Predictive Value of Serum HMGB1, NF-κB, and IL-17 Gene Expression in Acute Pancreatitis Outcomes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
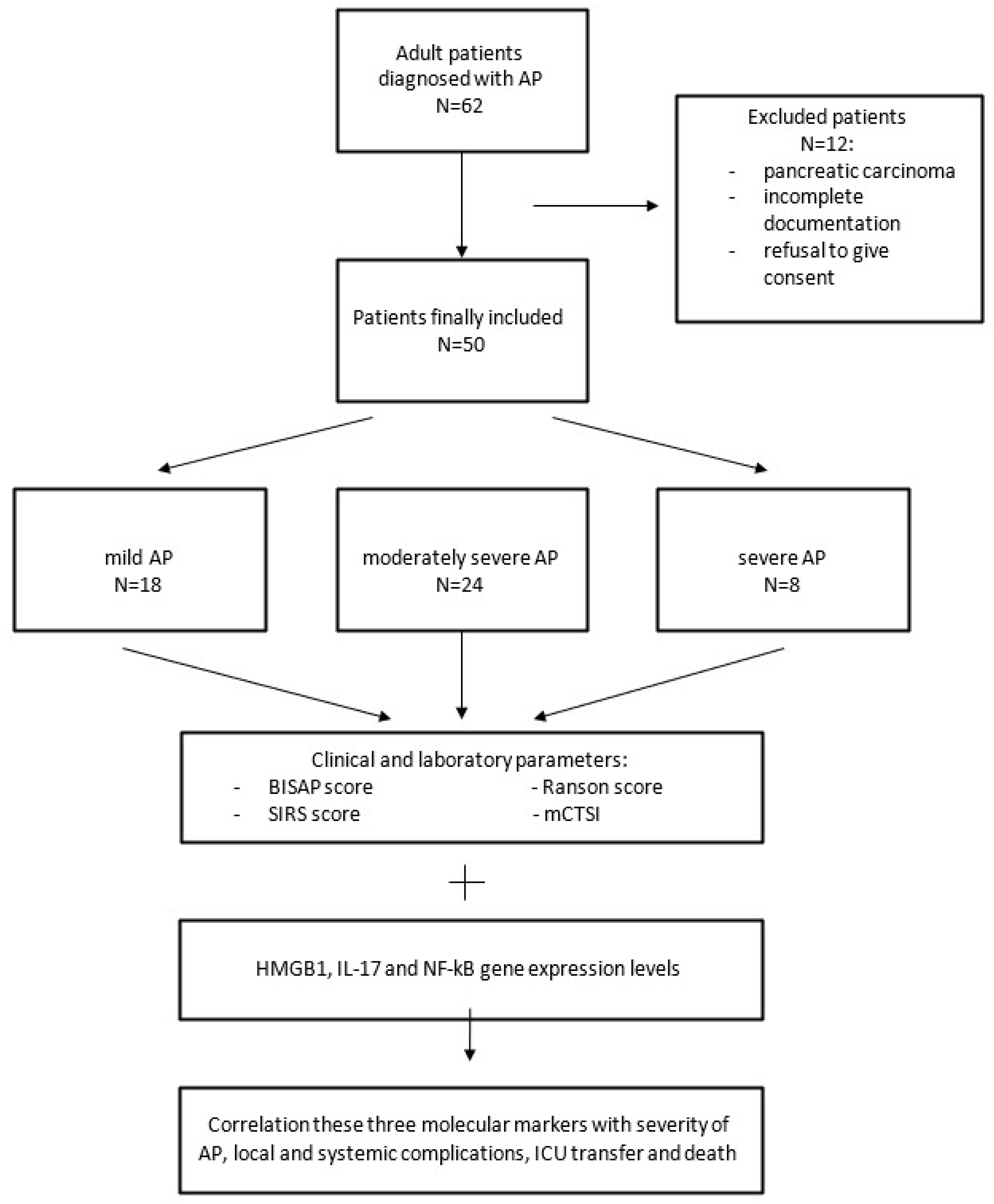
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. Isolation of RNA from Patient Serum
2.3. Reverse Transcription
2.4. Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)
2.5. Statistical Analysis
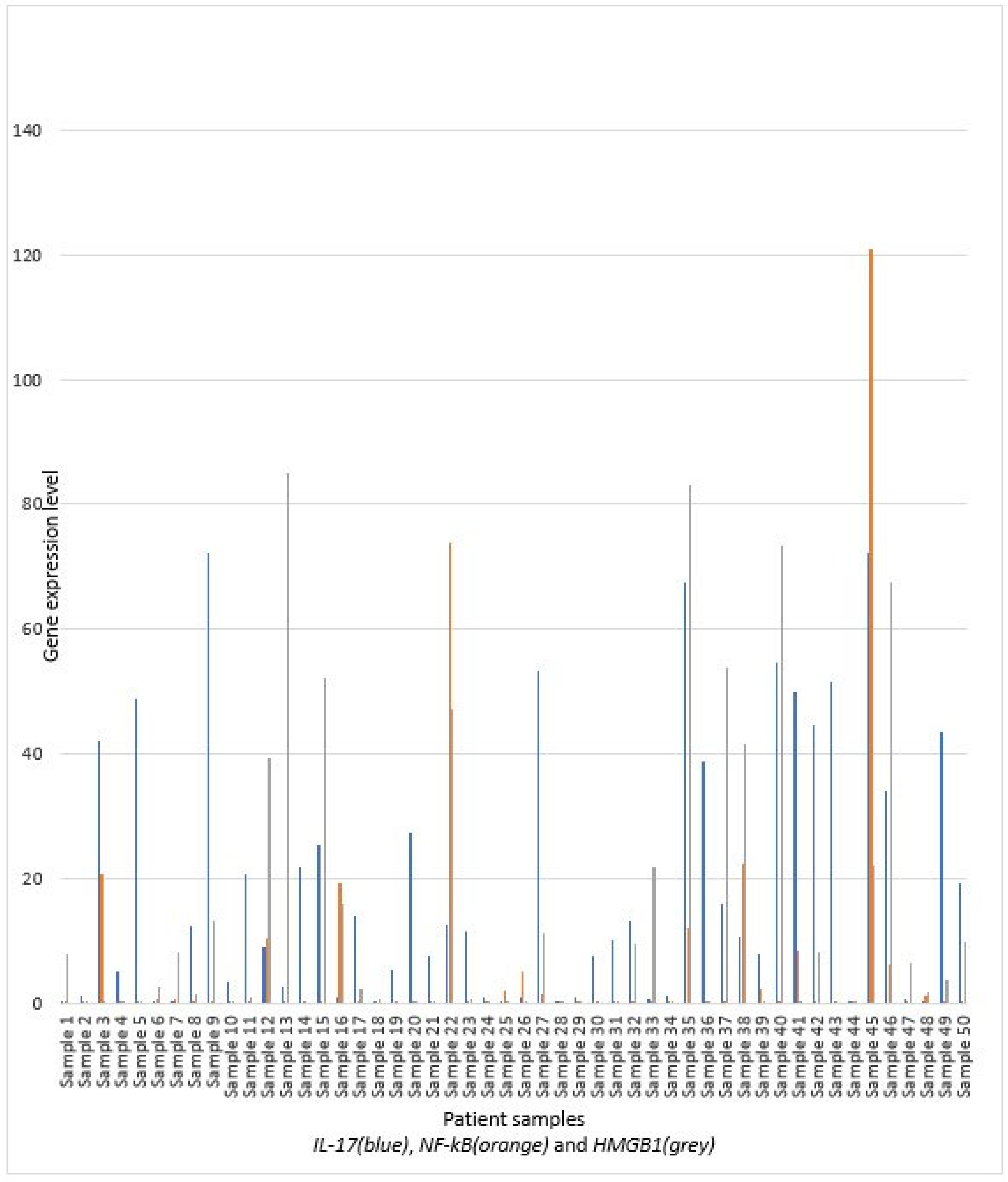
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marshall, J.C.; Cook, D.J.; Christou, N.V.; Bernard, G.R.; Sprung, C.L.; Sibbald, W.J. Multiple organ dysfunction score: A reliable descriptor of a complex clinical outcome. Crit. Care Med. 1995, 23, 1638–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, P.A.; Bollen, T.L.; Dervenis, C.; Gooszen, H.G.; Johnson, C.D.; Sarr, M.G.; Tsiotos, G.G.; Vege, S.S.; Acute Pancreatitis Classification Working Group. Classification of acute pancreatitis—2012: Revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus. Gut 2013, 62, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerem, E.; Kurtcehajic, A.; Kunosić, S.; Malkočević, D.Z.; Zerem, O. Current trends in acute pancreatitis: Diagnostic and therapeutic challenges. World J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 29, 2747–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva-Vaz, P.; Abrantes, A.M.; Castelo-Branco, M.; Gouveia, A.; Botelho, M.F.; Tralhão, J.G. Multifactorial Scores and Biomarkers of Prognosis of Acute Pancreatitis: Applications to Research and Practice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.H.; Kim, T.N.; Kim, K.H. Comparison of scoring systems in predicting the severity of acute pancreatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 2387–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papachristou, G.I.; Muddana, V.; Yadav, D.; O’connell, M.; Sanders, M.K.; Slivka, A.; Whitcomb, D.C. Comparison of BISAP, Ranson’s, APACHE-II, and CTSI scores in predicting organ failure, complications, and mortality in acute pancreatitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 105, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gukovsky, I.; Gukovskaya, A. Nuclear factor-κB in pancreatitis: Jack-of-all-trades, but which one is more important? Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mofidi, R.; Duff, M.D.; Wigmore, S.J.; Madhavan, K.K.; Garden, O.J.; Parks, R. Association between early systemic inflammatory response, severity of multiorgan dysfunction and death in acute pancreatitis. Br. J. Surg. 2006, 93, 738–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikó, A.; Vigh, É.; Mátrai, P.; Soós, A.; Garami, A.; Balaskó, M.; Czakó, L.; Mosdósi, B.; Sarlós, P.; Erőss, B.; et al. Computed Tomography Severity Index vs. Other Indices in the Prediction of Severity and Mortality in Acute Pancreatitis: A Predictive Accuracy Meta-analysis. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Huang, Z.; Li, H.; Song, B.; Yuan, F. Evaluation of extrapancreatic inflammation on abdominal computed tomography as an early predictor of organ failure in acute pancreatitis as defined by the revised Atlanta classification. Medicine 2017, 96, e6517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.J.; Kim, H.M.; Choi, J.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Cho, J.H. Comparison of Predictive Systems in Severe Acute Pancreatitis According to the Revised Atlanta Classification. Pancreas 2016, 45, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pooran, N.; Indaram, A.; Singh, P.; Bank, S. Cytokines (IL-6, IL-8, TNF): Early and reliable predictors of severe acute pancreatitis. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2003, 37, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, N.; Yan, C.; Zhang, G. Changes of Serum Procalcitonin (PCT), C-Reactive Protein (CRP), Interleukin-17 (IL-17), Interleukin-6 (IL-6), High Mobility Group Protein-B1 (HMGB1) and D-Dimer in Patients with Severe Acute Pancreatitis Treated with Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT) and Its Clinical Significance. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 5881–5886. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dai, S.R.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.B. Serum interleukin 17 as an early prognostic biomarker of severe acute pancreatitis receiving continuous blood purification. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2015, 38, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, F.; Zhuang, M.; Fei, S. The relationship between inflammatory cytokines and in-hospital complications of acute pancreatitis. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2024, 12, e1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternby, H.; Hartman, H.; Thorlacius, H.; Regnér, S. The Initial Course of IL1β, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IL-12, IFN-γ and TNF-α with Regard to Severity Grade in Acute Pancreatitis. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoun, E.; Chen, J.; Reighard, D.; Gleeson, F.C.; Whitcomb, D.C.; Papachristou, G.I. Diagnostic Accuracy of Interleukin-6 and Interleukin-8 in Predicting Severe Acute Pancreatitis: A Meta-Analysis. Pancreatology 2009, 9, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieminen, A.; Maksimow, M.; Mentula, P.; Kyhälä, L.; Kylänpää, L.; Puolakkainen, P.; Kemppainen, E.; Repo, H.; Salmi, M. Circulating cytokines in predicting development of severe acute pancreatitis. Crit. Care 2014, 18, R104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte-Rojo, A.; Suazo-Barahona, J.; Ramírez-Iglesias, M.T.; Uscanga, L.F.; Robles-Díaz, G. Time Frames for Analysis of Inflammatory Mediators in Acute Pancreatitis: Improving Admission Triage. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2009, 54, 2282–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Kudo, M.; Strober, W. Immunopathogenesis of pancreatitis. Mucosal Immunol. 2017, 10, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, R. Update on innate immunity and perspectives on metabolite regulation in acute pancreatitis. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2016, 32, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Jin, S.; Pan, J.; Lin, Q.; Yang, S.; Ambe, P.C.; Basharat, Z.; Zimmer, V.; Wang, W.; Hong, W. Damage associated molecular patterns and neutrophil extracellular traps in acute pancreatitis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 927193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Zheng, Z.; Duan, J.; Wang, X.; Wu, S.; Wang, W.; Xu, L.; Han, S.; Qiao, Z. Quantitation of nuclear factor kappa B activation in pancreatic acinar cells during rat acute pancreatitis by flow cytometry. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 10143–10151. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Ji, B.; Han, B.; Ernst, S.A.; Simeone, D.; Logsdon, C.D. NF-κB activation in pancreas induces pancreatic and systemic inflammatory response. Gastroenterology 2002, 122, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotze, M.T.; Tracey, K.J. High-mobility group box 1 protein (HMGB1): Nuclear weapon in the immune arsenal. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsung, A.; Tohme, S.; Billiar, T.R. High-mobility group box-1 in sterile inflammation. J. Intern. Med. 2014, 276, 425–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arriaga-Pizano, L.; Boscó-Gárate, I.; Martínez-Ordaz, J.L.; Wong-Baeza, I.; Gutiérrez-Mendoza, M.; Sánchez-Fernandez, P.; López-Macías, C.; Isibasi, A.; Pelaez-Luna, M.; Cérbulo-Vázquez, A.; et al. High Serum Levels of High-Mobility Group Box 1 (HMGB1) and Low Levels of Heat Shock Protein 70 (Hsp70) are Associated with Poor Prognosis in Patients with Acute Pancreatitis. Arch. Med. Res. 2018, 49, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundén-Cullberg, J.; Norrby-Teglund, A.; Rouhiainen, A.; Rauvala, H.; Herman, G.; Tracey, K.J.; Lee, M.L.; Andersson, J.; Tokics, L.; Treutiger, C.J. Persistent elevation of high mobility group box-1 protein (HMGB1) in patients with severe sepsis and septic shock. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 33, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, H.; Matsuda, T.; Hashimoto, S.; Amaya, F.; Kitamura, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Kobayashi, A.; Maruyama, I.; Yamada, S.; Hasegawa, N.; et al. Contributions of High Mobility Group Box Protein in Experimental and Clinical Acute Lung Injury. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 170, 1310–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocsis, Á.; Szabolcs, A.; Hofner, P.; Takács, T.; Farkas, G.; Boda, K.; Mándi, Y. Plasma Concentrations of High-Mobility Group Box Protein 1, Soluble Receptor for Advanced Glycation End-Products and Circulating DNA in Patients with Acute Pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2009, 9, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, U.; Wang, H.; Palmblad, K.; Aveberger, A.-C.; Bloom, O.; Erlandsson-Harris, H.; Janson, A.; Kokkola, R.; Zhang, M.; Yang, H.; et al. High Mobility Group 1 Protein (Hmg-1) Stimulates Proinflammatory Cytokine Synthesis in Human Monocytes. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 192, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Wu, X.; Yang, L.; He, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jin, X.; Yuan, H. TLR4-mediated NF-κB signaling pathway mediates HMGB1-induced pancreatic injury in mice with severe acute pancreatitis. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 37, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakonczay, Z.; Hegyi, P.; Takacs, T.; McCarroll, J.; Saluja, A.K. The role of NF- B activation in the pathogenesis of acute pancreatitis. Gut 2007, 57, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawra, R.; Sah, R.P.; Dudeja, V.; Rishi, L.; Talukdar, R.; Garg, P.; Saluja, A.K. Intra-acinar Trypsinogen Activation Mediates Early Stages of Pancreatic Injury but Not Inflammation in Mice with Acute Pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 2210–2217.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hietaranta, A.J.; Saluja, A.K.; Bhagat, L.; Singh, V.P.; Song, A.M.; Steer, M.L. Relationship between NF-κB and Trypsinogen Activation in Rat Pancreas after Supramaximal Caerulein Stimulation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 280, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tando, Y.; Algül, H.; Schneider, G.; Weber, C.K.; Weidenbach, H.; Adler, G.; Schmid, R.M. Induction of IκB-Kinase by Cholecystokinin Is Mediated by Trypsinogen Activation in Rat Pancreatic Lobules. Digestion 2002, 66, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakkampudi, A.; Jangala, R.; Reddy, B.R.; Mitnala, S.; Reddy, D.N.; Talukdar, R. NF-κB in acute pancreatitis: Mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Pancreatology 2016, 16, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cua, D.J.; Tato, C.M. Innate IL-17-Producing Cells: The Sentinels of the Immune System. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Chen, H.; Liu, L.; Xiao, P.; Xie, Y.; Geng, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, T.; Tan, H.; et al. Role of Interleukin-17 in Acute Pancreatitis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 674803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora-Ruíz, M.D.; Blanco-Favela, F.; Rueda, A.K.C.; Legorreta-Haquet, M.V.; Chávez-Sánchez, L. Role of interleukin-17 in acute myocardial infarction. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 107, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Qiao, Q.; Liu, M.; He, T.; Shi, J.; Bai, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Cai, W.; Han, S.; et al. IL-17 Promotes Scar Formation by Inducing Macrophage Infiltration. Am. J. Pathol. 2018, 188, 1693–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettelli, E.; Korn, T.; Oukka, M.; Kuchroo, V.K. Induction and Effector Functions of T(H)17 Cells. Nature 2008, 453, 1051–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, J.; Ren, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, X.; Xia, L.; Lu, N. The Role of Neutrophils and Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Acute Pancreatitis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 8, 565758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, R.; Chen, Y.; Qi, M.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Z.; Xu, H.; Yuan, Y.; Nie, H.; Zhou, T.; et al. Increased frequency of circulating Tfh cells in patients with acute pancreatitis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2018, 11, 5300–5308. [Google Scholar]
- Yasuda, T.; Ueda, T.; Takeyama, Y.; Shinzeki, M.; Sawa, H.; Nakajima, T.; Ajiki, T.; Fujino, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Kuroda, Y. Significant Increase of Serum High-Mobility Group Box Chromosomal Protein 1 Levels in Patients with Severe Acute Pancreatitis. Pancreas 2006, 33, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.-F.; Guo, M.; Tian, Z.-Q.; Wu, G.-Z.; Zou, X.-P.; Zhang, W.-J. Increased of serum high-mobility group box chromosomal protein 1 correlated with intestinal mucosal barrier injury in patients with severe acute pancreatitis. World J. Emerg. Surg. 2014, 9, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wang, B.; Cai, S.; Liu, P. The Role of Serum High Mobility Group Box 1 and Interleukin-6 Levels in Acute Pancreatitis: A Meta-Analysis. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaffidi, P.; Misteli, T.; Bianchi, M.E. Release of chromatin protein HMGB1 by necrotic cells triggers inflammation. Nature 2002, 418, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, E.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Z.; Xue, D.; Zhang, W. Association between high mobility group box-1 protein expression and cell death in acute pancreatitis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 15, 4021–4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawa, H.; Ueda, T.; Takeyama, Y.; Yasuda, T.; Shinzeki, M.; Nakajima, T.; Kuroda, Y. Blockade of high mobility group box-1 protein attenuates experimental severe acute pancreatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 7666–7670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhan, E.; Türkyılmaz, S.; Erçin, C.; Kural, B.V.; Flinte, D. Does nuclear factor-kappa B in peripheral mononuclear cells have a prognostic role during acute necrotizing pancreatitis in rats? Eur. Surg. Res. 2012, 48, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachos, S.; Tsaroucha, A.K.; Konstantoudakis, G.; Papachristou, F.; Trypsianis, G.; Schizas, D.; Vaos, G.; Simopoulos, C. Serum profiles of M30, M65 and interleukin-17 compared with C-reactive protein in patients with mild and severe acute pancreatitis. J. Hepato-Biliary-Pancreat. Sci. 2014, 21, 911–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satoh, A.; Masamune, A.; Kimura, K.; Kaneko, K.; Sakai, Y.; Yamagiwa, T.; Satoh, M.; Kikuta, K.; Asakura, T.; Shimosegawa, T. Nuclear Factor Kappa B Expression in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells of Patients with Acute Pancreatitis. Pancreas 2003, 26, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Reilly, D.A.; Roberts, J.R.; Cartmell, M.T.; Demaine, A.G.; Kingsnorth, A.N. Heat shock factor-1 and nuclear factor-kappa B are systemically activated in human acute pancreatitis. JOP 2006, 7, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Liu, Y.; Daniluk, J.; Gaiser, S.; Chu, J.; Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Logsdon, C.D.; Ji, B. Activation of Nuclear Factor-κB in Acinar Cells Increases the Severity of Pancreatitis in Mice. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, M.D.; Moore, E.E.; Moore, F.A.; Shenkar, R.; Moine, P.; Haenel, J.B.; Abraham, E. Nuclear factor-kappa B is activated in alveolar macrophages from patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit. Care Med. 1996, 24, 1285–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moine, P.; McIntyre, R.; Schwartz, M.D.; Kaneko, D.; Shenkar, R.; Le Tulzo, Y.; Moore, E.E.; Abraham, E. NF-κB regulatory mechanisms in alveolar macrophages from patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Shock 2000, 13, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.; Mehta, D.K.; Dhanawat, M. Medicinal Plants in Cancer Treatment: Contribution of Nuclear Factor- Kappa B (NF-kB) Inhibitors. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2022, 22, 1938–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Jin, Y.; Chen, X.; Ye, X.; Shen, X.; Lin, M.; Zeng, C.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, J. NF-κB in biology and targeted therapy: New insights and translational implications. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shi, C.; Li, X.; Jiang, Y.; Mao, R. NF-κB: A mediator that promotes or inhibits angiogenesis in human diseases? Expert. Rev. Mol. Med. 2023, 25, e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.; Yuan, Y.; Qian, A.; Sun, Y.; Qiao, M. Pioglitazone, a PPAR gamma ligand, suppresses NF-kappa B activation through inhibition of Ikappa B kinase activation in caerulein-treated AR42J cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2008, 62, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.Y.; Wang, W.; Tang, J.X.; Yuan, Z.R. The adipocytokine resistin stimulates the production of proinflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-6 in pancreatic acinar cells via NF-κB activation. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2013, 36, 986–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Han, Y.; Liu, L.; Shen, W.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Cui, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, G.; Qi, R. Protective Effects and Mechanisms of G5 PAMAM Dendrimers against Acute Pancreatitis Induced by Caerulein in Mice. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Genes | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| β-actin | 5′-AAGCAGGAGTATGACGAGTCCG-3′ | 5′-GCCTTCATACATCTCAAGTTGG-3′ |
| HMGB1 | 5′-GCTCAGAGAGGTGGAAGAC-3′ | 5′-CCAATGGATAAGCCAGGAT-3′ |
| NF-kapa B | 5′-ATGGCTTCTATGAGGCTGAG-3′ | 5′-GTTGTTGTTGGTCTGGATGC-3′ |
| IL-17 | 5′-AGAGATATCCCTCTGTGATC-3′ | 5′-TACCCCAAAGTTATCTCAGG-3′ |
| N/Mean ± SD | IL-17 | p Value | NF-kB | p Value | HMGB1 | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 32 (64%) | 8.15 (16.04) | 0.176 a | 0.223 (0.805) | 0.686 a | 2.604 (11.543) | 0.396 a |
| Female | 18 (36%) | 13.17 (47.32) | 0.268 (3.007) | 0.500 (8.277) | ||||
| Duration of symptoms before hospitalization | ||||||||
| (days) | Rho | 2 (4) | 0.190 | 0.196 b | 0.129 | 0.380 | −0.135 | 0.362 |
| Age | Rho | 62.6 ± 15.6 | −0.097 | 0.504 b | 0.051 | 0.723 | −0.080 | 0.579 |
| Age 65+ | No | 24 (48%) | 14.18 (39.44) | 0.077 a | 0.167 (1.248) | 0.522 a | 2.623 (27.684) | 0.426 a |
| Yes | 26 (52%) | 7.44 (14.3) | 0.373 (1.230) | 0.716 (8.26) | ||||
| Comorbid. | No | 11 (22%) | 0.8 (10.32) | 0.081 a | 0.163 (11.341) | 0.566 a | 4.215 (12.851) | 0.266 a |
| Yes | 39 (78%) | 12.12 (35.58) | 0.355 (1.224) | 0.586 (10.247) | ||||
| Cardiovasc. Dis. | No | 13 (26%) | 3.41 (12.82) | 0.196 a | 0.263 (0.343) | 0.699 a | 3.752 (7.536) | 0.420 a |
| Yes | 37 (74%) | 11.73 (35.58) | 0.184 (1.224) | 0.586 (10.247) | ||||
| Smoking | No | 33 (66%) | 11.73 (40.7) | 0.112 a | 0.377 (4.345) | 0.108 a | 2.861 (10.218) | 0.532 a |
| Yes | 17 (34%) | 3.37 (14.23) | 0.168 (0.316) | 0.327 (4.115) | ||||
| N | IL-17 | p Value | NF-kB | p Value | HMGB1 | p Value a | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Local complications | No | 26 (52%) | 11.7 (26.38) | 0.969 | 0.359 (1.044) | 0.846 | 0.416 (4.127) | 0.162 |
| Yes | 24 (48%) | 6.57 (38.86) | 0.170 (1.983) | 4.581 (16.289) | ||||
| Ascites | No | 27 (54%) | 11.52 (14.88) | 0.553 | 0.184 (1.044) | 0.899 | 0.327 (5.096) | 0.170 |
| Yes | 23 (46%) | 10.60 (41.34) | 0.263 (2.742) | 3.752 (16.243) | ||||
| Pancreatic pseudocyst | No | 40 (80%) | 11.59 (36.31) | 0.528 | 0.360 (1.567) | 0.115 | 0.675 (6.009) | 0.127 |
| Yes | 10 (20%) | 3.99 (15.33) | 0.113 (0.248) | 9.005 (36.276) | ||||
| Pancreatic necrosis | No | 40 (80%) | 11.06 (35.54) | 0.771 | 0.27 (0.852) | 0.961 | 0.416 (4.611) | 0.007 |
| Yes | 10 (20%) | 7.73 (17.40) | 0.193 (3.027) | 11.662 (58.823) | ||||
| Abscess † | No | 49 (98%) | 11.52 (35.19) | 0.263 (1.224) | 2.437 (10.218) | |||
| Yes | 1 (2%) | 4.58 | 0.015 | 0.049 | ||||
| Systemic complications | No | 29 (58%) | 3.37 (17.4) | 0.030 | 0.184 (0.393) | 0.461 | 0.847 (8.249) | 0.930 |
| Yes | 21 (42%) | 12.12 (34.12) | 0.263 (3.015) | 2.437 (10.191) | ||||
| Pleural effusion | No | 32 (64%) | 3.39 (22.22) | 0.048 | 0.173 (0.41) | 0.130 | 0.587 (7.926) | 0.455 |
| Yes | 18 (36%) | 11.93 (34.12) | 0.552 (11.309) | 2.649 (16.278) | ||||
| Renal insuff. | No | 37 (74%) | 7.71 (35.3) | 0.304 | 0.178 (0.557) | 0.325 | 0.586 (7.604) | 0.283 |
| Yes | 13 (26%) | 12.12 (8.26) | 0.492 (3.015) | 2.861 (15.93) | ||||
| ARDS/MV + | No | 45 (90%) | 7.75 (26.87) | 0.140 | 0.168 (0.669) | 0.059 | 0.764 (8.26) | 0.253 |
| Yes | 5 (10%) | 12.12 (38.75) | 2.776 (2.57) | 2.861 (7.881) | ||||
| Transfer to ICU | No | 33 (66%) | 10.60 (35.19) | 0.767 | 0.167 (0.331) | 0.015 | 0.143 (4.153) | 0.004 |
| Yes | 17 (34%) | 11.66 (15.20) | 1.279 (16.836) | 7.692 (20.623) | ||||
| Death outcome + | No | 46 (92%) | 9.17 (35.21) | 0.436 | 0.173 (1.047) | 0.132 | 0.806 (8.26) | 0.256 |
| Yes | 4 (8%) | 11.89 (21.15) | 1.634 (6.689) | 6.378 (52.637) | ||||
| Yes | 4 (8%) | 11.89 (21.15) | 1.634 (6.689) | 6.378 (52.637) | ||||
| SIRS + | No | 42 (84%) | 8.15 (35.30) | 0.204 | 0.181 (1.044) | 0.594 | 0.675 (7.621) | 0.069 |
| Yes | 8 (16%) | 13.85 (25.67) | 0.378 (2.848) | 7.864 (31.43) |
| N | IL-17 | p Value | NF-kB | p Value | HMGB1 | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mCTSI | ||||||||
| pancreatic inflammation | Normal | 22 | 12.35 (36.26) | 0.404 b | 0.173 (1.047) | 0.741 b | 0.138 (5.096) | 0.186 b |
| Changed | 6 | 13.28 (25.4) | 0.488 (0.532) | 0.675 (0.343) | ||||
| Liquid collections | 22 | 3.99 (17.31) | 0.309 (2.685) | 4.581 (16.278) | ||||
| pancreatic necrosis | No | 40 | 11.06 (35.54) | 0.223 | 0.27 (0.852) | 0.200 | 0.416 (4.611) | 0.018 |
| ≤30% | 7 | 0.8 (17.48) | 0.091 (3.045) | 7.692 (61.371) | ||||
| >30% | 3 | 16 (38.29) | 2.776 (61.532) | 16.434 (87.58) | ||||
| pancreatic necrosis + | No | 40 | 11.06 (35.54) | 0.771 a | 0.27 (0.852) | 0.961 a | 0.416 (4.611) | 0.007 a |
| Yes | 10 | 7.73 (17.4) | 0.193 (3.027) | 11.662 (58.823) | ||||
| extrapanc. comp. | No | 24 | 12.35 (31.09) | 0.698 a | 0.27 (0.386) | 0.472 a | 0.24 (4.611) | 0.200 a |
| Yes | 26 | 9.58 (34.1) | 0.22 (3.013) | 3.307 (16.243) | ||||
| Score | Mild | 23 | 13.17 (36.26) | 0.828 b | 0.178 (1.047) | 0.866 b | 0.143 (5.096) | 0.065 b |
| Moderate | 18 | 9.58 (26.87) | 0.357 (0.613) | 0.675 (16.277) | ||||
| Severe | 9 | 3.34 (15.65) | 0.263 (3.027) | 10.318 (11.025) | ||||
| Ranson score | ||||||||
| Heavy form + | ≤3 | 41 | 11.66 (36.26) | 0.272 a | 0.263 (0.667) | 0.455 a | 0.847 (7.592) | 0.804 a |
| 4+ | 9 | 3.37 (11.44) | 0.178 (2.637) | 2.903 (22.933) | ||||
| Mortality | 2% | 21 | 13.17 (32.54) | Rho −0.105 | 0.168 (0.296) | Rho 0.175 | 0.764 (4.072) | Rho 0.101 |
| 15% | 16 | 3.39 (39.25) | 0.271 (2.118) | 0.122 (6.048) | ||||
| 40% | 11 | 7.75 (15.33) | 0.167 (16.91) | 16.377 (29.643) | ||||
| 100% | 2 | 10.11 (3.1) | 5.925 (10.865) | 1.471 (1.933) | ||||
| Bedside index (mortality) | Low | 40 | 10.60 (36.47) | 0.550 a | 0.168 (0.566) | 0.104 a | 0.586 (7.604) | 0.131 a |
| High | 10 | 11.66 (13.05) | 1.279 (11.309) | 5.409 (29.266) | ||||
| Atlanta classification | Mild | 18 | 9.61 (35.66) | 0.592 b | 0.373 (0.926) | 0.036 b | 0.24 (5.079) | 0.467 b |
| Moderate | 24 | 9.17 (30.24) | 0.097 (0.229) | 1.768 (17.953) | ||||
| Severe | 8 | 11.89 (28.53) | 2.028 (6.832) | 4.135 (11.905) | ||||
| Atlanta Moderate/Severe | No | 18 | 9.61 (35.66) | 0.372 a | 0.373 (0.926) | 0.394 a | 0.24 (5.079) | 0.934 a |
| Yes | 32 | 11.13 (30.24) | 0.151 (1.985) | 2.79 (14.607) | ||||
| Atlanta Severe + | No | 42 | 9.17 (35.21) | 0.474 a | 0.167 (0.566) | 0.044 a | 0.675 (8.26) | 0.278 a |
| Yes | 8 | 11.89 (28.53) | 2.028 (6.832) | 4.135 (11.905) |
| Area | 95% CI | p Value | Cut Off | Sn | Sp | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-17 | ||||||
| Systemic compl. | 0.681 | 0.535–0.828 | 0.030 | 3.99 | 0.810 | 0.552 |
| Pleural effusion | 0.670 | 0.521–0.820 | 0.048 | 3.99 | 0.833 | 0.531 |
| NF-kB | ||||||
| ARDS | 0.760 | 0.613–0.907 | 0.059 | 0.488 | 0.800 | 0.711 |
| ICU | 0.711 | 0.540–0.883 | 0.015 | 0.488 | 0.647 | 0.788 |
| Atlanta severe form | 0.726 | 0.534–0.919 | 0.044 | 0.488 | 0.750 | 0.738 |
| HMGB1 | ||||||
| Panc. Necrosis | 0.777 | 0.594–0.961 | 0.007 | 2.835 | 0.900 | 0.675 |
| ICU | 0.754 | 0.617–0.891 | 0.004 | 0.154 | 0.941 | 0.545 |
| SIRS | 0.705 | 0.530–0.881 | 0.068 | 2.835 | 0.750 | 0.619 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pantelić, M.; Cvetković, D.; Jovankić, J.; Soldatović, I.; Pantelić, M.; Dujović, M.; Vučinić, T.; Cvetković, A. Predictive Value of Serum HMGB1, NF-κB, and IL-17 Gene Expression in Acute Pancreatitis Outcomes. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2160. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15172160
Pantelić M, Cvetković D, Jovankić J, Soldatović I, Pantelić M, Dujović M, Vučinić T, Cvetković A. Predictive Value of Serum HMGB1, NF-κB, and IL-17 Gene Expression in Acute Pancreatitis Outcomes. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(17):2160. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15172160
Chicago/Turabian StylePantelić, Milan, Danijela Cvetković, Jovana Jovankić, Ivan Soldatović, Maša Pantelić, Miloš Dujović, Tamara Vučinić, and Aleksandar Cvetković. 2025. "Predictive Value of Serum HMGB1, NF-κB, and IL-17 Gene Expression in Acute Pancreatitis Outcomes" Diagnostics 15, no. 17: 2160. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15172160
APA StylePantelić, M., Cvetković, D., Jovankić, J., Soldatović, I., Pantelić, M., Dujović, M., Vučinić, T., & Cvetković, A. (2025). Predictive Value of Serum HMGB1, NF-κB, and IL-17 Gene Expression in Acute Pancreatitis Outcomes. Diagnostics, 15(17), 2160. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15172160







