Sarcopenia as a Risk Factor in Patients Undergoing Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS) Implantation
Abstract
1. Introduction
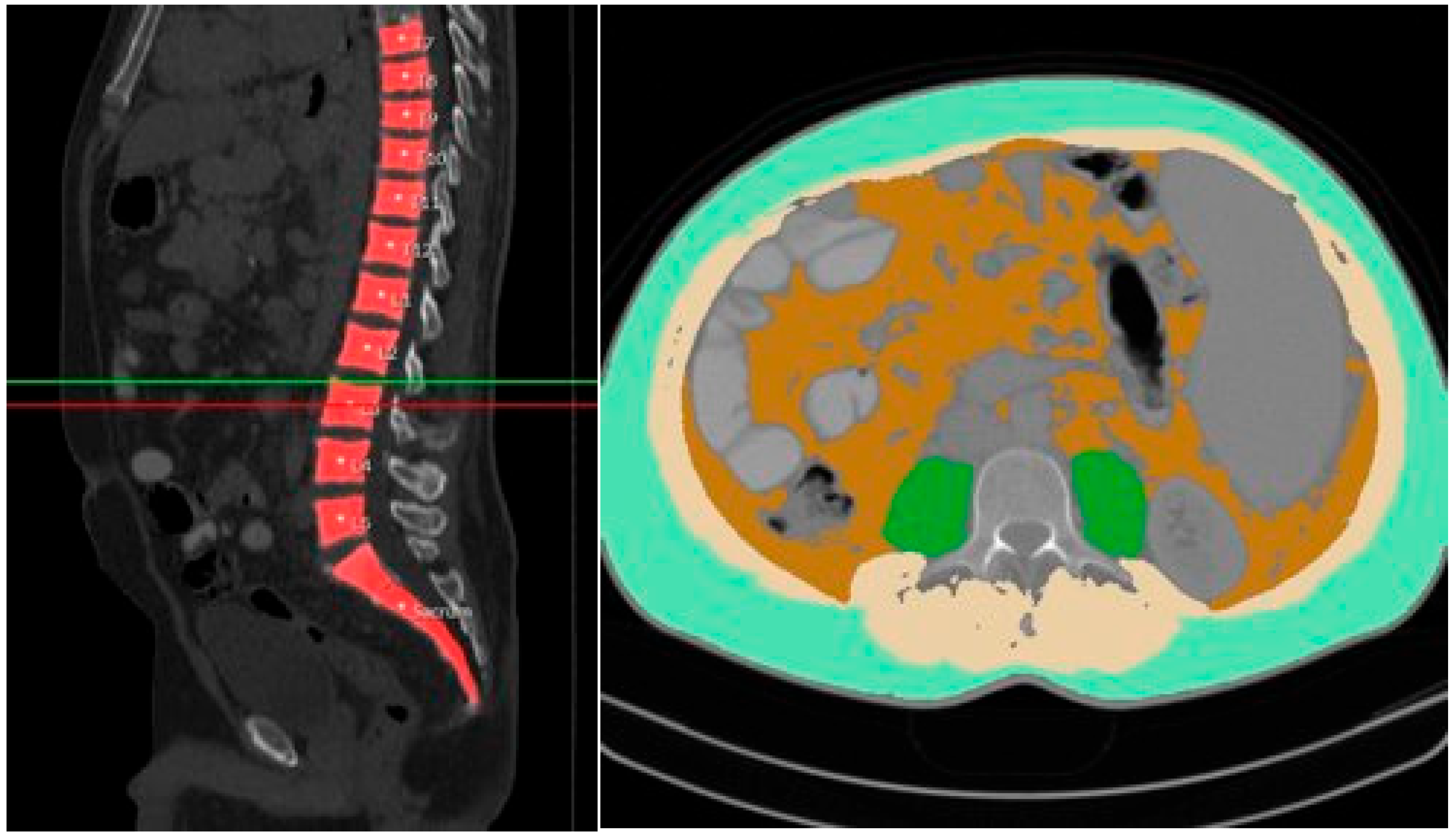
2. Materials and Methods
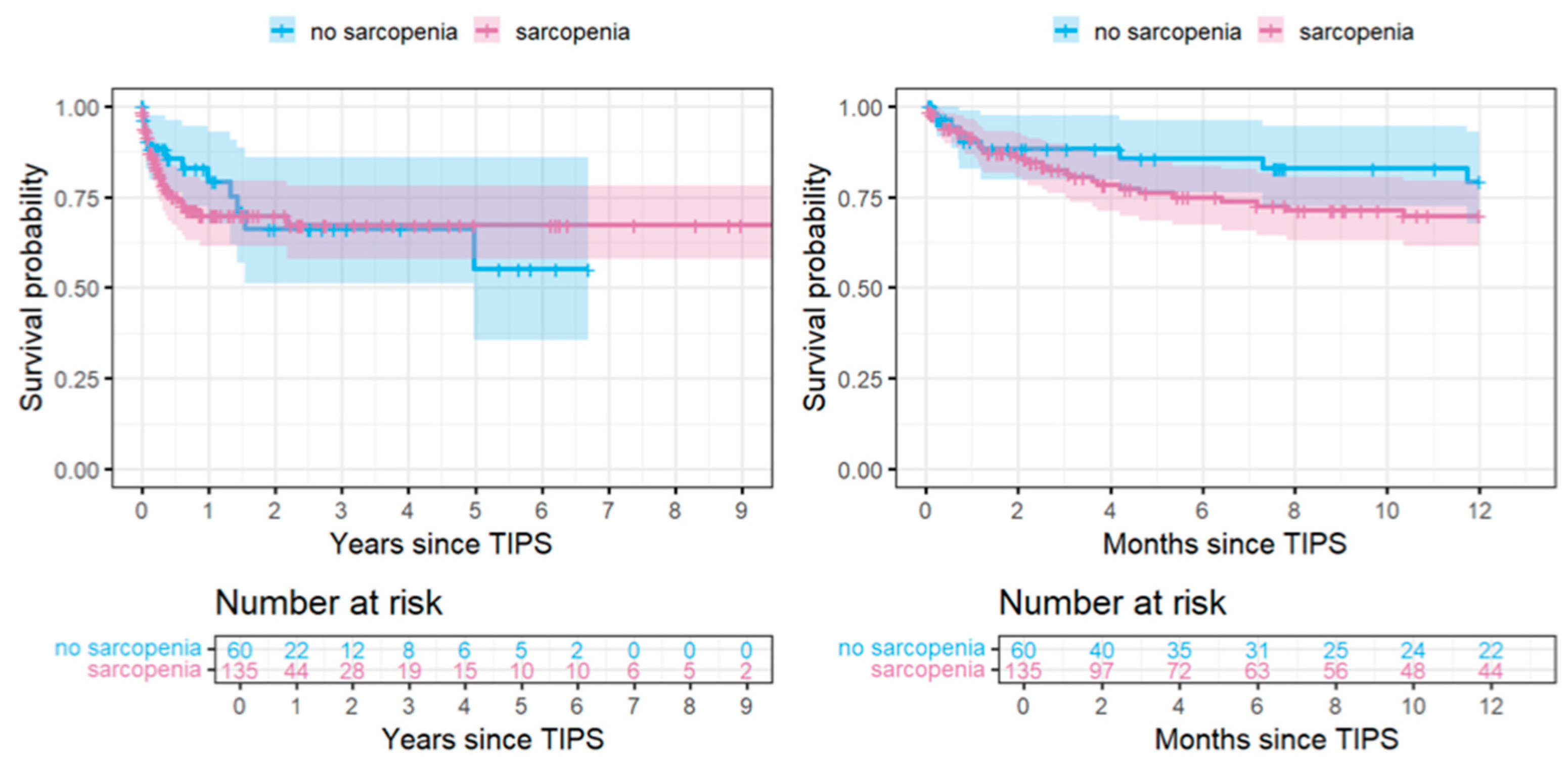
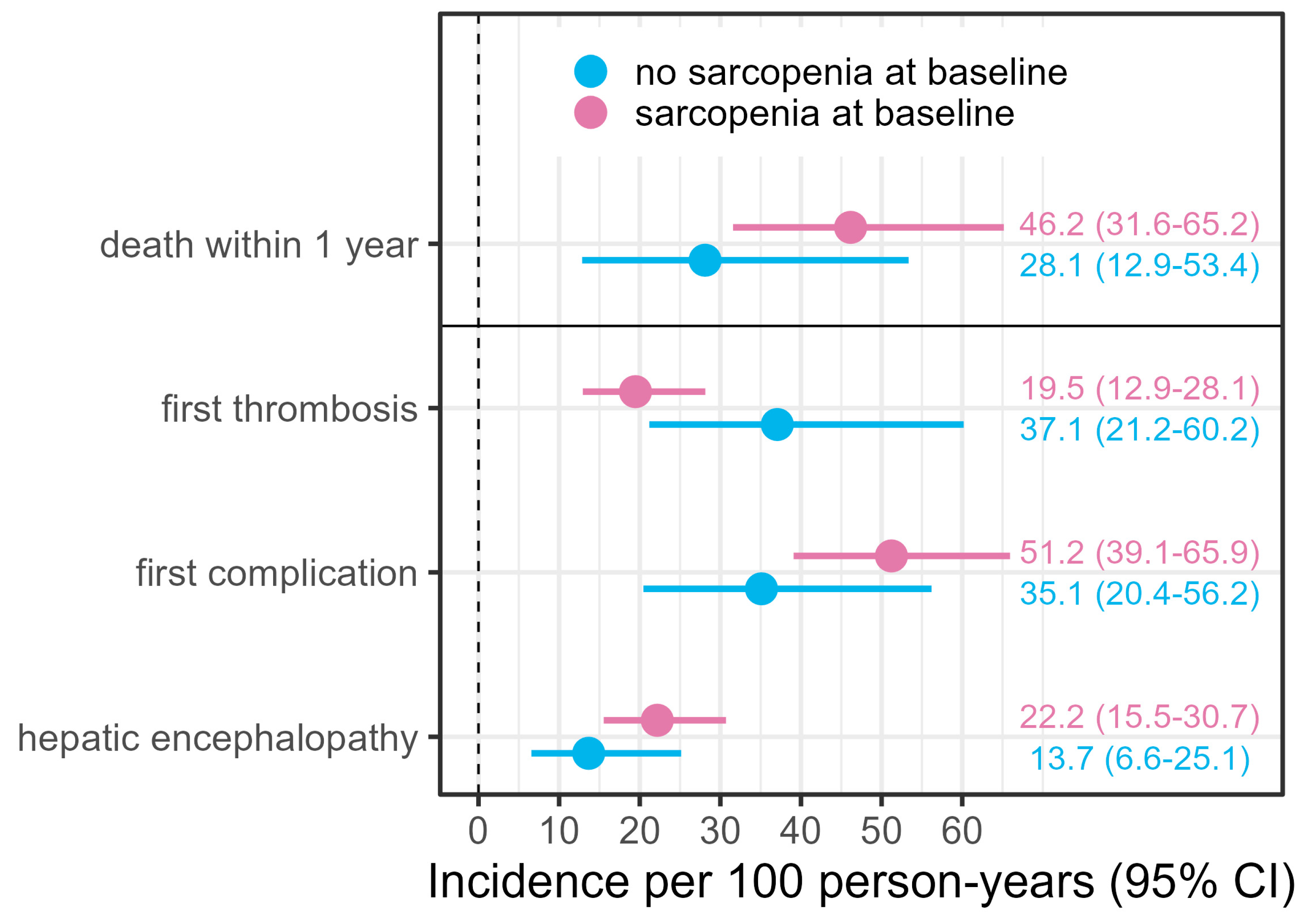
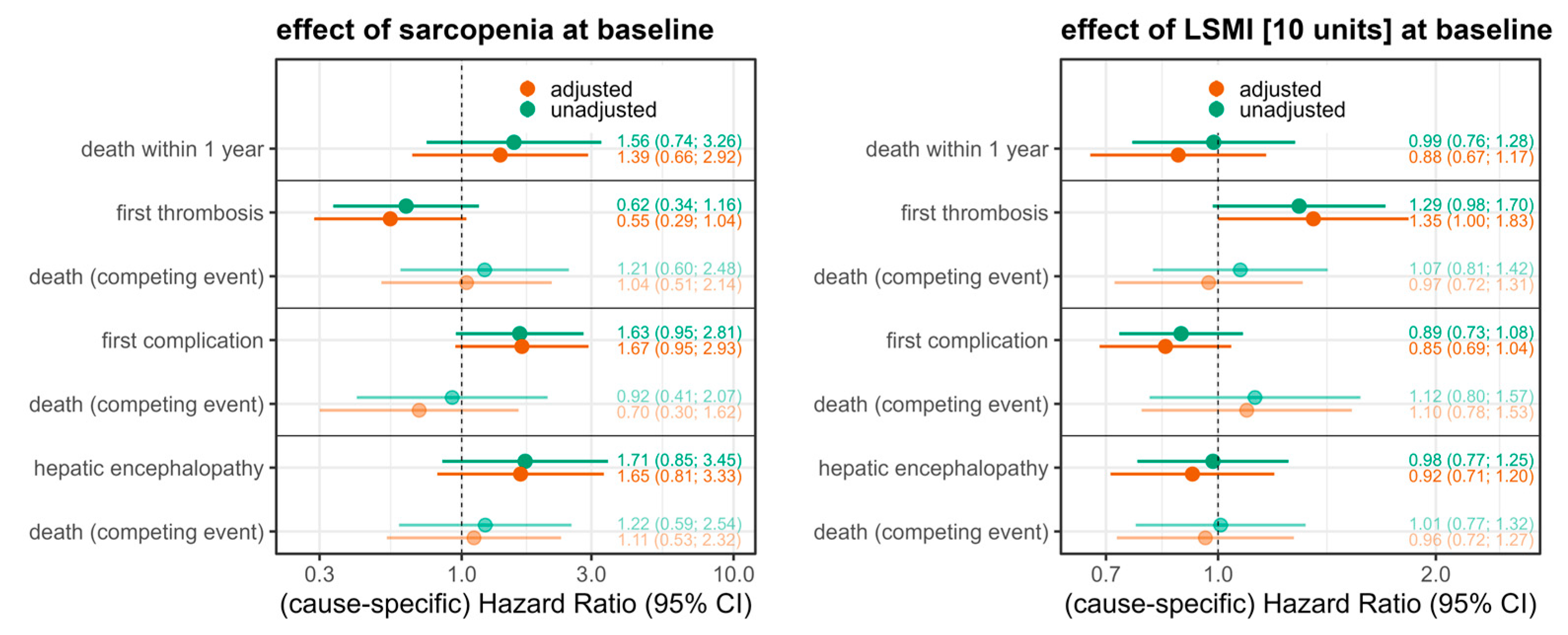
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial intelligence |
| ATR | Adipose tissue ratio |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| DICOM | Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine |
| HE | Hepatic encephalopathy |
| HR | Hazard ratio |
| LSMI | Lumbar skeletal muscle index |
| PACS | Picture archiving and communication system |
| PMA | Psoas muscle area |
| PPG | Portal Pressure Gradient |
| SAT | Subcutaneous adipose tissue |
| SF | Subcutaneous Fat Area |
| SFT | Subcutaneous Fat Thickness |
| SMA | Skeletal muscle area |
| SMI | Skeletal muscle index |
| TAMA | Total abdominal muscle area |
| TIPS | Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt |
| VAT | Visceral adipose tissue |
References
- Rössle, M.; Richter, G.M.; Noeldge, G.; Siegerstetter, V.; Palmaz, J.C.; Wenz, W.; Gerok, W. The intrahepatic portosystemic shunt. Initial clinical experiences with patients with liver cirrhosis. Dtsch. Med. Wochenschr. 1989, 114, 1511–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultheiß, M.; Bettinger, D.; Thimme, R.; Rössle, M. 30 Years of Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS): Casting a retrospective glance and future perspectives. Z. Gastroenterol. 2020, 58, 877–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsien, C.; Shah, S.N.; McCullough, A.J.; Dasarathy, S. Reversal of sarcopenia predicts survival after a transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stent. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 25, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronald, J.; Bozdogan, E.; Zaki, I.H.; Kappus, M.R.; Choi, S.S.; Martin, J.G.; Suhocki, P.V.; Smith, T.P.; Kim, C.Y.; Bashir, M.R. Relative Sarcopenia With Excess Adiposity Predicts Survival After Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt Creation. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2019, 214, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ma, J.; Yang, C.; Chen, M.; Shi, Q.; Zhou, C.; Huang, S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, T.; et al. Sarcopenia in Patients with Cirrhosis after Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt Placement. Radiology 2022, 303, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardelli, S.; Bellafante, D.; Ridola, L.; Faccioli, J.; Riggio, O.; Gioia, S. Prevention of post-tips hepatic encephalopathy: The search of the ideal candidate. Metab. Brain. Dis. 2023, 38, 1729–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periyalwar, P.; Dasarathy, S. Malnutrition in cirrhosis: Contribution and consequences of sarcopenia on metabolic and clinical responses. Clin. Liver Dis. 2012, 16, 95–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, K.; Kirchner, H.; Lochs, H.; Pirlich, M. Malnutrition affects quality of life in gastroenterology patients. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 3380–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehrenbach, U.; Wuensch, T.; Gabriel, P.; Segger, L.; Yamaguchi, T.; Auer, T.A.; Beetz, N.L.; Denecke, C.; Kröll, D.; Raakow, J.; et al. CT Body Composition of Sarcopenia and Sarcopenic Obesity: Predictors of Postoperative Complications and Survival in Patients with Locally Advanced Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beetz, N.L.; Geisel, D.; Maier, C.; Auer, T.A.; Shnayien, S.; Malinka, T.; Neumann, C.C.M.; Pelzer, U.; Fehrenbach, U. Influence of Baseline CT Body Composition Parameters on Survival in Patients with Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlmann, S.; Bressem, K.; Bashian, B.; Ulas, S.T.; Rattunde, M.; Busch, F.; Makowski, M.R.; Ziegeler, K.; Adams, L. Sex Differences in Renal Cell Carcinoma: The Importance of Body Composition. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2023, 30, 1269–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beetz, N.L.; Geisel, D.; Shnayien, S.; Auer, T.A.; Globke, B.; Öllinger, R.; Trippel, T.D.; Schachtner, T.; Fehrenbach, U. Effects of Artificial Intelligence-Derived Body Composition on Kidney Graft and Patient Survival in the Eurotransplant Senior Program. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beetz, N.L.; Maier, C.; Shnayien, S.; Trippel, T.D.; Gehle, P.; Fehrenbach, U.; Geisel, D. Artificial intelligence-based analysis of body composition in Marfan: Skeletal muscle density and psoas muscle index predict aortic enlargement. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2021, 12, 993–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miljkovic, I.; Vella, C.A.; Allison, M. Computed Tomography-Derived Myosteatosis and Metabolic Disorders. Diabetes Metab. J. 2021, 45, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyère, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines on nutrition in chronic liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 172–193. [CrossRef]
- Büttner, L.; Aigner, A.; Pick, L.; Brittinger, J.; Steib, C.J.; Böning, G.; Streitparth, F. 25 years of experience with transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS): Changes in patient selection and procedural aspects. Insights Imaging 2022, 13, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Ruan, J.; Chen, T.; Lin, E.; Shi, L. CT-assessed sarcopenia is a predictive factor for both long-term and short-term outcomes in gastrointestinal oncology patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Imaging 2019, 19, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, C.M.; Lieffers, J.R.; McCargar, L.J.; Reiman, T.; Sawyer, M.B.; Martin, L.; Baracos, V.E. Prevalence and clinical implications of sarcopenic obesity in patients with solid tumours of the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts: A population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2008, 9, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therneau, T.M.; Grambsch, P.M. (Eds.) The Cox Model. In Modeling Survival Data: Extending the Cox Model; Springer New York: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 39–77. [Google Scholar]
- Therneau, T. A Package for Survival Analysis in R, R package version 3.5-0; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2023.
- Wickham, H.; Averick, M.; Bryan, J.; Chang, W.; McGowan, L.D.A.; François, R.; Grolemund, G.; Hayes, A.; Henry, L.; Hester, J. Welcome to the Tidyverse. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R-Core-Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Plauth, M.; Schütz, T.; Buckendahl, D.P.; Kreymann, G.; Pirlich, M.; Grüngreiff, S.; Romaniuk, P.; Ertl, S.; Weiss, M.L.; Lochs, H. Weight gain after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt is associated with improvement in body composition in malnourished patients with cirrhosis and hypermetabolism. J. Hepatol. 2004, 40, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, N.; Zhao, C.; Li, J.; Li, L.; Yang, X.; Yang, M.; Wu, Z.; Feng, D. Body mass index changes after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in individuals with cirrhosis. Nutrition 2021, 84, 111095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, K.; Lee, S.S.; Raman, M. Prevalence and mechanisms of malnutrition in patients with advanced liver disease, and nutrition management strategies. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allard, J.P.; Chau, J.; Sandokji, K.; Blendis, L.M.; Wong, F. Effects of ascites resolution after successful TIPS on nutrition in cirrhotic patients with refractory ascites. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2001, 96, 2442–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montano-Loza, A.J.; Meza-Junco, J.; Prado, C.M.; Lieffers, J.R.; Baracos, V.E.; Bain, V.G.; Sawyer, M.B. Muscle wasting is associated with mortality in patients with cirrhosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 166–173.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebadi, M.; Bhanji, R.A.; Tandon, P.; Mazurak, V.; Baracos, V.E.; Montano-Loza, A.J. Review article: Prognostic significance of body composition abnormalities in patients with cirrhosis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 52, 600–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praktiknjo, M.; Book, M.; Luetkens, J.; Pohlmann, A.; Meyer, C.; Thomas, D.; Jansen, C.; Feist, A.; Chang, J.; Grimm, J.; et al. Fat-free muscle mass in magnetic resonance imaging predicts acute-on-chronic liver failure and survival in decompensated cirrhosis. Hepatology 2018, 67, 1014–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.H.; Jeong, W.K.; Baik, S.K.; Cha, S.H.; Kim, M.Y. Impact of sarcopenia on prognostic value of cirrhosis: Going beyond the hepatic venous pressure gradient and MELD score. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2018, 9, 860–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benmassaoud, A.; Roccarina, D.; Arico, F.; Leandro, G.; Yu, B.; Cheng, F.; Yu, D.; Patch, D.; Tsochatzis, E. Sarcopenia Does Not Worsen Survival in Patients With Cirrhosis Undergoing Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt for Refractory Ascites. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 115, 1911–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praktiknjo, M.; Clees, C.; Pigliacelli, A.; Fischer, S.; Jansen, C.; Lehmann, J.; Pohlmann, A.; Lattanzi, B.; Krabbe, V.K.; Strassburg, C.P.; et al. Sarcopenia Is Associated With Development of Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure in Decompensated Liver Cirrhosis Receiving Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2019, 10, e00025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, B.C.; Wei, J.; Plastaras, J.P.; Lukens, J.N.; Damjanov, N.; Hoteit, M.; Hsu, C.; Levine, M.; Mondschein, J.; Nadolski, G.; et al. Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: High Rates of Local Control With Low Toxicity. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 41, 1118–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merli, M.; Giusto, M.; Lucidi, C.; Giannelli, V.; Pentassuglio, I.; Di Gregorio, V.; Lattanzi, B.; Riggio, O. Muscle depletion increases the risk of overt and minimal hepatic encephalopathy: Results of a prospective study. Metab. Brain Dis. 2013, 28, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardelli, S.; Lattanzi, B.; Torrisi, S.; Greco, F.; Farcomeni, A.; Gioia, S.; Merli, M.; Riggio, O. Sarcopenia Is Risk Factor for Development of Hepatic Encephalopathy After Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt Placement. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 15, 934–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhanji, R.A.; Moctezuma-Velazquez, C.; Duarte-Rojo, A.; Ebadi, M.; Ghosh, S.; Rose, C.; Montano-Loza, A.J. Myosteatosis and sarcopenia are associated with hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatol. Int. 2018, 12, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioia, S.; Merli, M.; Nardelli, S.; Lattanzi, B.; Pitocchi, F.; Ridola, L.; Riggio, O. The modification of quantity and quality of muscle mass improves the cognitive impairment after TIPS. Liver Int. 2019, 39, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
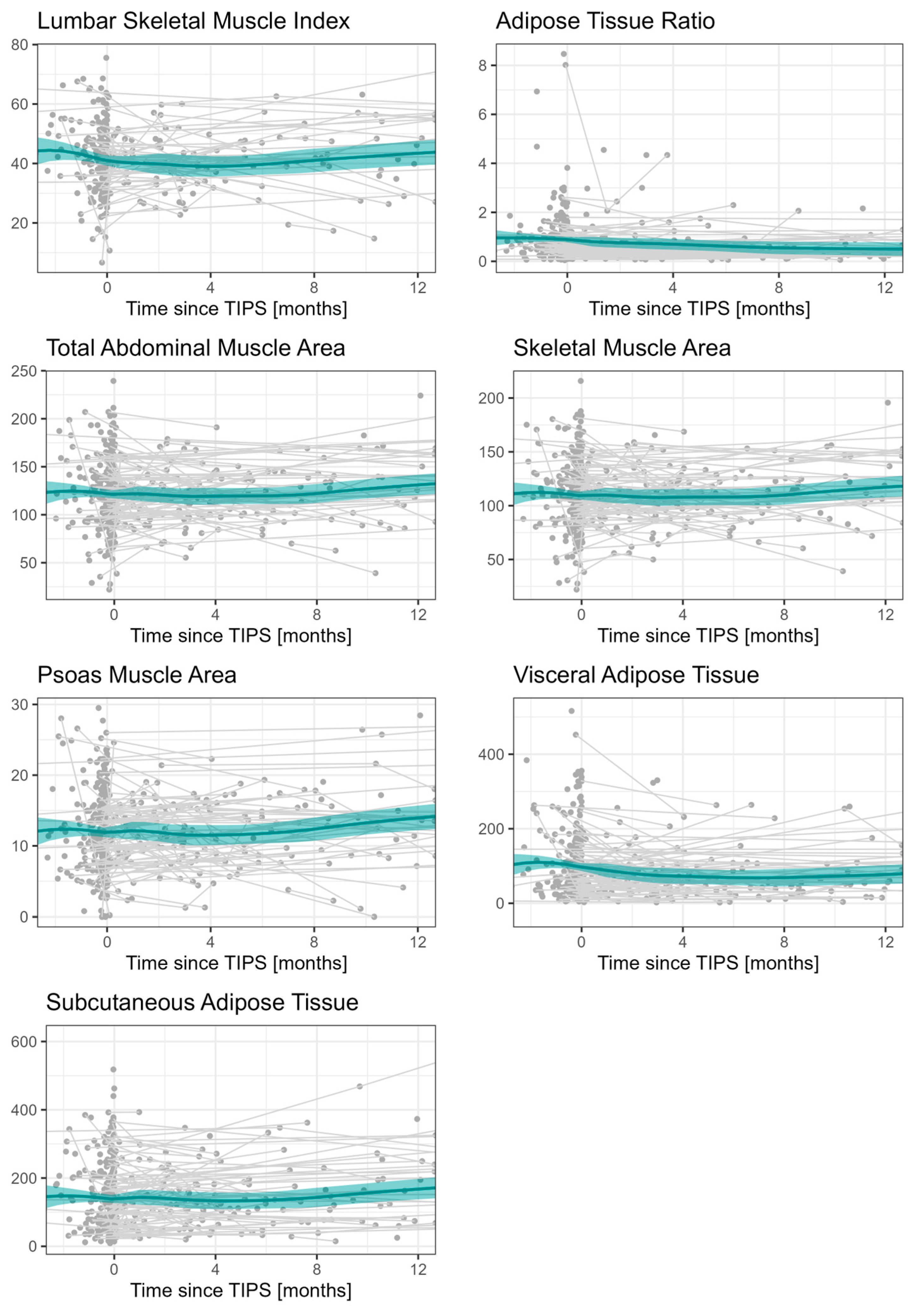
| No Sarcopenia (n = 60) | Sarcopenia (n = 135) | Total (n = 195) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| BMI (Median (IQR)) | 29.05 (26.1, 33.1) | 24.86 (21.9, 28.6) | 26.26 (23.03, 30.0) |
| TAMA (Median (IQR)) | 158.5 (121.7, 179.8) | 113.1(89.1, 137.3) | 124.5 (97.2, 147.7) |
| VAT (Median (IQR)) | 127.9 (70.6, 196.4) | 62.5 (31.5, 121.4) | 77.4 (41.5, 150.9) |
| SMA (Median (IQR)) | 142.3 (110.5, 160.2) | 100.0 (82.4, 122.1) | 111.3 (88.4, 131.5) |
| ATR (Median (IQR)) | 0.6 (0.4, 0.9) | 0.7 (0.4, 1.1) | 0.7 (0.4, 1.0) |
| LSMI (Median (IQR)) | 54.0 (45.0, 60.1) | 37.4 (31.6, 43.7) | 41.8 (33.9, 49.7) |
| PMA (Median (IQR)) | 14.7 (11.1, 20.0) | 11.2 (7.8, 14.9) | 12.2 (8.6, 15.8) |
| SAT (Median (IQR)) | 211.4 (147.1, 289.3) | 90.1 (54.4, 164.9) | 132.8 (63.1, 212.6) |
| Outcome Parameters | Sarcopenia (n = 135) | No Sarcopenia (n = 60) | Sarcopenic Obesity (n = 22) | No Sarcopenic Obesity (n = 171) | LSMI [cm2/m2] 41.8 (33.9, 49.7) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HE | Yes | 36 (26.7%) | 10 (16.7% | 7 (31.8%) | 38 (22.2%) | 41.70 (34.48, 48.26) |
| No | 99 (73.3%) | 50 (83.3%) | 15 (68.2%) | 133 (77.8%) | 42.03 (33.85, 49.83) | |
| Complication | Yes | 60 (44.4%) | 17 (28.3%) | 8 (36.4%) | 67 (39.2%) | 40.61 (31.62, 49.59) |
| No | 75 (55.6%) | 43 (71.7%) | 14 (63.6%) | 104 (60.8%) | 42.56 (36.23, 49.78) | |
| TIPS dysfunction | Yes | 28 (20.7%) | 16 (26.7%) | 9 (40.9%) | 34 (19.9%) | 42.49 (33.74, 52.50) |
| No | 107 (79.3%) | 44 (73.3%) | 13 (59.1%) | 137 (80.1%) | 41.59 (34.23, 48.26) | |
| Death | Yes | 34 (25.2%) | 13 (21.7%) | 3 (13.6%) | 44 (25.7%) | 42.64 (36.90, 50.16) |
| No | 101 (74.8%) | 47 (78.3%) | 19 (86.4%) | 127 (74.3%) | 41.51 (33.69, 49.62) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Büttner, L.; Aigner, A.; Stegherr, R.; Iseke, S.; Jonczyk, M.; Lüdemann, W.M.; Auer, T.A.; Collettini, F.; Schnapauff, D.; de Bucourt, M.; et al. Sarcopenia as a Risk Factor in Patients Undergoing Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS) Implantation. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1440. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15111440
Büttner L, Aigner A, Stegherr R, Iseke S, Jonczyk M, Lüdemann WM, Auer TA, Collettini F, Schnapauff D, de Bucourt M, et al. Sarcopenia as a Risk Factor in Patients Undergoing Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS) Implantation. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(11):1440. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15111440
Chicago/Turabian StyleBüttner, Laura, Annette Aigner, Regina Stegherr, Simon Iseke, Martin Jonczyk, Willie Magnus Lüdemann, Timo Alexander Auer, Federico Collettini, Dirk Schnapauff, Maximilian de Bucourt, and et al. 2025. "Sarcopenia as a Risk Factor in Patients Undergoing Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS) Implantation" Diagnostics 15, no. 11: 1440. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15111440
APA StyleBüttner, L., Aigner, A., Stegherr, R., Iseke, S., Jonczyk, M., Lüdemann, W. M., Auer, T. A., Collettini, F., Schnapauff, D., de Bucourt, M., Gebauer, B., Geisel, D., & Böning, G. (2025). Sarcopenia as a Risk Factor in Patients Undergoing Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS) Implantation. Diagnostics, 15(11), 1440. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15111440





