Regulatory T Cell Sub-Populations in Patients with Distinct Autoimmune/Inflammatory Diseases With or Without Inborn Errors of Immunity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Flow Cytometry
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
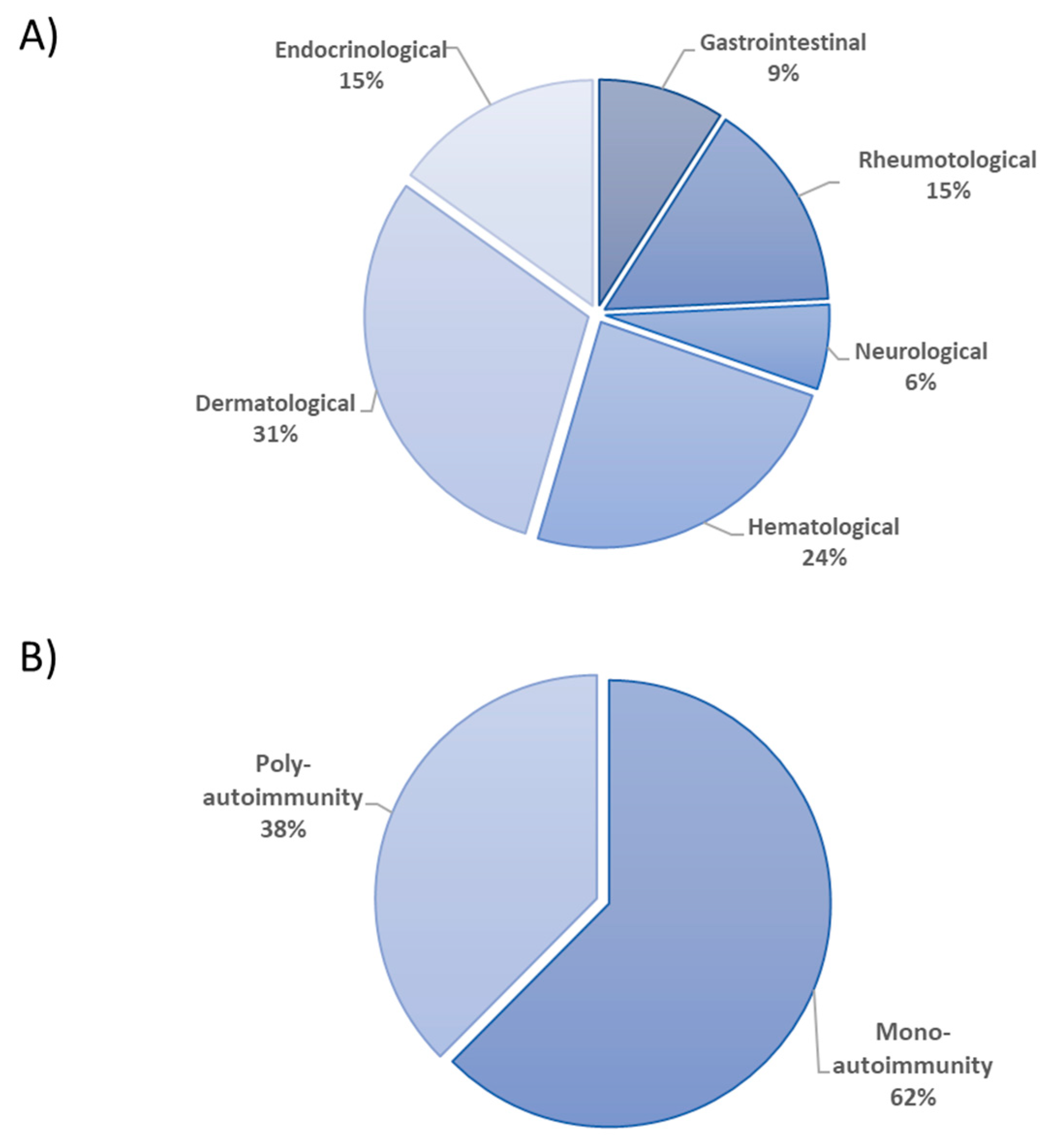
3.1. Patients’ Characteristics
3.2. Analysis of Treg Cell Sub-Populations
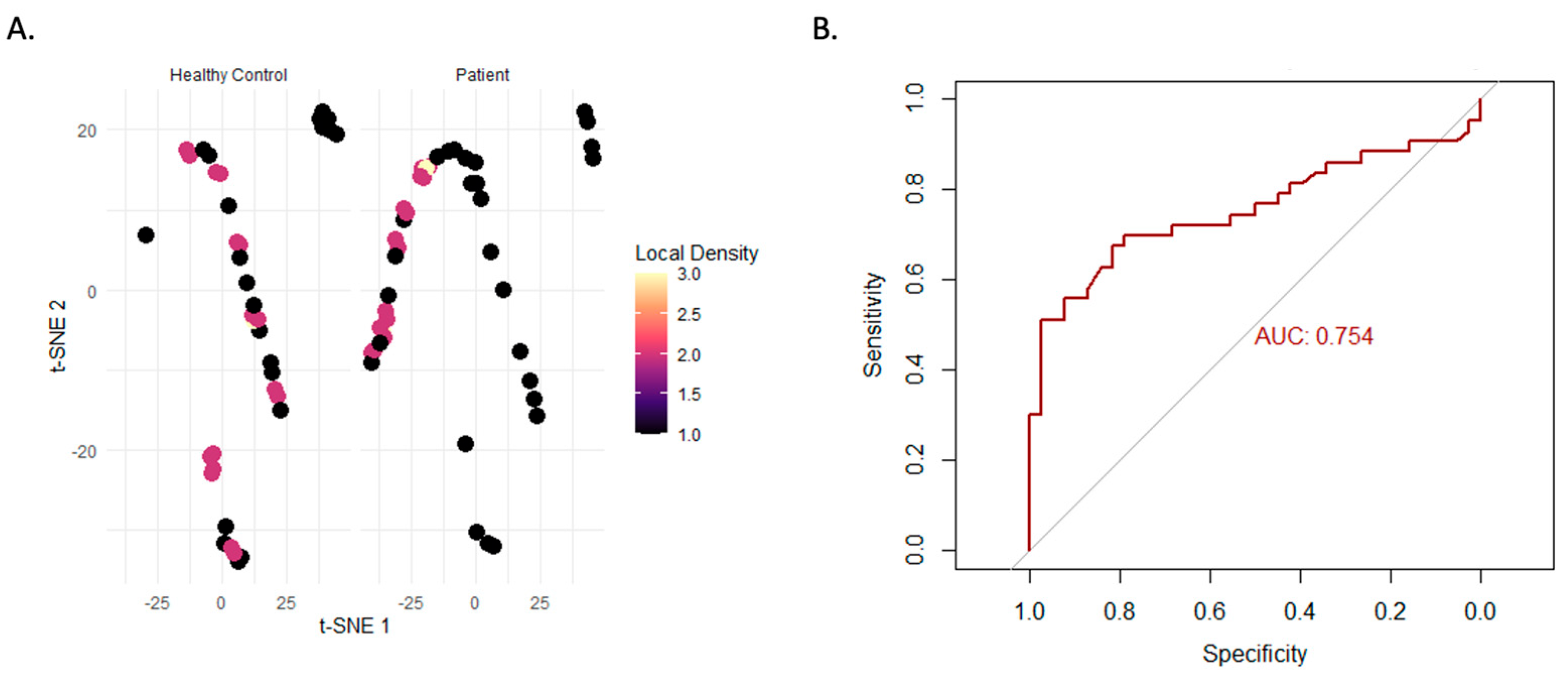
3.3. Multidimensional and Machine Learning-Based Analysis
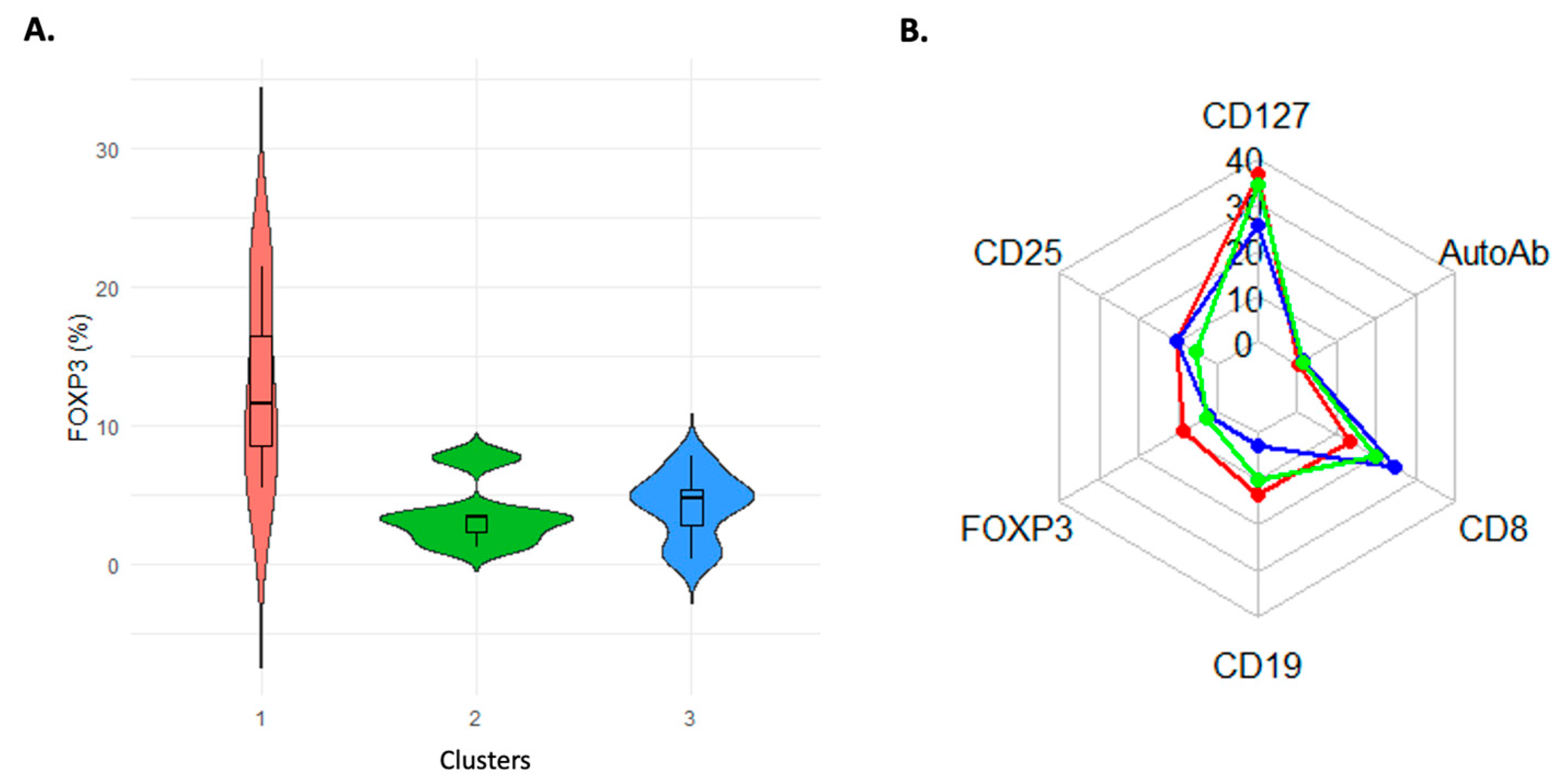
3.4. Data-Driven Immune Clusters in the Patients Show Different Characteristics
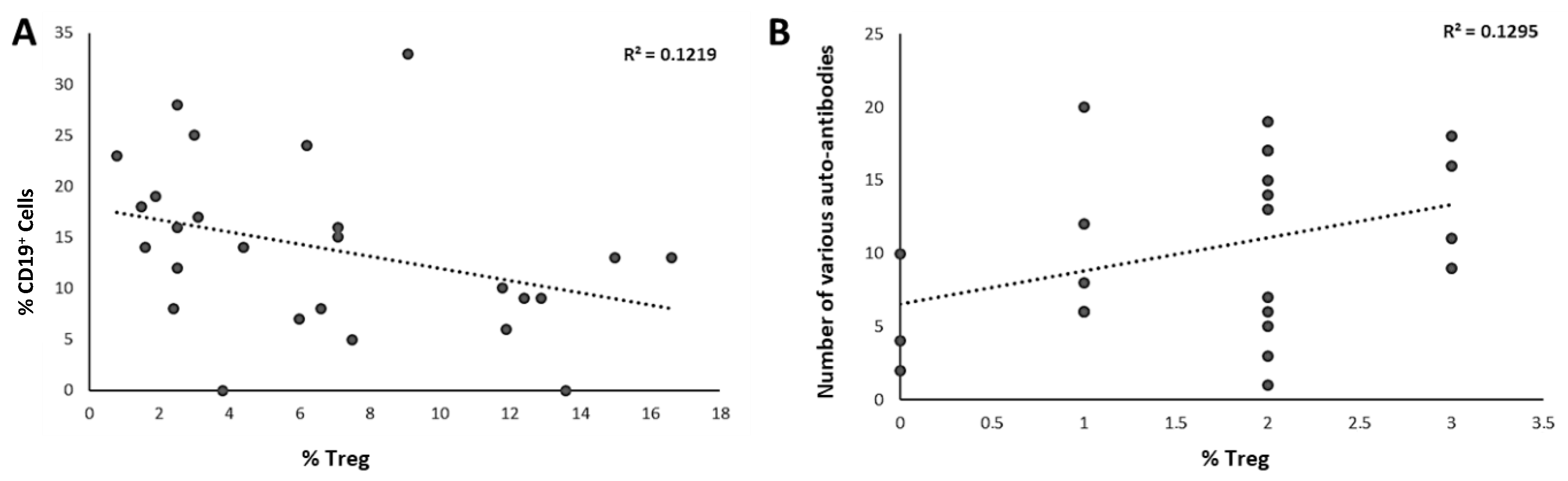
3.5. Correlations of Immunologic Markers with Treg Percentages
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Theofilopoulos, A.N.; Kono, D.H.; Baccala, R. The Multiple Pathways to Autoimmunity. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gül, A. Dynamics of Inflammatory Response in Autoinflammatory Disorders: Autonomous and Hyperinflammatory States. Front. Immunol. 2018, 17, 2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaya-Uribe, L.; Rojas, M.; Azizi, G.; Anoya, J.M.; Gercwin, M.E. Primary immunodeficiency and autoimmunity: A comprehensive review. J. Autoimmun. 2019, 99, 52–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waltera, J.E.; Ayalad, I.A.; Milojevice, D. Autoimmunity as a continuum in primary immunodeficiency. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2019, 31, 851–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gámez-Díaz, L.; Seidel, M.G. Different Apples, Same Tree: Visualizing Current Biological and Clinical Insights into CTLA-4 Insufficiency and LRBA and DEF6 Deficiencies. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 28, 2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, M.; Arturo, L.; Marta, E.; Anna, M.V.; Ana, E.; Estibaliz, R.; Navarro, G.E.A.; Roca, G.; Angela, E.D.; Plaza, A.M.; et al. From Primary Immunodeficiency to Autoimmunity: How Extreme Situations Highlight the Main Genetic Factors Involved in Autoimmune Disease. MOJ Immunol. 2016, 4, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Freeborn, J.; Armbrister, S.A.; Tran, D.Q.; Rhoads, J.M. Treg-associated monogenic autoimmune disorders and gut microbial dysbiosis. Pediatr. Res. 2021, 91, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azimi, T.; Nasiri, M.J.; Chirani, A.S.; Pourıran, R.; Dabırı, H. The role of bacteria in the inflammatory bowel disease development: A narrative review. Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Immunol. Scand. 2018, 126, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheinecker, C.; Göschl, L.; Bonelli, M. Treg cells in health and autoimmune diseases: New insights from single cell analysis. J. Autoimmun. 2020, 110, 102376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangye, S.G.; Pelham, S.J.; Deenick, E.K.; Cindy, S.M. Cytokine-mediated regulation of human lymphocyte development and function: Insights from primary immunodeficiencies. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 1949–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Putnam, A.L.; Xu-Yu, Z.; Szot, G.L.; Lee, M.R.; Zhu, S.; Gottlieb, P.A.; Kapranov, P.; Gingeras, T.R.; de St Groth, B.F.; et al. CD127 expression inversely correlates with FoxP3 and suppressive function of human CD4+ T reg cells. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 1701–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunham, J.; Lee, F.L.; Nvan, D.; Laman, J.D.; Ni, I.; Zhai, W.; Tu, G.-H.; Lin, J.C.; Bauer, J.; Hart, B.A.; et al. Blockade of CD127 Exerts a Dichotomous clinical effect in marmoset experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2016, 11, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colamatteo, A.; Carbone, F.; Bruzzaniti, S.; Galgani, M.; Fusco, C.; Maniscalco, G.T.; Di Rella, F.; de Candia, P.; De Rosa, V. Molecular Mechanisms Controlling Foxp3 Expression in Health and Autoimmunity: From Epigenetic to Post-translational Regulation. Front. Immunol. 2020, 10, 3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Olsen, N.; Zheng, S.G. The progress and prospect of regulatory T cells in autoimmune diseases. J. Autoimmun. 2020, 111, 102461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiev, P.; Charbonnier, L.-M.; Chatila, T.A. Regulatory T Cells: The Many Faces of Foxp3. J. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 39, 623–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, S.; Kretz, C.C.; Krammer, P.H.; Kuhn, A. CD127low/- and FoxP3+ Expression Levels Characterize Different Regulatory T-Cell Populations in Human Peripheral Blood. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ioan-Facsinay, A.; van der Voort, E.I.H.; Huizinga, T.W.J.; Toes, R.E.M. Transient expression of FOXP3 in human activated nonregulatory CD4+ T cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2007, 37, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, A.; Atif, M.; Balderas, R.; Gorochov, G.; Miyara, M. The role of FOXP3 + regulatory T cells in human autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2019, 197, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitz, A.; Singer, E. Regulatory T Cells: From Discovery to Autoimmunity. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2018, 8, 29041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez-Villar, M. Hafler Regulatory T cells in autoimmune disease. Nat. Immunol. 2018, 19, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinath, J.; Bayry, J. Current trends with FOXP3+ regulatory T cell immunotherapy to contest autoimmunity and inflammation. Immunotherapy 2019, 11, 755–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wing, J.B.; Tanaka, A.; Sakaguchi, S. Human FOXP3+ Regulatory T Cell Heterogeneity and Function in Autoimmunity and Cancer. Immunity 2019, 50, 302–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romano, M.; Fanelli, G.; Albany, C.J.; Giganti, G.; Lombardi, G. Past, Present, and Future of Regulatory T Cell Therapy in Transplantation and Autoimmunity. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arellano, B.; Graber, D.J.; Sentman, C.L. Regulatory T Cell-based Therapies for Autoimmunity. Discov. Med. 2016, 22, 73–80. [Google Scholar]
- Eggenhuizen, P.J.; Ng, B.H.; Ooi, J.D. Treg Enhancing Therapies to Treat Autoimmune Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2020, 21, 7015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossowski, A.; Moniuszko, M.; Idźkowska, E.; Grubczak, K.; Singh, P.; Bossowska, A.; Diana, T.; Kahaly, G.J. Decreased proportions of CD4 + IL17+/ CD4 + CD25 + CD127− and CD4 + IL17+/ CD4 + CD25 + CD127 − FoxP3+ T cells in children with autoimmune thyroid diseases. Autoimmunity 2016, 49, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, E.M.; Galicia-Carreón, J.; Novak, N. In vitro Conversion into CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ induced Regulatory T Cells Is Reduced in Atopic Dermatitis Patients. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2020, 181, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, W.; Yao, J.; Cheng, H.; Sun, X.; Li, L. Correlation of Blood FoxP3+ Regulatory T Cells and Disease Activity of Atopic Dermatitis. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 18, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.C.; Chen, K.H.; Lin, C.H.; CCKuo Kuo, C.-C.; Ling, Q.-D.; Chan, C.-H. The quantitative analysis of peripheral blood FOXP3-expressing T cells in systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis patients. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 37, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellor-Pita, S.; Citores, M.J.; Castejon RTutor-Ureta, P.; Yebra-Bango, M.; Andreu, J.L.; Vargas, J.A. Decrease of regulatory T cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2006, 65, 553–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, J.; Whittington, A.; Mitchell, P.; Tutor-Ureta, P.; Yebra-Bango, M.; Andreu, J.L.; Vargas, J.A. Natural regulatory T cells: Number and function are normal in the majority of patients with lupus nephritis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2008, 153, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, B.; Ye, S.; Chen, G.; Shen, N.; Chen, S. Dysfunctional CD4+,CD25+ regulatory T cells in untreated active systemic lupus erythematosus secondary tointerferon-alpha-producing antigen-presenting cells. Arthritis Rheum 2008, 58, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brusko, T.M.; Wasserfall, C.H.; Clare-Salzler, M.J.; Schatz, D.A.; Atkinson, M.A. Functional defects and the influence of age on the frequency of CD4+ CD25+ Tcells in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 2005, 54, 1407–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.A.; Cerosaletti, K.; Bollyky, P.L.; Tatum, M.; Shilling, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Pihoker, C.; Sanda, S.; Greenbaum, C.; et al. Defects in IL-2R signaling contribute to diminished maintenance of FOXP3 expression in CD4[+]CD25[+] regulatory T-cells of type 1 diabetic subjects. Diabetes 2010, 59, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venken, K.; Hellings, N.; Thewissen, M.; Somers, V.; Hensen Ka Rummens, J.-L.; Medaer, R.; Hupperts, R.; Stinissen, P. Compromised CD4+ CD25[high] regulatory T-cell function in patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis is correlated with a reduced frequency of FOXP3-positive cells and reduced FOXP3 expression at the single-cell level. Immunology 2008, 123, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viglietta, V.; Baecher-Allan, C.; Weiner, H.L.; David, A. Hafler Loss of functional suppression by CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in patients with multiple sclerosis. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 199, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torgerson, T.R.; Ochs, H.D. Regulatory T cells in primary immunodeficiency diseases. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 7, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, H.; Abolhassani, F.; Kiaeeb, N.; Rafiemanesh, H.; Yazdani, R.; Mahdaviani, S.A.; Mohammadikhajehdehi, S.; Tavakol, M.; Ziaee, V.; Negahdari, B. Autoimmunity and its association with regulatory T cells and B cell subsets in patients with common variable immunodeficiency. Front. Immunol. 2018, 46, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fevang, B.; Yndestad, A.; Sandberg, W.J.; Holm, A.M.; Müller, F.; Aukrust, P.; Frøland, S.S. Low numbers of regulatory T cells in common variable immunodeficiency: Association with chronic inflammation in vivo. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2007, 147, 521–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Herrera, G.; Segura-Méndez, N.H.; O’Farril-Romanillos, P.; Nuñez-Nuñez, M.E.; Zarate-Hernández, M.C.; Mogica-Martínez, D.; Yamazaki-Nakashimada, M.A.; Staines-Boone, A.T.; Santos-Argumedo, L.; Berrón-Ruiz, L.; et al. Low percentages of regulatory T cells in common variable immunodeficiency [CVID] patients with autoimmune diseases and its association with increased numbers of CD4+CD45RO+ T and CD21low B cells. Allergol. Immunopathol. 2019, 47, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, M.C.; Tangye, S.G. Primary immune deficiencies affecting lymphocyte differentiation: Lessons from the spectrum of resulting infections. Int. Immunol. 2009, 21, 1003–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo, K.M.; Carvalho, K.I.; Bruno, F.R.; Ndhlovu, L.C.; Ballan, W.M.; Nixon, D.F.; Kallas, E.G.; Costa-Carvalho, B.T. A Decreased Frequency of Regulatory T Cells in Patients with Common Variable Immunodeficiency. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, 6269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbsky, J.W.; Chatila, T.A. T Regulatory Cells in Primary Immune Deficiencies. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 11, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zemmour, D.; Charbonnier Louis-Marie Six, L.J.E.; Keles, S.; Delville, M.; Benamar, M.; Baris, S.; Zuber, J.; Chen, K. Single-cell analysis of FOXP3 deficiencies in humans and mice unmasks intrinsic and extrinsic CD4+ T cell perturbations. Nat. Immunol. 2021, 22, 607–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecilia Poli, M.; Aksentijevich, I.; Bousfiha, A.A.; Cunningham-Rundles, C.; Hambleton, S.; Klein, C.; Morio, T.; Picard, C.; Puel, A.; Rezaei, N.; et al. Human inborn errors of immunity: 2024 update on the classification from the International Union of Immunological Societies Expert Committee. J. Hum. Immun. 2025, 1, e20250003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsubo, K.; Kanegane, H.; Kamachi, Y.; Kobayashi, I.; Tsuge, I.; Imaizumi, M.; Kobayashi, I.; Tsuge, I.; Imaizumi, M.; Sasahara, Y.; et al. Identification of FOXP3-negative regulatory T-like (CD4(+)CD25(+)CD127(low)) cells in patients with immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-linked syndrome. Clin. Immunol. 2011, 141, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, W.; Zhu, W. Foxp3+ Treg Cells Are Associated with Pathological Process of Autoimmune Hepatitis by Activating Methylation Modification in Autoimmune Hepatitis Patients. Med. Sci. Monit. 2019, 25, 604–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santegoets Saskia, J.A.M.; Dijkgraaf, E.M.; Battaglia, A.; Beckhove, P.; Britten, C.M.; Gallimore, A.; Godkin, A.; Gouttefangeas, C.; de Gruijl, T.D.; Koenen, H.J.P.M.; et al. Monitoring regulatory T cells in clinical samples: Consensus on an essential marker set and gating strategy for regulatory T cell analysis by flow cytometry. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2015, 64, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajendiran, A.; Tenbrock, K. Regulatory T cell function in autoimmune disease. J. Transl. Autoimmunity. 2021, 4, 100130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzaghi, F.; Passerini, L. IPEX Syndrome: Improved Knowledge of Immune Pathogenesis Empowers Diagnosis. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 22, 612760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, M.; Torgerson, T.R.; Selmi, C.; Gambineri, E.; Carneiro-Sampaio, M.; Mannurita, S.C.; Leung, P.S.C.; Norman, G.L.; Gershwin, M.E. The spectrum of autoantibodies in IPEX syndrome is broad and includes anti-mitochondrial autoantibodies. J. Autoimmun. 2010, 35, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Patients’ | Age | Sex | Clinical Diagnosis | Affected Gene | % CD4+CD127lo | FOXP3 | Presence of Autoantibody |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | CD25hi FOXP3+ | Expression | |||||
| P1 | 6 y 1 m | Female | IBD | IL10RA and MEFV | 11.7 | N | nd |
| P2 | 38 y | Female | IBD | STAT1 | 15.4 | N | neg |
| P3 | 16 y 1 m | Male | SLE, Hemolytic anemia, | nd | 6.4 | N | Anti-dsDNA, anti-thyroglobulin, |
| Hashimoto thyroiditis | ENA, anti-TPO | ||||||
| P4 | 1 y 11 m | Male | FHI | nd | 6.6 | N | Anti-thyroglobulin, anti-TPO |
| P5 | 30 y | Female | MS, CVID | nd | 12.9 | N | Anti-thyroglobulin, anti-TPO |
| P6 | 2 y 1 m | Male | Pustular psoriasis, Cow milk allergy | nd | 9.1 | N | nd |
| P7 | 33 y 11 m | Female | CVID, AIHA, SLE, Livedo vasculitis | nd | 3.6 | N | Anti-thyroglobulin, anti-TPO |
| P8 | 13 y 10 m | Male | Cytopenia | nd | 15 | N | Anti-thyroglobulin, anti-TPO |
| P9 | 8 y 10 m | Male | Ectodermal dysplasia | nd | 11.9 | N | Anti-thyroglobulin, anti-TPO |
| P10 | 3 y 7 m | Female | Type 1 DM, Atopic dermatitis | nd | 4.4 | N | neg |
| P11 | 1 y 8 m | Male | Atopic dermatitis | nd | 12.4 | N | nd |
| P12 | 13 y 7 m | Female | Castleman Disease, Paraneoplastic pemphigus, | nd | 13.6 | N | Anti-dsDNA, anti-thyroglobulin, |
| Myasthenia gravis, SLE | anti-TPO | ||||||
| P13 | 12 y 5 m | Male | IBD, sclerosing cholangitis, | DOCK8 | 4.6 | N | Anti-thyroglobulin, anti-TPO |
| portal hypertension, FMF | |||||||
| P14 | 14 y 10 m | Male | Aplastic anemia, hyperglycemia | nd | 2.1 | N | neg |
| P15 | 9 y 8 m | Male | Autoimmune neutropenia, MDS | nd | 6.2 | N | neg |
| P16 | 13 y | Male | JIA, CF | MEFV | 11.8 | N | neg |
| P17 | 10 y 1 m | Male | Atopic dermatitis | nd | 7.5 | N | Anti-thyroglobulin, anti-TPO |
| P18 | 7 y 4 m | Male | Vitiligo | nd | 7.1 | N | nd |
| P19 | 5 y 8 m | Male | Hypothyroidism, Tubulopathy, | nd | 3.8 | N | Anti-dsDNA, anti-thyroglobulin, |
| Milk and egg allergy, IEI | ENA, anti-TPO | ||||||
| P20 | 16 y 6 m | Female | Autoimmune hypophysitis, | nd | 6 | N | Anti-thyroglobulin, anti-TPO |
| Autoimmune polyglandular syndrome | |||||||
| P21 | 1 y | Male | Autoinflammatory disease, | nd | 2.4 | N | Anti-thyroglobulin, anti-TPO |
| Graft versus host disease, psoriasis | |||||||
| P22 | 8 y 11 m | Male | Aplastic anemia | ADA2 | 2.5 | N | Anti-thyroglobulin, anti-TPO |
| P23 | 8 m | Male | Atopic dermatitis, milk and egg allergy | nd | 1.6 | N | Anti-dsDNA |
| P24 | 8 y 7 m | Female | DM, Hashimoto’s thyroiditis | nd | 2.5 | N | Anti-thyroglobulin, anti-TPO |
| P25 | 3 y 2 m | Male | Neutropenia, hypogammaglobulinemia | MPO | 1.9 | N | neg |
| P26 | 10 m | Male | Atopic dermatitis | nd | 0.8 | Severely | nd |
| decreased | |||||||
| P27 | 1 y 6 m | Male | IPEX | nd | 0.9 | Severely | Anti-thyroglobulin, anti-TPO |
| decreased | |||||||
| P28 | 12 y 3 m | Female | IBD | nd | 11 | N | Anti-dsDNA |
| P29 | 14 y 1 m | Male | Type 1 DM | nd | 4.1 | N | Anti-thyroglobulin, anti-TPO |
| P30 | 3 y 10 m | Male | Hypogammaglobulinemia, | nd | 2.3 | N | nd |
| resistant atopic dermatitis, | |||||||
| multiple nutrient allergies | |||||||
| P31 | 17 y 11 m | Female | Congenital neutropenia | HAX1 | 4.7 | N | Anti-TPO, anti-thyroglobulin |
| P32 | 14 y 7 m | Female | Recurrent ITP | LRBA | 3.9 | N | Anti-thyroglobulin, anti-TPO |
| P33 | 46 y | Female | SLE, AIHA, CVID | LRBA | 4.8 | N | neg |
| P34 | 12 y 7 m | Female | ITP, CVID | LRBA | 5.2 | N | nd |
| P35 | 6 y 4 m | Female | AIHA | LRBA | 5.3 | N | nd |
| P36 | 4 y 3 m | Male | Alopecia areata, vitiligo | nd | 4.9 | N | Anti-thyroglobulin, anti-TPO |
| P37 | 16 y 5 m | Male | Autoimmune hypothyroiditis, | nd | 5.3 | N | nd |
| Alopecia areata, CVID | |||||||
| P38 | 14 y 9 m | Male | AIHA, Crohn’s disease, Oligo JIA | LRBA | 6.5 | N | nd |
| P39 | 6 y 7 m | Male | JIA | nd | 10.3 | N | nd |
| P40 | 41 y | Male | Autoimmune hepatitis, sjogren’s syndrome primary | nd | 11 | N | Anti-thyroglobulin, ANA |
| biliary cholangitis, PFO |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oskay Halacli, S.; Inan, D.; Esenboga, S.; Bildik, H.N.; Bolat, A.B.; Tezcan, I.; Cagdas, D. Regulatory T Cell Sub-Populations in Patients with Distinct Autoimmune/Inflammatory Diseases With or Without Inborn Errors of Immunity. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15151879
Oskay Halacli S, Inan D, Esenboga S, Bildik HN, Bolat AB, Tezcan I, Cagdas D. Regulatory T Cell Sub-Populations in Patients with Distinct Autoimmune/Inflammatory Diseases With or Without Inborn Errors of Immunity. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(15):1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15151879
Chicago/Turabian StyleOskay Halacli, Sevil, Dilan Inan, Saliha Esenboga, Hacer Neslihan Bildik, Aslihan Berra Bolat, Ilhan Tezcan, and Deniz Cagdas. 2025. "Regulatory T Cell Sub-Populations in Patients with Distinct Autoimmune/Inflammatory Diseases With or Without Inborn Errors of Immunity" Diagnostics 15, no. 15: 1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15151879
APA StyleOskay Halacli, S., Inan, D., Esenboga, S., Bildik, H. N., Bolat, A. B., Tezcan, I., & Cagdas, D. (2025). Regulatory T Cell Sub-Populations in Patients with Distinct Autoimmune/Inflammatory Diseases With or Without Inborn Errors of Immunity. Diagnostics, 15(15), 1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15151879






