Imaging and Clinical Outcomes Six Months After Middle Meningeal Artery Embolization with Squid for Chronic Subdural Hematoma: A Prospective Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
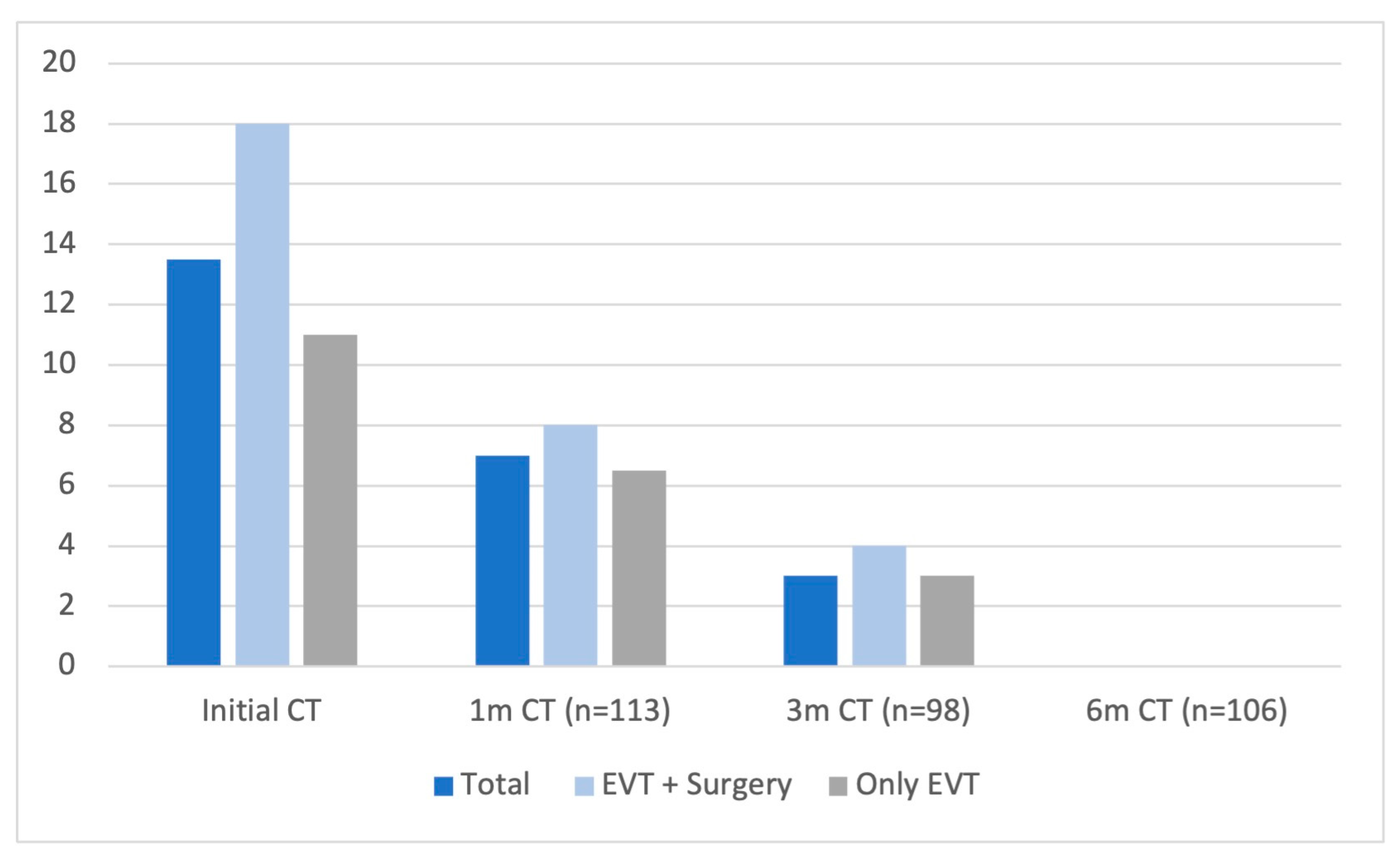
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CCA | Common carotid artery |
| CSDH | Chronic subdural hematoma |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| ECA | External carotid artery |
| ICA | Internal carotid artery |
| MMA | Middle meningeal artery |
References
- Yang, W.; Huang, J. Chronic Subdural Hematoma. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 28, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onyinzo, C.; Berlis, A.; Abel, M.; Kudernatsch, M.; Maurer, C.J. Efficacy and mid-term outcome of middle meningeal artery embolization with or without burr hole evacuation for chronic subdural hematoma compared with burr hole evacuation alone. J. NeuroInterv. Surg. 2022, 14, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almenawer, S.A.; Farrokhyar, F.; Hong, C.; Alhazzani, W.; Manoranjan, B.; Yarascavitch, B.; Arjmand, P.; Baronia, B.; Reddy, K.; Murty, N.; et al. Chronic subdural hematoma management: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 34829 patients. Ann. Surg. 2014, 259, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mack, J.; Squier, W.; Eastman, J.T. Anatomy and development of the meninges: Implications for subdural collections and CSF circulation. Pediatr. Radiol. 2009, 39, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edlmann, E.; Giorgi-Coll, S.; Whitfield, P.C.; Carpenter, K.L.H.; Hutchinson, P.J. Pathophysiology of chronic subdural haematoma: Inflammation, angiogenesis and implications for pharmacotherapy. J. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 14, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabeshima, S.; Reese, T.S.; Landis, D.M.D.; Brightman, M.W. Junctions in the meninge sand marginal glia. J. Comp. Neurol. 1975, 164, 127–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Link, T.W.; Boddu, S.; Paine, S.M.; Kamel, H.; Knopman, J. Middle Meningeal Artery Embolization for Chronic Subdural Hematoma: A Series of 60 Cases. Neurosurgery 2019, 85, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E. Embolization Therapy for Refractory Hemorrhage in Patients with Chronic Subdural Hematomas. World Neurosurg. 2017, 101, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shotar, E.; Meyblum, L.; Premat, K.; Lenck, S.; Degos, V.; Grand, T.; Cortese, J.; Pouvelle, A.; Pouliquen, G.; Mouyal, S.; et al. Middle meningeal artery embolization reduces the post-operative recurrence rate of at-risk chronic subdural hematoma. J. NeuroInterv. Surg. 2020, 12, 1209–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ban, S.P.; Hwang, G.; Byoun, H.S.; Kim, T.; Lee, S.U.; Bang, J.S.; Han, J.H.; Kim, C.-Y.; Kwon, O.-K.; Oh, C.W. Middle Meningeal Artery Embolization for Chronic Subdural Hematoma. Radiology 2018, 286, 992–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liebert, A.; Voit-Höhne, H.; Ritter, L.; Eibl, T.; Hammer, A.; Städt, M.; Eff, F.; Holtmannspötter, M.; Steiner, H.-H. Embolization of the middle meningeal artery vs. second surgery—Treatment response and volume course of recurrent chronic subdural hematomas. Acta Neurochir. 2023, 165, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kan, P.; Maragkos, G.A.; Srivatsan, A.; Srinivasan, V.; Johnson, J.; Burkhardt, J.-K.; Robinson, T.M.; Salem, M.M.; Chen, S.; Riina, H.A.; et al. Middle meningeal artery embolization for chronic subdural hematoma: A multi-center experience of 154 consecutive embolizations. Neurosurgery 2021, 88, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, M.M.; Kuybu, O.; NguyenHoang, A.; Baig, A.A.; Khorasanizadeh, M.; Baker, C.; Hunsaker, J.C.; Mendez, A.A.; Cortez, G.; Davies, J.M.; et al. Middle Meningeal Artery Embolization for Chronic Subdural Hematoma: Predictors of Clinical and Radiographic Failure from 636 Embolizations. Radiology 2023, 307, 222045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, S.; Derraz, I.; Boetto, J.; Dargazanli, C.; Poulen, G.; Gascou, G.; Lefevre, P.-H.; Molinari, N.; Lonjon, N.; Costalat, V. Middle meningeal artery embolization as an adjuvant treatment to surgery for symptomatic chronic subdural hematoma: A pilot study assessing hematoma volume resorption. J. NeuroInterv. Surg. 2020, 12, 695–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catapano, J.S.; Ducruet, A.F.; Nguyen, C.L.; Baranoski, J.F.; Cole, T.S.; Majmundar, N.; Wilkinson, D.A.; Fredrickson, V.L.; Cavalcanti, D.D.; Albuquerque, F.C. Middle meningeal artery embolization for chronic subdural hematoma: An institutional technical analysis. J. NeuroInterv. Surg. 2021, 13, 657–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khorasanizadeh, M.; Maroufi, S.F.; Mukherjee, R.; Sankaranarayanan, M.; Moore, J.M.; Ogilvy, C.S. Middle Meningeal Artery Embolization in Adjunction to Surgical Evacuation for Treatment of Subdural Hematomas: A Nationwide Comparison of Outcomes With Isolated Surgical Evacuation. Neurosurgery 2023, 93, 1082–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, J.M.; Knopman, J.; Mokin, M.; Hassan, A.E.; Harbaugh, R.E.; Khalessi, A.; Fiehler, J.; Gross, B.A.; Grandhi, R.; Tarpley, J.; et al. Adjunctive middle meningeal artery embolization for subdural hematoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 391, 1890–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Ni, W.; Zuo, Q.; Yang, H.; Peng, Y.; Lin, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhen, Y.; Luo, J.; et al. Middle meningeal artery embolization for nonacute subdural hematoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 391, 1901–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorella, D.; Monteith, S.J.; Hanel, R.; Atchie, B.; Boo, S.; McTaggart, R.A.; Zauner, A.; Tjoumakaris, S.; Barbier, C.; Benitez, R.; et al. Embolization of the Middle Meningeal Artery for Chronic Subdural Hematoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 392, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Total n = 101 | EVT + Surgery n = 52 (51.5%) | Only EVT n = 49 (48.5%) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Men | 69 (68.3%) | 37 (71.2%) | 32 (65.3%) | 0.528 |
| Women | 32 (31.7%) | 15 (28.8%) | 17 (34.7%) | |
| Age | 82 (75–87) | 82 (75–87) | 82 (74.5–87.5) | 0.854 |
| Smoker | 32 (31.7%) | 19 (36.5%) | 13 (26.5%) | 0.280 |
| DM | 35 (34.7%) | 18 (34.6%) | 17 (34.7%) | 0.993 |
| HTN | 71 (70.3%) | 35 (67.3%) | 36 (73.5%) | 0.498 |
| DL | 54 (53.5%) | 29 (55.8%) | 25 (51%) | 0.633 |
| Alcoholism | 7 (6.9%) | 5 (9.6%) | 2 (4.1%) | 0.438 |
| CKD | 13 (12.9%) | 7 (13.5%) | 6 (12.2%) | 0.855 |
| HF | 24 (23.8%) | 12 (23.1%) | 12 (24.5%) | 0.868 |
| Stroke history | 16 (15.8%) | 6 (11.1%) | 10 (20.4%) | 0.222 |
| Thrombocytopenia | 3 (3%) | 0 (0%) | 3 (6.1%) | 0.111 |
| Coagulopathy | 1 (1%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (2%) | 0.485 |
| APT | 22 (21.8%) | 14 (26.9%) | 8 (16.3%) | 0.197 |
| AT | 42 (41.6%) | 17 (32.7%) | 25 (51%) | 0.062 |
| Initial right-sidewidth (mm) | 14 (10–18) | 16 (10–24) | 12.5 (10–14) | 0.031 |
| Initial left-side width (mm) | 13 (10–19) | 17 (12–22) | 11 (8.25–16) | 0.002 |
| Symptomatic | 81 (80.2%) | 50 (96.2%) | 31 (63.3%) | 0.000 |
| Right side | 27 (26.7%) | 14 (26.9%) | 13 (26.5%) | 0.979 |
| Left side | 42 (41.6%) | 22 (42.3%) | 20 (40.8%) | |
| Bilateral | 32 (31.7%) | 16 (30.8%) | 16 (32.7%) | |
| Recurrence | 8 (7.9%) | 6 (11.5%) | 2 (4.1%) | 0.271 |
| Cerebral atrophy | 57 (56.4%) | 29 (55.8%) | 28 (57.1%) | 0.889 |
| MLS initial CT | 49 (48.5%) | 31 (59.6%) | 18 (36.7%) | 0.002 |
| Sulcal effacement initial CT | 67 (66.3%) | 37 (71.2%) | 30 (61.2%) | 0.291 |
| Total n = 101 | EVT + Surgery n = 52 (51.5%) | Only EVT n = 49 (48.5%) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Local anesthesia | 2 (2%) | 0 (0%) | 2 (4.1%) | 0.324 |
| Conscious sedation | 26 (25.7%) | 13 (25%) | 13 (26.5%) | |
| General anesthesia | 73 (72.3%) | 39 (75%) | 34 (69.4%) | |
| Radial access | 54 (53.5%) | 24 (46.2%) | 30 (61.2%) | 0.129 |
| Femoral access | 47 (46.5%) | 28 (53.8%) | 19 (38.8%) | |
| Right-side EVT | 26 (25.7%) | 14 (26.9%) | 13 (26.5%) | 0.617 |
| Left-side EVT | 42 (41.6%) | 20 (38.5%) | 23 846.9%) | |
| Bilateral EVT | 33 (32.7%) | 18 (34.6%) | 13 (26.5%) | 0.668 |
| I.A. anesthesia | 44 (43.6%) | 24 (46.2%) | 20 (40.8%) | 0.589 |
| EVT duration (min) | 53 (42–77.5) | 53 (45–77) | 51 (38.5–77.5) | 0.306 |
| Complications (total) | 6 (5.9%) | 3 (5.8%) | 3 (6.1%) | 1.000 |
| Puncture site complications a | 1 (1%) | 1 (1.9%) | 0 (0%) | 1.000 |
| Catheterization complications b | 2 (2%) | 1 (1.9%) * | 1 (2%) ** | 1.000 |
| Embolization complications c | 3 (3%) | 1 (1.9%) † | 2 (4.1%) ‡,¶ | 0.610 |
| Total n = 134 | EVT + Surgery n = 61 | Only EVT n = 73 | p Values | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proximal EVT | 5 (3.7%) | 3 (4.9%) | 2 (2.7%) | 0.659 |
| Distal EVT | 129 (96.3%) | 58 (95.1%) | 71 (97.3%) | |
| Squid | 126 (94%) | 58 (95.1%) | 68 (93.2%) | 0.727 |
| Squid 12 | 120 (89.6%) | 52 (85.1%) | 68 (93.2%) | 0.136 |
| Squid 18 | 11 (8.2%) | 6 (9.8%) | 5 (6.8%) | 0.531 |
| Squid + glue | 1 (0.7%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (1.4%) | 1.000 |
| Squid + coils | 4 (3%) | 0 (0%) | 4 (5.5%) | 0.125 |
| Glue | 3 (2.2%) | 3 (4.9%) | 0 (0%) | 0.092 |
| Squid employed (cc) | 0.4 (0.1–0.6) | 0.3 (0.1–0.6) | 0.4 (0.2–0.6) | 0.087 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schmolling, Á.H.; Pérez-García, C.; Bérmudez, I.; López-Frías, A.; Fandiño, E.; Trejo, C.; Rosati, S.; Padrón, D.; Guardado, L.; Méndez, J.C.; et al. Imaging and Clinical Outcomes Six Months After Middle Meningeal Artery Embolization with Squid for Chronic Subdural Hematoma: A Prospective Study. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1424. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15111424
Schmolling ÁH, Pérez-García C, Bérmudez I, López-Frías A, Fandiño E, Trejo C, Rosati S, Padrón D, Guardado L, Méndez JC, et al. Imaging and Clinical Outcomes Six Months After Middle Meningeal Artery Embolization with Squid for Chronic Subdural Hematoma: A Prospective Study. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(11):1424. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15111424
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchmolling, Ángela H., Carlos Pérez-García, Isabel Bérmudez, Alfonso López-Frías, Eduardo Fandiño, Carmen Trejo, Santiago Rosati, Daniel Padrón, Lara Guardado, José Carlos Méndez, and et al. 2025. "Imaging and Clinical Outcomes Six Months After Middle Meningeal Artery Embolization with Squid for Chronic Subdural Hematoma: A Prospective Study" Diagnostics 15, no. 11: 1424. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15111424
APA StyleSchmolling, Á. H., Pérez-García, C., Bérmudez, I., López-Frías, A., Fandiño, E., Trejo, C., Rosati, S., Padrón, D., Guardado, L., Méndez, J. C., Arrazola, J., & Moreu, M. (2025). Imaging and Clinical Outcomes Six Months After Middle Meningeal Artery Embolization with Squid for Chronic Subdural Hematoma: A Prospective Study. Diagnostics, 15(11), 1424. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15111424






