Imaging Features of Plantar Vein Thrombosis: An Easily Overlooked Condition in the Differential Diagnosis of Foot Pain
Abstract
1. Introduction
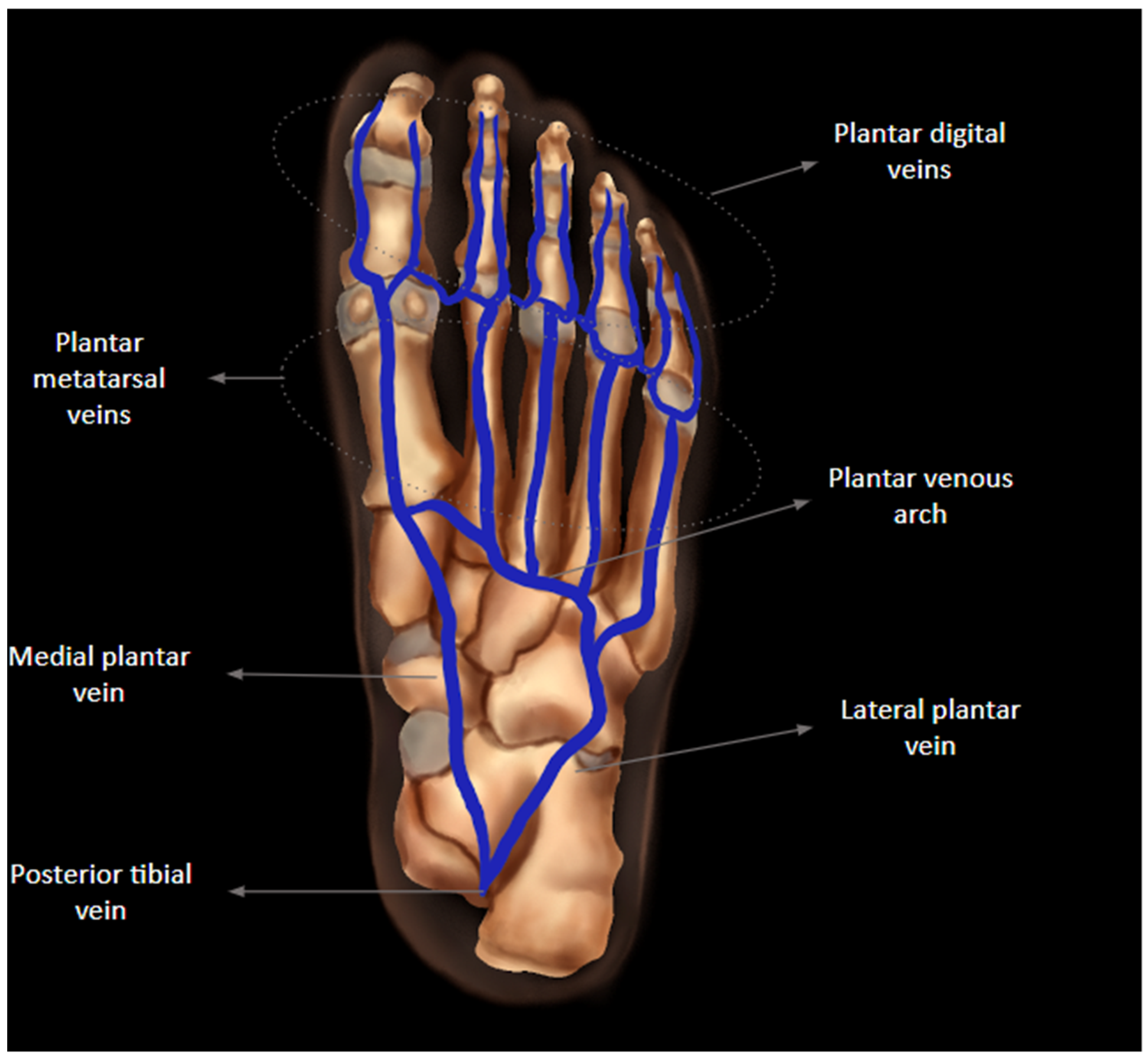
2. Anatomy
3. Predisposing Factors
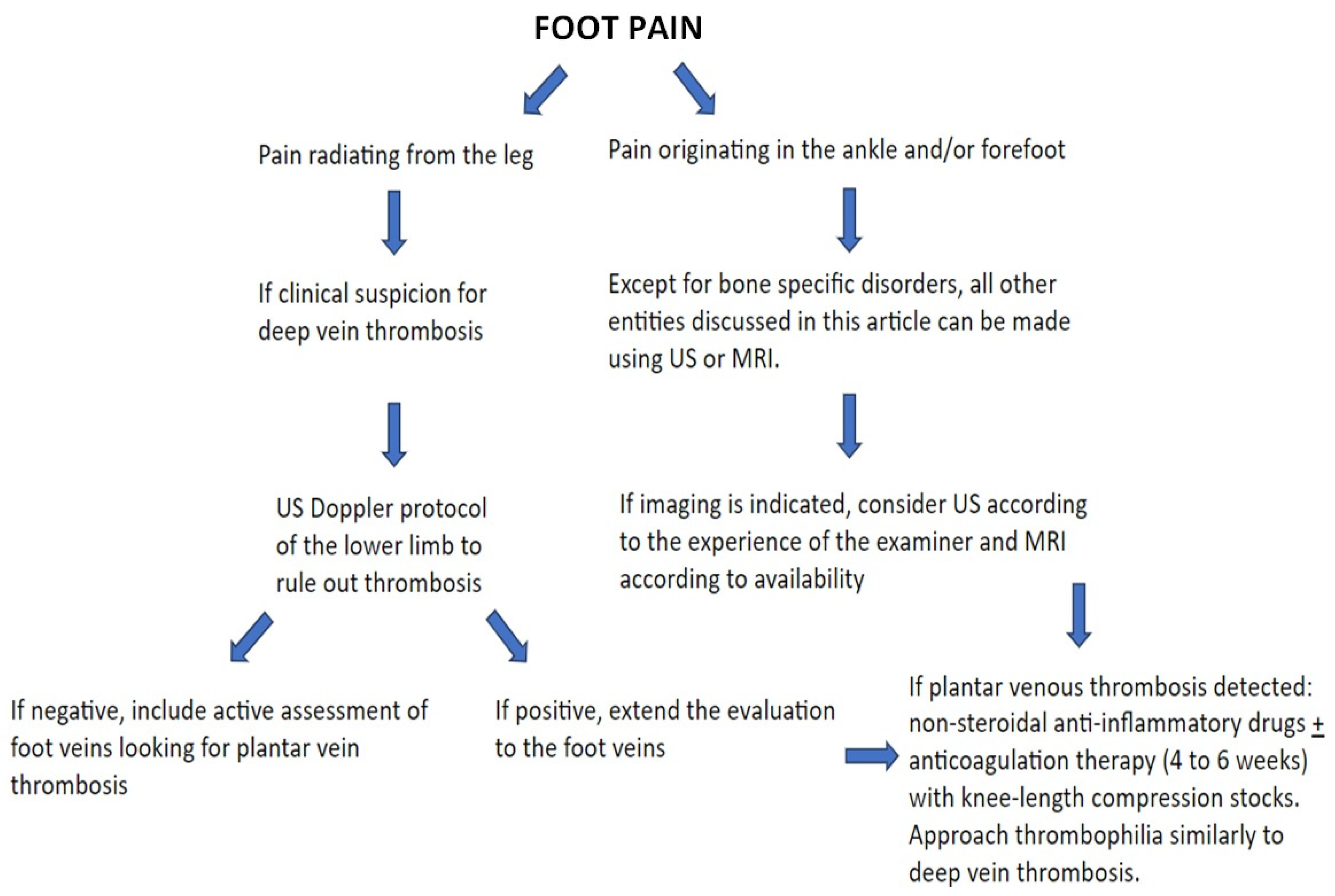
4. Clinical and Laboratorial Findings
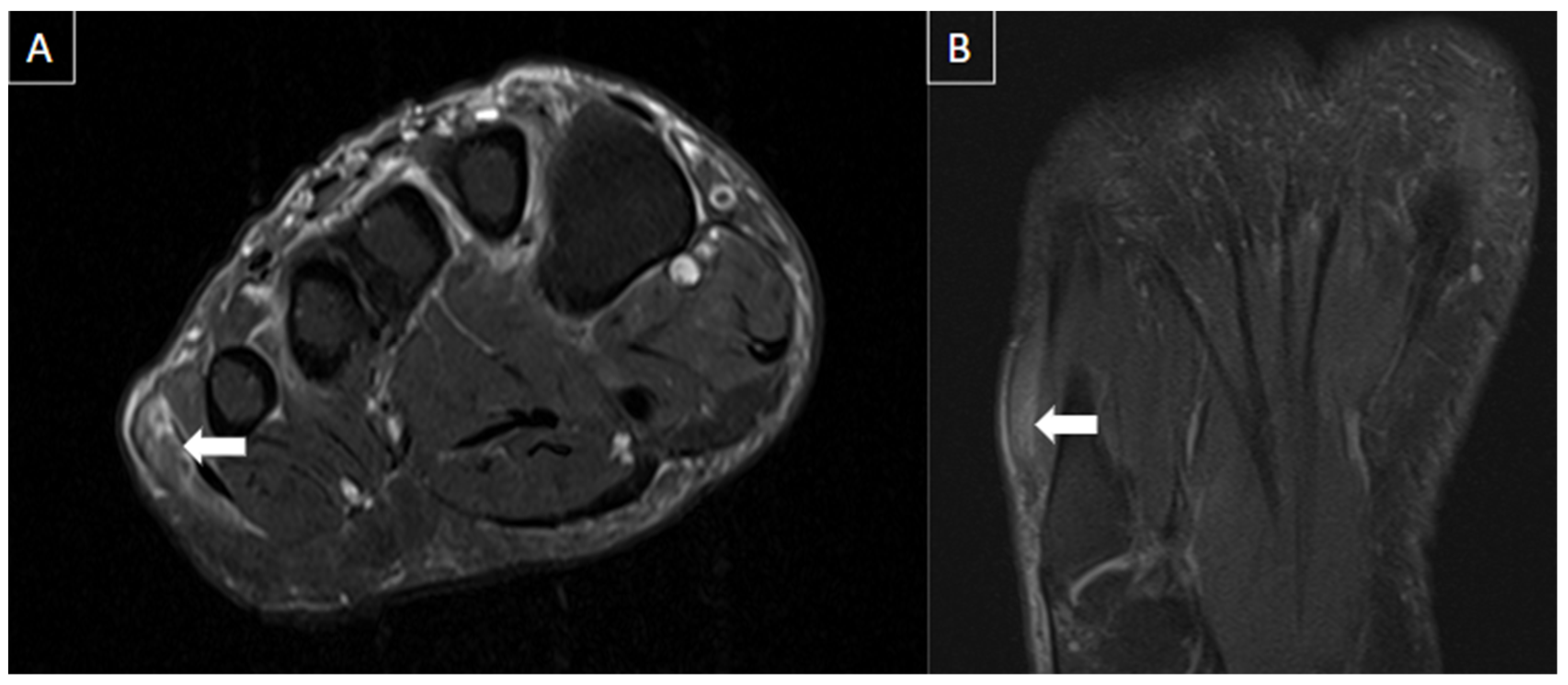
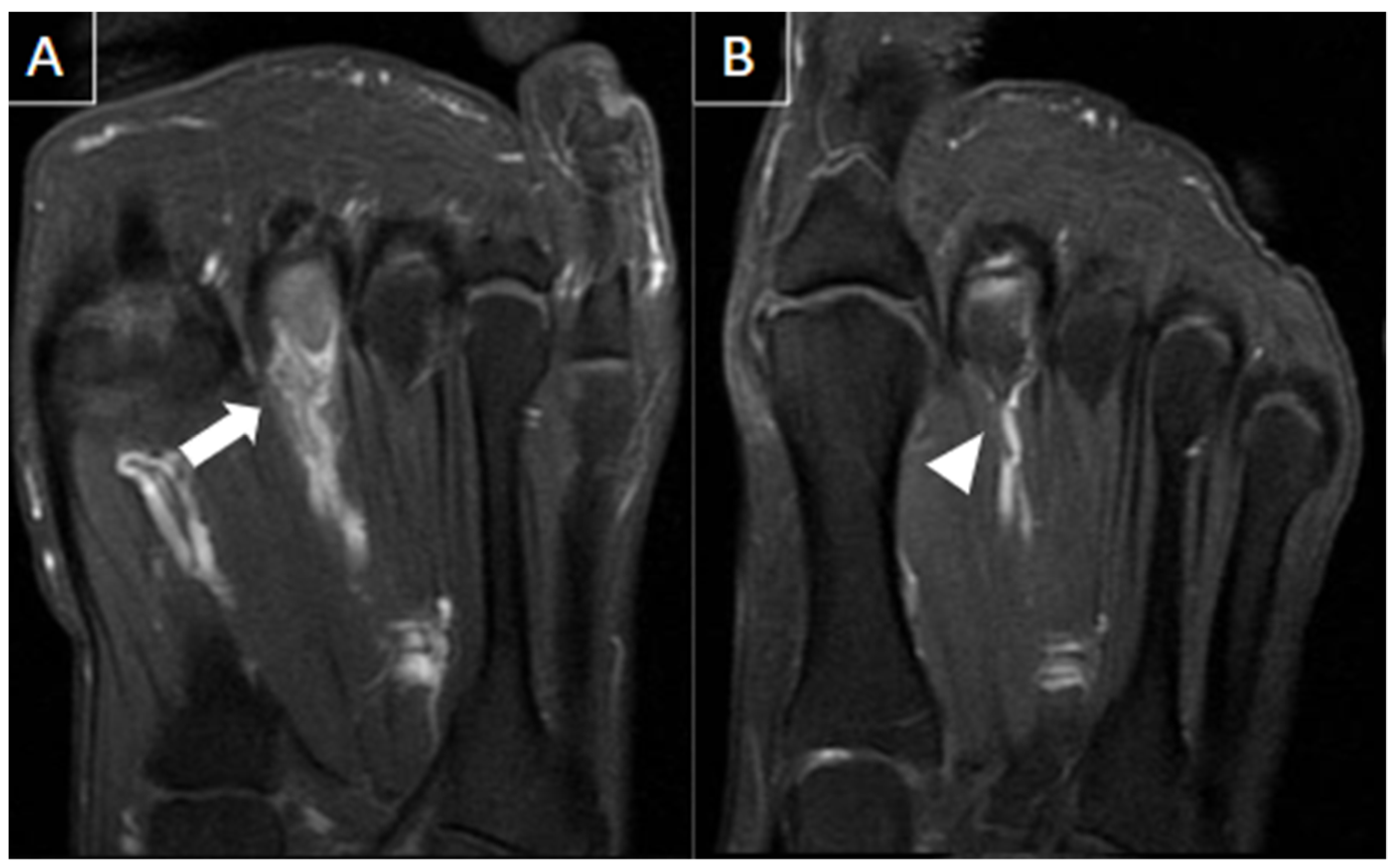
5. Imaging Evaluation
6. Differential Diagnosis
6.1. Intermetatarsal Bursitis
6.2. Morton’s Neuroma
6.3. Sesamoiditis
6.4. Plantar Fasciitis
6.5. Plantar Fibromatosis
6.6. Tendon Pathologies
6.7. Ganglion/Synovial Cysts
6.8. Stress Fractures
6.9. Plantar Plate Injuries
6.10. Freiberg’s Infraction
6.11. Crystal Arthropathies
6.12. Baxter Neuropathy
7. Complications
8. Treatment
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kruger, P.C.; Eikelboom, J.W.; Douketis, J.D.; Hankey, G.J. Deep vein thrombosis: Update on diagnosis and management. Med. J. Aust. 2019, 210, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, S.R.; Wood, O.D. Plantar vein thrombosis. Phlebol. J. Venous Dis. 2021, 36, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karam, L.; Tabet, G.; Nakad, J.; Gerard, J.L. Spontaneous plantar vein thrombosis: State of the art. Phlebology 2013, 28, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, F.C.; Carneiro, R.D.; Longo, C.H.; Fernandes, T.D.; Rosemberg, L.A.; Funari, M.B.D.G. Plantar thrombophlebitis: Magnetic resonance imaging findings. Rev. Bras. Ortop. 2012, 47, 765–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastel, D. Four new cases of isolated foot vein thrombosis: Is the first metatarsal interspace perforator responsible? J. Médecine Vasc. 2021, 46, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, M.L.; O’Dwyer, J.A. A phlebographic study of the incidence and significance of venous thrombosis in the foot. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1978, 130, 751–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czihal, M.; Röling, J.; Rademacher, A.; Schröttle, A.; Kuhlencordt, P.; Hoffmann, U. Clinical characteristics and course of plantar vein thrombosis: A series of 22 cases. Phlebology 2015, 30, 714–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vansevenant, M.; Vanhoenacker, F.M. Plantar Vein Thrombosis: An Unusual Cause of Plantar Pain. J. Belg. Soc. Radiol. 2015, 99, 98–101. [Google Scholar]
- Ricci, S.; Moro, L.; Antonelli Incalzi, R. The foot venous system: Anatomy, physiology and relevance to clinical practice. Dermatol. Surg. 2014, 40, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corley, G.J.; Broderick, B.J.; Nestor, S.M.; Breen, P.P.; Grace, P.A.; Quondamatteo, F.; Ólaighin, G. The anatomy and physiology of the venous foot pump. Anat. Rec. Adv. Integr. Anat. Evol. Biol. 2010, 293, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhl, J.F.; Gillot, C. Anatomy of Perforating veins of the lower limb. Phlebologie 2021, 50, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karip, B.; Ertaş, A. Abnormal vein patterns on the feet: Two case reports. Folia Morphol. 2023, 82, 732–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubincova, M.; Vanhoenacker, F. Plantar Vein Thrombosis Mimicking Tendinopathy. J. Belg. Soc. Radiol. 2022, 106, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, J.V.; Katz, M.L.; Cisek, P.; Kreithen, J. Venous outflow of the leg: Anatomy and physiologic mechanism of the plantar venous plexus. J. Vasc. Surg. 1996, 24, 819–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, M.V.L.; Labropoulos, N. Plantar vein thrombosis—Evaluation by ultrasound and clinical outcome. Angiology 2010, 61, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skeik, N.; Smith, J.E.; Jensen, J.D.; Nowariak, M.E.; Manunga, J.M.; Mirza, A.K. Literature review of distal deep vein thrombosis. J. Vasc. Surg. Venous Lymphat. Disord. 2021, 9, 1062–1070.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swellengrebel, H.J.C.; Backus, T.; Zijta, F.M.; van der Zwaal, P. Plantar vein thrombosis provoked by mechanical strain to the foot: A rare cause of plantar heel pain. BMJ Case Rep. 2019, 12, e230054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becciolini, M.; Galletti, S.; Vallone, G.; Stella, S.M.; Ricci, V. Sonographic diagnosis of clinically unsuspected thrombosis of the medial marginal vein and dorsal arch of the foot. J. Ultrasound 2021, 24, 515–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza Bernardo, B.; Pagnano, R.G.; Pereira Filho, M.V.; de Faria Freitas, M.; e Dinato, M.C.M. Plantar Vein Thrombosis in a Patient with COVID-19: Case Report. J. Am. Podiatr. Med. Assoc. 2023, 113, 21–184. [Google Scholar]
- Lins, S.; Kolbinger, A.; Maier, K.L. Bilateral Plantar Phlebothrombosis After AstraZeneca Vaccination. Dtsch. Arzteblatt. Int. 2021, 118, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leão, R.V.; Bernal, E.C.B.A.; Rodrigues, M.B.; Amaral, D.T.; de Paula Correa, M.F.; Helito, P.V.P. Venous thrombosis: A mimic of musculoskeletal injury on MR imaging. Skeletal Radiol. 2023, 52, 1263–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parakh, R.S.; Sabath, D.E. Venous Thromboembolism: Role of the Clinical Laboratory in Diagnosis and Management. J. Appl. Lab. Med. 2019, 3, 870–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parellada, A.J.; Morrison, W.B.; Reiter, S.B.; Carrino, J.A.; Glickman, P.L.; Kloss, L.A.; Patel, P. Unsuspected lower extremity deep venous thrombosis simulating musculoskeletal pathology. Skeletal Radiol. 2006, 35, 659–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orbell, J.H.; Smith, A.; Burnand, K.G.; Waltham, M. Imaging of deep vein thrombosis. Br. J. Surg. 2008, 95, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.T.; Ilaslan, H. Unicompartmental muscle edema: An early sign of deep venous thrombosis. Skeletal Radiol. 2003, 32, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabro, M.; Fabro, S.R.M.; Sales, R.S.O.; Machado, C.A.; de Araújo, G.L. Plantar vein thrombosis: A rare differential diagnosis in patients with plantar pain. Radiol. Bras. 2015, 48, 399–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodes, A.; Umans, H. Metatarsalgia. Radiol. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 56, 877–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, V.; Slullitel, G. Metatarsalgia: Assessment Algorithm and Decision Making. Foot Ankle Clin. 2019, 24, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonso, P.D.; Britto, S.V.; Spritzer, C.E.; Martins e Souza, P. Differential Diagnosis of Metatarsalgia. Semin. Musculoskelet. Radiol. 2023, 27, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, A.; Warner, J.; Aniq, H. Central Metatarsalgia and Walking on Pebbles: Beyond Morton Neuroma. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2018, 210, 821–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galley, J.; Sutter, R.; Germann, C.; Pfirrmann, C.W.A. The Vulcan salute sign: A non-sensitive but specific sign for Morton’s neuroma on radiographs. Skeletal Radiol. 2022, 51, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torriani, M.; Kattapuram, S.V. Technical innovation. Dynamic sonography of the forefoot: The sonographic Mulder sign. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2003, 180, 1121–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulstaert, T.; Shahabpour, M.; Provyn, S.; Lenchik, L.; Simons, P.; Vanheste, R.; De Maeseneer, M. Forefoot Pain in the Lesser Toes: Anatomical Considerations and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings. Can. Assoc. Radiol. J. 2019, 70, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallinan, J.T.; Statum, S.M.; Huang, B.K.; Bezerra, H.G.; Garcia, D.A.; Bydder, G.M.; Chung, C.B. High-Resolution MRI of the First Metatarsophalangeal Joint: Gross Anatomy and Injury Characterization. Radiographics 2020, 40, 1107–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latt, L.D.; Jaffe, D.E.; Tang, Y.; Taljanovic, M.S. Evaluation and Treatment of Chronic Plantar Fasciitis. Foot Ankle Orthop. 2020, 5, 2473011419896763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draghi, F.; Gitto, S.; Bortolotto, C.; Draghi, A.G.; Ori Belometti, G. Imaging of plantar fascia disorders: Findings on plain radiography, ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging. Insights Imaging 2017, 8, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khammas, A.S.A.; Mahmud, R.; Hassan, H.A.; Ibrahim, I.; Mohammed, S.S. An assessment of plantar fascia with ultrasound findings in patients with plantar fasciitis: A systematic review. J. Ultrasound 2023, 26, 13–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drake, C.; Whittaker, G.A.; Kaminski, M.R.; Chen, J.; Keenan, A.M.; Rathleff, M.S.; Robinson, P.; Landorf, K.B. Medical imaging for plantar heel pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Foot Ankle Res. 2022, 15, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeswani, T.; Morlese, J.; McNally, E.G. Getting to the heel of the problem: Plantar fascia lesions. Clin. Radiol. 2009, 64, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, A.; Backman, L.J.; Speed, C. Tendinopathy: Update on Pathophysiology. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2015, 45, 833–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abat, F.; Alfredson, H.; Cucchiarini, M.; Madry, H.; Marmotti, A.; Mouton, C.; Oliveira, J.M.; Pereira, H.; Peretti, G.M.; Romero-Rodriguez, D.; et al. Current trends in tendinopathy: Consensus of the ESSKA basic science committee. Part I: Biology, biomechanics, anatomy and an exercise-based approach. J. Exp. Orthop. 2017, 4, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taneja, A.K.; Simeone, F.J.; Chang, C.Y.; Kumar, V.; Daley, S.; Bredella, M.A.; Torriani, M. Peroneal tendon abnormalities in subjects with an enlarged peroneal tubercle. Skeletal Radiol. 2013, 42, 1703–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jungmann, P.M.; Schaeffeler, C. Bone Stress Injuries at the Ankle and Foot. Semin. Musculoskelet. Radiol. 2023, 27, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, S.; Chhabra, A.; Taneja, A.K. 3D isotropic MRI of ankle: Review of literature with comparison to, 2D MRI. Skeletal Radiol. 2023, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Saifuddin, A. Magnetic resonance imaging of subchondral insufficiency fractures of the lower limb. Skeletal Radiol. 2019, 48, 1011–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enge, D.J.; Fonseca, E.K.U.N.; Baptista, E.; Santos, D.D.C.B.; Rosemberg, L.A. Avascular necrosis: Radiological findings and main sites of involvement-pictorial essay. Radiol. Bras. 2019, 52, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teh, J.; McQueen, F.; Eshed, I.; Plagou, A.; Klauser, A. Advanced Imaging in the Diagnosis of Gout and Other Crystal Arthropathies. Semin. Musculoskelet. Radiol. 2018, 22, 225–236. [Google Scholar]
- Jaring, M.R.F.; Khan, A.Z.; Livingstone, J.A.; Chakraverty, J. A Case of Bilateral Baxter’s Neuropathy Secondary to Plantar Fasciitis. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2019, 58, 771–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, M.; Nascimento, I.; Barros, T.; Labropoulos, N. Plantar vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Phlebology 2015, 30, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colucci, G.; Tsakiris, D.A. Thrombophilia screening revisited: An issue of personalized medicine. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2020, 49, 618–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
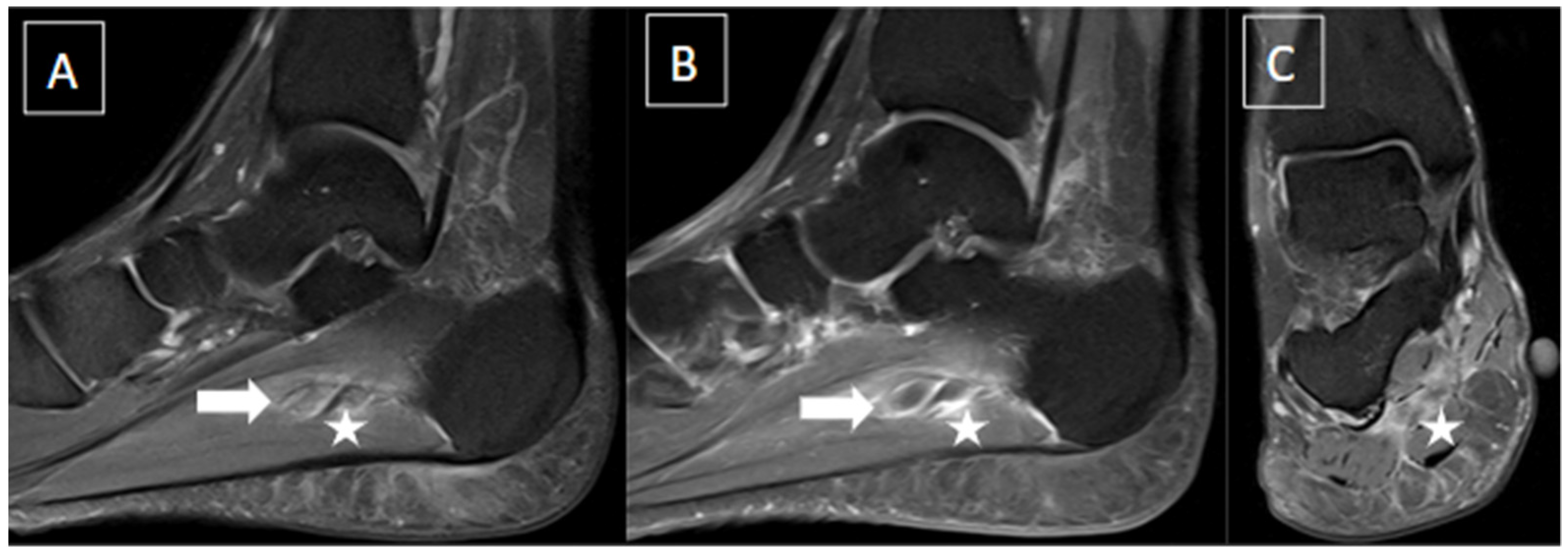
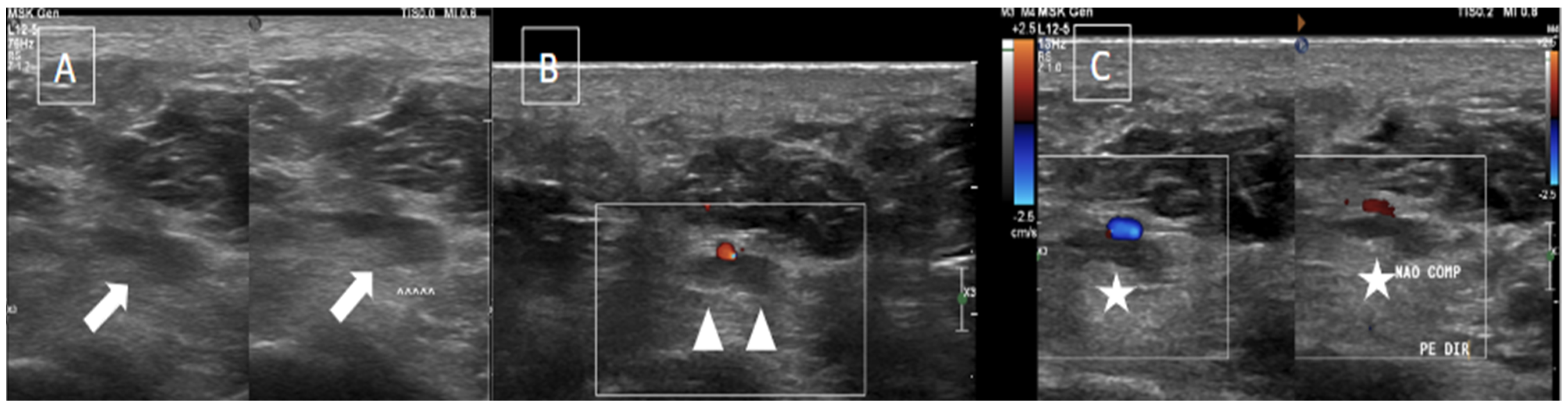
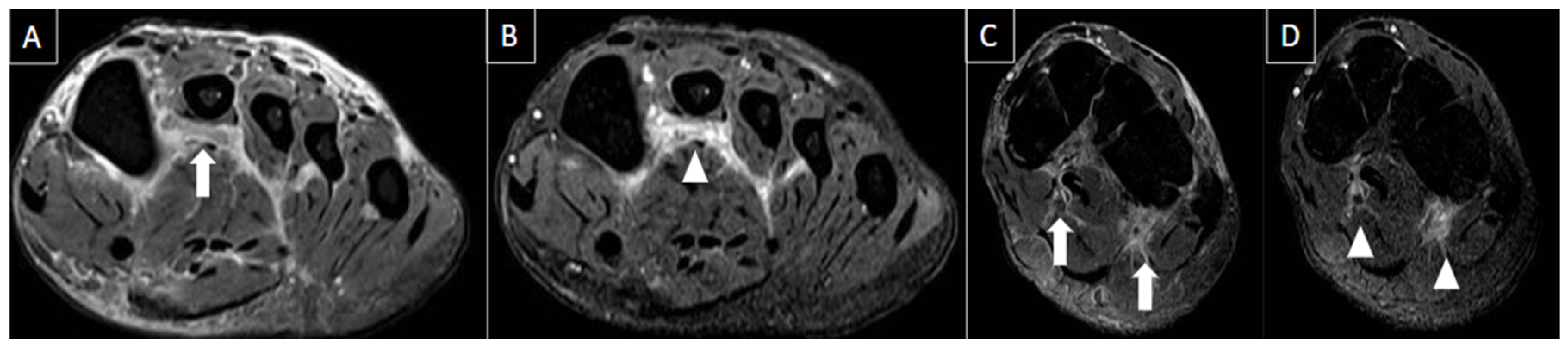
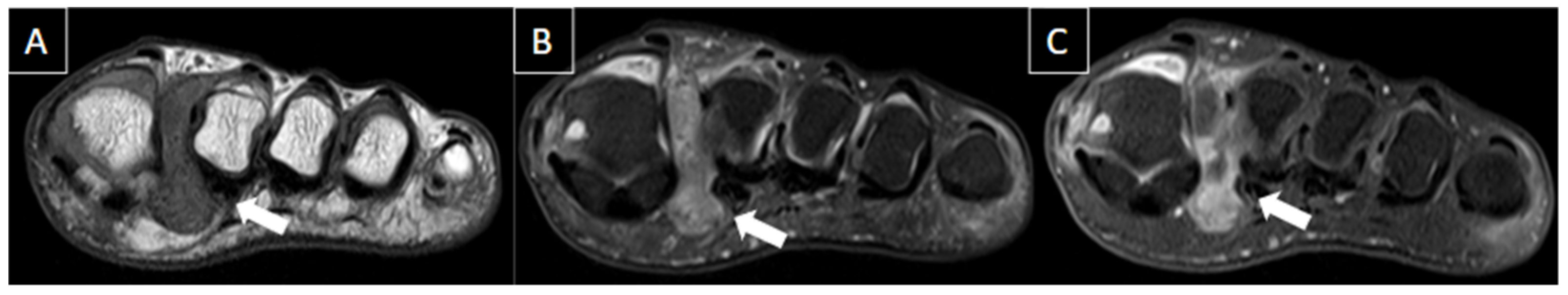
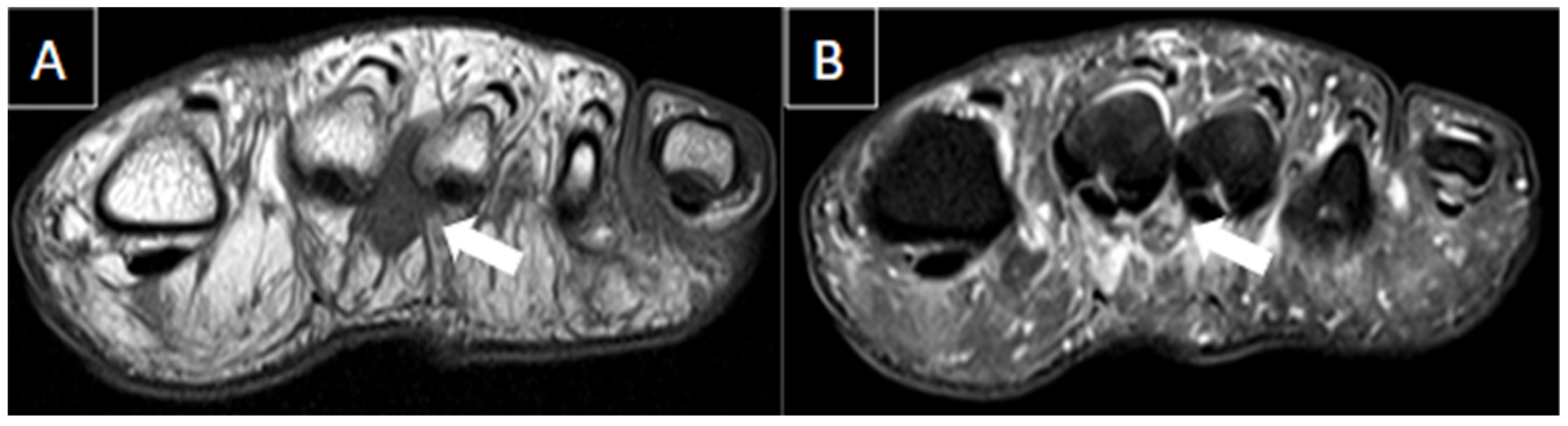

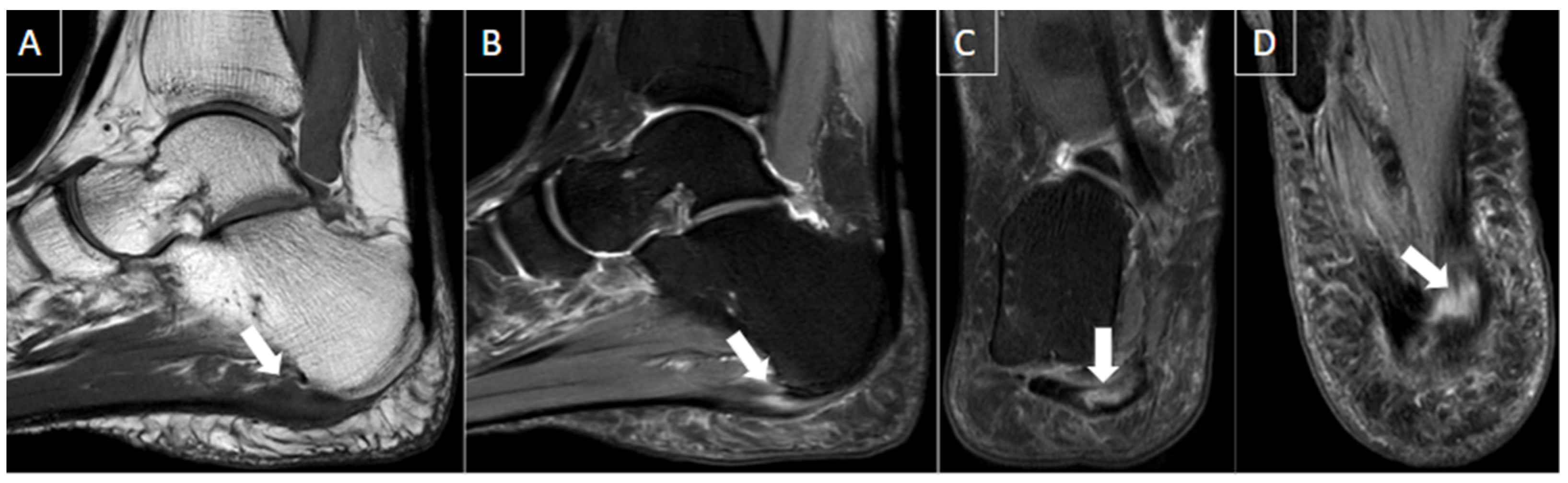
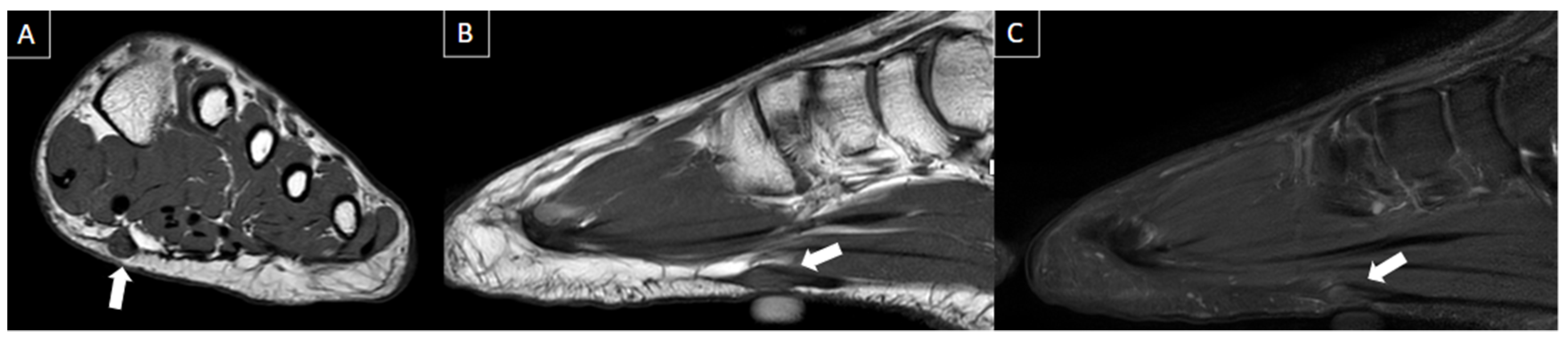
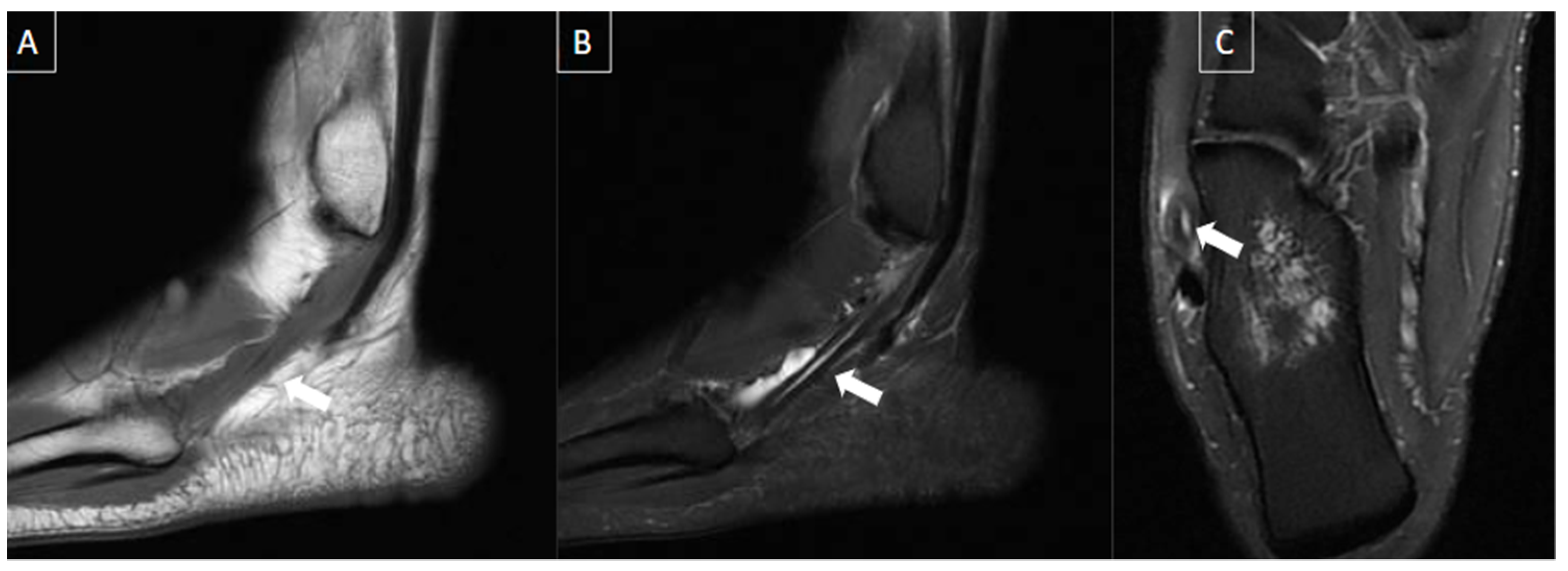

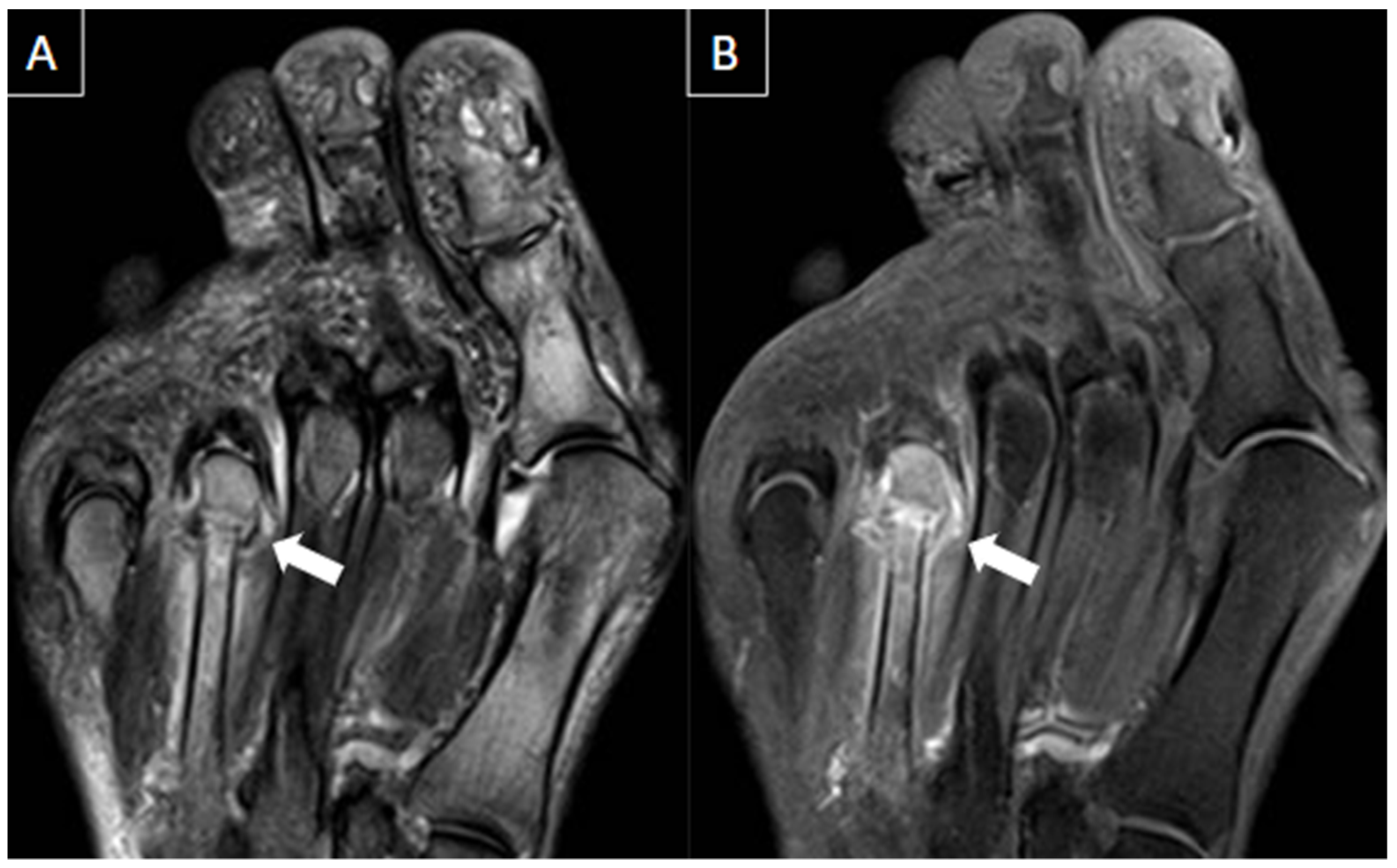
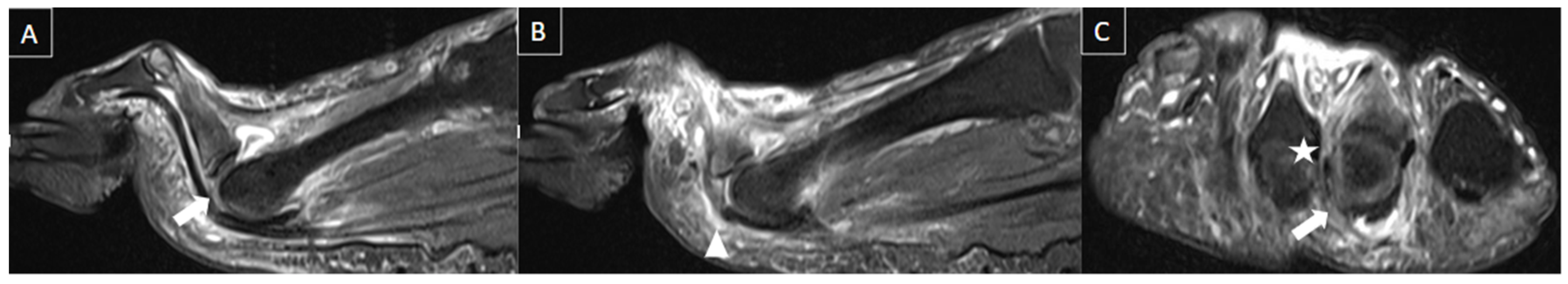
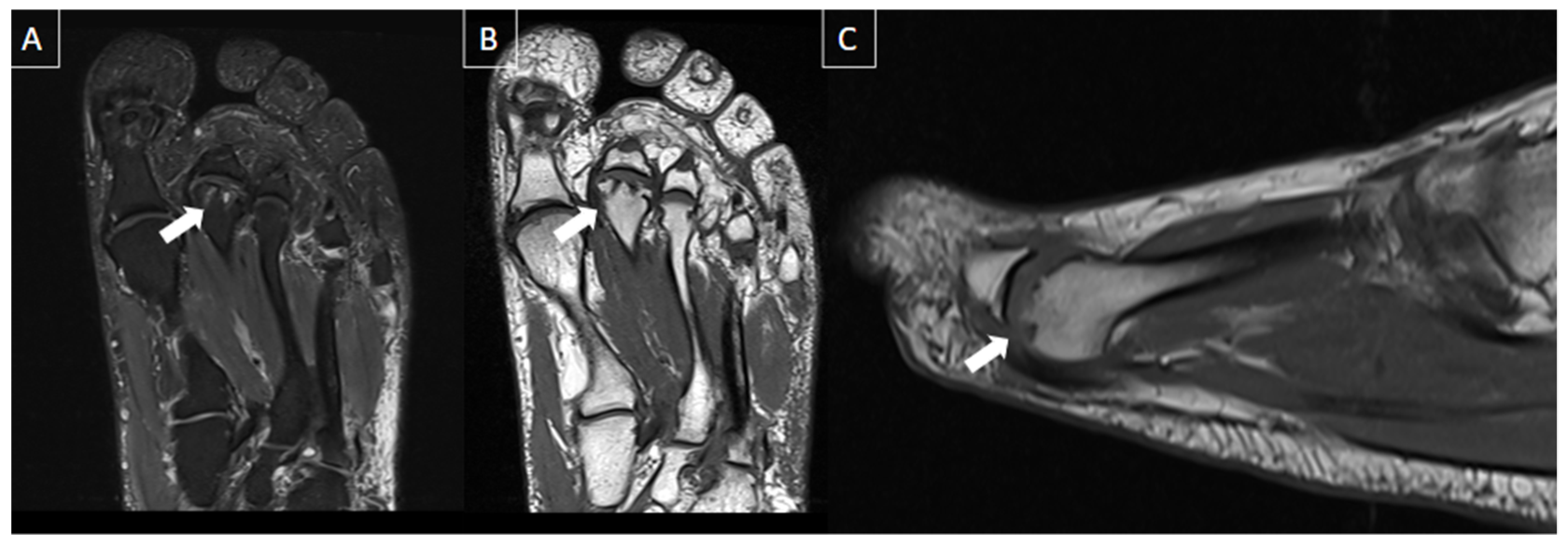

| MRI | B-Mode US | Color and Pulsed-Wave Doppler US |
|---|---|---|
| Perivascular edema and enhancement Muscle edema Intraluminal signal change Venous enlargement Presence of collateral veins Venous filling defects (post-gadolinium injection) | Local tenderness Loss of compressibility Venous enlargement Intraluminal content Perivascular edema | Local tenderness Loss of flow Filling defects |
| Differential Diagnosis | Clinical | US | MRI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intermetatarsal bursitis | Metatarsalgia, frequently associated with Morton’s neuroma and plantar plate tears. | Thin-walled bursa distended with hypoechoic fluid and peri bursal hyperemia (acute). Thickened bursal wall, chronic synovial proliferation, more echogenic content, and intrabursal hyperemia (chronic). | Hypointense on T1-weighted and hyperintense on T2-weighted fat-suppressed images. Peripheral enhancement may be seen post gadolinium. |
| Morton’s neuroma | Forefoot pain which radiates from the midfoot to toes. Symptoms are often progressive and worsened by activity. | Well-defined ovoid mass with variable echogenicity with continuity with the interdigital nerve in the long axis. The mass can be tender and mobile when compressed, with vascularity on power Doppler. | Hypointense to isointense on T1-weighted images and hypointense to hyperintense on T2-weighted fat-suppressed images. |
| Sesamoiditis | Painful inflammatory/mechanical condition caused by repetitive injury to the plantar aspect of the forefoot. | Not generally used but can show shrinking and fragmentation in chronic cases. | Increased signal intensity on fluid-sensitive sequences due to marrow edema (acute phase). In chronic stages, it can manifest with sclerosis. |
| Plantar fasciitis | Most common cause of unilateral heel pain. | Ultrasound findings include thickening greater than 4.5 mm (the most useful sign), hypoechogenicity of the plantar fascia, and loss of normal fibrillar reflective echotexture. | Hypointense or isointense fascial thickening at calcaneal insertion on T1-weighted images. |
| Plantar fibromatosis | Pain due to mass effect or infiltration of adjacent muscles or neurovascular structures. | Fusiform-shaped nodule at the plantar fascia away from the calcaneal insertion, either hypoechoic or isoechoic to the fascia. | Isointense plantar fascia nodule on T1-weighted and T2-weighted fat-suppressed images with contrast enhancement. |
| Tendon pathologies | Varies according to the cause (tendinosis/ tendinopathy, tenosynovitis, and peritendinitis). | Intra and peritendinous alterations with enlargement of the tendon and various degrees of hypoechogenicity. | Enlargement and signal abnormalities in the affected tendon. High signal intensity can be seen involving the tendon and peritendinous soft tissues. |
| Ganglion/synovial cysts | Mass effect on adjacent structures (frequently related to trauma history). | Well-defined uni or multilocular fluid-filled anechoic masses with posterior acoustic enhancement. | Mass with water equivalent signal (uniformly hyperintense on T2), and the walls can show post-gadolinium enhancement. |
| Stress fractures | Most common bony cause of metatarsalgia. | Thickening and hypervascularity of the periosteum, cortical irregularities, and soft tissue edema. | Periosteal, bone marrow, and soft tissue edema. |
| Plantar plate injuries | Metatarsalgia and/or deformity in cases of full-thickness plantar plate tears. | Thickening and hypoechogenicity or discontinuity and entheseal irregularity at the base of the proximal phalanx. | Ligament rupture, thickening, laxity, and redundancy. Bone marrow edema of the metatarsal head and phalanx base due to mechanical changes. |
| Freiberg’s infraction | Pain on weight-bearing with swelling and tenderness. | Not generally used but can show deformity and depression of the metatarsal head in advanced cases. | Linear subchondral hypointense line on T1 and T2-weighted images with surrounding bone marrow edema. |
| Crystal arthropathies | Severe acute or subacute pain, swelling, erythema, and warmth of one or more joints and is usually self-limited. | Periarticular edema. | Erosions, chondral defect, and periarticular edema. Hypointense signal intensity areas on both T1 and T2-weighted images (hydroxyapatite deposition). |
| Baxter neuropathy | Pain, related to the entrapment of the inferior calcaneal nerve. | Edema within the affected muscle. | Edema, atrophy, and fatty infiltration, according to the denervation stage |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miranda, F.C.; e Castro, A.d.A.; Yoshimura, F.B.; Godoy-Santos, A.L.; Santos, D.d.C.B.; Rosemberg, L.A.; Taneja, A.K. Imaging Features of Plantar Vein Thrombosis: An Easily Overlooked Condition in the Differential Diagnosis of Foot Pain. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14020126
Miranda FC, e Castro AdA, Yoshimura FB, Godoy-Santos AL, Santos DdCB, Rosemberg LA, Taneja AK. Imaging Features of Plantar Vein Thrombosis: An Easily Overlooked Condition in the Differential Diagnosis of Foot Pain. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(2):126. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14020126
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiranda, Frederico Celestino, Adham do Amaral e Castro, Fábio Brandão Yoshimura, Alexandre Leme Godoy-Santos, Durval do Carmo Barros Santos, Laercio Alberto Rosemberg, and Atul Kumar Taneja. 2024. "Imaging Features of Plantar Vein Thrombosis: An Easily Overlooked Condition in the Differential Diagnosis of Foot Pain" Diagnostics 14, no. 2: 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14020126
APA StyleMiranda, F. C., e Castro, A. d. A., Yoshimura, F. B., Godoy-Santos, A. L., Santos, D. d. C. B., Rosemberg, L. A., & Taneja, A. K. (2024). Imaging Features of Plantar Vein Thrombosis: An Easily Overlooked Condition in the Differential Diagnosis of Foot Pain. Diagnostics, 14(2), 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14020126







