33, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimoto, M.; Takagi, T.; Suzuki, R.; Konno, N.; Watanabe, K.; Nakamura, J.; Kikuchi, H.; Waragai, Y.; Asama, H.; Takasumi, M.; et al. Efficacy of Steroid Pulse Therapy for Autoimmune Pancreatitis Type 1: A Retrospective Study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backhus, J.; Neumann, C.; Perkhofer, L.; Schulte, L.A.; Mayer, B.; Seufferlein, T.; Müller, M.; Kleger, A. A Follow-Up Study of a European IgG4-Related Disease Cohort Treated with Rituximab. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zongfei, J.; Lingli, C.; Ying, S.; Lingying, M.; Lijuan, Z.; Dongmei, L.; Xiaomin, D.; Yingyong, H.; Huiyong, C.; Lili, M.; et al. Clinical and pathological predictors of relapse in IgG4-related disease. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2022, 24, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
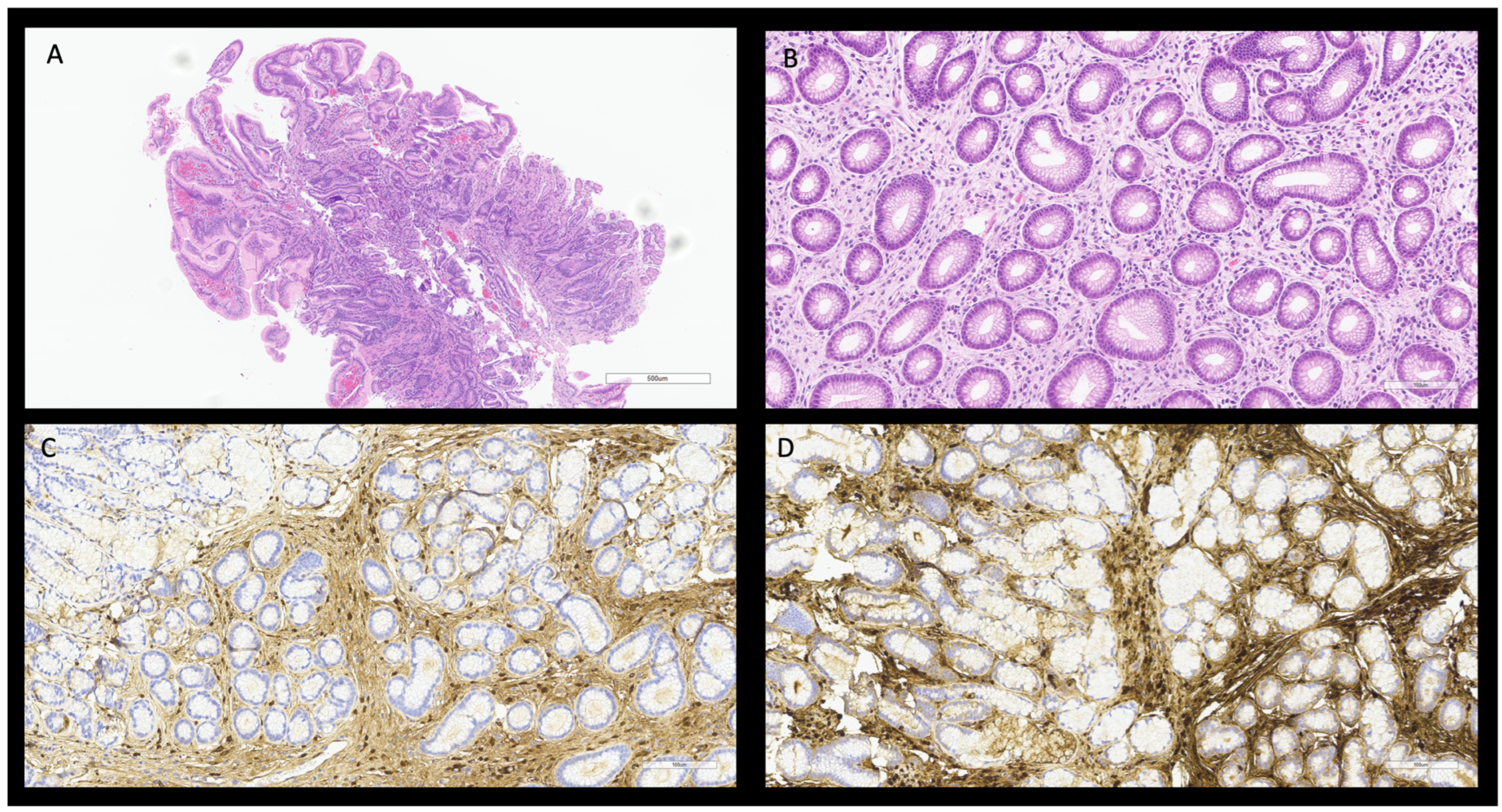
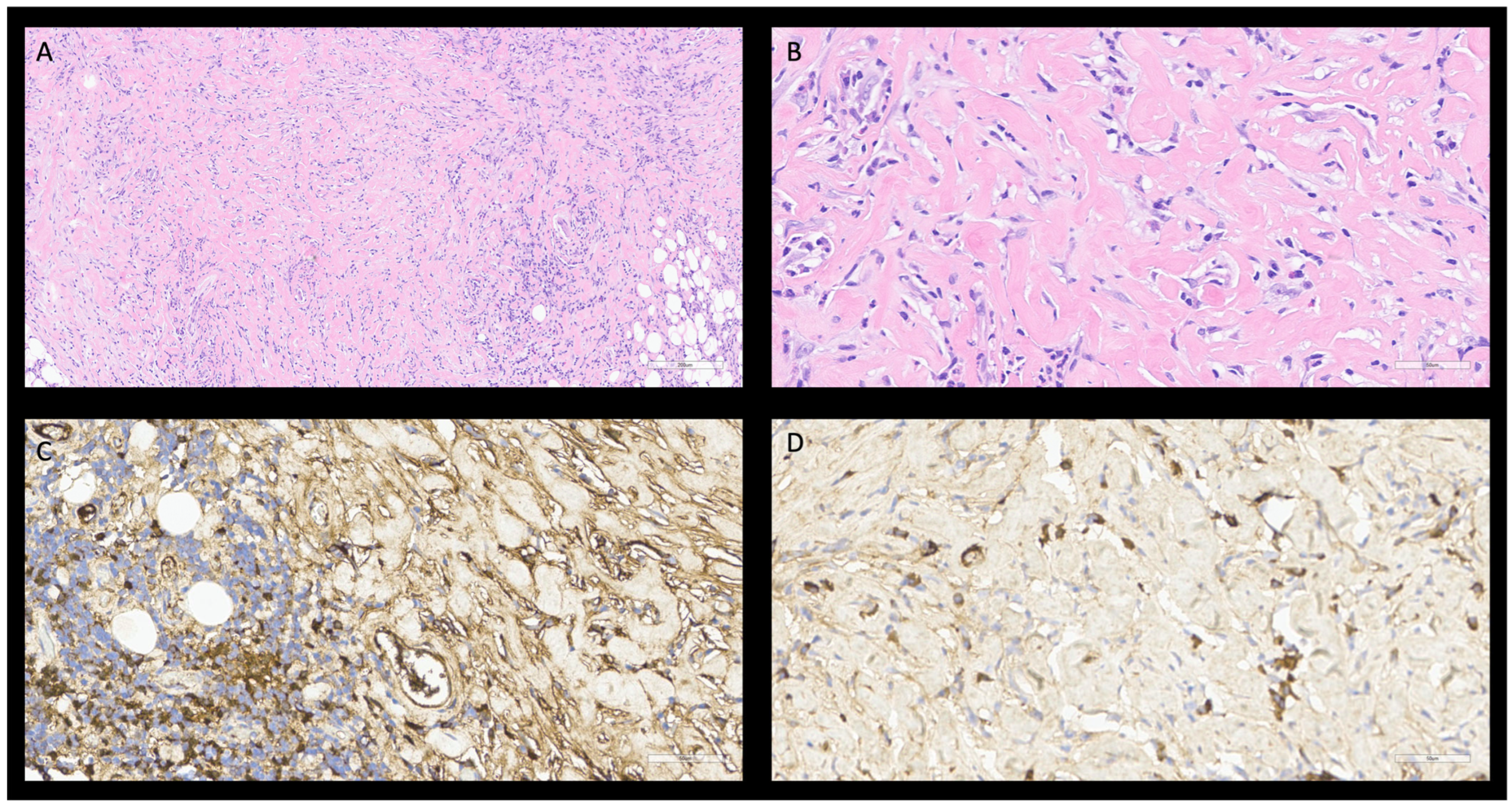
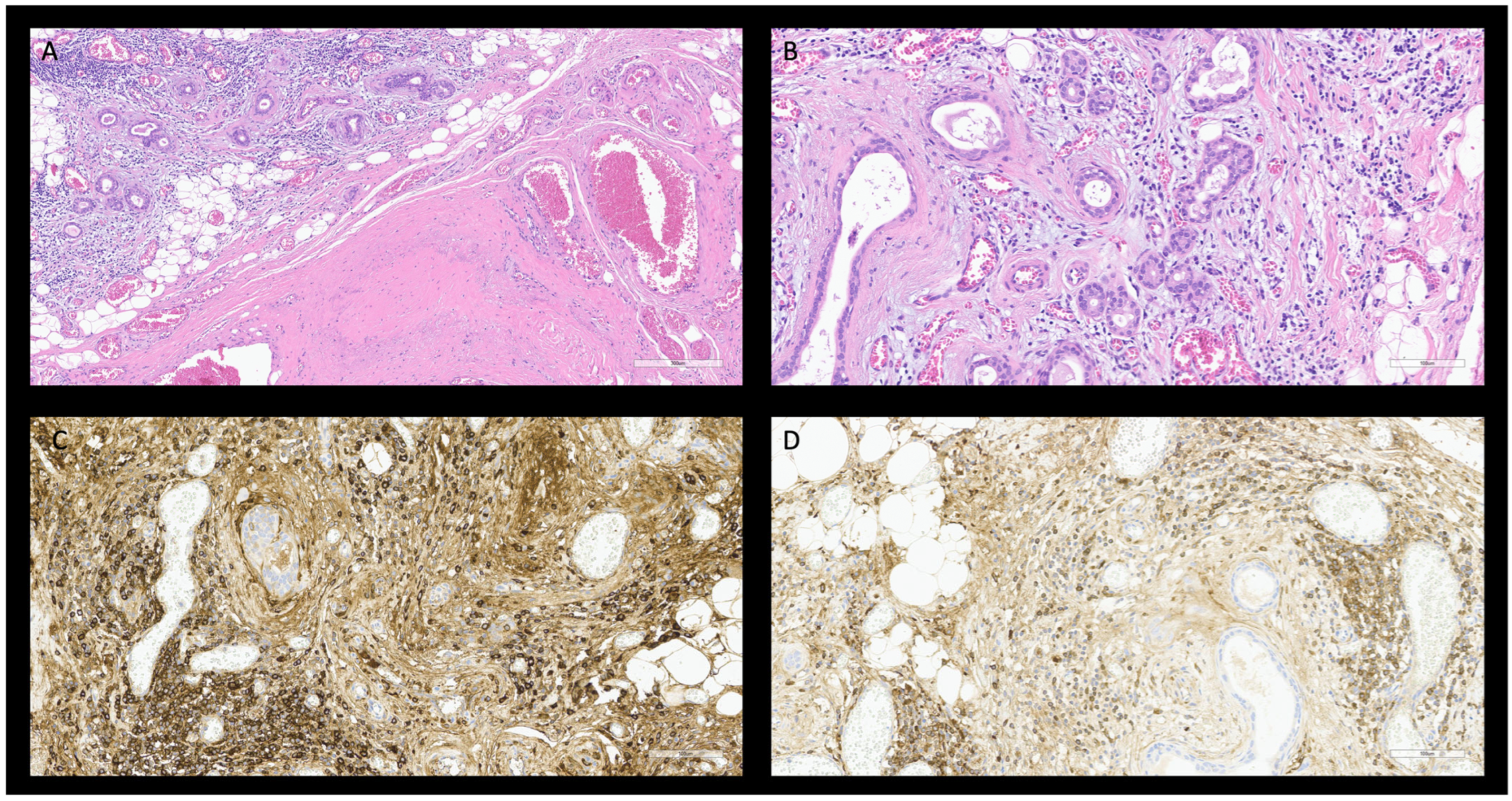

| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical presentation | Hyperemesis, diarrhea and stypsis, proptosis, symptoms relapse after steroid withdrawal. | Asthenia, loss of appetite, weight loss, jaundice. | Mild xerostomia, suspicious submandibular mass. |
| Serology | IgG4: 334 mg/dL, CRP 10–30 mg/dL. ANA negative TSH 1 UI/L. | IgG4 157 mg/dL, CRP 10–30 mg/dL. ANA negative. Bilirubin 7.85 mg/dL. | IgG4 24 mg/dL (after surgery). ANA negative. |
| Imaging | Abdomen CT: ascites, pleural effusion, thickened bowel with strictures. Brain and Abdomen MRI: ascites, bowel strictures, gastric wall thickening with signs of pachymeningitis 18FDG-PET/CT: Gastric, colonic and bone marrow uptake. | Abdomen CT: mass-forming, infiltrative lesion surrounding the main bile duct (3.5 cm diameter), satellite lesions to gallbladder and right lung, highly suspicious for metastatic cholangiocarcinoma. 18FDG-PET/CT: Not performed. | US: mass-forming expansive lesion of submandibular gland (2.5 cm diameter), satellite lymph nodes, suspicious for adenocarcinoma. 18FDG-PET/CT: mild head–neck lymphnode uptake. |
| Other tests | CSF: mild protein increase. EGDS: signs of nonspecific chronic gastropathy. Colonoscopy: signs of nonspecific chronic colitis. Explorative laparoscopy: bowel wall and omental thickening, mesenterial nodule (3 cm diameter). | ERCP and EUS: Confirmed lesion of main bile duct. Explorative laparoscopy: firm, woody, infiltrative lesion at the hepatoduodenal ligament involving vascular structures. | Surgery: Sialoadenectomy. |
| Pathology | Colon biopsy: nonspecific chronic colitis. Laparoscopy biopsies: inflammatory peritoneal and omental fibrosclerotic nodules with no significant lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate; steroid therapy ongoing. Gastric biopsy: Chronic gastritis with fibrosis, IgG4 plasma cells > 10× HPF, IgG4/IgG > 0.4. | EUS-FNB: No malignant cell, presence of nonspecific fibroconnective tissue. Intraoperative biopsy: storiform fibrosis and phlebitis with IgG4 plasma cells > 10× HPF, IgG4/IgG > 0.4. Negative for cholangiocarcinoma. | Submandibular gland histology: storiform fibrosis and phlebitis with IgG4 plasma cells ≈ 95–105× HPF, IgG4/IgG > 0.4. Negative for adenocarcinoma. |
| Therapy | Steroid pulses and rituximab | Steroid pulses and rituximab | Adenectomy |
| Outcome | Symptoms solved; gastric biopsy fully restored | Mass reduced; symptoms solved | No other sign of disease |
| Involved Site | Symptoms Related to the Involved Site | Possible Misdiagnosis | Serology | Imaging | Pathology | Other Commonly Performed Tests |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lymphnode [20,27,28,29] | Asymptomatic Single or multiple lymphadenopathy Local compression symptoms | Lymphoma Metastatic neoplasms Multicentric Castleman disease | ANA, RF negative RDSAbs negative IgG4 >135 mg/dL, usually >350 mg/dL IgG4/IgG ratio >10% IgG4/IgG1 ratio >24% | US: multiple lymphadenopathy. CT: lymphadenopathy (1–3 cm) with homogeneous contrast enhancement. PET-CT: 18FDG lymphadenopathy uptake. | Histology: Storiform fibrosis Obliterative phlebitis. Dense lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate. Immunophenotype: IgG4 plasm-cells > 50 cell/HPF IgG4/IgG ratio > 40%. | Electrophoresis: negative for monoclonal component. BMB: negative for lymphoproliferative disease. |
| Pancreas [14,20,29,30,31] | Diarrhea Weight loss Jaundice Diabetes | Pancreatic malignancy Other pancreatitis Lymphoma | ANA, RF negative RDSAbs negative Anti-SPINK1, antilactoferrin, anti-carbonic-anidrase II, anti-trypsinogen may be positive IgG4 > 135 mg/dL, usually >350 mg/dL IgG4/IgG ratio > 10% IgG4/IgG1 ratio > 24% | CT: pancreas enlargement with “sausage-like” shape, main duct stricture, no upstream dilation, edematous peripancreatic fat tissue and capsule-like rim. Delayed contrast enhancement. MRI: like CT with lower T1 SI with loss of pancreas lobulation, higher T2 SI, impeded water diffusion signal. Delayed contrast enhancement. PET-CT: patchy increase of 18FDG uptake. | Histology: Storiform fibrosis Obliterative phlebitis Dense lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate. Immunophenotype: Biopsy: IgG4 plasm-cells > 10 cell/HPF. IgG4/IgG ratio > 40%. Surgical specimen: IgG4 plasm-cell > 50 cell/HPF. IgG4/IgG ratio > 40%. | US: pancreas enlargement, with low echogenicity. EUS: diffuse or focal hypoechoic pancreas enlargement, hyperechoic strands and foci, parenchyma lobularity, hyperechoic wall of the main pancreatic duct, narrowing of the main pancreatic duct, duct-penetrating sign. MRCP and ERCP: Long main pancreas duct narrowing with no upstream dilation, skipped narrowed lesions, narrowing branches. |
| Retroperitoneal [20,29,31,32,33] | Asymptomatic Lower back pain Abdomen pain Lymphadenopathy | Retroperitoneal malignancy Lymphoma Multicentric Castleman disease Aortic vasculitis | ANA, RF negative RDSAbs negative IgG4 > 99 mg/dL, usually around 450 mg/dL IgG4/IgG ratio > 10% IgG4/IgG1 ratio > 24% | CT: retroperitoneal mass-forming lesions with homogeneous delayed phase contrast enhancement, usually in perivascular areas, hydroureteronephrosis, aortitis with aneurismal lesions or stenosing lesions. MRI: High T2 SI as in edema and inflammation. PET-CT: increase of 18FDG uptake in active disease areas. | Histology: Storiform fibrosis Obliterative phlebitis. Dense lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate. Immunophenotype: IgG4 plasm-cell > 30 cell/HPF. IgG4/IgG ratio > 40%. | |
| Biliary ducts [20,21,29,34,35] | Diarrhea Weight loss Jaundice | Cholangiocarcinoma Primitive sclerosing cholangitis | ANA, RF negative RDSAbs negative IgG4 > 135 mg/dL IgG4/IgG ratio > 10% IgG4/IgG1 ratio > 24% | CT: diffuse or long-segmental bile duct stricture, with funnel image and bile duct concentric thickening. Single-layered late phase contrast enhancement [35]. MRI: thicker bile ducts wall with contrast enhancement, without liver lesion. PET-CT: usually not performed. | Histology: Storiform fibrosis Obliterative phlebitis. Dense lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate. Immunophenotype: Biopsy: IgG4 plasm-cells > 10 cell/HPF. IgG4/IgG ratio > 40%. Surgical specimen: IgG4 plasm-cell > 50 cell/HPF. IgG4/IgG ratio > 40%. | Bile IgG4 levels 13 mg/dL. EUS: Regular homogeneous bile duct wall thickening can involve the cystic duct and the gallbladder. MRCP and ERCP: funnel-shaped, long-segmental stenosis. |
| Salivary [20,29,36,37,38,39] | Asymptomatic Monolateral or bilateral mass-forming lesions Xerostomia | Benign head–neck diseases Salivary neoplasms Sjögren Syndrome Lymphomas | ANA, RF negative RDSAbs negative IgG4 > 135 mg/dL IgG4/IgG ratio > 10% IgG4/IgG1 ratio > 24% | CT: bilateral asymmetric salivary gland swelling with regular borders and homogeneous or crazy-paving appearance at contrast enhanced imaging. Rarely suspicious infiltrating pattern. | Histology: Storiform fibrosis with acinar atrophy Obliterative phlebitis. Dense lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate. Immunophenotype: Biopsy: IgG4 positive plasm-cells > 10 cell/HPF. IgG4/IgG ratio > 40%. Surgical specimen: IgG4 positive plasm-cell > 100 cell/HPF. IgG4/IgG ratio > 40%. | US: homogeneous bilateral asymmetric salivary gland swelling. |
| Lacrimal gland [20,29,40,41,42] | Upper eyelid swelling Xeropthalmia Xerostomia (synchronous salivary involvement) | Sjögren Syndrome | ANA, RF negative RDSAbs negative IgG4 > 135 mg/dL IgG4/IgG ratio > 10% IgG4/IgG1 ratio > 24% | CT: enlargement of lacrimal gland, often symmetrical, usually homogeneous with contrast enhancement. Nodular lesions may be evident in the gland. | Histology: Storiform fibrosis with acinar atrophy Obliterative phlebitis. Dense lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate. Immunophenotype: IgG4 positive plasm-cells > 40–100 cell/HPF. IgG4/IgG ratio > 40%. | |
| Retrobulbar involvement [29,40,43,44,45,46] | Diplopia Proptosis Eyelid swelling Eye movement impairment | Hyperthyroidism Sjögren Syndrome Lymphoma | ANA, RF negative RDSAbs negative IgG4 > 135 mg/dL IgG4/IgG ratio > 10% IgG4/IgG1 ratio > 24% | CT: mass-forming, pseudotumoral lesions with infiltration of retrobulbar fat tissue, or infiltration of EOM. Infiltration of supraorbital or infraorbital nerves. | Histology: Storiform fibrosis Obliterative phlebitis. Lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate. Immunophenotype: Biopsy IgG4 positive plasm-cells > 10 cell/HPF. IgG4/IgG ratio > 40%. | |
| Meninges [20,29,44,47,48,49,50] | Headache Ataxia Seizures Cognitive impairment Intracranial hypertension Vascular compression Nerve compression | Meningioma Glial neoplasms Lymphoma Dementia | ANA, RF negative RDSAbs negative IgG4 > 135 mg/dL, usually >200 mg/dL IgG4/IgG ratio > 10% IgG4/IgG1 ratio > 24% | CT: linear thickening or mass-forming meningioma-like lesion of dura mater. MRI: dura mater thickening with diffuse T2-hypointensity and hyperintense spots, T1 contrast enhancement, meningioma-like mass-forming lesions. | Histology: Storiform fibrosis Obliterative phlebitis. Lymphoplasmacytic and mild eosinophilic infiltrate. Immunophenotype: IgG4 plasm-cells > 10 cell/HPF. IgG4/IgG ratio > 40%. | CSF: mild protein increase, lymphocytosis, intrathecal production of oligoclonal IgG4 bands during active phase. |
| Chest involvement [20,29,51,52] | Asymptomatic Chest pain Asthenia Dyspnea Fever Cough Hemoptysis Asthma | Interstitial lung diseases Sarcoidosis Malignancy Connective tissue diseases Rheumatoid arthritis Multicentric Castleman Disease | ANA < 1:160, RF negative RDSAbs negative IgG4 > 135 mg/dL IgG4/IgG ratio > 10% IgG4/IgG1 ratio > 24% | Thorax Rx: pleural effusion CT: pleural thickening, pleural effusion, bronchial wall thickening, interstitial lung disease (with either ground-glass, reticular nodular or peri bronchial pattern), mediastinal adenopathy. PET-CT: increased 18FDG uptake in other organs. | Histology: Storiform fibrosis (may be absent) Obliterative phlebitis (may be absent), arteritis Lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate. Immunophenotype: Lung biopsy: IgG4 plasm-cells > 20 cell/HPF. IgG4/IgG ratio > 40%. Lung surgical specimen IgG4 plasm-cell > 50 cell/HPF. IgG4/IgG ratio > 40%. Pleural specimen: IgG4 plasm-cell > 50 cell/HPF. IgG4/IgG ratio > 40%. Mediastinal biopsy: IgG4 plasm-cell > 30 cell/HPF. IgG4/IgG ratio > 40%. | Pleural liquid: slight increase in IgG4 and adenosine deaminase. Pleural liquid cytology: negative for malignant cells. |
| Sclerosing mesenteritis [29,53,54,55,56,57,58] | Asymptomatic Weight loss Diarrhea or stypsis Abdominal pain Ascites Bowel obstruction | Chronic infective disease Neoplastic diseases with or without carcinomatosis Lymphoma Multicentric Castleman disease Other edema causes | ANA, RF negative RDSAbs negative IgG4 > 135 mg/dL IgG4/IgG ratio > 10% IgG4/IgG1 ratio > 24% | CT: increased mesenterial fat tissue density, well-defined, non-infiltrating mass-forming lesions. MRI: masses with signs of fibrosis or edema in T2 weighted images. PET-CT: mild increased 18FDG uptake areas suspicious for malignancy. | Histology: Storiform fibrosis, fat necrosis Obliterative phlebitis. Dense lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate. Immunophenotype: IgG4 plasm-cells > 40–100 cell/HPF. IgG4/IgG ratio > 40%. | US: well-defined intrabdominal masses, no splenomegaly. |
| Kidney [9,20,29,31,59] | Proteinuria, sometimes with nephrotic syndrome Progressive kidney function loss Acute kidney injury or failure | Systemic lupus erythematosus Sjögren related nephropathy ANCA-vasculitis Kidney malignancy Other tubular interstitial nephritis causes (drugs, infection, myeloma) Multicentric Castleman’s disease | ANA positive 30% cases, RF negative Anti-PLA2R may be positive RDSAbs negative Low serum C3 and C4 Blood eosinophilia IgG4 > 135 mg/dL IgG4/IgG ratio > 10% IgG4/IgG1 ratio > 24% | CT: low-contrast enhanced low-density lesions. Lesions with mass-forming pattern, bilateral cortex nodulations, wedgy pattern or patchy pattens. Whole kidney enlargement. Renal pelvis thickening. MRI: mass-forming lesions, low-iso T1 signal intensity, T2 signal intensity inversely proportional to fibrosis, mild or none contrast enhancement. PET-CT: 18FDG uptake area in other organs. | Histology: Storiform fibrosis with tubular atrophy or acute interstitial nephritis associated with dense lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate. Membranous glomerulonephritis with IgG4 deposits. Rarely arteritis or phlebitis. Immunophenotype: Biopsy IgG4 positive plasm-cells > 10 cell/HPF. Surgical specimen IgG4 positive plasm-cell > 30 cell/HPF. IgG4/IgG ratio > 40% (sometimes can be missing). | US: ill-defined areas of low echogenicity, diffuse kidney swelling. |
| Skin [20,29,60] | Red or brown swelling nodule or plaques or masses, frequently at head neck region. Psoriasis like lesions | Kimura disease Angio-lymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia Eosinophilic angiocentric fibrosis Granuloma faciale Cutaneous plasmacytosis Multicentric Castleman disease | ANA, RF negative RDSAbs negative IgG4 > 135 mg/dL IgG4/IgG ratio > 10% IgG4/IgG1 ratio > 24% | CT: signs of other organ involvement. PET-CT: signs of other organ involvement. | Histology Storiform fibrosis Obliterative phlebitis. Dense lymphoplasmacytic and eosinophilic infiltrate. Immunophenotype: IgG4 plasm-cell > 200 cell/HPF. IgG4/IgG ratio > 40%. | |
| Gastroenteric tract [29,46,61,62] | Asymptomatic or abdominal pain Nausea and vomit Stypsis or diarrhea | IBDs or other colitis Malignancy | ANA, RF negative RDSAbs negative IgG4 > 135 mg/dL, usually 350 mg/dL IgG4/IgG ratio > 10% IgG4/IgG1 ratio > 24% | CT and MRI: mass-forming lesions, focal or diffuse gastroenteric wall thickening, sub-stenosis, gastric and bowel nodules. PET-CT: diffuse 18FDG uptake, corresponding to active disease sites. | Histology Storiform fibrosis patches. Obliterative phlebitis. Bottom heavy lymphoplasmacytic infiltration. Immunophenotype: IgG4 plasm-cells > 10–50 cell/HPF. IgG4/IgG ratio > 40–50%. | Endoscopy submucosal mass or chronic mucosal inflammation, sometimes with ulceration or polypoid lesions. |
| Liver (non-cholangitis involvement) [20,29,63,64,65] | Dysgeusia Abdomen distension Generalized edema Liver failure | Other causes of cirrhosis Autoimmune hepatitis | ANA may be present, RF negative ASMA may be positive RDSAbs negative GOT, GPT, GGT increased IgG4 > 135 mg/dL IgG4/IgG ratio > 10% IgG4/IgG1 ratio > 24% | CT hepatic mass-forming lesions, liver cirrhosis and portal hypertension signs. MRI liver cirrhosis, portal hypertension signs, no bile ducts abnormalities. MCRP no bile ducts abnormalities. | Histology Fibrosis, portal inflammation, interface hepatitis, confluent necrosis, rosette formation. Obliterative phlebitis. Dense lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate. Immunophenotype: Biopsy IgG4 plasm-cells > 10 cell/HPF. IgG4/IgG ratio > 40%. Surgical specimen IgG4 plasm-cell > 50 cell/HPF. IgG4/IgG ratio > 40%. | ERCP no bile ducts abnormalities. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sina, S.; Bonisoli, G.L.; Vitale, S.; Marzano, L.; Crinò, S.F.; Conti Bellocchi, M.C.; Boninsegna, S.; Conci, S.; Maiolini, F.; Nocini, R.; et al. Clinicopathological Pearls and Diagnostic Pitfalls in IgG4-Related Disease: Challenging Case Series and Literature Review. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2299. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15182299
Sina S, Bonisoli GL, Vitale S, Marzano L, Crinò SF, Conti Bellocchi MC, Boninsegna S, Conci S, Maiolini F, Nocini R, et al. Clinicopathological Pearls and Diagnostic Pitfalls in IgG4-Related Disease: Challenging Case Series and Literature Review. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(18):2299. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15182299
Chicago/Turabian StyleSina, Sokol, Giulio Luigi Bonisoli, Sofia Vitale, Luigi Marzano, Stefano Francesco Crinò, Maria Cristina Conti Bellocchi, Sara Boninsegna, Simone Conci, Federica Maiolini, Riccardo Nocini, and et al. 2025. "Clinicopathological Pearls and Diagnostic Pitfalls in IgG4-Related Disease: Challenging Case Series and Literature Review" Diagnostics 15, no. 18: 2299. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15182299
APA StyleSina, S., Bonisoli, G. L., Vitale, S., Marzano, L., Crinò, S. F., Conti Bellocchi, M. C., Boninsegna, S., Conci, S., Maiolini, F., Nocini, R., Sacchetto, L., Barbera, G., Fior, A., Kalaja, N., Malloggi, E., Brighenti, A., Parisi, A., Cardobi, N., Scarpa, A., ... Tinazzi, E. (2025). Clinicopathological Pearls and Diagnostic Pitfalls in IgG4-Related Disease: Challenging Case Series and Literature Review. Diagnostics, 15(18), 2299. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15182299









