Prediction of Immunotherapy Response in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Using Pretreatment CT Images
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection and Preprocessing
2.2. CT Acquisition and Preprocessing
2.3. Manual Segmentation
2.4. Treatment Outcome Prediction Modelling
2.5. Radiomic Analysis and AI-Driven Model Development
2.5.1. Extraction of Radiomic Features
2.5.2. Identification of Predictive Features
2.5.3. Binary Classification of Responders and Non-Responders
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics
3.2. Radiomic Predictor of Treatment Response
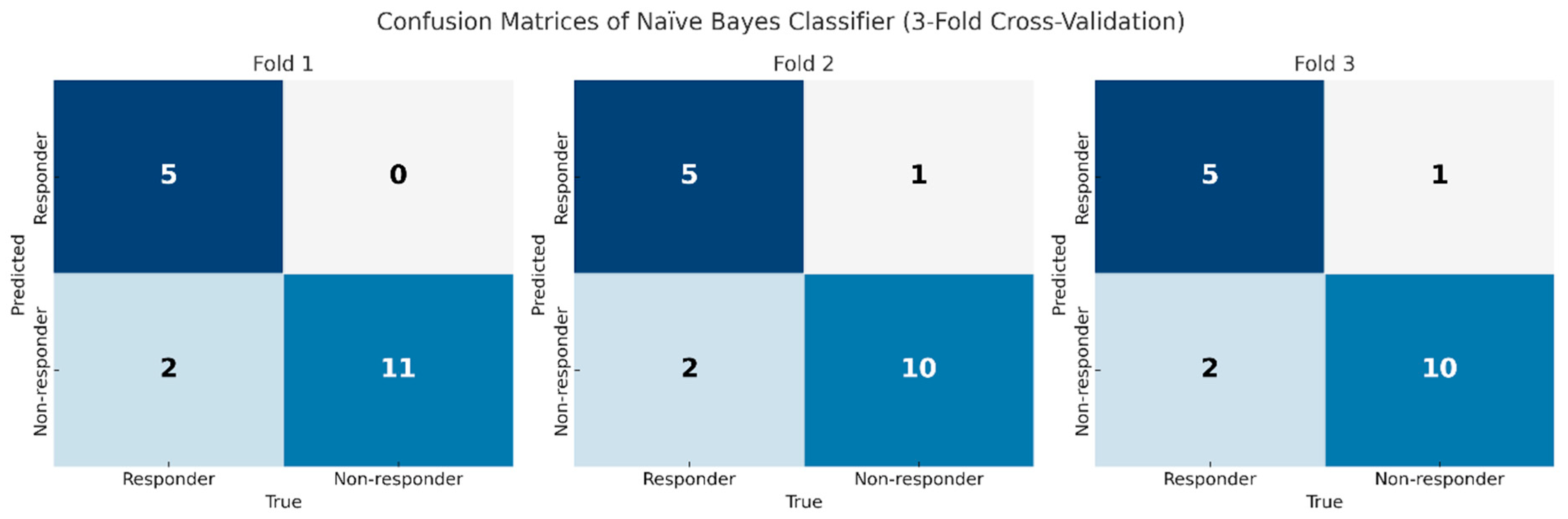
3.3. Performance of AI-Driven Radiomic Models for the Prediction of Treatment Responses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Recommendations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Rumgay, H.; Arnold, M.; Ferlay, J.; Lesi, O.; Cabasag, C.J.; Vignat, J.; Laversanne, M.; McGlynn, K.A.; Soerjomataram, I. Global burden of primary liver cancer in 2020 and predictions to 2040. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, 1598–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.D.; Heimbach, J.K. New advances in the diagnosis and management of hepatocellular carcinoma. BMJ 2020, 371, m3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forner, A.; Reig, M.; Bruix, J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet 2018, 391, 1301–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villanueva, A. Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1450–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Zhu, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, M.; Liu, B.; Chen, J.; Shen, J. CT radiomics-based biomarkers can predict response to immunotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 20027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Shi, H.; Wang, H. Machine Learning and AI in Cancer Prognosis, Prediction, and Treatment Selection: A Critical Approach. J. Multidiscip. Healthc. 2023, 16, 1779–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reginelli, A.; Nardone, V.; Giacobbe, G.; Belfiore, M.P.; Grassi, R.; Schettino, F.; Del Canto, M.; Grassi, R.; Cappabianca, S. Radiomics as a New Frontier of Imaging for Cancer Prognosis: A Narrative Review. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.; Laguna, A.; Ikeda, I.; Maxwell, A.W.P.; Chapiro, J.; Nadolski, G.; Jiao, Z.; Bai, H.X. Using Machine Learning to Predict Response to Image-guided Therapies for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Radiology 2023, 309, e222891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Sun, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Li, H.; Ma, X.; Luo, X.; Tan, W.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, C.; et al. Pretreatment CT-based machine learning radiomics model predicts response in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma treated with lenvatinib plus PD-1 inhibitors and interventional therapy. J. Immunother. Cancer 2024, 12, e008953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, E.E.L.; Law, M.; Yu, Z.; Yong, J.N.; Tan, C.S.; Tan, E.Y.; Takahashi, H.; Danpanichkul, P.; Nah, B.; Soon, G.S.T.; et al. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Predicting Transarterial Chemoembolization Outcomes: A Systematic Review. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2025, 70, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, L.; Liu, R.; Li, W.; Li, S.; Hou, X. Deep learning-based CT radiomics predicts prognosis of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma treated with TACE-HAIC combined with PD-1 inhibitors and tyrosine kinase inhibitors. BMC Gastroenterol. 2025, 25, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lencioni, R.; Llovet, J.M. Modified RECIST (mRECIST) assessment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin. Liver Dis. 2010, 30, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yushkevich, P.A.; Piven, J.; Hazlett, H.C.; Smith, R.G.; Ho, S.; Gee, J.C.; Gerig, G. User-guided 3D active contour segmentation of anatomical structures: Significantly improved efficiency and reliability. Neuroimage 2006, 31, 1116–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javed, S.; Qureshi, T.A.; Wang, L.; Azab, L.; Gaddam, S.; Pandol, S.J.; Li, D. An insight to PDAC tumor heterogeneity across pancreatic subregions using computed tomography images. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1378691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Ju, L.; Tong, J.; Zhou, C.M.; Yang, J.J. Machine Learning Algorithms for Predicting the Recurrence of Stage IV Colorectal Cancer After Tumor Resection. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascianelli, S.; Molineris, I.; Isella, C.; Masseroli, M.; Medico, E. Machine learning for RNA sequencing-based intrinsic subtyping of breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, T.A.; Gaddam, S.; Wachsman, A.M.; Wang, L.; Azab, L.; Asadpour, V.; Chen, W.; Xie, Y.; Wu, B.; Pandol, S.J.; et al. Predicting pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma using artificial intelligence analysis of pre-diagnostic computed tomography images. Cancer Biomarks 2022, 33, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Khoueiry, A.B.; Sangro, B.; Yau, T.; Crocenzi, T.S.; Kudo, M.; Hsu, C.; Kim, T.Y.; Choo, S.P.; Trojan, J.; Welling, T.H.R.; et al. Nivolumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (CheckMate 040): An open-label, non-comparative, phase 1/2 dose escalation and expansion trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 2492–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.S.; Qin, S.; Ikeda, M.; Galle, P.R.; Ducreux, M.; Kim, T.Y.; Kudo, M.; Breder, V.; Merle, P.; Kaseb, A.O.; et al. Atezolizumab plus Bevacizumab in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1894–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.X.; Abbas, A.R.; de Galarreta, M.R.; Guan, Y.; Lu, S.; Koeppen, H.; Zhang, W.; Hsu, C.H.; He, A.R.; Ryoo, B.Y.; et al. Molecular correlates of clinical response and resistance to atezolizumab in combination with bevacizumab in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1599–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinter, M.; Jain, R.K.; Duda, D.G. The Current Landscape of Immune Checkpoint Blockade in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Review. JAMA Oncol. 2021, 7, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd El Aziz, M.A.; Facciorusso, A.; Nayfeh, T.; Saadi, S.; Elnaggar, M.; Cotsoglou, C.; Sacco, R. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors for Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Vaccines 2020, 8, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Li, J.; Wang, T.; Luo, X.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Song, R.; Yang, L.Z.; et al. Predicting treatment response and prognosis of immune checkpoint inhibitors-based combination therapy in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma using a longitudinal CT-based radiomics model: A multicenter study. BMC Cancer 2025, 25, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vithayathil, M.; Koku, D.; Campani, C.; Nault, J.C.; Sutter, O.; Ganne-Carrie, N.; Aboagye, E.O.; Sharma, R. Machine learning based radiomic models outperform clinical biomarkers in predicting outcomes after immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donne, R.; Lujambio, A. The liver cancer immune microenvironment: Therapeutic implications for hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2023, 77, 1773–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringelhan, M.; Pfister, D.; O’Connor, T.; Pikarsky, E.; Heikenwalder, M. The immunology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Immunol. 2018, 19, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, B.A.; Cen, S.Y.; Hwang, D.H.; Duddalwar, V.A. Texture Analysis of Imaging: What Radiologists Need to Know. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2019, 212, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Feature Type | Feature Examples | No. of Features |
|---|---|---|
| First Order Statistics | Kurtosis, Percentiles, Range | 15 |
| Gray Level Co-occurrence Matrix | Cluster shade, Contrast, Autocorrelation | 20 |
| Gray Level Run Length Matrix | Run percentage, Run entropy | 15 |
| Gray Level Size Zone Matrix | Zone percentage, Zone variance | 14 |
| Gray Level Dependence Matrix | Small dependence emphasis | 12 |
| Shape-based Features 2D and 3D | Volume, Surface area, Sphericity | 20 |
| Additional Features | Complexity, Busyness | 5 |
| Variable | Value |
|---|---|
| Age (years), median (IQR) | 69 (63, 73) |
| Sex, male | 42 (76.4) |
| Etiology of chronic liver disease | |
| HCV | 20 (36.4) |
| HBV | 13 (23.6) |
| MASLD | 9 (16.4) |
| Alcohol | 7 (12.7) |
| Alcohol + HCV | 1 (1.8) |
| Alcohol + MASLD | 1 (1.8) |
| BCLC stage, A/B/C/D | 4/16/30/5 |
| Previous treatment history | 36 (65.5) |
| Immunotherapy type | |
| Nivolumab | 20 (36.4) |
| Atezolizumab with/without bevacizumab | 20 (36.4) |
| Pembrolizumab | 14 (25.5) |
| Durvalumab + tremelimumab | 1 (1.8) |
| Duration of immunotherapy (weeks), median (IQR) | 19 (10, 52) |
| Treatment response | |
| Responder (PR + CR) | 21 (38.2) |
| Non-responder (PD + SD) | 34 (61.8) |
| Classifier | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 (Liver alone) | ||||
| Naïve Bayes (NB) | 0.77 | 0.76 | 0.78 | 0.77 |
| Model 2 (Liver + viable HCC) | ||||
| Naïve Bayes (NB) | 0.86 | 0.71 | 0.94 | 0.83 |
| k-NN (KNN) | 0.79 | 0.60 | 0.86 | 0.84 |
| SVM | 0.82 | 0.70 | 0.86 | 0.77 |
| Logistic Regression (LR) | 0.76 | 0.70 | 0.78 | 0.74 |
| Decision Tree (DT) | 0.74 | 0.60 | 0.78 | 0.69 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Min, J.H.; Chen, P.-J.; Qureshi, T.A.; Javed, S.; Xie, Y.; Azab, L.; Wang, L.; Kim, H.-s.; Li, D.; Yang, J.D. Prediction of Immunotherapy Response in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Using Pretreatment CT Images. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2090. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15162090
Min JH, Chen P-J, Qureshi TA, Javed S, Xie Y, Azab L, Wang L, Kim H-s, Li D, Yang JD. Prediction of Immunotherapy Response in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Using Pretreatment CT Images. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(16):2090. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15162090
Chicago/Turabian StyleMin, Ji Hye, Pin-Jung Chen, Touseef Ahmad Qureshi, Sehrish Javed, Yibin Xie, Linda Azab, Lixia Wang, Hyun-seok Kim, Debiao Li, and Ju Dong Yang. 2025. "Prediction of Immunotherapy Response in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Using Pretreatment CT Images" Diagnostics 15, no. 16: 2090. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15162090
APA StyleMin, J. H., Chen, P.-J., Qureshi, T. A., Javed, S., Xie, Y., Azab, L., Wang, L., Kim, H.-s., Li, D., & Yang, J. D. (2025). Prediction of Immunotherapy Response in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Using Pretreatment CT Images. Diagnostics, 15(16), 2090. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15162090






