Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.J.J. and P.G.; methodology, A.E.G.; software, A.E.G.; validation, M.R.; formal analysis, A.E.G.; investigation, A.E.G., C.T.S. and S.C.; resources, S.C.; data curation, A.E.G.; writing—original draft preparation, A.E.G.; writing—review and editing, A.E.G.; visualization, A.E.G.; supervision, P.G.; project administration, H.J.J.; funding acquisition, P.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
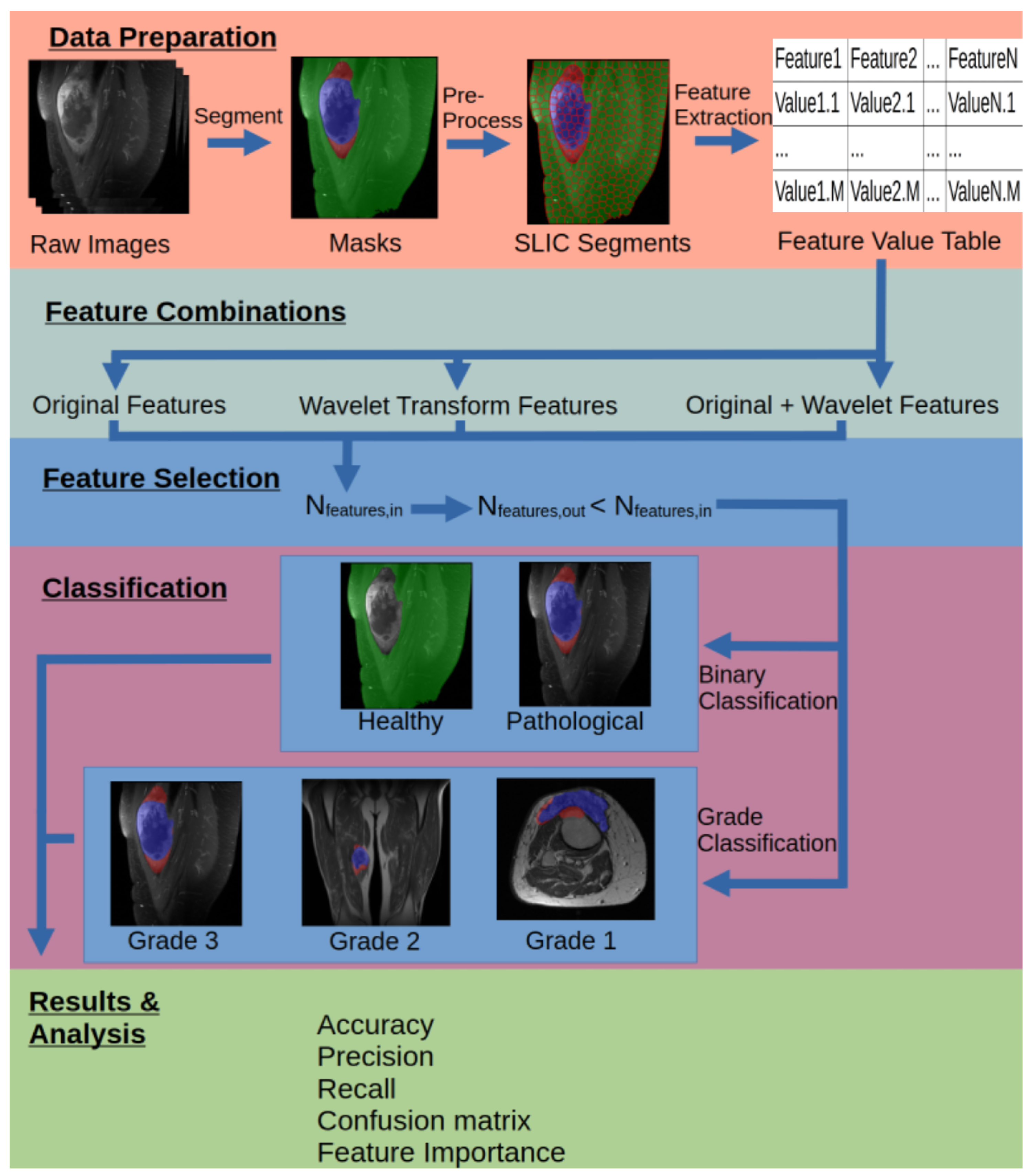
Figure 1.
Visual representation of the steps in the workflow.
Figure 1.
Visual representation of the steps in the workflow.
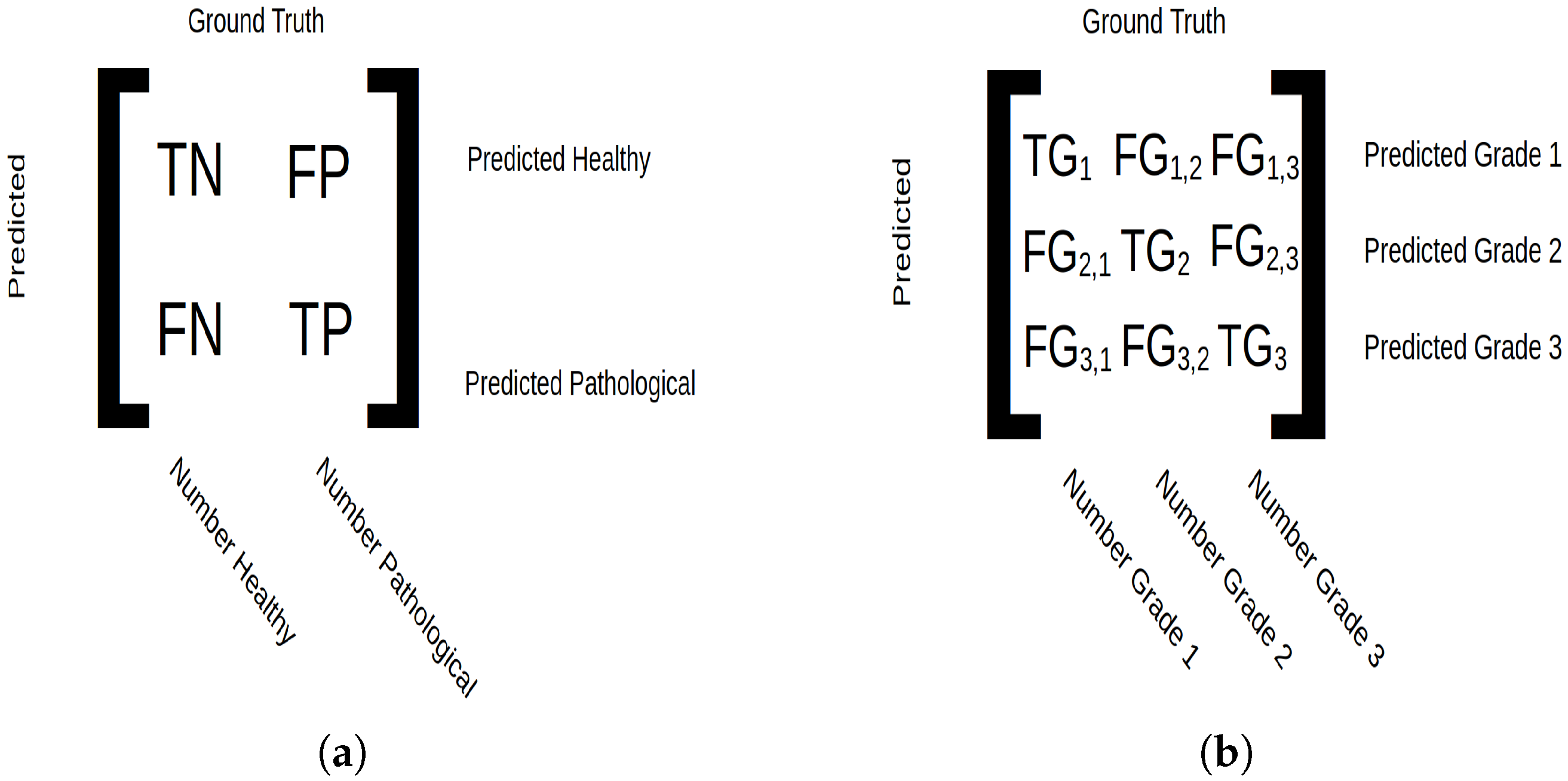
Figure 2.
Confusion matrix setup. (a) For binary classification, true negative (TN) indicates tissue correctly predicted as healthy, true positive (TP) indicates tissue correctly predicted as pathological, false negative (FN) indicates pathological tissue predicted as healthy and false positive (FP) indicates pathological tissue predicted as healthy. The micro average displays the number of samples classified in integers, and macro average displays classification in ratios. (b) For grade classification, true grade () is the number of samples belonging to class i and predicted as such, and false grade () corresponds to samples predicted as grade i but belonging to grade j. The micro average shows the total number of classified data points, and the macro average shows number of classified patients.
Figure 2.
Confusion matrix setup. (a) For binary classification, true negative (TN) indicates tissue correctly predicted as healthy, true positive (TP) indicates tissue correctly predicted as pathological, false negative (FN) indicates pathological tissue predicted as healthy and false positive (FP) indicates pathological tissue predicted as healthy. The micro average displays the number of samples classified in integers, and macro average displays classification in ratios. (b) For grade classification, true grade () is the number of samples belonging to class i and predicted as such, and false grade () corresponds to samples predicted as grade i but belonging to grade j. The micro average shows the total number of classified data points, and the macro average shows number of classified patients.
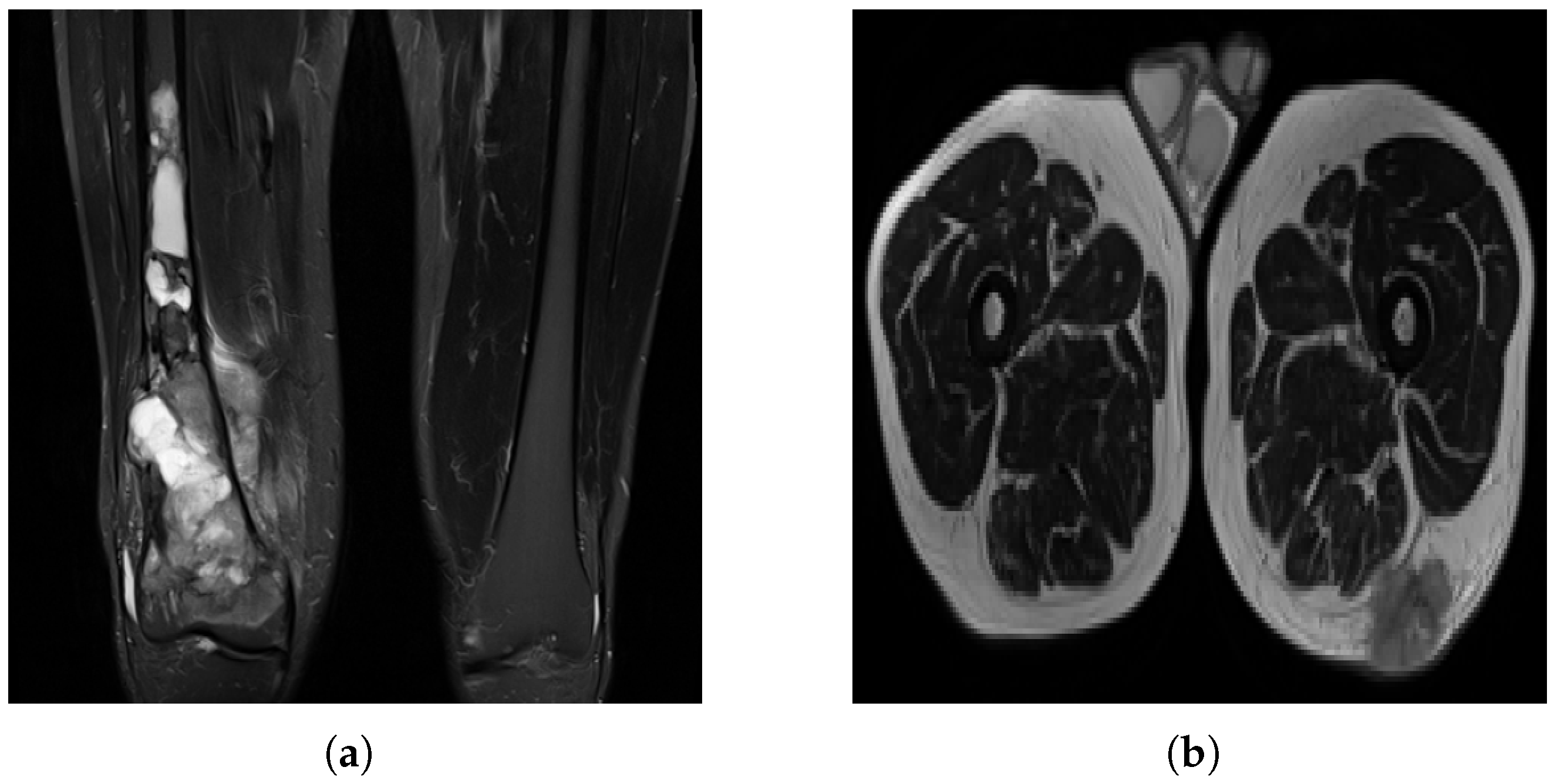
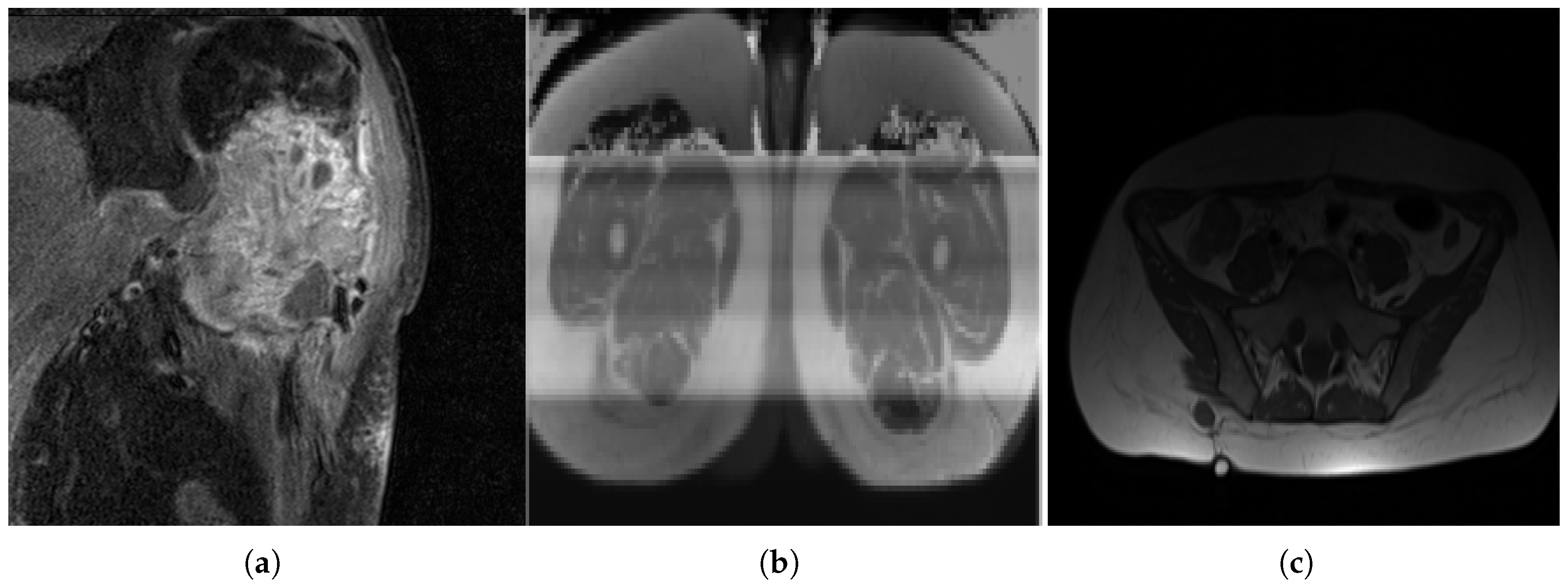
Figure 3.
MRI slices: (a) A case of OS where the machine uses specific settings and contrast media to brighten the tumor region and suppress fat response. (b) Another patient (with liposarcoma in this case) where the tumor region is dark in contrast and fat tissue is not suppressed.
Figure 3.
MRI slices: (a) A case of OS where the machine uses specific settings and contrast media to brighten the tumor region and suppress fat response. (b) Another patient (with liposarcoma in this case) where the tumor region is dark in contrast and fat tissue is not suppressed.
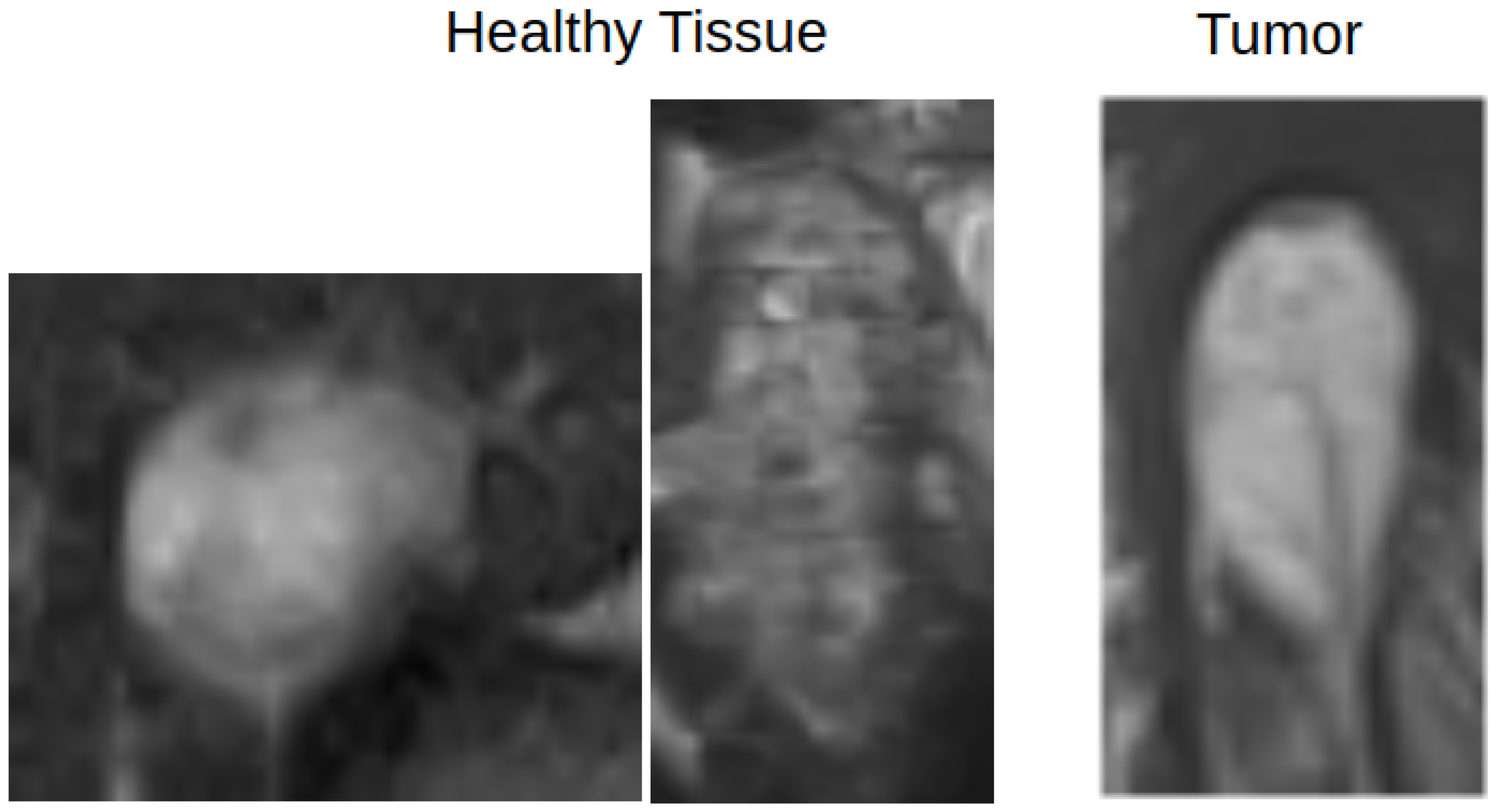
Figure 4.
An example of how healthy and pathological tissue can overlap in terms of appearance. The left two images show healthy tissue, and the rightmost image shows a tumor region.
Figure 4.
An example of how healthy and pathological tissue can overlap in terms of appearance. The left two images show healthy tissue, and the rightmost image shows a tumor region.
Figure 5.
Variance in image quality. (a) A grainy slice with relatively high noise. (b) A corrupted image. (c) An example of uneven lighting distribution.
Figure 5.
Variance in image quality. (a) A grainy slice with relatively high noise. (b) A corrupted image. (c) An example of uneven lighting distribution.
Table 1.
Dataset demographics. Included sarcoma subtypes are chondrosarcoma (CS), dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP), Ewing sarcoma (ES), giant cell tumor of bone (GCTB), osteosarcoma (OS) and soft tissue sarcoma (STS).
Table 1.
Dataset demographics. Included sarcoma subtypes are chondrosarcoma (CS), dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP), Ewing sarcoma (ES), giant cell tumor of bone (GCTB), osteosarcoma (OS) and soft tissue sarcoma (STS).
| Age Group | 0–19 | 20–39 | 40–59 | 60–79 | 80+ |
|---|
| Subtype | | | | | | | | | | |
| STS | 4 | 3.96% | 10 | 9.90% | 19 | 18.81% | 22 | 21.78% | 10 | 9.90% |
| OS | 10 | 9.90% | 0 | 0.00% | 3 | 2.97% | 1 | 0.99% | 0 | 0.00% |
| CS | 0 | 0.00% | 1 | 0.99% | 6 | 5.94% | 0 | 0.00% | 1 | 0.99% |
| ES | 5 | 4.95% | 4 | 3.96% | 1 | 0.99% | 1 | 0.99% | 0 | 0.00% |
| DFSP | 0 | 0.00% | 1 | 0.99% | 0 | 0.00% | 0 | 0.00% | 0 | 0.00% |
| GCTB | 1 | 0.99% | 0 | 0.00% | 1 | 0.99% | 0 | 0.00% | 0 | 0.00% |
| Grade | | | | | | | | | | |
| 1 | 3 | 2.97% | 0 | 0.00% | 10 | 9.90% | 3 | 2.97% | 3 | 2.97% |
| 2 | 1 | 0.99% | 2 | 1.98% | 3 | 2.97% | 8 | 7.92% | 2 | 1.98% |
| 3 | 16 | 15.84% | 14 | 13.86% | 17 | 16.83% | 13 | 12.87% | 6 | 5.94% |
| Sex | | | | | | | | | | |
| male | 12 | 11.88% | 8 | 7.92% | 17 | 16.83% | 14 | 13.86% | 8 | 7.92% |
| female | 8 | 7.92% | 8 | 7.92% | 13 | 12.87% | 10 | 9.90% | 3 | 2.97% |
Table 2.
Types of wavelet sub-band passes and captured details [
19].
Table 2.
Types of wavelet sub-band passes and captured details [
19].
| Sub-Band Symbol | X-Axis | Y-Axis | Details |
|---|
| LL | Low-pass | Low-pass | Approximationof original image |
| LH | Low-pass | High-pass | Images’ horizontal details |
| HL | High-pass | Low-pass | Images’ vertical details |
| HH | High-pass | High-pass | Images’ diagonal details |
Table 3.
The combination of image transforms for each run.
Table 3.
The combination of image transforms for each run.
| | Image Transform Group | Description | Number of Features |
|---|
| 1. | Original | Raw image features | 93 features |
| 2. | Wavelet | Wavelet-transformed features | 279 features |
| 3. | Wavelet + Original | Raw and wavelet-transformed features | 465 features |
Table 4.
Binary classification results. Both macro-averaged and micro-averaged metrics are displayed.
Table 4.
Binary classification results. Both macro-averaged and micro-averaged metrics are displayed.
| | Macro-Averaged | Micro-Averaged |
|---|
| |
Accuracy
|
Precision
|
Recall
|
Accuracy
|
Precision
|
Recall
|
|---|
| Original | | | | | | |
| Wavelet | | | | | | |
| Combined | | | | | | |
Table 5.
Number of features chosen for each feature group for the binary classifier for the original transform group.
Table 5.
Number of features chosen for each feature group for the binary classifier for the original transform group.
| Feature Group | Selected Features |
|---|
| First Order | 14 |
| GLCM | 9 |
| GLDM | 8 |
| GLRLM | 6 |
| GLSZM | 5 |
| NGTDM | 5 |
| Total | 47 |
Table 6.
Feature importance considering purely the original transform group for binary classification.
Table 6.
Feature importance considering purely the original transform group for binary classification.
| Feature Group | Original |
|---|
| First Order | 35.60% |
| GLCM | 16.75% |
| GLDM | 15.95% |
| GLRLM | 12.23% |
| GLSZM | 9.58% |
| NGTDM | 9.90% |
| Total | 100.00% |
Table 7.
Number of features chosen for each feature group for the binary classifier for the wavelet transform group.
Table 7.
Number of features chosen for each feature group for the binary classifier for the wavelet transform group.
| | Selected Features | |
|---|
|
Feature Group
|
Wavelet-LH
|
Wavelet-HL
|
Wavelet-HH
|
Total
|
|---|
| First Order | 9 | 10 | 4 | 23 |
| GLCM | 9 | 5 | 5 | 19 |
| GLDM | 6 | 5 | 1 | 12 |
| GLRLM | 5 | 2 | 4 | 11 |
| GLSZM | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| NGTDM | 1 | 2 | 1 | 4 |
| Total | 32 | 24 | 15 | 71 |
Table 8.
Feature importance considering only the wavelet transform group for binary classification.
Table 8.
Feature importance considering only the wavelet transform group for binary classification.
| | Feature-Transform Group Importance | |
|---|
|
Feature Group
|
Wavelet-LH
|
Wavelet-HL
|
Wavelet-HH
|
Total
|
|---|
| Firstorder | 14.28% | 16.08% | 5.39% | 35.76% |
| GLCM | 12.12% | 7.04% | 7.06% | 26.22% |
| GLDM | 8.25% | 6.65% | 1.38% | 16.28% |
| GLRLM | 6.34% | 2.78% | 5.33% | 14.45% |
| GLSZM | 2.31% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 2.31% |
| NGTDM | 1.19% | 2.50% | 1.30% | 4.99% |
| Total | 44.49% | 35.05% | 20.46% | 100.00% |
Table 9.
Feature importance considering both original and wavelet transform groups for binary classification.
Table 9.
Feature importance considering both original and wavelet transform groups for binary classification.
| | Feature Transform Group Importance | |
|---|
| |
Original
|
Wavelet-LL
|
Wavelet-LH
|
Wavelet-HL
|
Wavelet-HH
|
Total
|
|---|
| First Order | 13.75% | 7.85% | 1.86% | 2.96% | 3.26% | 29.67% |
| GLCM | 4.00% | 4.56% | 3.51% | 5.05% | 5.35% | 22.47% |
| GLDM | 3.99% | 3.48% | 4.06% | 2.38% | 2.70% | 16.61% |
| GLRLM | 2.57% | 3.58% | 3.27% | 2.83% | 4.71% | 16.96% |
| GLSZM | 2.10% | 2.67% | 0.78% | 0.80% | 0.00% | 6.34% |
| NGTDM | 1.65% | 2.18% | 1.37% | 1.50% | 1.26% | 7.95% |
| Total | 28.06% | 24.32% | 14.84% | 15.51% | 17.26% | 100.00% |
Table 10.
Number of features chosen from each feature group for the binary classifier of all transform groups.
Table 10.
Number of features chosen from each feature group for the binary classifier of all transform groups.
| | Selected Features | |
|---|
| |
Original
|
Wavelet-LL
|
Wavelet-LH
|
Wavelet-HL
|
Wavelet-HH
|
Total
|
|---|
| First Order | 15 | 10 | 4 | 7 | 9 | 45 |
| GLCM | 10 | 9 | 6 | 12 | 12 | 49 |
| GLDM | 8 | 7 | 8 | 6 | 7 | 36 |
| GLRLM | 5 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 10 | 36 |
| GLSZM | 6 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 16 |
| NGTDM | 4 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 18 |
| Total | 48 | 43 | 30 | 38 | 41 | 200 |
Table 11.
Macro- and micro-averaged results for grade classification using original features.
Table 11.
Macro- and micro-averaged results for grade classification using original features.
| | Macro | Micro |
|---|
| |
Grade 1
|
Grade 2
|
Grade 3
|
Grade 1
|
Grade 2
|
Grade 3
|
|---|
| Accuracy | | |
| Precision | | | | | | |
| Recall | | | | | | |
Table 12.
Number of features selected when considering the original transform group for grade classification.
Table 12.
Number of features selected when considering the original transform group for grade classification.
| Feature Group | Selected Features |
|---|
| First Order | 11 |
| GLCM | 3 |
| GLDM | 3 |
| GLRLM | 1 |
| GLSZM | 8 |
| NGTDM | 5 |
| Total | 31 |
Table 13.
Feature importance considering purely the original feature groups for grade classification.
Table 13.
Feature importance considering purely the original feature groups for grade classification.
| Feature Group | Feature Group Importance |
|---|
| Firstorder | 37.81% |
| GLCM | 8.94% |
| GLDM | 8.88% |
| GLRLM | 3.12% |
| GLSZM | 22.82% |
| NGTDM | 18.43% |
| Total | 100.00% |
Table 14.
Macro- and micro-averaged results for grade classification using wavelet features.
Table 14.
Macro- and micro-averaged results for grade classification using wavelet features.
| | Macro | Micro |
|---|
| |
Grade 1
|
Grade 2
|
Grade 3
|
Grade 1
|
Grade 2
|
Grade 3
|
|---|
| Accuracy | | |
| Precision | | | | | | |
| Recall | | | | | | |
Table 15.
Number of features selected when considering the wavelet transform group for grade classification.
Table 15.
Number of features selected when considering the wavelet transform group for grade classification.
| | Selected Features | |
|---|
| |
Wavelet-LH
|
Wavelet-HL
|
Wavelet-HH
|
Total
|
|---|
| First Order | 0 | 2 | 3 | 5 |
| GLCM | 4 | 4 | 3 | 11 |
| GLDM | 0 | 0 | 4 | 4 |
| GLRLM | 1 | 1 | 4 | 6 |
| GLSZM | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| NGTDM | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Total | 5 | 8 | 14 | 27 |
Table 16.
Feature importance considering only wavelet transform feature groups for grade classification.
Table 16.
Feature importance considering only wavelet transform feature groups for grade classification.
| | Feature Transform Group Importance | |
|---|
| |
Wavelet-LH
|
Wavelet-HL
|
Wavelet-HH
|
Total
|
|---|
| First Order | 0.00% | 7.29% | 12.36% | 19.65% |
| GLCM | 17.78% | 18.00% | 9.47% | 45.25% |
| GLDM | 0.00% | 0.00% | 11.81% | 11.81% |
| GLRLM | 3.34% | 3.48% | 13.02% | 19.84% |
| GLSZM | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% |
| NGTDM | 0.00% | 3.44% | 0.00% | 3.44% |
| Total | 21.12% | 32.22% | 46.67% | 100.00% |
Table 17.
Macro- and micro-averaged results for grade classification using all transform groups.
Table 17.
Macro- and micro-averaged results for grade classification using all transform groups.
| | Macro | Micro |
|---|
| |
Grade 1
|
Grade 2
|
Grade 3
|
Grade 1
|
Grade 2
|
Grade 3
|
|---|
| Accuracy | | |
| Precision | | | | | | |
| Recall | | | | | | |
Table 18.
Number of features selected when considering both original and wavelet transform groups for grade classification.
Table 18.
Number of features selected when considering both original and wavelet transform groups for grade classification.
| | Selected Features | |
|---|
| |
Original
|
Wavelet-LL
|
Wavelet-LH
|
Wavelet-HL
|
Wavelet-HH
|
Total
|
|---|
| First Order | 10 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 16 |
| GLCM | 0 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 10 |
| GLDM | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 4 |
| GLRLM | 1 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 6 | 12 |
| GLSZM | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| NGTDM | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| Total | 14 | 11 | 3 | 7 | 14 | 49 |
Table 19.
Feature importance considering both the original and wavelet transform feature groups for grade classification.
Table 19.
Feature importance considering both the original and wavelet transform feature groups for grade classification.
| | Feature Transform Group Importance | |
|---|
| |
Original
|
Wavelet-LL
|
Wavelet-LH
|
Wavelet-HL
|
Wavelet-HH
|
Total
|
|---|
| First Order | 19.57% | 11.05% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 2.47% | 33.08% |
| GLCM | 0.00% | 1.62% | 5.91% | 9.19% | 5.93% | 22.65% |
| GLDM | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 7.60% | 7.60% |
| GLRLM | 1.64% | 2.62% | 0.00% | 6.16% | 11.68% | 22.10% |
| GLSZM | 1.35% | 1.36% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 2.71% |
| NGTDM | 4.57% | 4.31% | 2.97% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 11.86% |
| Total | 27.13% | 20.97% | 8.88% | 15.34% | 27.68% | 100.00% |