Explainable Machine Learning in the Prediction of Depression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sample and Research Design
2.2. Ethics
2.3. Questionnaire Design—Covariates
2.4. Assessment of Depression
2.5. Problem Definition
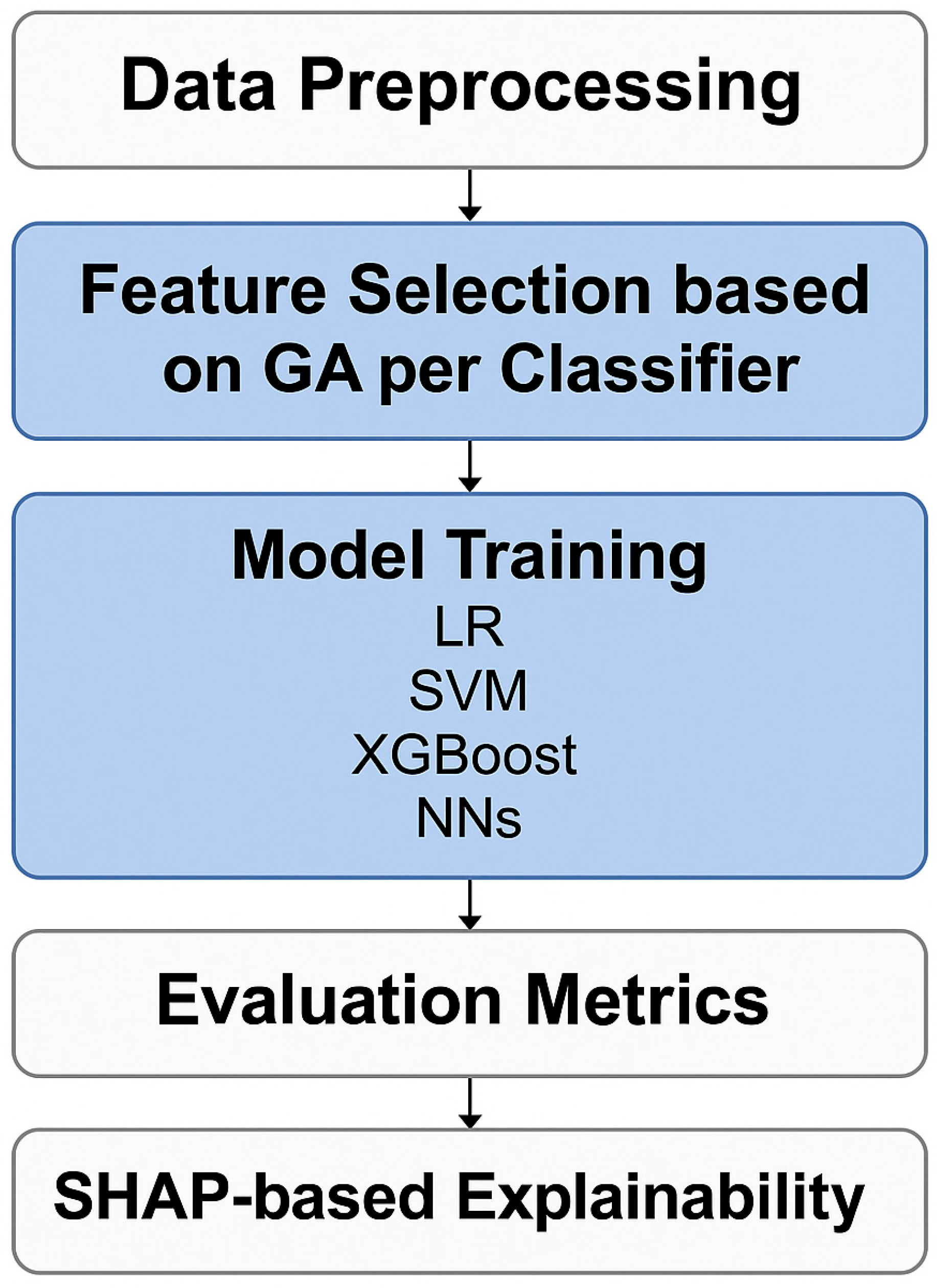
2.6. Machine Learning Workflow
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
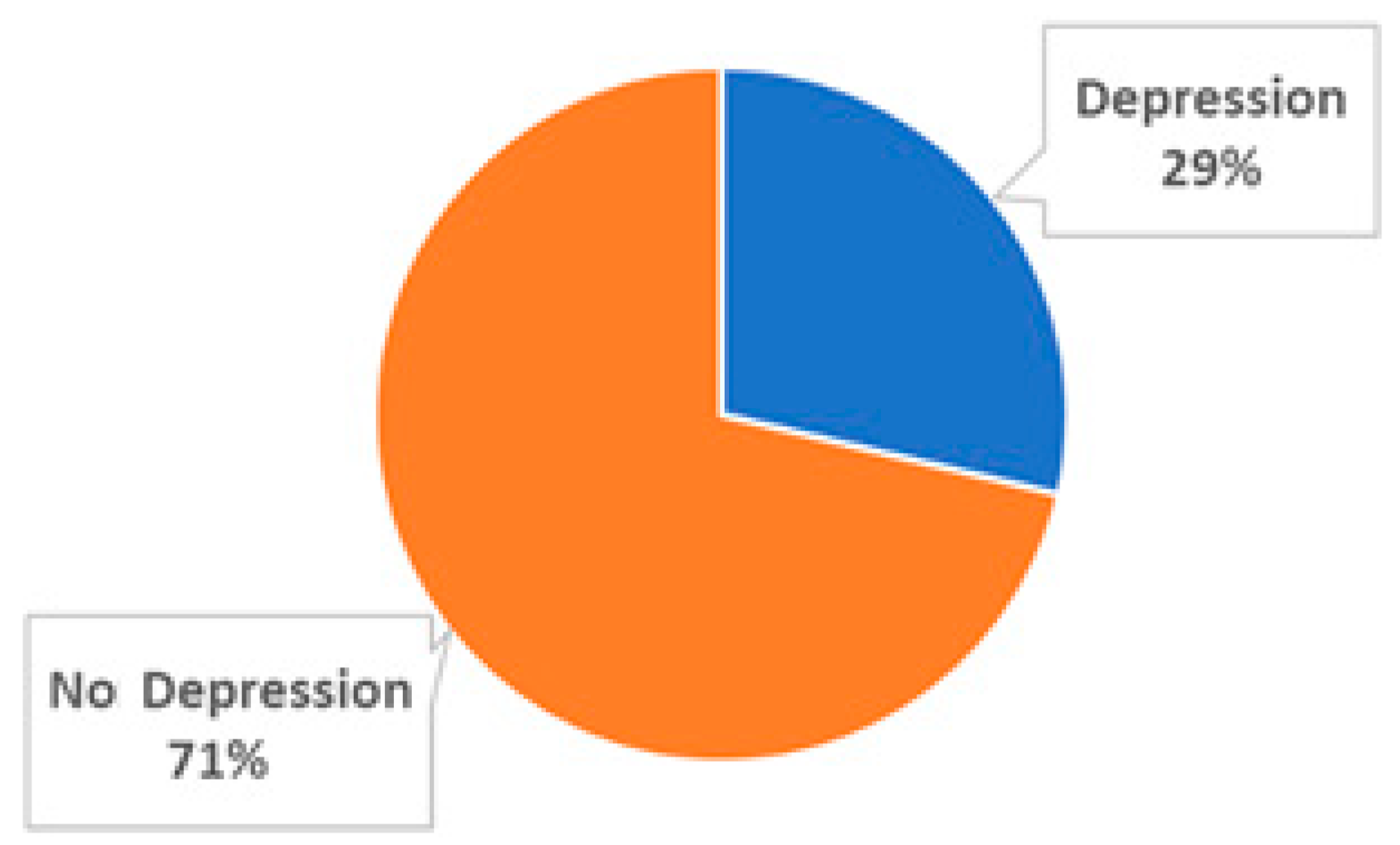
3.1. Epidemiological Profile and Depression Prevalence Among Subjects
3.2. Feature Selection
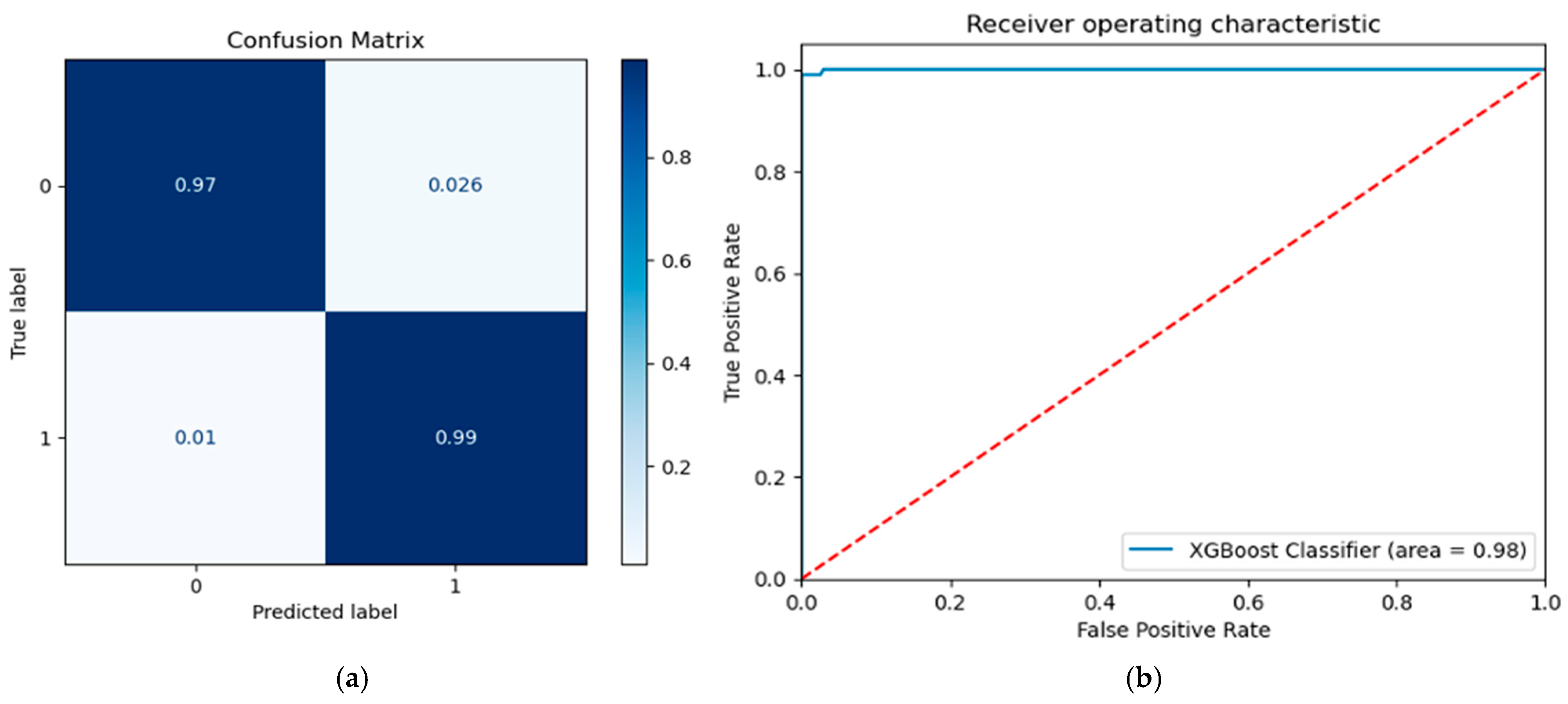
3.3. Testing Performance
3.4. Explainability
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Future Directions
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chand, S.P.; Arif, H.; Kutlenios, R.M. Depression (Nursing). In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Tampa, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Sousa, R.D.; Henriques, A.R.; Caldas de Almeida, J.; Canhão, H.; Rodrigues, A.M. Unraveling Depressive Symptomatology and Risk Factors in a Changing World. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2023, 20, 6575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathers, C.D.; Loncar, D. Projections of Global Mortality and Burden of Disease from 2002 to 2030. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, e442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, J.D.; Huang, X.; Fox, K.R.; Franklin, J.C. Depression and Hopelessness as Risk Factors for Suicide Ideation, Attempts and Death: Meta-Analysis of Longitudinal Studies. Br. J. Psychiatry 2018, 212, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobieraj, M.; Williams, J.; Marley, J.; Ryan, P. The Impact of Depression on the Physical Health of Family Members. Br. J. Gen. Pract. 1998, 48, 1653–1655. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dagnino, P.; Ugarte, M.J.; Morales, F.; González, S.; Saralegui, D.; Ehrenthal, J.C. Risk Factors for Adult Depression: Adverse Childhood Experiences and Personality Functioning. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 594698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuch, F.B.; Vancampfort, D.; Firth, J.; Rosenbaum, S.; Ward, P.B.; Silva, E.S.; Hallgren, M.; Ponce De Leon, A.; Dunn, A.L.; Deslandes, A.C. Physical Activity and Incident Depression: A Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. Am. J. Psychiatry 2018, 175, 631–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacka, F.N.; Pasco, J.A.; Mykletun, A.; Williams, L.J.; Hodge, A.M.; O’Reilly, S.L.; Nicholson, G.C.; Kotowicz, M.A.; Berk, M. Association of Western and Traditional Diets with Depression and Anxiety in Women. Am. J. Psychiatry 2010, 167, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baglioni, C.; Nanovska, S.; Regen, W.; Spiegelhalder, K.; Feige, B.; Nissen, C.; Reynolds, C.F., III; Riemann, D. Sleep and Mental Disorders: A Meta-Analysis of Polysomnographic Research. Psychol. Bull. 2016, 142, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weich, S.; Blanchard, M.; Prince, M.; Burton, E.; Erens, B.; Sproston, K. Mental Health and the Built Environment: Cross–Sectional Survey of Individual and Contextual Risk Factors for Depression. Br. J. Psychiatry 2002, 180, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabeshima, T.; Kim, H.-C. Involvement of Genetic and Environmental Factors in the Onset of Depression. Exp. Neurobiol. 2013, 22, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, R.Y.; Coyner, A.S.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; Chiang, M.F.; Campbell, J.P. Introduction to Machine Learning, Neural Networks, and Deep Learning. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2020, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schlick, T.; Wei, G.-W. Machine Learning Tools Advance Biophysics. Biophys. J. 2024, 123, E1–E3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, Q.; Goodman, K.E.; Kaminsky, J.; Lessler, J. What Is Machine Learning? A Primer for the Epidemiologist. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2019, 188, 2222–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanson, K.; Wu, E.; Zhang, A.; Alizadeh, A.A.; Zou, J. From Patterns to Patients: Advances in Clinical Machine Learning for Cancer Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Treatment. Cell 2023, 186, 1772–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ata, N.; Zahoor, I.; Hoda, N.; Adnan, S.M.; Vijayakumar, S.; Louis, F.; Poisson, L.; Rattan, R.; Kumar, N.; Cerghet, M. Artificial Neural Network-Based Prediction of Multiple Sclerosis Using Blood-Based Metabolomics Data. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2024, 92, 105942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egert, M.; Steward, J.E.; Sundaram, C.P. Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence in Surgical Fields. Indian J. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 11, 573–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Goyal, L.; Mallick, D.C.; Surani, S.R.; Kaushik, N.; Chandramohan, D.; Simhadri, P.K. Artificial Intelligence in Nephrology: Clinical Applications and Challenges. Kidney Med. 2024, 7, 100927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chafai, N.; Bonizzi, L.; Botti, S.; Badaoui, B. Emerging Applications of Machine Learning in Genomic Medicine and Healthcare. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2024, 61, 140–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderone, A.; Latella, D.; Bonanno, M.; Quartarone, A.; Mojdehdehbaher, S.; Celesti, A.; Calabrò, R.S. Towards Transforming Neurorehabilitation: The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Diagnosis and Treatment of Neurological Disorders. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macpherson, T.; Churchland, A.; Sejnowski, T.; DiCarlo, J.; Kamitani, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Hikida, T. Natural and Artificial Intelligence: A Brief Introduction to the Interplay between AI and Neuroscience Research. Neural Netw. 2021, 144, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.E.; Torous, J.; De Choudhury, M.; Depp, C.A.; Graham, S.A.; Kim, H.-C.; Paulus, M.P.; Krystal, J.H.; Jeste, D.V. Artificial Intelligence for Mental Health Care: Clinical Applications, Barriers, Facilitators, and Artificial Wisdom. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2021, 6, 856–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levkovich, I. Is Artificial Intelligence the Next Co-Pilot for Primary Care in Diagnosing and Recommending Treatments for Depression? Med. Sci. 2025, 13, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoor, M.A.; Ansari, K.H. Early Detection of Mental Health Crises through Artifical-Intelligence-Powered Social Media Analysis: A Prospective Observational Study. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.; Park, S.; Lee, M. Effectiveness of Artificial Intelligence in Detecting and Managing Depressive Disorders: Systematic Literature Review. J. Affect. Disord. 2024, 361, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiaohua, L.; Jiang, K. Why Is Diagnosing MDD Challenging? Shanghai Arch. Psychiatry 2016, 28, 343. [Google Scholar]
- Cuijpers, P.; Beekman, A.T.; Reynolds, C.F. Preventing Depression: A Global Priority. JAMA 2012, 307, 1033–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López Steinmetz, L.C.; Sison, M.; Zhumagambetov, R.; Godoy, J.C.; Haufe, S. Machine Learning Models Predict the Emergence of Depression in Argentinean College Students during Periods of COVID-19 Quarantine. Front. Psychiatry 2024, 15, 1376784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, F.; Alam, L.F.; Vivas, R.R.; Wang, J.; Whei, S.J.; Mehmood, S.; Sadeghzadegan, A.; Lakkimsetti, M.; Nazir, Z. The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Identifying Depression and Anxiety: A Comprehensive Literature Review. Cureus 2024, 16, e56472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnaggar, K.; El-Gayar, M.M.; Elmogy, M. Depression Detection and Diagnosis Based on Electroencephalogram (EEG) Analysis: A Systematic Review. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasib, K.M.; Islam, M.R.; Sakib, S.; Akbar, M.A.; Razzak, I.; Alam, M.S. Depression Detection from Social Networks Data Based on Machine Learning and Deep Learning Techniques: An Interrogative Survey. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 2023, 10, 1568–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altomi, Z.A.; Alsakar, Y.M.; El-Gayar, M.M.; Elmogy, M.; Fouda, Y.M. Autism Spectrum Disorder Diagnosis Based on Attentional Feature Fusion Using NasNetMobile and DeiT Networks. Electronics 2025, 14, 1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serdari, A.; Manolis, A.; Tsiptsios, D.; Vorvolakos, T.; Terzoudi, A.; Nena, E.; Tsamakis, K.; Steiropoulos, P.; Tripsianis, G. Insight into the Relationship between Sleep Characteristics and Anxiety: A Cross-Sectional Study in Indigenous and Minority Populations in Northeastern Greece. Psychiatry Res. 2020, 292, 113361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paparrigopoulos, T.; Tzavara, C.; Theleritis, C.; Psarros, C.; Soldatos, C.; Tountas, Y. Insomnia and Its Correlates in a Representative Sample of the Greek Population. BMC Public Health 2010, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touloumi, G.; Karakatsani, A.; Karakosta, A.; Sofianopoulou, E.; Koustenis, P.; Gavana, M.; Alamanos, Y.; Kantzanou, M.; Konstantakopoulos, G.; Chryssochoou, X. National Survey of Morbidity and Risk Factors (EMENO): Protocol for a Health Examination Survey Representative of the Adult Greek Population. JMIR Res. Protoc. 2019, 8, e10997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotakos, D.B.; Pitsavos, C.; Arvaniti, F.; Stefanadis, C. Adherence to the Mediterranean Food Pattern Predicts the Prevalence of Hypertension, Hypercholesterolemia, Diabetes and Obesity, among Healthy Adults; the Accuracy of the MedDietScore. Prev. Med. 2007, 44, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. The World Health Report 2000: Health Systems: Improving Performance; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2000; ISBN 92-4-156198-X. [Google Scholar]
- Samakouri, M.; Bouhos, G.; Kadoglou, M.; Giantzelidou, A.; Tsolaki, K.; Livaditis, M. Standardization of the Greek Version of Zung’s Self-Rating Anxiety Scale (SAS). Psychiatr. Psychiatr. 2012, 23, 212–220. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, A.T.; Ward, C.H.; Mendelson, M.; Mock, J.; Erbaugh, J. An Inventory for Measuring Depression. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1961, 4, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldatos, C.R.; Dikeos, D.G.; Paparrigopoulos, T.J. Athens Insomnia Scale: Validation of an Instrument Based on ICD-10 Criteria. J. Psychosom. Res. 2000, 48, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsara, V.; Eva, S.; Amfilochiou, A.; Constantinidis, T.; Christaki, P. Greek Version of the Epworth Sleepiness Scale. Sleep Breath. 2004, 8, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotronoulas, G.C.; Papadopoulou, C.N.; Papapetrou, A.; Patiraki, E. Psychometric Evaluation and Feasibility of the Greek Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (GR-PSQI) in Patients with Cancer Receiving Chemotherapy. Support. Care Cancer 2011, 19, 1831–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasa, L.; Ayuso-Mateos, J.L.; Vázquez-Barquero, J.L.; Díez-Manrique, F.J.; Dowrick, C.F. The Use of the Beck Depression Inventory to Screen for Depression in the General Population: A Preliminary Analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 2000, 57, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannakou, M.; Roussi, P.; Kosmides, M.-E.; Kiosseoglou, G.; Adamopoulou, A.; Garyfallos, G. Adaptation of the Beck Depression Inventory-II to Greek Population. Hell. J. Psychol. 2013, 10, 120–146. [Google Scholar]
- Kokaliari, E. Quality of Life, Anxiety, Depression, and Stress among Adults in Greece Following the Global Financial Crisis. Int. Soc. Work 2018, 61, 410–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, F.; Petridou, E.; Argyropoulou, S.; Kontaxakis, V.; Dessypris, N.; Anastasiou, A.; Katsiardani, K.; Trichopoulos, D.; Lyketsos, C. Prevalence and Correlates of Depression in Late Life: A Population Based Study from a Rural Greek Town. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry J. Psychiatry Late Life Allied Sci. 2005, 20, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelstein, B.A.; Drozdick, L.W.; Ciliberti, C.M. Chapter 1—Assessment of Depression and Bereavement in Older Adults. In Handbook of Assessment in Clinical Gerontology, 2nd ed.; Lichtenberg, P.A., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2010; pp. 3–43. ISBN 978-0-12-374961-1. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, R.K.; Mokonogho, J.; Kumar, A. Racial and Ethnic Differences in Depression: Current Perspectives. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2019, 15, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brance, K.; Chatzimpyros, V.; Bentall, R.P. Increased Social Identification Is Linked with Lower Depressive and Anxiety Symptoms among Ethnic Minorities and Migrants: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2023, 99, 102216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Ning, G.; Wang, L.; Chen, F. More Income, Less Depression? Revisiting the Nonlinear and Heterogeneous Relationship between Income and Mental Health. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 1016286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parra-Mujica, F.; Johnson, E.; Reed, H.; Cookson, R.; Johnson, M. Understanding the Relationship between Income and Mental Health among 16-to 24-Year-Olds: Analysis of 10 Waves (2009–2020) of Understanding Society to Enable Modelling of Income Interventions. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0279845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stylianidis, S.; Souliotis, K. The Impact of the Long-Lasting Socioeconomic Crisis in Greece. BJPsych Int. 2019, 16, 16–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, M.M.; Das, K.C.; Sheikh, I. Psychological Implications of Unemployment among Higher Educated Migrant Youth in Kolkata City, India. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 10171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiller, J.W. Depression and Anxiety. Med. J. Aust. 2013, 16, S28–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santomauro, D.F.; Herrera, A.M.M.; Shadid, J.; Zheng, P.; Ashbaugh, C.; Pigott, D.M.; Abbafati, C.; Adolph, C.; Amlag, J.O.; Aravkin, A.Y. Global Prevalence and Burden of Depressive and Anxiety Disorders in 204 Countries and Territories in 2020 Due to the COVID-19 Pandemic. Lancet 2021, 398, 1700–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittchen, H.-U.; Kessler, R.C.; Pfister, H.; Höfler, M.; Lieb, R. Why Do People with Anxiety Disorders Become Depressed? A Prospective-Longitudinal Community Study. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2000, 102, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, P.J.; Wuyek, L.A. Anxiety Disorders as a Risk Factor for Subsequent Depression. Int. J. Psychiatry Clin. Pract. 2010, 14, 244–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, N.C.; Newman, M.G. Avoidance Mediates the Relationship between Anxiety and Depression over a Decade Later. J. Anxiety Disord. 2014, 28, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McTeague, L.M.; Rosenberg, B.M.; Lopez, J.W.; Carreon, D.M.; Huemer, J.; Jiang, Y.; Chick, C.F.; Eickhoff, S.B.; Etkin, A. Identification of Common Neural Circuit Disruptions in Emotional Processing across Psychiatric Disorders. Am. J. Psychiatry 2020, 177, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fava, M.; Alpert, J.E.; Carmin, C.N.; Wisniewski, S.R.; Trivedi, M.H.; Biggs, M.M.; Shores-Wilson, K.; Morgan, D.; Schwartz, T.; Balasubramani, G. Clinical Correlates and Symptom Patterns of Anxious Depression among Patients with Major Depressive Disorder in STAR* D. Psychol. Med. 2004, 34, 1299–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salk, R.H.; Hyde, J.S.; Abramson, L.Y. Gender Differences in Depression in Representative National Samples: Meta-Analyses of Diagnoses and Symptoms. Psychol. Bull. 2017, 143, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartels, M.; Cacioppo, J.T.; van Beijsterveldt, T.C.; Boomsma, D.I. Exploring the Association between Well-Being and Psychopathology in Adolescents. Behav. Genet. 2013, 43, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendler, K.S.; Gardner, C.O. Sex Differences in the Pathways to Major Depression: A Study of Opposite-Sex Twin Pairs. Am. J. Psychiatry 2014, 171, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuria, M.W.; Ndetei, D.M.; Obot, I.S.; Khasakhala, L.I.; Bagaka, B.M.; Mbugua, M.N.; Kamau, J. The Association between Alcohol Dependence and Depression before and after Treatment for Alcohol Dependence. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2012, 2012, 482802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baum-Baicker, C. The Psychological Benefits of Moderate Alcohol Consumption: A Review of the Literature. Drug Alcohol Depend. 1985, 15, 305–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraus, C.; Kautzky, A.; Watzal, V.; Gramser, A.; Kadriu, B.; Deng, Z.-D.; Bartova, L.; Zarate Jr, C.A.; Lanzenberger, R.; Souery, D. Body Mass Index and Clinical Outcomes in Individuals with Major Depressive Disorder: Findings from the GSRD European Multicenter Database. J. Affect. Disord. 2023, 335, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badillo, N.; Khatib, M.; Kahar, P.; Khanna, D. Correlation between Body Mass Index and Depression/Depression-like Symptoms among Different Genders and Races. Cureus 2022, 14, e21841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, C.; Ye, J.; Zhao, W. The Relationship between BMI and Depression: A Cross-Sectional Study. Front. Psychiatry 2024, 15, 1410782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, D. Sleep Duration and Depression among Adults: A Meta-analysis of Prospective Studies. Depress. Anxiety 2015, 32, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorvolakos, T.; Leontidou, E.; Tsiptsios, D.; Mueller, C.; Serdari, A.; Terzoudi, A.; Nena, E.; Tsamakis, K.; Constantinidis, T.C.; Tripsianis, G. The Association between Sleep Pathology and Depression: A Cross-Sectional Study among Adults in Greece. Psychiatry Res. 2020, 294, 113502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehrman, P.; Seelig, A.D.; Jacobson, I.G.; Boyko, E.J.; Hooper, T.I.; Gackstetter, G.D.; Ulmer, C.S.; Smith, T.C. Millennium Cohort Study Team Predeployment Sleep Duration and Insomnia Symptoms as Risk Factors for New-Onset Mental Health Disorders Following Military Deployment. Sleep 2013, 36, 1009–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narita, Z.; Hidese, S.; Kanehara, R.; Tachimori, H.; Hori, H.; Kim, Y.; Kunugi, H.; Arima, K.; Mizukami, S.; Tanno, K. Association of Sugary Drinks, Carbonated Beverages, Vegetable and Fruit Juices, Sweetened and Black Coffee, and Green Tea with Subsequent Depression: A Five-Year Cohort Study. Clin. Nutr. 2024, 43, 1395–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfaliany, M.; Bowe, S.J.; Kowal, P.; Orellana, L.; Berk, M.; Mohebbi, M. Depression and Chronic Diseases: Co-Occurrence and Communality of Risk Factors. J. Affect. Disord. 2018, 241, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera Salinas, P.A.; Campos Romero, S.; Szabo Lagos, W.M.; Martínez, P.; Guajardo Tobar, V.A.; Rojas Castillo, M.G. Understanding the Relationship between Depression and Chronic Diseases Such as Diabetes and Hypertension: A Grounded Theory Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12130. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Villegas, A.; Henríquez, P.; Bes-Rastrollo, M.; Doreste, J. Mediterranean Diet and Depression. Public Health Nutr. 2006, 9, 1104–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamalaki, E.; Ntanasi, E.; Hatzimanolis, A.; Basta, M.; Kosmidis, M.H.; Dardiotis, E.; Hadjigeorgiou, G.M.; Sakka, P.; Scarmeas, N.; Yannakoulia, M. The Association of Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet with Depression in Older Adults Longitudinally Taking into Account Cognitive Status: Results from the HELIAD Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, W.; Löf, M.; Chen, R.; Hultman, C.M.; Fang, F.; Sandin, S. Mediterranean Diet and Depression: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2021, 18, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radkhah, N.; Rasouli, A.; Majnouni, A.; Eskandari, E.; Parastouei, K. The Effect of Mediterranean Diet Instructions on Depression, Anxiety, Stress, and Anthropometric Indices: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Controlled Clinical Trial. Prev. Med. Rep. 2023, 36, 102469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérès, K.; Ouvrard, C.; Koleck, M.; Rascle, N.; Dartigues, J.; Bergua, V.; Amieva, H. Living in Rural Area: A Protective Factor for a Negative Experience of the Lockdown and the COVID-19 Crisis in the Oldest Old Population? Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2021, 36, 1950–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, S.M.; Peterson, T.A.; Seo, K.Y.; Han, H.W.; Kang, J.I. Discovery of Depression-Associated Factors from a Nationwide Population-Based Survey: Epidemiological Study Using Machine Learning and Network Analysis. J. Med. Internet Res. 2021, 23, e27344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasrawi, R.; Vicuna Polo, S.; Al-Halawa, D.A.; Hallaq, S.; Abdeen, Z. Schoolchildren’depression and Anxiety Risk Factors Assessment and Prediction: Machine Learning Techniques Performance Analysis. JMIR Form. Res. 2022, 31, e32736. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, A.; Verbeke, W.J. Improving Diagnosis of Depression with XGBOOST Machine Learning Model and a Large Biomarkers Dutch Dataset (N = 11,081). Front. Big Data 2020, 3, 523466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, R.C.; van Loo, H.M.; Wardenaar, K.J.; Bossarte, R.M.; Brenner, L.A.; Cai, T.; Ebert, D.D.; Hwang, I.; Li, J.; de Jonge, P. Testing a Machine-Learning Algorithm to Predict the Persistence and Severity of Major Depressive Disorder from Baseline Self-Reports. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 1366–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, T.; Fishbain, B.; Richter-Levin, G.; Okon-Singer, H. Machine Learning-Based Behavioral Diagnostic Tools for Depression: Advances, Challenges, and Future Directions. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Depression | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number (%) | Frequency | Proportion (%) | p Value | |
| Gender | 0.145 | |||
| Males | 570 (46.5) | 152 | 26.7 | |
| Females | 657 (53.5) | 200 | 30.4 | |
| Age (years) | <0.001 | |||
| ≤40 | 341 (27.8) | 42 | 12.3 | |
| 41–60 | 571 (46.5) | 164 | 28.7 | |
| >60 | 315 (25.7) | 146 | 46.3 | |
| Marital status | <0.001 | |||
| Married | 825 (67.2) | 257 | 31.2 | |
| Single | 252 (20.5) | 41 | 16.3 | |
| Divorced | 102 (8.3) | 42 | 41.2 | |
| Widowed | 48 (3.9) | 12 | 25.0 | |
| Cultural status | <0.001 | |||
| Greek Christians | 807 (65.7) | 194 | 24.0 | |
| Greek Muslims | 358 (29.2) | 132 | 36.9 | |
| Expatriated Greeks | 62 (5.1) | 26 | 41.9 | |
| Place of residence | <0.001 | |||
| Urban | 524 (42.7) | 88 | 16.8 | |
| Rural | 703 (57.3) | 264 | 37.6 | |
| Education level | <0.001 | |||
| Low | 406 (33.1) | 211 | 52.0 | |
| Medium | 431 (35.1) | 98 | 22.7 | |
| High | 390 (31.8) | 43 | 11.0 | |
| Presence of child <6 years | 0.029 | |||
| No | 1128 (91.9) | 333 | 29.5 | |
| Yes | 99 (8.1) | 19 | 19.2 | |
| Unemployment | <0.001 | |||
| No | 1121 (91.4) | 303 | 27.0 | |
| Yes | 106 (8.6) | 49 | 46.2 | |
| Financial status | <0.001 | |||
| Low | 614 (50.0) | 213 | 34.7 | |
| Medium | 258 (21.0) | 33 | 12.8 | |
| High | 180 (14.7) | 29 | 16.1 | |
| Depression | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number (%) | Frequency | Proportion (%) | p Value | |
| Smoking status | 0.242 | |||
| Never/ex-smoker | 808 (65.9) | 223 | 27.6 | |
| Current smoker | 419 (34.1) | 129 | 30.8 | |
| Alcohol consumption | <0.001 | |||
| None | 621 (50.6) | 212 | 34.1 | |
| 1–3 glasses/week | 316 (25.8) | 69 | 21.8 | |
| 4–6 glasses/week | 215 (17.5) | 42 | 19.5 | |
| >6 glasses/week | 75 (6.1) | 29 | 38.7 | |
| Coffee consumption | <0.001 | |||
| None | 113 (9.2) | 33 | 29.2 | |
| 1–2 cups/day | 723 (58.9) | 179 | 24.8 | |
| 3–4 cups/day | 322 (26.2) | 99 | 30.7 | |
| >4 cups/day | 69 (5.6) | 41 | 59.4 | |
| Adherence to Mediterranean diet | 0.080 | |||
| Low | 968 (78.9) | 289 | 29.9 | |
| High | 259 (21.1) | 63 | 24.3 | |
| Physical activity | <0.001 | |||
| Low | 1031 (84.0) | 321 | 31.1 | |
| High | 196 (16.0) | 31 | 15.8 | |
| Midday sleep | 0.101 | |||
| No | 520 (42.4) | 162 | 31.2 | |
| Yes | 707 (57.6) | 190 | 26.9 | |
| Sleep duration | <0.001 | |||
| Short | 273 (22.2) | 130 | 47.6 | |
| Normal | 780 (63.6) | 176 | 22.6 | |
| Long | 174 (14.2) | 46 | 26.4 | |
| Depression | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number (%) | Frequency | Proportion (%) | p Value | |
| BMI status | 0.103 | |||
| Normal | 415 (33.8) | 113 | 27.2 | |
| Overweight | 352 (28.7) | 91 | 25.9 | |
| Obese | 460 (37.5) | 148 | 32.2 | |
| Subjective health status | <0.001 | |||
| Good | 941 (76.7) | 168 | 17.9 | |
| Bad | 286 (23.3) | 184 | 64.3 | |
| Morbidity of chronic illness | <0.001 | |||
| No | 534 (43.5) | 94 | 17.6 | |
| Yes | 693 (56.5) | 258 | 37.2 | |
| Number of chronic diseases | <0.001 | |||
| None | 534 (43.5) | 94 | 17.6 | |
| One | 360 (29.3) | 97 | 26.9 | |
| Two | 208 (17.0) | 87 | 41.8 | |
| More than two | 125 (10.2) | 74 | 59.2 | |
| Family history of depression | <0.001 | |||
| No | 812 (66.2) | 199 | 24.5 | |
| Yes | 415 (33.8) | 153 | 36.9 | |
| Traumatic events in life | <0.001 | |||
| No | 716 (58.4) | 155 | 21.6 | |
| Yes | 511 (41.6) | 197 | 38.6 | |
| Anxiety symptoms | <0.001 | |||
| No | 813 (66.3) | 119 | 14.6 | |
| Yes | 414 (33.7) | 233 | 56.3 | |
| Excessive daytime sleepiness | 0.704 | |||
| No | 1120 (91.3) | 323 | 28.8 | |
| Yes | 107 (8.7) | 29 | 27.1 | |
| Presence of insomnia | 0.042 | |||
| No | 1015 (82.7) | 279 | 27.5 | |
| Yes | 212 (17.3) | 73 | 34.4 | |
| Sleep quality | 0.008 | |||
| Good | 765 (62.3) | 199 | 26.0 | |
| Bad | 462 (37.7) | 153 | 33.1 | |
| Risk Factor | Description | Type of Variable |
|---|---|---|
| Gender | Gender (male/female) | Categorical |
| Marital status | Marital status (single/married/divorced/widowed) | Categorical |
| Residence | Area of residence (urban/rural) | Categorical |
| Education | Education level (low/medium/high) | Categorical |
| Unemployment | Unemployment (no/yes) | Categorical |
| Income | Income (low/medium/high) | Categorical |
| Chronic diseases | Chronic diseases (no/yes) | Categorical |
| BMI | Body mass index (normal/overweight/obese) | Categorical |
| Alcohol | Alcohol consumption/week (none/1–3 glasses/4–6 glasses/>6 glasses) | Categorical |
| Coffee | Coffee consumption/day (none/1–2 glasses/3–4 glasses/>4 glasses) | Categorical |
| Mediterranean diet | Adherence to Mediterranean diet (no/yes) | Categorical |
| Child <6 years | Presence of a child younger than 6 years of age (no/yes) | Categorical |
| Sleep duration | Sleep duration (short/normal/long) | Categorical |
| Sleepiness | Excessive daytime sleepiness (no/yes) | Categorical |
| Anxiety | Anxiety (no/yes) | Categorical |
| Classifier | Accuracy (%) | F1 Score (%) | Precision (%) | Sensitivity (Recall) (%) | Specificity (%) | Hyperparameters |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LR | 79.95 | 79.04 | 78.82 | 79.95 | 90.48 | C: 1, penalty: l2 |
| SVM | 95.66 | 95.64 | 95.63 | 95.66 | 97.80 | C: 10, kernel: rbf |
| XGBoost | 97.83 | 97.85 | 97.94 | 98.96 | 97.44 | gamma: 0, max_depth: 7, min_child_weight: 1 |
| NN | 97.02 | 97.03 | 97.06 | 97.02 | 97.44 | activation: tanh, alpha: 0.0001, hidden_layer_sizes: (10, 20, 50), learning_rate: constant, solver: adam |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mimikou, C.; Kokkotis, C.; Tsiptsios, D.; Tsamakis, K.; Savvidou, S.; Modig, L.; Christidi, F.; Kaltsatou, A.; Doskas, T.; Mueller, C.; et al. Explainable Machine Learning in the Prediction of Depression. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1412. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15111412
Mimikou C, Kokkotis C, Tsiptsios D, Tsamakis K, Savvidou S, Modig L, Christidi F, Kaltsatou A, Doskas T, Mueller C, et al. Explainable Machine Learning in the Prediction of Depression. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(11):1412. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15111412
Chicago/Turabian StyleMimikou, Christina, Christos Kokkotis, Dimitrios Tsiptsios, Konstantinos Tsamakis, Stella Savvidou, Lillian Modig, Foteini Christidi, Antonia Kaltsatou, Triantafyllos Doskas, Christoph Mueller, and et al. 2025. "Explainable Machine Learning in the Prediction of Depression" Diagnostics 15, no. 11: 1412. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15111412
APA StyleMimikou, C., Kokkotis, C., Tsiptsios, D., Tsamakis, K., Savvidou, S., Modig, L., Christidi, F., Kaltsatou, A., Doskas, T., Mueller, C., Serdari, A., Anagnostopoulos, K., & Tripsianis, G. (2025). Explainable Machine Learning in the Prediction of Depression. Diagnostics, 15(11), 1412. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15111412










