Ultrasonography and Biomarkers in the Diagnostic Evaluation of Peritoneal Tuberculosis: A Case Series Analysis
Abstract
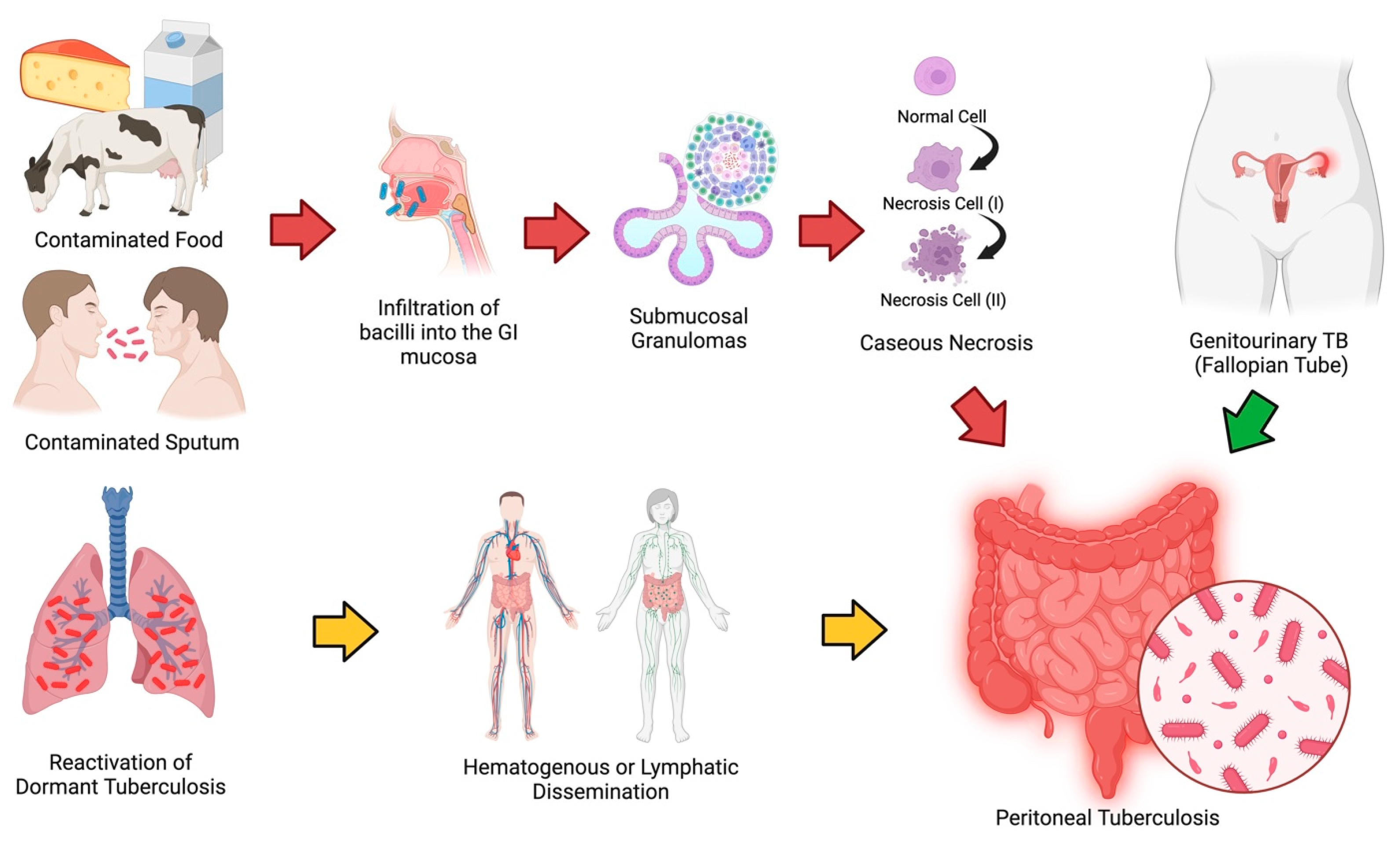
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Ethical Clearance
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Measurement of Biomarker Levels and Ultrasonography
3. Results
4. Discussion
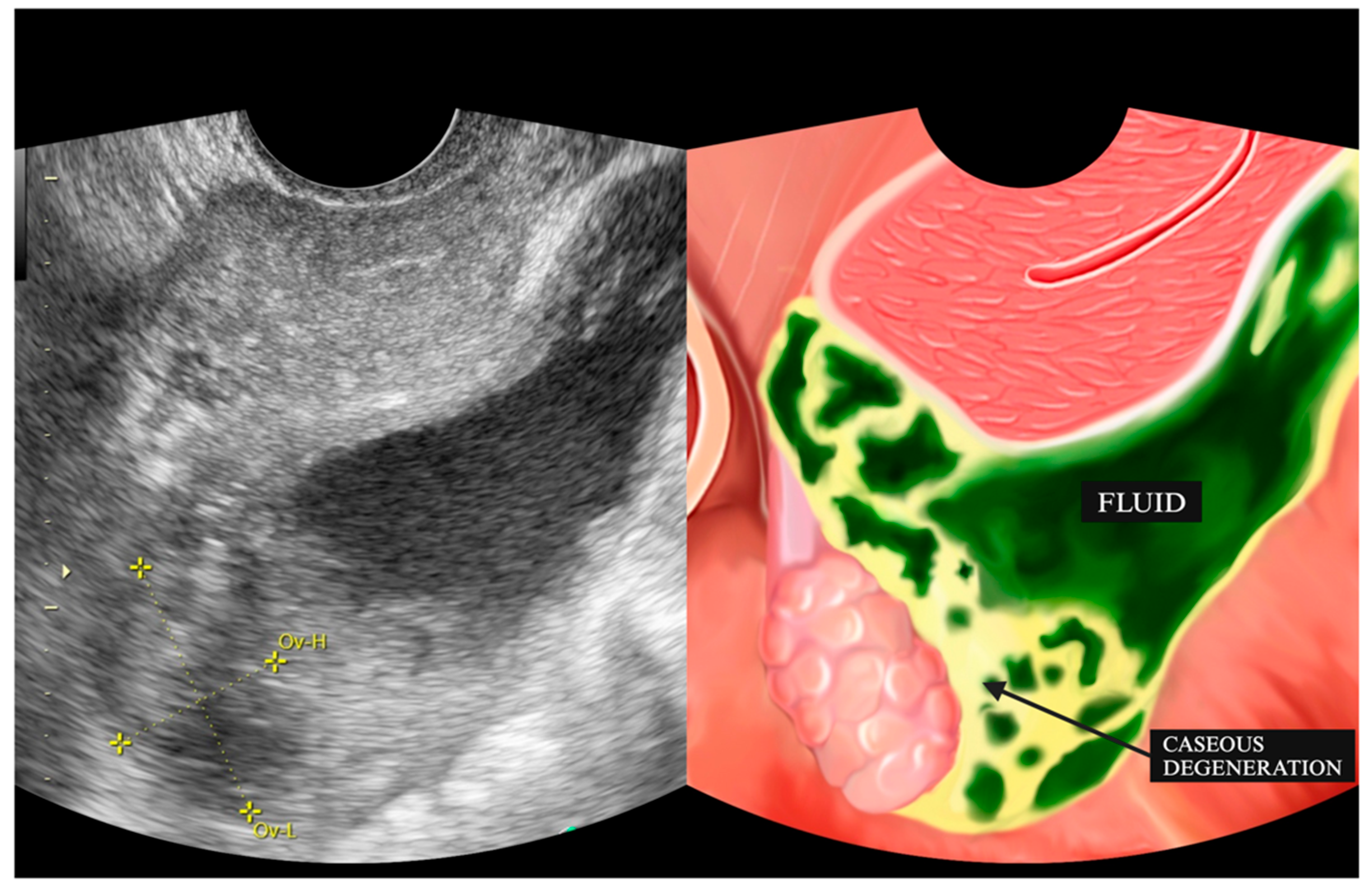
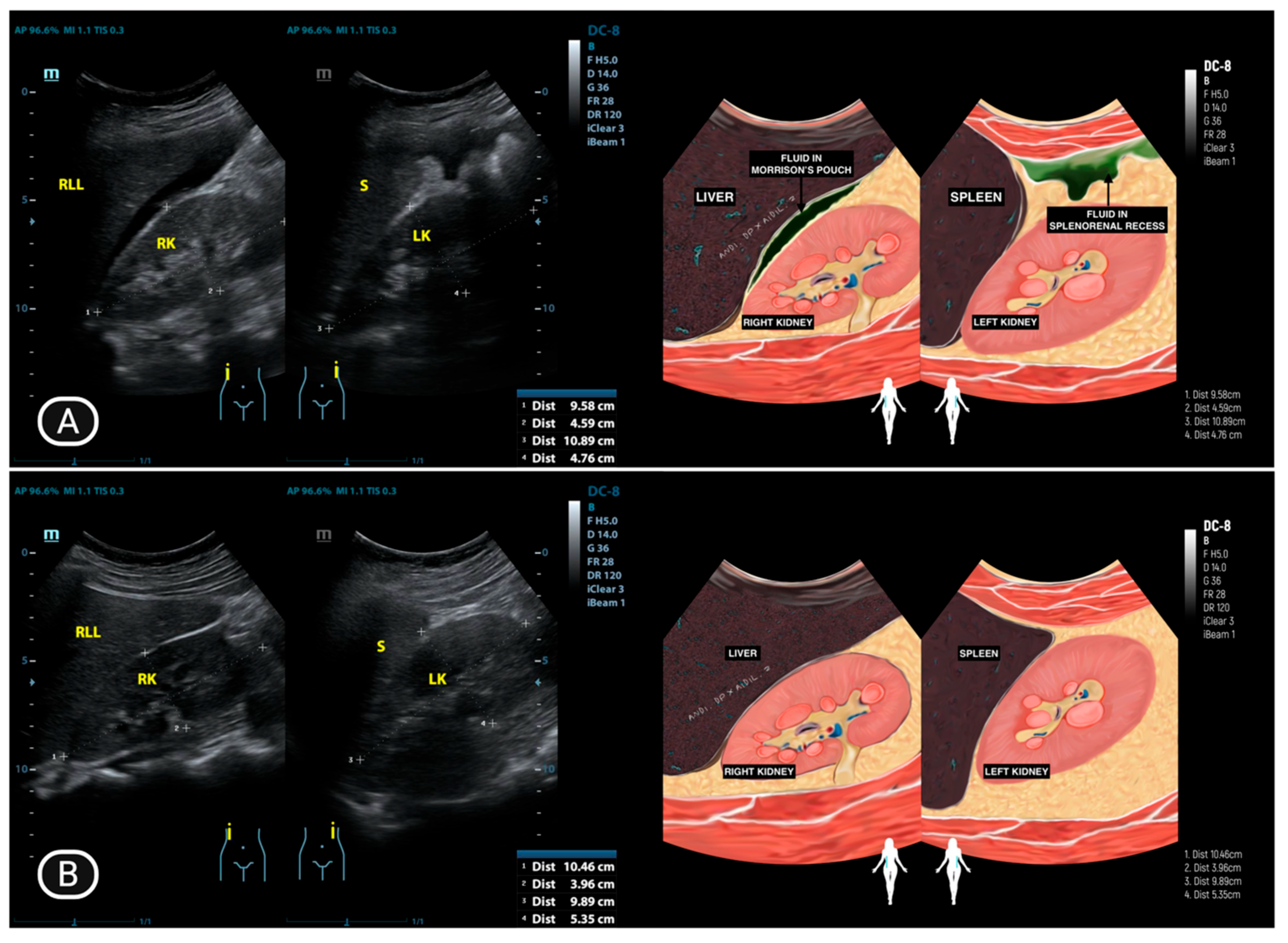
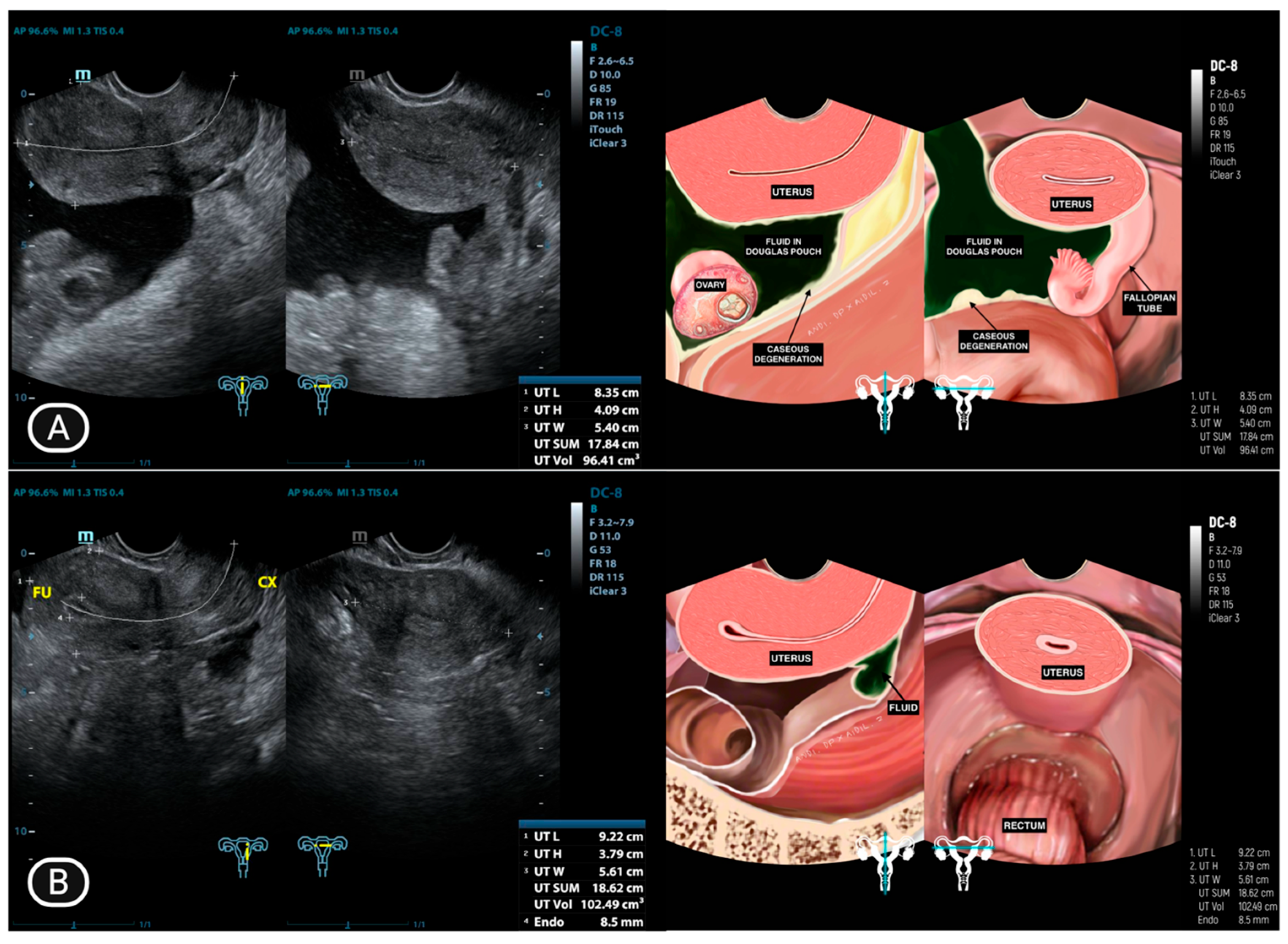
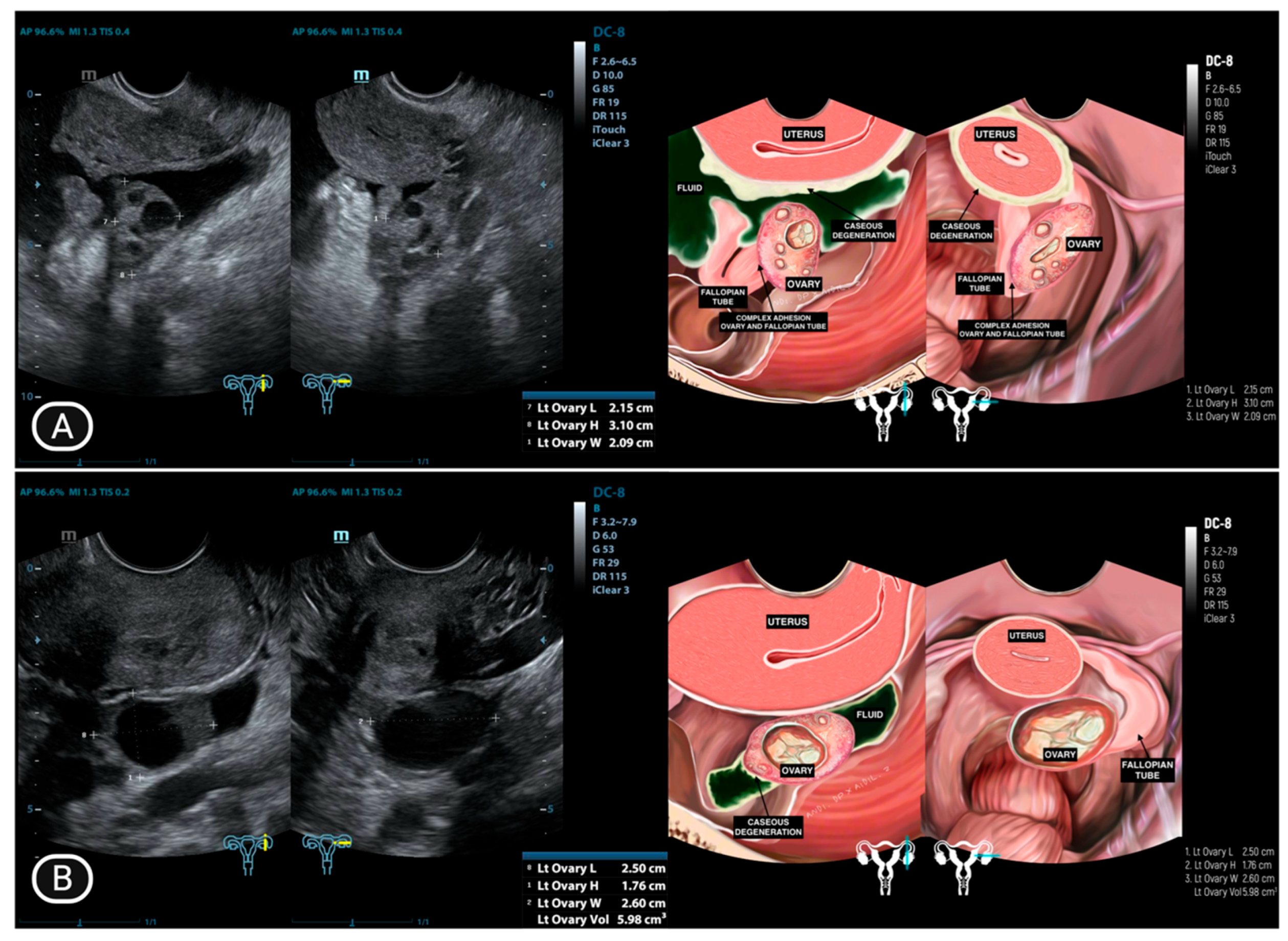
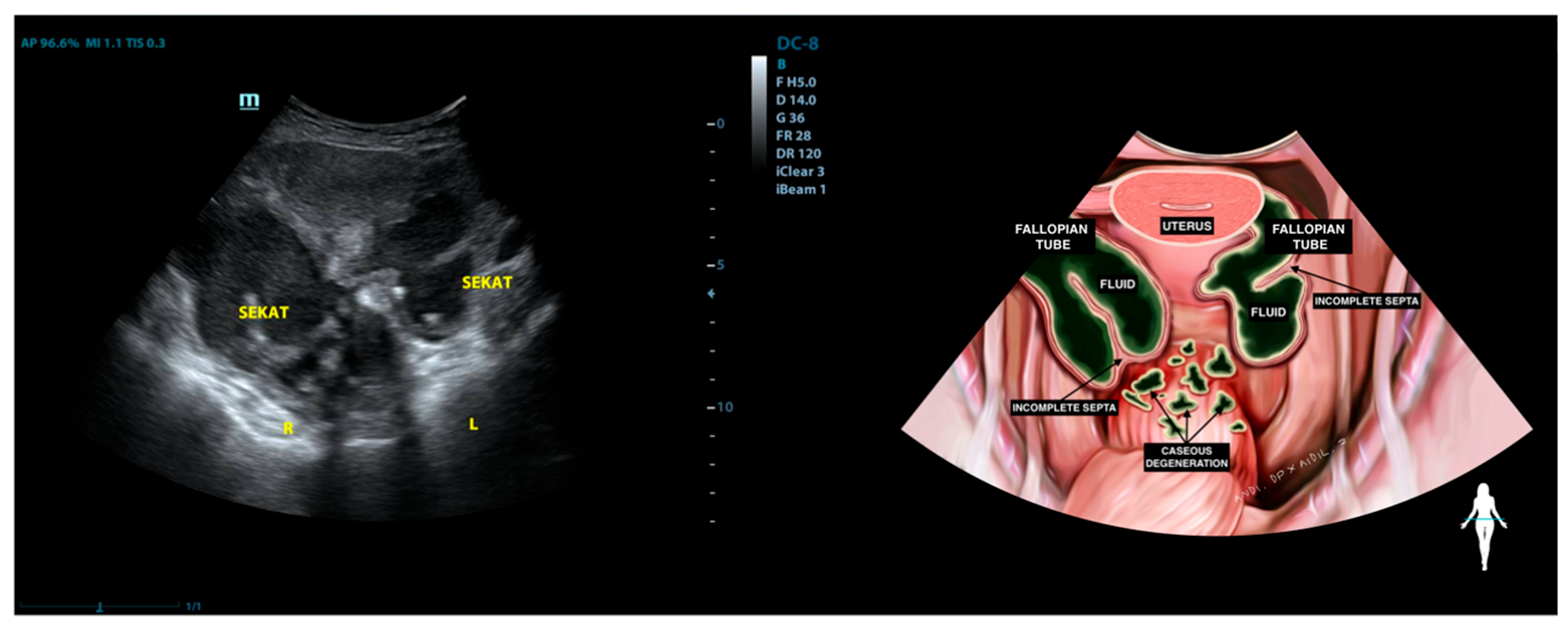
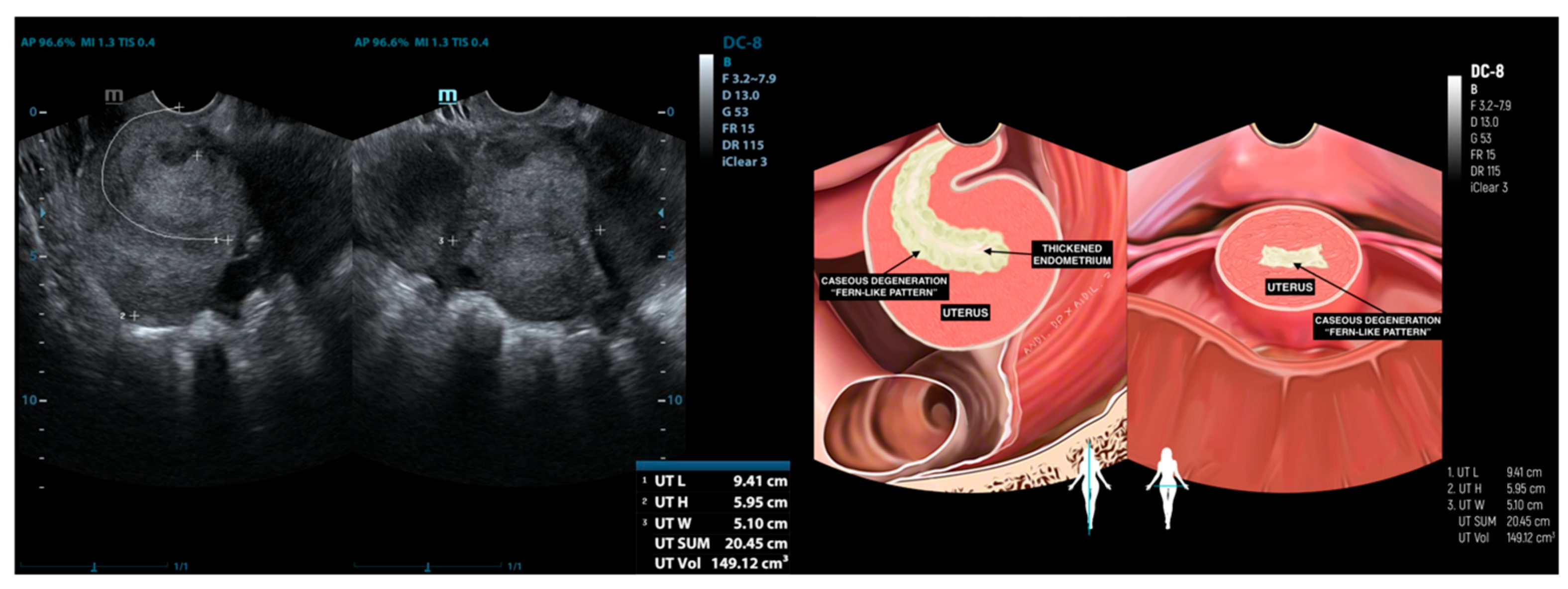
4.1. Ultrasonography Findings
4.2. Biomarker Profiles
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koff, A.; Azar, M.M. Diagnosing peritoneal tuberculosis. BMJ Case Rep. 2020, 13, e233131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozturk, N.B.; Tsagkaris, C.; Dolek, N.; Iliaz, R. Clinical presentation of peritoneal tuberculosis. Bayl. Univ. Med. Cent. Proc. 2023, 36, 259–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaid, U.; Kane, G.C. Tuberculous Peritonitis. In Tuberculosis and Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Infections; Schlossberg, D., Ed.; American Society for Microbiology: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; pp. 433–438. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.C.; Averbukh, L.D.; Wu, G.Y. Diagnostic and Therapeutic Strategies for Peritoneal Tuberculosis: A Review. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2019, 7, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciambrone, L.; Gioffrè, A.; Musarella, R.; Samele, P.; Visaggio, D.; Pirolo, M.; Clausi, M.T.; Di Natale, R.; Gherardi, M.; Spatari, G.; et al. Presence of Mycobacterium bovis in slaughterhouses and risks for workers. Prev. Vet. Med. 2020, 181, 105072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, N.B.; Payeur, J.; Bravo, D.; Osorio, R.; Stuber, T.; Farrell, D.; Paulson, D.; Treviso, S.; Mikolon, A.; Rodriguez-Lainz, A.; et al. Recovery of Mycobacterium bovis from Soft Fresh Cheese Originating in Mexico. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 1025–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debi, U.; Ravisankar, V.; Prasad, K.K.; Sinha, S.K.; Sharma, A.K. Abdominal tuberculosis of the gastrointestinal tract: Revisited. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 14831–14840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.K.; Choi, Y.M.; Lee, S.S.; Park, H.K.; Cha, R.R.; Kim, W.S.; Kim, J.J.; Lee, J.M.; Kim, H.J.; Ha, C.Y.; et al. Clinical features and outcomes of abdominal tuberculosis in southeastern Korea: 12 years of experience. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guirat, A.; Koubaa, M.; Mzali, R.; Abid, B.; Ellouz, S.; Affes, N.; Jemaa, M.B.; Frikha, F.; Amar, M.B.; Beyrouti, M.I. Peritoneal tuberculosis. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2011, 35, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purbadi, S.; Indarti, J.; Winarto, H.; Putra, A.D.; Nuryanto, K.H.; Utami, T.W.; Sotarduga, G.E. Peritoneal tuberculosis mimicking advanced ovarian cancer case report: Laparoscopy as diagnostic modality. Int. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2021, 88, 106495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, K.M.; Chow, V.C.Y.; Szeto, C.C. Indication for peritoneal biopsy in tuberculous peritonitis. Am. J. Surg. 2003, 185, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mbengue, A.; Ndiaye, A.R.; Amar, N.I.; Diallo, M.; Diack, A.; Ndao, M.D.; Diop, M.; Fall, A.; Diouf, C.T.; Soko, T.O.; et al. Ultrasonography of peritoneal tuberculosis. J. Ultrason. 2019, 19, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, J.C.W.; Fang, C.L.; Chan, W.P. Peritoneal tuberculosis with elevated CA-125 mimicking ovarian cancer with carcinomatosis peritonei: Crucial CT findings. EXCLI J. 2016, 15, 711–715. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, K. Evaluating the clinical significances of serum HE4 with CA125 in peritoneal tuberculosis and epithelial ovarian cancer. Biomarkers 2016, 21, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, M.; Kaplan, M.; Isikdogan, A.; Celik, Y. Differentiation of tuberculous peritonitis from peritonitis carcinomatosa without surgical intervention. Saudi J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 17, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riquelme, A.; Calvo, M.; Salech, F.; Valderrama, S.; Pattillo, A.; Arellano, M.; Arrese, M.; Soza, A.; Viviani, P.; Letelier, L.M. Value of Adenosine Deaminase (ADA) in Ascitic Fluid for the Diagnosis of Tuberculous Peritonitis. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2006, 40, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, S.B.; Qin, S.Y.; Guo, X.Y.; Luo, W.; Jiang, H.X. Assessment by meta-analysis of interferon-gamma for the diagnosis of tuberculous peritonitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 1645–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilgin, T.; Karabay, A.; Dolar, E.; Develioglu, O.H. Peritoneal tuberculosis with pelvic abdominal mass, ascites and elevated CA 125 mimicking advanced ovarian carcinoma: A series of 10 cases. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2001, 11, 290–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoori, B.; Herrmann, K.A. Mesentery, Omentum, Peritoneum: Fluid Collections (Ascites, Abscess, Hemorrhage). In Abdominal Imaging; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 1601–1622. [Google Scholar]
- Rudralingam, V.; Footitt, C.; Layton, B. Ascites matters. Ultrasound 2017, 25, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, S.; Newsholme, W.; Gibson, T. Diagnosis and management of intra-abdominal tuberculosis. Br. J. Hosp. Med. 2018, 79, C86–C89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, M.L.; Mahalingaiah, S. Case report of pelvic tuberculosis resulting in Asherman’s syndrome and infertility. Fertil. Res. Pract. 2019, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Grotta, L.M.; Dyer, R.B.; Holbert, B.L. The “cogwheel” sign of hydrosalpinx. Abdom. Radiol. 2019, 44, 3486–3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oge, T.; Ozalp, S.S.; Yalcin, O.T.; Kabukcuoglu, S.; Kebapci, M.; Arik, D.; Isikci, T. Peritoneal tuberculosis mimicking ovarian cancer. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2012, 162, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arezzo, F.; Cazzato, G.; Loizzi, V.; Ingravallo, G.; Resta, L.; Cormio, G. Peritoneal Tuberculosis Mimicking Ovarian Cancer: Gynecologic Ultrasound Evaluation with Histopathological Confirmation. Gastroenterol. Insights 2021, 12, 278–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djuwantono, T.; Permadi, W.; Septiani, L.; Faried, A.; Halim, D.; Parwati, I. Female genital tuberculosis and infertility: Serial cases report in Bandung, Indonesia and literature review. BMC Res. Notes 2017, 10, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, G.A.; Devaleenal, D.B.; Natrajan, M. Genital tuberculosis in females. Indian J. Med. Res. 2017, 154, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatongi, D.K.; Gitau, G.; Kay, V.; Ngwenya, S.; Lafong, C.; Hasan, A. Female genital tuberculosis. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2005, 7, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hoving, D.J.; Griesel, R.; Meintjes, G.; Takwoingi, Y.; Maartens, G.; Ochodo, E.A. Abdominal ultrasound for diagnosing abdominal tuberculosis or disseminated tuberculosis with abdominal involvement in HIV-positive individuals. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 2019, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholler, N.; Urban, N. CA125 in Ovarian Cancer. Biomark. Med. 2007, 1, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, A.R.; Baggerly, K.; Bast, R.C. The emerging role of HE4 in the evaluation of epithelial ovarian and endometrial carcinomas. Oncology 2013, 27, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Dowdy, S.; Tipton, T.; Podratz, K.; Lu, W.G.; Xie, X.; Jiang, S.W. HE4 as a biomarker for ovarian and endometrial cancer management. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2009, 9, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angioli, R.; Plotti, F.; Capriglione, S.; Aloisi, A.; Montera, R.; Luvero, D.; Miranda, A.; Cafà, E.V.; Damiani, P.; Benedetti-Panici, P.; et al. Can the preoperative HE4 level predict optimal cytoreduction in patients with advanced ovarian carcinoma? Gynecol. Oncol. 2013, 128, 579–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Wang, Y.; Cai, G.; Liang, J.; Yue, C.; Wang, F.; Song, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, M.; Luo, J.; et al. Elevated serum concentrations of HE4 as a novel biomarker of disease severity and renal fibrosis in kidney disease. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 67748–67759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.W. The Roles of Carcinoembryonic Antigen in Liver Metastasis and Therapeutic Approaches. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2017, 2017, 7521987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, M.J.; Mitchell, E.P. Carcinoembryonic Antigen in the Staging and Follow-up of Patients with Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Invest. 2005, 23, 338–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Wang, Q.; Li, P. Significance of carcinoembryonic antigen detection in the early diagnosis of colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2023, 15, 2907–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmanzadeh, S.; Tavakkol, H.; Bavieh, K.; Alavi, S.M. Diagnostic value of serum adenosine deaminase (ADA) level for pulmonary tuberculosis. Jundishapur J. Microbiol. 2015, 8, e21760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.; Nath, N.C.; Parvin, R.; Rahman, A.; Bhuiyan, T.M.; Rahman, M.; Mohsin, M.N. Role of ascitic fluid adenosine deaminase (ADA) and serum CA-125 in the diagnosis of tuberculous peritonitis. Bangladesh Med. Res. Counc. Bull. 2015, 40, 89–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumabe, A.; Hatakeyama, S.; Kanda, N.; Yamamoto, Y.; Matsumura, M. Utility of Ascitic Fluid Adenosine Deaminase Levels in the Diagnosis of Tuberculous Peritonitis in General Medical Practice. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2020, 2020, 5792937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahore, P.; Solanke, G.; Patil, C. Diagnostic role of adenosine deaminase (ADA) in ascites. MedPulse Int. J. Med. 2019, 12, 55–59. Available online: https://www.medpulse.in/Medicine/html_12_2_6.php (accessed on 28 March 2025). [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Brizuela, E.; Apriani, L.; Mukherjee, T.; Lachapelle-Chisholm, S.; Miedy, M.; Lan, Z.; Korobitsyn, A.; Ismail, N.; Menzies, D. Assessing the Diagnostic Performance of New Commercial Interferon-γRelease Assays for Mycobacterium tuberculosis Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2023, 76, 1989–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollock, L.; Basu Roy, R.; Kampmann, B. How to use: Interferon γ release assays for tuberculosis. Arch. Dis. Child Educ. Pract. Ed. 2013, 98, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazurek, G.H.; Jereb, J.; Vernon, A.; LoBue, P.; Goldberg, S.; Castro, K.; IGRA Expert Committee; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Updated guidelines for using Interferon Gamma Release Assays to detect Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection—United States, 2010. MMWR Recomm. Rep. 2010, 59, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | Value |
|---|---|
| Mean age (±SD) | 33.0 ± 9.7 years |
| Median age (range) | 30.5 (16–53) years |
| Menstrual Status | |
| Premenopausal | 10 (83.3%) |
| Postmenopausal | 2 (16.7%) |
| Marital Status | |
| Married | 9 (75%) |
| Not Married | 3 (25%) |
| History of TB Exposure | |
| Yes | 3 (25%) |
| No/Unknown | 9 (75%) |
| Histopathology-confirmed TB | |
| Yes | 4 (33.3%) |
| No/Clinical Diagnosis only | 8 (66.7%) |
| No. | Initial (Age) | Uterus | Right Ovarium | Right Fallopian Tube | Left Ovarium | Left Fallopian Tube | Ascites | Other Organ Surfaces |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | LA (25) | Normal | Adhesion complex with hydrosalpinx right fallopian tube | Hydrosalpinx, filled with caseous degeneration inside | Adhesion complex with hydrosalpinx left fallopian tube | Hydrosalpinx, filled with complex fluid | Complex ascites | (−) |
| 2 | AY (33) | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal | Occlusion | Free ascites | (−) |
| 3 | IO (31) * | Caseous degeneration on the surface | Adhesion complex | Normal | Adhesion complex | Normal | (−) | Caseous degeneration on the surface of rectosigmoid colon and small bowel |
| 4 | SMK (29) * | Caseous degeneration on the surface. Complex fluid behind uterus | Normal | Not visualized | Adhesion complex with left fallopian tube | Hydrosalpinx | Complex fluid in cavum of Douglas with caseous degeneration | Caseous degeneration on the surface of rectosigmoid colon |
| 5 | TDW (45) | Normal | Normal | Not visualized | Normal | Normal | Free ascites | (−) |
| 6 | STG (53) | Adherent to both masses in the adnexa and the rectosigmoid | Not visualized | Mass with incomplete septation (Hydrosalpinx) | Normal | Mass with incomplete septation (Hydrosalpinx) | (−) | (−) |
| 7 | EF (30) | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal | Mass with incomplete septation, filled with complex fluid (Hydrosalpinx) | (−) | (−) |
| 8 | OO (16) | Normal | Normal | Not visualized | Normal | Not visualized | Pocket Abscess | (−) |
| 9 | IHS (44) | Normal | Enlarged, cystic, unilocular, and contains simple fluid | Not visualized | Normal | Not visualized | Massive ascites | (−) |
| 10 | AS (44) * | Ill−defined mass at the anterior | Adhesion complex with hydrosalpinx right fallopian tube | Hydrosalpinx | Enlarged with multilocular cystic filled with complex fluid | Not visualized | (−) | (−) |
| 11 | Y (30) * | Normal | Adhesion to pelvic wall | Not visualized | Adhesion complex with left fallopian tube | Hydrosalpinx, filled with caseous degeneration inside | Complex ascites | (−) |
| 12 | DR (24) | Complex fluid in uterine cavity (10.98 mm) | Normal | Hydrosalpinx | Adhesion | Normal | (−) | (−) |
| No. | Initial (Age) | CA-125 (U/mL) | HE-4 (pmol/L) | CEA (ng/mL) | ADA (U/L) | IGRA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | LA (25) | 612.8 | 79.4 | 1.5 | 49 | 1st test: Negative 2nd test: Positive (Repeated after one month) |
| 2 | AY (33) | 836.3 | 47.7 | 0.6 | 50 | Positive |
| 3 | IO (31) * | 337.7 | 73.3 | 1.2 | - | Positive |
| 4 | SMK (29) * | 460.4 | 77.0 | 0.9 | 44 | Positive |
| 5 | TDW (45) | 333 | 47.8 | 1.1 | 40 | Positive |
| 6 | STG (53) | 358.8 | 50.9 | 1.3 | - | Positive |
| 7 | EF (30) | 1425.8 | 50.6 | 1.2 | - | Positive |
| 8 | OO (16) | 183.1 | 52.2 | 1.1 | 55 | Indeterminate |
| 9 | IHS (44) | 208.8 | 60.0 | 1.9 | 44 | Positive |
| 10 | AS (44) * | 525.2 | 74.7 | 1.7 | - | Positive |
| 11 | Y (30) * | 432.2 | 130.4 | 7.1 | 39 | Positive |
| 12 | DR (24) | 96.9 | 57.6 | 1.1 | - | Negative |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Putra, A.D.; Purwoto, G.; Sachi, Y.; Suhendar, C.W.; Nugroho, I.; Saidah, I.; Wirasugianto, J.; Amelia; Syariatin, L.; Lukas, G.A. Ultrasonography and Biomarkers in the Diagnostic Evaluation of Peritoneal Tuberculosis: A Case Series Analysis. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2008. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15162008
Putra AD, Purwoto G, Sachi Y, Suhendar CW, Nugroho I, Saidah I, Wirasugianto J, Amelia, Syariatin L, Lukas GA. Ultrasonography and Biomarkers in the Diagnostic Evaluation of Peritoneal Tuberculosis: A Case Series Analysis. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(16):2008. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15162008
Chicago/Turabian StylePutra, Andi Darma, Gatot Purwoto, Yumeico Sachi, Chandra William Suhendar, Ilham Nugroho, Izzati Saidah, Jourdan Wirasugianto, Amelia, Lasmini Syariatin, and Graciella Angelica Lukas. 2025. "Ultrasonography and Biomarkers in the Diagnostic Evaluation of Peritoneal Tuberculosis: A Case Series Analysis" Diagnostics 15, no. 16: 2008. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15162008
APA StylePutra, A. D., Purwoto, G., Sachi, Y., Suhendar, C. W., Nugroho, I., Saidah, I., Wirasugianto, J., Amelia, Syariatin, L., & Lukas, G. A. (2025). Ultrasonography and Biomarkers in the Diagnostic Evaluation of Peritoneal Tuberculosis: A Case Series Analysis. Diagnostics, 15(16), 2008. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15162008







