Is a 3-Minute Knee MRI Protocol Sufficient for Daily Clinical Practice? A SuperResolution Reconstruction Approach Using AI and Compressed Sensing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. MRI Acquisition
2.3. MRI Reconstruction
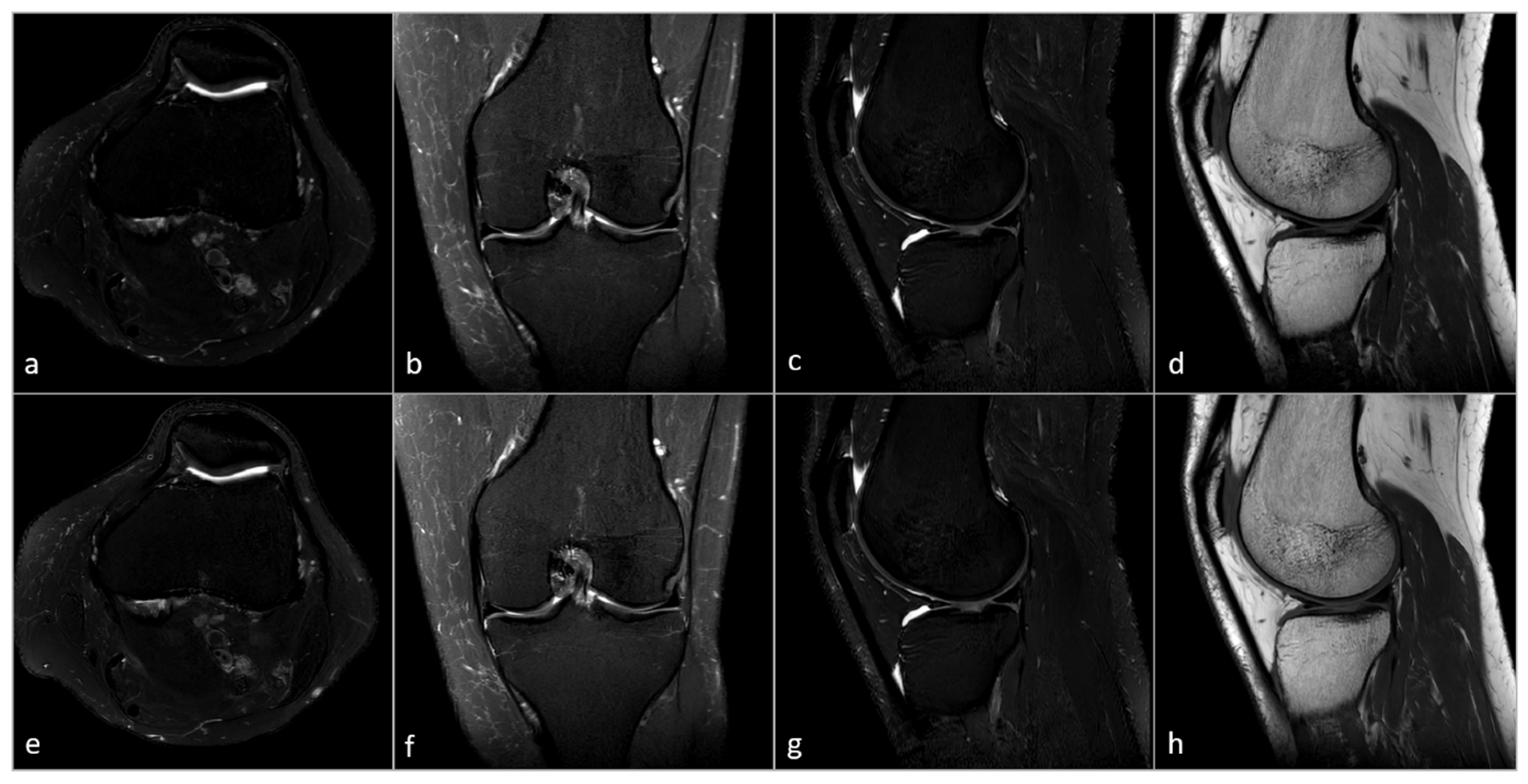
2.4. Subjective Image Analysis
2.5. Objective Image Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
3.2. MRI Acquisition
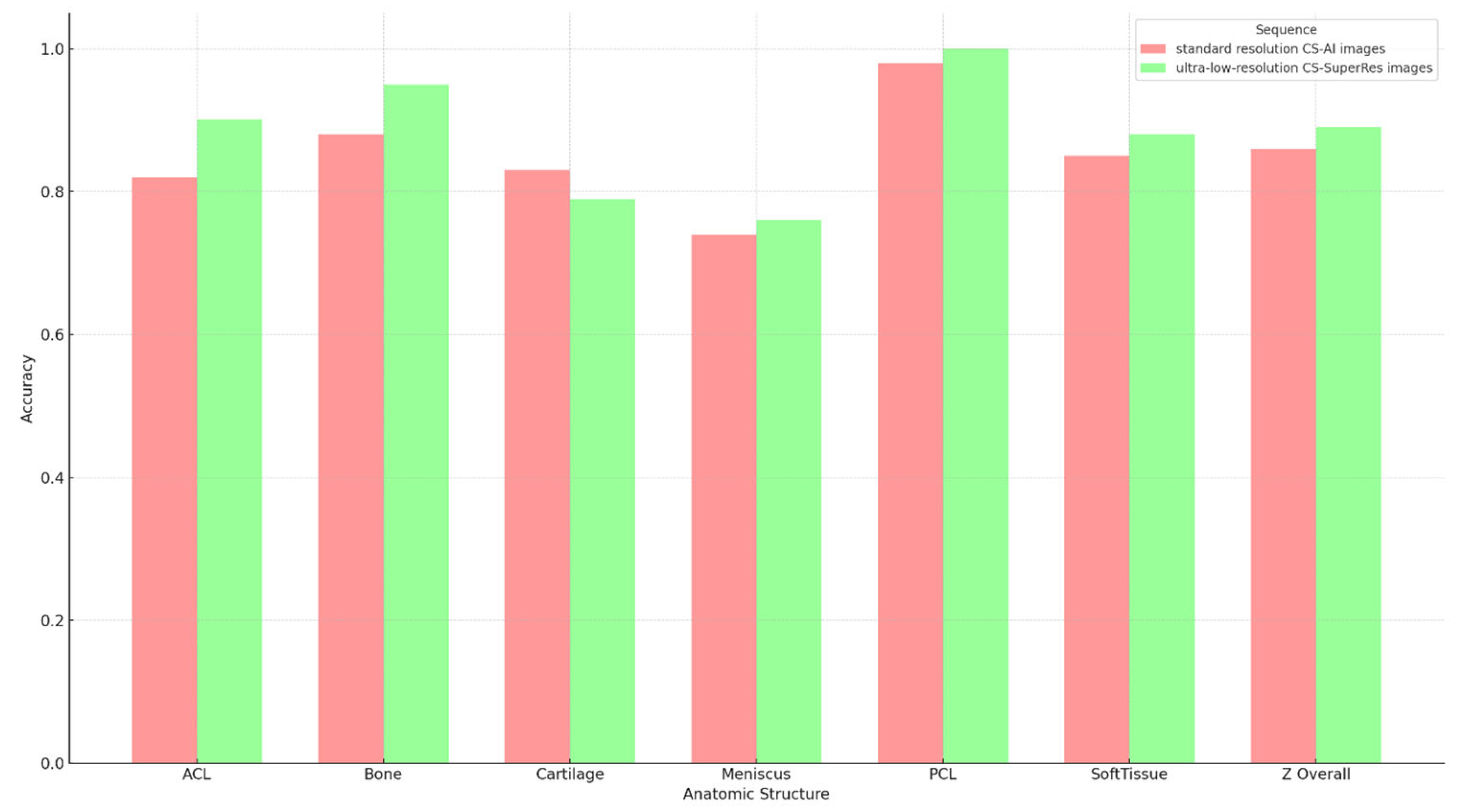
3.3. Subjective Image Analysis
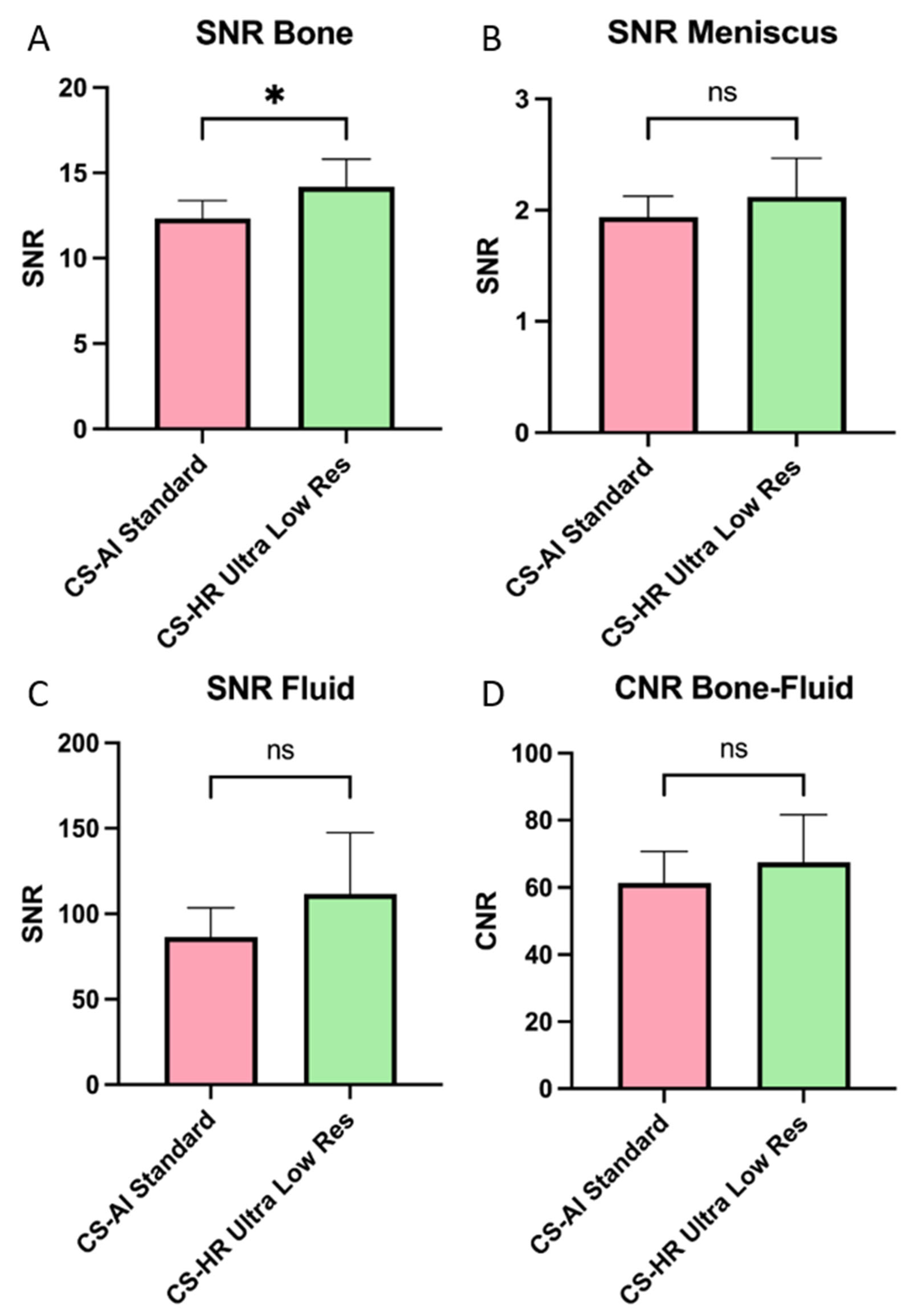
3.4. Objective Image Analysis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| CS | Compressed Sensing |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| CNN | Convolutional neural network |
| FOV | Field-of-view |
| SNR | Signal-to-noise ratio |
| CNR | Contrast-to-noise ratio |
| PD | Proton Density |
| ACL | Anterior cruciate ligament |
| PCL | Posterior cruciate ligament |
| MCL | Medial collateral ligament |
| LCL | Lateral collateral ligament |
| SI | Signal intensity |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| ROI | Region of interest |
References
- Farr, J., II; Miller, L.E.; Block, J.E. Quality of Life in Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis: A Commentary on Nonsurgical and Surgical Treatments. Open Orthop. J. 2013, 7, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartvigsen, J.; Hancock, M.J.; Kongsted, A.; Louw, Q.; Ferreira, M.L.; Genevay, S.; Hoy, D.; Karppinen, J.; Pransky, G.; Sieper, J.; et al. Low Back Pain 1 What Low Back Pain Is and Why We Need to Pay Attention. Lancet 2018, 391, 2356–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, A.; Kamper, S.J.; Wiggers, J.H.; O’brien, K.M.; Lee, H.; Wolfenden, L.; Yoong, S.L.; Robson, E.; Mcauley, J.H.; Hartvigsen, J.; et al. Musculoskeletal Conditions May Increase the Risk of Chronic Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies. BMC Med. 2018, 16, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GBD 2019 Diseases and Injuries Collaborators. Global Burden of 369 Diseases and Injuries in 204 Countries and Territories, 1990-2019: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1204–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.Q.; Covey, C.J.; Marvin, H.; Sineath, J.R. Nonsurgical Management of Knee Pain in Adults. Am. Fam. Physician 2015, 92, 875–883. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, U.S.D.T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Niu, J.; Zhang, B.; Felson, D.T. Increasing Prevalence of Knee Pain and Symptomatic Knee Osteoarthritis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2011, 155, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisternas, M.G.; Murphy, L.; Sacks, J.J.; Solomon, D.H.; Pasta, D.J.; Helmick, C.G. Alternative Methods for Defining Osteoarthritis and the Impact on Estimating Prevalence in a US Population-Based Survey. Arthritis Care Res. 2016, 68, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grobe, T.G.; Steinmann, S.; Szecsenyi, J. Psychotherapie-Veränderter Zugang, Verbesserte Versorgung? Schriftenreihe Zur Gesundheitsanalyse—Band 21; BARMER: Frankfurt, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- St Sauver, J.L.; Warner, D.O.; Yawn, B.P.; Jacobson, D.J.; Mc Gree, M.E.; Pankratz, J.J.; Joseph Melton, L., III; Roger, V.L.; Ebbert, J.O.; Rocca, W.A. Why Do Patients Visit Their Doctors? Assessing the Most Prevalent Conditions in a Defined US Population. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2013, 88, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariyachaipanich, A.; Bae, W.C.; Statum, S.; Chung, C.B. Update on MRI Pulse Sequences for the Knee: Imaging of Cartilage, Meniscus, Tendon, and Hardware. Semin. Musculoskelet. Radiol. 2017, 21, 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Exams. Available online: https://www.oecd.org/en/data/indicators/magnetic-resonance-imaging-mri-exams.html (accessed on 2 May 2023).
- Oztek, M.A.; Brunnquell, C.L.; Hoff, M.N.; Boulter, D.J.; Mossa-Basha, M.; Beauchamp, L.H.; Haynor, D.L.; Nguyen, X.V. Practical Considerations for Radiologists in Implementing a Patient-Friendly MRI Experience. Top. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 29, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iuga, A.I.; Abdullayev, N.; Weiss, K.; Haneder, S.; Brüggemann-Bratke, L.; Maintz, D.; Rau, R.; Bratke, G. Accelerated MRI of the Knee. Quality and Efficiency of Compressed Sensing. Eur. J. Radiol. 2020, 132, 109273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollingsworth, G.K. Reducing Acquisition Time in Clinical MRI by Data Undersampling and Compressed Sensing Reconstruction. Phys. Med. Biol. 2015, 60, R297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezzotti, N.; De Weerdt, E.; Yousefi, S.; Elmahdy, M.S.; Van Gemert, J.; Schülke, C.; Doneva, M.; Nielsen, T.; Kastryulin, S.; Lelieveldt, B.P.F.; et al. Adaptive-CS-Net: FastMRI with Adaptive Intelligence. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1912.12259. [Google Scholar]
- Pezzotti, N.; Yousefi, S.; Elmahdy, M.S.; Van Gemert, J.; Schülke, C.; Doneva, M.; Nielsen, T.; Kastryulin, S.; Lelieveldt, B.P.F.; Van Osch, M.J.P.; et al. An Adaptive Intelligence Algorithm for Undersampled Knee MRI Reconstruction. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 204825–204838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoll, F.; Murrell, T.; Sriram, A.; Yakubova, N.; Zbontar, J.; Rabbat, M.; Defazio, A.; Muckley, M.J.; Sodickson, D.K.; Zitnick, C.L.; et al. Advancing Machine Learning for MR Image Reconstruction with an Open Competition: Overview of the 2019 FastMRI Challenge. Magn. Reson. Med. 2020, 84, 3054–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Loy, C.C.; He, K.; Tang, X. Image Super-Resolution Using Deep Convolutional Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 38, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sixou, B.; Peyrin, F. A Review of the Deep Learning Methods for Medical Images Super Resolution Problems. IRBM 2020, 42, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, S.S.; Vosshenrich, J.; Cantarelli Rodrigues, T.; Dalili, D.; Fritz, B.; Kijowski, R.; Park, E.H.; Serfaty, A.; Stern, S.E.; Brinkmann, I.; et al. Deep Learning Superresolution for Simultaneous Multislice Parallel Imaging-Accelerated Knee MRI Using Arthroscopy Validation. Radiology 2025, 314, e241249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Grande, F.; Rashidi, A.; Luna, R.; Delcogliano, M.; Stern, S.E.; Dalili, D.; Fritz, J. Five-Minute Five-Sequence Knee MRI Using Combined Simultaneous Multislice and Parallel Imaging Acceleration: Comparison with 10-Minute Parallel Imaging Knee MRI. Radiology 2021, 299, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DGMSR. Empfehlungen Der Deutschen Gesellschaft Für Muskuloskelettale Radiologie (DGMSR) Zur Muskuloskelettalen MRT-Diagnostik. Available online: https://www.dgmsr.de/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/DGMSR-Protokolle-_MSK_Version1_Juli2019.pdf (accessed on 11 March 2024).
- European Society of Musculoskeletal Radiology. 2016. Available online: https://essr.org/content-essr/uploads/2016/10/ESSR-MRI-Protocols-Knee.pdf (accessed on 4 May 2023).
- Lee, S.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Suh, J.S. Accelerating Knee MR Imaging: Compressed Sensing in Isotropic Three-Dimensional Fast Spin-Echo Sequence. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2018, 40, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altahawi, F.F.; Blount, K.J.; Morley, N.P.; Raithel, E.; Omar, I.M. Comparing an Accelerated 3D Fast Spin-Echo Sequence (CS-SPACE) for Knee 3-T Magnetic Resonance Imaging with Traditional 3D Fast Spin-Echo (SPACE) and Routine 2D Sequences. Skelet. Radiol. 2017, 46, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bratke, G.; Rau, R.; Weiss, K.; Kabbasch, C.; Sircar, K.; Morelli, J.N.; Persigehl, T.; Maintz, D.; Giese, D.; Haneder, S. Accelerated MRI of the Lumbar Spine Using Compressed Sensing: Quality and Efficiency. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 49, e164–e175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Song, H.T.; Suh, J.S. Rapid Acquisition of Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Shoulder Using Three-Dimensional Fast Spin Echo Sequence with Compressed Sensing. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2017, 42, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kijowski, R.; Rosas, H.; Samsonov, A.; King, K.; Peters, R.; Liu, F. Knee Imaging: Rapid Three-Dimensional Fast Spin-Echo Using Compressed Sensing. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2017, 45, 1712–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vosshenrich, J.; Koerzdoerfer, G.; Fritz, J. Modern Acceleration in Musculoskeletal MRI: Applications, Implications, and Challenges. Skelet. Radiol. 2024, 53, 1799–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Tang, L.; Li, W.; He, S.; Yue, X.; Peng, P.; Wu, T.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Z.; He, Y.; et al. Feasibility of Accelerated Non-Contrast-Enhanced Whole-Heart BSSFP Coronary MR Angiography by Deep Learning-Constrained Compressed Sensing. Eur. Radiol. 2023, 33, 8180–8190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foreman, S.C.; Neumann, J.; Han, J.; Harrasser, N.; Weiss, K.; Peeters, J.M.; Karampinos, D.C.; Makowski, M.R.; Gersing, A.S.; Woertler, K. Deep Learning-Based Acceleration of Compressed Sense MR Imaging of the Ankle. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 29, 8376–8385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iuga, A.-I.; Rauen, P.S.; Siedek, F.; Große-Hokamp, N.; Sonnabend, K.; Maintz, D.; Lennartz, S.; Bratke, G. A Deep Learning-Based Reconstruction Approach for Accelerated Magnetic Resonance Image of the Knee with Compressed Sense: Evaluation in Healthy Volunteers. Br. J. Radiol. 2023, 96, 20220074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dratsch, T.; Zäske, C.; Siedek, F.; Rauen, P.; Hokamp, N.G.; Sonnabend, K.; Maintz, D.; Bratke, G.; Iuga, A. Reconstruction of 3D Knee MRI Using Deep Learning and Compressed Sensing: A Validation Study on Healthy Volunteers. Eur. Radiol. Exp. 2024, 8, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fervers, P.; Zaeske, C.; Rauen, P.; Iuga, A.I.; Kottlors, J.; Persigehl, T.; Sonnabend, K.; Weiss, K.; Bratke, G. Conventional and Deep-Learning-Based Image Reconstructions of Undersampled K-Space Data of the Lumbar Spine Using Compressed Sensing in MRI: A Comparative Study on 20 Subjects. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dratsch, T.; Siedek, F.; Zäske, C.; Sonnabend, K.; Rauen, P.; Terzis, R.; Hahnfeldt, R.; Maintz, D.; Persigehl, T.; Bratke, G.; et al. Reconstruction of Shoulder MRI Using Deep Learning and Compressed Sensing: A Validation Study on Healthy Volunteers. Eur. Radiol. Exp. 2023, 7, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, S.; Yi, J.; Lee, H.-J.; Lee, Y.; Lee, J.; Wang, X.; Fung, M.; Fung MaggieFung, M. Comparison of Deep Learning-Based Reconstruction of PROPELLER Shoulder MRI with Conventional Reconstruction. Skelet. Radiol. 2023, 52, 1545–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, A.; Finkelstein, M.; Koo, C.; Doshi, A.H. Impact of Deep Learning Image Reconstruction Methods on MRI Throughput. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 2024, 6, e230181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartoretti, E.; Sartoretti, T.; Binkert, C.; Najafi, A.; Schwenk, Á.; Hinnen, M.; Van Smoorenburg, L.; Eichenberger, B.; Sartoretti-Schefer, S. Reduction of Procedure Times in Routine Clinical Practice with Compressed SENSE Magnetic Resonance Imaging Technique. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Recht, M.P.; Block, K.T.; Chandarana, H.; Friedland, J.; Mullholland, T.; Teahan, D.; Wiggins, R. Optimization of MRI Turnaround Times Through the Use of Dockable Tables and Innovative Architectural Design Strategies. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2019, 212, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Li, C.; Zou, J.; Liu, X.; Zheng, H.; Wang, S. Generalizable Reconstruction for Accelerating MR Imaging via Federated Learning With Neural Architecture Search. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2025, 44, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obuchowicz, R.; Piórkowski, A.; Urbanik, A.; Strzelecki, M. Influence of Acquisition Time on MR Image Quality Estimated with Nonparametric Measures Based on Texture Features. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 3706581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vosshenrich, J.; Breit, H.-C.; Donners, R.; Obmann, M.M.; Walter, S.S.; Serfaty, A.; Rodrigues, T.C.; Recht, M.; Stern, S.E.; Fritz, J. Clinical Implementation of Sixfold-Accelerated Deep Learning Super-Resolution Knee MRI in Under 5 Minutes: Arthroscopy-Validated Diagnostic Performance. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| PD SPAIR | T1 TSE | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coronal | Transversal | Sagittal | Sagittal | |||||
| Sequence | Standard | Ultra-Low Resolution | Standard | Ultra-Low Resolution | Standard | Ultra-Low Resolution | Standard | Ultra-Low Resolution |
| Echo time [ms] | 45 | 45 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 12 | 12 |
| Repetition time [ms] | 2618 | 2248 | 3105 | 2840 | 2673 | 2104 | 724 | 823 |
| Flip angle [deg.] | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 |
| Field of view [mm] | 160 × 160 | 160 × 160 | 150 × 150 | 150 × 150 | 160 × 160 | 160 × 160 | 160 × 160 | 160 × 160 |
| Slice thickness [mm] | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Number of slices | 27 | 27 | 36 | 36 | 27 | 27 | 30 | 30 |
| Gap [mm] | 3.3 | 3.3 | 3.3 | 3.3 | 3.3 | 3.3 | 3.3 | 3.3 |
| Acquisition voxel size [mm] | 0.38 × 0.55 | 0.6 × 0.8 | 0.38 × 0.53 | 0.55 × 0.69 | 0.38 × 0.51 | 0.65 × 0.85 | 0.3 × 0.43 | 0.55 × 0.75 |
| Reconstruction voxel size [mm] | 0.22 × 0.22 | 0.22× 0.22 | 0.22 × 0.22 | 0.22 × 0.22 | 0.22 × 0.22 | 0.22 × 0.22 | 0.22 × 0.22 | 0.23 × 0.23 |
| Turbo factor/Echo train length | 15 | 16 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 7 | 7 |
| CS-AI factor | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Scan time [s] | 178 | 54 | 230 | 79 | 160 | 42 | 93 | 41 |
| Saved scan time [s] | 0 | 124 | 0 | 151 | 0 | 118 | 0 | 52 |
| Scan time reduction [%] | 0 | 69.6 | 0 | 65.6 | 0 | 73.4 | 0 | 55.9 |
| Anatomic Structure | Accuracy A | Sensitivity A | Specificity A | Accuracy B | Sensitivity B | Specificity B | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACL | 0.825 | NA | 0.825 | 0.9 | NA | 0.9 | 0.170 |
| Bone | 0.875 | 0.75 | 0.906 | 0.95 | 0.813 | 0.984 | 0.099 |
| Cartilage | 0.825 | 0.75 | 0.844 | 0.788 | 0.688 | 0.813 | 0.610 |
| Meniscus | 0.7375 | 0 | 0.776 | 0.763 | 0 | 0.803 | 0.702 |
| PCL | 0.975 | NA | 0.975 | 0.988 | NA | 0.988 | 0.563 |
| Soft Tissue | 0.838 | 0.5 | 0.855 | 0.863 | 0 | 0.908 | 0.431 |
| Overall | 0.846 | 0.65 | 0.864 | 0.875 | 0.6 | 0.9 | 0.130 |
| Anatomic Structure | A (True Positive/Total Number of Pathologies | B (True Positive/Total Number of Pathologies |
|---|---|---|
| Bone | 12/16 | 13/16 |
| Cartilage | 12/16 | 11/16 |
| Meniscus | 0/4 | 0/4 |
| Soft tissue | 2/4 | 0/4 |
| Total | 26/40 | 24/40 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hahnfeldt, R.; Terzis, R.; Dratsch, T.; Basten, L.M.; Rauen, P.; Oppermann, J.; Grevenstein, D.; Janßen, J.P.; Zeid, N.E.-H.A.; Sonnabend, K.; et al. Is a 3-Minute Knee MRI Protocol Sufficient for Daily Clinical Practice? A SuperResolution Reconstruction Approach Using AI and Compressed Sensing. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1206. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15101206
Hahnfeldt R, Terzis R, Dratsch T, Basten LM, Rauen P, Oppermann J, Grevenstein D, Janßen JP, Zeid NE-HA, Sonnabend K, et al. Is a 3-Minute Knee MRI Protocol Sufficient for Daily Clinical Practice? A SuperResolution Reconstruction Approach Using AI and Compressed Sensing. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(10):1206. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15101206
Chicago/Turabian StyleHahnfeldt, Robert, Robert Terzis, Thomas Dratsch, Lajos Maximilian Basten, Philip Rauen, Johannes Oppermann, David Grevenstein, Jan Paul Janßen, Nour El-Hoda Abou Zeid, Kristina Sonnabend, and et al. 2025. "Is a 3-Minute Knee MRI Protocol Sufficient for Daily Clinical Practice? A SuperResolution Reconstruction Approach Using AI and Compressed Sensing" Diagnostics 15, no. 10: 1206. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15101206
APA StyleHahnfeldt, R., Terzis, R., Dratsch, T., Basten, L. M., Rauen, P., Oppermann, J., Grevenstein, D., Janßen, J. P., Zeid, N. E.-H. A., Sonnabend, K., Katemann, C., Skornitzke, S., Maintz, D., Kottlors, J., Bratke, G., & Iuga, A.-I. (2025). Is a 3-Minute Knee MRI Protocol Sufficient for Daily Clinical Practice? A SuperResolution Reconstruction Approach Using AI and Compressed Sensing. Diagnostics, 15(10), 1206. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15101206








