The Sensory Gatekeeper of the Larynx: Anatomy and Clinical Importance of the Internal Branch of the Superior Laryngeal Nerve
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Search and Selection Criteria
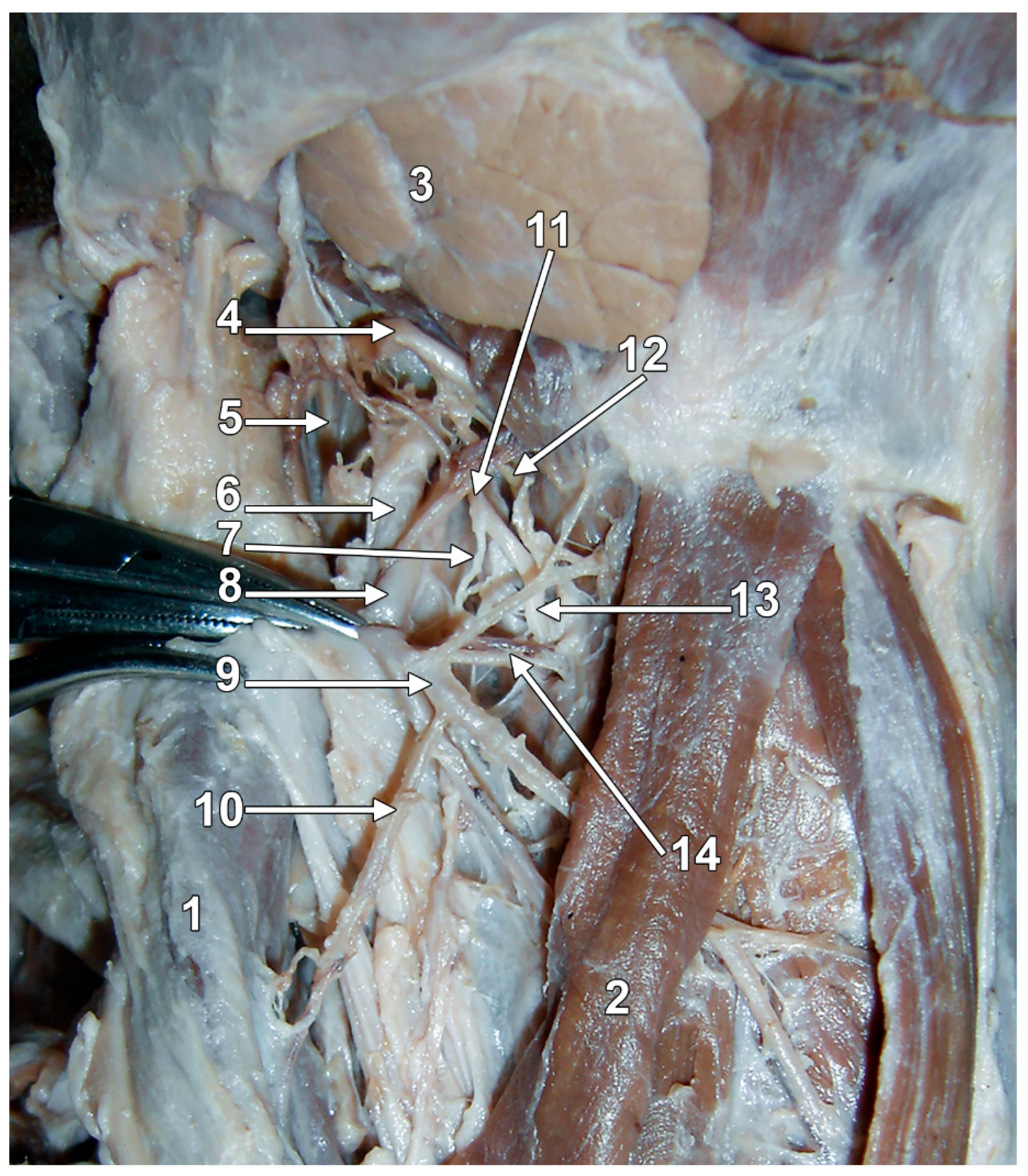
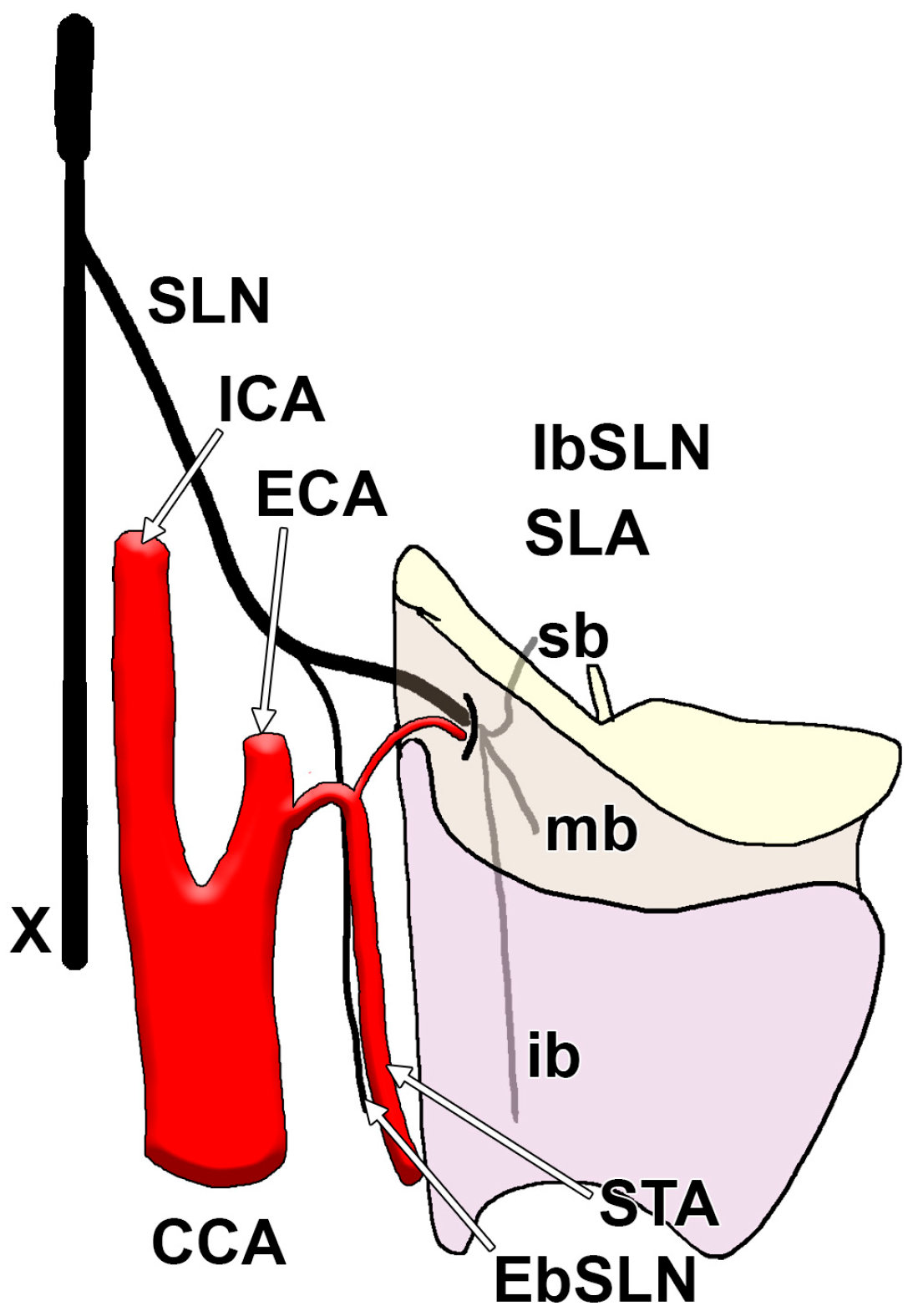
3. The Gross Anatomy of the IbSLN
4. The Origin Level of the IbSLN
5. The Relations Between the SLA and the IbSLN
6. The Location of the Penetration Point of the IbSLN
7. The Relationship of the IbSLN with the Thyroid Foramen
8. The Branching Pattern of the IbSLN
9. The Branches of the IbSLN
10. The Anastomoses of the IbSLN
11. The Identification or Avoidance Areas of the IbSLN
12. The Injury of the IbSLN
13. The IbSLN Nerve Block
14. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Neuhuber, W.L.; Berthoud, H.R. Functional anatomy of the vagus system: How does the polyvagal theory comply? Biol. Psychol. 2022, 174, 108425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Ma, Y.; Saleh, E.; Qiu, T.; Zhuang, P. Exploring the Clinical Characteristics of Superior Laryngeal Nerve Injury. J. Voice 2024, 38, 1478–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Hirano, M.; Nakashima, T. Sensory innervation of the pharynx and larynx. Am. J. Med. 2000, 108 (Suppl. S4a), 51S–61S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, A.; Jiao, Z.; Yao, J.; Chen, X.; Luo, L.; Zhang, H. Effect of ultrasound-guided internal branch of superior laryngeal nerve block on postoperative sore throat induced by a NIM-EMG-ETT: Study protocol for a double-blinded randomized controlled trial. Trials 2024, 25, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Xu, K.; Peng, X.; Min, X. Key points for protecting the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve in open thyroidectomy: A possible exploration technique. Surg. Oncol. 2024, 53, 102059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melamed, H.; Harris, M.B.; Awasthi, D. Anatomic considerations of superior laryngeal nerve during anterior cervical spine procedures. Spine 2002, 27, E83–E86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standring, S.; Anand, N.; Birch, R.; Collins, P.; Crossman, A.; Gleeson, M.; Jawaheer, G.; Smith, A.L.; Spratt, J.D.; Stringer, M.D.; et al. Gray’s Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice; Elsevier: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Furlan, J.C. Sympathetic fiber origin of the superior laryngeal nerve and its branches: An anatomic study. Clin. Anat. 2002, 15, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambic, V.; Zargi, M.; Radsel, Z. Topographic anatomy of the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve. Its importance in head and neck surgery. J. Laryngol. Otol. 1984, 98, 1121–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, Z.; Shen, H.; Wang, C.; Chen, J.; Xiao, S. Clinical anatomy of superior laryngeal artery via transoral approach. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2022, 7, 702–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiray, A.; Naderi, S.; Ergur, I.; Korman, E. Surgical anatomy of the internal branch of the superior laryngeal nerve. Eur. Spine J. 2006, 15, 1320–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erfan, S.; Saha, S.; Guha, R.; Sen, I.; Kulkarni, S. Varying Course of External Branch of Superior Laryngeal Nerve (EBSLN) and Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve (RLN) in Thyroidectomy-An Observational Study. Indian J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2024, 76, 1959–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widdicombe, J.G.; Tatar, M. Upper airway reflex control. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1988, 533, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orestes, M.I.; Chhetri, D.K. Superior laryngeal nerve injury: Effects, clinical findings, prognosis, and management options. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2014, 22, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Wen, W.P.; Zhu, X.L. Preservation of Internal Branch of Superior Laryngeal Nerve during Surgery for Hypopharyngeal Cancer. Ear Nose Throat J. 2022, 101, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Oviedo, C.; Maranillo, E.; Sanudo, J.R.; Perez-Lloret, P.; Verdu, E.; Martinez-Guirado, T.; Alvarez-Montero, O.; Gomez Martin-Zarco, J.M.; Vazquez, T. The Human Laryngeal Innervation Revisited—The Role of the Neural Connections. Anat. Rec. 2019, 302, 646–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Saraf, A.; Kishore, K.; Kalsotra, P. Relation of Superior Laryngeal Nerve and Superior Thyroid Artery with Superior Pole of Thyroid During Thyroid Surgery. Indian J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2022, 74, 2095–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraskevas, G.K.; Raikos, A.; Ioannidis, O.; Brand-Saberi, B. Topographic anatomy of the internal laryngeal nerve: Surgical considerations. Head Neck 2012, 34, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Deek, A.M.; Shafik, A.M.; Eltohry, A.S.M.A.; Al Fawal, S.M. Comparison between ultrasound-guided and anatomical landmark-guided block of internal branch of the superior laryngeal nerve for awake fiber-optic intubation in suspected difficult intubation: A randomized controlled study. Ain-Shams J. Anesthesiol. 2021, 13, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhipeng, L.; Meiyi, H.; Meirong, W.; Qunmeng, J.; Zhenhua, J.; Yuezhen, H.; Jinfang, Z.; Chuiliang, L. Ultrasound-guided internal branch of superior laryngeal nerve block on postoperative sore throat: A randomized controlled trial. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0241834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, R.E.; Wendel, K.H.; Addington, W.R. Anatomy of the internal branch of the superior laryngeal nerve. Clin. Anat. 1999, 12, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stopar-Pintaric, T.; Vlassakov, K.; Azman, J.; Cvetko, E. The thyrohyoid membrane as a target for ultrasonography-guided block of the internal branch of the superior laryngeal nerve. J. Clin. Anesth. 2015, 27, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlan, J.C.; Brandao, L.G.; Ferraz, A.R.; Rodrigues, A.J., Jr. Surgical anatomy of the extralaryngeal aspect of the superior laryngeal nerve. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2003, 129, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.U.; Sung, J.K.; Nam, K.H.; Cho, D.C. Bilateral internal superior laryngeal nerve palsy of traumatic cervical injury patient who presented as loss of cough reflex after anterior cervical discectomy with fusion. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2012, 52, 264–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, J.H.; Olson, N.R. The surgical anatomy of the spinal accessory nerve and the internal branch of the superior laryngeal nerve. Laryngoscope 1979, 89, 1935–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharathadevi, M.S.T. A cadaveric study of internal branch of superior laryngeal nerve. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2019, 8, 21–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monfared, A.; Kim, D.; Jaikumar, S.; Gorti, G.; Kam, A. Microsurgical anatomy of the superior and recurrent laryngeal nerves. Neurosurgery 2001, 49, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozgur, Z.; Govsa, F.; Celik, S.; Ozgur, T. Clinically relevant variations of the superior thyroid artery: An anatomic guide for surgical neck dissection. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2009, 31, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekhou, A.S.; Morrison, R.J.; Gemechu, J.M. The Superior Laryngeal Nerve and Its Vulnerability in Surgeries of the Neck. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guven, E.M.; Karacan, K.; Guven, M.; Elden, H.; Ozcelik Korkmaz, M. Topographic anatomy of the internal branch of the superior laryngeal nerve. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2021, 278, 727–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calota, R.N.; Rusu, M.C.; Rusu, M.I.; Dumitru, C.C.; Vrapciu, A.D. Anatomical Variables of the Superior Thyroid Artery on Computed Tomography Angiograms. Medicina 2025, 61, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, S.S.; Randolph, G.W.; Seidman, M.D.; Rosenfeld, R.M.; Angelos, P.; Barkmeier-Kraemer, J.; Benninger, M.S.; Blumin, J.H.; Dennis, G.; Hanks, J.J.O.H.; et al. Clinical practice guideline: Improving voice outcomes after thyroid surgery. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2013, 148, S1–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, B.; Canda, B.; Pence, K.B.; Yuzbasioglu, N.; Turgut, S. Surgical landmarks for identification and preservation of the internal branch of the superior laryngeal nerve. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2023, 45, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uludağ, M.; Tanal, M.; İşgör, A. A review of methods for the preservation of laryngeal nerves during thyroidectomy. J. Clin. Anesth. 2018, 52, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulica, L. The superior laryngeal nerve: Function and dysfunction. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2004, 37, 183–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilworth, T.F. The Nerves of the Human Larynx. J. Anat. 1921, 56, 48–52. [Google Scholar]
- Devaraja, K.; Punja, R.; Kalthur, S.G.; Pujary, K. Unmapped landmarks around branches of the Superior Laryngeal Nerve: An exploratory cadaveric study. J. Taibah Univ. Med. Sci. 2021, 16, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poutoglidis, A.; Paraskevas, G.K.; Lazaridis, N.; Anastasopoulos, N.; Asouhidou, I.; Argyroulis, A.; Galanis, N.; Karamitsou, P.; Paraskevas, G.J.C. Bilateral Thyroid Foramina in a Completely Ossified Laryngeal Framework: A Case Report. Cureus 2023, 15, e37551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srichaphan, N.; Yurasakpong, L.; Taradolpisut, N.; Senarai, T.; Kruepunga, N.; Suwannakhan, A. The thyroid foramen: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2024, 46, 1673–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, X.; Maranillo, E.; Mirapeix, R.M.; Quer, M.; Sanudo, J.R. Foramen thyroideum: A comparative study in embryos, fetuses, and adults. Laryngoscope 1997, 107, 1146–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsaroop, L.; Hurrinarain, K.; Partab, P.; Satyapal, K.S. The incidence of the foramen thyroideum in the South African population. Int. J. Morphol. 2010, 28, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Ye, C.; Carrat, X.; Traissac, L. Anatomical study of the thyroid foramen in human larynx: A study of 100 dissections. Rev. Laryngol. Otol. Rhinol. (Bord) 1999, 120, 127–129. [Google Scholar]
- Sanudo, J.R.; Maranillo, E.; Leon, X.; Mirapeix, R.M.; Orus, C.; Quer, M. An anatomical study of anastomoses between the laryngeal nerves. Laryngoscope 1999, 109, 983–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueger, R.S. The superior laryngeal nerve and the interarytenoid muscle in humans: An anatomical study. Laryngoscope 1972, 82, 2008–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, I.; Mu, L. Anatomy of the human internal superior laryngeal nerve. Anat. Rec. A Discov. Mol. Cell Evol. Biol. 1998, 252, 646–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraskevas, G.K.; Poutoglidis, A.; Lazaridis, N.; Anastasopoulos, N.; Tsetsos, N. Early Internal Branch of Superior Laryngeal Nerve Bifurcation Passes Through Double Thyroid Foramen. Ear Nose Throat J. 2023, 102, NP545–NP546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Lee, H.; Ji, J.Y.; Mohammad, R.T.; Huh, G.; Jeong, W.J.; Cha, W. Superior Laryngeal Nerve Block in Transcutaneous Vocal Fold Injection: A Pilot Study. J. Voice 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemere, F.J.T.A.R. Innervation of the larynx. II. Ramus anastomoticus and ganglion cells of the superior laryngeal nerve. Anat. Rec. 1932, 54, 389–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoso, L.F.; Jafari, S.; Kim, D.Y.; Paydarfar, D. The Internal Superior Laryngeal Nerve in Humans: Evidence for Pure Sensory Function. Laryngoscope 2021, 131, E207–E211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual-Font, A.; Cubillos, L.; Vazquez, T.; McHanwell, S.; Sanudo, J.R.; Maranillo, E. Are the interarytenoid muscles supplied by branches of both the recurrent and superior laryngeal nerves? Laryngoscope 2016, 126, 1117–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, L.; Sanders, I.; Wu, B.L.; Biller, H.F. The intramuscular innervation of the human interarytenoid muscle. Laryngoscope 1994, 104, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotby, M.N.; Haugen, L.K. Attempts at evaluation of the function of various laryngeal muscles in the light of muscle and nerve stimulation experiments in man. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 1970, 70, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegelman, E.F. Laryngeal nerves: Surgical importance in relation to the thyroid arteries, thyroid gland and larynx. Arch. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 1933, 18, 793–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, Y. Interrelationships between the innervations from the laryngeal nerves and the pharyngeal plexus to the inferior pharyngeal constrictor. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2013, 35, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, G.; Kosztyla-Hojna, B.; Chyczewski, L. Impact of the anatomy of laryngeal nerves on intraoperative neuromonitoring results in surgery of thyroid gland and functional results after partial laryngectomies. Pol. Przegl. Chir. 2018, 91, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreyer, R.; Pomaroli, A. Anastomosis between the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve and the recurrent laryngeal nerve. Clin. Anat. 2000, 13, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisa, Y. Neuroanatomy and Neurophysiology of the Larynx; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kochilas, X.; Bibas, A.; Xenellis, J.; Anagnostopoulou, S. Surgical anatomy of the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve and its clinical significance in head and neck surgery. Clin. Anat. 2008, 21, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, G.P.; Tomazic, P.V.; Vasicek, S.; Graupp, M.; Gugatschka, M.; Baumann, A.; Konstantiniuk, P.; Koter, S.H. Carotid endarterectomy significantly improves postoperative laryngeal sensitivity. J. Vasc. Surg. 2016, 64, 1303–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uluisik, I.E.; Elbizim, D.S.; Ortug, G. A Microdissectional Study on Galen’s Anastomosis: Anatomical Perspective with Clinical Emphasis. J. Anat. Soc. India 2023, 72, 290–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ónodi, A. Die Anatomie und Physiologie der Kehlkopfnerven: Mit Ergänzenden Pathologischen Beiträgen; Oscar Coblentz: Berlin, Germany, 1902. [Google Scholar]
- Stefanou, C.K.; Papathanakos, G.; Stefanou, S.K.; Tepelenis, K.; Kitsouli, A.; Barbouti, A.; Tsoumanis, P.; Kanavaros, P.; Kitsoulis, P. Surgical tips and techniques to avoid complications of thyroid surgery. Innov. Surg. Sci. 2022, 7, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, B.M.; Pekala, P.A.; Sanna, B.; Vikse, J.; Sanna, S.; Saganiak, K.; Tomaszewska, I.M.; Tubbs, R.S.; Tomaszewski, K.A. The Anastomoses of the Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve in the Larynx: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. J. Voice 2017, 31, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maranillo, E.; Leon, X.; Orus, C.; Quer, M.; Sanudo, J.R. Variability in nerve patterns of the adductor muscle group supplied by the recurrent laryngeal nerve. Laryngoscope 2005, 115, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partab, P.; Hurrinarain, K.; Ramsaroop, L.; Satyapal, K.S. Atypical anastomosis of laryngeal nerves. Clin. Anat. 2006, 19, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, R.; Raj, P. Superior laryngeal nerve dysfunction following thyroid surgery: Assessment of incidence and long-term effect. Int. J. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2020, 6, 1683–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, C.P.; Raffaelli, M.; D’Alatri, L.; Marchese, M.R.; Rigante, M.; Paludetti, G.; Bellantone, R. Voice and swallowing changes after thyroidectomy in patients without inferior laryngeal nerve injuries. Surgery 2006, 140, 1026–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Ren, H.C.; Huang, Y.; Yin, L. Hybrid Surgery for Revascularization of Chronic Occlusion of Internal Carotid Artery. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2024, 35, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tempel, Z.J.; Smith, J.S.; Shaffrey, C.; Arnold, P.M.; Fehlings, M.G.; Mroz, T.E.; Riew, K.D.; Kanter, A.S. A Multicenter Review of Superior Laryngeal Nerve Injury Following Anterior Cervical Spine Surgery. Glob. Spine J. 2017, 7, 7S–11S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, J.; Nachbaur, S.; Fischer, K.; Vogel, E. The superior laryngeal nerve and the superior laryngeal artery. Acta Anat. 1987, 130, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.N.; Ding, J.W.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, J.J.; Zhou, L.; Peng, Y.; Shen, J.; Lu, S.; Sun, S.H.; Ni, Y.Q.; et al. The Anatomical and Clinical Significance of the Superior Laryngeal Nerve. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2021, 165, 690–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserman, J.M.; Sundaram, K.; Alfonso, A.E.; Rosenfeld, R.M.; Har-El, G. Determination of the function of the internal branch of the superior laryngeal nerve after thyroidectomy. Head Neck 2008, 30, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potenza, A.S.; Araujo Filho, V.J.F.; Cernea, C.R. Injury of the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve in thyroid surgery. Gland. Surg. 2017, 6, 552–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourabaa, S.; Settaf, A. Is identification and dissection of the external laryngeal nerve necessary during thyroidectomy? A prospective study. BMC Surg. 2024, 24, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Singh, I.; Meher, R.; Kumar, J.; Gopal, A.; Sahoo, A.; Sharma, R. Incidence of Injury to External Branch of Superior Laryngeal Nerve as Diagnosed by Acoustic Voice Analysis After Thyroidectomy. Indian J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2025, 77, 1401–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barman, S.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Mahanta, B.; Nath, K. Role of Intraoperative Neuromonitoring to Identify External Branch of Superior Laryngeal Nerve During Thyroidectomy. Indian J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2025, 77, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhu, R.; Zhu, P.; Du, Y.; Tanu, C.; Han, Z.; Jiang, N.; Pan, L.; Xie, C.; Zhao, Q.; et al. Effectiveness and feasibility of nerve real-time monitoring and intermittent monitoring in endoscopic thyroidectomy: A multicenter retrospective cohort study of 1621 patients. Int. J. Surg. 2025, 111, 904–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cernea, C.R.; Brandao, L.G.; Hojaij, F.C.; De Carlucci, D.; Montenegro, F.L.; Plopper, C.; Vanderlei, F.; Gotoda, R.; Dias, F.L.; Lima, R.A. How to minimize complications in thyroid surgery? Auris Nasus Larynx 2010, 37, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cernea, C.R.; Ferraz, A.R.; Nishio, S.; Dutra, A., Jr.; Hojaij, F.C.; dos Santos, L.R. Surgical anatomy of the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve. Head Neck 1992, 14, 380–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cernea, C.R.; Nishio, S.; Hojaij, F.C. Identification of the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve (EBSLN) in large goiters. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 1995, 16, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, M.; LoSavio, P.; Ibrahim, H. Superior laryngeal nerve identification and preservation in thyroidectomy. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2002, 128, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dip, F.; Aleman, R.; Marinelli, F.; Guiselli, J.; Rosenthal, R.; Rancati, A.; Sinagra, D. High-Precision Identification of Sensory and Motor Branches of the Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve Via Autofluorescence System in Thyroid Surgery. Cureus 2025, 17, e80262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.K.; Agarwal, P.; Sharma, D. Critical View of Safety: Anatomical Key to Avoid Injury to Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve in Transoral Endoscopic Thyroidectomy. Laryngoscope 2025, 135, 1227–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.Y.; Li, X.; Yu, B.; Liu, S.R.; Wang, B.Y.; Lu, S.Y.; Li, H.W.; Song, S.B.; Cui, L.G.; Tan, S. Ultrasound Visualization of the Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve: A Prospective Clinical Validation Study. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2025, 32, 1309–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafki, S.; Chrysikos, D.; Manoli, A.; Troupis, T. Anatomical Variations of the External Branch of the Superior Laryngeal Nerve and its Correlations with the Superior Thyroid Artery and the Upper Pole of the Thyroid Gland: A Review of the Literature. J. Surg. Surg. Spec. 2023, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmonds, C.E.; German, R.Z.; Bond, L.E.; Mayerl, C.J. Oropharyngeal capsaicin exposure improves infant feeding performance in an animal model of superior laryngeal nerve damage. J. Neurophysiol. 2022, 128, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, D.H. Laryngeal reinnervation. Laryngoscope 1982, 92, 1049–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Q.; Wu, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X. Ultrasound-guided medial branch of the superior laryngeal nerve block to reduce peri-operative opioids dosage and accelerate patient recovery. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0295127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Jin, Y.; Lu, G.; Jin, Y.; Feng, C.; Zhao, X. Preoperative Ultrasound-Guided Internal Branch Block of Superior Laryngeal Nerve Reduces Postoperative Sore Throat Caused by Double Lumen Endotracheal Intubation: A Randomized Trial. Anesth. Analg. 2023, 137, 1270–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Zhou, X.; Chen, X.; Cai, J.; Zhao, Q.; Huang, X.; Pan, Y.; Sun, J. Internal branch of superior laryngeal nerve block by dexamethasone alleviates sore throat after thyroidectomy: A randomized controlled trial. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2022, 279, 5877–5884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Xiong, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, Q.; Wang, G. Ultrasound-Guided Block of the Internal Branch of the Superior Laryngeal Nerve Reduces Postoperative Sore Throat Caused by Suspension Laryngoscopic Surgery: A Prospective Randomized Trial. Front. Surg. 2022, 9, 829811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, C.-H.; Cheng, W.-C.; Yang, Y.-L. A new method for ultrasound-guided superior laryngeal nerve block. Tzu Chi Med. J. 2013, 25, 161–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, B.; Xiong, Y.; Yu, X. The Efficacy of Ultrasound-Guided Superior Laryngeal Nerve Block as an Adjuvant to General Anesthesia during Suspension Laryngoscopy Vocal Cord Polypectomy. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2022, 2022, 1594829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockwell, M.; Lozanoff, S.; Lang, S.A.; Nyssen, J. Superior laryngeal nerve block: An anatomical study. Clin. Anat. 1995, 8, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, B.; Tang, R.; Sawka, A.; Krebs, C.; Vaghadia, H. A method for ultrasonographic visualization and injection of the superior laryngeal nerve: Volunteer study and cadaver simulation. Anesth. Analg. 2012, 115, 1242–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaghadia, H.; Lawson, R.; Tang, R.; Sawka, A. Failure to visualise the superior laryngeal nerve using ultrasound imaging. Anaesth. Intensive Care 2011, 39, 503. [Google Scholar]
- Green, J.S.; Tsui, B.C. Applications of ultrasonography in ENT: Airway assessment and nerve blockade. Anesth. Clin. 2010, 28, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talbot, N.; Heller, M.; Nyirjesy, S.; Kim, B.; DeSilva, B.; Matrka, L. Superior Laryngeal Nerve Block Response Rates in 54 Neurogenic Cough Patients. Laryngoscope 2023, 133, 2647–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, S.; Neema, P.K.; Rathod, R.C. Ultrasound-guided bilateral superior laryngeal nerve block to aid awake endotracheal intubation in a patient with cervical spine disease for emergency surgery. Anesthesiol. Intensive Care 2010, 38, 946–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, C.B.; Tibbetts, K.M.; Loochtan, M.J.; Dominguez, L.M. Treatment of chronic neurogenic cough with in-office superior laryngeal nerve block. Laryngoscope 2018, 128, 1898–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinton, B.A.; Tierney, W.S.; Benninger, M.S.; Nelson, R.C.; Gau, V.L.; Hrelec, C.M.; Bryson, P.C. The Role of Bilateral Superior Laryngeal Nerve Block in Managing Refractory Chronic Cough. Laryngoscope 2024, 134, 1773–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campagnolo, A.; Nickel, V.; Benninger, M.S. Efficacy and Safety of Superior Laryngeal Nerve Block in the Management of Neuropathic Cough: A Systematic Review. Lung 2025, 203, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, V.K. Superior laryngeal nerve block for neurogenic cough: A case series. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2019, 4, 410–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, L.; Lu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, D.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, H.; Jin, Y.; Zhao, X.; Jin, Y. Effects of Dexmedetomidine as an Adjuvant in Preoperative Ultrasound-Guided Internal Branch of Superior Laryngeal Nerve Block on Postoperative Sore Throat and Hemodynamics in Patients With Double-Lumen Endotracheal Intubation: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Pain Res. 2025, 18, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, A.J.; Roitman, A.; Ring, S.; Francis, D.O.; Davis, R.J.; McCulloch, T.; Dailey, S.H. Bilateral internal superior laryngeal nerve injections for unexplained chronic cough. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2025, 46, 104568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asi, K.; Vance, D.G.; Tritter, A.G. Survey of Practice Patterns in the Use of Superior Laryngeal Nerve Blocks. Laryngoscope 2025, 135, 1455–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Cervical Level of the IbSLN Origin from the SLN | Prevalence | Sample | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 21% | 12 cadavers | [11] |
| C2 | 58% | 12 cadavers | [11] |
| C2–C3 intervertebral disk | 21% | 12 cadavers | [11] |
| C2 | unspecified | 25 cadavers | [26] |
| Landmark | Distance (cm) | Observation | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Greater horn of the hyoid bone | 1.65 ± 0.38 | No significant gender difference | [33] |
| 1.59 ± 0.59 | [37] | ||
| Midpoint of the hyoid body | 2.04 ± 0.30 | No significant gender difference | [33] |
| Inferior border of the hyoid bone | 0.93 ± 0.16 | [30] | |
| Genu of the hyoid bone | average 0.7 (range 0.4–1.1) | [6] | |
| Carotid bifurcation | 1.67 ± 0.32 | Significantly longer in males (1.94 cm) than in females (1.56 cm), p = 0.012 | [33] |
| 2.07 ± 0.59 | [37] | ||
| Common carotid artery | 7.0 ± 6.3 | [11] | |
| Superior border of thyroid cartilage | 6.0 ± 1.4 | No significant gender difference | [33] |
| varying from 0 to 1.8 | Most frequently (87.5% of cases), the distance varied between 0.1 and 1.2 cm | [18] | |
| 1.2 ± 0.26 | [30] | ||
| Midpoint of the thyroid notch | 1.97 ± 0.29 | Significantly higher in males, 2.10 ± 0.19 SD cm in males versus 1.88 ± 0.24 SD cm in female cadavers (p = 0.034) | [33] |
| Laryngeal prominence | 13.7 ± 2.8 | [11] | |
| 3.29 ± 0.47 | [37] | ||
| STA origin | 1.63 ± 0.42 | [37] | |
| 0.59 ± 0.49 | [28] | ||
| Posterior border of the thyrohyoid muscle | ranging from 0.0 to 1.6 | In 80.56% ranged from 0.1 to 0.9 | [18] |
| Sample Size | Cervical Level of Penetration Point | Frequency | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20 IbSLN from 10 cadavers | C3–C4 intervertebral disc | Not specified | [6] |
| 24 IbSLN from 12 cadavers | C4 | 50% | [11] |
| C4–C5 intervertebral disc | 25% | ||
| C5 | 25% | ||
| 50 IbSLN from 25 cadavers | C4 | Not specified | [26] |
| Study Type | Sample Size | Branching Pattern | Site of Branching | Pre-THm (%) | Post-THm (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intraoperatively | 29 IbSLN of 15 patients | Trifurcation (58.6%), bifurcation (41.4%) | Mixed (pre-THm and post-THm) | 4 | 96 | [30] |
| Cadaveric | 22 IbSLN of 12 larynges | Bifurcation (10%), trifurcation (80%), quadrifurcation (15%), pentafurcation (5%) | Post-THm | 0 | 100 | [44] |
| Cadaveric | 10 IbSLN of 5 larynges | Trifurcation | Post-THm | 0 | 100 | [45] |
| Cadaveric | 24 IbSLNs of 12 larynges | Trifurcation | Mixed (Pre-THm and Post-THm) | 37.5 | 62.5 | [11] |
| Cadaveric | 36 cadavers | Trifurcation (72.22%), bifurcation (27.78%) | Pre-THm | 100 | 0 | [18] |
| Cadaveric | 25 IbSLN of 19 larynges | Trifurcation | Mixed | 84 | 16 | [21] |
| Cadaveric | 25 larynges | Trifurcation | Mixed | 14 | 76 | [26] |
| in 10%, the nerve could not be traced | ||||||
| IbSLN Length (mm) | Observation | Study Type | Sample | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 64 | Average length | cadaveric | 44 halved heads | [70] |
| 44.9 ± 1.0 | cadaveric | 50 cadaveric | [23] | |
| 57.2 ± 7.7 | cadaveric | 12 cadavers/24 sides | [11] | |
| 6.95 ± 3.71 | Length of the IbSLN from the GhHb to the branching point | cadaveric | 21 specimens | [21] |
| 23.4 ± 6.9 | Chinese | cadaveric | 17 cadavers/132 sides | [71] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vrapciu, A.D.; Brezean, I.; Tudose, R.C.; Rusu, M.C.; Triantafyllou, G.; Piagkou, M. The Sensory Gatekeeper of the Larynx: Anatomy and Clinical Importance of the Internal Branch of the Superior Laryngeal Nerve. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1711. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131711
Vrapciu AD, Brezean I, Tudose RC, Rusu MC, Triantafyllou G, Piagkou M. The Sensory Gatekeeper of the Larynx: Anatomy and Clinical Importance of the Internal Branch of the Superior Laryngeal Nerve. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(13):1711. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131711
Chicago/Turabian StyleVrapciu, Alexandra Diana, Iulian Brezean, Răzvan Costin Tudose, Mugurel Constantin Rusu, George Triantafyllou, and Maria Piagkou. 2025. "The Sensory Gatekeeper of the Larynx: Anatomy and Clinical Importance of the Internal Branch of the Superior Laryngeal Nerve" Diagnostics 15, no. 13: 1711. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131711
APA StyleVrapciu, A. D., Brezean, I., Tudose, R. C., Rusu, M. C., Triantafyllou, G., & Piagkou, M. (2025). The Sensory Gatekeeper of the Larynx: Anatomy and Clinical Importance of the Internal Branch of the Superior Laryngeal Nerve. Diagnostics, 15(13), 1711. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131711









