Deep Learning-Enhanced T1-Weighted Imaging for Breast MRI at 1.5T
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
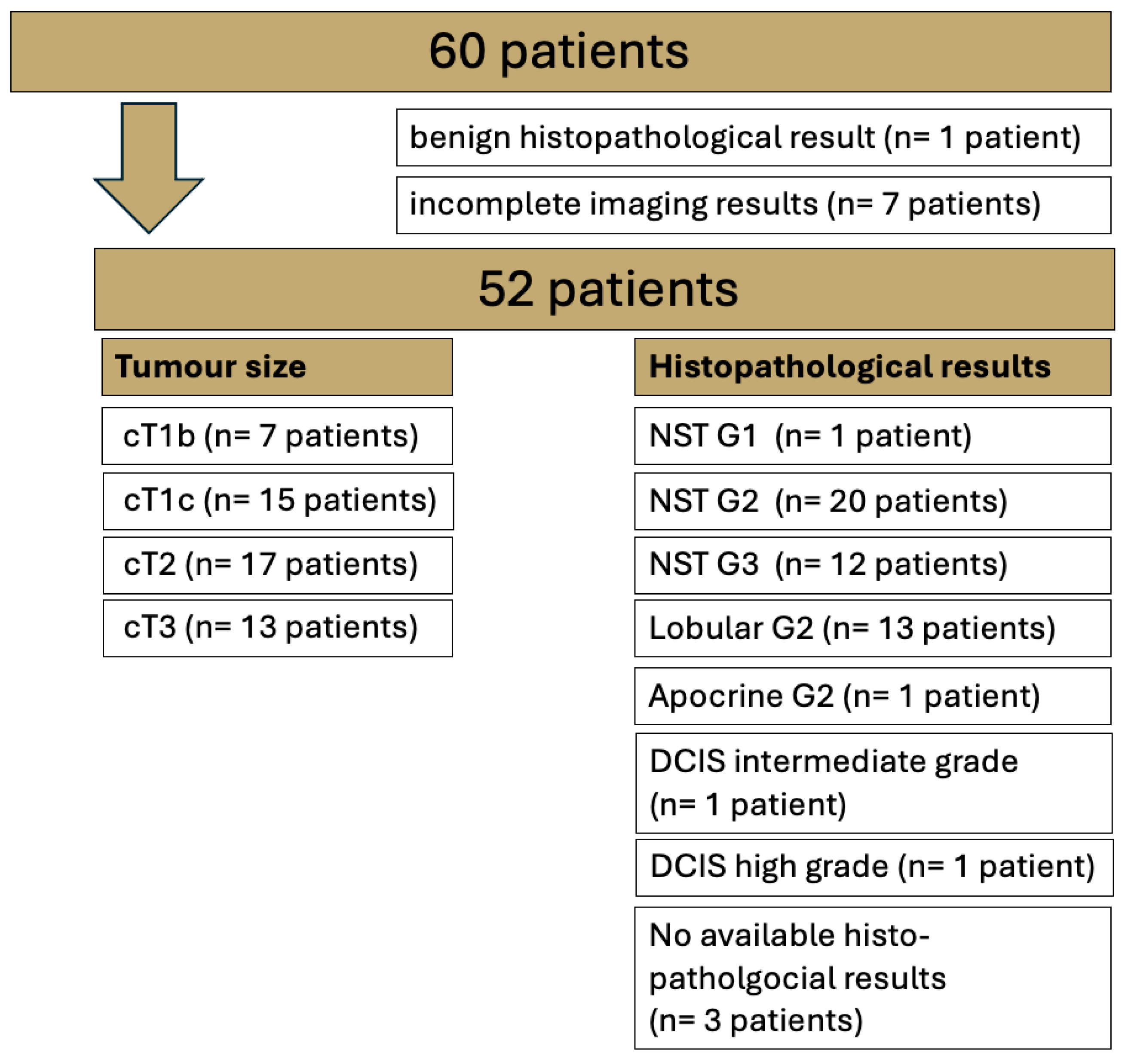
2.1. Patient Cohort
2.2. Image Acquisition
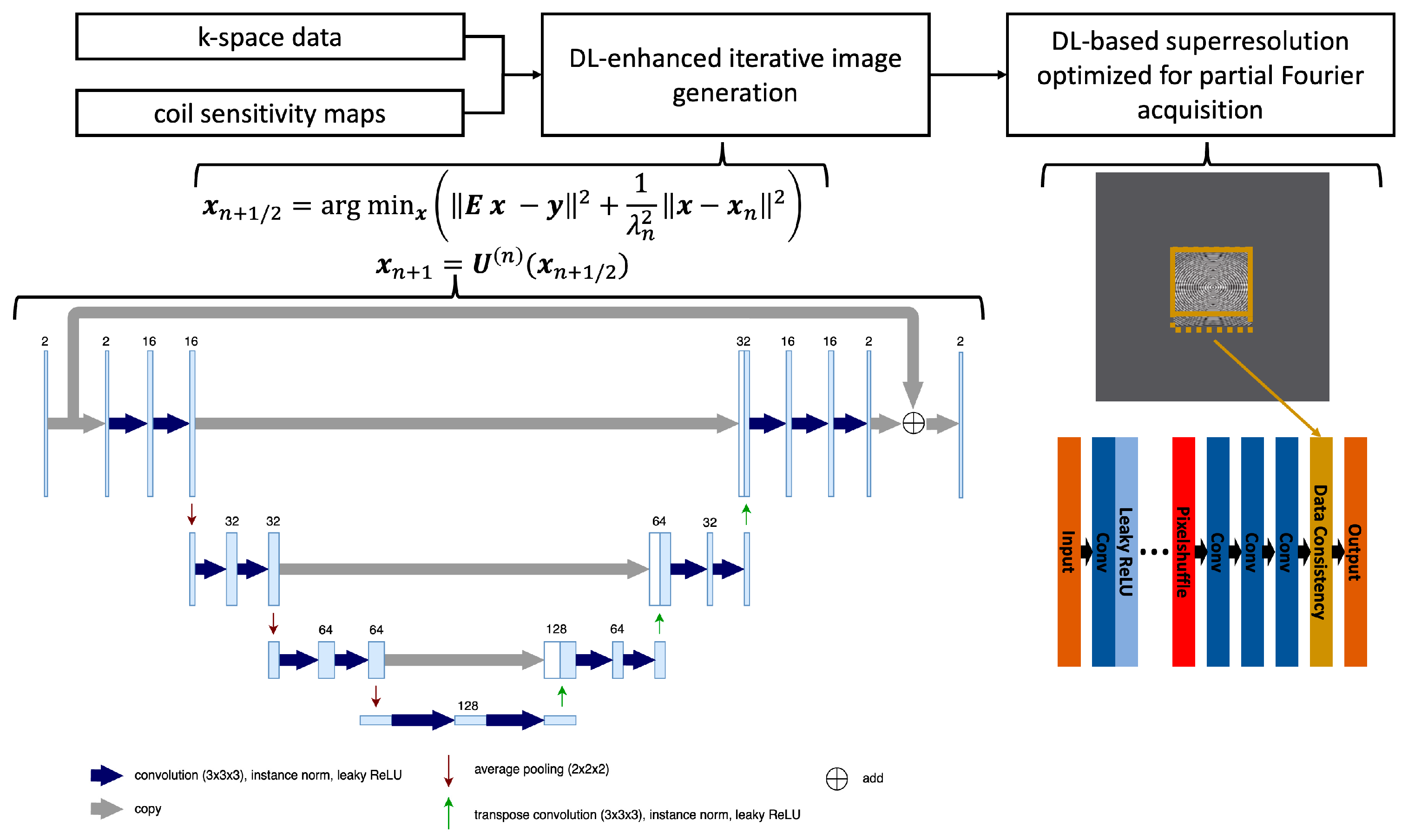
2.3. Deep Learning-Accelerated VIBEDL Sequence
2.4. Image Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients
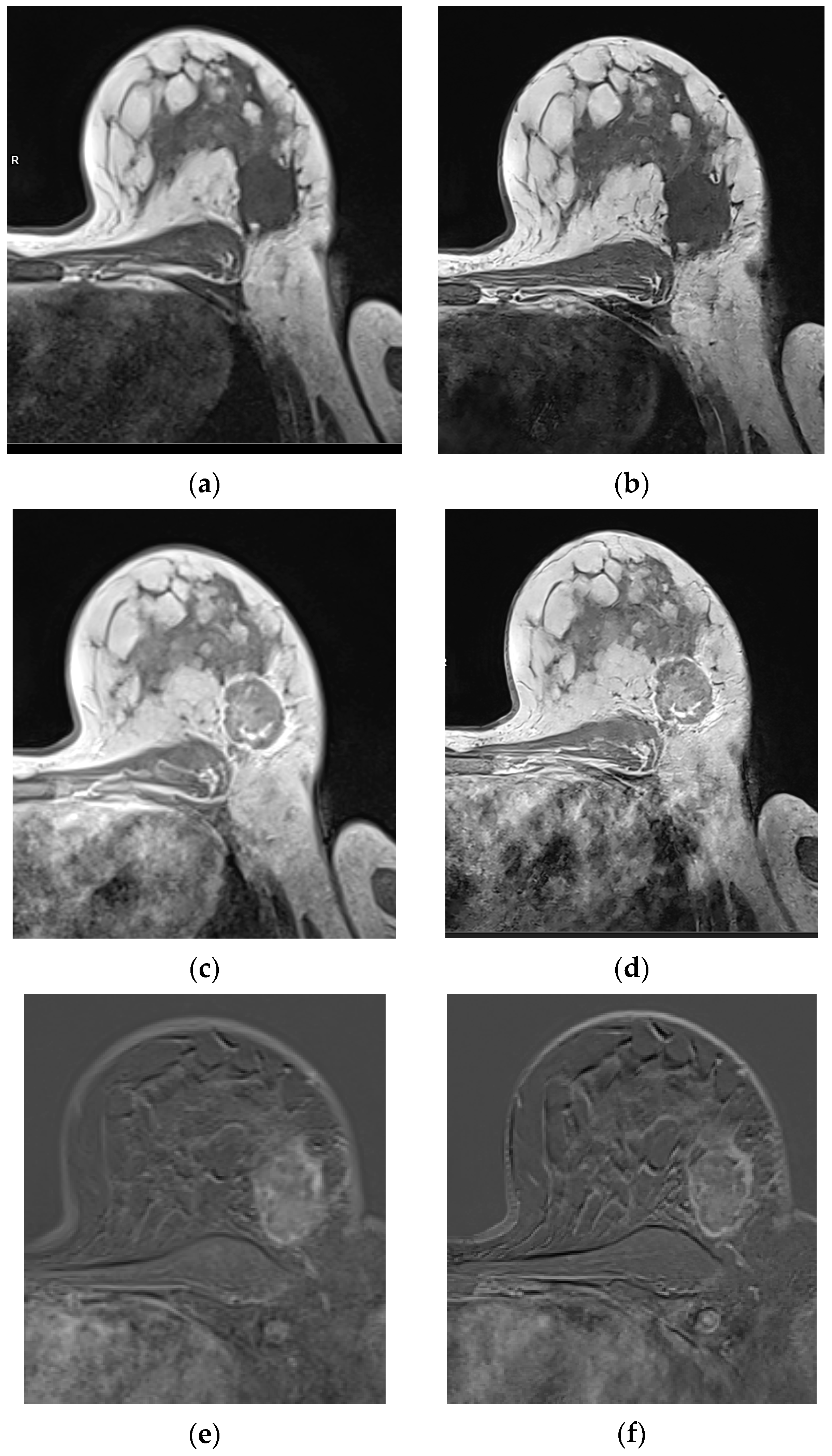
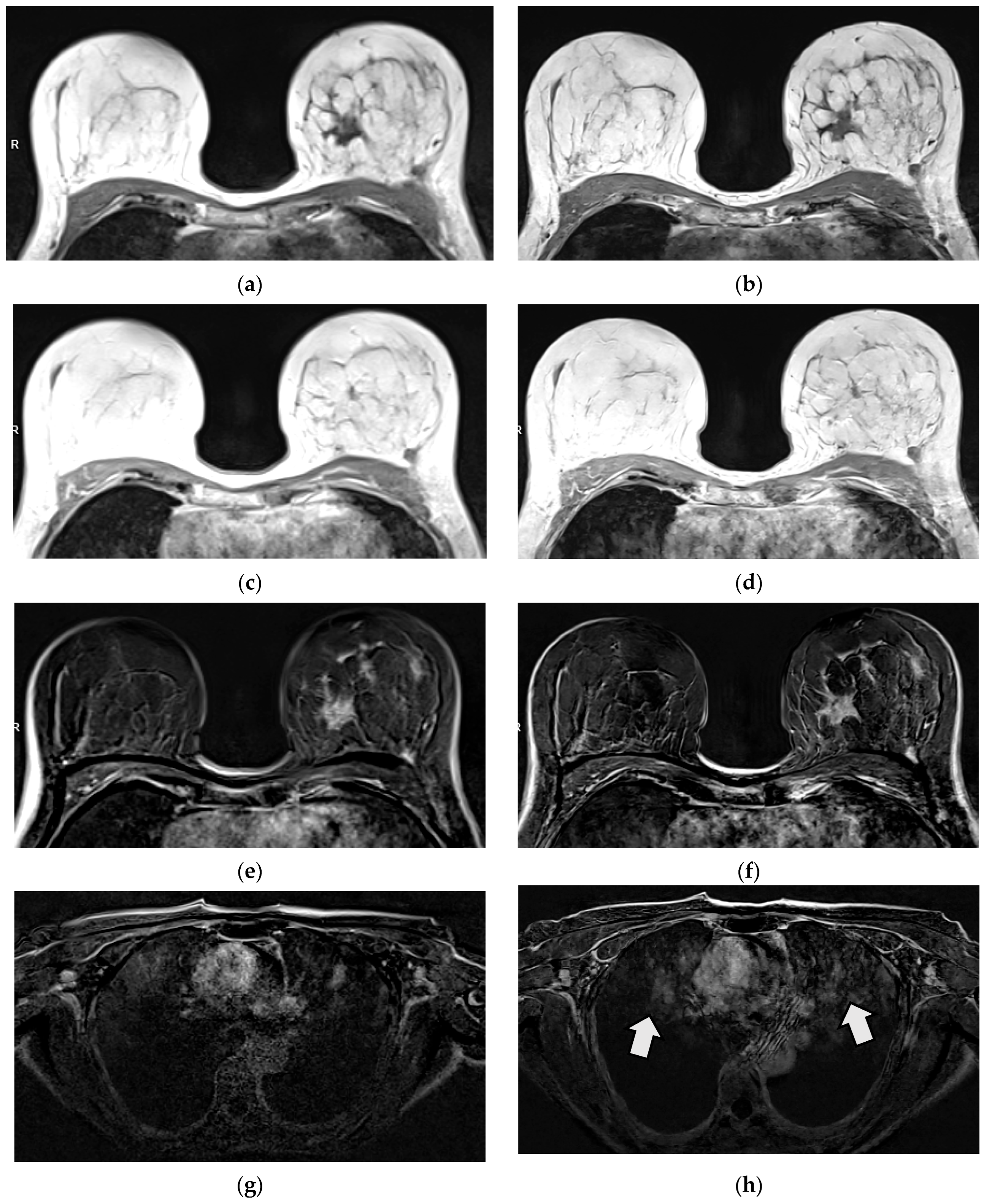
3.2. Qualitative Image Evaluation
3.2.1. Qualitative Image Evaluation for T1w VIBE Pre-Contrast
3.2.2. Qualitative Image Evaluation for T1w VIBE Post-Contrast
3.3. Qualitative Image Evaluation for Post-Contrast Subtraction Images (SUB)
3.4. Quantitative Image Evaluation: Lesion Visibility and Diameter
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations
4.2. Scientific Contribution
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BI-RADS | Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System |
| BRCA | Breast cancer gene |
| CAIPIRINHA | Controlled aliasing in parallel imaging results in higher acceleration |
| CNR | Contrast-to-noise ratio |
| DL | Deep learning |
| DCIS | Ductal carcinoma in situ |
| DCE MRI | Dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI |
| EUSOBI | European Society of Breast Imaging |
| ILC | Invasive lobular breast carcinoma |
| NST | No special type |
| ROI | Region of interest |
| SNR | Signal–to-noise ratio |
| SUB | Subtraction |
| TA | Acquisition time |
| TE | Echo time |
| TR | Repetition time |
| VIBE | Volumetric interpolated breath-hold |
| W | Weighted |
| WIP | Work-in-progress |
References
- Mann, R.M.; Balleyguier, C.; Baltzer, P.A.; Bick, U.; Colin, C.; Cornford, E.; Evans, A.; Fallenberg, E.; Forrai, G.; Fuchsjager, M.H.; et al. Breast MRI: EUSOBI recommendations for women’s information. Eur. Radiol. 2015, 25, 3669–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, R.M.; Kuhl, C.K.; Moy, L. Contrast-enhanced MRI for breast cancer screening. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 50, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Vicenty-Latorre, F.G.; Elsherif, S.; Sharma, S. Role of MRI in Breast Cancer Staging: A Case-Based Review. Cureus 2021, 13, e20752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teichgraeber, D.C.; Guirguis, M.S.; Whitman, G.J. Breast Cancer Staging: Updates in the AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, 8th Edition, and Current Challenges for Radiologists, From the AJR Special Series on Cancer Staging. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2021, 217, 278–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, R.M.; Cho, N.; Moy, L. Breast MRI: State of the Art. Radiology 2019, 292, 520–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radak, M.; Lafta, H.Y.; Fallahi, H. Machine learning and deep learning techniques for breast cancer diagnosis and classification: A comprehensive review of medical imaging studies. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 149, 10473–10491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, E.P.V.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Hickman, S.; Gilbert, F.J. Artificial intelligence in breast imaging. Clin. Radiol. 2019, 74, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Din, N.M.U.; Dar, R.A.; Rasool, M.; Assad, A. Breast cancer detection using deep learning: Datasets, methods, and challenges ahead. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 149, 106073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Bao, L.; He, S.; Chen, X.; Jin, Z.; Ye, Y. Deep learning applications in breast cancer histopathological imaging: Diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis. Breast Cancer Res. 2024, 26, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Pawar, K.; Ekanayake, M.; Pain, C.; Zhong, S.; Egan, G.F. Deep Learning for Image Enhancement and Correction in Magnetic Resonance Imaging-State-of-the-Art and Challenges. J. Digit. Imaging 2023, 36, 204–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayareh-Mancilla, R.; Medina-Ramos, L.A.; Toriz-Vazquez, A.; Hernandez-Rodriguez, Y.M.; Cigarroa-Mayorga, O.E. Automated Computer-Assisted Medical Decision-Making System Based on Morphological Shape and Skin Thickness Analysis for Asymmetry Detection in Mammographic Images. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimokawa, D.; Takahashi, K.; Kurosawa, D.; Takaya, E.; Oba, K.; Yagishita, K.; Fukuda, T.; Tsunoda, H.; Ueda, T. Deep learning model for breast cancer diagnosis based on bilateral asymmetrical detection (BilAD) in digital breast tomosynthesis images. Radiol. Phys. Technol. 2023, 16, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.Z.; Ni, D.; Chou, Y.H.; Qin, J.; Tiu, C.M.; Chang, Y.C.; Huang, C.S.; Shen, D.; Chen, C.M. Computer-Aided Diagnosis with Deep Learning Architecture: Applications to Breast Lesions in US Images and Pulmonary Nodules in CT Scans. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witowski, J.; Heacock, L.; Reig, B.; Kang, S.K.; Lewin, A.; Pysarenko, K.; Patel, S.; Samreen, N.; Rudnicki, W.; Luczynska, E.; et al. Improving breast cancer diagnostics with deep learning for MRI. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eabo4802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqub, M.; Jinchao, F.; Arshid, K.; Ahmed, S.; Zhang, W.; Nawaz, M.Z.; Mahmood, T. Deep Learning-Based Image Reconstruction for Different Medical Imaging Modalities. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2022, 2022, 8750648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaika, M.; Afat, S.; Wessling, D.; Afat, C.; Nickel, D.; Kannengiesser, S.; Herrmann, J.; Almansour, H.; Mannlin, S.; Othman, A.E.; et al. Deep learning-based super-resolution gradient echo imaging of the pancreas: Improvement of image quality and reduction of acquisition time. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2022, 104, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessling, D.; Gassenmaier, S.; Olthof, S.C.; Benkert, T.; Weiland, E.; Afat, S.; Preibsch, H. Novel deep-learning-based diffusion weighted imaging sequence in 1.5 T breast MRI. Eur. J. Radiol. 2023, 166, 110948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almansour, H.; Herrmann, J.; Gassenmaier, S.; Lingg, A.; Nickel, M.D.; Kannengiesser, S.; Arberet, S.; Othman, A.E.; Afat, S. Combined Deep Learning-based Super-Resolution and Partial Fourier Reconstruction for Gradient Echo Sequences in Abdominal MRI at 3 Tesla: Shortening Breath-Hold Time and Improving Image Sharpness and Lesion Conspicuity. Acad. Radiol. 2023, 30, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassenmaier, S.; Warm, V.; Nickel, D.; Weiland, E.; Herrmann, J.; Almansour, H.; Wessling, D.; Afat, S. Thin-Slice Prostate MRI Enabled by Deep Learning Image Reconstruction. Cancers 2023, 15, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, C.; Lau, V.; Su, S.; Zhao, Y.; Xiao, L.; Ding, Y.; Leung, G.K.K.; Leong, A.T.L.; Wu, E.X. Deep learning enabled fast 3D brain MRI at 0.055 tesla. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadi9327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brendel, J.M.; Jacoby, J.; Dehdab, R.; Ursprung, S.; Fritz, V.; Werner, S.; Herrmann, J.; Brendlin, A.S.; Gassenmaier, S.; Schick, F.; et al. Prospective Deployment of Deep Learning Reconstruction Facilitates Highly Accelerated Upper Abdominal MRI. Acad. Radiol. 2024, 31, 4965–4973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammernik, K.; Klatzer, T.; Kobler, E.; Recht, M.P.; Sodickson, D.K.; Pock, T.; Knoll, F. Learning a variational network for reconstruction of accelerated MRI data. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018, 79, 3055–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiryu, S.; Akai, H.; Yasaka, K.; Tajima, T.; Kunimatsu, A.; Yoshioka, N.; Akahane, M.; Abe, O.; Ohtomo, K. Clinical Impact of Deep Learning Reconstruction in MRI. Radiographics 2023, 43, e220133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Yoon, J.H.; Jeon, S.K.; Choi, J.W.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.H.; Nickel, M.D.; Song, B.; Duan, T.; Lee, J.M. Enhancing gadoxetic acid-enhanced liver MRI: A synergistic approach with deep learning CAIPIRINHA-VIBE and optimized fat suppression techniques. Eur. Radiol. 2024, 34, 6712–6725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesropyan, N.; Katemann, C.; Leutner, C.; Sommer, A.; Isaak, A.; Weber, O.M.; Peeters, J.M.; Dell, T.; Bischoff, L.; Kuetting, D.; et al. Accelerated High-resolution T1- and T2-weighted Breast MRI with Deep Learning Super-resolution Reconstruction. Acad. Radiol. 2025, 32, 3147–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Protocol Parameter | T1 VIBEStd | T1 VIBEDL |
|---|---|---|
| Resolution | 0.9 × 0.9 × 2.0 mm3 | 0.4 (i) × 0.4 (i) × 2.0 mm3 |
| Matrix | 448 | 544 |
| FOV | 420 × 420 mm2 | 420 × 420 mm2 |
| TA/scan | 73 s | 73 s |
| Number of scans (Pre-/post-contrast) | 1/7 | 1/1 |
| TR/TE | 7.73/4.77 ms | 7.69/4.77 ms |
| Fat saturation | None | None |
| Parallel imaging factor | 2 | 2 |
| Partial Fourier (phase, slice) | 7/8, 5/8 | 6/8, 6/8 |
| Reconstruction mode | CAIPIRINHA | DL enhanced CAIPIRINHA with partial Fourier optimized super-resolution |
| Reader 1 | Reader 2 | Percentage of Agreement Between Raters | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Image Parameters T1 VIBE Sequence Precontrast | T1 VIBEStd Mean (SD) | T1 VIBEDL Mean (SD) | p-Value | T1 VIBEStd Mean (SD) | T1 VIBEDL Mean (SD) | p-Value | T1 VIBEStd | T1 VIBEDL |
| Motion artefacts | 4.96 (0.19) | 4.96 (0.02) | >0.99 | 4.98 (0.13) | 4.96 (0.19) | 0.322 | 94% | 96% |
| Image quality (IQ) | 4.17 (0.61) | 4.91 (0.35) | <0.001 | 3.98 (0.13) | 5.00 (0.00) | <0.001 | 60% | 92% |
| Artefacts | 4.96 (0.19) | 5.000 (0.00) | 0.159 | 4.75 (0.43) | 4.30 (0.60) | <0.001 | 72% | 38% |
| Sharpness | 3.47 (0.54) | 4.71 (0.57) | <0.001 | 3.04 (0.28) | 4.98 (0.14) | <0.001 | 51% | 76% |
| SNR | 4.02 (0.58) | 4.78 (0.57) | <0.001 | 4.00 (0.34) | 4.92 (0.03) | <0.001 | 59% | 84% |
| DC | 4.51 (0.78) | 4.67 (0.73) | 0.004 | 4.39 (0.69) | 4.61 (0.56) | 0.001 | 61% | 71% |
| Reader 1 | Reader 2 | Percentage of Agreement Between Raters | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Image Parameters T1 VIBE Sequence Postcontrast | T1 VIBEStd Mean (SD) | T1 VIBEDL Mean (SD) | p- Value | T1 VIBEStd Mean (SD) | T1 VIBEDL Mean (SD) | p- Value | T1 VIBEStd | T1 VIBEDL |
| Motion artefacts | 4.94 (0.23) | 4.89 (0.42) | 0.261 | 4.98 (0.13) | 4.96 (0.19) | 0.322 | 92% | 87% |
| Image quality (IQ) | 4.04 (0.55) | 4.75 (0.51) | <0.001 | 3.98 (0.13) | 4.98 (0.13) | * | 68% | 77% |
| Artefacts | 4.81 (0.39) | 4.25 (0.55) | <0.001 | 4.75 (0.43) | 4.30 (0.60) | <0.001 | 53% | 70% |
| Sharpness | 3.55 (0.57) | 4.71 (0.64) | <0.001 | 3.06 (0.31) | 4.92 (0.33) | <0.001 | 51% | 76% |
| SNR | 4.65 (0.60) | 4.43 (0.74) | <0.001 | 4.06 (0.23) | 4.92 (0.27) | <0.001 | 67% | 75% |
| DC | 4.43 (0.80) | 4.53 (0.83) | 0.058 | 4.59 (0.72) | 4.82 (0.43) | 0.001 | 63% | 76% |
| Reader 1 | Reader 2 | Percentage of Agreement Between Raters | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Image Parameters T1 VIBE SUB | T1 VIBEStd Mean (SD) | T1 VIBEDL Mean (SD) | p-Value | T1 VIBEStd Mean (SD) | T1 VIBEDL Mean (SD) | p-Value | T1 VIBEStd | T1 VIBEDL |
| Motion artefacts | 4.25 (0.67) | 4.09 (0.79) | 0.10 | 4.02 (0.36) | 4.00 (0.39) | 0.766 | 55% | 49% |
| Image quality (IQ) | 3.79 (0.66) | 4.58 (0.71) | <0.001 | 3.94 (0.30) | 4.45 (0.63) | <0.001 | 70% | 40% |
| Artefacts | 4.83 (0.42) | 4.36 (0.73) | <0.001 | 4.58 (0.49) | 4.19 (0.55) | <0.001 | 47% | 34% |
| Sharpness | 3.57 (0.60) | 4.83 (0.612) | <0.001 | 3.11 (0.32) | 4.89 (0.37) | <0.001 | 43% | 85% |
| SNR | 4.17 (0.70) | 4.83 (0.61) | <0.001 | 3.98 (0.23) | 4.70 (0.54) | <0.001 | 53% | 66% |
| DC | 4.79 (0.68) | 4.85 (0.63) | 0.083 | 4.77 (0.46) | 4.92 (0.26) | 0.004 | 81% | 91% |
| Lesion Size in mm (Std) | Mean Value Reader 1 | Mean Value Reader 2 |
|---|---|---|
| SUB VIBEStd | 26.71 (25.09) | 30.89 (26.64) |
| SUB VIBEDL | 26.63 (25.00) | 30.04 (26.65) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Olthof, S.-C.; Nickel, M.D.; Weiland, E.; Leyhr, D.; Afat, S.; Nikolaou, K.; Preibsch, H. Deep Learning-Enhanced T1-Weighted Imaging for Breast MRI at 1.5T. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1681. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131681
Olthof S-C, Nickel MD, Weiland E, Leyhr D, Afat S, Nikolaou K, Preibsch H. Deep Learning-Enhanced T1-Weighted Imaging for Breast MRI at 1.5T. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(13):1681. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131681
Chicago/Turabian StyleOlthof, Susann-Cathrin, Marcel Dominik Nickel, Elisabeth Weiland, Daniel Leyhr, Saif Afat, Konstantin Nikolaou, and Heike Preibsch. 2025. "Deep Learning-Enhanced T1-Weighted Imaging for Breast MRI at 1.5T" Diagnostics 15, no. 13: 1681. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131681
APA StyleOlthof, S.-C., Nickel, M. D., Weiland, E., Leyhr, D., Afat, S., Nikolaou, K., & Preibsch, H. (2025). Deep Learning-Enhanced T1-Weighted Imaging for Breast MRI at 1.5T. Diagnostics, 15(13), 1681. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131681







