Simplified Artificial Intelligence Terminology for Pathologists
Abstract
1. Introduction
AI in Pathology
2. AI Technologies and Algorithms
2.1. Machine Learning and Neural Network Applications in Pathology
2.2. Deep Learning and Convolutional Neural Network Applications in Pathology
2.3. Generative AI
3. Common Frameworks for Training AI Models
3.1. Supervised Learning
3.2. Unsupervised Learning
3.3. Weakly Supervised Learning
3.4. Multiple-Instance Learning
3.5. Self-Supervised Learning
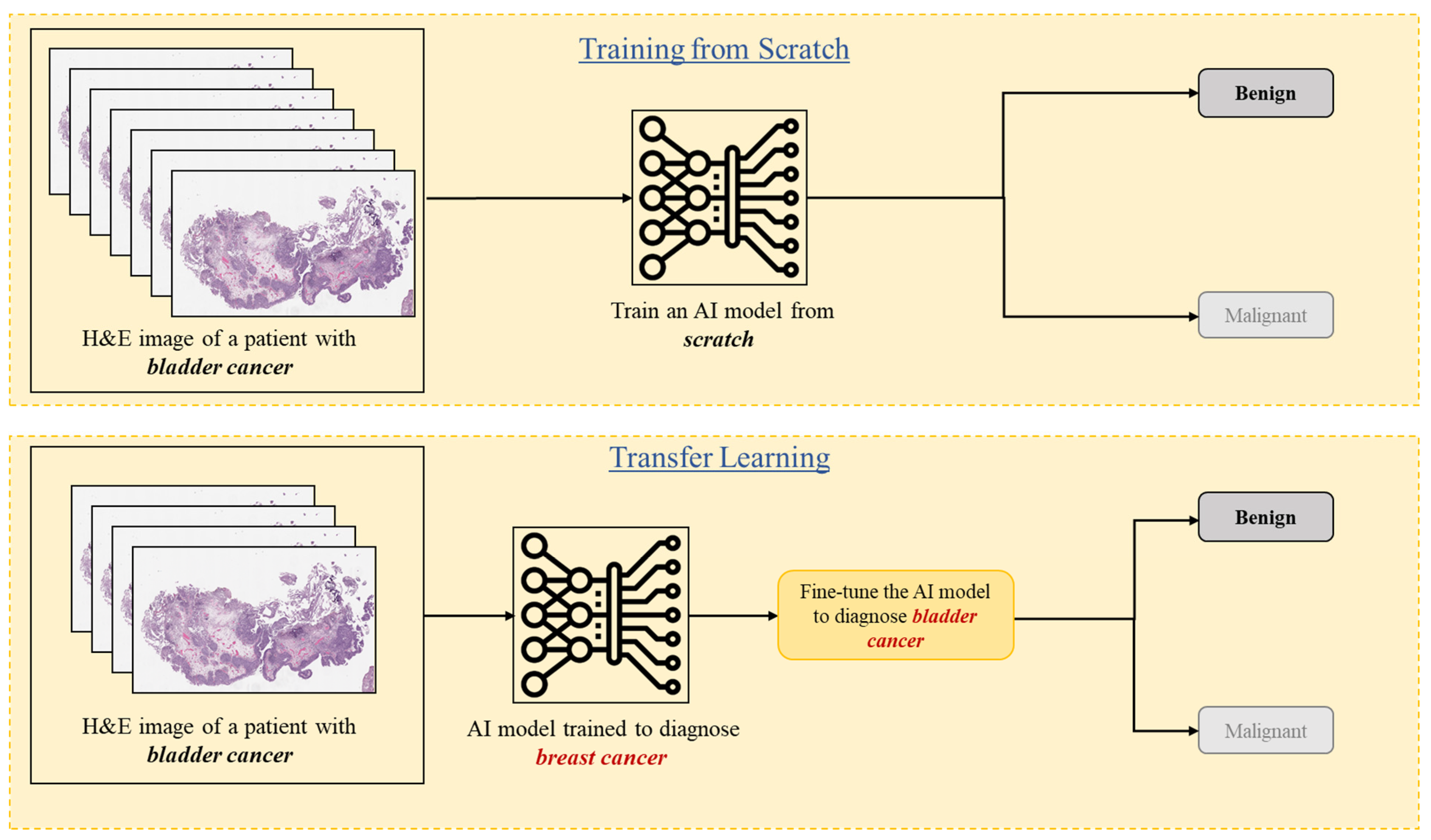
3.6. Transfer Learning
3.7. Federated Learning
4. Nomenclature of Image Analysis
4.1. Image Classification
4.2. Image Segmentation
4.3. The Gold Standard and Ground Truth
5. Datasets in Computational Pathology
6. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bruce, C.; Prassas, I.; Mokhtar, M.; Clarke, B.; Youssef, E.; Wang, C.; Yousef, G.M. Transforming diagnostics: The implementation of digital pathology in clinical laboratories. Histopathology 2024, 85, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prassas, I.; Clarke, B.; Youssef, T.; Phlamon, J.; Dimitrakopoulos, L.; Rofaeil, A.; Yousef, G.M. Computational pathology: An evolving concept. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2024, 62, 2148–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinz, C.N.; Echle, A.; Foersch, S.; Bychkov, A.; Kather, J.N. The future of artificial intelligence in digital pathology—Results of a survey across stakeholder groups. Histopathology 2022, 80, 1121–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessier, L.; González-Gonzalo, C.; Tellez, D.; Bulten, W.; Balkenhol, M.C.A.; van der Laak, J.A.W.M. Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Mitosis Counting in Breast Cancer: A Large-Scale Validation Study. J. Pathol. Clin. Res. 2024, 10, 123–130. [Google Scholar]
- Zabihollahy, F.; Yuan, X.; Mohareb, M.; Boehm-North, D.; Dimitrakopoulos, L.; Wangulu, C.; Prassas, I.; Fleshner, N.; Chang, H.; Yousef, G.M. Automated Quantification of TP53 Using Digital Immunohistochemistry for Acute Myeloid Leukemia Prognosis. In SPIE Medical Imaging: Digital and Computational Pathology; SPIE: San Diego, CA, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Selcuk, S.Y.; Yang, X.; Bai, B.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Aydin, M.; Unal, A.F.; Gomatam, A.; Guo, Z.; Angus, D.M.; et al. Automated HER2 Scoring in Breast Cancer Images Using Deep Learning and Pyramid Sampling. BME Front. 2024, 5, 0048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y. AI-Based Tumor Size Measurement in Digital Pathology: A Comparative Study. J. Digit. Pathol. 2023, 12, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Bulten, W.; Pinckaers, H.; van Boven, H.; Vink, R.; van de Sande, M.G.; van der Laak, J.A.; Litjens, G. Automated Deep-Learning System for Gleason Grading of Prostate Cancer Using Biopsies: A Diagnostic Study. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ström, P.; Kartasalo, K.; Olsson, H.; Delahunt, B.; Berney, D.M.; Bostrom, P.J.; Stattin, P.; Rantalainen, M.; Egevad, L. Artificial intelligence for prediction of perineural invasion in prostate biopsies. Virchows Arch. 2022, 481, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Xu, M.; Liu, C. Deep Learning-Based Detection of Lymphovascular Invasion in Breast Invasive Ductal Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1023980. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Ma, H.; Liu, C. Artificial Intelligence-Based Histopathological Analysis for Detection of Lymphovascular Invasion in Urothelial Carcinoma. Cancers 2023, 15, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.H.C.; Gadepalli, K.; MacDonald, R. An Accurate Deep Learning System for Lymph Node Metastasis Detection. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1608.01658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Q.; Xie, H.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, H. Enhanced EfficientNet with Attention for Lymph Node Metastasis Detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.05027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X. Deep learning-based detection of metastatic colorectal carcinoma in lymph nodes. Diagn. Pathol. 2024, 19, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.; Kaczmarzyk, J.; Kobayashi, S.; Kurc, T.; Saltz, J. AI and Pathology: Steering Treatment and Predicting Outcomes. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.07573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, S.; Iftikhar, M.A.; Mourelatos, Z. Prediction of Overall Survival and Molecular Markers in Gliomas via Analysis of Digital Pathology Images Using Deep Learning. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.09124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.J.; Lu, M.Y.; Williamson, D.F.K.; Mahmood, F.; Mahmood, F. Pathomic Fusion: An Integrated Framework for Fusing Histopathology and Genomic Features for Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1912.08937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Chen, R.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, L.; Dong, J.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, X.; Ying, J.; Lin, D.; et al. Histopathology Images-Based Deep Learning Prediction of Prognosis and Therapeutic Response in Small Cell Lung Cancer. NPJ Digit. Med. 2024, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kartasalo, K.; Weitz, P.; Ács, B.; Valkonen, M.; Larsson, C.; Ruusuvuori, P.; Hartman, J.; Rantalainen, M. Predicting Molecular Phenotypes from Histopathology Images: A Transcriptome-Wide Expression-Morphology Analysis in Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 5115–5126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.Y.; Chen, T.Y.; Williamson, D.F.K.; Zhao, M.; Shady, M.; Lipkova, J.; Mahmood, F.; Shaban, M.; Cireşan, D.C.; Rajpoot, N.; et al. AI-Based Pathology Predicts Origins for Cancers of Unknown Primary. Nature 2021, 594, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salto-Tellez, M.; Hamilton, P. Integrated Diagnostics as the Fourth Revolution in Pathology. In Proceedings of a Workshop—Incorporating Integrated Diagnostics into Precision Oncology Care; National Center for Biotechnology Information: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2019. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK605928/ (accessed on 17 June 2025).
- Stenzinger, A.; Endris, V.; Budczies, J.; Weichert, W. Integrated Diagnostics: The Future of Laboratory Medicine? Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 181–182. [Google Scholar]
- Tayou, J.; Maher, B.; Beltran, L.; Hrebien, S.; Trabelsi, S.; Morgensztern, D.; Bian, S. Integrated Noninvasive Diagnostics for Prediction of Survival in Immunotherapy. Immuno-Oncol. Technol. 2024, 10, 100723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Xu, M.; Zhuang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Zheng, S.; Zhu, B.; Guan, G.; Liu, X. Pathomics-based machine learning models for predicting pathological complete response and prognosis in locally advanced rectal cancer patients post-neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy: Insights from two independent institutional studies. BMC Cancer 2024, 24, 1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Jiang, L.; Zheng, X.; Shao, J.; Wang, T.; Zhang, E.; Gao, F.; Wang, X.; Zheng, J. Clinical use of machine learning-based pathomics signature for diagnosis and survival prediction of bladder cancer. Cancer Sci. 2021, 112, 2905–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Jiang, L.; Gao, F.; Shao, J.; Wang, T.; Zhang, E.; Zheng, X.; Wang, X.; Zheng, J. Machine learning-based pathomics signature could act as a novel prognostic marker for patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2022, 126, 771–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.A.; Abouzid, M.; Kaczmarek, E. Deep Learning Approaches in Histopathology. Cancers 2022, 14, 5235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelsamea, M.M.; Zidan, U.; Senousy, Z.; Gaber, M.M.; Rakha, E.A.; Ilyas, M.A. A survey on artificial intelligence in histopathology image analysis. WIREs Data Mining Knowl. Discov. 2022, 12, e1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidi, H.H.; Pantanowitz, J.; Chamanzar, A.; Fennell, B.; Wang, Y.; Gullapalli, R.R.; Tafti, A.; Deebajah, M.; Albahra, S.; Glassy, E.; et al. Generative Artificial Intelligence in Pathology and Medicine: A Deeper Dive. Mod. Pathol. 2024, 38, 100687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantanowitz, J.; Manko, C.D.; Pantanowitz, L.; Rashidi, H.H. Synthetic Data and Its Utility in Pathology and Laboratory Medicine. Lab Invest. 2024, 104, 102095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koohi-Moghadam, M.; Bae, K.T. Generative AI in Medical Imaging: Applications, Challenges, and Ethics. J. Med. Syst. 2023, 47, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GeeksforGeeks. Machine Learning Algorithms. 2024. Available online: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/machine-learning-algorithms/ (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Wu, S.; Wang, Y.; Hong, G.; Luo, Y.; Lin, Z.; Shen, R.; Zeng, H.; Xu, A.; Wu, P.; Xiao, M.; et al. An artificial intelligence model for detecting pathological lymph node metastasis in prostate cancer using whole slide images: A retrospective, multicentre, diagnostic study. EClinicalMedicine 2024, 71, 102580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arevalo, J.E.O.; Cruz-Roa, A.A.; Arias, V.; Romero, E.; González, F.A.; Gilmore, H.; Basavanhally, A.; Madabhushi, A.; Shih, N.; Tomaszewski, J.; et al. An unsupervised feature learning framework for basal cell carcinoma image analysis. Artif. Intell. Med. 2015, 64, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campanella, G.; Hanna, M.G.; Geneslaw, L.; Miraflor, A.; Werneck Krauss Silva, V.; Busam, K.J.; Brogi, E.; Reuter, V.E.; Klimstra, D.S.; Fuchs, T.J. Clinical-grade computational pathology using weakly supervised deep learning on whole slide images. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1301–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.H. A brief introduction to weakly supervised learning. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2018, 5, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.; Zimmermann, E.; Tenenholtz, N.; Hall, J.; Shaikovski, G.; Zelechowski, M.; Casson, A.; Milletari, F.; Viret, J.; Vorontsov, E.; et al. Adapting Self-Supervised Learning for Computational Pathology. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.01688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talo, M. Automated classification of histopathology images using transfer learning. Artif. Intell. Med. 2019, 101, 101743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mormont, R.; Geurts, P.; Maree, R. Comparison of Deep Transfer Learning Strategies for Digital Pathology. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW); IEEE: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, S.; Ghazal, T.M.; Khan, M.A.; Zubair, M.; Naseem, M.T.; Faiz, T.; Ahmad, M. Malignancy Detection in Lung and Colon Histopathology Images Using Transfer Learning With Class Selective Image Processing. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 25657–25668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Yan, X.; Xiao, M.; Gao, M. Breast cancer image classification method based on deep transfer learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Image Processing, Machine Learning and Pattern Recognition, Guangzhou, China, 13–15 September 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Plataniotis, K.N. How much off-the-shelf knowledge is transferable from natural images to pathology images? PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorontsov, E.; Bozkurt, A.; Casson, A.; Shaikovski, G.; Zelechowski, M.; Severson, K.; Zimmermann, E.; Hall, J.; Tenenholtz, N.; Fusi, N.; et al. A foundation model for clinical-grade computational pathology and rare cancers detection. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 2924–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Usuyama, N.; Bagga, J.; Zhang, S.; Rao, R.; Naumann, T.; Wong, C.; Gero, Z.; González, J.; Gu, Y.; et al. A whole-slide foundation model for digital pathology from real-world data. Nature 2024, 630, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.J.; Ding, T.; Lu, M.Y.; Williamson, D.F.K.; Jaume, G.; Song, A.H.; Chen, B.; Zhang, A.; Shao, D.; Shaban, M.; et al. Towards a general-purpose foundation model for computational pathology. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 850–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.Y.; Chen, B.; Williamson, D.F.K.; Chen, R.J.; Liang, I.; Ding, T.; Jaume, G.; Odintsov, I.; Le, L.P.; Gerber, G.; et al. A visual-language foundation model for computational pathology. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 863–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neidlinger, P.; El Nahhas, O.S.M.; Muti, H.S.; Lenz, T.; Hoffmeister, M.; Brenner, H.; van Treeck, M.; Langer, R.; Dislich, B.; Behrens, H.M.; et al. Benchmarking foundation models as feature extractors for weakly-supervised computational pathology. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.15823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.Y.; Chen, R.J.; Kong, D.; Lipkova, J.; Singh, R.; Williamson, D.F.K.; Chen, T.Y.; Mahmood, F. Federated learning for computational pathology on gigapixel whole slide images. Med. Image Anal. 2022, 76, 102298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhlin, A.; Shvets, A.; Iglovikov, V.; Kalinin, A.A. Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Breast Cancer Histology Image Analysis. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.00752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaus, A.; Seibold, C.; Reiß, S.; Heine, L.; Schily, A.; Kim, M.; Bahnsen, F.H.; Herrmann, K.; Stiefelhagen, R.; Kleesiek, J. Anatomy-Guided Pathology Segmentation. In Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2024; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; Volume 15008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wu, H.; Qin, J. Incremental Nuclei Segmentation from Histopathological Images via Future-class Awareness and Compatibility-inspired Distillation. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 11408–11417. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, R.; Liu, Q.; Cui, C.; Yao, T.; Yue, J.; Xiong, J.; Yu, L.; Wu, Y.; Yin, M.; Wang, Y.; et al. PrPSeg: Universal Proposition Learning for Panoramic Renal Pathology Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 11736–11746. [Google Scholar]
- Tizhoosh, H.R.; Diamandis, P.; Campbell, C.J.V.; Safarpoor, A.; Kalra, S.; Maleki, D.; Riasatian, A.; Babaie, M. Searching Images for Consensus: Can AI Remove Observer Variability in Pathology? Am. J. Pathol. 2021, 191, 1702–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuiveling, M.; Liu, H.; Eek, D.; Breimer, G.E.; Suijkerbuijk, K.P.M.; Blokx, W.A.M.; Veta, M. A Novel Dataset for Nuclei and Tissue Segmentation in Melanoma with baseline nuclei segmentation and tissue segmentation benchmarks. GigaScience 2025, 14, giaf011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulten, W.; Kartasalo, K.; Chen, P.H.C.; Ström, P.; Pinckaers, H.; Nagpal, K.; Cai, Y.; Steiner, D.F.; van Boven, H.; Vink, R.; et al. Artificial intelligence for diagnosis and Gleason grading of prostate cancer: The PANDA challenge. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faryna, K.; Grisi, C.; Uysal, N.; Jaquet, S.F.K.; van der Laak, J.; Litjens, G. The LEOPARD challenge: Learning Biochemical Prostate Cancer Recurrence From Histopathology Slides. Grand Challenge. 2024. Available online: https://leopard.grand-challenge.org/leopard/ (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Studer, L.; van Midden, D.; Ayatollahi, F.; Hilbrands, L.; Kers, J.; van der Laak, J. Monkey Challenge: Machine-Learning for Optimal Detection of Inflammatory Cells in the Kidney. Grand Challenge. 2024. Available online: https://monkey.grand-challenge.org/monkey/ (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Russakovsky, O.; Deng, J.; Su, H.; Krause, J.; Satheesh, S.; Ma, S.; Huang, Z.; Karpathy, A.; Khosla, A.; Bernstein, M.; et al. ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2015, 115, 211–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Application of AI in Pathology | Examples |
|---|---|
| Image analytics | Counting mitotic figures Quantifying IHC markers such as ER and PR Measuring tumor size |
| Disease diagnostics | Detection of prostate cancer Gleason grading for prostate cancer Breast cancer grading H. pylori detection |
| Outcome prediction | Predict disease prognosis Predict therapy response Patient triage for molecular testing |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zabihollahy, F.; Mankaruos, M.; Mohareb, M.; Youssef, T.; Soleymani, Y.; Yousef, G.M. Simplified Artificial Intelligence Terminology for Pathologists. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1699. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131699
Zabihollahy F, Mankaruos M, Mohareb M, Youssef T, Soleymani Y, Yousef GM. Simplified Artificial Intelligence Terminology for Pathologists. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(13):1699. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131699
Chicago/Turabian StyleZabihollahy, Fatemeh, Michael Mankaruos, Maxim Mohareb, Timothy Youssef, Yasaman Soleymani, and George M. Yousef. 2025. "Simplified Artificial Intelligence Terminology for Pathologists" Diagnostics 15, no. 13: 1699. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131699
APA StyleZabihollahy, F., Mankaruos, M., Mohareb, M., Youssef, T., Soleymani, Y., & Yousef, G. M. (2025). Simplified Artificial Intelligence Terminology for Pathologists. Diagnostics, 15(13), 1699. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131699






