Evaluation of a Simplified Upper Arm Device for Vacuum-Assisted Collection of Capillary Blood Specimens
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
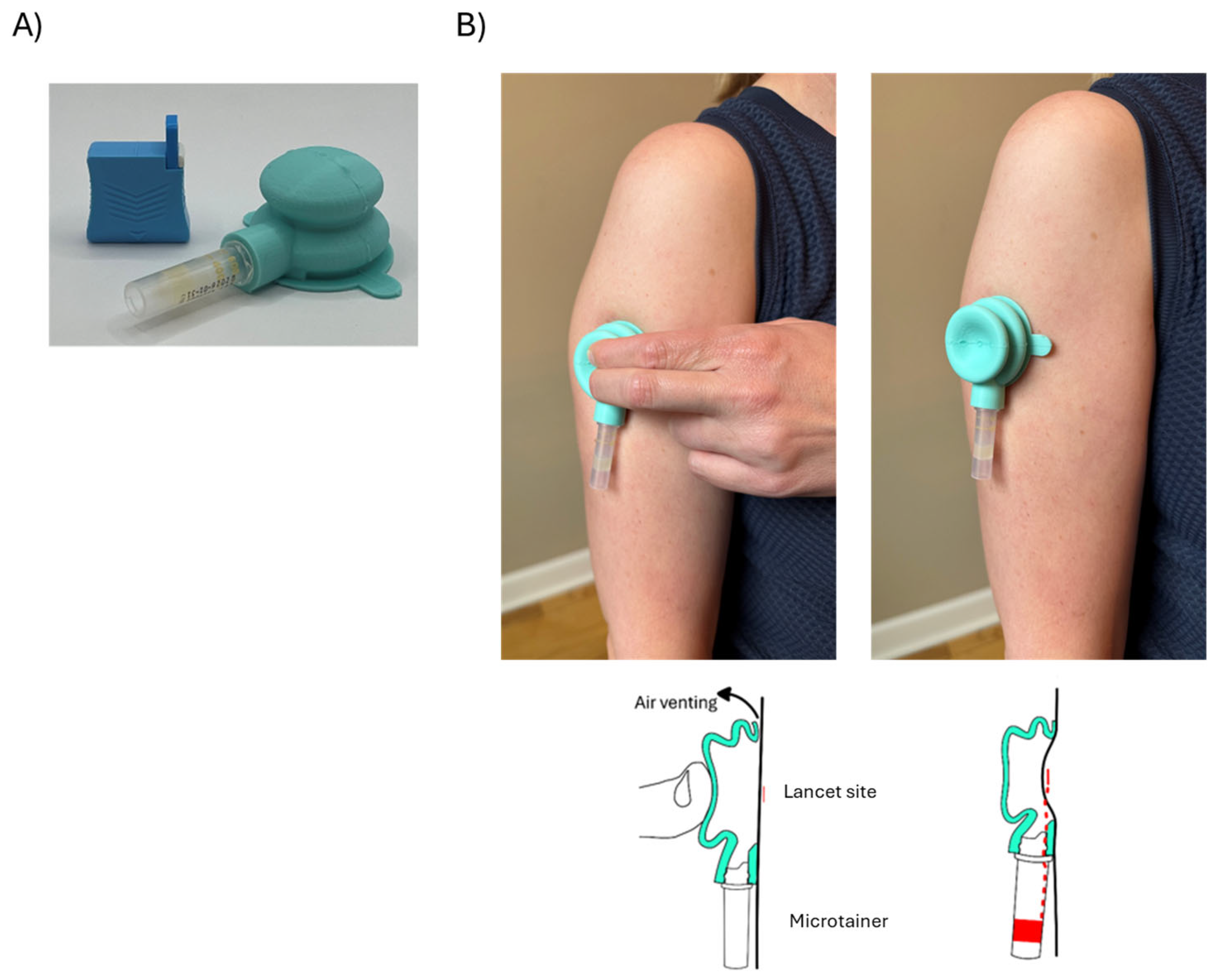
2.1. Device Design
2.2. Materials
2.3. Vacuum Pressure and Skin Temperature Measurement
2.4. Evaluation of Blood Collection Volume and Analyte Integrity
3. Results
3.1. Vacuum Pressure and Skin Temperature
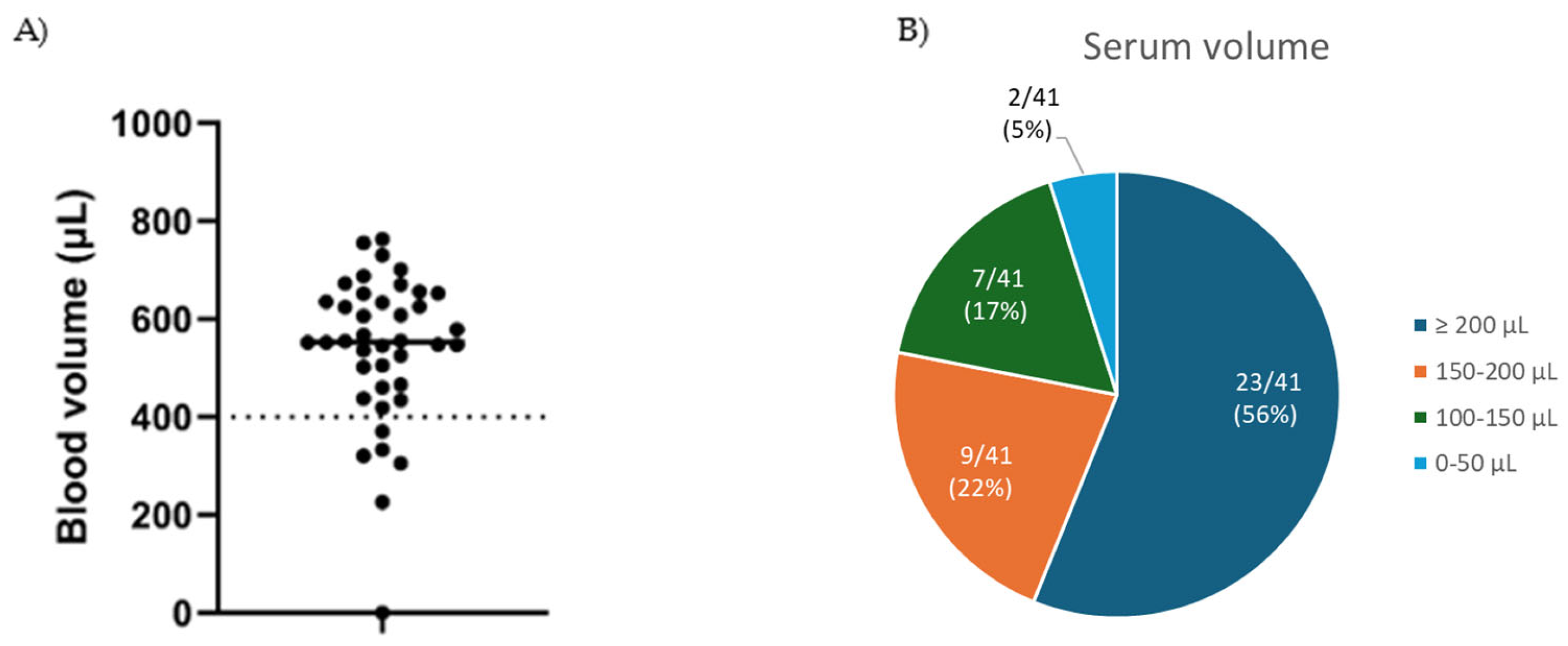
3.2. Blood Volume and Analyte Evaluation
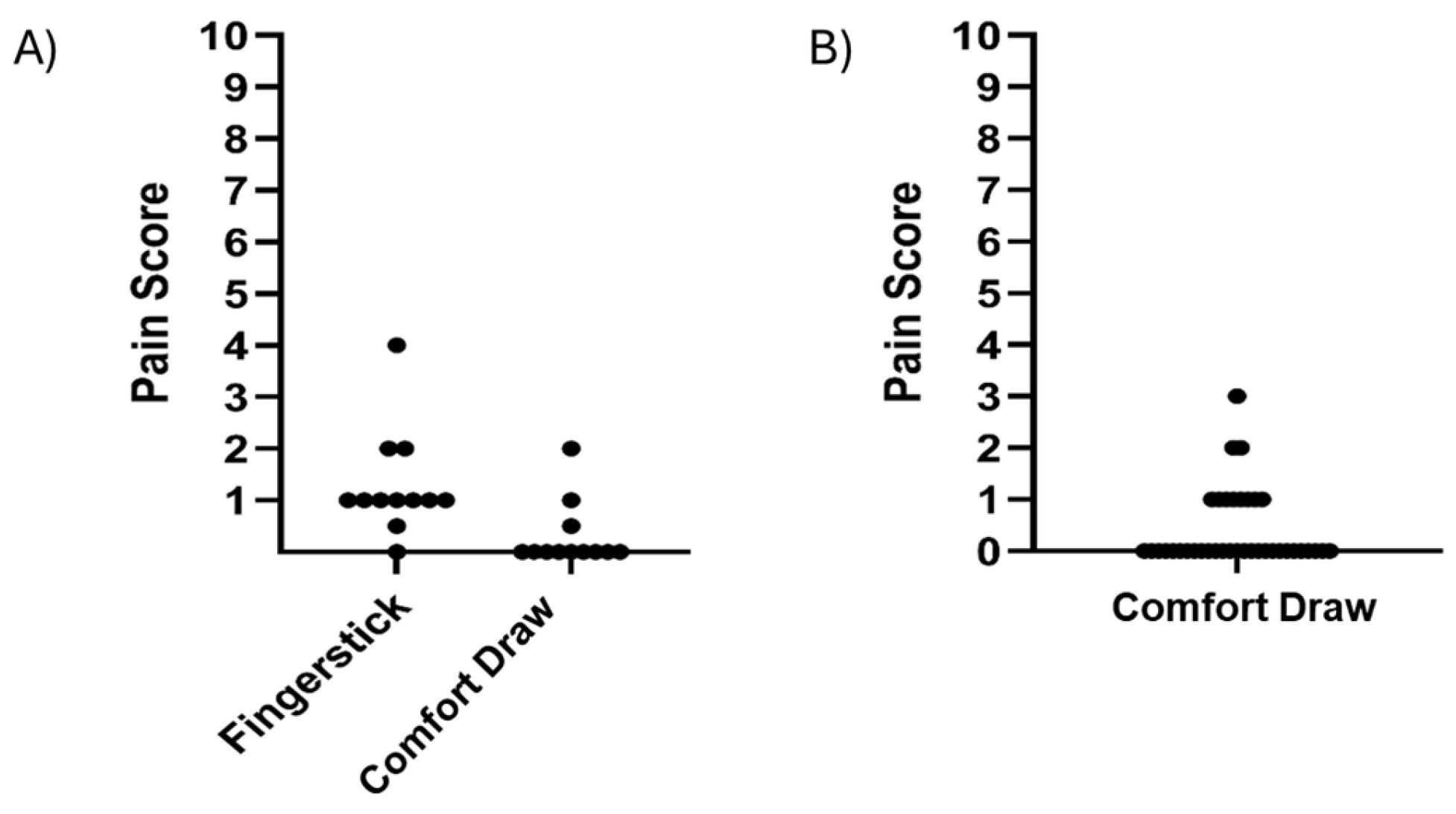
3.3. Pain Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALP | Alkaline phosphatase |
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| BUN | Blood urea nitrogen |
| CRPhs | C-Reactive Protein using a high-sensitivity assay |
| CV | Coefficient of variation |
| HDL | High-density lipoprotein |
| LDL | Low-density lipoprotein |
References
- Tang, R.; Yang, H.; Choi, J.R.; Gong, Y.; You, M.; Wen, T.; Li, A.; Li, X.; Xu, B.; Zhang, S.; et al. Capillary blood for point-of-care testing. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2017, 54, 294–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, M.S.F.; McKeage, J.W.; Xu, J.; Ruddy, B.P.; Nielsen, P.M.F.; Taberner, A.J. Minimally invasive capillary blood sampling methods. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2023, 20, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furhad, S.; Sina, R.E.; Bokhari, A.A. Cupping Therapy; StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Boffel, L.; Van Mensel, A.; Pauwels, J.; Hond, E.D.; Bessems, J.; Van Uytfanghe, K.; Stove, C.P. Self-Sampling by Adolescents at Home: Assessment of the Feasibility to Successfully Collect Blood Microsamples by Inexperienced Individuals. AAPS J. 2024, 26, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catala, A.; Culp-Hill, R.; Nemkov, T.; D’aLessandro, A. Quantitative metabolomics comparison of traditional blood draws and TAP capillary blood collection. Metabolomics 2018, 14, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collier, B.B.; Brandon, W.C.; Chappell, M.R.; Kovach, P.M.; Grant, R.P. Maximizing Microsampling: Measurement of Comprehensive Metabolic and Lipid Panels Using a Novel Capillary Blood Collection Device. J. Appl. Lab. Med. 2023, 8, 1115–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasari, H.; Smyrnova, A.; Leng, J.; Ducharme, F.M. Feasibility, acceptability, and safety of a novel device for self-collecting capillary blood samples in clinical trials in the context of the pandemic and beyond. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0304155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koulman, A.; Rennie, K.L.; Parkington, D.; Tyrrell, C.S.; Catt, M.; Gkrania-Klotsas, E.; Wareham, N.J. The development, validation and application of remote blood sample collection in telehealth programmes. J. Telemed. Telecare 2024, 30, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, L.; Smith, M.; Boutard, K.; Fedoruk, M.; Miller, G. Comparison of Microcapillary Blood Sampling Devices for Use in Anti-Doping. Drug Test. Anal. 2024. Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silliman, E.; Chung, E.H.; Fitzpatrick, E.; Jolin, J.A.; Brown, M.; Hotaling, J.; Styer, A.K.; Karmon, A.E. Evaluation of at-home serum anti-Müllerian hormone testing: A head-to-head comparison study. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2022, 20, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickremsinhe, E.; Fantana, A.; Berthier, E.; Quist, B.A.; de Castilla, D.L.; Fix, C.; Chan, K.; Shi, J.; Walker, M.G.; Kherani, J.F.; et al. Standard Venipuncture vs a Capillary Blood Collection Device for the Prospective Determination of Abnormal Liver Chemistry. J. Appl. Lab. Med. 2022, 8, 535–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarbl, J.; Eimer, E.; Gigg, C.; Bendzuck, G.; Korinth, M.; Elling-Audersch, C.; Kleyer, A.; Simon, D.; Boeltz, S.; Krusche, M.; et al. Remote self-collection of capillary blood using upper arm devices for autoantibody analysis in patients with immune-mediated inflammatory rheumatic diseases. RMD Open 2022, 8, e002641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 510 (k) Number K242664: Single Use Only Blood Lancet with an Integral Sharps Injury Prevention Feature; Decision Date 11 May 2024. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfpmn/pmn.cfm?id=K242664 (accessed on 14 July 2025).
- Johnson, J.M.; Kellogg, D.L., Jr. Local thermal control of the human cutaneous circulation. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 109, 1229–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampson, M.; Ling, C.; Sun, Q.; Harb, R.; Ashmaig, M.; Warnick, R.; Sethi, A.; Fleming, J.K.; Otvos, J.D.; Meeusen, J.W.; et al. A New Equation for Calculation of Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol in Patients With Normolipidemia and/or Hypertriglyceridemia. JAMA Cardiol. 2020, 5, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendelman, T.; Chaudhary, A.; LeClair, A.C.; van Leuven, K.; Chee, J.; Fink, S.L.; Welch, E.J.; Berthier, E.; Quist, B.A.; Wald, A.; et al. Self-collection of capillary blood using Tasso-SST devices for Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibody testing. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0255841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bina, D.M.; Anderson, R.L.; Johnson, M.L.; Bergenstal, R.M.; Kendall, D.M. Clinical impact of prandial state, exercise, and site preparation on the equivalence of alternative-site blood glucose testing. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 981–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koschinsky, T.; Jungheim, K.; Heinemann, L. Glucose sensors and the alternate site testing-like phenomenon: Relationship between rapid blood glucose changes and glucose sensor signals. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2003, 5, 829–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topping, J.; Reardon, M.; Coleman, J.; Hunter, B.; Shojima-Perera, H.; Thyer, L.; Simpson, P. A Comparison of Venous versus Capillary Blood Samples when Measuring Blood Glucose Using a Point-of-Care, Capillary-Based Glucometer. Prehospital Disaster Med. 2019, 34, 506–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 2024 Silicone Rubber Price Guide: Types, Costs, and Key Factors. Available online: https://rissochem.com/2024-silicone-rubber-price/ (accessed on 14 July 2025).
- Cardinal Health Gentleheel Heel Incision Devices. Available online: https://www.graylinemedical.com/products/cardinal-health-gentleheel-heel-incision-devices-lancet-heel-toddler-blue-3x2mm-ght10x50 (accessed on 14 July 2025).
- Tasso + Self Blood Collection Device. Available online: https://www.diagenta.com/store/p/tasso-self-blood-collection-device (accessed on 16 July 2025).
- TAP Micro Select Painless Blood Collection Device. Available online: https://stat-technologies.com/product/tap-micro-select-painless-blood-collection-device/ (accessed on 16 July 2025).
- Fields, J.M.; Piela, N.E.; Au, A.K.; Ku, B.S. Risk factors associated with difficult venous access in adult ED patients. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2014, 32, 1179–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eren, H. Difficult Intravenous Access and Its Management. In Ultimate Guide to Outpatient Care; Zaman, G.S., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sou, V.; McManus, C.; Mifflin, N.; Frost, S.A.; Ale, J.; Alexandrou, E. A clinical pathway for the management of difficult venous access. BMC Nurs. 2017, 16, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Specimen Quality Metric | Acceptance Criteria | Proportion of Samples Meeting Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Blood volume | >400 µL | 85.4% (35/41) |
| Serum volume | >100 µL | 95.1% (39/41) |
| Hemolysis index | <40 | 100.0% (39/39) |
| Analyte | CLIA Limit | Mean Result (Control) | Mean Result (Comfort Draw) | Mean Bias | Percentage of Specimens Within CLIA Limits |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Albumin | ±8.0% | 4.47 g/dL | 4.54 g/dL | +1.6% | 97.4% |
| ALP | ±20.0% | 59.8 U/L | 60.2 U/L | +1.2% | 100% |
| ALT | ±15.0% | 22.6 U/L | 22.6 U/L | −0.1% | 83.8% |
| AST | ±15.0% | 20.1 U/L | 20.3 U/L | +1.8% | 84.2% |
| Total Bilirubin | ±20.0% | 0.40 mg/dL | 0.37 mg/dL | −7.0% | 92.3% |
| BUN | ±9.0% | 12.7 mg/dL | 13.2 mg/dL | +3.4% | 74.4% |
| Calcium | ±1.0 mg/dL | 9.57 mg/dL | 9.49 mg/dL | −0.08 mg/dL | 100% |
| Carbon Dioxide | ±20.0% | 24.4 mmol/L | 20.10 mmol/L | −17.7% | 75% |
| Chloride | ±5.0% | 102.1 mmol/L | 104.8 mmol/L | +2.6% | 100% |
| Cholesterol | ±10.0% | 179.0 mg/dL | 180.9 mg/dL | +1.0% | 100% |
| Creatinine | ±10.0% | 0.912 mg/dL | 0.834 mg/dL | −5.3% | 84.2% |
| Glucose | ±8.0% | 95.4 mg/dL | 103.6 mg/dL | +8.6% | 56.8% |
| HDL | ±20.0% | 52.5 mg/dL | 52.8 mg/dL | +0.6% | 100% |
| LDL (calculated) | ±20.0% | 101.1 mg/dL | 101.4 mg/dL | +0.3% | 100% |
| Potassium | ±0.3 mmol/L | 4.32 mmol/L | 4.57 mmol/L | +0.26 mmol/L | 61.5% |
| Sodium | ±4.0 mmol/L | 138.0 mmol/L | 137.8 mmol/L | −0.22 mmol/L | 100% |
| Total Protein | ±8.0% | 7.20 g/dL | 7.27 g/dL | +1.0% | 100% |
| Triglycerides | ±15.0% | 123.1 | 129.0 | +4.8% | 91.7% |
| CRPhs | ±30.0% | 5.11 mg/L | 5.22 mg/L | +2.3% | 100% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schaff, U.Y.; Collier, B.B.; Iacovetti, G.; Peevler, M.; Ragar, J.; Tokunaga, N.; Brandon, W.C.; Chappell, M.R.; Grant, R.P.; Sommer, G.J. Evaluation of a Simplified Upper Arm Device for Vacuum-Assisted Collection of Capillary Blood Specimens. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1935. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15151935
Schaff UY, Collier BB, Iacovetti G, Peevler M, Ragar J, Tokunaga N, Brandon WC, Chappell MR, Grant RP, Sommer GJ. Evaluation of a Simplified Upper Arm Device for Vacuum-Assisted Collection of Capillary Blood Specimens. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(15):1935. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15151935
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchaff, Ulrich Y., Bradley B. Collier, Gabriella Iacovetti, Mitchell Peevler, Jason Ragar, Nicolas Tokunaga, Whitney C. Brandon, Matthew R. Chappell, Russell P. Grant, and Greg J. Sommer. 2025. "Evaluation of a Simplified Upper Arm Device for Vacuum-Assisted Collection of Capillary Blood Specimens" Diagnostics 15, no. 15: 1935. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15151935
APA StyleSchaff, U. Y., Collier, B. B., Iacovetti, G., Peevler, M., Ragar, J., Tokunaga, N., Brandon, W. C., Chappell, M. R., Grant, R. P., & Sommer, G. J. (2025). Evaluation of a Simplified Upper Arm Device for Vacuum-Assisted Collection of Capillary Blood Specimens. Diagnostics, 15(15), 1935. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15151935






