Intraglomerular Inflammation as a Guide for Mycophenolate Mofetil-Based Treatment in IgA Nephropathy
Abstract
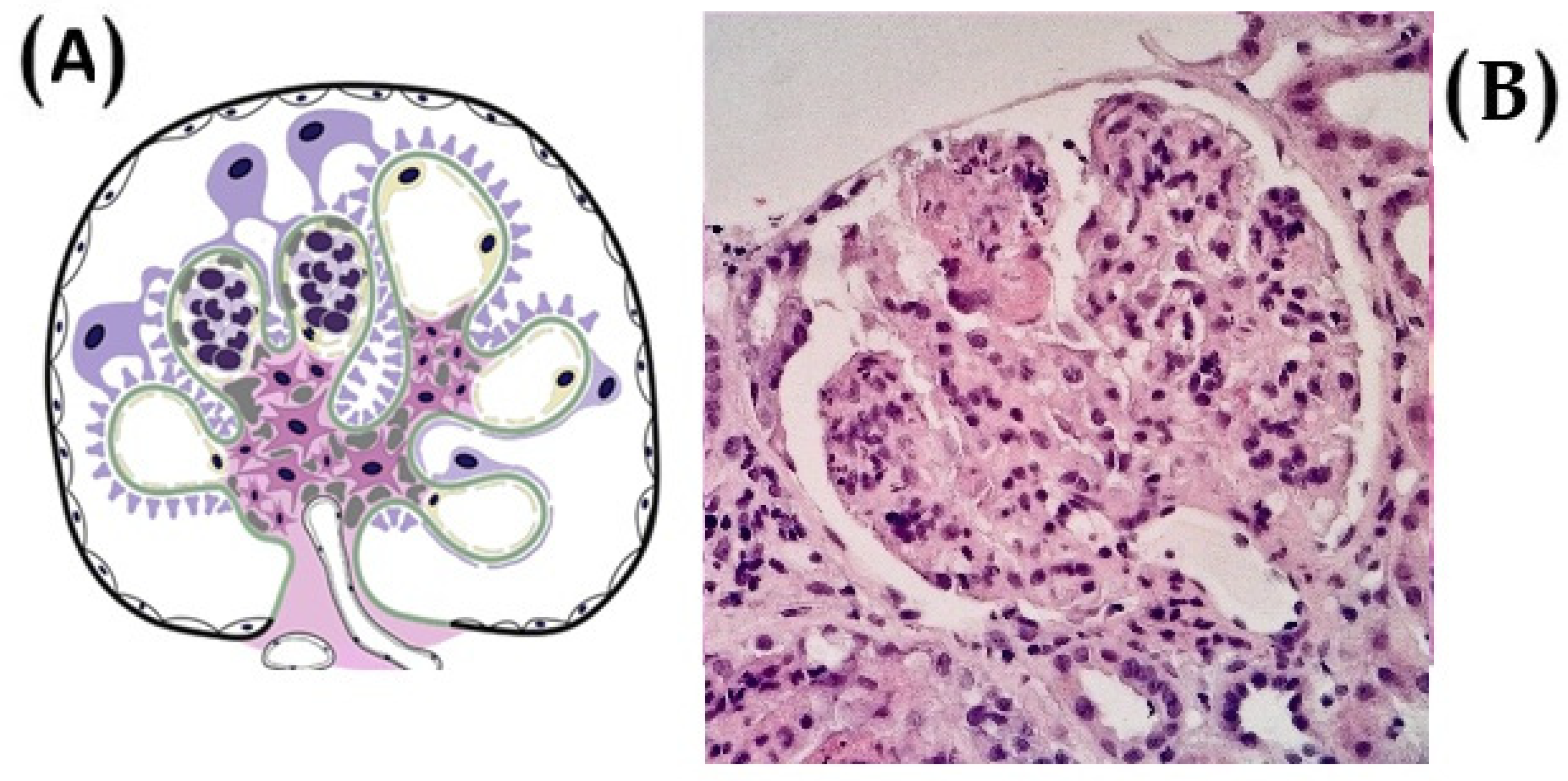
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Timeline of Main Clinical Trials in MMF
3.2. MMF Dosage and Co-Administered Treatment
3.3. Efficacy of MMF Treatment in IgAN
3.4. Histologic Stratification and Predictive Markers of MMF Response
4. Discussion
4.1. MMF Dosage
4.2. Randomized Controlled Trials
4.3. Observational Studies
4.4. Disease Activity and Chronicity
4.5. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheung, C.K.; Alexander, S.; Reich, H.N.; Selvaskandan, H.; Zhang, H.; Barratt, J. The pathogenesis of IgA nephropathy and implications for treatment. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2024, 21, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskinis, C.; Moysidou, E.; Christodoulou, M.; Pateinakis, P.; Stangou, M. Diagnosing and Treating IgAN: Steroids, Budesonide, or Maybe Both? Diagnostics 2024, 14, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, J.K.; Cheung, C.K.; Molyneux, K.; Feehally, J.; Barratt, J. An update on the pathogenesis and treatment of IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2012, 81, 833–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, G. The commonest glomerulonephritis in the world: IgA nephropathy. QJM Int. J. Med. 1987, 64, 709–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrogan, A.; Franssen, C.F.M.; de Vries, C.S. The incidence of primary glomerulonephritis worldwide: A systematic review of the literature. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2010, 26, 414–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, J.; Hinglais, N. Intercapillary deposits of IgA-IgC. J. Urol. Nephrol. (Paris) 74:694-695, 1968 (with comments by Liliane Striker)]. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2000, 11, 1957–1959. [Google Scholar]
- Floege, J.D.; Feehally, J. IgA nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2000, 11, 2395–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattrapornpisut, P.; Avila-Casado, C.; Reich, H.N. IgA Nephropathy: Core Curriculum 2021. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2021, 78, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Li, X.-K. The Role of Immune Modulation in Pathogenesis of IgA Nephropathy. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovin, B.H.; Adler, S.G.; Barratt, J.; Bridoux, F.; Burdge, K.A.; Chan, T.M.; Cook, H.T.; Fervenza, F.C.; Gibson, K.L.; Glassock, R.J.; et al. KDIGO 2021 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Glomerular Diseases. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, S1–S276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, H.-J.; Kitching, A.R.; Leung, N.; Romagnani, P. Glomerulonephritis: Immunopathogenesis and immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 23, 453–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskinis, C.; Moysidou, E.; Stai, S.; Christodoulou, M.; Lioulios, G.; Vamvakas, S.-S.; Trivyza, M.S.; Pateinakis, P.; Papasotiriou, M.; Stangou, M. Prognostic Value of Urinary Biomarkers in Proteinuria Progression in IgA Nephropathy Patients Treated with Budesonide. Medicina 2025, 61, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romagnani, P.; Kitching, A.R.; Leung, N.; Anders, H.-J. The five types of glomerulonephritis classified by pathogenesis, activity and chronicity (GN-AC). Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2023, 38, ii3–ii10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Working Group of the International IgA Nephropathy Network and the Renal Pathology Society; Roberts, I.S.; Cook, H.T.; Troyanov, S.; Alpers, C.E.; Amore, A.; Barratt, J.; Berthoux, F.; Bonsib, S.; Bruijn, J.A.; et al. The Oxford classification of IgA nephropathy: Pathology definitions, correlations, and reproducibility. Kidney Int. 2009, 76, 546–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbour, S.J.; Espino-Hernandez, G.; Reich, H.N.; Coppo, R.; Roberts, I.S.; Feehally, J.; Herzenberg, A.M.; Cattran, D.C.; Bavbek, N.; Cook, T.; et al. The MEST score provides earlier risk prediction in lgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2016, 89, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howie, A.J.; Lalayiannis, A.D. Systematic Review of the Oxford Classification of IgA Nephropathy: Reproducibility and Prognostic Value. Kidney360 2023, 4, 1103–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimarchi, H.; Barratt, J.; Cattran, D.C.; Cook, H.T.; Coppo, R.; Haas, M.; Liu, Z.-H.; Roberts, I.S.; Yuzawa, Y.; Zhang, H.; et al. Oxford Classification of IgA nephropathy 2016: An update from the IgA Nephropathy Classification Working Group. Kidney Int. 2017, 91, 1014–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palamuthusingam, D.; Castledine, C.; Lawman, S. Outcomes of immunosuppression in IgA nephropathy based on the oxford classification. Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transplant. 2018, 29, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Hou, P.; Lv, J.; Moldoveanu, Z.; Li, Y.; Kiryluk, K.; Gharavi, A.G.; Novak, J.; Zhang, H. The level of galactose-deficient IgA1 in the sera of patients with IgA nephropathy is associated with disease progression. Kidney Int. 2012, 82, 790–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthoux, F.; Suzuki, H.; Thibaudin, L.; Yanagawa, H.; Maillard, N.; Mariat, C.; Tomino, Y.; Julian, B.A.; Novak, J. Autoantibodies Targeting Galactose-Deficient IgA1 Associate with Progression of IgA Nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 23, 1579–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maixnerova, D.; Ling, C.; Hall, S.; Reily, C.; Brown, R.; Neprasova, M.; Suchanek, M.; Honsova, E.; Zima, T.; Novak, J.; et al. Galactose-deficient IgA1 and the corresponding IgG autoantibodies predict IgA nephropathy progression. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Matsuzaki, K.; Suzuki, H.; Okazaki, K.; Yanagawa, H.; Ieiri, N.; Sato, M.; Sato, T.; Taguma, Y.; Matsuoka, J.; et al. Serum levels of galactose-deficient immunoglobulin (Ig) A1 and related immune complex are associated with disease activity of IgA nephropathy. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2014, 18, 770–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamabe, H.; Ozawa, K.; Fukushi, K.; Kubota, H.; Ohsawa, H.; Seino, S.; Inuma, H.; Miyata, M.; Sasaki, T.; Onodera, K. Elevated Elevated serum secretory IgA in patients with IgA nephropathy. Nephron 1989, 51, 499–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostoker, G.; Terzidis, H.; Petit-Phar, M.; Meillet, D.; Lang, P.; Dubert, J.M.; Lagrue, G.; Weil, B. Secretory IgA are elevated in both saliva and serum of patients with various types of primary glomerulonephritis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1992, 90, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitcher, D.; Braddon, F.; Hendry, B.; Mercer, A.; Osmaston, K.; Saleem, M.A.; Steenkamp, R.; Wong, K.; Turner, A.N.; Wang, K.; et al. Long-Term Outcomes in IgA Nephropathy. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2023, 18, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoppova, B.; Reily, C.; King, R.G.; Julian, B.A.; Novak, J.; Green, T.J. Pathogenesis of IgA Nephropathy: Current Understanding and Implications for Development of Disease-Specific Treatment. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barratt, J.; Floege, J. SGLT-2 inhibition in IgA nephropathy: The new standard of care? Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 24–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, D.C.; Stefánsson, B.V.; Jongs, N.; Chertow, G.M.; Greene, T.; Hou, F.F.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Rossing, P.; Toto, R.D.; et al. Effects of dapagliflozin on major adverse kidney and cardiovascular events in patients with diabetic and non-diabetic chronic kidney disease: A prespecified analysis from the DAPA-CKD trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovin, B.H.; Adler, S.G.; Barratt, J.; Bridoux, F.; Burdge, K.A.; Chan, T.M.; Cook, H.T.; Fervenza, F.C.; Gibson, K.L.; Glassock, R.J.; et al. Executive summary of the KDIGO 2021 Guideline for the Management of Glomerular Diseases. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 753–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, C.K.; Barratt, J. First do no harm: Systemic glucocorticoids should not be used for the treatment of progressive IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2023, 103, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Wong, M.G.; Hladunewich, M.A.; Jha, V.; Hooi, L.S.; Monaghan, H.; Zhao, M.; Barbour, S.; Jardine, M.J.; Reich, H.N.; et al. Effect of Oral Methylprednisolone on Decline in Kidney Function or Kidney Failure in Patients With IgA Nephropathy. JAMA 2022, 327, 1888–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.H.R.; Loh, P.T.; Yang, W.S.; Chan, C.M. Mycophenolate mofetil in the treatment of IgA nephropathy: A systematic review. Singap. Med. J. 2008, 49, 780–785. [Google Scholar]
- Barratt, J.; Lafayette, R.A.; Floege, J. Therapy of IgA nephropathy: Time for a paradigm change. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1461879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozzi, C.; Bolasco, P.; Fogazzi, G.; Andrulli, S.; Altieri, P.; Ponticelli, C.; Locatelli, F. Corticosteroids in IgA nephropathy: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 1999, 353, 883–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Li, G.; Jiang, L.; Singh, A.K.; Wang, H. Combination therapy of prednisone and ACE inhibitor versus ACE-inhibitor therapy alone in patients with IgA nephropathy: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2009, 53, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manno, C.; Torres, D.D.; Rossini, M.; Pesce, F.; Schena, F.P. Randomized controlled clinical trial of corticosteroids plus ACE-inhibitors with long-term follow-up in proteinuric IgA nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2009, 24, 3694–3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauen, T.; Eitner, F.; Fitzner, C.; Sommerer, C.; Zeier, M.; Otte, B.; Panzer, U.; Peters, H.; Benck, U.; Mertens, P.R.; et al. Intensive Supportive Care plus Immunosuppression in IgA Nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2225–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Zhang, H.; Wong, M.G.; Jardine, M.J.; Hladunewich, M.; Jha, V.; Monaghan, H.; Zhao, M.; Barbour, S.; Reich, H.; et al. Effect of Oral Methylprednisolone on Clinical Outcomes in Patients With IgA Nephropathy. JAMA 2017, 318, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellström, B.C.; Barratt, J.; Cook, H.; Coppo, R.; Feehally, J.; de Fijter, J.W.; Floege, J.; Hetzel, G.; Jardine, A.G.; Locatelli, F.; et al. Targeted-release budesonide versus placebo in patients with IgA nephropathy (NEFIGAN): A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2b trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 2117–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafayette, R.; Kristensen, J.; Stone, A.; Floege, J.; Tesař, V.; Trimarchi, H.; Zhang, H.; Eren, N.; Paliege, A.; Reich, H.N.; et al. Efficacy and safety of a targeted-release formulation of budesonide in patients with primary IgA nephropathy (NefIgArd): 2-year results from a randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet 2023, 402, 859–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smerud, H.K.; Bárány, P.; Lindström, K.; Fernström, A.; Sandell, A.; Påhlsson, P.; Fellström, B. New treatment for IgA nephropathy: Enteric budesonide targeted to the ileocecal region ameliorates proteinuria. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 3237–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locatelli, F.; Del Vecchio, L.; Ponticelli, C. Systemic and targeted steroids for the treatment of IgA nephropathy. Clin. Kidney J. 2023, 16, ii40–ii46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scionti, K.; Molyneux, K.; Selvaskandan, H.; Barratt, J.; Cheung, C.K. New Insights into the Pathogenesis and Treatment Strategies in IgA Nephropathy. Glomerular Dis. 2021, 2, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaskandan, H.; Jhaveri, K.D.; Rizk, D.V. Primary IgA Nephropathy: New Insights and Emerging Therapies. Adv. Kidney Dis. Health 2024, 31, 180–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, R.S.; Yeo, S.C.; Barratt, J.; Rizk, D.V. An Update on Current Therapeutic Options in IgA Nephropathy. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.C.; Tang, A.W.; Wong, S.S.; Leung, J.C.; Ho, Y.W.; Lai, K.N. Long-term study of mycophenolate mofetil treatment in IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2010, 77, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.-H.; Le, W.-B.; Chen, N.; Wang, W.-M.; Liu, Z.-S.; Liu, D.; Chen, J.-H.; Tian, J.; Fu, P.; Hu, Z.-X.; et al. Mycophenolate Mofetil Combined With Prednisone Versus Full-Dose Prednisone in IgA Nephropathy With Active Proliferative Lesions: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2017, 69, 788–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, B.D.; Oyen, R.; Claes, K.; Evenepoel, P.; Kuypers, D.; Vanwalleghem, J.; Van Damme, B.; Vanrenterghem, Y.F.C. Mycophenolate mofetil in IgA nephropathy: Results of a 3-year prospective placebo-controlled randomized study. Kidney Int. 2004, 65, 1842–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, G.; Lin, J.; Rosenstock, J.; Markowitz, G.; D’AGati, V.; Radhakrishnan, J.; Preddie, D.; Crew, J.; Valeri, A.; Appel, G. Mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) vs placebo in patients with moderately advanced IgA nephropathy: A double-blind randomized controlled trial. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2005, 20, 2139–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Leung, J.C.; Chan, L.Y.; Lui, Y.H.; Tang, C.S.; Kan, C.H.; Ho, Y.W.; Lai, K.N. Mycophenolate mofetil alleviates persistent proteinuria in IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2005, 68, 802–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, F.F.; Xie, D.; Wang, J.; Xu, X.; Yang, X.; Ai, J.; Nie, S.; Liang, M.; Wang, G.; Jia, N.; et al. Effectiveness of Mycophenolate Mofetil Among Patients With Progressive IgA Nephropathy. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2254054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogg, R.J.; Bay, R.C.; Jennette, J.C.; Sibley, R.; Kumar, S.; Fervenza, F.C.; Appel, G.; Cattran, D.; Fischer, D.; Hurley, R.M.; et al. Randomized controlled trial of mycophenolate mofetil in children, adolescents, and adults with IgA nephropathy. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2015, 66, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Floege, J. Prognostic assessment of IgA nephropathy: How much does histology add? Kidney Int. 2016, 89, 19–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keskinis, C.; Pateinakis, P.; Stangou, M. Re-biopsy may guide novel immunosuppressive therapy in long-standing IgA nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2025, gfaf039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, M.; Verhave, J.C.; Liu, Z.-H.; Alpers, C.E.; Barratt, J.; Becker, J.U.; Cattran, D.; Cook, H.T.; Coppo, R.; Feehally, J.; et al. A Multicenter Study of the Predictive Value of Crescents in IgA Nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 28, 691–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Study | Location | Sample Size | Design | Intervention | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tang et al., 2005 [50] | China | 40 | RCT | MMF vs. control | 24-week + 72-week follow-up |
| Tang et al., 2010 [46] | China | 40 | Observational | MMF vs. control | 6-year follow-up |
| Hogg et al., 2015 [52] | USA/Canada | 52 | RCT | MMF vs. placebo | 12 months |
| Frisch et al., 2005 [49] | USA | 32 | RCT | MMF vs. placebo | 24 months |
| Maes et al., 2004 [48] | Belgium | 34 | RCT | MMF vs. placebo | 36 months |
| Hou et al., 2017 [47] | China | 176 | RCT | MMF + low-dose steroid vs. steroid | 12 months |
| Hou et al., 2023 [51] | China | 170 | RCT | MMF + SC vs. SC | 36 months |
| Study | MMF Dose | Co-Administered Therapy |
|---|---|---|
| Tang et al., 2005 [50] | 1.5–2 g/day | RAS blockade |
| Tang et al., 2010 [46] | Uknown | RAS blockade |
| Hogg et al., 2015 [52] | 25–36 mg/kg/day | ACEi/ARB + omega-3 fatty acids |
| Frisch et al., 2005 [49] | 1 g twice daily (BID) | ACEi/ARB |
| Maes et al., 2004 [48] | 2 g/day | ACEi + sodium restriction |
| Hou et al., 2017 [47] | 1.5 g/day | RAS blockade + low-dose corticosteroids |
| Hou et al., 2023 [51] | 1.5 g/day tapered to 0.75–1 g/day | Losartan |
| Study | Outcome | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|
| Tang et al., 2005 [50] | 80% reduction in proteinuria vs. 30% in control | Significant benefit |
| Tang et al., 2010 [46] | 10% ESRD in MMF vs. 45% in control (6-year data) | Long-term protection |
| Hogg et al., 2015 [52] | No significant difference in UPCR or remission | No benefit |
| Frisch et al., 2005 [49] | No difference in serum Cr or ESRD | No benefit |
| Maes et al., 2004 [48] | No significant change in renal outcomes | No benefit |
| Hou et al., 2017 [47] | Similar remission rates; fewer adverse effects with MMF | Safer profile |
| Hou et al., 2023 [51] | HR of 0.23 for primary renal endpoint (favoring MMF) | Significant benefit |
| Study | Histological Criteria | Stratification Used | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hou et al., 2017 [47] | Crescents, endocapillary hypercellularity | Yes | Favorable response |
| Tang et al., 2005 [50] | Mild to moderate lesions | Yes | Improved proteinuria |
| Hou et al., 2023 [51] | CKD stage 2–3 (clinical surrogate) | Yes | Reduced progression |
| Hogg et al., 2015 [52] | No histologic stratification (Oxford MEST absent) | No | No benefit |
| Frisch et al., 2005 [49] | Advanced fibrosis, sclerosis | No | No benefit |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Keskinis, C.; Pateinakis, P.; Stangou, M. Intraglomerular Inflammation as a Guide for Mycophenolate Mofetil-Based Treatment in IgA Nephropathy. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2101. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15162101
Keskinis C, Pateinakis P, Stangou M. Intraglomerular Inflammation as a Guide for Mycophenolate Mofetil-Based Treatment in IgA Nephropathy. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(16):2101. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15162101
Chicago/Turabian StyleKeskinis, Christodoulos, Panagiotis Pateinakis, and Maria Stangou. 2025. "Intraglomerular Inflammation as a Guide for Mycophenolate Mofetil-Based Treatment in IgA Nephropathy" Diagnostics 15, no. 16: 2101. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15162101
APA StyleKeskinis, C., Pateinakis, P., & Stangou, M. (2025). Intraglomerular Inflammation as a Guide for Mycophenolate Mofetil-Based Treatment in IgA Nephropathy. Diagnostics, 15(16), 2101. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15162101






