Deep Learning-Based Detection of Separated Root Canal Instruments in Panoramic Radiographs Using a U2-Net Architecture
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Preparation and Labelling
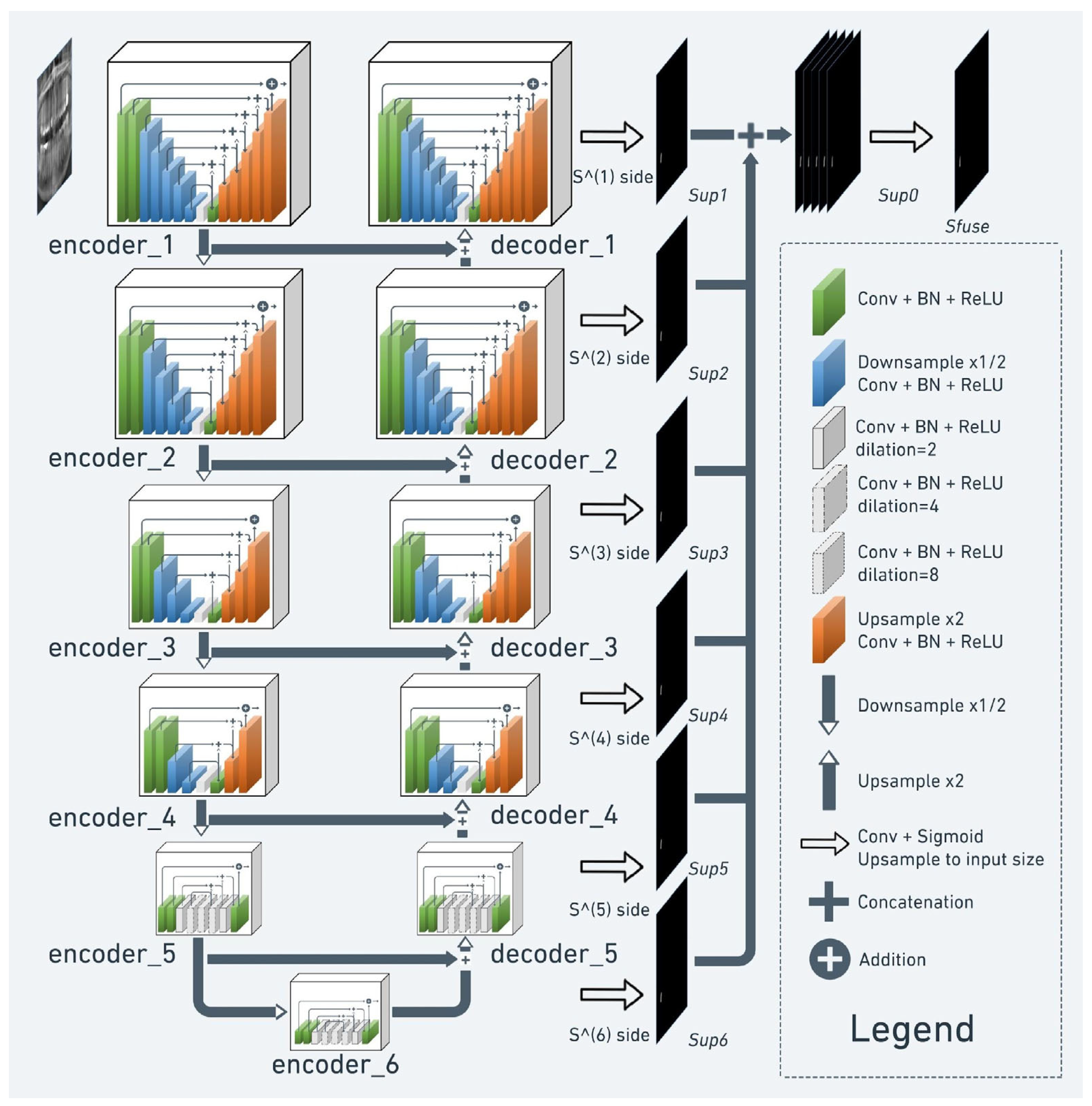
2.2. Model Pipeline
2.3. Preprocessing
2.4. Semantic Segmentation
2.5. Implementation
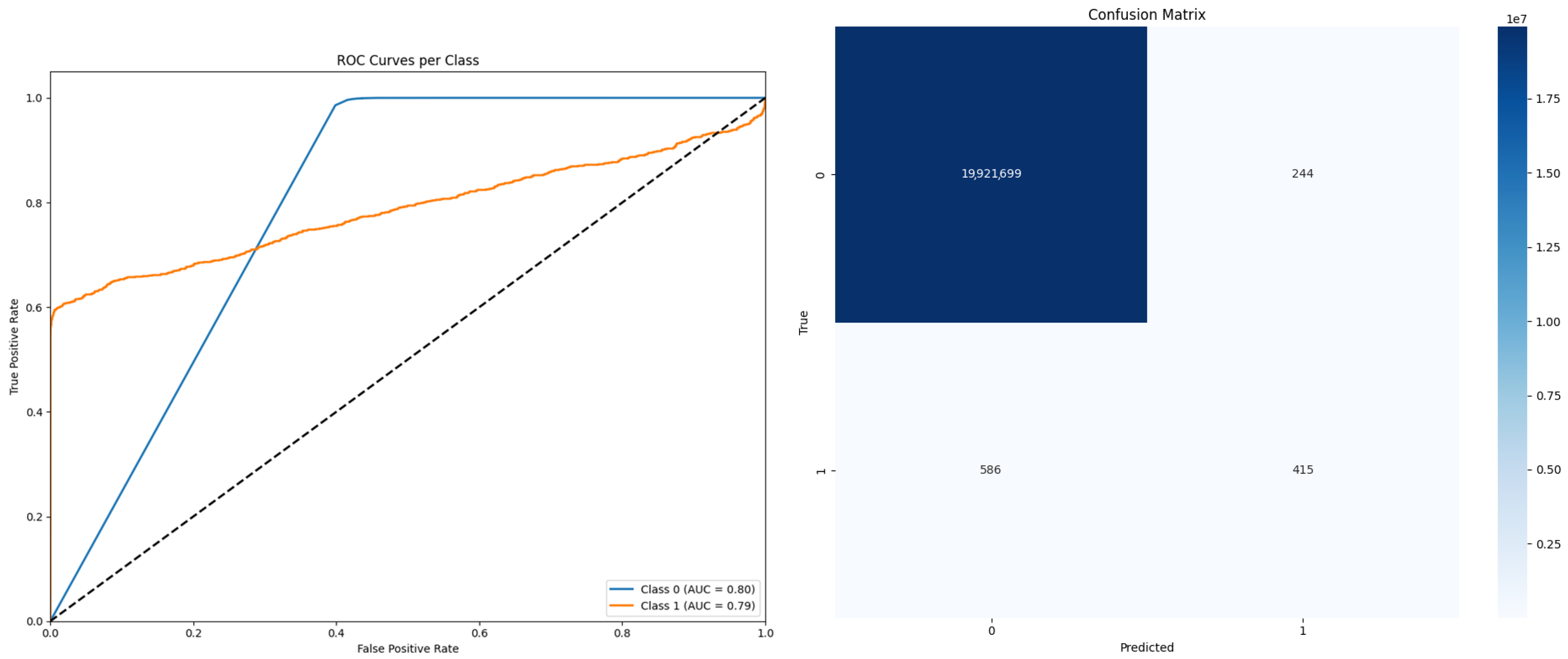
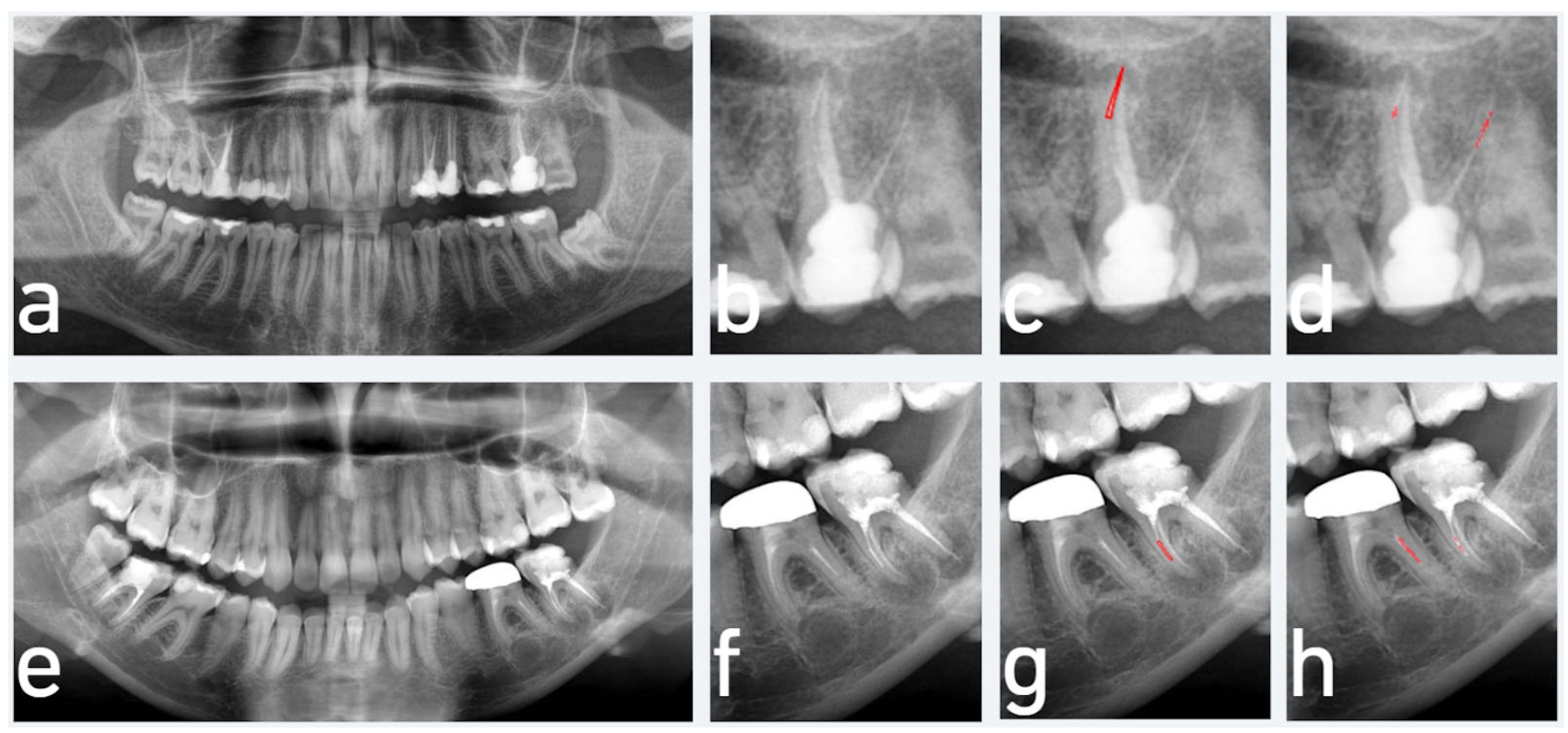
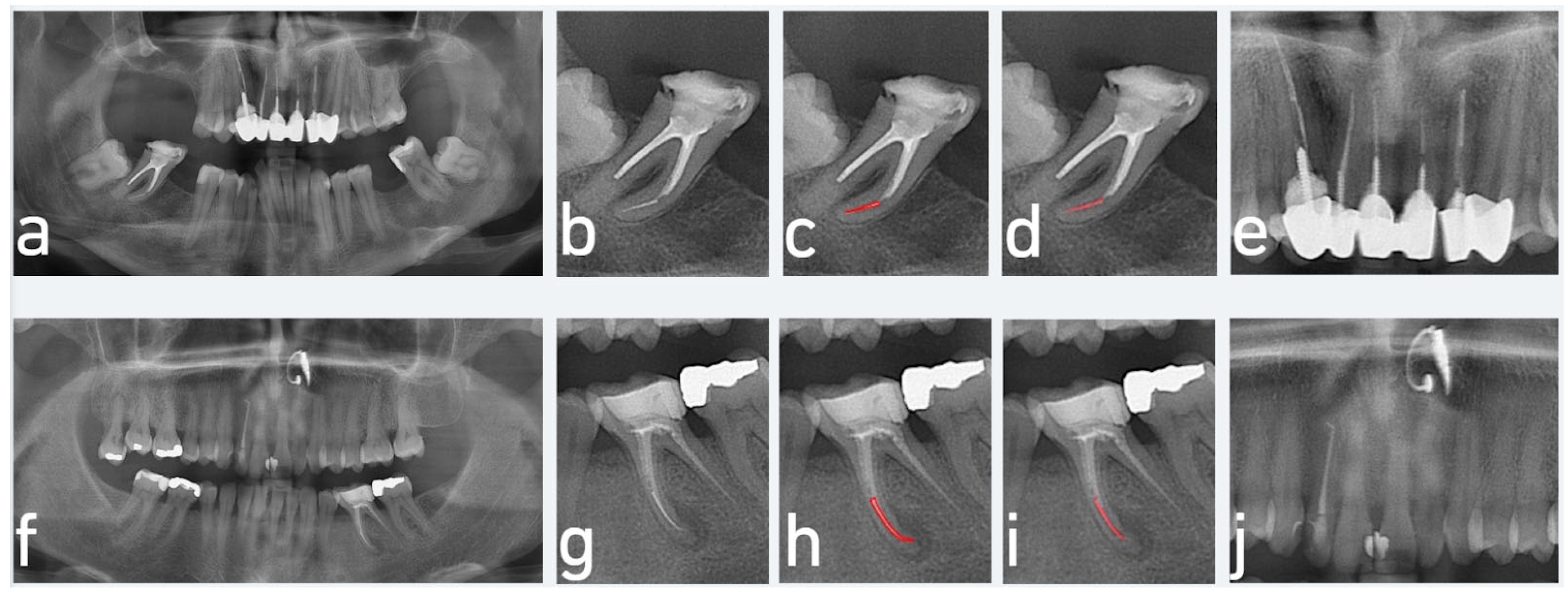
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RCT | Root canal treatment |
| NiTi | Nickel–titanium |
| OPGs | Orthopantomograms |
| CBCT | Cone beam computed tomography |
| AI | Artificial intelligence |
| DL | Deep learning |
| CNN | Convolutional neural networks |
| CVAT | Computer Vision Annotation Tool |
| IoU | Intersection over Union |
| LSTM | Long short-term memory |
| RSU | Residual u-block |
References
- Gulabivala, K.; Ng, Y.L. Factors That Affect the Outcomes of Root Canal Treatment and Retreatment—A Reframing of the Principles. Int. Endod. J. 2023, 56, 82–115. [Google Scholar]
- Arias, A.; Peters, O.A. Present Status and Future Directions: Canal Shaping. Int. Endod. J. 2022, 55, 637–655. [Google Scholar]
- Spili, P.; Parashos, P.; Messer, H.H. The Impact of Instrument Fracture on Outcome of Endodontic Treatment. J. Endod. 2005, 31, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McGuigan, M.B.; Louca, C.; Duncan, H.F. Clinical Decision-Making after Endodontic Instrument Fracture. Br. Dent. J. 2013, 214, 395–400. [Google Scholar]
- Natanasabapathy, V.; Varghese, A.; Karthikeyan, P.K.A.; Narasimhan, S. Pattern of Endodontic Instrument Separation and Factors Affecting Its Retrieval: A 10-Year Retrospective Observational Study in a Postgraduate Institute. Restor. Dent. Endod. 2025, 50, rde-2025. [Google Scholar]
- Brito, A.C.R.; Verner, F.S.; Junqueira, R.B.; Yamasaki, M.C.; Queiroz, P.M.; Freitas, D.Q.; Oliveira-Santos, C. Detection of Fractured Endodontic Instruments in Root Canals: Comparison between Different Digital Radiography Systems and Cone-Beam Computed Tomography. J. Endod. 2017, 43, 544–549. [Google Scholar]
- Madarati, A.A.; Hunter, M.J.; Dummer, P.M. Management of Intracanal Separated Instruments. J. Endod. 2013, 39, 569–581. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, S.; Dawood, A.; Ford, T.P.; Whaites, E. The Potential Applications of Cone Beam Computed Tomography in the Management of Endodontic Problems. Int. Endod. J. 2007, 40, 818–830. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, S.; Dawood, A.; Whaites, E.; Pitt Ford, T. New Dimensions in Endodontic Imaging: Part 1. Conventional and Alternative Radiographic Systems. Int. Endod. J. 2009, 42, 447–462. [Google Scholar]
- Katsumata, A. Deep Learning and Artificial Intelligence in Dental Diagnostic Imaging. Jpn. Dent. Sci. Rev. 2023, 59, 329–333. [Google Scholar]
- Orhan, K.; Bayrakdar, I.S.; Ezhov, M.; Kravtsov, A.; Özyürek, T. Evaluation of Artificial Intelligence for Detecting Periapical Pathosis on Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Scans. Int. Endod. J. 2020, 53, 680–689. [Google Scholar]
- Yaji, A.; Prasad, S.; Pai, A. Artificial Intelligence in Dento-Maxillofacial Radiology. Acta Sci. Dent. Sci. 2019, 3, 116–121. [Google Scholar]
- Orhan, K.; Aksoy, U.; Aksoy, S. Applications of AI in Endodontics and Restorative Dentistry. In Artificial Intelligence in Dentistry; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 69–81. [Google Scholar]
- Çatmabacak, E.D.; Çetinkaya, İ. Deep Learning Algorithms for Detecting Fractured Instruments in Root Canals. BMC Oral Health 2025, 25, 293. [Google Scholar]
- Özbay, Y.; Kazangirler, B.Y.; Özcan, C.; Pekince, A. Detection of the Separated Endodontic Instrument on Periapical Radiographs Using a Deep Learning-Based Convolutional Neural Network Algorithm. Aust. Endod. J. 2024, 50, 131–139. [Google Scholar]
- Buyuk, C.; Arican Alpay, B.; Er, F. Detection of the Separated Root Canal Instrument on Panoramic Radiograph: A Comparison of LSTM and CNN Deep Learning Methods. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2023, 52, 20220209. [Google Scholar]
- Çetinkaya, İ.; Çatmabacak, E.D.; Öztürk, E. Detection of Fractured Endodontic Instruments in Periapical Radiographs: A Comparative Study of YOLOv8 and Mask R-CNN. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, C.; Dehghan, M.; Zaiane, O.R.; Jagersand, M. U2-Net: Going deeper with nested U-structure for salient object detection. Pattern Recognit. 2020, 106, 107404. [Google Scholar]
- Azad, R.; Aghdam, E.K.; Rauland, A.; Jia, Y.; Avval, A.H.; Bozorgpour, A.; Merhof, D. Medical image segmentation review: The success of U-Net. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2024, 46, 10076–10095. [Google Scholar]
- Gardiyanoğlu, E.; Ünsal, G.; Akkaya, N.; Aksoy, S.; Orhan, K. Automatic segmentation of teeth, crown–bridge restorations, dental implants, restorative fillings, dental caries, residual roots, and root canal fillings on orthopantomographs: Convenience and pitfalls. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyuk, C.; Akkaya, N.; Arsan, B.; Unsal, G.; Aksoy, S.; Orhan, K. A fused deep learning architecture for the detection of the relationship between the mandibular third molar and the mandibular canal. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sin, Ç.; Akkaya, N.; Aksoy, S.; Orhan, K.; Öz, U. A deep learning algorithm proposal to automatic pharyngeal airway detection and segmentation on CBCT images. Orthod. Craniofac. Res. 2021, 24 (Suppl. 2), 117–123. [Google Scholar]
- Bayrakdar, I.S.; Orhan, K.; Çelik, Ö.; Bilgir, E.; Sağlam, H.; Kaplan, F.A.; Różyło-Kalinowska, I. AU-net approach to apical lesion segmentation on panoramic radiographs. Biomed. Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 7035367. [Google Scholar]
- Boztuna, M.; Firincioglulari, M.; Akkaya, N.; Orhan, K. Segmentation of periapical lesions with automatic deep learning on panoramic radiographs: An artificial intelligence study. BMC Oral Health 2024, 24, 1332. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, N.K.; Raza, K. TeethU 2 Net: A Deep Learning-Based Approach for Tooth Saliency Detection in Dental Panoramic Radiographs. In Communications in Computer and Information Science, Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Information Processing (ICONIP 2022); Tanveer, M., Agarwal, S., Ozawa, S., Ekbal, A., Jatowt, A., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 224–234. [Google Scholar]
- Shiri, I.; Amini, M.; Yousefirizi, F.; Vafaei Sadr, A.; Hajianfar, G.; Salimi, Y.; Mansouri, Z.; Jenabi, E.; Maghsudi, M.; Mainta, I.; et al. Information Fusion for Fully Automated Segmentation of Head and Neck Tumors from PET and CT Images. Med. Phys. 2024, 51, 319–333. [Google Scholar]
- McGuigan, M.B.; Louca, C.; Duncan, H.F. Endodontic Instrument Fracture: Causes and Prevention. Br. Dent. J. 2013, 214, 341–348. [Google Scholar]
- McGuigan, M.B.; Louca, C.; Duncan, H.F. The Impact of Fractured Endodontic Instruments on Treatment Outcome. Br. Dent. J. 2013, 214, 285–289. [Google Scholar]
- Thakur, V.S.; Kankar, P.K.; Parey, A.; Jain, A.; Jain, P.K. The Implication of Oversampling on the Effectiveness of Force Signals in the Fault Detection of Endodontic Instruments during RCT. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H J. Eng. Med. 2023, 237, 958–974. [Google Scholar]
- Terauchi, Y.; Ali, W.T.; Abielhassan, M.M. Present Status and Future Directions: Removal of Fractured Instruments. Int. Endod. J. 2022, 55, 685–709. [Google Scholar]

| Inclusion Criteria | Exclusion Criteria |
|---|---|
| Panoramic radiographs of single or multirooted RCT teeth with the presence of a radiographically confirmed separated endodontic instrument | Radiographs without the RCT and separated endodontic instruments |
| Patient with permanent teeth | Patient with primary teeth or without any teeth (edentulous patient) |
| Panoramic radiographs obtained using Orthophos SL 3D, Orthophos XG, and PM 2002 CC Proline, with standardized exposure settings (60–90 kV, 3–16 mA for Orthophos devices; 60–70 kV, 2–7 mA for Planmeca) to ensure consistency across imaging systems. | Radiographs taken with devices other than Orthophos SL 3D, Orthophos XG, or PM 2002 CC Proline, or with non-standard exposure settings, leading to variations in image quality. |
| Radiographs free of imaging artifacts such as motion blur, positioning errors, or foreign objects interfering with assessment. | Radiographs with significant imaging artifacts (motion blur, positioning errors) that compromise accurate evaluation. |
| Radiographs of teeth with complete root formation and no history of previous endodontic surgery. | Radiographs of teeth with evidence of previous endodontic surgery, retreatment, or root resorption affecting the periapical area. |
| Radiographs obtained with proper angulation and minimal distortion, ensuring accurate representation of the root canal anatomy and separated instruments. | Radiographs with severe distortion or non-standard angulation, misrepresenting the actual location of separated instruments. |
| No presence of large periapical lesions (>5 mm) that could interfere with the assessment of separated instruments. | Radiographs showing extensive periapical pathology or overlapping anatomical structures, making identification of separated instruments difficult. |
| Radiographs with RCT cases containing intracanal posts, pins, or other restorative materials |
| Architecture | Cross-Entropy | Weighted CE | Dice | Weighted Dice |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HRNet | 0.618 | 0.642 | 0.673 | 0.672 |
| Attention U-Net | 0.659 | 0.751 | 0.782 | 0.803 |
| ResUNet | 0.651 | 0.689 | 0.665 | 0.661 |
| U2-Net | 0.6 | 0.696 | 0.847 | 0.863 |
| UNet | 0.652 | 0.775 | 0.81 | 0.774 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
İnönü, N.; Aksoy, U.; Kırmızı, D.; Aksoy, S.; Akkaya, N.; Orhan, K. Deep Learning-Based Detection of Separated Root Canal Instruments in Panoramic Radiographs Using a U2-Net Architecture. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1744. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15141744
İnönü N, Aksoy U, Kırmızı D, Aksoy S, Akkaya N, Orhan K. Deep Learning-Based Detection of Separated Root Canal Instruments in Panoramic Radiographs Using a U2-Net Architecture. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(14):1744. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15141744
Chicago/Turabian Styleİnönü, Nildem, Umut Aksoy, Dilan Kırmızı, Seçil Aksoy, Nurullah Akkaya, and Kaan Orhan. 2025. "Deep Learning-Based Detection of Separated Root Canal Instruments in Panoramic Radiographs Using a U2-Net Architecture" Diagnostics 15, no. 14: 1744. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15141744
APA Styleİnönü, N., Aksoy, U., Kırmızı, D., Aksoy, S., Akkaya, N., & Orhan, K. (2025). Deep Learning-Based Detection of Separated Root Canal Instruments in Panoramic Radiographs Using a U2-Net Architecture. Diagnostics, 15(14), 1744. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15141744







