Identifying Acute Aortic Syndrome and Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm from Chest Radiography in the Emergency Department Using Convolutional Neural Network Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
- This study compares the performance of four various CNN architectures on medical imaging, demonstrating the varying effectiveness of different models in CXR diagnosis.
- The ground truth for disease diagnosis in this study was established using CTA, which is the gold standard imaging tool for aortic disease.
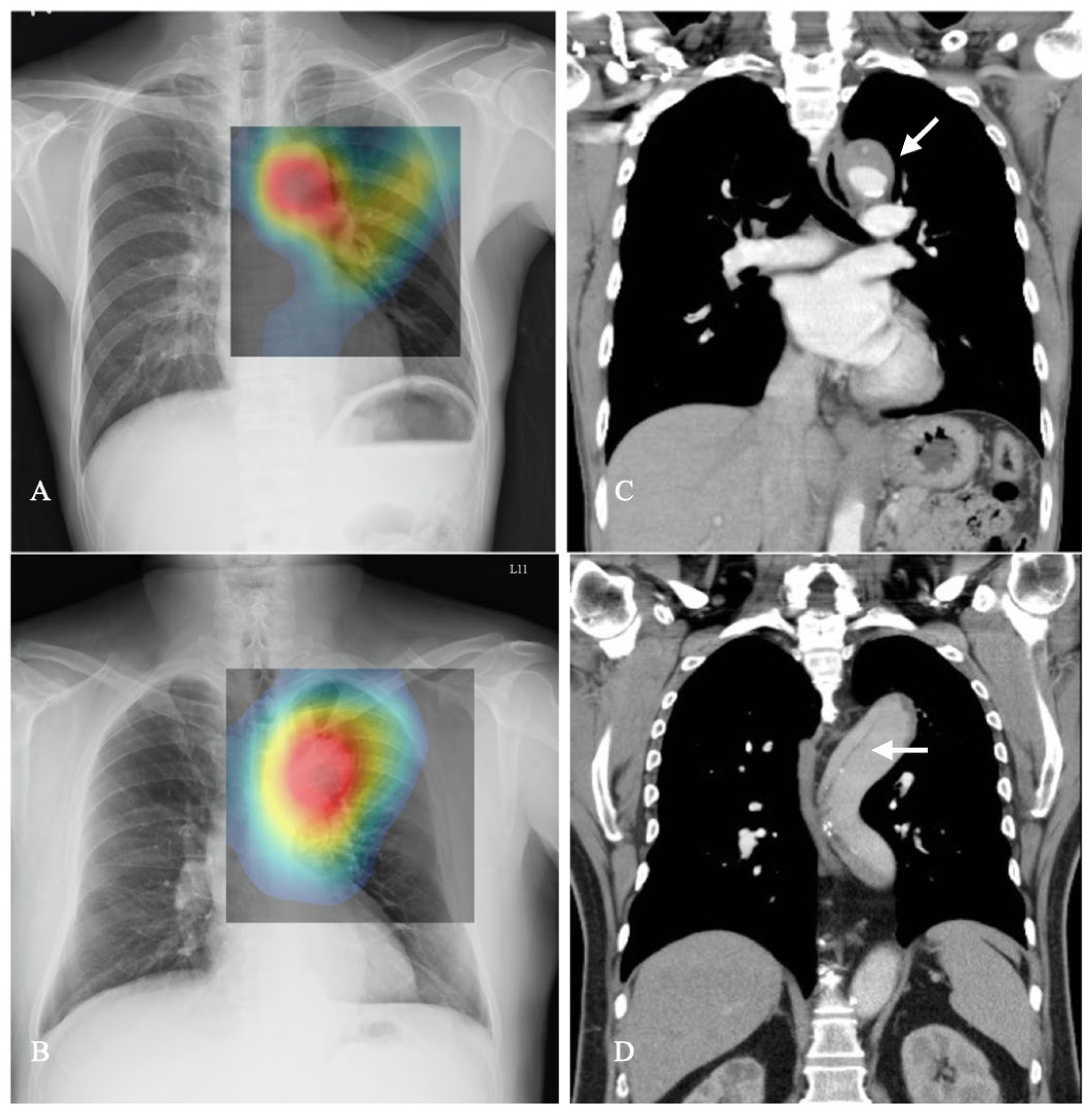
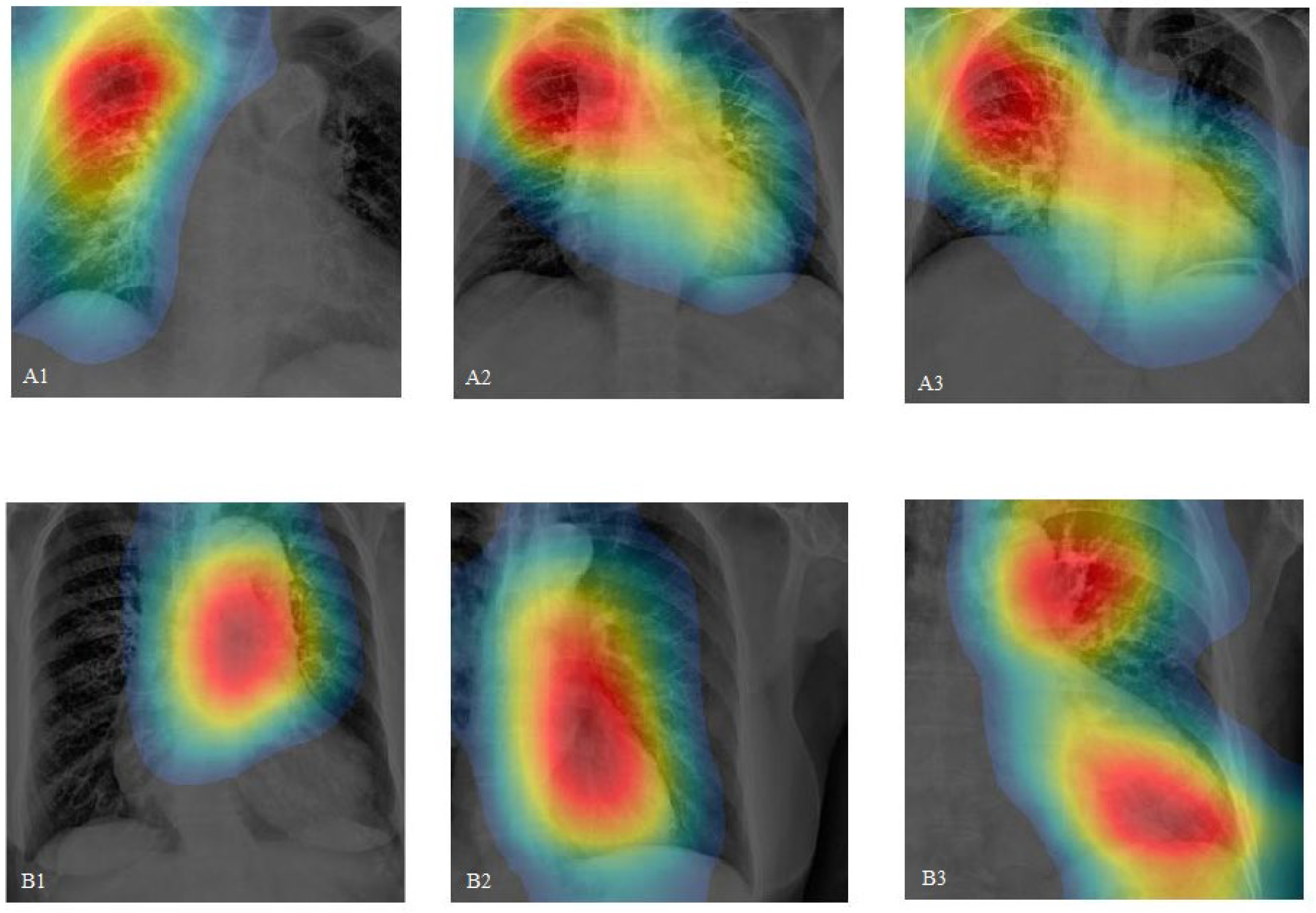
- By incorporating class activation mapping (CAM) in CXRs and comparing it with CTA, our study demonstrates that CNNs have the potential to accurately pinpoint aortic lesions.
- This research highlights the specificity of CNNs in disease diagnosis, suggesting that they can be practically applied in emergency clinical settings.
2. Method
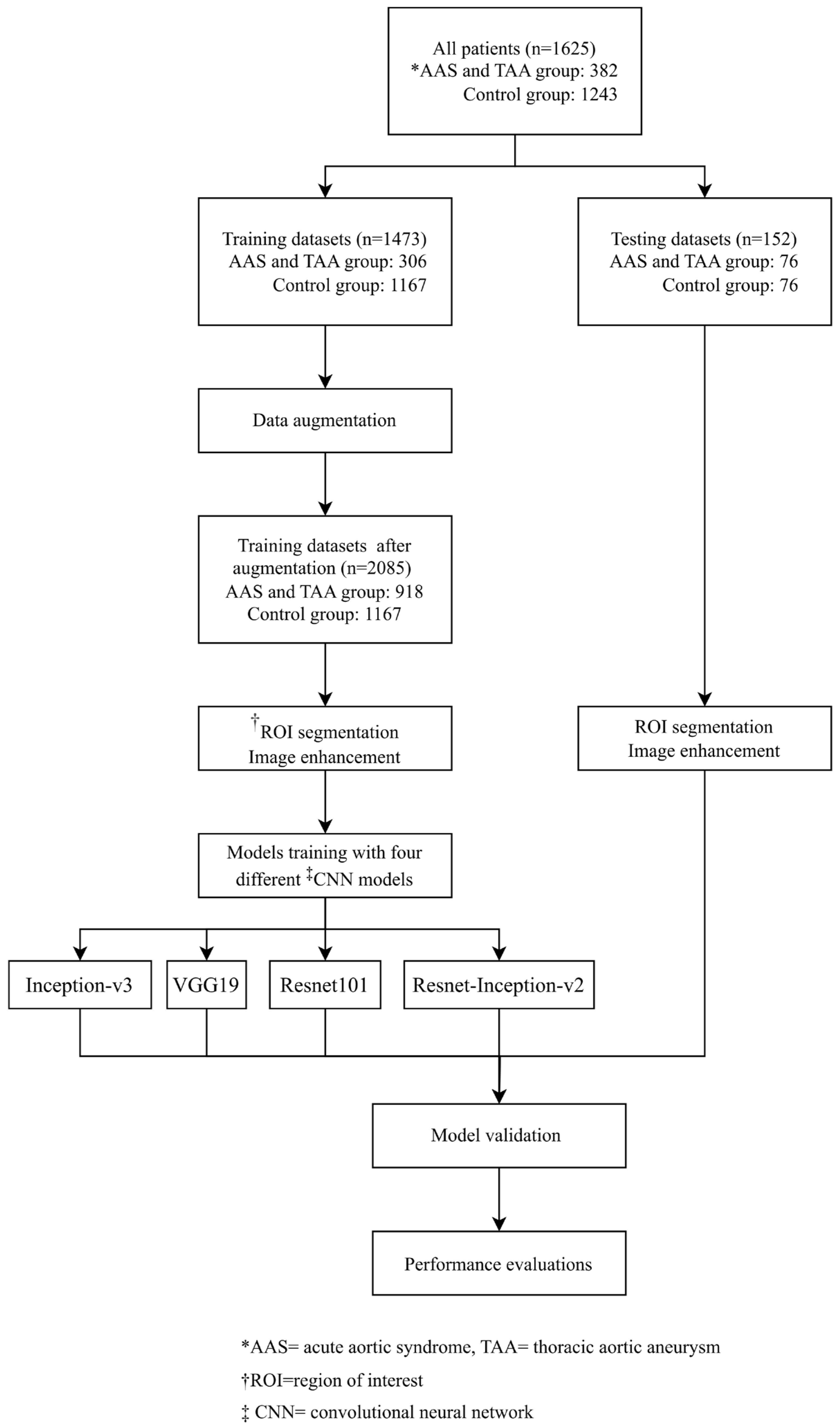
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Data Collection and Assignment to Case and Control Groups
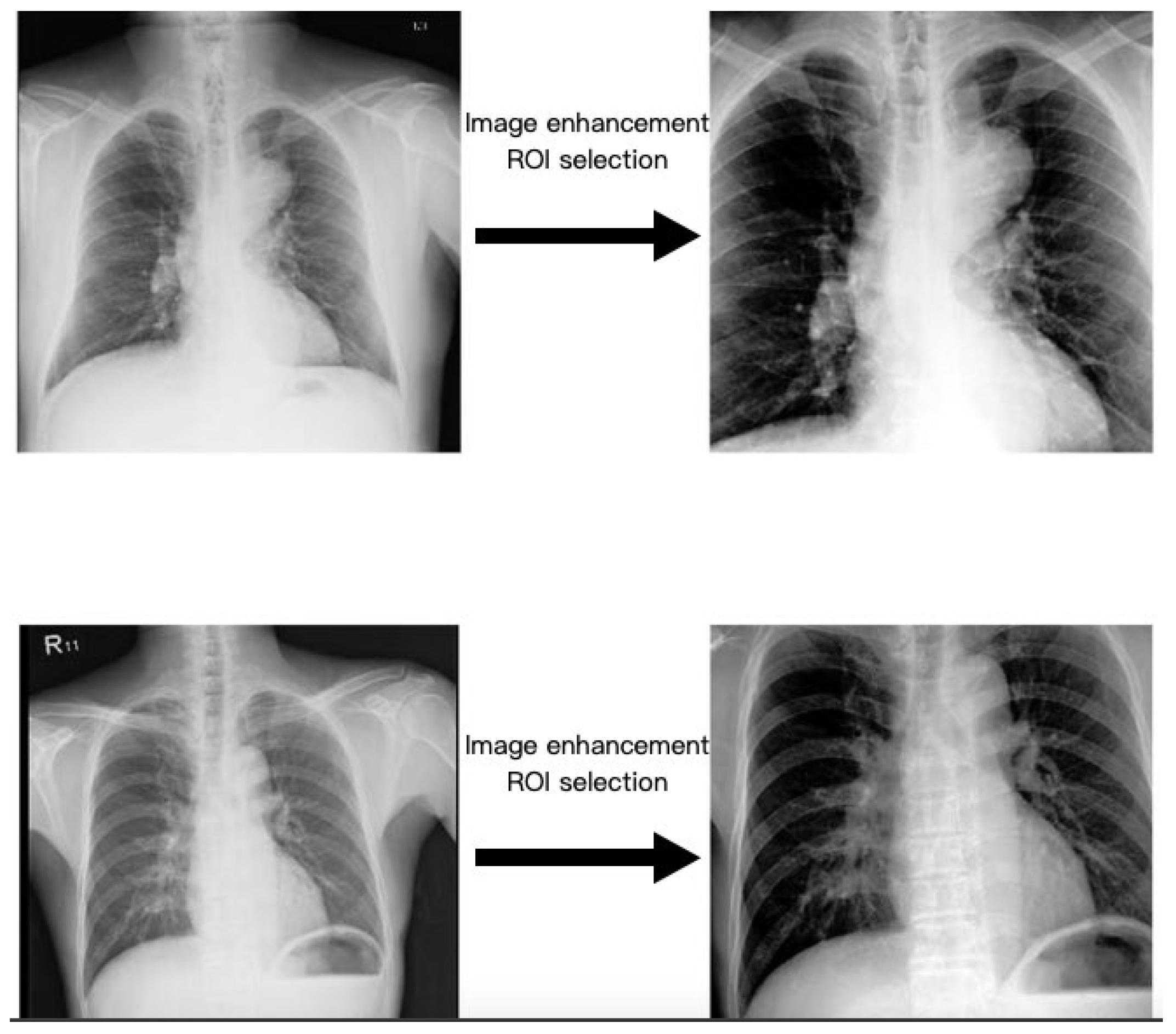
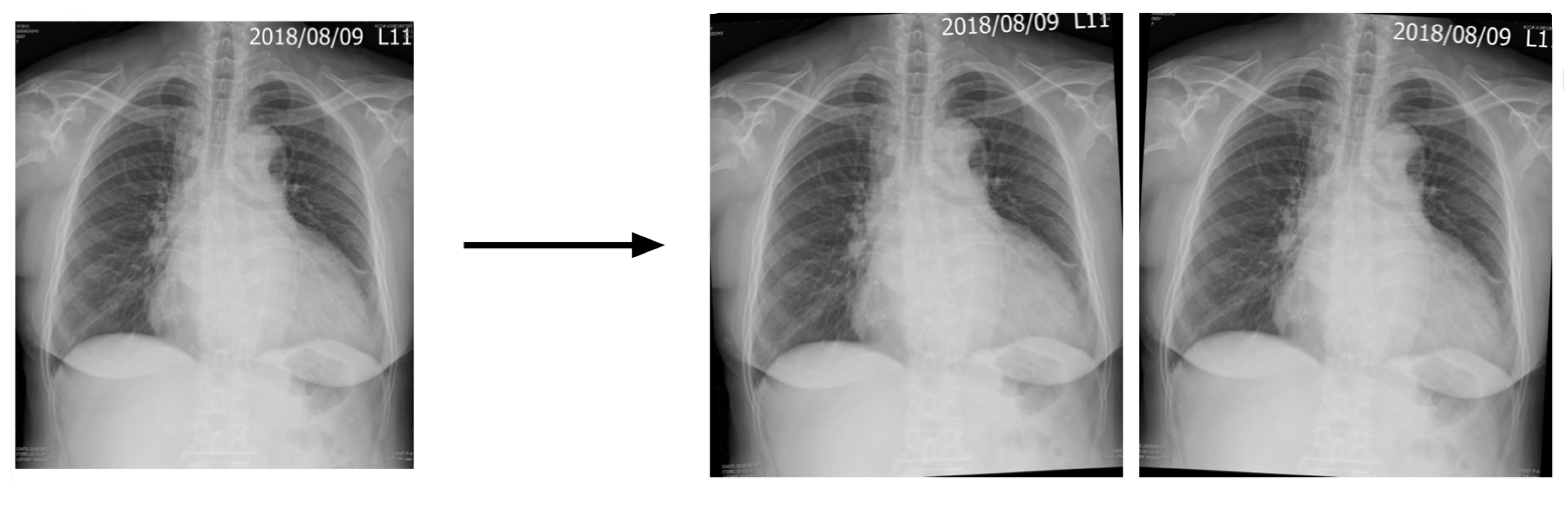
2.3. Region of Interest
2.4. Image Enhancement
2.5. Data Augmentation
2.6. Pre-Trained CNN Model
2.7. Statistical Analysis and Model Performance Evaluations
2.8. Training Parameters, Software, and Hardware
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vilacosta, I.; Román, J.A.S.; Aragoncillo, P.; Ferreirós, J.; Mendez, R.; Graupner, C.; Batlle, E.; Serrano, J.; Pinto, A.; Oyonarte, J.M. Penetrating atherosclerotic aortic ulcer: Documentation by transesophageal echocardiography. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1998, 32, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bossone, E.; LaBounty, T.M.; Eagle, K.A. Acute aortic syndromes: Diagnosis and management, an update. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 739–749d. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, G.; Markström, U.; Swedenborg, J. Ruptured thoracic aortic aneurysms: A study of incidence and mortality rates. J. Vasc. Surg. 1995, 21, 985–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagan, P.G.; Nienaber, C.A.; Isselbacher, E.M.; Bruckman, D.; Karavite, D.J.; Russman, P.L.; Evangelista, A.; Fattori, R.; Suzuki, T.; Oh, J.K.; et al. The International Registry of Acute Aortic Dissection (IRAD). J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2000, 283, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.-M.; Kim, H.; Kwon, O.; Om, S.Y.; Heo, R.; Lee, S.; Kim, D.-H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.B.; Jung, S.H.; et al. Differential clinical features and long-term prognosis of acute aortic syndrome according to disease entity. Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, 2727–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earnest, F.T.; Muhm, J.R.; Sheedy, P.F., 2nd. Roentgenographic findings in thoracic aortic dissection. Mayo Clin. Proc. 1979, 54, 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- JaJagannath, A.; Sos, T.; Lockhart, S.; Saddekni, S.; Sniderman, K.; Jagannath, T.S.A.; LePage, M.A.; Quint, L.E.; Sonnad, S.S.; Deeb, G.M.; et al. Aortic dissection: A statistical analysis of the usefulness of plain chest radiographic findings. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1986, 147, 1123–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klompas, M. Does this patient have an acute thoracic aortic dissection? JAMA 2002, 287, 2262–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- vovon Kodolitsch, Y.; A Nienaber, C.; Dieckmann, C.; Schwartz, A.G.; Hofmann, T.; Brekenfeld, C.; Nicolas, V.; Berger, J.; Meinertz, T. Chest radiography for the diagnosis of acute aortic syndrome. Am. J. Med. 2004, 116, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiga, T.; Wajima, Z.I.; Apfel, C.C.; Inoue, T.; Ohe, Y. Diagnostic accuracy of transesophageal echocardiography, helical computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging for suspected thoracic aortic dissection: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Intern. Med. 2006, 166, 1350–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- YoshidYoshida, S.; Akiba, H.; Tamakawa, M.; Yama, N.; Hareyama, M.; Morishita, K.; Abe, T. Thoracic involvement of type A aortic dissection and intramural hematoma: Diagnostic accuracy—Comparison of emergency helical CT and surgical findings. Radiology 2003, 228, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarle, W.S. Neural Networks and Statistical Models. 1994. Available online: https://people.orie.cornell.edu/davidr/or474/nn_sas.pdf (accessed on 24 August 2020).
- Schmidhuber, J. Deep learning in neural networks: An overview. Neural Netw. Off. J. Int. Neural Netw. Soc. 2015, 61, 85–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topol, E.J. High-performance medicine: The convergence of human and artificial intelligence. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, C.; Kumar, I.; Vijayakumar, V.; Singh, K.U.; Kumar, A. The state of the art of deep learning models in medical science and their challenges. Multimed. Syst. 2021, 27, 599–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, I.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, V.D.A.; Kannan, R.; Vimal, V.; Singh, K.U.; Mahmud, M. Dense Tissue Pattern Characterization Using Deep Neural Network. Cogn. Comput. 2022, 14, 1728–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, D.; Kou, B.; Zhou, Z.; Lv, M. A machine learning model to classify aortic dissection patients in the early diagnosis phase. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hata, A.; Yanagawa, M.; Yamagata, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Kido, S.; Kawata, A.; Doi, S.; Yoshida, Y.; Miyata, T.; Tsubamoto, M.; et al. Deep learning algorithm for detection of aortic dissection on non-contrast-enhanced CT. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 1151–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajpurkar, P.; Irvin, J.; Zhu, K.; Yang, B.; Mehta, H.; Duan, T.; Ding, D.; Bagul, A.; Langlotz, C.; Shpanskaya, K.; et al. Chexnet: Radiologist-level pneumonia detection on chest x-rays with deep learning. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.05225v3. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, C.; Yao, D.; Shi, Y.; Song, Z. Computer-aided detection in chest radiography based on artificial intelligence: A survey. Biomedical engineering online 2018, 17, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Cheshire, N.; Hamady, M. Acute aortic syndrome: Pathology and therapeutic strategies. Postgrad. Med. J. 2006, 82, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, D.; Soltaninejad, S.; Hazarika, D.; Mbuyi, G.; Barnwal, R.; Basu, A. Medical image compression based on region of interest using better portable graphics (BPG). In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), Banff, AB, Canada, 5–8 October 2017; Volume 2017, pp. 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xiao, H. Extracting regions of interest in biomedical images. In Proceedings of the 2008 International Seminar on Future BioMedical Information Engineering, Wuhan, China, 18 December 2008; pp. 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dollar, P.; Appel, R.; Belongie, S.; Perona, P. Fast Feature Pyramids for Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2014, 36, 1532–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza, A.M. Realization of the contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization (CLAHE) for real-time image enhancement. J. VLSI Signal Process. Syst. Signal Image Video Technol. 2004, 38, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 2818–2826. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Ioffe, S.; Vanhoucke, V.; Alemi, A. Inception V4, inception-resnet and the impact of residual connections on learning. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, CA, USA, 4–9 February 2017; Volume 31. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Ling, C. Using AUC and accuracy in evaluating learning algorithms. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2005, 17, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Khosla, A.; Lapedriza, A.; Oliva, A.; Torralba, A. Learning deep features for discriminative localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 2921–2929. [Google Scholar]
- Aneja, J.; Deshpande, A.; Schwing, A.G. Convolutional Image Captioning. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 5561–5570. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.K.; Kim, J.H.; Oh, J.; Kim, T.H.; Yoon, M.S.; Im, D.J.; Chung, J.H.; Byun, H. Author Correction: Detection of acute thoracic aortic dissection based on plain chest radiography and a residual neural network (Resnet). Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, E.; Cardenas, D.A.C.; Dias, F.M.; E Krieger, J.; A Gutierrez, M. Explainable AI in Deep Learning-Based Detection of Aortic Elongation on Chest X-ray Images. Eur. Heart J. Digit. Health 2024, ztae045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hautz, S.C.; Schuler, L.; Kammer, J.E.; Schauber, S.K.; Ricklin, M.E.; Sauter, T.C.; Maier, V.; Birrenbach, T.; Exadaktylos, A.; Hautz, W.E. Factors predicting a change in diagnosis in patients hospitalised through the emergency room: A prospective observational study. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e011585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, K.; McParland, A. Applications of artificial intelligence in emergency medicine. Univ. Tor. Med. J. 2019, 96, 37–39. [Google Scholar]
- Shih, B.-H.; Yeh, C.-C. Advancements in Artificial Intelligence in Emergency Medicine in Taiwan: A Narrative Review. J. Acute Med. 2024, 14, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-T.; Shia, B.-C.; Chang, C.-J.; Wu, Y.; Yang, J.-D.; Kang, J.-H. Using Transfer Learning of Convolutional Neural Network on Neck Radiographs to Identify Acute Epiglottitis. J. Digit. Imaging 2023, 36, 893–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stepinska, J.; Lettino, M.; Ahrens, I.; Bueno, H.; Garcia-Castrillo, L.; Khoury, A.; Lancellotti, P.; Mueller, C.; Muenzel, T.; Oleksiak, A.; et al. Diagnosis and risk stratification of chest pain patients in the emergency department: Focus on acute coronary syndromes. A position paper of the Acute Cardiovascular Care Association. Eur. Heart J. Acute Cardiovasc. Care 2020, 9, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polanczyk, A.; Piechota-Polanczyk, A.; Huk, I.; Neumayer, C.; Balcer, J.; Strzelecki, M. Computational Fluid Dynamic Technique for Assessment of How Changing Character of Blood Flow and Different Value of Hct Influence Blood Hemodynamic in Dissected Aorta. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Xu, X.; Rosendahl, U.; Pepper, J.; Mirsadraee, S. Advanced risk prediction for aortic dissection patients using imaging-based computational flow analysis. Clin. Radiol. 2023, 78, e155–e165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Patient Characteristic | AAS and TAA Groups (N = 382) | Control Group (N = 1243) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, n (%) | 0.04 | ||
| Male | 246 (64.4) | 727 (58.5) | |
| Female | 136 (35.6) | 516 (41.5) | |
| Age-yr (Mean ± SD) | 69.5 ± 15.5 | 65.1 ± 17.0 | <0.01 |
| Underlying medical condition, n (%) | 294 (77.0) | 874 (70.3) | 0.01 |
| Hypertension | 264 (69.1) | 689 (55.4) | <0.01 |
| Atherosclerosis | 57 (14.9) | 251 (20.2) | 0.02 |
| Renal insufficiency | 63 (16.5) | 205 (16.5) | 0.10 |
| Ischemic heart disease | 77 (20.2) | 378 (30.4) | <0.01 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 69 (18.1) | 391 (31.5) | <0.01 |
| Cerebral vascular disease | 81 (21.2) | 203 (16.3) | 0.03 |
| CNN Pre-Trained Models | Sensitivity (%, 95% CI) | Specificity (%, 95% CI) | Precision (%, 95% CI) | F1 Score (95% CI) | Accuracy (%, 95% CI) | * AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inception-v3 | 68 [50, 86] | 88 [75, 100] | 85 [68, 100] | 0.76 [0.58, 0.91] | 78 [65, 92] | 0.82 |
| VGG19 | 56 [39, 73] | 88 [73, 97] | 82 [66, 92] | 0.67 [0.53, 0.80] | 72 [61, 83] | 0.84 |
| Resnet101 | 64 [45, 83] | 68 [50, 87] | 67 [48, 86] | 0.65 [0.46, 0.84] | 66 [58, 89] | 0.68 |
| Resnet-Inception-v2 | 64 [45, 83] | 64 [45, 83] | 64 [45, 83] | 0.64 [0.45, 0,83] | 64 [45, 83] | 0.67 |
| This Study | Ribeiro et al. (2024) [35] | Lee et al. (2023) [34] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Case numbers | N = 1473 (normal= 1167, AAS and TAA= 306) | N = 8752 (Aortic elongation = 2350, non-aortic elongation = 6402) | N = 3331 (Positive images = 716, negative images = 2615) |
| Data source | Three hospitals: one medical center, one regional hospital, and one district hospital | VinDr-CXR dataset | Three tertiary academic hospitals |
| CNN type | Inception-v3 VGG19 Resnet101 Resnet-Inception-v2 | DenseNet 121 EfficientNet B4 | ResNet 18 |
| Abnormalities targeted | AAS and TAA | Aortic elongation | Acute thoracic aortic dissection |
| Disease label | CTA report | Interpretation by radiologist | CTA report and surgery record |
| Image augmentation protocol | Rotation | Rotation, horizontal flipping, and vertical flipping | Rotation, horizontal flipping, and vertical flipping |
| ROI model architecture | Aggregate channel features object detector | * UNet | UNet |
| Image enhancement | CLAHE | Histogram equalization | Histogram equalization |
| CAM application | Yes, and comparison with patients’ CTA image | Yes | Yes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, Y.-T.; Wang, B.-C.; Chung, J.-Y. Identifying Acute Aortic Syndrome and Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm from Chest Radiography in the Emergency Department Using Convolutional Neural Network Models. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1646. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14151646
Lin Y-T, Wang B-C, Chung J-Y. Identifying Acute Aortic Syndrome and Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm from Chest Radiography in the Emergency Department Using Convolutional Neural Network Models. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(15):1646. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14151646
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Yang-Tse, Bing-Cheng Wang, and Jui-Yuan Chung. 2024. "Identifying Acute Aortic Syndrome and Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm from Chest Radiography in the Emergency Department Using Convolutional Neural Network Models" Diagnostics 14, no. 15: 1646. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14151646
APA StyleLin, Y.-T., Wang, B.-C., & Chung, J.-Y. (2024). Identifying Acute Aortic Syndrome and Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm from Chest Radiography in the Emergency Department Using Convolutional Neural Network Models. Diagnostics, 14(15), 1646. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14151646









