Abstract
Ewing sarcomas are rare tumors arising mainly in the bones and the surrounding soft tissues. Primary extraosseous Ewing sarcomas have also been described in several other organs and locations other than bones, including the pancreas. These tumors have well-defined histological, immunohistochemical, and molecular characteristics. In this manuscript, we present a case of primary Ewing sarcoma of the pancreas in a 29-year-old patient, and we systematically review the literature on both primary and metastatic Ewing sarcomas of the pancreas, describing their clinicopathological characteristics. We also discuss the differential diagnosis and the treatment of this rare entity.
1. Introduction
Primary pancreatic carcinoma ranks as the third most common cause of cancer-related death in the U.S. [1]. Metastases to the pancreas are far less common. There are reports of several different malignancies, including melanoma, breast, lung, gastrointestinal tract, and renal carcinomas, as well as lymphomas [2]. It is very difficult to calculate the true incidence of pancreatic metastases. They range from 1.6% to 39% during autopsies of patients with cancer, depending on the primary tumor [2]. In most instances, patients with pancreatic metastases have widespread disease with a multitude of other metastatic sites [2].
Ewing sarcoma (ES) is a rare tumor involving the bones or soft tissue surrounding the bone. It is the second most common primary malignant bone tumor. Its peak incidence is in the second decade of life. Almost 80% of patients are younger than 20 years of age and it is uncommon in patients older than 30 years [3]. It is a poorly differentiated and aggressive small-blue-round-cell neoplasm of neuroectodermal origin that affects children and young adolescents. It most commonly affects Caucasians and, less commonly, Asians and African Americans [4]. It was first described in 1921 by James Ewing as a diffuse endothelioma of the bone. Tefft first described the extraosseous form of ESs in 1969 [5]. The ES family of tumors includes entities such as classical ES, extraosseous ES, peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumor (PNET), and Askin tumor of the chest wall. These tumors share common morphological features, being composed of small blue round cells with extensive areas of necrosis but viable tumors usually retained around blood vessels, an immunohistochemical profile expressing the MIC2-protein (CD99), and cytogenetics displaying the same chromosomal translocation t (11; 22) (q24; q12) in about 85% of the cases [5]. These sarcomas are prone to metastatic involvement. Lung, pleura, and other bones are the most common metastatic sites. Several other metastatic sites have been described. However, pancreatic metastasis is very rare, with few reported cases in the English literature.
On the other hand, primary extraosseous ES/PNETs have been described in a variety of organs, including the kidney, urinary bladder, ureter, prostate, penis, seminal vesicle, testis, small bowel, rectum, liver, gall bladder, maxillary sinus, trachea, lung, parotid gland, vulva, vagina, ovary, uterine cervix, uterus, and breast [3].
A primary extraosseous ES/PNET of the pancreas is a very rare tumor, with around 50 cases reported in the English literature.
Regarding the prognosis of these tumors, the presence of metastatic disease is the most important prognostic factor [3].
Also, another favorable prognostic factor is the complete pathologic response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. In contrast, the presence of early relapse and its occurrence in the trunk and pelvis predicts an unfavorable outcome [6].
In this manuscript, we present a case of primary ES/PNETs of the pancreas and review the literature on primary and metastatic ES/PNETs of the pancreas. We also discuss the differential diagnosis and treatment strategy of these tumors. Finally, we performed a statistical analysis based on the collected data from individual patients to evaluate the potential role of metastatic disease on patient survival and disease recurrence.
2. Materials and Methods
The patient provided written informed consent to participate in this study. The case report (involving a human participant) was reviewed and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Attikon University Hospital (ΕΒΔ210/27-03-2023).
We performed a systematic review of the literature according to the PRISMA (“Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses”) guidelines (http://www.prismastatement.org/; accessed on 15 July 2024).
Our retrospective observational study search was conducted through the PICO process:
- Population: Men or women with a diagnosis of primary or metastatic ESs of the pancreas;
- Intervention: Surgical treatment of the primary or metastatic ES;
- Comparison: None;
- Outcome: Patients’ treatment and follow-up.
We searched for Ewing sarcomas involving the pancreas on PubMed (all fields; 116 results; https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, accessed on 15 July 2024), Scopus (title/abstract/keywords; 528 results; https://www.scopus.com/home, accessed on 15 July 2024), and Web of Science (all fields; 118 results; https://login.webofknowledge.com, accessed on 15 July 2024) using the terms ((“Ewing”) AND (“Sarcoma”) AND (“pancreas” OR “pancreatic”)). We did not set any additional limitations while performing the search. We applied the following criteria:
- Eligibility/inclusion criteria
- (1)
- Study design: We only included original studies and case reports describing cases of primary pancreatic ES and ES metastatic to the pancreas.
- (2)
- Population: Studies involving patients diagnosed with ES that provided adequate surgical and/or oncological information.
- (3)
- Intervention or exposure: We included studies that examined any treatment or intervention for ES, including surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or targeted therapies.
- (4)
- Outcome: We included studies that reported on the presence or absence of disease relapse as an outcome measure.
- (5)
- Language: The included studies were written in the English language.
- Exclusion criteria
- (1)
- Review articles and editorials: We excluded narrative or systematic reviews, meta-analyses, opinion pieces, and other articles that did not present original research findings.
- (2)
- Insufficient information: We excluded cases with insufficient or too much aggregated data.
- (3)
- Language: We excluded manuscripts in languages other than English.
- (4)
- Uncertain diagnosis: Cases with an uncertain/doubtful diagnosis were excluded.
We included all primary articles and case reports in the English language describing primary and metastatic ESs of the pancreas. We excluded abstracts from medical conferences, previous review articles, and articles describing cases with unclear diagnoses and too much missing or aggregated data. Two authors [NK and MGS] reviewed the literature and collected data. Discrepancies were corrected in consensus. After applying inclusion and exclusion criteria, 33 manuscripts describing 51 primary [7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39] cases and 8 manuscripts describing 8 metastatic ES/PNET cases to the pancreas [40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47] remained for data extraction. A PRISMA flowchart with a summary of search results is shown in Figure 1.
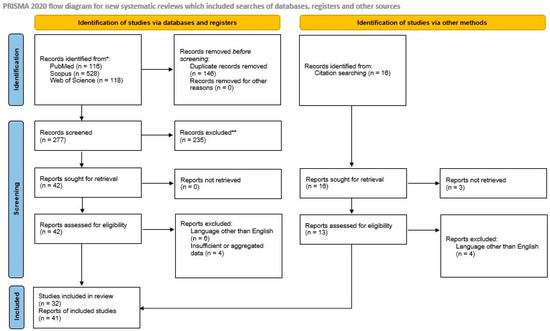
Figure 1.
The PRISMA 2020 flowchart shows the search strategy, excluded studies, and, finally, the included primary and metastatic pancreatic Ewing sarcoma reports.
Statistical analysis was performed within the environment of the R language (version 4.4.0). Continuous variables were expressed as mean ± standard deviation when normally distributed and as a median minimum with a quartile 1 to quartile 3 range and minimum and maximum values; the categorical data are presented as frequency and the relevant percentage. Paired t-tests or Mann–Whitney U test were conducted to compare changes between groups according to normality conditions as this was evaluated by the Shapiro–Wilk test. Survival was analyzed with Kaplan–Meier estimates and log-rank tests. The significance level was set to 0.05, and tests were two-sided when appropriate.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Detailed Case Description
A 29-year-old male patient was admitted to the hospital due to a history of abdominal pain for two months and jaundice. Past medical history as well as family history were unremarkable. An abdominal ultrasound revealed a heterogeneous mass located in the head of the pancreas. A computed tomography (CT) scan showed a mixed-density lesion of the head of the pancreas with a size of about 40 mm with high suspicion of pancreatic cancer. Serum markers were within normal limits. A CT-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy was performed.
Histologically, tumor cells were small, round, and discohesive and had irregular nuclear membranes with occasional cleaving (Figure 2A). There was no finely granular “salt-and-pepper” chromatin texture consistent with neuroendocrine neoplasm. Nucleoli were absent. There were several mitotic figures per 10 high-power fields. There was no evidence of glandular differentiation, Homer-Wright rosettes, or organoid configuration. Also, distinct nuclear molding was not present. An extensive immunohistochemical panel was applied. Membranous CD99 (mouse monoclonal BSB-9, Bio SB) (Figure 2B) and nuclear FLI1 (mouse monoclonal G146-222, Medac Gmbh) (Figure 2C) were positivity was noted. In contrast, CKAE1/AE3 (mouse monoclonal AE1/AE3, Dako), CK8/18 (mouse monoclonal 5D3, Thermoscientific), Chromogranin (mouse monoclonal DAK-A3, Dako), Synaptophysin (mouse monoclonal DAK-Synap, Dako), CD56 (rabbit monoclonal RCD-56, Zytomed), SMA (mouse monoclonal 1A4, Dako), and Desmin (mouse monoclonal D33, Zytomed) were negative. Ki67 (rabbit monoclonal EP1, Dako) stained 40–50% of tumor cells. Based on the above results, we made the diagnosis of malignant neoplasm, which was morphologically and immunohistochemically consistent with an ES. Molecular testing revealed an EWSR1-FLI1 gene fusion, considered pathognomonic for diagnosing ESs.
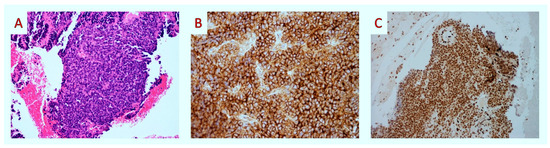
Figure 2.
Fine-needle aspiration biopsy: histopathologic findings. (A) Upon medium-power examination, the tumor was composed of uniform small blue round cells (H&E × 100). (B,C) After immunohistochemistry, tumor cells showed membranous staining for CD99 (CD99 × 100) and nuclear staining for FLI-1 (FLI-1 × 40).
The patient received six cycles of neoadjuvant therapy consisting of CAV (vincristine, adriamycin, and cyclophosphamide) alternating with IE (ifosfamide and etoposide). The patient tolerated the treatment well. After completion of neoadjuvant therapy, a pancreatoduodenectomy was performed. Histological evaluation of the specimen showed extensive necrosis with no viable tumor cells. The patient’s recovery was uneventful. He received five additional cycles of CAV/IE. Two and half years after the diagnosis, imaging studies revealed metastasis to the femur and lower lobe of the right lung. A lobectomy was performed, and the patient received irinotecan and temozolomide. After three cycles, imaging studies showed disease progression. The patient died a few weeks later, 37 months after the initial diagnosis.
3.2. Primary Pancreatic Ewing Sarcoma
3.2.1. Demographic and Clinicopathological Features
Primary pancreatic ES is a rare entity. Our review found 33 manuscripts describing 51 cases of primary pancreatic ES/PNET. Out of 50 patients, 28/50 (56%) [8,9,10,12,13,14,19,22,23,27,28,29,30,34,37,38,39] were male, and 22/50 (44%) [7,9,11,15,16,17,18,21,24,25,26,30,31,32,33,35,36] were female. In one case, the patient’s gender was not mentioned [20]. The mean patient age was 26 years (range 2–78 years). The mean tumor size was 80.4 mm (range 30–200 mm). The specific location of the tumor was mentioned in 49/51 (96%) [7,8,9,10,11,12,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39] cases. The head of the pancreas was the most common location in 26/49 (53%) [7,8,9,14,16,20,22,23,28,30,32] cases, followed by the body and tail in 10/49 (20.4%) [15,17,19,26,28,30,31,36,37,39] cases, the body in 5/49 (10.2%) [11,21,27,30] cases, the tail in 2/49 (4.1%) [12,34] cases, the head and uncinate process in 2/49 (4.1%) [25,33] cases, and the head and tail [10], the uncinate process [18], the head and body [24], and the body and neck [34] in 1/49 (2%) cases each. Symptoms were mentioned in 47/51 (92.1%) [7,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39] patients. The most common symptom was abdominal or epigastric pain in 35/47 (74.5%) [9,12,14,16,17,18,19,20,22,23,24,26,27,28,29,30,31,34,36,37,39] cases followed by jaundice in 14/47 (29.8%) [9,13,24,25,28,30] patients, loss of weight in 5/47 (10.6%) [18,27,29,33,39] cases, loss of appetite in 5/47 (10.6%) patients, abdominal mass in 4/47 (8.5%) [23,29,36,38] patients, nausea in 3/47 (6.4%) [19,31,36] patients, vomiting in 3/47 (6.4%) [12,31,35] patients, and fatigue in 2/47 (4.2%) [7,14] patients. A multitude of other symptoms were also present in the patients. The demographic, clinicopathological, and treatment features of the cases are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Clinicopathological and treatment data of primary ES/PNETs of the pancreas.
3.2.2. Imaging Findings
Imaging findings are not specific for this type of tumor. On pre-contrast CT images, the tumors are isodense with regions of necrosis. Contrast-enhanced CT images display heterogeneity with mild to medium enhancement and patchy intratumor unenhanced areas [48]. ESs appear typically isointense on T1-weighted images and display variable isointensity or hyperintensity on T2-weighted images on MRIs [49]. Since these findings are similar to pancreatic carcinoma, the accurate diagnosis of ESs of the pancreas depends on the results of the histopathologic examination.
3.2.3. Histological Findings and Differential Diagnosis
The diagnosis of ES can be particularly challenging. Clinical, radiological, pathological, and cytogenetic data can provide valuable diagnostic information.
Grossly, the tumor has a grayish-white color. Microscopically, primary extraskeletal Ewing sarcomas are characterized by small (1–2× size of lymphocytes), uniform, monotonous, round cells with finely stippled chromatin, inconspicuous nucleoli, scant cytoplasm, and indistinct cytoplasmic membranes. Tumor cells are arranged in a sheet-like growth pattern in islands separated by dense fibrous tissue. Tumor necrosis can be seen in several cases. Sometimes, there is neuroectodermal differentiation evidentiated by the presence of Homer-Wright pseudorosettes [50]. One of the cases showed adamantinoma-like Ewing sarcoma morphology [37], which is characterized by nests of basaloid cells, peripheral palisading and cording, prominent myxoid, fibromyxoid or hyalinized stroma, focal keratin pearl formation, and high-grade features with minimal pleomorphism [51]. Immunohistochemically, tumor cells show strong and diffuse membranous expression for CD99 [52], positivity for NKX2.2 [53], and Vimentin in 80–90% of cases. FLI1 shows nuclear staining in around 90% of cases with EWSR1-FLI1 fusion [54,55]. ERG displays nuclear staining in cases with EWSR1-ERG fusion [56]. Cases with adamantinoma-like morphology show diffuse positivity for pan-cytokeratin, CK5/6, p63, and p40. ES/PNETs may sometimes express neuroendocrine markers such as Synaptophysin and/or CD56 [3]. The histological differential diagnosis of ES/PNETs includes small-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma, a more typical finding in the pancreas [57]. ES and small-cell carcinoma have a similar morphology, composed of small round cells with minimal cytoplasm [58]. In imaging studies, these entities have similar findings with irregular borders and heterogeneous enhancement [59]. It is important to differentiate between these tumors since the treatment is distinct. Another pancreatic tumor that enters the differential diagnosis is solid pseudopapillary neoplasm. Upon imaging, it is usually well defined and heterogeneous with cysts [45]. Other differential diagnoses considered are desmoplastic small-round-cell tumors and pancreatoblastomas since they have similar morphological findings with the ES family of tumors (small monomorphic round cells with small nuclei and scant cytoplasm). In desmoplastic small-round-cell tumors, one can notice desmoplasia, while immunohistochemically, tumor cells are positive for cytokeratin and Desmin [60]. Pancreatoblastomas display, microscopically, cells with acinar-like differentiation and the formation of small squamoid nests [61]. In most cases, immunohistochemical analysis provides a diagnostic solution. An ES is usually positive for CD99 and FLI-1 in contrast to small-cell carcinoma and solid pseudopapillary neoplasm. Markers of epithelial (AE1/AE3, EMA, CK8/18, and CK7) and neuroendocrine differentiation (NSE, Chromogranin A, Synaptophysin, and CD56) may display variable results in ESs [3]. In difficult cases, molecular analysis by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) or reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction (rt-PCR) of the EWSR-FLI1 fusion gene, which is specific to ESs, can help confirm the diagnosis.
3.2.4. Molecular Studies
In ES/PNETs, the result of the EWS-FLI1 gene fusion is the karyotype of t(11;22) (q24;q12), and the EWS-ERG gene fusion results in t(21;22) (q22;q12), which account for 85% and 10%, respectively [62,63,64]. On rare occasions, an ES shows fusions of EWS to other ETS-family genes (ETV1, ETV4, and FEV) or similar fusions of the EWS-related gene FUS (FUS-ERG or FUS-FEV) [65,66].
Molecular studies have been performed in the majority of pancreatic ESs. Most cases displayed the t(11;22) (q24;q12) translocation while fewer displayed the 22q12 rearrangement.
3.2.5. Treatment
Surgical treatment data were reported in all cases. In 24/51 (47%) cases, treatment consisted of a Whipple procedure [7,8,10,13,14,16,22,23,25,30,33,38] or distal pancreatectomy in 5/51 (9.8%) [11,15,17,19,26,31] cases, en bloc resection of pancreas and kidney in 2/51 (3.9%) [30], central pancreatectomy in 1/51 (1.9%) [35], gastropancreatoduodenectomy in 1/51 (1.9%) [24], left pancreatectomy in 1/51 (1.9%) [12], and total mass excision in 1/51 (1.9%) [34]. Biopsies were performed in 4/51 (9.3%) [9,21] cases, and open laparotomy and surgical biopsies were taken in 2/43 (4.6%) [20,27] cases. Additionally, in some cases, other procedures such as Roux-en-Y choledochojejunostomy [28,29], splenectomy [12,15,17,19,26,31,39], partial gastric resection [12], nephrectomy [34], adrenalectomy [34,37], and colectomy [31,38] were performed.
Information regarding adjuvant treatment was provided in 38/51 (74.5%) [7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,23,24,25,26,28,29,30,31,32,34,35,36,37,38] cases. Chemotherapy either in the adjuvant or neoadjuvant setting was offered in 30/38 (78.9%) [9,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,23,25,26,29,30,31,34,35,37,38] cases and radiotherapy in 5/33 (15.1%) [13,17,18,25,34] cases. In three cases, patients or their families refused the proposed chemotherapy [7,8,10]. The most common regimen used consisted of vincristine, adriamycin, and cyclophosphamide alternating with ifosfamide and etoposide, while the second most common regimen consisted of vincristine, adriamycin, and cyclophosphamide administered in eight and six cases, respectively. Among ten cases with recurrence, six received additional chemotherapy, sometimes combined with surgery [8,10,12,17,18,30], two received other treatment (surgical for the first and radioablation for the second case) [13,27], and three patients received no further treatment [7,28,31]. ES/PNETs are famous for displaying extremely malignant behavior with frequent relapse and metastasis. The treatment of ESs consists of surgery followed by chemotherapy.
A five-drug regimen (vincristine, adriamycin, cyclophosphamide, ifosfamide, and etoposide) has been established as the gold standard for treating ES/PNETs [64]. Radiation therapy can be used with some therapeutic efficacy in patients with residual disease [43].
3.2.6. Outcome
Follow-up information was available in 38/51 (77.5%) [7,8,9,10,11,12,13,15,16,17,18,20,23,24,26,28,29,30,31,32,34,35,36,37,38,39] cases. Briefly, 18/38 (47.4%) patients were alive without evidence of disease [9,11,12,15,23,24,26,29,30,34,35,37,38], 6/38 (15.8%) were alive with disease [8,9,13,30], and 12/38 (31.6%) died of disease [7,9,10,17,18,30,32,36] in a timeline ranging from 1 to 120 months. In two out of thirty-eight (5.2%) cases, patients died of other causes [16,28], one of them due to postoperative complications and the second due to severe infection and multiple organ failure. A small number of studies have claimed that an extraskeletal ES has a more favorable prognosis compared to its skeletal counterpart [67,68]. Tural et al. have reported that tumor size equal to or exceeding 8 cm is a significant predictor of worse overall survival [69].
3.3. Ewing Sarcoma Metastasis to the Pancreas
3.3.1. Demographic and Clinicopathological Features
Metastatic disease of the pancreas is rare. It accounts for 2% of all pancreatic cancers [70]. The primary tumors that most frequently provide pancreatic metastasis are lung cancer, renal cell carcinoma, breast cancer, and melanoma [71]. However, it should be noted that pancreatic metastasis is a good prognostic factor for renal cell carcinoma, with excellent response to treatment with tyrosine kinase inhibition [72].
The prognosis of metastasis to the pancreas is poor. In soft tissue sarcoma, the role of surgical treatment is not clear. Reports of prolonged survival after removal of isolated metastatic foci have been published for different neoplasms, including carcinomas [73,74,75] and soft tissue sarcomas [76].
Metastatic ESs to the pancreas have been reported even less frequently than primary ES/PNETs of the pancreas. Our review found eight articles describing eight ES cases with metastasis to the pancreas. Gender was reported in all cases, with 7/8 (87.5%) [40,41,42,43,45,46,47] patients being male and 1/8 (12.5%) [44] being female. The individual patient’s age was reported in all cases. The mean age was 23.2 years (range 13–37 years). The mean tumor size of the metastatic focus was 29.7 mm (range 21–40 mm). The most common symptoms are not specific, including abdominal or epigastric pain in 3/8 (37.5%) [42,44,45] patients and vomiting in 2/8 (25%) [44,45] patients. Other less common symptoms include nausea and jaundice [45]. These symptoms are similar to those of primary pancreatic ES/PNETs. The summary of the demographic, clinicopathological, and treatment features of these cases is displayed in Table 2.

Table 2.
Clinicopathological and treatment data of metastatic ESs to the pancreas.
3.3.2. Imaging Findings
The imaging features of metastatic ESs to the pancreas are not pathognomonic. They show solid and cystic components [42], a hypodense mass [45], a heterogeneously enhancing lesion [47] on computed tomography scans, or a hypoechoic mass on endoscopic ultrasounds [43].
3.3.3. Histological Findings
On microscopic examination, the histologic appearance of metastatic ES/PNETs is identical to that of the primary one, which consists of small, round neoplastic cells. The same is true for immunohistochemistry, which displays positivity for CD99, NKX2.2, either FLI-1 or ERG, and sometimes for Chromogranin, Synaptophysin, and CD56.
3.3.4. Molecular Studies
In two cases, the presence of EWSR1-FLI1 rearrangement was mentioned.
3.3.5. Treatment
There was information regarding surgical treatment in 7/8 (87.5%) [40,41,42,44,45,46,47] cases. In 5/7 (71.4%) [40,44,45,46,47] patients, surgical treatment was not performed. In 1/7 (14.3%) [42], the patient underwent left lung lobectomy and lymph node dissection, and in 1/7 (14.2%) [41], an open surgical biopsy was performed.
Detailed information regarding adjuvant therapy was provided for 7/8 (87.5%) [40,41,42,43,45,46,47] patients. Chemotherapy was administered in 6/7 (85.7%) [40,41,43,45,46,47] patients; 2 received the VAC-IE regimen and 1 received VAC. In one case, prednisone, vincristine, and cyclophosphamide (for lymphoma diagnosis) were administered because the neoplasm was misdiagnosed as a lymphoma [40]. In another case, the patient received cisplatin and etoposide due to small-cell lung carcinoma misdiagnosis, which was later changed to a VAC regimen [45]. Radiotherapy was provided in 3/7 (42.8%) [41,45,46] patients. In cases of recurrence, patients received adjuvant chemotherapy and, in some cases, surgical treatment and radiotherapy. In 1/7 (14.3%) [42] cases, the patient refused adjuvant chemotherapy. It should be noted that according to the REECUR trial, the preferred regimen for metastatic or recurrent ESs is ifosfamide [77]. On the other hand, trials reported with tyrosine kinase inhibitors such as regorafenib or cabozantinib in metastatic/recurrent ESs do not describe the activity of these regimens in patients with pancreatic metastases [78,79].
3.3.6. Outcome
Follow-up information was available for 6/8 (75%) [40,41,42,43,45,46] patients. Follow-up time ranged from 5 to 402 months (mean 93). In 4/6 (66.7%) [42,43,45,46] cases, patients were alive with the disease, and 2/6 (33.3%) [40,41] succumbed to the disease.
3.4. Patient Survival, Disease Recurrence, and Comparisons Between Survivors and Non-Survivors and Patients with Recurrence and Non-Recurrence
As the collected data had details for each patient, it was feasible to perform various inferential statistics to evaluate possible differences related to diseases, patients, or other characteristics. Differences in the survival of patients with metastatic disease from patients with primary tumors were not possible to be confirmed (p = 0.95) (see Figure 3) nor were the differences between the groups of patients with and without recurrence (p = 0.29). Notably, there is a trend for better survival of the patients without recurrence; however, larger data sets are required for robust statistical confirmation.
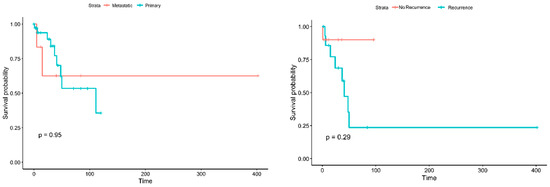
Figure 3.
Kaplan–Meier curves for the survival of patients with metastatic vs. primary tumors (left) and for the patients with and without recurrence (right).
A detailed analysis among patients with metastatic (N = 8) and with primary ESs (N = 52) showed a marginal difference (p = 0.0857) for abdominal pain as a symptom. More specifically, 63% of the patients with primary tumors had abdominal pain, while only 25% of the patients with metastatic disease displayed this symptom. Furthermore, differences were found (p = 0.0183) in the patient’s status (as reported in the studies), with 35% of the patients with primary tumors being reported as alive without evidence of disease, while none of the patients with metastatic disease was reported to be cured (see Supplementary Table S1 for details). Additional analysis of the patients with recurrent disease (N = 19) and those without (N = 13) indicates that the major difference lies in the life status during the study, as 47.4% of the patients with recurrence were deceased due to the disease while only 15.4% of the patients without recurrence succumbed to the disease (see Supplementary Table S2 for more details).
4. Conclusions
In conclusion, we have presented a new case of primary ESs of the pancreas and reviewed the literature on primary and metastatic ESs of the pancreas. Both represent rare entities, with few cases reported in the English literature. Further studies of these tumors with long-term follow-ups need to be reported to fully understand their behavior.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/diagnostics14232694/s1: Table S1: Comparisons between the patients with metastatic disease and primary sarcomas. Table S2: Comparisons between the patients with and without recurrence. Bold p values indicate statistical significance.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.I.K. and A.P. (Abraham Pouliakis); methodology, M.Z. (Magda Zanelli) and M.G.S.; software, M.Z. (Maurizio Zizzo); validation, K.S., C.K. and M.G.S.; formal analysis, A.P. (Abraham Pouliakis); investigation, I.B.; resources, A.K.; data curation, G.B.; writing—original draft preparation, N.I.K., A.P. (Abraham Pouliakis) and M.G.S.; writing—review and editing, M.Z. (Magda Zanelli), A.P. (Andrea Palicelli), K.S., C.K., M.Z. (Maurizio Zizzo), G.B., A.I.K., D.G. and R.C.; visualization, R.C.; supervision, D.G.; project administration, D.G.; funding acquisition, M.Z. (Magda Zanelli) and A.P. (Andrea Palicelli). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding. The study was partially supported by the Italian Ministry of Health—Ricerca Corrente Annual Program 2025.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The case report (involving a human participant) was reviewed and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Attikon University Hospital (ΕΒΔ210/27 March 2023).
Informed Consent Statement
We have managed to contact the patient’s father (the patient is deceased) and obtained approval for publication.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Francesca Sabrina Vinci, Giovanni Mattia, and Virginia Dolcini of the Grant Office and Research Administration (Azienda USL-IRCCS di Reggio Emilia) for their support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Halbrook, C.J.; Lyssiotis, C.A.; di Magliano, M.P.; Maitra, A. Pancreatic cancer: Advances and challenges. Cell 2023, 186, 1729–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adsay, N.V.; Andea, A.; Basturk, O.; Kilinc, N.; Nassar, H.; Cheng, J.D. Secondary tumors of the pancreas: An analysis of a surgical and autopsy database and review of the literature. Virchows Arch. 2004, 444, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koufopoulos, N.; Kokkali, S.; Manatakis, D.; Balalis, D.; Nasi, D.; Ardavanis, A.; Korkolis, D.; Khaldi, L. Primary peripheral neuroectodermal tumor (PNET) of the adrenal gland: A rare entity. J. BUON 2019, 24, 770–778. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Beck, R.; Monument, M.J.; Watkins, W.S.; Smith, R.; Boucher, K.M.; Schiffman, J.D.; Jorde, L.B.; Randall, R.L.; Lessnick, S.L. EWS/FLI-responsive GGAA microsatellites exhibit polymorphic differences between European and African populations. Cancer Genet. 2012, 205, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Alava, E.; Gerald, W.L. Molecular biology of the Ewing’s sarcoma/primitive neuroectodermal tumor family. J. Clin. Oncol. 2000, 18, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albergo, J.I.; Gaston, C.L.; Laitinen, M.; Darbyshire, A.; Jeys, L.M.; Sumathi, V.; Parry, M.; Peake, D.; Carter, S.R.; Tillman, R.; et al. Ewing’s sarcoma: Only patients with 100% of necrosis after chemotherapy should be classified as having a good response. Bone Jt. J. 2016, 98-B, 1138–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bülchmann, G.; Schuster, T.; Haas, R.; Joppich, I. Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor of the Pancreas An Extremely Rare Tumor. Klin. Padiatr. 2000, 212, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, M.J.; Perlman, E.J.; Furman, J.; Humphrey, P.A.; Dehner, L.P.; Pfeifer, J.D. Visceral primitive peripheral neuroectodermal tumors: A clinicopathologic and molecular study. Hum. Pathol. 2001, 32, 1109–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movahedi-Lankarani, S.; Hruban, R.H.; Westra, W.H.; Klimstra, D.S. Primitive neuroectodermal tumors of the pancreas: A report of seven cases of a rare neoplasm. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2002, 26, 1040–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perek, S.; Perek, A.; Sarman, K.; Tuzun, H.; Buyukunal, E. Primitive neuroectodermal tumor of the pancreas: A case report of an extremely rare tumor. Pancreatology 2003, 3, 352–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutte, W.P.; Knight, P.J. Precocious puberty because of a pancreatic neuroectodermal tumor. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2006, 41, 1916–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welsch, T.; Mechtersheimer, G.; Aulmann, S.; Mueller, S.A.; Buechler, M.W.; Schmidt, J.; Kienle, P. Huge primitive neuroectodermal tumor of the pancreas: Report of a case and review of the literature. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 6070–6073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doi, H.; Ichikawa, S.; Hiraoka, A.; Ichiryu, M.; Nakahara, H.; Ochi, H.; Tanabe, A.; Kodama, A.; Hasebe, A.; Miyamoto, Y.; et al. Primitive neuroectodermal tumor of the pancreas. Intern. Med. 2009, 48, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Maxwell, L.; Hederman, A.; Jackson, C.; Sawaya, D.; Giles, H.; Nowicki, M.J. Uncommon Presentation of Rare Disorder—Duodenal Ulcer Secondary to Invasive Pancreatic Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor: Case Report and Review of the Literature. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2011, 33, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, P.; Murugan, P.; Gillies, E.; Holter, J.L. Extraosseous Ewing’s sarcoma of the pancreas. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 17, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, A.R.; Arantes, T.; Sampaio, R.C.; Jureidini, R.; Cunha, J.E.M.d.; Cecconello, I. Pancreatic primitive neuroectodermal tumor: Case report. Arq. Bras. Cir. Dig. 2013, 26, 159–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayant, K.; Agrawal, S.; Agarwal, R.; Khoiwal, S. Pancreatic Ewings sarcoma-a dreadful tumor. Am. J. Cancer Prev. 2013, 1, 24–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Sang, X.; Liang, N.; Yang, H.; Lu, X.; Yang, Z.; Du, S.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zhong, S.; et al. Peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumors arising in the pancreas: The first case report in Asia and a review of the 14 total reported cases in the world. Hepatobiliary Surg. Nutr. 2013, 2, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly, C.; Zenoni, S.; Hasan, M.K.; Varadarajulu, S.; Tran, T.A.; de la Fuente, S.G.; Arnoletti, J.P. Primary pancreatic Ewing’s sarcoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2013, 17, 1015–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changal, K.H.; Mir, M.H.; Azaz, S.A.; Qadri, S.K.; Lone, A.R. Primitive neuroectodermal tumour of pancreas; second case from Asia. Malays. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 21, 65–69. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.Y.; Song, J.S.; Park, H.; Byun, J.H.; Song, K.B.; Kim, K.P.; Kim, S.C.; Hong, S.M. Primary mesenchymal tumors of the pancreas: Single-center experience over 16 years. Pancreas 2014, 43, 959–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishizawa, N.; Kumamoto, Y.; Igarashi, K.; Nishiyama, R.; Tajima, H.; Kawamata, H.; Kaizu, T.; Watanabe, M. A peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumor originating from the pancreas: A case report and review of the literature. Surg. Case Rep. 2015, 11, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, D.; Sharma, D.; Gupta, D.; Daga, D.; Hussain, D.; Khan, D. Large operable Ewing sarcoma of the pancreas: Report of a case and review of the literature. SAS J. Surg. 2015, 1, 152–156. [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira, U.; Goldoni, M.; Unterleider, M.; Diedrich, J.; Balbinot, D.; Rodrigues, P.; Monteiro, R.; Gomes, D.; Sampaio, J.; Fontes, P.; et al. Primitive neuroectodermal tumor of the pancreas: A case report and review of the literature. Case Rep. Surg. 2015, 2015, 276869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Golhar, A.; Ray, S.; Haugk, B.; Singhvi, S.K. Cytogenetically confirmed primary Ewing’s sarcoma of the pancreas. BMJ Case Rep. 2017, 2017, bcr-2017-219219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saif, M.W.; Kaley, K. Extraosseous Ewing’s sarcoma of the pancreas: An uncommon but treatable disease. Cureus 2017, 9, e1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komforti, M.K.; Sokolovskaya, E.; D’Agostino, C.A.; Benayed, R.; Thomas, R.M. Extra-osseous Ewing sarcoma of the pancreas: Case report with radiologic, pathologic, and molecular correlation, and brief review of the literature. Virchows Arch. 2018, 473, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Xiao, D.; Yi, X.; Li, W. Pancreatic primitive neuroectodermal tumor: Focus on radiological features and differential diagnosis–A case report and literature review. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2018, 14, S793–S795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, R.N.; Cesário, F.K.O.d.S.; Mondragon, J.P.M.; Silva, F.D.B.d.; Fontoura, R.P.; Netto, J.D.d.S.; Botelho, C.H.D.A. Therapeutic approach of a pancreatic Ewing Sarcoma/PNET: Case report and literature review. Braz. J. Oncol. 2020, 16, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achufusi, T.G.; Sohal, R.; Zamora, E.; Harne, P.; Russo, R. Primitive neuroectodermal tumor of the pancreas. Bayl. Univ. Med. Cent. Proc. 2021, 34, 144–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.L.; Roy-Chowdhuri, S.; Illei, P.; James, A.; Hruban, R.H.; Ali, S.Z. Primary pancreatic Ewing sarcoma: A cytomorphologic and histopathologic study of 13 cases. J. Am. Soc. Cytopathol. 2020, 9, 502–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yohannan, B.; Feldman, M. A nonpediatric extraosseous Ewing sarcoma of the pancreas: Differential diagnosis and therapeutic strategies. Case Rep. Oncol. Med. 2020, 2020, 2792750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakshi, N.; Dhawan, S.; Bhalla, S.; Verma, R. Primary non hodgkin lymphoma and Ewing’s sarcoma/PNET: Two rare pancreatic round cell tumors with diverse clinical outlook. Indian. J. Pathol. Microbiol. 2021, 64, S184–S187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.C.; Yeh, T.C.; Wu, P.S.; Sheu, J.C.; Lee, H.C.; Yeung, C.Y.; Jiang, C.B.; Liu, H.C.; Hou, J.Y.; Chan, W.T. Rare presentation in a rare case of pancreatic extraosseous Ewing’s sarcoma: A case report. Medicine 2022, 101, e31752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gecici, N.N.; Camurdan, V.B.; Al Khatalin, M.; Yildirim, O. Extraosseous Ewing sarcoma of the pancreas: A case report. Korean J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 19, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.M.; Verma, S.; Kakkar, L.; Thakur, P.B.; Deswal, S.; Maurya, M.K.; Sharma, A. Primary pancreatic Ewing sarcoma with metastases on FDG PET/CT. Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med. 2023, 54, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X. Adamantinoma-like ewing sarcoma arising in the pancreatic tail: A case report of a rare entity and review of the literature. Diagn. Pathol. 2023, 18, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Bian, J.; Yang, Y.; Wei, D.; Qi, S. Ewing sarcoma of the pancreas: A pediatric case report and narrative literature review. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1368564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, S.; Osman, T.A.M.; Amer, S. Primary Extraskeletal Ewing Sarcoma of the Pancreas-A Case Report. Middle East. J. Cancer. 2024, 15, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappo, A.; Cheah, M.; Saldivar, V.; Britton, H.; Parmley, R. Disseminated primitive neuroectodermal tumor: Diagnosis using immunocytochemistry, electron microscopy, and molecular probes. Cancer 1989, 63, 2515–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulligan, M.E.; Fellows, D.W.; Mullen, S.E. Pancreatic metastasis from Ewing’s sarcoma. Clin. Imaging 1997, 21, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Guo, Z.; Wu, X. Primary pulmonary primitive neuroectodermal tumor metastasis to the pancreas: A rare case with seven-year follow-up. Diagn. Pathol. 2013, 8, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polimera, H.; Moku, P.; Abusharar, S.P.; Vasekar, M.; Chintanaboina, J. Metastasis of Ewing sarcoma to the pancreas: Case report and literature review. Case Rep. Oncol. Med. 2020, 2020, 7075048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapatia, G.; Rajwanshi, A. Pancreatic space-occupying lesion: ‘Keep me in your mind’. Cytopathology 2021, 32, 142–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guduguntla, B.A.; Shi, J.; Kwon, R.S. Ewing sarcoma: Rare metastasis to the pancreas. ACG Case Rep. J. 2022, 9, e00930. [Google Scholar]
- Kapoor, S.; Patel, T.; Kaur, K.; Trivedi, P. “Wnt/β-catenin-activated Ewing’s sarcoma with metastasis to pancreas”: A rare case report. Annals Oncol. Res. Ther. 2022, 2, 101–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmast, S.Z.A.; Kaur, A. Multifocal Ewing Sarcoma with Pancreatic and Cutaneous Metastasis-A Rare Case Report. Indian J. Appl. Radiol. 2023, 9, 187. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Song, T.; Sun, C.; Shen, Y. Primitive neuroectodermal tumor arising in the abdominopelvic region: CT features and pathology characteristics. Abdom. Imaging 2011, 36, 590–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ma, G.L.; Xiao, E.H.; Wang, X.C. Peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumor: Dynamic CT, MRI and clinicopathological characteristics-analysis of 36 cases and review of the literature. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 12968–12977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llombart-Bosch, A.; Machado, I.; Navarro, S.; Bertoni, F.; Bacchini, P.; Alberghini, M.; Karzeladze, A.; Savelov, N.; Petrov, S.; Alvarado-Cabrero, I.; et al. Histological heterogeneity of Ewing’s sarcoma/PNET: An immunohistochemical analysis of 415 genetically confirmed cases with clinical support. Virchows Arch. 2009, 455, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooper, L.M.; Bishop, J.A. Soft tissue special issue: Adamantinoma-like Ewing sarcoma of the head and neck: A practical review of a challenging emerging entity. Head Neck Pathol. 2020, 14, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folpe, A.L.; Goldblum, J.R.; Rubin, B.P.; Shehata, B.M.; Liu, W.; Dei Tos, A.P.; Weiss, S.W. Morphologic and immunophenotypic diversity in Ewing family tumors: A study of 66 genetically confirmed cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2005, 29, 1025–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, A.; Sekine, S.; Tsuta, K.; Fukayama, M.; Furuta, K.; Tsuda, H. NKX2. 2 is a useful immunohistochemical marker for Ewing sarcoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2012, 36, 993–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folpe, A.L.; Hill, C.E.; Parham, D.M.; O’Shea, P.A.; Weiss, S.W. Immunohistochemical detection of FLI-1 protein expression: A study of 132 round cell tumors with emphasis on CD99-positive mimics of Ewing’s sarcoma/primitive neuroectodermal tumor. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2000, 24, 1657–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llombart-Bosch, A.; Navarro, S. Immunohistochemical detection of EWS and FLI-1 proteins in Ewing sarcoma and primitive neuroectodermal tumors: Comparative analysis with CD99 (MIC-2) expression. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2001, 9, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.L.; Patel, N.R.; Caragea, M.; Hogendoorn, P.C.; Lopez-Terrada, D.; Hornick, J.L.; Lazar, A.J. Expression of ERG, an Ets family transcription factor, identifies ERG-rearranged Ewing sarcoma. Mod. Pathol. 2012, 25, 1378–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, N.A.; Suortamo, S.; George, E.; Beavers, S. Paraduodenal/pancreatic Ewing sarcoma is very rare and therefore may be mistaken for neuroendocrine carcinoma. J. Clin. Pathol. 2022, 75, 71–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvajal, R.; Meyers, P. Ewing’s sarcoma and primitive neuroectodermal family of tumors. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2005, 19, 501–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, D.; Nandu, N.S.; Reddy, A. Extraosseus Ewing’s sarcoma in pancreas: A review. Cureus 2020, 12, e7505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danner, D.; Hruban, R.; Pitt, H.; Hayashi, R.; Griffin, C.; Perlman, E. Primitive neuroectodermal tumor arising in the pancreas. Mod. Pathol. 1994, 7, 200–204. [Google Scholar]
- Savastano, S.; d’Amore, E.; Zuccarotto, D.; Banzato, O.; Beghetto, M.; Famengo, B. Pancreatoblastoma in an adult patient. A case report. JOP 2009, 10, 192–195. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pagani, A.; Macri, L.; Rosolen, A.; Toffolatti, L.; Stella, A.; Bussolati, G. Neuroendocrine differentiation in Ewing’s sarcomas and primitive neuroectodermal tumors revealed by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction of chromogranin mRNA. Diagn. Mol. Pathol. 1998, 7, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandberg, A.A.; Bridge, J.A. Updates on cytogenetics and molecular genetics of bone and soft tissue tumors:: Ewing sarcoma and peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumors. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 2000, 123, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grier, H.E. The Ewing family of tumors: Ewing’s sarcoma and primitive neuroectodermal tumors. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 1997, 44, 991–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, S.S.; Jambhekar, N.A. Pathology of Ewing’s sarcoma/PNET: Current opinion and emerging concepts. Indian J. Orthop. 2010, 44, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessnick, S.L.; Ladanyi, M. Molecular pathogenesis of Ewing sarcoma: New therapeutic and transcriptional targets. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2012, 7, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cash, T.; McIlvaine, E.; Krailo, M.D.; Lessnick, S.L.; Lawlor, E.R.; Laack, N.; Sorger, J.; Marina, N.; Grier, H.E.; Granowetter, L.; et al. Comparison of clinical features and outcomes in patients with extraskeletal versus skeletal localized Ewing sarcoma: A report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2016, 63, 1771–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, A.D.; Gani, F.; Meyer, C.F.; Morris, C.D.; Ahuja, N.; Johnston, F.M. Extraskeletal versus skeletal Ewing sarcoma in the adult population: Controversies in care. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 27, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tural, D.; Molinas Mandel, N.; Dervisoglu, S.; Oner Dincbas, F.; Koca, S.; Colpan Oksuz, D.; Kantarci, F.; Turna, H.; Selcukbiricik, F.; Hiz, M. Extraskeletal Ewing’s sarcoma family of tumors in adults: Prognostic factors and clinical outcome. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 42, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperti, C.; Moletta, L.; Patanè, G. Metastatic tumors to the pancreas: The role of surgery. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2014, 6, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantopoulou, C.; Kolliakou, E.; Karoumpalis, I.; Yarmenitis, S.; Dervenis, C. Metastatic disease to the pancreas: An imaging challenge. Insights Imaging 2012, 3, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirashita, T.; Iwashita, Y.; Endo, Y.; Fujinaga, A.; Shin, T.; Mimata, H.; Inomata, M. How should we treat pancreatic metastases from renal cell carcinoma? A meta-analysis. World J. Surg. 2021, 45, 2191–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirota, T.; Tomida, T.; Iwasa, M.; Takahashi, K.; Kaneda, M.; Tamaki, H. Solitary pancreatic metastasis occurring eight years after nephrectomy for renal cell carcinoma: A case report and surgical review. Int. J. Pancreatol. 1996, 19, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperti, C.; Pasquali, C.; Berselli, M.; Frison, L.; Vicario, G.; Pedrazzoli, S. Metastasis to the pancreas from colorectal cancer: Is there a place for pancreatic resection? Dis. Colon Rectum 2009, 52, 1154–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperti, C.; Pasquali, C.; Liessi, G.; Pinciroli, L.; Decet, G.; Pedrazzoli, S. Pancreatic resection for metastatic tumors to the pancreas. J. Surg. Oncol. 2003, 83, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, H.; Watanabe, K.; Nagata, M.; Honda, I.; Watanabe, S.; Soda, H.; Tatezaki, S. Surgical treatment for pancreatic metastasis from soft-tissue sarcoma: Report of two cases. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2001, 24, 198–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, G.E.; Graves, L.A.; Rubin, E.M.; Reed, D.R.; Riedel, R.F.; Strauss, S.J. Bad to the bone: Emerging approaches to aggressive bone sarcomas. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book. 2023, 43, e390306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffaud, F.; Blay, J.Y.; Le Cesne, A.; Chevreau, C.; Boudou-Rouquette, P.; Kalbacher, E.; Penel, N.; Perrin, C.; Laurence, V.; Bompas, E.; et al. Regorafenib in patients with advanced Ewing sarcoma: Results of a non-comparative, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre Phase II study. Br. J. Cancer 2023, 129, 1940–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Italiano, A.; Mir, O.; Mathoulin-Pelissier, S.; Penel, N.; Piperno-Neumann, S.; Bompas, E.; Chevreau, C.; Duffaud, F.; Entz-Werlé, N.; Saada, E.; et al. Cabozantinib in patients with advanced Ewing sarcoma or osteosarcoma (CABONE): A multicentre, single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).