Automatic Segmentation of the Infraorbital Canal in CBCT Images: Anatomical Structure Recognition Using Artificial Intelligence
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Study Design and Sample Size Criteria
- Individuals aged 18 years or older;
- Individuals who had not undergone any surgical procedures in the head and neck region;
- Individuals with no history of trauma or metabolic bone diseases;
- Patients with CBCT images in which the boundaries of the IOC could clearly be visualized.
- CBCT images in which the boundaries of the IOC could not be clearly visualized;
- CBCT images containing artifacts caused by the device or the patient.
2.2. Acquisition and Evaluation of the CBCT Images
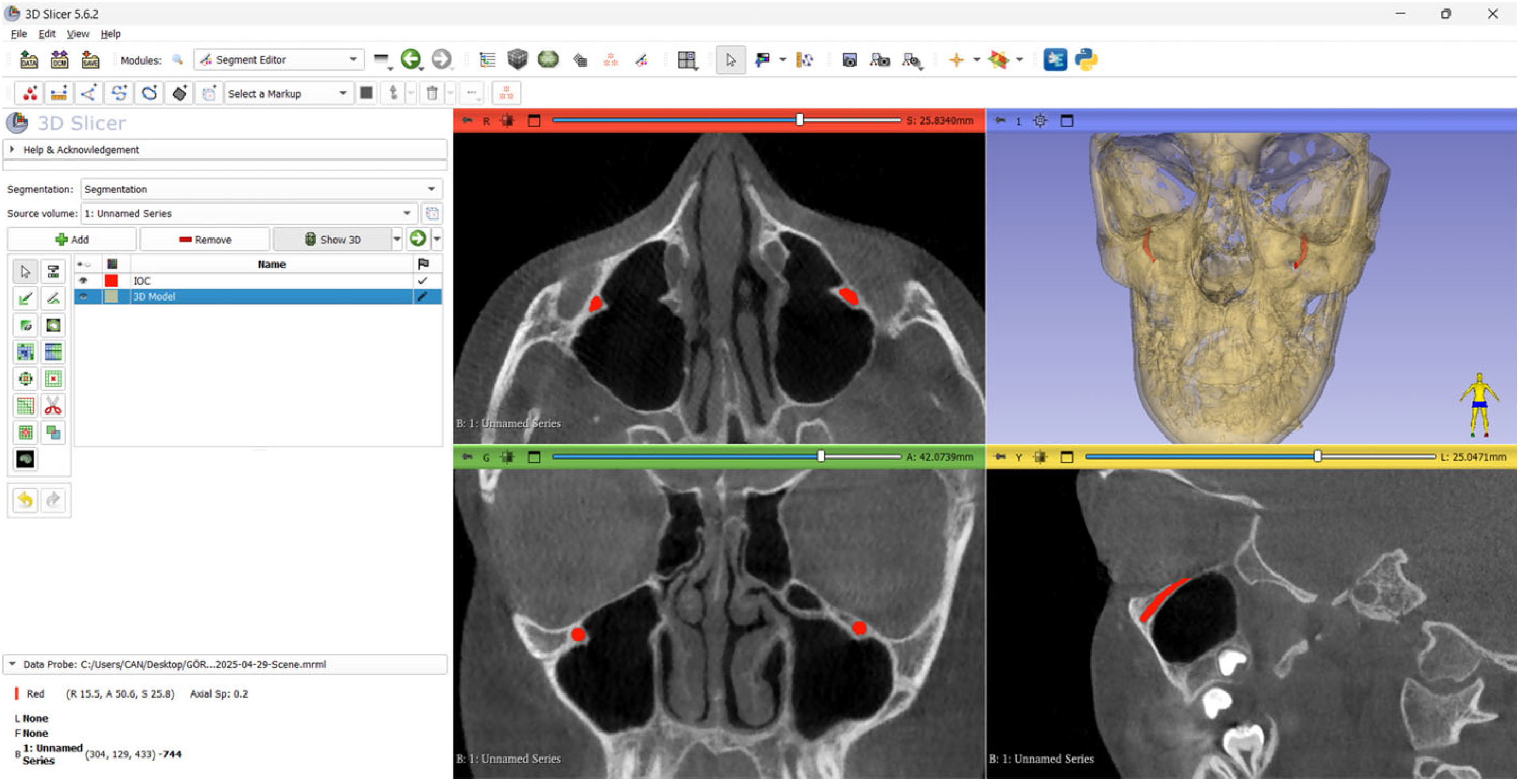
2.3. The Ground Truth
2.4. Test Data
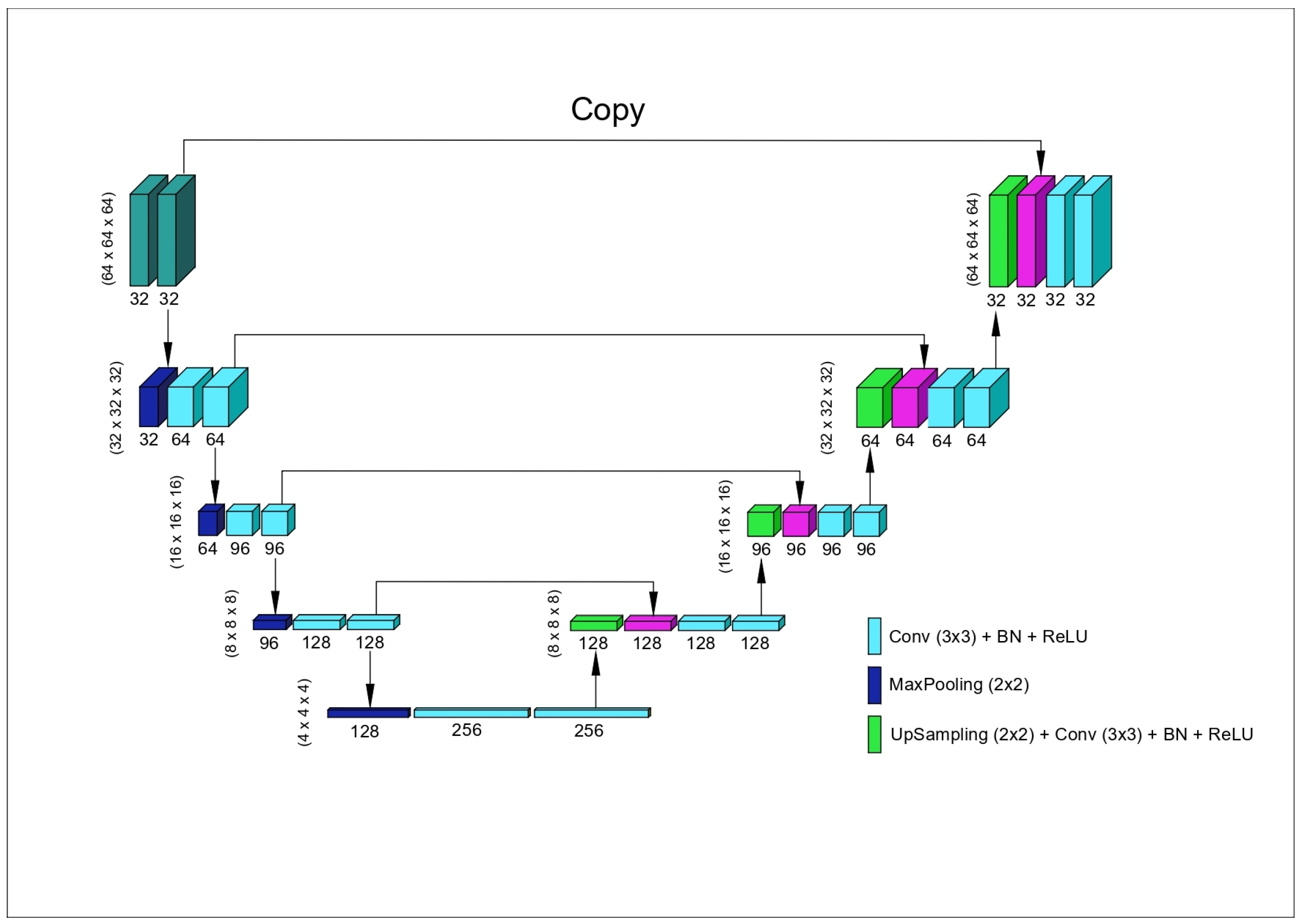
2.5. The Model
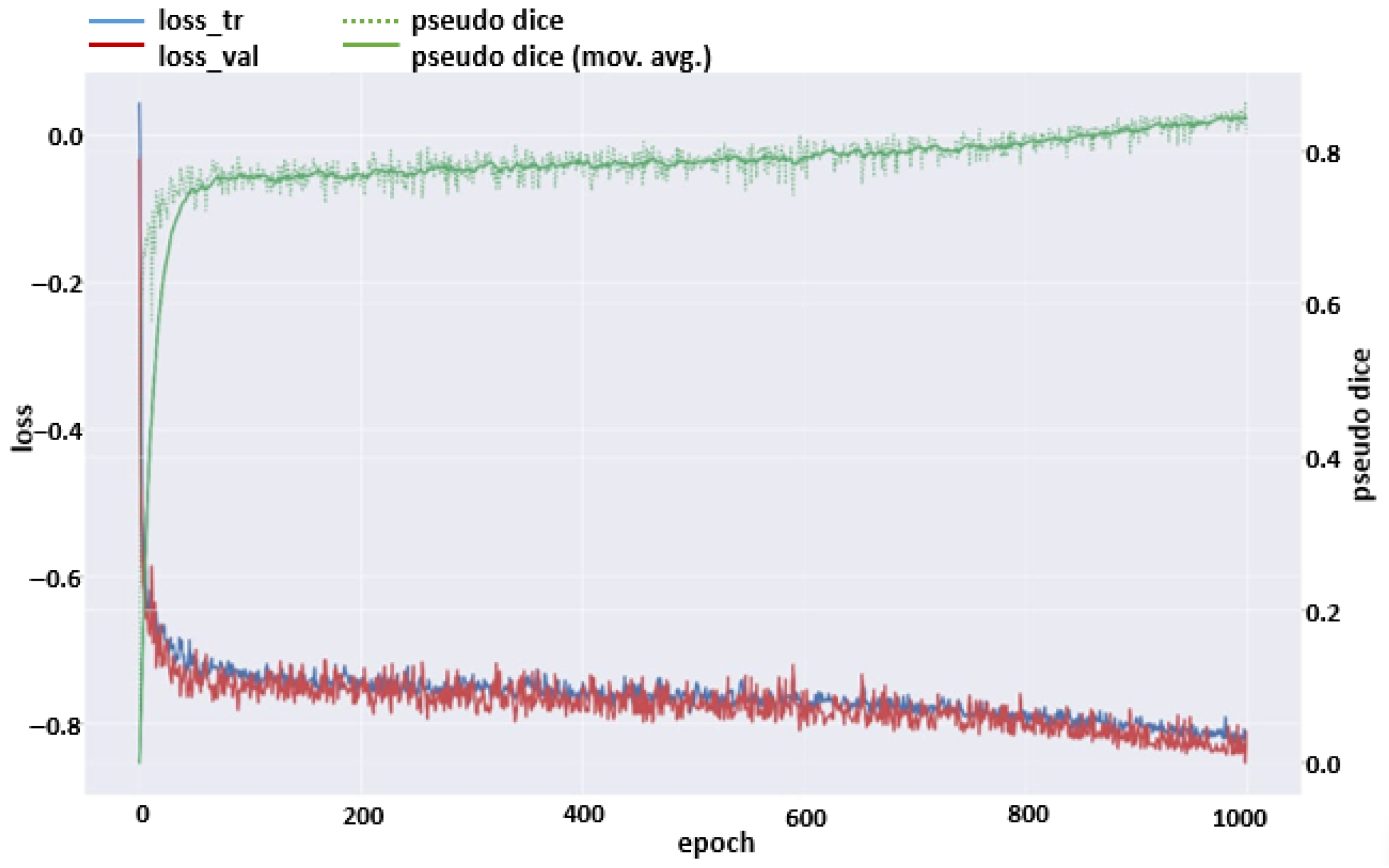
2.6. Evaluation
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ference, E.H.; Smith, S.S.; Conley, D.; Chandra, R.K. Surgical anatomy and variations of the infraorbital nerve. Laryngoscope 2015, 125, 1296–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Açar, G.; Özen, K.E.; Güler, İ.; Büyükmumcu, M. Computed tomography evaluation of the morphometry and variations of the infraorbital canal relating to endoscopic surgery. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2018, 84, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontolliet, M.; Bornstein, M.M.; von Arx, T. Characteristics and dimensions of the infraorbital canal: A radiographic analysis using cone beam computed tomography (CBCT). Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2019, 41, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalabalık, F.; Aktaş, T.; Akan, E.; Aytuğar, E. Radiographic evaluation of infraorbital canal protrusion into maxillary sinus using cone-beam computed tomography. J. Oral Maxillofac. Res. 2020, 11, e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghnegahdar, A.; Khojastepour, L.; Naderi, A. Evaluation of infraorbital canal in cone beam computed tomography of maxillary sinus. J. Dent. 2018, 19, 41. [Google Scholar]
- Orellana-Donoso, M.; Romero-Zucchino, D.; Fuentes-Abarca, A.; Aravena-Ríos, P.; Sanchis-Gimeno, J.; Konschake, M.; Nova-Baeza, P.; Valenzuela-Fuenzalida, J.J. Infraorbital canal variants and its clinical and surgical implications. A systematic review. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2024, 46, 1027–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balsiger, F.; Steindel, C.; Arn, M.; Wagner, B.; Grunder, L.; El-Koussy, M.; Valenzuela, W.; Reyes, M.; Scheidegger, O. Segmentation of peripheral nerves from magnetic resonance neurography: A fully-automatic, deep learning-based approach. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minnema, J.; Ernst, A.; van Eijnatten, M.; Pauwels, R.; Forouzanfar, T.; Batenburg, K.J.; Wolff, J. A review on the application of deep learning for CT reconstruction, bone segmentation and surgical planning in oral and maxillofacial surgery. Dentomaxillofacial Radiol. 2022, 51, 20210437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menchón-Lara, R.-M.; Sancho-Gómez, J.-L. Fully automatic segmentation of ultrasound common carotid artery images based on machine learning. Neurocomputing 2015, 151, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinayahalingam, S.; Berends, B.; Baan, F.; Moin, D.A.; van Luijn, R.; Bergé, S.; Xi, T. Deep learning for automated segmentation of the temporomandibular joint. J. Dent. 2023, 132, 104475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, W.; Lv, J.; Xu, J.; Zhou, H.; Li, G.; Ai, K. Advancements in oral and maxillofacial surgery medical images segmentation techniques: An overview. J. Dent. 2023, 138, 104727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koç, U.; Sezer, E.A.; Özkaya, Y.A.; Yarbay, Y.; Beşler, M.S.; Taydaş, O.; Yalçın, A.; Evrimler, Ş.; Kızıloğlu, H.A.; Kesimal, U. Elevating Healthcare through Artificial Intelligence: Analyzing the Abdominal Emergencies Data Set (TR_ABDOMEN_RAD_EMERGENCY) at TEKNOFEST-2022. Eur. Radiol. 2024, 34, 3588–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orhan, K.; Misirli, M.; Aksoy, S.; Hincal, U.S.E.; Ormeci, T.; Arslan, A. Morphometric analysis of the infraorbital foramen, canal and groove using cone beam CT: Considerations for creating artificial organs. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2016, 39, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryanezhad, S.S.; Jafari-Pozve, N.; Abrishami, M.; Arianezhad, S.M. Investigating the anatomy and location of the infraorbital canal in relation to the adjacent structures in cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) images. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 2024, 24, 542–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karatag, O.; Guclu, O.; Ozer, S.; Oztoprak, B.; Resorlu, M.; Oztoprak, I. Computed tomography analysis of the infraorbital canal and adjacent anatomical structures. J. Anat. 2024, 246, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, D.; Rana, K.; Caltabiano, C.; Patel, S.; Selva, D. Normative Measurements of the Infraorbital Nerve by Magnetic Resonance Imaging in an Australia Cohort. Ophthalmic Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2024, 10, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalek, P.; Donaldson, W.; McAleavey, F.; Johnston, P.; Kiska, R. Ultrasound imaging of the infraorbital foramen and simulation of the ultrasound-guided infraorbital nerve block using a skull model. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2013, 35, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peris-Celda, M.; Pinheiro-Neto, C.D.; Scopel, T.F.; Fernandez-Miranda, J.C.; Gardner, P.A.; Snyderman, C.H. Endoscopic endonasal approach to the infraorbital nerve with nasolacrimal duct preservation. J. Neurol. Surg. Part B Skull Base 2013, 74, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umapathy, L.; Winegar, B.; MacKinnon, L.; Hill, M.; Altbach, M.; Miller, J.; Bilgin, A. Fully automated segmentation of globes for volume quantification in CT images of orbits using deep learning. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2020, 41, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Jeon, K.J.; Kim, Y.H.; Ha, E.-G.; Lee, C.; Han, S.-S. Deep learning-based fully automatic segmentation of the maxillary sinus on cone-beam computed tomographic images. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, N.L.; Ong, S.H.; Foong, K.W.C. Automatic segmentation of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses from cone-beam CT images. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2015, 10, 1269–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savjani, R. nnU-Net: Further automating biomedical image autosegmentation. Radiol. Imaging Cancer 2021, 3, e209039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masabni, O.; Ahmad, M. Infraorbital foramen and pterygopalatine fossa location in dry skulls: Anatomical guidelines for local anesthesia. Anat. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 1403120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, A.; Kaur, H.; Gupta, T.; Tubbs, R.S.; Sahni, D.; Batra, Y.; Sondekoppam, R.V. Anatomical study of the infraorbital foramen: A basis for successful infraorbital nerve block. Clin. Anat. 2015, 28, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeya Patil, S.C.; Basavarajappa, R.; Christopher, V.S.; Niranjan, S. Anatomical interrelationship between infraorbital canal and maxillary sinus: A CBCT-driven exploratory study. Eur. J. Anat. 2025, 29, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins-Júnior, P.A.; Rodrigues, C.P.; De Maria, M.L.d.A.; Nogueira, L.M.; da Silva, J.H.; e Silva, M.R.M.A. Analysis of anatomical characteristics and morphometric aspects of infraorbital and accessory infraorbital foramina. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2017, 28, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubron, K.; Verbist, M.; Shaheen, E.; Dormaar, T.J.; Jacobs, R.; Politis, C. Incidence, aetiology, and associated fracture patterns of infraorbital nerve injuries following zygomaticomaxillary complex fractures: A retrospective analysis of 272 patients. Craniomaxillofacial Trauma Reconstr. 2022, 15, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiid, S.B.; Mohamed, A.A. Protrusion of the infraorbital canal into the maxillary sinus: A cross-sectional study in Cairo, Egypt. Imaging Sci. Dent. 2022, 52, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haylaz, E.; Gumussoy, I.; Duman, S.B.; Kalabalik, F.; Eren, M.C.; Demirsoy, M.S.; Celik, O.; Bayrakdar, I.S. Automatic Segmentation of the Nasolacrimal Canal: Application of the nnU-Net v2 Model in CBCT Imaging. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deniz, H.A.; Bayrakdar, İ.Ş.; Nalçacı, R.; Orhan, K. Segmentation of the nasopalatine canal and detection of canal furcation status with artificial intelligence on cone-beam computed tomography images. Oral Radiol. 2025, 41, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mureșanu, S.; Almășan, O.; Hedeșiu, M.; Dioșan, L.; Dinu, C.; Jacobs, R. Artificial intelligence models for clinical usage in dentistry with a focus on dentomaxillofacial CBCT: A systematic review. Oral Radiol. 2023, 39, 18–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, G.H.; Kwak, E.-J.; Song, J.M.; Park, H.R.; Jung, Y.-H.; Cho, B.-H.; Hui, P.; Hwang, J.J. Automatic mandibular canal detection using a deep convolutional neural network. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, D.; Mazen, S.; Tsujiko, S.; Otake, Y.; Sato, Y.; Numajiri, T. Deep-learning-based automatic facial bone segmentation using a two-dimensional U-Net. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2023, 52, 787–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahoud, P.; Diels, S.; Niclaes, L.; Van Aelst, S.; Willems, H.; Van Gerven, A.; Quirynen, M.; Jacobs, R. Development and validation of a novel artificial intelligence driven tool for accurate mandibular canal segmentation on CBCT. J. Dent. 2022, 116, 103891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, B.; Taspinar, Y.S.; Koklu, M.; Tassoker, M. Automatic segmentation of the maxillary sinus on cone beam computed tomographic images with U-Net deep learning model. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2024, 281, 6111–6121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jindanil, T.; Marinho-Vieira, L.E.; de-Azevedo-Vaz, S.L.; Jacobs, R. A unique artificial intelligence-based tool for automated CBCT segmentation of mandibular incisive canal. Dentomaxillofacial Radiol. 2023, 52, 20230321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumussoy, I.; Demirezer, K.; Duman, S.B.; Haylaz, E.; Bayrakdar, I.S.; Celik, O.; Syed, A.Z. AI-powered segmentation of bifid mandibular canals using CBCT. BMC Oral Health 2025, 25, 20230321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asci, E.; Kilic, M.; Celik, O.; Cantekin, K.; Bircan, H.B.; Bayrakdar, İ.S.; Orhan, K. A Deep Learning Approach to Automatic Tooth Caries Segmentation in Panoramic Radiographs of Children in Primary Dentition, Mixed Dentition, and Permanent Dentition. Children 2024, 11, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlu, F.; Çetinel, G.; Gül, S. A fully-automated computer-aided breast lesion detection and classification system. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2020, 62, 102157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Model | nnU-Net v2 |
| Epoch | 1000 |
| Batch Size | 2 |
| Learning Rate | 0.00001 |
| Optimization | ADAM |
| Activation | ReLU |
| Metrics | Metric Formula | Metric Value |
|---|---|---|
| True Positive | 17,288.7 | |
| False Positive | 4043.5 | |
| False Negative | 3073.1 | |
| Precision | TP/(TP + FP) | 0.7479 |
| Recall (Sensitivity) | TP/(TP + FN) | 0.8231 |
| Accuracy | (TP + TN)/(TP + TN+ FP + FN) | 0.9999 |
| Dice Score (DC) | (2 × TP)/(2 × TP + FP + FN) | 0.7792 |
| Intersection over the Union (IoU) | (|A∩B|)/(|A∪B|) | 0.6402 |
| F1-Score | 2 × (Precision × Recall)/(Precision + Recall) | 0.7837 |
| 95% Hausdorff Distance (95% HD) mm | dH95(A, B) = max(d95(A, B), d95(A, B)) | 0.7661 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gumussoy, I.; Haylaz, E.; Duman, S.B.; Kalabalık, F.; Eren, M.C.; Say, S.; Celik, O.; Bayrakdar, I.S. Automatic Segmentation of the Infraorbital Canal in CBCT Images: Anatomical Structure Recognition Using Artificial Intelligence. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1713. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131713
Gumussoy I, Haylaz E, Duman SB, Kalabalık F, Eren MC, Say S, Celik O, Bayrakdar IS. Automatic Segmentation of the Infraorbital Canal in CBCT Images: Anatomical Structure Recognition Using Artificial Intelligence. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(13):1713. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131713
Chicago/Turabian StyleGumussoy, Ismail, Emre Haylaz, Suayip Burak Duman, Fahrettin Kalabalık, Muhammet Can Eren, Seyda Say, Ozer Celik, and Ibrahim Sevki Bayrakdar. 2025. "Automatic Segmentation of the Infraorbital Canal in CBCT Images: Anatomical Structure Recognition Using Artificial Intelligence" Diagnostics 15, no. 13: 1713. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131713
APA StyleGumussoy, I., Haylaz, E., Duman, S. B., Kalabalık, F., Eren, M. C., Say, S., Celik, O., & Bayrakdar, I. S. (2025). Automatic Segmentation of the Infraorbital Canal in CBCT Images: Anatomical Structure Recognition Using Artificial Intelligence. Diagnostics, 15(13), 1713. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131713






