Whale Optimization Algorithm with a Hybrid Relation Vector Machine: A Highly Robust Respiratory Rate Prediction Model Using Photoplethysmography Signals
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
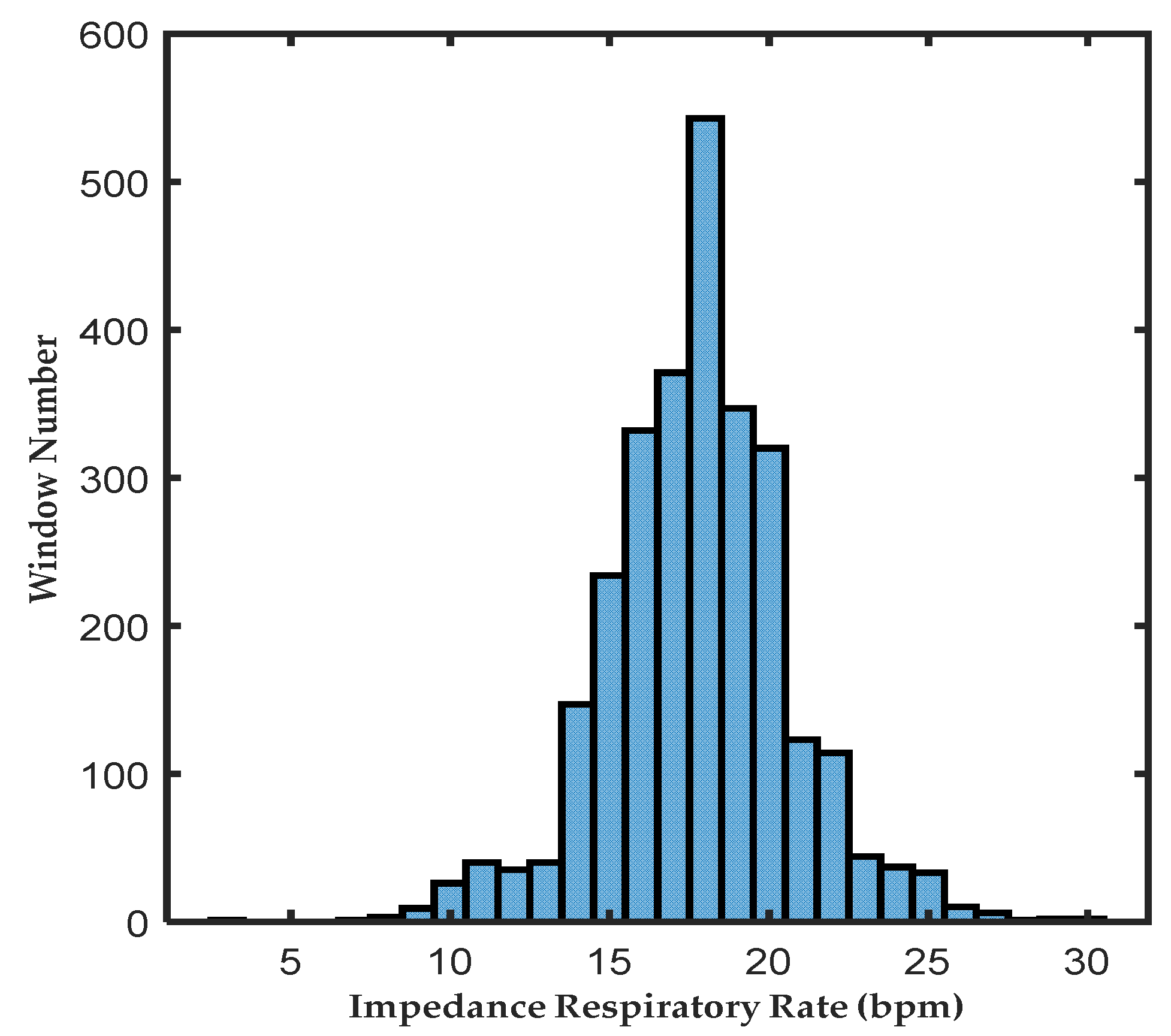
2.1. Database
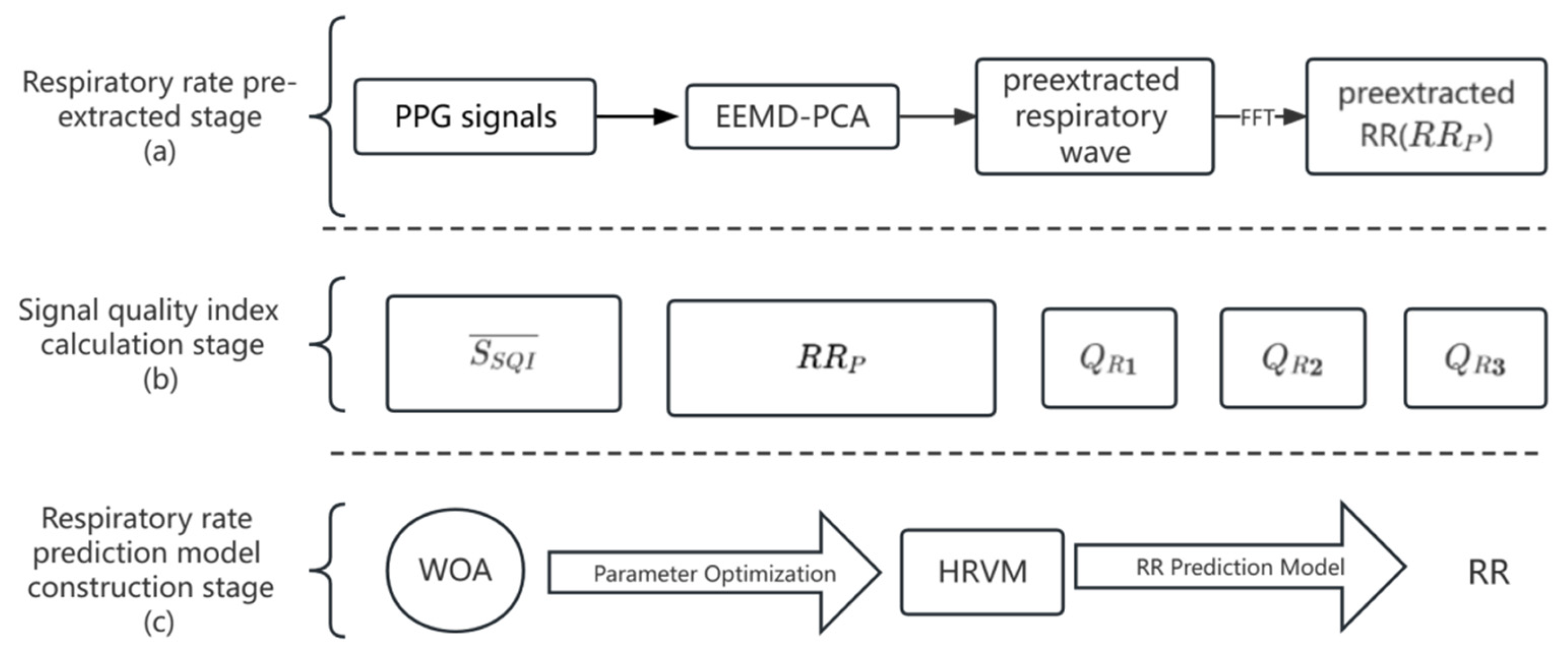
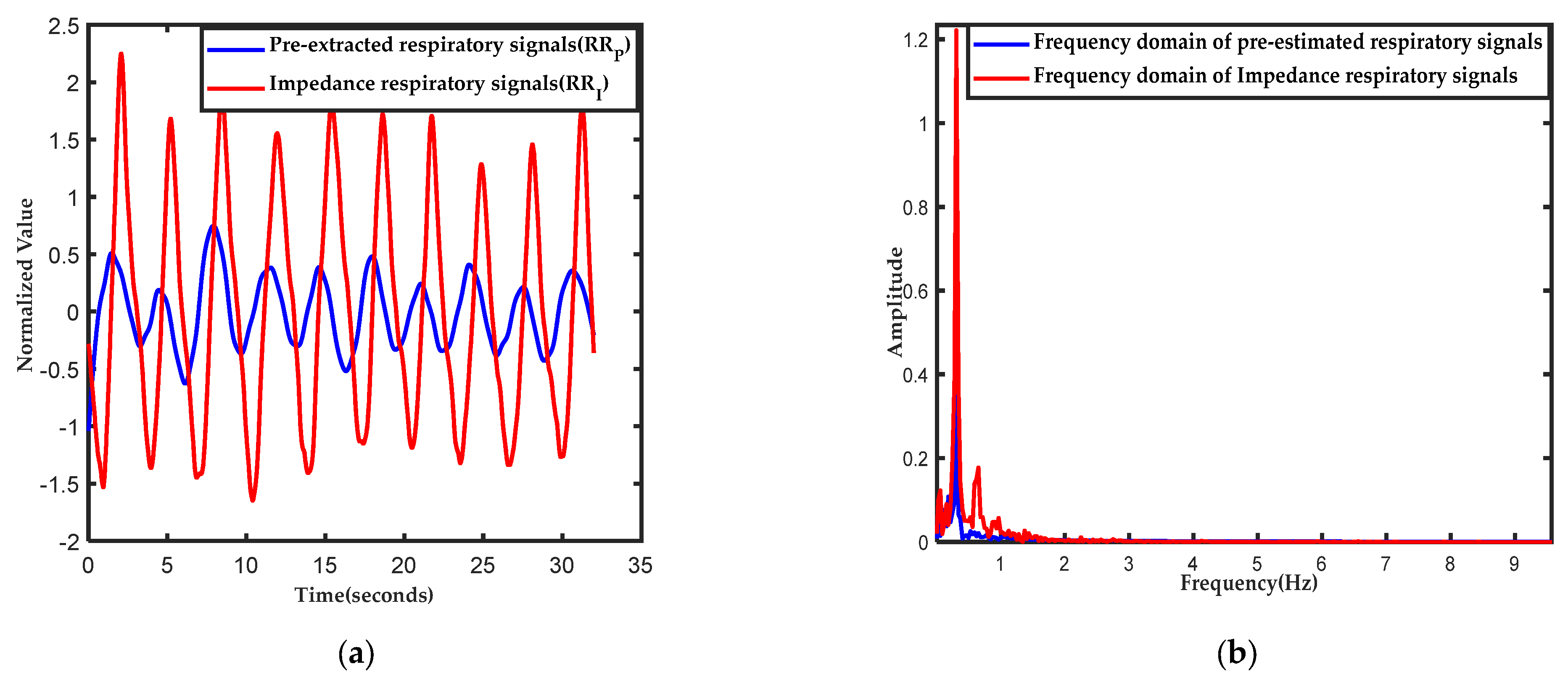
2.2. Pre-Extracted Respiratory Wave and Respiratory Rate by the EEMD-PCA Method
2.3. Signal Quality Index Calculation
2.3.1. PPG Signal Quality Index (SQI) Calculation
2.3.2. Respiratory Quality Index (RQI) Calculation
2.4. WOA-HRVM Model
2.5. Performance Measurement
3. Results
4. Discussion
| References | Method | Length (sec) | Subjects | Overlap (sec) | MAE | RMSE | Dis (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| This study | WOA-HRVM | 32 | 53 | 24 | 1.24 | 1.79 | 6.6% |
| Adami [18] | EMD and DWT + EKF | 60 | 53 | 30 | 0.73 | - | - |
| Pongpanut [25] | RRWaveNet | 32 | 53 | - | 1.62 | - | 1.9% |
| Sharma [20] | EEMD + KF | 32 | 53 | 29 | 1.90 | - | - |
| Aqajari [33] | CycleGAN | 30 | 53 | - | 1.90 | - | - |
| Lee [26] | CAGBA | 32 | 20 | 0 | 1.94 | 0.61 | 62.26% |
| Bian [32] | Deep learning | 60 | 53 | 59 | 2.50 | - | - |
| Karlen [12] | SmartQualityFusion method | 60 | 53 | - | 2.60 | - | - |
| Birrenkott [14] | RQI calculation and fusion | 32 | 53 | 17 | 3.12 | 4.39 | 23.2% |
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- AL-Khalidi, F.Q.; Saatchi, R.; Burke, D.; Elphick, H.; Tan, S. Respiration rate monitoring methods: A review. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2011, 46, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orphanidou, C. Derivation of respiration rate from ambulatory ECG and PPG using ensemble empirical mode decomposition: Comparison and fusion. Comput. Biol. Med. 2017, 81, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvakumar, K.; Kumar, E.V.; Sailesh, M.; Varun, M.; Allan, A.; Biswajit, N.; Namrata, P.; Upasana, S. Realtime PPG based respiration rate estimation for remote health monitoring applications. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2022, 77, 103746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alian, A.A.; Shelley, K.H. Photoplethysmography. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol. 2014, 28, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginsburg, A.S.; Lenahan, J.L.; Izadnegahdar, R.; Ansermino, J.M. A systematic review of tools to measure respiratory rate in order to identify childhood pneumonia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 197, 1116–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Kassem MA, M.; Zhou, Y.; Shabsigh, M.; Wang, Q.; Xu, X. A brief review of non-invasive monitoring of respiratory condition for extubated patients with or at risk for obstructive sleep apnea after surgery. Front. Med. 2017, 4, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolfe, S. The importance of respiratory rate monitoring. Br. J. Nurs. 2019, 28, 504–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruangsetakit, C.; Nuntiwattana, N.; Hahtapornsawan, S.; Hongku, K.; Wangwanit, C.; Chinsakchai, K.; Sermthanasawadi, N.; Mutirangura, P. Digital photoplethysmography in the diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis in Thai patients. J. Med. Assoc. Thai. 2017, 100, S155–S161. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Wang, X.; Liu, D. Association between elevated central venous pressure and outcomes in critically ill patients. Ann. Intensive Care 2017, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Choi, S.J.; Park, K.S. Advance continuous monitoring of blood pressure and respiration rate using denoising auto encoder and LSTM. Microsyst. Technol. 2022, 28, 2181–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, K.; Tamura, T.; Miike, H. Monitoring of heart and respiratory rates by photoplethysmography using a digital filtering technique. Med. Eng. Phys. 1996, 18, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlen, W.; Raman, S.; Ansermino, J.M.; Dumont, G.A. Multiparameter respiratory rate estimation from the photoplethysmogram. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 60, 1946–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meredith, D.J.; Clifton, D.; Charlton, P.; Brooks, J.; Pugh, C.W.; Tarassenko, L. Photoplethysmographic derivation of respiratory rate: A review of relevant physiology. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 2012, 36, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birrenkott, D.A.; Pimentel, M.A.; Watkinson, P.J.; Clifton, D.A. A robust fusion model for estimating respiratory rate from photoplethysmography and electrocardiography. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 65, 2033–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlton, P.H.; Birrenkott, D.A.; Bonnici, T.; Pimentel, M.A.F.; Johnson, A.E.W.; Alastruey, J.; Tarassenko, L.; Watkinson, P.J.; Beale, R.; Clifton, D.A.; et al. Breathing rate estimation from the electrocardiogram and photoplethysmogram: A review. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 11, 2–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambekar, M.R.; Prabhu, S. A novel algorithm to obtain respiratory rate from the PPG signal. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2015, 126, 9–12. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Sapna-Prabhu-2/publication/281910024_A_Novel_Algorithm_to_Obtain_Respiratory_Rate_from_the_PPG_Signal/links/59f0122b0f7e9baeb26ad4bc/A-Novel-Algorithm-to-Obtain-Respiratory-Rate-from-the-PPG-Signal.pdf (accessed on 14 January 2023).
- Colominas, M.A.; Schlotthauer, G.; Torres, M.E. Improved complete ensemble EMD: A suitable tool for biomedical signal processing. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2014, 14, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adami, A.; Boostani, R.; Marzbanrad, F.; Charlton, P.H. A new framework to estimate breathing rate from electrocardiogram, photoplethysmogram, and blood pressure signals. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 45832–45844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motin, M.A.; Karmakar, C.K.; Palaniswami, M. Selection of empirical mode decomposition techniques for extracting breathing rate from PPG. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2019, 26, 592–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H. Extraction of respiratory rate from PPG using ensemble empirical mode decomposition with Kalman filter. Electron. Lett. 2020, 56, 650–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhav, K.V.; Raghuram, M.; Krishna, E.H.; Komalla, N.R.; Reddy, K.A.; Komalla, A.R. Use of multi scale PCA for extraction of respiratory activity from photoplethysmographic signals. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference Proceedings, Graz, Austria, 13–16 May 2012; pp. 1784–1787. [Google Scholar]
- Motin, M.A.; Karmakar, C.K.; Palaniswami, M. Ensemble empirical mode decomposition with principal component analysis: A novel approach for extracting respiratory rate and heart rate from photoplethysmographic signal. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2017, 22, 766–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prathyusha, B.; Rao, T.S.; Asha, D. Extraction of respiratory rate from PPG signals using PCA and EMD. Int. J. Res. Eng. Technol. 2012, 1, 164–184. [Google Scholar]
- Shuzan, M.N.I.; Chowdhury, M.H.; Hossain, M.S.; Chowdhury, M.E.H.; Reaz, M.B.I.; Monir Uddin, M.; Khandakar, A.; Mahbub, Z.B.; Hamid, M.; Ali, S. A novel non-invasive estimation of respiration rate from motion corrupted photoplethysmograph signal using machine learning model. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 96775–96790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osathitporn, P.; Sawadwuthikul, G.; Thuwajit, P.; Ueafuea, K.; Mateepithaktham, T.; Kunaseth, N.; Choxtchawathi, T.; Punyabukkana, P.; Mignot, E.; Wilaiprasitporn, T. RRWaveNet: A Compact End-to-End Multi-Scale Residual CNN for Robust PPG Respiratory Rate Estimation. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2208.08672. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Moon, H.; Son, C.-H.; Lee, G. Respiratory Rate Estimation Combining Autocorrelation Function-Based Power Spectral Feature Extraction with Gradient Boosting Algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgendi, M. Optimal signal quality index for photoplethysmogram signals. Bioengineering 2016, 3, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Yue, M.; Wu, Z. A novel intrusion detection method based on WOA optimized hybrid kernel RVM[C]//2021 IEEE 6th International Conference on Computer and Communication Systems (ICCCS). In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 6th International Conference on Computer and Communication Systems (ICCCS), Chengdu, China, 23–26 April 2021; pp. 1063–1069. [Google Scholar]
- Rafi, M.; Shaikh, M.S. A comparison of SVM and RVM for Document Classification. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1301.2785. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; He, Y.; Yuan, L.; Xiang, S. A multiple heterogeneous kernel RVM approach for analog circuit fault prognostic. Clust. Comput. 2019, 22, 3849–3861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Lewis, A. The whale optimization algorithm. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2016, 95, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, D.; Mehta, P.; Selvaraj, N. Respiratory rate estimation using PPG: A deep learning approach. In Proceedings of the 42nd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 July 2020; pp. 5948–5952. [Google Scholar]
- Aqajari, S.A.H.; Cao, R.; Zargari AH, A.; Rahmani, A.M. An end-to-end and accurate ppg-based respiratory rate estimation approach using cycle generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the 2021 43rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Mexico, 1–5 November 2021; pp. 744–747. [Google Scholar]
- Kyriacou, P.A.; Allen, J. (Eds.) Photoplethysmography: Technology, Signal Analysis and Applications; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]

| References | Database | Subjects | Methodology | Innovation | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nakajima [11] | Self-collection | 11 | Digital filtering technique | Real-time PPG-based respiration rate detection | Lack of universal applicability |
| Karlen [12] | CapnoBase | 94 | Smart fusion method | Set discard thresholds with PPG signal quality metrics | Discard 45% of data |
| Birrenkott [14] | CapnoBase | 42 | RQI calculation and fusion | Adjustable threshold value to change accuracy | Inaccurate estimation of low-quality PPG signals |
| Selvakumar [3] | CapnoBase | 42 | RIAV based on FFT | Respiration rate detection on low-cost hardware | Low accuracy in detecting too-fast breathing |
| Sharma [20] | BIDMC | 53 | EEMD + KF | Kalman filtering is applied to the reconstructed signal | KF is not suitable for non-linear PPG signals |
| Adami [18] | BIDMC | 53 | CEEMDAN + DWT + EKF | Leverage time and frequency domain information | Framework calculation is too complicated |
| Mohammad [19] | MIMIC | 121 | EMD family and PCA | Free from parameter selection | Sensitivity to high-amplitude noise in the respiratory range |
| Shuzan [24] | VORTAL | 39 | Machine-learning model | Hyperparameter optimization | Tested only on resting young people |
| Pongpanut [25] | BIDMC | 53 | RRWaveNet | Improve model robustness using transfer learning | Discarded low-quality signals by SQI metric |
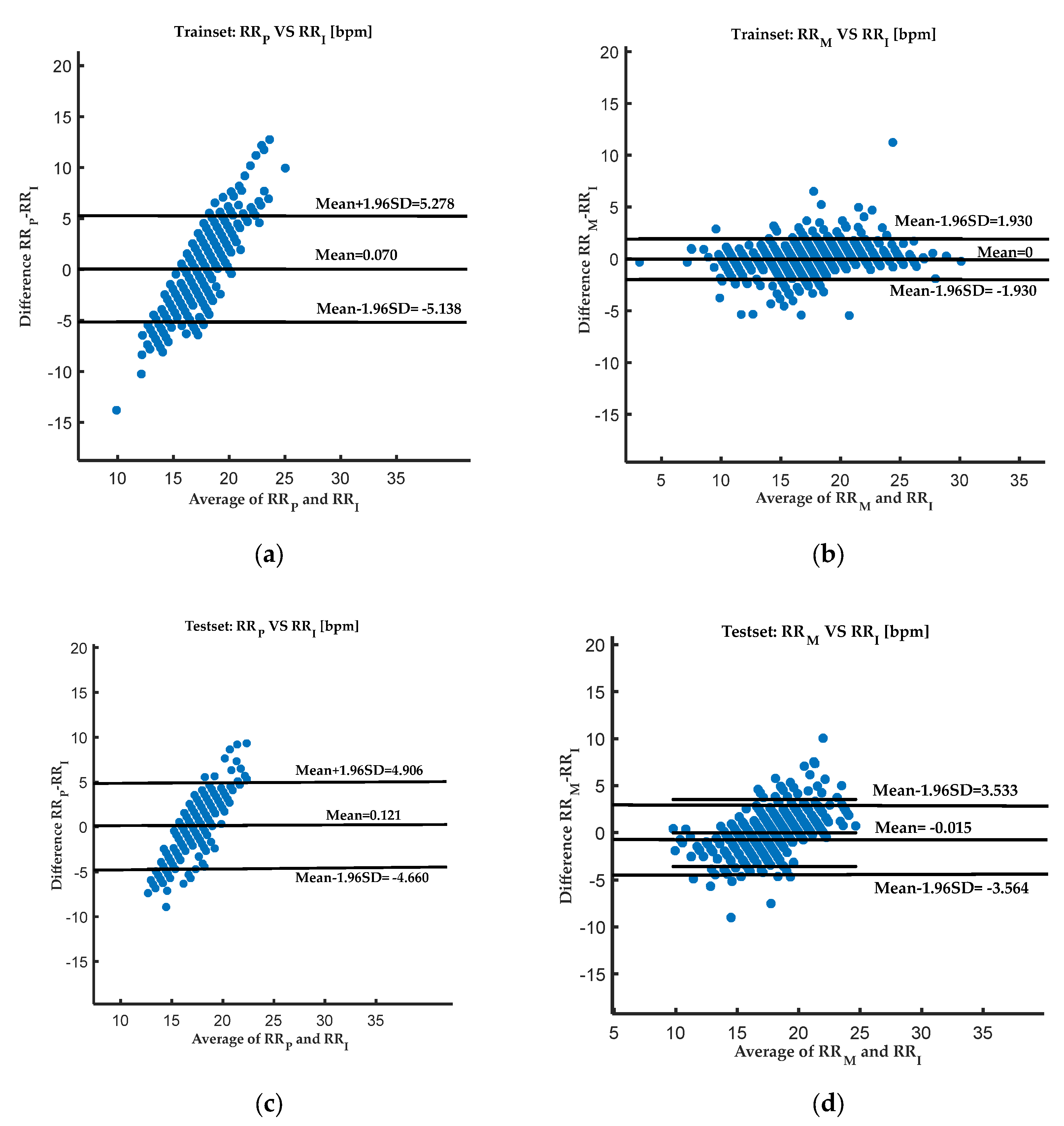
| Dataset | Method | Mean | Mean +1.96SD | Mean −1.96SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| training set | This study | 0 | 1.930 | −1.930 |
| EEMD-PCA | 0.070 | 5.278 | −5.138 | |
| test set | This study | −0.015 | 3.533 | −3.564 |
| EEMD-PCA | 0.121 | 4.906 | −4.660 |
| Dataset | Method | MAE | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|
| training set | This study | 0.71 | 0.99 |
| EEMD-PCA | 1.99 | 2.66 | |
| test set | This study | 1.24 | 1.79 |
| EEMD-PCA | 1.86 | 2.44 |
| RRI (bpm) | Training Set | Test Set | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | MAEthis study [MAEEEMD-PCA] | RMSEthis study [RMSEEEMD-PCA] | N | MAEthis study [MAEEEMD-PCA] | RMSEthis study [RMSEEEMD-PCA] | |
| below 12 | 61 | 1.08 [6.40] | 1.56 [6.57] | 16 | 2.68 [6.25] | 3.52 [6.34] |
| 12–16 | 563 | 0.79 [2.34] | 1.08 [2.65] | 202 | 1.45 [2.21] | 1.90 [2.50] |
| 17–20 | 1118 | 0.63 [1.05] | 0.82 [1.36] | 407 | 0.91 [1.03] | 1.21 [1.32] |
| 21–24 | 211 | 0.75 [3.72] | 1.16 [3.89] | 88 | 1.80 [3.41] | 2.45 [3.56] |
| above 24 | 40 | 0.98 [7.17] | 2.14 [7.47] | 13 | 4.28 [6.62] | 5.01 [6.77] |
| Subject | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subject 01 | 0.14 | 0.70 | −0.24 | −0.70 |
| Subject 02 | 0.30 | −0.10 | 0.07 | 0.08 |
| Subject 03 | −0.22 | 0.07 | −0.27 | −0.54 |
| Subject 04 | −0.07 | 0.43 | −0.16 | −0.43 |
| … | … | … | … | … |
| Subject 53 | −0.32 | −0.29 | −0.29 | −0.16 |
| Average | 0.28 | 0.24 | 0.27 | 0.28 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, X.; Wang, Z.; Cao, L.; Chen, Z.; Liang, Y. Whale Optimization Algorithm with a Hybrid Relation Vector Machine: A Highly Robust Respiratory Rate Prediction Model Using Photoplethysmography Signals. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 913. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13050913
Dong X, Wang Z, Cao L, Chen Z, Liang Y. Whale Optimization Algorithm with a Hybrid Relation Vector Machine: A Highly Robust Respiratory Rate Prediction Model Using Photoplethysmography Signals. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(5):913. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13050913
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Xuhao, Ziyi Wang, Liangli Cao, Zhencheng Chen, and Yongbo Liang. 2023. "Whale Optimization Algorithm with a Hybrid Relation Vector Machine: A Highly Robust Respiratory Rate Prediction Model Using Photoplethysmography Signals" Diagnostics 13, no. 5: 913. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13050913
APA StyleDong, X., Wang, Z., Cao, L., Chen, Z., & Liang, Y. (2023). Whale Optimization Algorithm with a Hybrid Relation Vector Machine: A Highly Robust Respiratory Rate Prediction Model Using Photoplethysmography Signals. Diagnostics, 13(5), 913. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13050913






