Comparing the Carpal Tunnel Area and Carpal Boundaries in Patients with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Healthy Volunteers: A Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MN | Median nerve |
| CTS | Carpal tunnel syndrome |
| MICB | Most interior carpal boundary |
| ICB | Interior carpal boundary |
| ECB | Exterior carpal boundary |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
References
- Jarvik, J.G.; Kliot, M.; Maravilla, K.R. MR nerve imaging of the wrist and hand. Hand Clin. 2000, 16, 13–24, vii. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radack, D.M.; Schweitzer, M.E.; Taras, J. Carpal tunnel syndrome: Are the MR findings a result of population selection bias? AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1997, 169, 1649–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsujii, M.; Hirata, H.; Morita, A.; Uchida, A. Palmar bowing of the flexor retinaculum on wrist MRI correlates with subjective reports of pain in carpal tunnel syndrome. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2009, 29, 1102–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, A.W.H.; Griffith, J.F.; Tong, C.S.L.; Law, E.K.C.; Tse, W.L.; Wong, C.W.Y.; Ho, P.C. MRI criteria for diagnosis and predicting severity of carpal tunnel syndrome. Skeletal Radiol. 2020, 49, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Bai, Q.; Hu, X.; Alhaskawi, A.; Dong, Y.; Wang, Z.; Qi, B.; Fang, J.; Kota, V.G.; Abdulla, M.; et al. Deep CTS: A Deep Neural Network for Identification MRI of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. J. Digit. Imaging 2022, 35, 1433–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singla, M.; Sharma, M.K.; Khurana, D.; Lal, V. Role of High Frequency Ultrasound in Diagnosing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome as Compared with Conventional Nerve Conduction Studies. Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol. 2020, 23, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, T.T.; Lee, M.R.; Liao, Y.Y.; Chen, J.P.; Hsu, Y.W.; Yeh, C.K. Assessment of Median Nerve Mobility by Ultrasound Dynamic Imaging for Diagnosing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasundra, G.M.; Sood, I.; Bhargava, A.N.; Bhushan, B.; Rana, K.; Jangid, H.; Shubhkaran, K.; Pujar, G.S. Carpal tunnel syndrome: Analyzing efficacy and utility of clinical tests and various diagnostic modalities. J. Neurosci. Rural Pract. 2015, 6, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, J.G.; Han, J.K.; Im, S.B.; Kang, S.J. Median nerve T2 assessment in the wrist joints: Preliminary study in patients with carpal tunnel syndrome and healthy volunteers. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2014, 40, 789–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleindienst, A.; Hamm, B.; Lanksch, W.R. Carpal tunnel syndrome: Staging of median nerve compression by MR imaging. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 1998, 8, 1119–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboonq, M.S. Pathophysiology of carpal tunnel syndrome. Neurosciences 2015, 20, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Cho, H.R.; Yoo, J.S.; Kim, Y.U. The prognostic value of median nerve thickness in diagnosing carpal tunnel syndrome using magnetic resonance imaging: A pilot study. Korean J. Pain 2020, 33, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saggar, S.K.; Thaman, R.G.; Mohan, G.; Kumar, D. Mapping Neurophysiological Patterns in Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Correlations With Tinel’s and Phalen’s Signs. Cureus 2024, 16, e58168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padua, L.; Padua, R.; Aprile, I.; D’Amico, P.; Tonali, P. Carpal tunnel syndrome: Relationship between clinical and patient-oriented assessment. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2002, 395, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okura, T.; Sekimoto, T.; Matsuoka, T.; Fukuda, H.; Hamada, H.; Tajima, T.; Chosa, E. Efficacy of Diagnosing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Using the Median Nerve Stenosis Rate Measured on Ultrasonographic Sagittal Imagery: Clinical Case-Control Study. Hand 2023, 18, 133s–138s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.T.; Williams, L.; Zak, M.J.; Fredericson, M. Review of Ultrasonography in the Diagnosis of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and a Proposed Scanning Protocol. J. Ultrasound Med. 2016, 35, 2311–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visser, L.H.; Smidt, M.H.; Lee, M.L. High-resolution sonography versus EMG in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2008, 79, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filius, A.; Thoreson, A.R.; Wang, Y.; Passe, S.M.; Zhao, C.; An, K.N.; Amadio, P.C. The effect of tendon excursion velocity on longitudinal median nerve displacement: Differences between carpal tunnel syndrome patients and controls. J. Orthop. Res. 2015, 33, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olde Dubbelink, T.B.G.; De Kleermaeker, F.; Beekman, R.; Wijntjes, J.; Bartels, R.; Meulstee, J.; Verhagen, W.I.M. Wrist Circumference-Dependent Upper Limit of Normal for the Cross-Sectional Area Is Superior Over a Fixed Cut-Off Value in Confirming the Clinical Diagnosis of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 625565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olde Dubbelink, T.B.G.; De Kleermaeker, F.; Meulstee, J.; Bartels, R.; Claes, F.; Verhagen, W.I.M. Augmented Diagnostic Accuracy of Ultrasonography for Diagnosing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Using an Optimised Wrist Circumference-Dependent Cross-Sectional Area Equation. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 577052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, M.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, H.S. The usefulness of ultrasonography to diagnose the early stage of carpal tunnel syndrome in proximal to the carpal tunnel inlet: A prospective study. Medicine 2019, 98, e16039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goedee, H.S.; Herraets, I.J.T.; Visser, L.H.; Franssen, H.; van Asseldonk, J.H.; van der Pol, W.L.; van den Berg, L.H. Nerve ultrasound can identify treatment-responsive chronic neuropathies without electrodiagnostic features of demyelination. Muscle Nerve 2019, 60, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Rehemutula, A.; Peng, F.; Yu, C.; Wang, T.B.; Chen, L. Does the ratio of the carpal tunnel inlet and outlet cross-sectional areas in the median nerve reflect carpal tunnel syndrome severity? Neural Regen. Res. 2015, 10, 1172–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchberger, W.; Judmaier, W.; Birbamer, G.; Lener, M.; Schmidauer, C. Carpal tunnel syndrome: Diagnosis with high-resolution sonography. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1992, 159, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.S.; Joo, S.H.; Cho, H.K.; Kim, Y.W. Comparison of proximal and distal cross-sectional areas of the median nerve, carpal tunnel, and nerve/tunnel index in subjects with carpal tunnel syndrome. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2013, 94, 2151–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekel, S.; Coates, R. Primary carpal stenosis as a cause of “idiopathic” carpal-tunnel syndrome. Lancet 1979, 2, 1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassi, S.A.; Giddins, G. Gender differences in carpal tunnel relative cross-sectional area: A possible causative factor in idiopathic carpal tunnel syndrome. J. Hand Surg. Eur. Vol. 2016, 41, 638–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsaman, A.M.; Thabit, M.N.; Radwan, A.R.; Ohrndorf, S. Idiopathic Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Evaluation of the Depth of the Carpal Tunnel by Ultrasonography. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2015, 41, 2827–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, A.; Sdoudi, A.; Chahed, M.; Elbaitil, A.; Fakherdine, L.; Sbihi, Y.; Bennouna, D.; Fadili, M. Carpal tunnel syndrome secondary to a rare anatomical variation of the median nerve. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2018, 31, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gniadek, M.; Trybus, M. Carpal tunnel syndrome- etiology and treatment. Przegl Lek. 2016, 73, 520–524. [Google Scholar]
- Gabra, J.N.; Li, Z.M. Carpal Tunnel Cross-Sectional Area Affected by Soft Tissues Abutting the Carpal Bones. J. Wrist Surg. 2013, 2, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.M.; Jordan, D.B. Carpal tunnel mechanics and its relevance to carpal tunnel syndrome. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2023, 87, 103044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabra, J.N.; Kim, D.H.; Li, Z.M. Elliptical Morphology of the Carpal Tunnel Cross Section. Eur. J. Anat. 2015, 19, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oh, S. Trigger Wrist with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Accompanied with Trifid Median Nerve: A Case Report and Literature Review. Arch. Plast. Surg. 2022, 49, 750–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dekel, S.; Papaioannou, T.; Rushworth, G.; Coates, R. Idiopathic carpal tunnel syndrome caused by carpal stenosis. Br. Med. J. 1980, 280, 1297–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winn, F.J., Jr.; Habes, D.J. Carpal tunnel area as a risk factor for carpal tunnel syndrome. Muscle Nerve 1990, 13, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horng, Y.S.; Chang, H.C.; Lin, K.E.; Guo, Y.L.; Liu, D.H.; Wang, J.D. Accuracy of ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosing carpal tunnel syndrome using rest and grasp positions of the hands. J. Hand Surg. Am. 2012, 37, 1591–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogk, J.P.; Keir, P.J. Evaluation of the carpal tunnel based on 3-D reconstruction from MRI. J. Biomech. 2007, 40, 2222–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasternack, I.I.; Malmivaara, A.; Tervahartiala, P.; Forsberg, H.; Vehmas, T. Magnetic resonance imaging findings in respect to carpal tunnel syndrome. Scand. J. Work. Environ. Health 2003, 29, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, O.M.; Sears, E.D. The Impact of Reference Standard on Diagnostic Testing Characteristics for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Systematic Review. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2023, 11, e5067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabra, J.N.; Gordon, J.L.; Marquardt, T.L.; Li, Z.M. In vivo tissue interaction between the transverse carpal ligament and finger flexor tendons. Med. Eng. Phys. 2016, 38, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersh, B.; D’Auria, J.; Scott, M.; Fowler, J.R. A Comparison of Ultrasound and MRI Measurements of the Cross-Sectional Area of the Median Nerve at the Wrist. Hand 2019, 14, 746–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.T.; Liu, D.H.; Chen, C.J.; Wang, Y.W.; Wu, P.S.; Horng, Y.S. Effects of wrist extension on median nerve and flexor tendon excursions in patients with carpal tunnel syndrome: A case control study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2021, 22, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chhabra, A.; Duarte Silva, F.; Mogharrabi, B.; Guirguis, M.; Ashikyan, O.; Rasper, M.; Park, E.; Walter, S.S.; Umpierrez, M.; Pezeshk, P.; et al. MRI-based Neuropathy Score Reporting And Data System (NS-RADS): Multi-institutional wider-experience usability study of peripheral neuropathy conditions among 32 radiology readers. Eur. Radiol. 2024, 34, 5228–5238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.W.; Hsieh, T.C.; Tzeng, I.S.; Chiu, V.; Huang, P.J.; Horng, Y.S. Ratio and difference of the cross-sectional area of median nerve to ulnar nerve in diagnosing carpal tunnel syndrome: A case control study. BMC Med. Imaging 2019, 19, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Zou, X.; Xia, Y.; Hu, Y.; Chen, C.; Zheng, P. B-Mode ultrasound imaging in diagnosing carpal tunnel syndrome: An auxiliary diagnostic tool for hand surgeons. Front. Neurol. 2024, 15, 1325464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva Filho, H.R.; Elias, B.A.B.; Salomão Junior, M.S.B.; Paiva, V.G.N.; Oliveira, E.F.; Rocha, M.A. Is there an association between electroneuromyography and ultrasound in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome? Rev. Bras. Ortop. 2021, 56, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.W.; Chen, C.J.; Wang, Y.W.; Chiu, V.; Lin, S.K.; Horng, Y.S. Influence of temperature on sonographic images of the median nerve for the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome: A case control study. BMC Med. Imaging 2021, 21, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bland, J.D. A neurophysiological grading scale for carpal tunnel syndrome. Muscle Nerve 2000, 23, 1280–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchberger, W. Radiologic imaging of the carpal tunnel. Eur. J. Radiol. 1997, 25, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monagle, K.; Dai, G.; Chu, A.; Burnham, R.S.; Snyder, R.E. Quantitative MR imaging of carpal tunnel syndrome. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1999, 172, 1581–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleecker, M.L. Medical surveillance for carpal tunnel syndrome in workers. J. Hand Surg. Am. 1987, 12, 845–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Öten, E.; Uğur, L. 3D volumetric evaluation of the diagnosis and severity of carpal tunnel syndrome using MRI. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2022, 97, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.S.; Won, H.C.; Oh, J.Y.; Kim, D.H.; Hwang, S.C.; Yoo, J.I. Value of cross-sectional area of median nerve by MRI in carpal tunnel syndrome. Asian J. Surg. 2020, 43, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchiyama, S.; Itsubo, T.; Yasutomi, T.; Nakagawa, H.; Kamimura, M.; Kato, H. Quantitative MRI of the wrist and nerve conduction studies in patients with idiopathic carpal tunnel syndrome. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2005, 76, 1103–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tullie, S.; Wiberg, A.; Furniss, D.; Schmid, A. T2-weighted MRI defines critical compression in the distal carpal tunnel that is relieved after decompressive surgery. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2022, 75, 2251–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouyoumdjian, J.A.; Zanetta, D.M.; Morita, M.P. Evaluation of age, body mass index, and wrist index as risk factors for carpal tunnel syndrome severity. Muscle Nerve 2002, 25, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boz, C.; Ozmenoglu, M.; Altunayoglu, V.; Velioglu, S.; Alioglu, Z. Individual risk factors for carpal tunnel syndrome: An evaluation of body mass index, wrist index and hand anthropometric measurements. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2004, 106, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trybus, M.; Stepańczak, B.; Koziej, M.; Gniadek, M.; Kołodziej, M.; Hołda, M.K. Hand anthropometry in patients with carpal tunnel syndrome: A case-control study with a matched control group of healthy volunteers. Folia Morphol. 2019, 78, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiese, M.S.; Merryweather, A.; Koric, A.; Ott, U.; Wood, E.M.; Kapellusch, J.; Foster, J.; Garg, A.; Deckow-Schaefer, G.; Tomich, S.; et al. Association between wrist ratio and carpal tunnel syndrome: Effect modification by body mass index. Muscle Nerve 2017, 56, 1047–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neral, M.; Winger, D.; Imbriglia, J.; Wollstein, R. Hand Shape and Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. Curr. Rheumatol. Rev. 2016, 12, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiotis, K.; Dimisianos, N.; Rigopoulou, A.; Chrysanthopoulou, A.; Chroni, E. Role of anthropometric characteristics in idiopathic carpal tunnel syndrome. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2013, 94, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarvik, J.G.; Yuen, E.; Haynor, D.R.; Bradley, C.M.; Fulton-Kehoe, D.; Smith-Weller, T.; Wu, R.; Kliot, M.; Kraft, G.; Wang, L.; et al. MR nerve imaging in a prospective cohort of patients with suspected carpal tunnel syndrome. Neurology 2002, 58, 1597–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghtaderi, A.; Izadi, S.; Sharafadinzadeh, N. An evaluation of gender, body mass index, wrist circumference and wrist ratio as independent risk factors for carpal tunnel syndrome. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2005, 112, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.T.; Huang, Y.T.; Chiu, V.; Chang, Y.W.; Horng, Y.S. Diagnostic meta-analysis of the efficacy of ultrasonography for diagnosing carpal tunnel syndrome: A comparison between Asian and non-Asian populations. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onen, M.R.; Kayalar, A.E.; Ilbas, E.N.; Gokcan, R.; Gulec, I.; Naderi, S. The Role of Wrist Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Differential Diagnosis of the Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. Turk. Neurosurg. 2015, 25, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacotte, B.; Pierre-Jérôme, C.; Coessens, B.; Shahabpour, M.; Durdu, J. Carpal tunnel syndrome. Comparative studies of pre- and postoperative magnetic resonance and electromyography. Ann. Chir. Main. Memb. Super. 1991, 10, 300–307. [Google Scholar]
- Musluoğlu, L.; Celik, M.; Tabak, H.; Forta, H. Clinical, electrophysiological and magnetic resonance imaging findings in carpal tunnel syndrome. Electromyogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2004, 44, 161–165. [Google Scholar]
- Crnković, T.; Trkulja, V.; Bilić, R.; Gašpar, D.; Kolundžić, R. Carpal tunnel and median nerve volume changes after tunnel release in patients with the carpal tunnel syndrome: A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) study. Int. Orthop. 2016, 40, 981–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göktürk, Ş.; Göktürk, Y.; Koç, A.; Payas, A. Comparison of median nerve area measurement between MRI and electromyography in patients diagnosed with carpal tunnel syndrome. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2024, 34, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigham, L.R.; Mansouri, M.; Abujudeh, H.H. JOURNAL CLUB: Radiology Report Addenda: A Self-Report Approach to Error Identification, Quantification, and Classification. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2015, 205, 1230–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itri, J.N.; Tappouni, R.R.; McEachern, R.O.; Pesch, A.J.; Patel, S.H. Fundamentals of Diagnostic Error in Imaging. Radiographics 2018, 38, 1845–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richman, J.A.; Gelberman, R.H.; Rydevik, B.L.; Gylys-Morin, V.M.; Hajek, P.C.; Sartoris, D.J. Carpal tunnel volume determination by magnetic resonance imaging three-dimensional reconstruction. J. Hand Surg. Am. 1987, 12, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
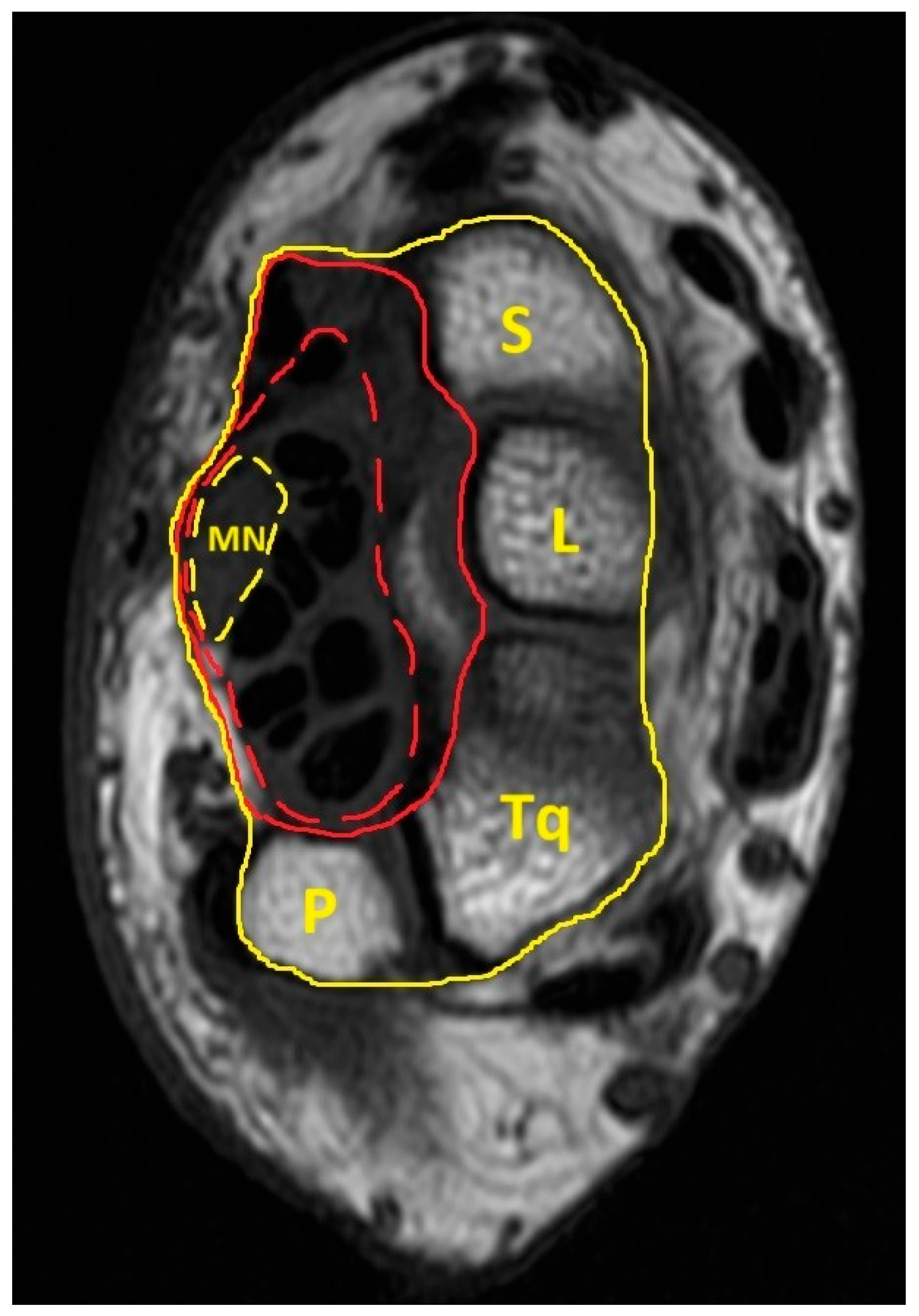
| Variables | Patient with CTS (n = 49) | Healthy Volunteer (n = 38) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean ± SD (years) | 50.22 ± 9.93 | 48.39 ± 9.20 | 0.381 |
| Gender, n (% of female) | 44 (89.80%) | 33 (86.84%) | 0.742 a |
| Height, mean ± SD (m) | 157.38 ± 6.74 | 160.32 ± 7.86 | 0.064 |
| BMI, mean ± SD (kg/m2) | 25.78 ± 3.93 | 21.65 ± 2.96 | <0.001 |
| Symptom score, mean ± SD | 2.35 ±0.77 | 1.07 ± 0.14 | <0.001 |
| Married, n (%) | 36 (75.00%) | 31 (81.58%) | 0.465 |
| Employed, n (%) | 24 (48.98%) | 29 (76.32%) | 0.010 |
| Smoking habit, n (%) | 3 (6.12%) | 1 (2.63%) | 0.629 a |
| Educational Level, n (%) | 0.018 | ||
| College/University or above | 18 (36.73%) | 25 (65.79%) | |
| Senior high school | 19 (38.78%) | 10 (26.32%) | |
| Junior high or less | 12 (24.49%) | 3 (7.89%) | |
| Disable score, mean ± SD | 1.77 ± 0.69 | 1.01 ± 0.05 | <0.001 |
| Dominant side, n (% of right hand) | 47 (95.92%) | 37 (97.37%) | 1.000 a |
| Lesion side, n (% of right hand) | |||
| Right-hand CTS | 6 (12.24%) | ||
| Left-hand CTS | 2 (4.08%) | ||
| Bilateral hand CTS | 41 (83.67%) |
| Variables | Patients with CTS (Patients/Hands = 49/90) | Healthy Volunteers (Persons/Hands = 38/76) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | ||
| Monofilament test | 30.063 ± 3.533 | 33.395 ± 1.980 | <0.001 |
| Grasp power (lb) | 36.231 ± 14.314 | 50.623 ± 17.259 | <0.001 |
| Palmar pinch power (lb) | 5.967 ± 3.378 | 8.261 ± 3.056 | 0.002 |
| Lateral pinch power (lb) | 8.790 ± 4.908 | 11.525 ± 3.836 | 0.006 |
| Wrist circumference (cm) | 15.598 ± 1.211 | 14.704 ± 1.078 | <0.001 |
| Midpalm latency (msec) | 2.043 ± 0.509 | 1.505 ± 0.240 | <0.001 |
| Distal sensory latency of MN (ms) | 3.581 ± 1.082 | 2.563 ± 0.299 | <0.001 |
| Distal motor latency of MN (ms) | 4.931 ± 1.262 | 3.431 ± 0.273 | <0.001 |
| Amplitude of compound motor action potential of MN (mV) | 12.955 ± 3.424 | 13.790 ± 3.585 | 0.276 |
| Variables | Patient with CTS (Patients/Hands = 49/90) | healthy Volunteer (Persons/Hands = 38/76) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD (mm2) | Mean ± SD (mm2) | ||
| CSA of MN | 13.292 ± 3.076 | 10.411 ± 1.743 | <0.001 |
| CSA of CTA | 171.101 ± 25.642 | 157.124 ± 26.679 | 0.034 |
| CSA of ICB | 279.327 ± 41.063 | 268.682 ± 42.234 | 0.733 |
| CSA of ECB | 758.254 ± 100.268 | 771.721 ± 111.959 | 0.826 |
| CSA of wrist | 1843.820 ± 238.826 | 1726.410 ± 258.983 | 0.470 |
| Transverse axis of MN | 6.453 ± 1.223 | 5.432 ± 0.816 | <0.001 |
| Anteroposterior axis of MN | 2.704 ± 0.561 | 2.605 ± 0.331 | 0.732 |
| Flattening ratio of MN | 2.452 ± 0.532 | 2.113 ± 0.391 | <0.001 |
| Transverse axis of wrist | 58.348 ± 4.231 | 57.121 ± 4.067 | 0.226 |
| Anteroposterior axis of wrist | 39.068 ± 3.009 | 37.498 ± 3.287 | 0.945 |
| Aspect ratio of wrist | 1.496 ± 0.087 | 1.527 ± 0.075 | 0.168 |
| Variables | Patient with CTS (Patients/Hands = 49/90) | Healthy Volunteer (Persons/Hands = 38/76) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| CSA of MN/CSA of CTA | 0.079 ± 0.020 | 0.067 ± 0.012 | <0.001 |
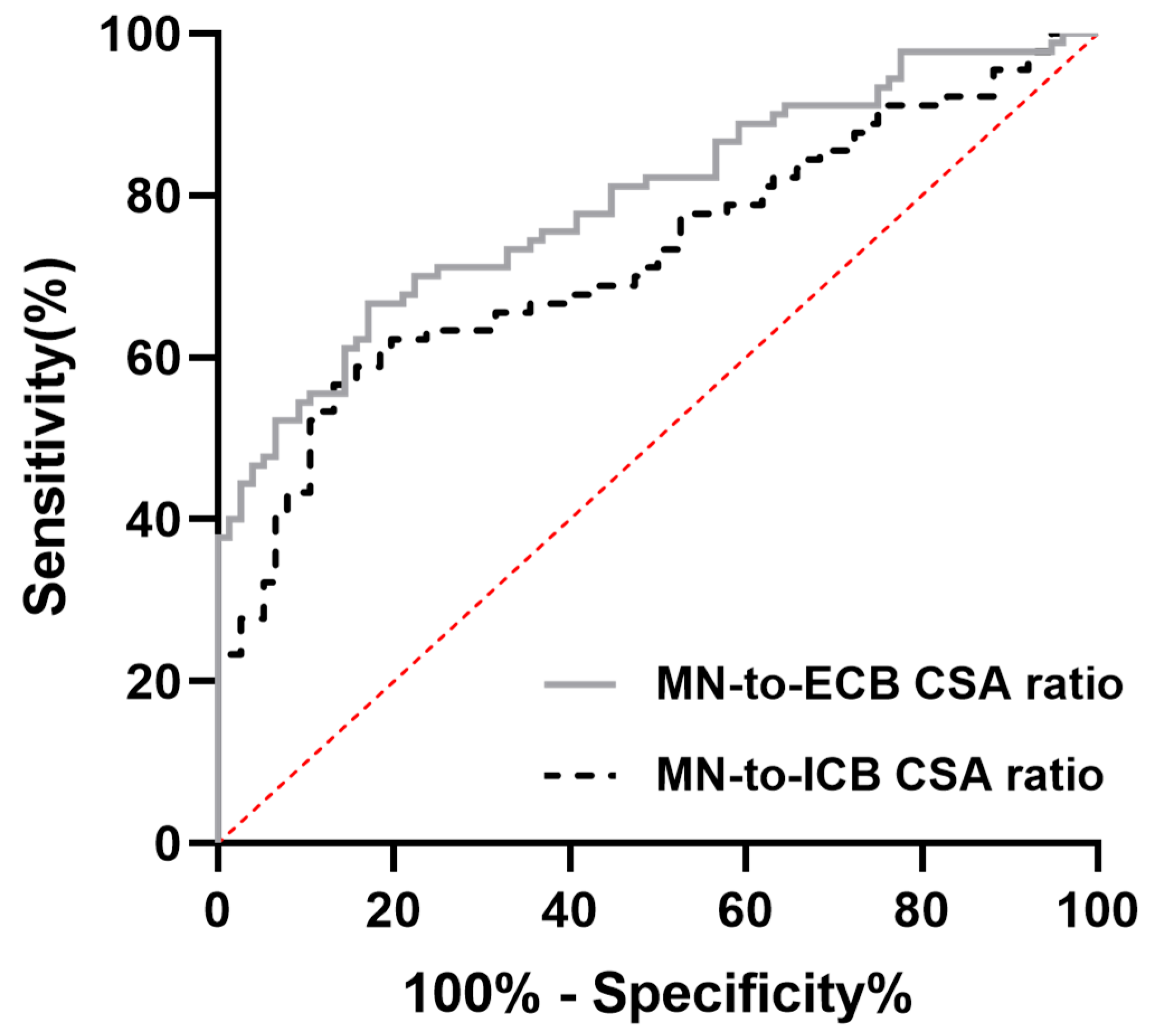
| CSA of MN/CSA of ICB | 0.048 ± 0.012 | 0.039 ± 0.007 | <0.001 |
| CSA of MN/CSA of ECB | 0.018 ± 0.004 | 0.014 ± 0.002 | <0.001 |
| CSA of MN/CSA of wrist | 0.007 ± 0.002 | 0.006 ± 0.001 | <0.001 |
| CTA/CSA of wrist | 0.094 ± 0.016 | 0.090 ± 0.017 | 0.009 |
| CTA/CSA of ICB | 0.615 ± 0.060 | 0.588 ± 0.068 | 0.005 |
| CTA/CSA of ECB | 0.227 ± 0.032 | 0.205 ± 0.028 | 0.005 |
| CSA of ICB/CSA of wrist | 0.153 ± 0.024 | 0.154 ± 0.027 | 0.253 |
| CSA of ECB/CSA of wrist | 0.414 ± 0.046 | 0.443 ± 0.065 | 0.550 |
| Pearson Correlation | Severity | Symptom Score | Disable Score | CSA of MN | Flattening Ratio of MN | CTA | CSA of ICB | CSA of ECB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Severity | 1.000 | 0.655 ** | 0.533 ** | 0.395 ** | 0.268 ** | 0.212 ** | 0.160 * | −0.005 |
| Symptom Score | 0.655 ** | 1.000 | 0.844 ** | 0.354 ** | 0.310 ** | 0.173 * | 0.098 | −0.031 |
| Disable score | 0.533 ** | 0.844 ** | 1.000 | 0.300 ** | 0.331 ** | 0.183 * | 0.120 | 0.015 |
| CSA of MN | 0.395 ** | 0.354 ** | 0.300 ** | 1.000 | 0.103 | 0.304 ** | 0.223 ** | 0.104 |
| Flattening ratio of MN | 0.268 ** | 0.310 ** | 0.331 ** | 0.103 | 1.000 | 0.155 * | 0.058 | −0.009 |
| CTA | 0.212 ** | 0.173 * | 0.183 * | 0.304 ** | 0.155 * | 1.000 | 0.768 ** | 0.488 ** |
| CSA of ICB | 0.160 * | 0.098 | 0.120 | 0.223 ** | 0.058 | 0.768 ** | 1.000 | 0.585 ** |
| CSA of ECB | −0.005 | −0.031 | 0.015 | 0.104 | −0.009 | 0.488 ** | 0.585 ** | 1.000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Y.-T.; Chen, C.-J.; Wang, Y.-W.; Horng, Y.-S. Comparing the Carpal Tunnel Area and Carpal Boundaries in Patients with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Healthy Volunteers: A Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15101205
Huang Y-T, Chen C-J, Wang Y-W, Horng Y-S. Comparing the Carpal Tunnel Area and Carpal Boundaries in Patients with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Healthy Volunteers: A Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(10):1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15101205
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Yu-Ting, Chii-Jen Chen, You-Wei Wang, and Yi-Shiung Horng. 2025. "Comparing the Carpal Tunnel Area and Carpal Boundaries in Patients with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Healthy Volunteers: A Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study" Diagnostics 15, no. 10: 1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15101205
APA StyleHuang, Y.-T., Chen, C.-J., Wang, Y.-W., & Horng, Y.-S. (2025). Comparing the Carpal Tunnel Area and Carpal Boundaries in Patients with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Healthy Volunteers: A Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study. Diagnostics, 15(10), 1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15101205






