Automated Detection of Necrotizing Soft Tissue Infection Features by Computed Tomography
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
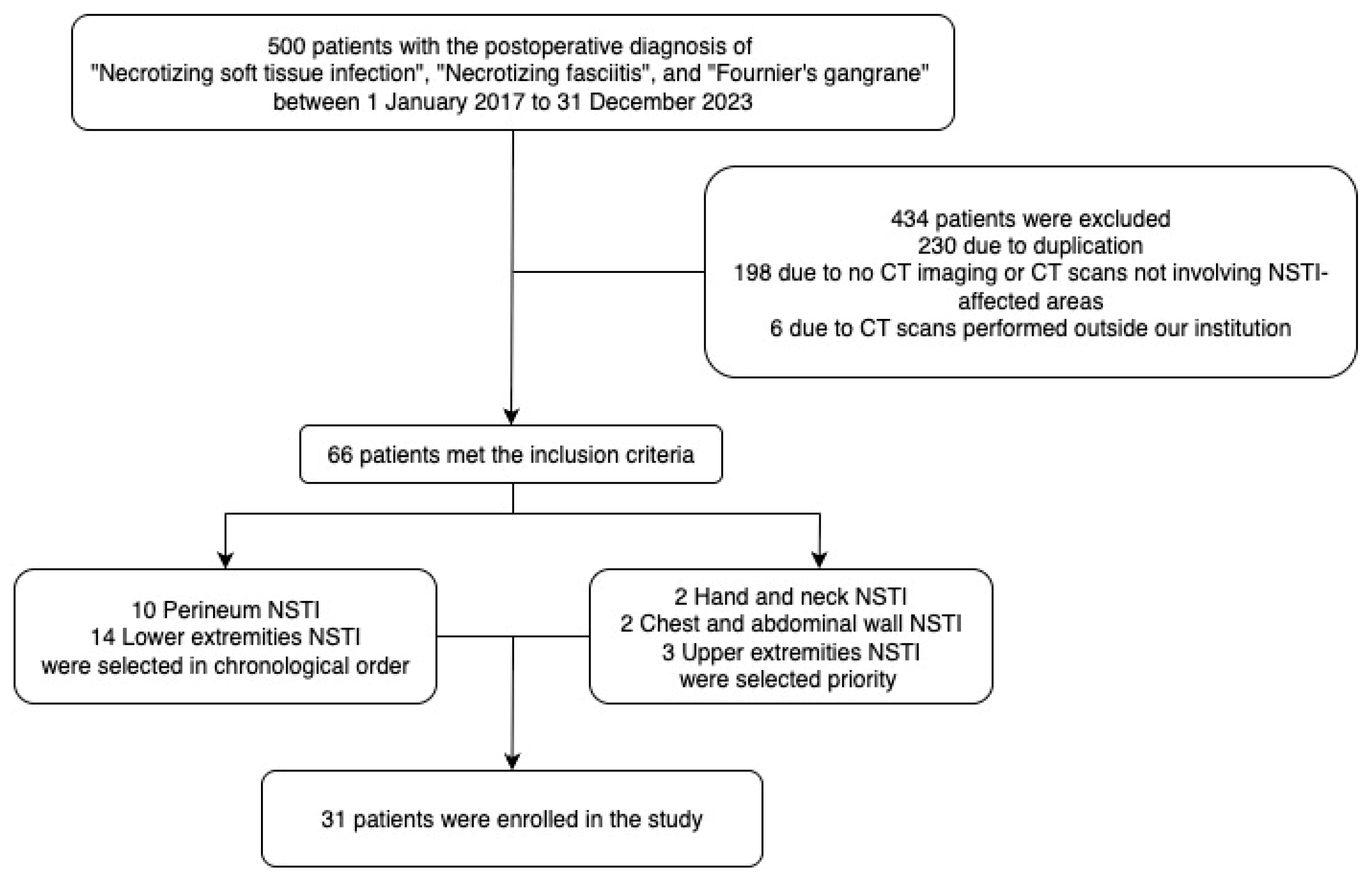
2.1. Dataset
2.2. Dataset Divisions
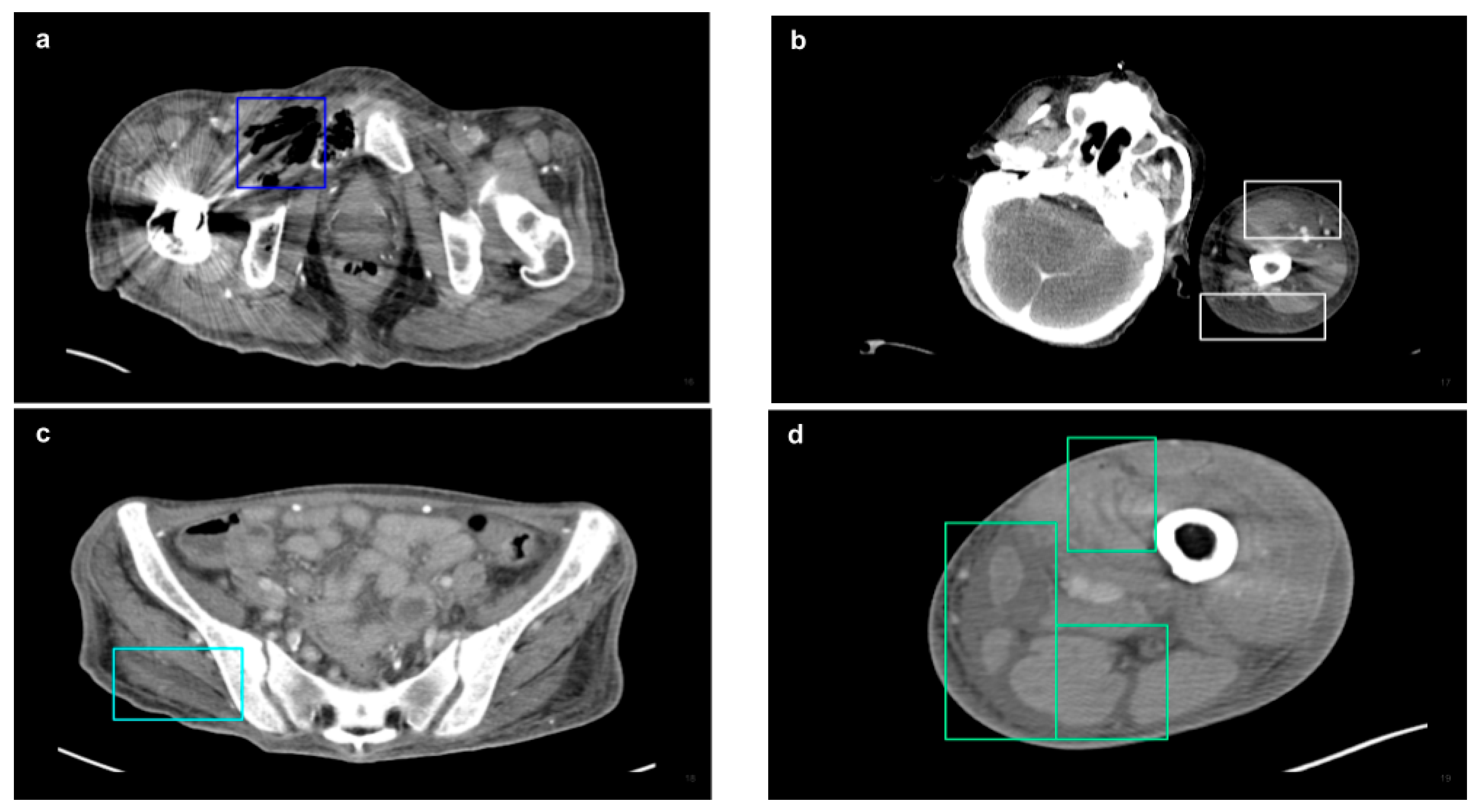
2.3. CT Acquisition and Analysis
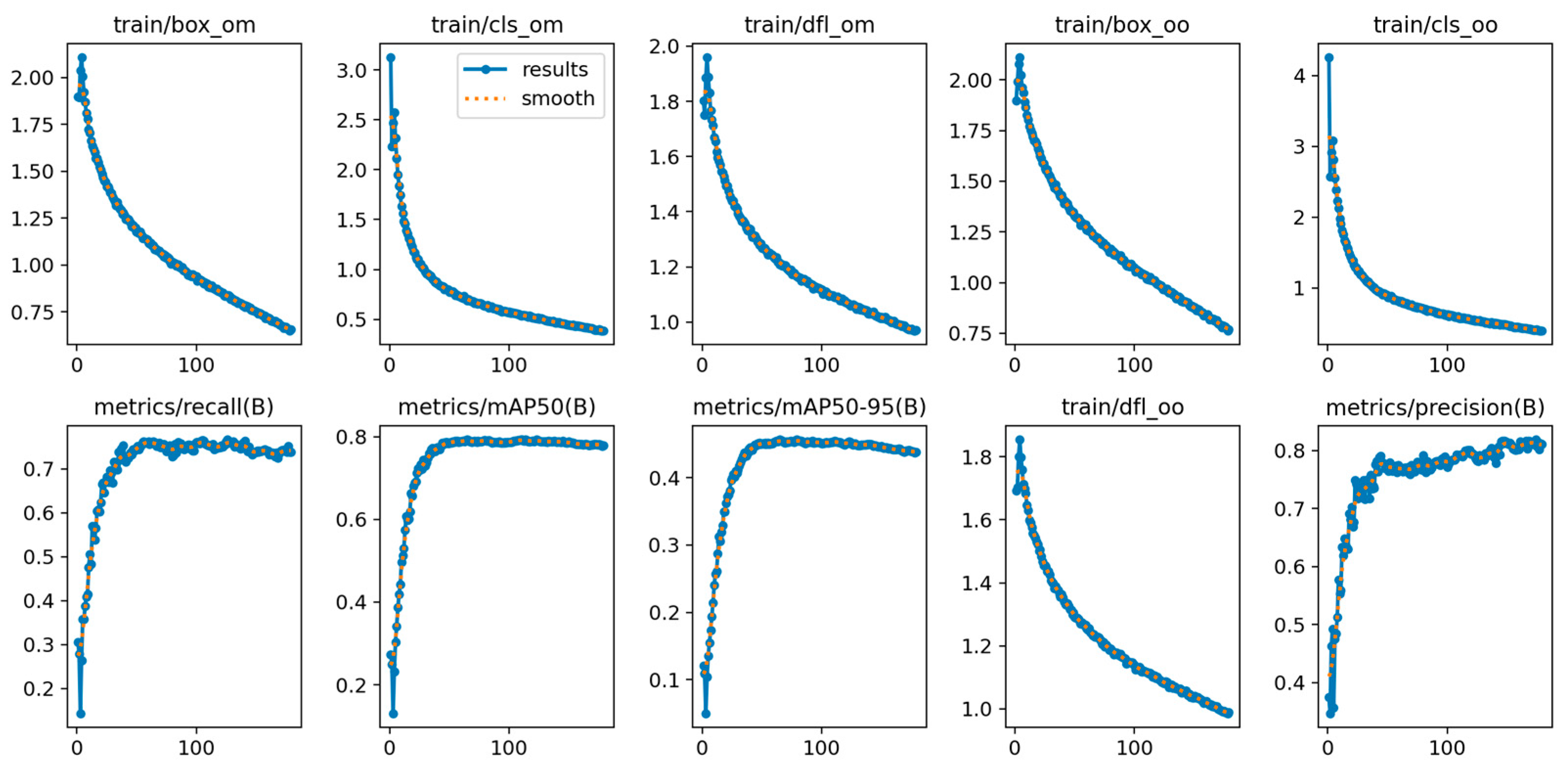
2.4. Model Training
2.5. Performance Evaluation
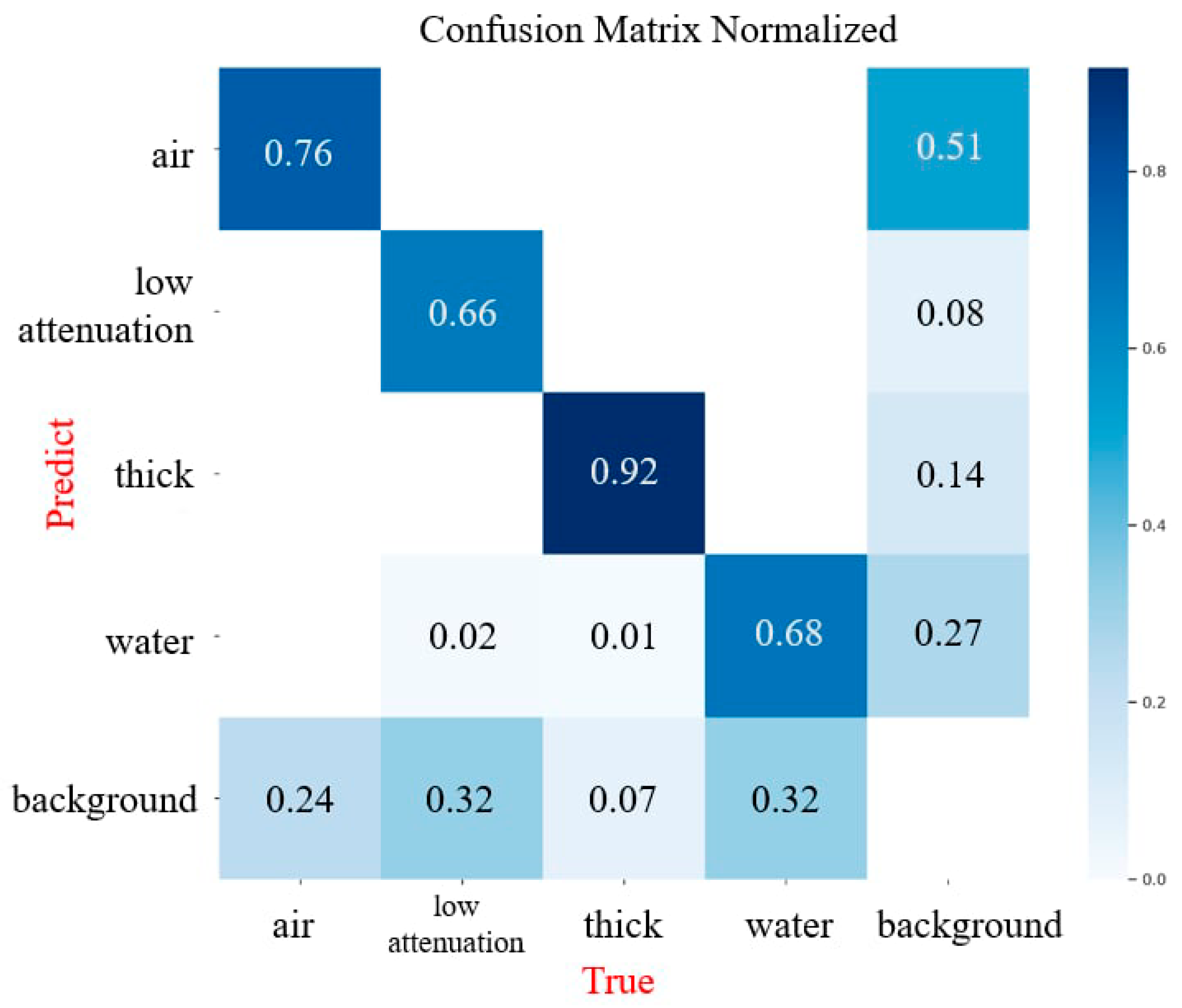
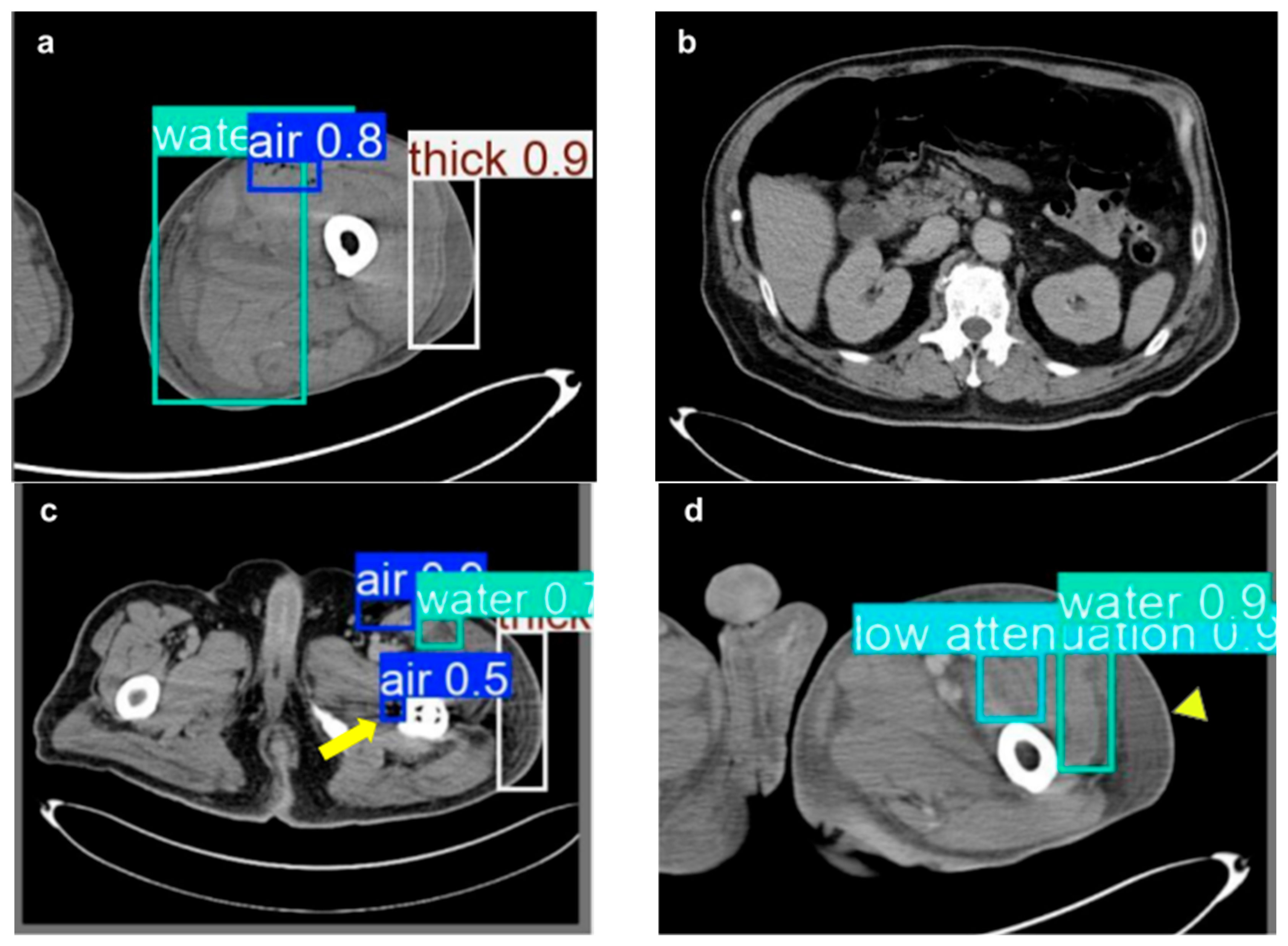
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NSTI | Necrotizing Soft Tissue Infection |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| Yolov10 | You Only Look Once version 10 |
| mAP | Mean Average Precision |
| LRINEC | Laboratory Risk Indicator for Necrotizing Fasciitis |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| CSPNet | Cross-Stage Partial Network |
| SCD | Spatial-Channel Decoupled Downsampling |
| PAN | Path Aggregation Network |
| NMS | Non-Maximum Suppression |
| SGD | Stochastic Gradient Descent |
| AP | Average Precision |
| TP | True Positive |
| FN | False Negative |
| FP | False Positive |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| IoU | Intersection over Union |
References
- Stevens, D.L.; Bryant, A.E. Necrotizing Soft-Tissue Infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2253–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedesco, S.; Di Grezia, M.; Tropeano, G.; Altieri, G.; Brisinda, G. Necrotizing soft tissue infections: A surgical narrative review. Updates Surg. 2025, 77, 1239–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisgaard, E.K.; Bulger, E.M. Current diagnosis and management of necrotizing soft tissue infections: What you need to know. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2023, 97, 678–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naseer, U.; Steinbakk, M.; Blystad, H.; Caugant, D. Epidemiology of invasive group A streptococcal infections in Norway 2010–2014: A retrospective cohort study. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 35, 1639–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakkarainen, T.W.; Kopari, N.M.; Pham, T.N.; Evans, H.L. Necrotizing soft tissue infections: Review and current concepts in treatment, systems of care, and outcomes. Curr. Probl. Surg. 2014, 51, 344–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lancerotto, L.; Tocco, I.; Salmaso, R.; Vindigni, V.; Bassetto, F. Necrotizing fasciitis: Classification, diagnosis, and management. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012, 72, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, S.M.; Tran, A.; Cheng, W.; Rochwerg, B.; Kyeremanteng, K.; Seely, A.J.E.; Inaba, K.; Perry, J.J. Necrotizing Soft Tissue Infection: Diagnostic Accuracy of Physical Examination, Imaging, and LRINEC Score: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ann. Surg. 2019, 269, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.K.; Huo, J.Y.; Yang, Q.; Li, J. Early diagnosis of necrotizing fasciitis: Imaging techniques and their combined application. Int. Wound J. 2024, 21, e14379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, A.; Patel, D.; Sundaram, T.; Johnson, J.; Gottlieb, M. Ultrasound for the diagnosis of necrotizing fasciitis: A systematic review of the literature. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2023, 65, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.L.; Fisher, K.L. Sonographic detection of necrotizing fasciitis. J. Diagn. Med. Sonogr. 2017, 33, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tso, D.K.; Singh, A.K. Necrotizing fasciitis of the lower extremity: Imaging pearls and pitfalls. Br. J. Radiol. 2018, 91, 20180093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-N.; Hsiao, C.-T.; Chang, C.-P.; Huang, T.-Y.; Hsiao, K.-Y.; Chen, Y.-C.; Fann, W.-C. The relationship between fluid accumulation in ultrasonography and the diagnosis and prognosis of patients with necrotizing fasciitis. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2019, 45, 1545–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, R.K.; Sanchez Martinez, A.; Abu Hasan, M.A.-S.; Castro Delgado, R.; Arcos González, P. Point-of-care ultrasonography in diagnosing necrotizing fasciitis—A literature review. J. Ultrasound 2023, 26, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, A.A.; Baker, K.S.; Gould, E.S.; Gupta, R. Necrotizing fasciitis and its mimics: What radiologists need to know. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2015, 204, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turecki, M.B.; Taljanovic, M.S.; Stubbs, A.Y.; Graham, A.R.; Holden, D.A.; Hunter, T.B.; Rogers, L.F. Imaging of musculoskeletal soft tissue infections. Skelet. Radiol. 2010, 39, 957–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGillicuddy, E.A.; Lischuk, A.W.; Schuster, K.M.; Kaplan, L.J.; Maung, A.; Lui, F.Y.; Bokhari, S.A.; Davis, K.A. Development of a computed tomography-based scoring system for necrotizing soft-tissue infections. J. Trauma 2011, 70, 894–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hames, K.; Patlas, M.N.; Mellnick, V.M.; Katz, D.S. Errors in emergency and trauma radiology: General principles. Errors Emerg. Trauma Radiol. 2019, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Katzman, B.D.; van der Pol, C.B.; Soyer, P.; Patlas, M.N. Artificial intelligence in emergency radiology: A review of applications and possibilities. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2023, 104, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, M.-C.; Tseng, T.-Y.; Chang, C.-C.; Chen, C.-C. Applying Deep Learning to Establish a Telemedicine Assistance System: A Case Study of the Stage Classification of Pressure Injuries. In Leveraging Transdisciplinary Engineering in a Changing and Connected World; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 433–442. [Google Scholar]
- Das, A.; Amin, S.; Hughes, J.A. Automatic Detection of Necrotizing Fasciitis: A Dataset and Early Results. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Conference on Computational Intelligence in Bioinformatics and Computational Biology (CIBCB), Melbourne, Australia, 13–15 October 2021; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Leturia Etxeberria, M.; Biurrun Mancisidor, M.C.; Ugarte Nuño, A.; Arenaza Choperena, G.; Mendoza Alonso, M.; Esnaola Albizu, M.; Serdio Mier, A.; Gredilla Sáenz, M.; Gomez Usabiaga, V. Imaging Assessment of Ectopic Gas Collections. Radiographics 2020, 40, 1318–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chingkoe, C.M.; Jahed, A.; Loreto, M.P.; Sarrazin, J.; McGregor, C.T.; Blaichman, J.I.; Glanc, P. Retroperitoneal fasciitis: Spectrum of CT findings in the abdomen and pelvis. Radiographics 2015, 35, 1095–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayeri, M.R.; Ziai, P.; Shehata, M.L.; Teytelboym, O.M.; Huang, B.K. Soft-Tissue Infections and Their Imaging Mimics: From Cellulitis to Necrotizing Fasciitis. Radiographics 2016, 36, 1888–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruls, R.J.; Kwee, R.M. CT in necrotizing soft tissue infection: Diagnostic criteria and comparison with LRINEC score. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 8536–8541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, H.-J.; Schnarkowski, B.; Leonhardi, J.; Mehdorn, M.; Ebel, S.; Goessmann, H.; Denecke, T. CT Texture analysis and CT scores for characterization of fluid collections. BMC Med. Imaging 2021, 21, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skusa, C.; Skusa, R.; Wohlfarth, M.; Warnke, P.; Podbielski, A.; Bath, K.; Groß, J.; Schafmayer, C.; Frickmann, H.; Weber, M.-A. Imaging and clinical parameters for distinction between infected and non-infected fluid collections in CT: Prospective study using extended microbiological approach. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinnato, P.; Patel, D.B.; Di Carlo, M.; Bartoloni, A.; Cevolani, L.; Matcuk, G.R.; Crombé, A. Imaging of musculoskeletal soft-tissue infections in clinical practice: A comprehensive updated review. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz Maya, S.; Dualde Beltrán, D.; Lemercier, P.; Leiva-Salinas, C. Necrotizing fasciitis: An urgent diagnosis. Skelet. Radiol. 2014, 43, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolinsky, D.C.; Liang, S.Y. Musculoskeletal Infections in the Emergency Department. Emerg. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 36, 751–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wysoki, M.G.; Santora, T.A.; Shah, R.M.; Friedman, A.C. Necrotizing fasciitis: CT characteristics. Radiology 1997, 203, 859–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fayad, L.M.; Carrino, J.A.; Fishman, E.K. Musculoskeletal infection: Role of CT in the emergency department. Radiographics 2007, 27, 1723–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonetti, F.; Cremona, A.; Carusi, V.; Guidi, M.; Iannicelli, E.; Di Girolamo, M.; Sergi, D.; Clarioni, A.; Baio, G.; Antonelli, G.; et al. The role of contrast enhanced computed tomography in the diagnosis of necrotizing fasciitis and comparison with the laboratory risk indicator for necrotizing fasciitis (LRINEC). Radiol. Med. 2016, 121, 106–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Yeerjiang, A.; Wang, Z.; Huang, X.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Q.; Qin, Y.; He, J. YOLOv1 to YOLOv10: A Comprehensive Review of YOLO Variants and Their Application in Medical Image Detection. J. Artif. Intell. Pract. 2024, 7, 112–122. [Google Scholar]
- Crombé, A.; Spinnato, P.; Italiano, A.; Brisse, H.J.; Feydy, A.; Fadli, D.; Kind, M. Radiomics and artificial intelligence for soft-tissue sarcomas: Current status and perspectives. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2023, 104, 567–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitto, S.; Interlenghi, M.; Cuocolo, R.; Salvatore, C.; Giannetta, V.; Badalyan, J.; Gallazzi, E.; Spinelli, M.S.; Gallazzi, M.; Serpi, F. MRI radiomics-based machine learning for classification of deep-seated lipoma and atypical lipomatous tumor of the extremities. La Radiol. Medica 2023, 128, 989–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Sun, M.; Sun, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, G.; Wang, X.; Meng, X.; Wang, Z.; Yu, H. Advancing musculoskeletal tumor diagnosis: Automated segmentation and predictive classification using deep learning and radiomics. Comput. Biol. Med. 2024, 175, 108502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, X.; Ma, X. MRI-based computer-aided diagnostic model to predict tumor grading and clinical outcomes in patients with soft tissue sarcoma. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2022, 56, 1733–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, M.-C.; Tsai, S.C.-S.; Bai, Z.-R.; Lin, A.; Chang, C.-C.; Wang, G.-Z.; Lin, F.C.-F. Radiographic chest wall abnormalities in primary spontaneous pneumothorax identified by artificial intelligence. Heliyon 2024, 10, e30023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Ergu, D.; Liu, F.; Cai, Y.; Ma, B. A Review of Yolo algorithm developments. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2022, 199, 1066–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huu, P.N.; Pham Thi, Q.; Tong Thi Quynh, P. Proposing Lane and Obstacle Detection Algorithm Using YOLO to Control Self-Driving Cars on Advanced Networks. Adv. Multimed. 2022, 2022, 3425295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Reis, D.H.; Welfer, D.; De Souza Leite Cuadros, M.A.; Gamarra, D.F.T. Mobile robot navigation using an object recognition software with RGBD images and the YOLO algorithm. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2019, 33, 1290–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Li, J.; Qin, L. YOLO-BYTE: An efficient multi-object tracking algorithm for automatic monitoring of dairy cows. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 209, 107857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byeon, H. YOLO v10-Based Brain Tumor Detection: An Innovative Approach in CT Imaging. Nanotechnol. Percept. 2024, 20, 113–125. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasu, P.N.; Kumari, G.L.A.; Narahari, S.C.; Ahmed, S.; Alhumam, A. Exploring the impact of hyperparameter and data augmentation in YOLO V10 for accurate bone fracture detection from X-ray images. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 9828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapadi, A.A.; Shirsath, V.; Pundge, A. Real-Time Diabetic Retinopathy Detection Using YOLO-v10 with Nature-Inspired Optimization. Biomed. Mater. Devices 2025, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Chen, H.; Liu, L.; Chen, K.; Lin, Z.; Han, J.; Ding, G. Yolov10: Real-time end-to-end object detection. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.14458. [Google Scholar]
- Sapkota, R.; Qureshi, R.; Calero, M.F.; Hussain, M.; Badjugar, C.; Nepal, U.; Poulose, A.; Zeno, P.; Vaddevolu, U.B.P.; Yan, H. Yolov10 to its genesis: A decadal and comprehensive review of the you only look once series. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.19407. [Google Scholar]
- Shreeram, P.; Krithik, P.; Sountharrajan, S.; Saranya, S. Automated Detection of Necrotizing Fasciitis in Patient Affected Area Images using YOLO v9. Curr. Sci. 2025, 5, 1378–1387. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, M.; Zbären, P.; Hermans, R.; Becker, C.D.; Marchal, F.; Kurt, A.-M.; Marre, S.; Rüfenacht, D.; Terrier, F. Necrotizing fasciitis of the head and neck: Role of CT in diagnosis and management. Radiology 1997, 202, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, T.-L.; Chiu, M.-C.; Chen, C.-C.; Lin, H.-Y. Develop a Real Time Necrotizing Fasciitis Identification Model to Enhance Clinical Diagnosis Efficiency and Accuracy in Computed Tomography Images. In Proceedings of the Asia Pacific Industrial Engineering & Management Systems Conference 2024, Chiang Mai, Thailand, 10–14 November 2024. [Google Scholar]


| Characteristic | Number (Mean) | Percentage (SD) |
|---|---|---|
| Gender | ||
| Male | 22 | 70.97% |
| Female | 9 | 29.03% |
| Age | ||
| 62.13 | 13.56 | |
| Admission source | ||
| Emergency | 27 | 87.10% |
| Inpatient | 3 | 9.68% |
| Outpatient | 1 | 3.23% |
| Comorbidity | ||
| Diabetes | 20 | 64.52% |
| Peripheral vascular disease | 1 | 3.23% |
| Trauma at the affected site | 4 | 12.90% |
| Cirrhosis | 4 | 12.90% |
| End stage renal disease | 4 | 12.90% |
| Chemotherapy | 2 | 6.45% |
| Hospitalization | ||
| General ward | 17 | 54.84% |
| Intensive care unit | 14 | 45.16% |
| Expire in 48 h | 2 | 6.45% |
| Causative pathogens | ||
| Monomicrobial | 16 | 51.61% |
| Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) | 2 | |
| Staphylococcus capitis | 1 | |
| Coagulase negative staphylococcus | 1 | |
| Enterococcus faecalis | 1 | |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae | 6 | |
| Vibrio vulnificus | 2 | |
| Vibrio parahaemolyticus | 1 | |
| Enterobacter cloacae | 1 | |
| Enterobacter bugandensis | 1 | |
| Polymicrobial | 12 | 38.71% |
| Mixed aerobic | 9 | |
| Mixed aerobic/anaerobic | 3 | |
| Mixed bacteria/fungus | 1 | |
| Culture negative | 3 | 9.68% |
| NSTI-affected region | ||
| Head and neck | 2 | 6.45% |
| Upper extremities | 3 | 9.68% |
| Chest and abdominal wall | 2 | 6.45% |
| Perineum | 10 | 32.26% |
| Lower extremities | 14 | 45.16% |
| Time from admission to surgery (day) | ||
| 2.53 | 6.07 | |
| Time from CT scan to report (hour) | ||
| 10.08 | 11.79 |
| Category | Number | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| NSTI-affected regions | ||
| Head and neck | 427 | 4.42% |
| Upper extremities | 598 | 6.19% |
| Chest and abdominal wall | 859 | 8.89% |
| Perineum | 3767 | 38.97% |
| Lower extremities | 4016 | 41.54% |
| Lesion images | ||
| NSTI images | 3332 | 37.02% |
| Health images | 5669 | 67.98% |
| NSTI features | ||
| Soft tissue ectopic gas | 1982 | 33.13% |
| Fluid accumulation | 1577 | 27.04% |
| Fascia edematous changes | 1872 | 32.10% |
| Soft tissue non-enhancement | 401 | 6.88% |
| Authors, Year | Study Design | Dataset | Model | Target Features | Performance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Das et al., 2021 [20] | Retrospective study | 693 images in total; 231 Clinical skin images containing NSTI; 231 Clinical skin images containing normal skin; 231 Augmented images containing NSTI | YOLOv3 | Skin appearance suggestive of NSTI | AP: 0.58 |
| P. Shreeram et al., 2025 [49] | Retrospective study | 693 images in total; 231 Clinical skin images containing NSTI; 231 Clinical skin images containing normal skin; 231 Augmented images containing NSTI | YOLOv9 | Skin appearance suggestive of NSTI | IoU: 0.649 |
| Heng-Yu Lin et al., 2025 | Retrospective study | 9001 CT images in total; 3332 NSTI images and 5669 healthy images. | YOLOv10 | Soft tissue ectopic gas, fluid accumulation, fascia edematous changes, soft tissue non-enhancement in CT images | mAP: 0.75 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, H.-Y.; Chiu, M.-C.; Kao, T.-L.; Chen, C.-C. Automated Detection of Necrotizing Soft Tissue Infection Features by Computed Tomography. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2030. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15162030
Lin H-Y, Chiu M-C, Kao T-L, Chen C-C. Automated Detection of Necrotizing Soft Tissue Infection Features by Computed Tomography. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(16):2030. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15162030
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Heng-Yu, Ming-Chuan Chiu, Tzu-Lun Kao, and Chun-Chia Chen. 2025. "Automated Detection of Necrotizing Soft Tissue Infection Features by Computed Tomography" Diagnostics 15, no. 16: 2030. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15162030
APA StyleLin, H.-Y., Chiu, M.-C., Kao, T.-L., & Chen, C.-C. (2025). Automated Detection of Necrotizing Soft Tissue Infection Features by Computed Tomography. Diagnostics, 15(16), 2030. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15162030







