The Aftermath of Pulmonary Embolism: Are Residual Thrombi Clinically Significant?
Abstract
1. Introduction
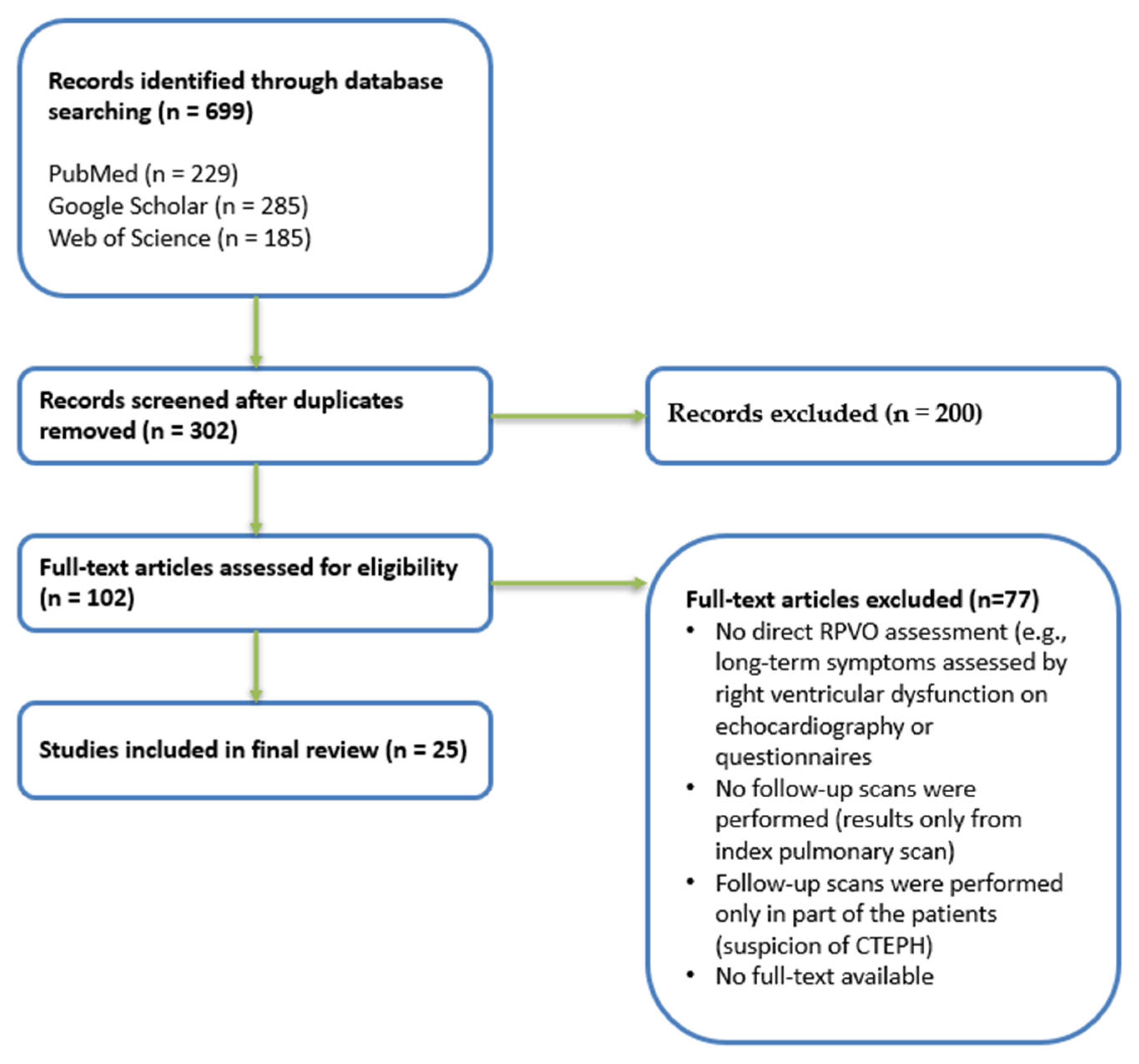
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.2. Information Sources and Search Strategy
2.3. Study Selection
3. Definitions in Pulmonary Embolism: Residual Thrombus, Chronic PE, PE Recurrence, and CTEPH
3.1. Residual Thrombus
3.2. Chronic Pulmonary Embolism
3.3. Pulmonary Embolism Recurrence
3.4. Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension
4. Pathophysiology of Thrombus Resolution
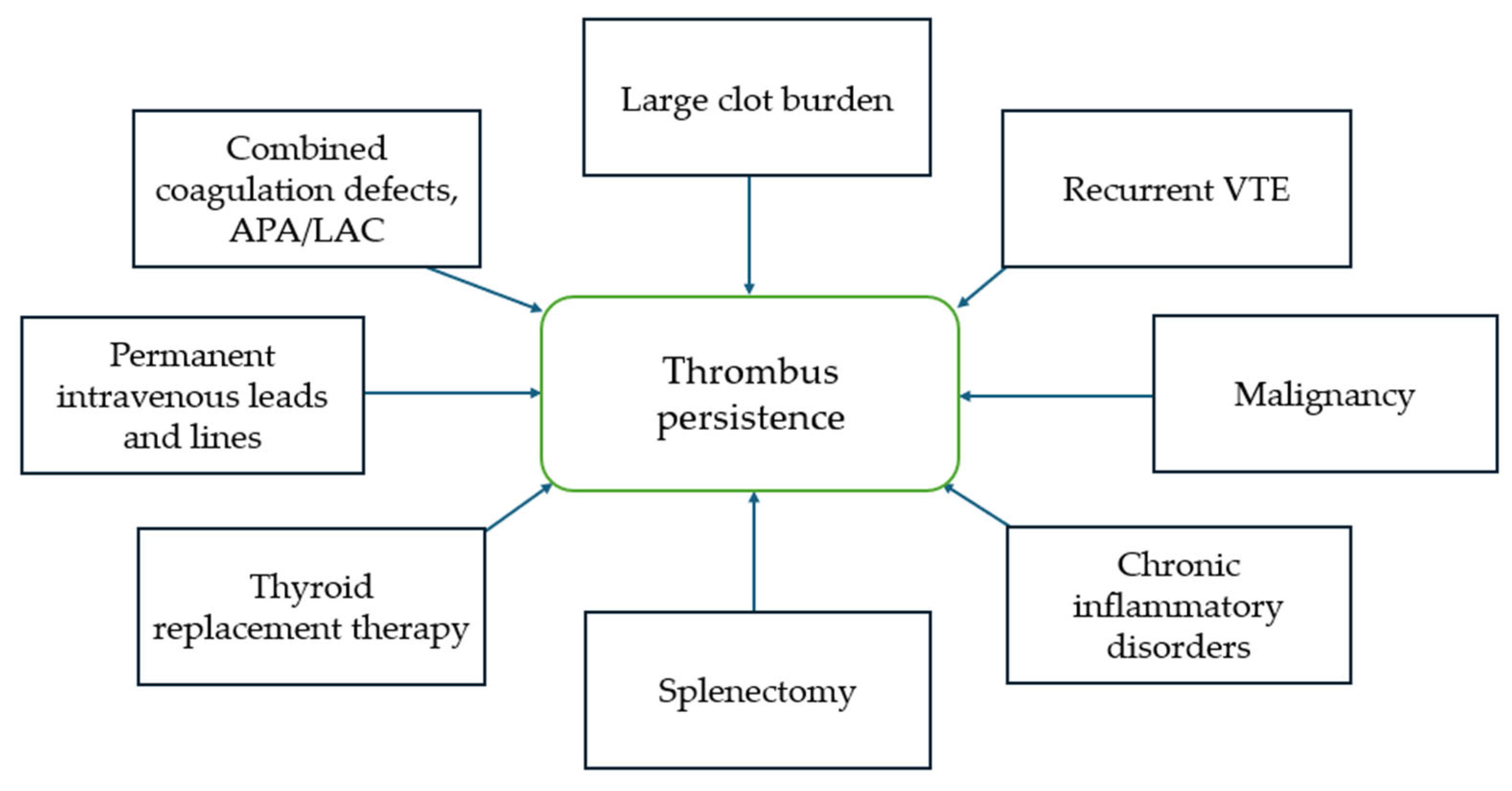
5. Risk Factors and Mechanisms of Incomplete Thrombus Resolution
6. Timing of Thrombus Resolution and Prevalence of Residual Thrombi After Acute PE
7. Clinical Significance of Residual Clots
7.1. Residual Thrombi and PE Recurrence
7.2. Residual Thrombi and CTEPH
7.3. Residual Thrombi and Long-Term Symptoms, Quality of Life
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PE | Pulmonary embolism |
| CTEPH | Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension |
| VTE | Venous thromboembolism |
| DVT | Deep vein thrombosis |
| RPVO | Residual pulmonary vascular obstruction |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
| FGR | Fibroblast growth factor |
| APA | Antiphospholipid antibodies |
| LAC | Lupus anticoagulant |
| Q | Perfusion |
| V/Q | Ventilation/Perfusion |
| CTPA | Computed tomography pulmonary angiography |
| MDCT | Multidetector computed tomography |
| NOACs | Novel oral anticoagulants |
| DOACs | Direct oral anticoagulants |
| VKA | Vitamin K antagonists |
| NA | Not available |
| RVD | Right ventricular dysfunction |
| sPAP | Systolic pulmonary artery pressure |
References
- Raskob, G.E.; Angchaisuksiri, P.; Blanco, A.N.; Buller, H.; Gallus, A.; Hunt, B.J.; Hylek, E.M.; Kakkar, A.; Konstantinides, S.V.; McCumber, M.; et al. Thrombosis: A major contributor to global disease burden. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 2363–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendelboe, A.M.; Raskob, G.E. Global burden of thrombosis: Epidemiologic aspects. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 1340–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Nisio, M.; van Es, N.; Büller, H.R. Deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Lancet 2016, 388, 3060–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Den Exter, P.L.; van der Hulle, T.; Klok, F.A.; Huisman, M.V. Advances in the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism. Thromb. Res. 2014, 133 (Suppl. 2), S10–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.J.; Shim, J.; Lee, S.M.; Im, D.J.; Hur, J. Dual-Energy CT for Pulmonary Embolism: Current and Evolving Clinical Applications. Korean J. Radiol. 2021, 22, 1555–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinides, S.V.; Meyer, G.; Becattini, C.; Bueno, H.; Geersing, G.J.; Harjola, V.P.; Huisman, M.V.; Humbert, M.; Jennings, C.S.; Jiménez, D.; et al. 2019 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism developed in collaboration with the European Respiratory Society (ERS). Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 543–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barco, S.; Mahmoudpour, S.H.; Valerio, L.; Klok, F.A.; Münzel, T.; Middeldorp, S.; Ageno, W.; Cohen, A.T.; Hunt, B.J.; Konstantinides, S.V. Trends in mortality related to pulmonary embolism in the European Region, 2000–2015: Analysis of vital registration data from the WHO Mortality Database. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesavento, R.; Filippi, L.; Palla, A.; Visonà, A.; Bova, C.; Marzolo, M.; Porro, F.; Villalta, S.; Ciammaichella, M.; Bucherini, E.; et al. Impact of residual pulmonary obstruction on the long-term outcome of patients with pulmonary embolism. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 49, 1601980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, O.; Helley, D.; Couchon, S.; Roux, A.; Delaval, A.; Trinquart, L.; Collignon, M.A.; Fischer, A.M.; Meyer, G. Perfusion defects after pulmonary embolism: Risk factors and clinical significance. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 8, 1248–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klok, F.A.; Tijmensen, J.E.; Haeck, M.L.; van Kralingen, K.W.; Huisman, M.V. Persistent dyspnea complaints at long-term follow-up after an episode of acute pulmonary embolism: Results of a questionnaire. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2008, 19, 625–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pengo, V.; Lensing, A.W.; Prins, M.H.; Marchiori, A.; Davidson, B.L.; Tiozzo, F.; Albanese, P.; Biasiolo, A.; Pegoraro, C.; Iliceto, S.; et al. Incidence of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension after pulmonary embolism. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 2257–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.; Tritschler, T.; Kimpton, M.; Wells, P.S.; Kearon, C.; Weitz, J.I.; Büller, H.R.; Raskob, G.E.; Ageno, W.; Couturaud, F.; et al. Long-term risk of recurrent venous thromboembolism among patients receiving extended oral anticoagulant therapy for first unprovoked venous thromboembolism: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2021, 19, 2801–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghayev, A.; Furlan, A.; Patil, A.; Gumus, S.; Jeon, K.N.; Park, B.; Bae, K.T. The rate of resolution of clot burden measured by pulmonary CT angiography in patients with acute pulmonary embolism. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2013, 200, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, D.; Cenci, C.; Antonucci, E.; Grifoni, E.; Arcangeli, C.; Prisco, D.; Abbate, R.; Miniati, M.; Poli, D. Risk of recurrence in patients with pulmonary embolism: Predictive role of D-dimer and of residual perfusion defects on lung scintigraphy. Thromb. Haemost. 2013, 109, 181–186. [Google Scholar]
- Valerio, L.; Mavromanoli, A.C.; Barco, S.; Abele, C.; Becker, D.; Bruch, L.; Ewert, R.; Faehling, M.; Fistera, D.; Gerhardt, F.; et al. Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension and impairment after pulmonary embolism: The FOCUS study. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 3387–3398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranda, C.; Gonzalez, P.; Gagliardi, L.; Peralta, L.; Jimenez, A. Prognostic factors of clot resolution on follow-up computed tomography angiography and recurrence after a first acute pulmonary embolism. Clin. Respir. J. 2021, 15, 949–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahn, S.R.; Hirsch, A.M.; Akaberi, A.; Hernandez, P.; Anderson, D.R.; Wells, P.S.; Rodger, M.A.; Solymoss, S.; Kovacs, M.J.; Rudski, L.; et al. Functional and Exercise Limitations After a First Episode of Pulmonary Embolism: Results of the ELOPE Prospective Cohort Study. Chest 2017, 151, 1058–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, T.; Rodger, M.; Zeng, W.; Robin, P.; Righini, M.; Kovacs, M.J.; Tan, M.; Carrier, M.; Kahn, S.R.; Wells, P.S.; et al. Residual pulmonary embolism as a predictor for recurrence after a first unprovoked episode: Results from the REVERSE cohort study. Thromb. Res. 2018, 162, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guérin, L.; Couturaud, F.; Parent, F.; Revel, M.P.; Gillaizeau, F.; Planquette, B.; Pontal, D.; Guégan, M.; Simonneau, G.; Meyer, G.; et al. Prevalence of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension after acute pulmonary embolism. Prevalence of CTEPH after pulmonary embolism. Thromb. Haemost. 2014, 112, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruggiero, A.; Screaton, N.J. Imaging of acute and chronic thromboembolic disease: State of the art. Clin. Radiol. 2017, 72, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muscogiuri, E.; De Wever, W.; Gopalan, D. Multimodality imaging of acute and chronic pulmonary thromboembolic disease. Breathe 2024, 20, 230130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- McCabe, C.; Dimopoulos, K.; Pitcher, A.; Orchard, E.; Price, L.C.; Kempny, A.; Wort, S.J. Chronic thromboembolic disease following pulmonary embolism: Time for a fresh look at old clot. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1901934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, Y.; Adachi, S.; Nishiyama, I.; Yasuda, K.; Imai, R.; Yoshida, M.; Iwano, S.; Kondo, T.; Murohara, T. Usefulness of a refined computed tomography imaging method to assess the prevalence of residual pulmonary thrombi in patients 1 year after acute pulmonary embolism: The Nagoya PE study. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2022, 20, 888–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Huisman, M.V.; Klok, F.A. Current challenges in diagnostic imaging of venous thromboembolism. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2015, 2015, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delcroix, M.; Torbicki, A.; Gopalan, D.; Sitbon, O.; Klok, F.A.; Lang, I.; Jenkins, D.; Kim, N.H.; Humbert, M.; Jais, X.; et al. ERS statement on chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 57, 2002828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacs, G.; Bartolome, S.; Denton, C.P.; Gatzoulis, M.A.; Gu, S.; Khanna, D.; Badesch, D.; Montani, D. Definition, classification and diagnosis of pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2024, 64, 2401324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kim, N.H.; D’Armini, A.M.; Delcroix, M.; Jaïs, X.; Jevnikar, M.; Madani, M.M.; Matsubara, H.; Palazzini, M.; Wiedenroth, C.B.; Simonneau, G.; et al. Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2024, 64, 2401294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Modarai, B.; Burnand, K.G.; Humphries, J.; Waltham, M.; Smith, A. The role of neovascularisation in the resolution of venous thrombus. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 93, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Johnson, T.A.; Duru, N.; Buzza, M.S.; Pawar, N.R.; Sarkar, R.; Antalis, T.M. Fibrinolysis and Inflammation in Venous Thrombus Resolution. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Grau, E.; Moroz, L.A. Fibrinolytic activity of normal human blood monocytes. Thromb. Res. 1989, 53, 145–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altmann, J.; Sharma, S.; Lang, I.M. Advances in our understanding of mechanisms of venous thrombus resolution. Expert. Rev. Hematol. 2016, 9, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagenvoort, C.A. Pathology of pulmonary thromboembolism. Chest 1995, 107, 10S–17S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kearon, C.; Akl, E.A. Duration of anticoagulant therapy for deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Blood 2014, 123, 1794–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, T.A. Why acute pulmonary embolism becomes chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: Clinical and genetic insights. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2013, 19, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpov, A.A.; Vaulina, D.D.; Smirnov, S.S.; Moiseeva, O.M.; Galagudza, M.M. Rodent models of pulmonary embolism and chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mansueto, G.; Costa, D.; Capasso, E.; Varavallo, F.; Brunitto, G.; Caserta, R.; Esposito, S.; Niola, M.; Sardu, C.; Marfella, R.; et al. The dating of thrombus organization in cases of pulmonary embolism: An autopsy study. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2019, 19, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lang, I.M.; Pesavento, R.; Bonderman, D.; Yuan, J.X. Risk factors and basic mechanisms of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: A current understanding. Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 41, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sista, A.K.; Klok, F.A. Late outcomes of pulmonary embolism: The post-PE syndrome. Thromb. Res. 2018, 164, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miniati, M.; Monti, S.; Bottai, M.; Scoscia, E.; Bauleo, C.; Tonelli, L.; Dainelli, A.; Giuntini, C. Survival and restoration of pulmonary perfusion in a long-term follow-up of patients after acute pulmonary embolism. Medicine 2006, 85, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosmi, B.; Nijkeuter, M.; Valentino, M.; Huisman, M.V.; Barozzi, L.; Palareti, G. Residual emboli on lung perfusion scan or multidetector computed tomography after a first episode of acute pulmonary embolism. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2011, 6, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planquette, B.; Ferré, A.; Peron, J.; Vial-Dupuy, A.; Pastre, J.; Mourin, G.; Emmerich, J.; Collignon, M.-A.; Meyer, G.; Sanchez, O. Residual pulmonary vascular obstruction and recurrence after acute pulmonary embolism. A single center cohort study. Thromb. Res. 2016, 148, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, K.A.; Kahn, S.R.; Akaberi, A.; Dennie, C.; Rush, C.; Granton, J.T.; Anderson, D.; Wells, P.S.; Rodger, M.A.; Solymoss, S.; et al. Serial imaging after pulmonary embolism and correlation with functional limitation at 12 months: Results of the ELOPE study. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 2, 670–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jervan, Ø.; Dhayyat, A.; Gleditsch, J.; Haukeland-Parker, S.; Tavoly, M.; Klok, F.A.; Rashid, D.; Stavem, K.; Ghanima, W.; Steine, K. Demographic, clinical, and echocardiographic factors associated with residual perfusion defects beyond six months after pulmonary embolism. Thromb. Res. 2023, 229, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The PIOPED Investigators. Value of the ventilation/perfusion scan in acute pulmonary embolism. Results of the prospective investigation of pulmonary embolism diagnosis (PIOPED). JAMA 1990, 263, 2753–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, S.M.; Woller, S.C.; Kreuziger, L.B.; Bounameaux, H.; Doerschug, K.; Geersing, G.J.; Huisman, M.V.; Kearon, C.; King, C.S.; Knighton, A.J.; et al. Antithrombotic Therapy for VTE Disease: Second Update of the CHEST Guideline and Expert Panel Report. Chest 2021, 160, e545–e608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng158 (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- Sardar, P.; Chatterjee, S.; Mukherjee, D. Efficacy and safety of new oral anticoagulants for extended treatment of venous thromboembolism: Systematic review and meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials. Drugs 2013, 73, 1171–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weitz, J.I.; Lensing, A.W.; Prins, M.H.; Bauersachs, R.; Beyer-Westendorf, J.; Bounameaux, H.; Brighton, T.A.; Cohen, A.T.; Davidson, B.L.; Decousus, H.; et al. Rivaroxaban or Aspirin for Extended Treatment of Venous Thromboembolism. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1211–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agnelli, G.; Buller, H.R.; Cohen, A.; Curto, M.; Gallus, A.S.; Johnson, M.; Porcari, A.; Raskob, G.E.; Weitz, J.I.; AMPLIFY-EXT Investigators. Apixaban for extended treatment of venous thromboembolism. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Es, N.; Coppens, M.; Schulman, S.; Middeldorp, S.; Büller, H.R. Direct oral anticoagulants compared with vitamin K antagonists for acute venous thromboembolism: Evidence from phase 3 trials. Blood 2014, 124, 1968–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marik, P.E.; Cavallazzi, R. Extended Anticoagulant and Aspirin Treatment for the Secondary Prevention of Thromboembolic Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bradbury, C.; Fletcher, K.; Sun, Y.; Heneghan, C.; Gardiner, C.; Roalfe, A.; Hardy, P.; McCahon, D.; Heritage, G.; Shackleford, H.; et al. A randomised controlled trial of extended anticoagulation treatment versus standard treatment for the prevention of recurrent venous thromboembolism (VTE) and post-thrombotic syndrome in patients being treated for a first episode of unprovoked VTE (the ExACT study). Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 188, 962–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baglin, T.; Douketis, J.; Tosetto, A.; Marcucci, M.; Cushman, M.; Kyrle, P.; Palareti, G.; Poli, D.; Tait, R.C.; Iorio, A. Does the clinical presentation and extent of venous thrombosis predict likelihood and type of recurrence? A patient level metaanalysis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 8, 2436–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhadad, A.; Miniati, M.; Alhadad, H.; Gottsäter, A.; Bajc, M. The value of tomographic ventilation/perfusion scintigraphy (V/PSPECT) for follow-up and prediction of recurrence in pulmonary embolism. Thromb. Res. 2012, 130, 877–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroft, L.J.M.; Erkens, P.M.G.; Douma, R.A.; Mos, I.C.M.; Jonkers, G.; Hovens, M.M.C.; Durian, M.F.; Cate, H.T.; Beenen, L.F.M.; Kamphuisen, P.W.; et al. Prometheus Follow-Up Investigators. Thromboembolic resolution assessed by CT pulmonary angiography after treatment for acute pulmonary embolism. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 114, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becattini, C.; Giustozzi, M.; Cerdà, P.; Cimini, L.A.; Riera-Mestre, A.; Agnelli, G. Risk of recurrent venous thromboembolism after acute pulmonary embolism: Role of residual pulmonary obstruction and persistent right ventricular dysfunction. A meta-analysis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 17, 1217–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robin, P.; Le Pennec, R.; Eddy, M.; Sikora, L.; Le Roux, P.Y.; Carrier, M.; Couturaud, F.; Tromeur, C.; Planquette, B.; Sanchez, O.; et al. Residual pulmonary vascular obstruction and recurrence after acute pulmonary embolism: A systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2023, 21, 1519–1528.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barco, S.; Konstantinides, S.; Huisman, M.V.; Klok, F.A. Diagnosis of recurrent venous thromboembolism. Thromb. Res. 2018, 163, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chopard, R.; Genet, B.; Ecarnot, F.; Chatot, M.; Napporn, G.; Hyvert, A.; Didier-Petit, K.; Schiele, F.; Meneveau, N. Detection of Residual Pulmonary Vascular Obstruction by Ventilation-Perfusion Lung Scan Late After a First Pulmonary Embolism. Am. J. Cardiol. 2017, 119, 1883–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fauché, A.; Presles, E.; Sanchez, O.; Jaïs, X.; Le Mao, R.; Robin, P.; Pernod, G.; Bertoletti, L.; Jego, P.; Parent, F.; et al. Frequency and predictors for chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension after a first unprovoked pulmonary embolism: Results from PADIS studies. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2022, 20, 2850–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klok, F.A.; van der Hulle, T.; den Exter, P.L.; Lankeit, M.; Huisman, M.V.; Konstantinides, S. The post-PE syndrome: A new concept for chronic complications of pulmonary embolism. Blood Rev. 2014, 28, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharepapagh, E.; Rahimi, F.; Koohi, A.; Bakhshandeh, H.; Mousavi-Aghdas, S.A.; Sadeghipoor, P.; Fakhari, A.; Amirnia, M.; Javadrashid, R.; Rashidi, F. Clot Burden As a Predictor of Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension After Acute Pulmonary Embolism: A Cohort Study. Thorac. Res. Pract. 2023, 24, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, G.; Wen, J.; Lv, C.; Liu, M.; Li, M.; Fang, K.; Fei, J.; Zhang, N.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; et al. Development and validation of a Prediction Model for Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Disease. Respir. Res. 2024, 25, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tavoly, M.; Utne, K.K.; Jelsness-Jørgensen, L.P.; Wik, H.S.; Klok, F.A.; Sandset, P.M.; Ghanima, W. Health-related quality of life after pulmonary embolism: A cross-sectional study. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e013086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Amato, R.D.; Ramírez Martín, M.P. Prevalence and clinical predictors of persistent perfusion defects after acute pulmonary embolism. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50 (Suppl. 61), PA566. [Google Scholar]
- Jervan, Ø.; Parker, S.; Gleditsch, J.; Hansen, K.; Risberg, M.A. Health-Related Quality of Life and Physical Capacity in Patients with Residual Perfusion Defects After Pulmonary Embolism [Poster Presentation]. ISTH 2022 Congress, London, UK. 2022. Available online: https://www.eventscribe.net/2022/program/fsPopup.asp?Mode=presInfo&PresentationID=1078256 (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- Cimini, L.A.; Luijten, D.; Barco, S.; Ghanima, W.; Jervan, Ø.; Kahn, S.R.; Konstantinides, S.; Lachant, D.; Nakano, Y.; Ninaber, M.; et al. Pulmonary perfusion defects or residual vascular obstruction and persistent symptoms after pulmonary embolism: A systematic review and meta-analysis. ERJ Open Res. 2024, 10, 01010-2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]

| Year | Study | Number of Patients | Time for Assessment | Imaging Techniques | Prevalence of Residual Abnormalities | Treatment | Treatment Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2006 | Miniati et al. [39] | 235 | 1 year | Q lung scan | 34.9% | VKA (91.9%) | 1 year |
| 2010 | Sanchez et al. [9] | 254 | 6–12 months | V/Q lung scan (>10% RPVO) | 29% | VKA | 6 months (median) |
| 2011 | Cosmi et al. [40] | 173 | 9 months | Q lung scan MDCT scan | 28% 15% | VKA | 9 months (median) |
| 2013 | Poli et al. [14] | 235 | 11 months | Q lung scan | 26% | VKA | 12 months (median) Indefinite treatment time in 41% of patients |
| 2016 | Planquette et al. [41] | 321 | 9 months | V/Q lung scan | 19% | VKA | 6.5 months |
| 2017 | Pesavento et al. [8] | 647 | 6 months | Q lung scan | 50.1% | VKA | at least 6 months |
| 2018 | K.A. Ma et al. [42] | 82 73 | 1 year | MDCT Q lung scan (>0% RPVO) | 15.9% 41.1% | VKA | 5.7 (mean) |
| 2022 | Yoshihisa Nakano et al. [23] | 43 | 1 year | MDCT | 79% | DOAC | 95% of patients are still on anticoagulation at 1 year |
| 2023 | Øyvind Jervan et al. [43] | 286 | 6–72 months | V/Q scan | 25.2% | NA | 8 months (no RPVO) 9 months (with RPVO) |
| Risk for Recurrence | Risk Factors |
|---|---|
| Low (<3%) | Major transient or reversible factors (e.g., surgery with general anaesthesia for >30 min.; trauma with fractures). |
| Intermediate (3–8%) |
|
| High (>8%) | Active cancer; previous VTE in the absence of a major transient or reversible factor; antiphospholipid antibody syndrome |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pocienė, I.; Danila, E. The Aftermath of Pulmonary Embolism: Are Residual Thrombi Clinically Significant? Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15111348
Pocienė I, Danila E. The Aftermath of Pulmonary Embolism: Are Residual Thrombi Clinically Significant? Diagnostics. 2025; 15(11):1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15111348
Chicago/Turabian StylePocienė, Irina, and Edvardas Danila. 2025. "The Aftermath of Pulmonary Embolism: Are Residual Thrombi Clinically Significant?" Diagnostics 15, no. 11: 1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15111348
APA StylePocienė, I., & Danila, E. (2025). The Aftermath of Pulmonary Embolism: Are Residual Thrombi Clinically Significant? Diagnostics, 15(11), 1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15111348





